Submitted:
02 July 2024
Posted:
04 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Study Overview
1.2. ICP-OES Detectable Elements in aquatic systems
1.2.1. Ecological Impacts of Detectable Elements
1.3. Regulated DE Water Quality Standards Applicable to UL
- 2A:
- “Protected for frequent primary contact recreation where there is a high likelihood of ingestion of water or a high degree of bodily contact with the water” (swimming, kayaking, diving, water skiing, etc.);
- 2B:
- “Protected for infrequent primary contact recreation. Also protected for secondary contact recreation where there is a low likelihood of ingestion of water or a low degree of bodily contact with water” (e.g. boating, wading, etc.) [86];
- 3B:
- “Protected for warm-water species of game fish and other warm water aquatic life, including the necessary aquatic organisms in their food chain;”
- 3D:
- “Protected for waterfowl, shore birds, and other water-oriented wildlife not included in Classes 3A, 3B, or 3C, including the necessary aquatic organisms in their food chain;”
- 4:
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Study
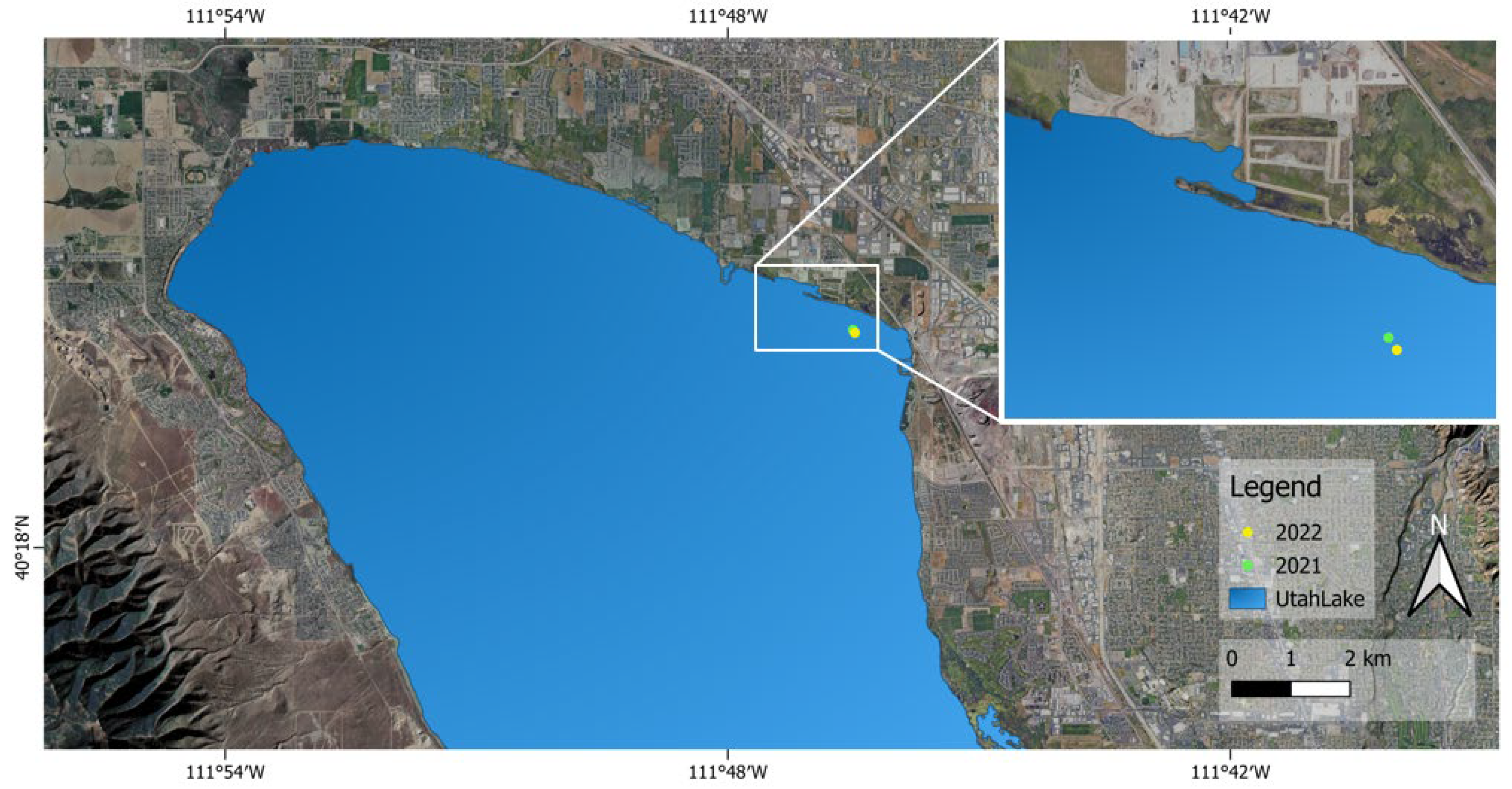
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Analysis Methods
2.3.1. Laboratory Analysis
2.3.2. Filtration
2.4. Data Cleaning
3. Results and Discussion: Regulation Levels
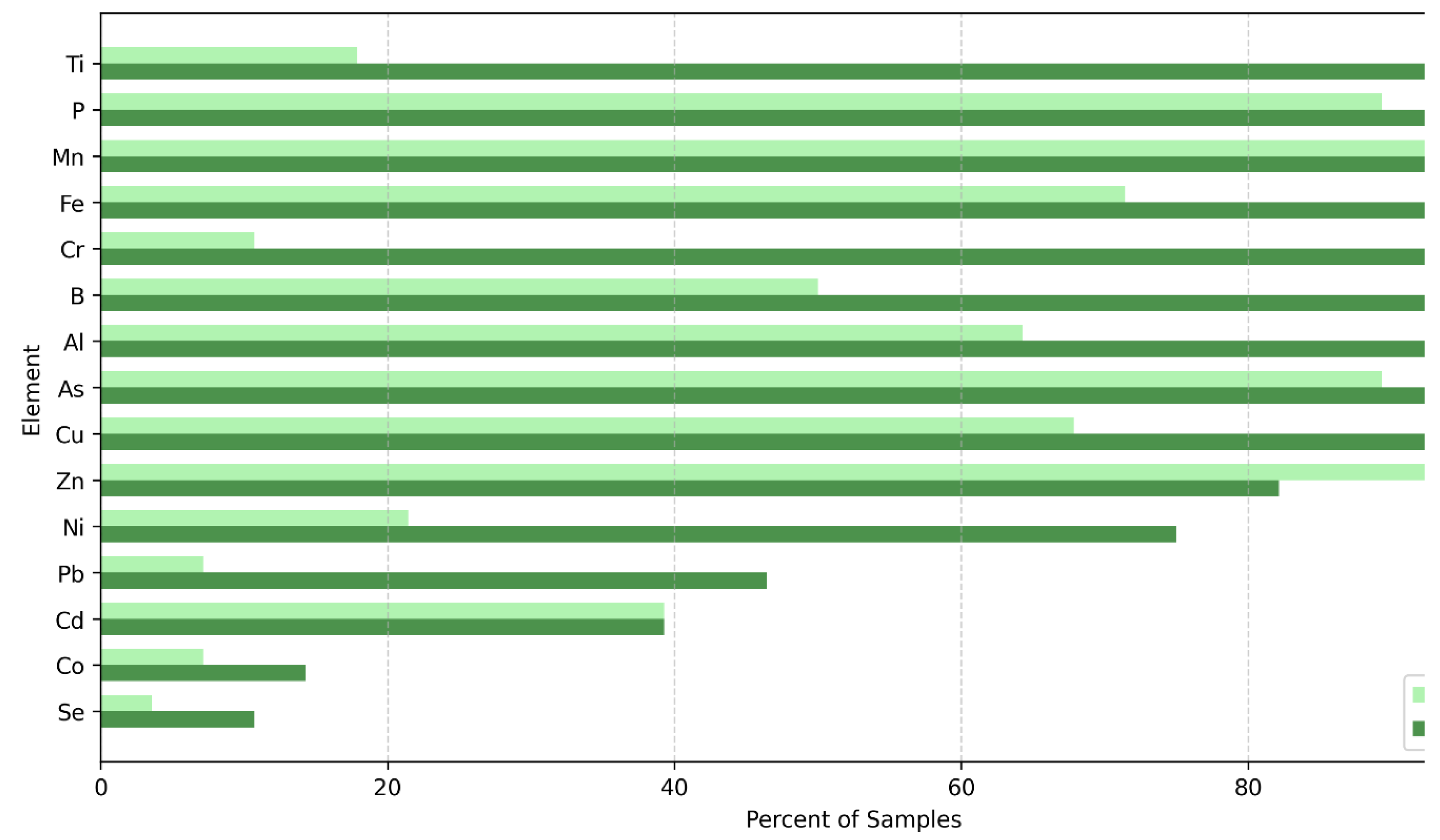
3.1. MDL Analysis
3.2. Specific Element Selection
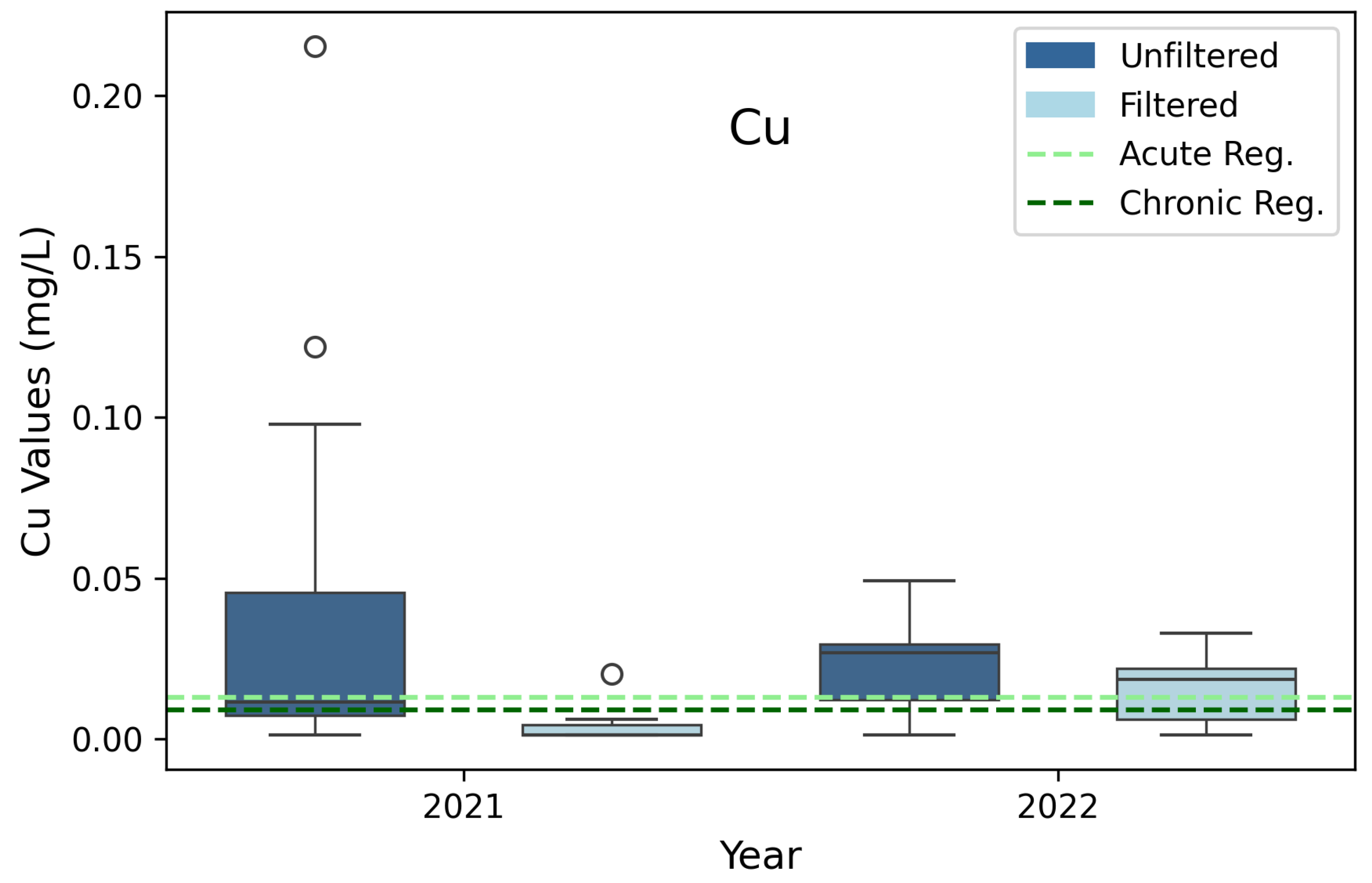
3.3. Copper (Cu)
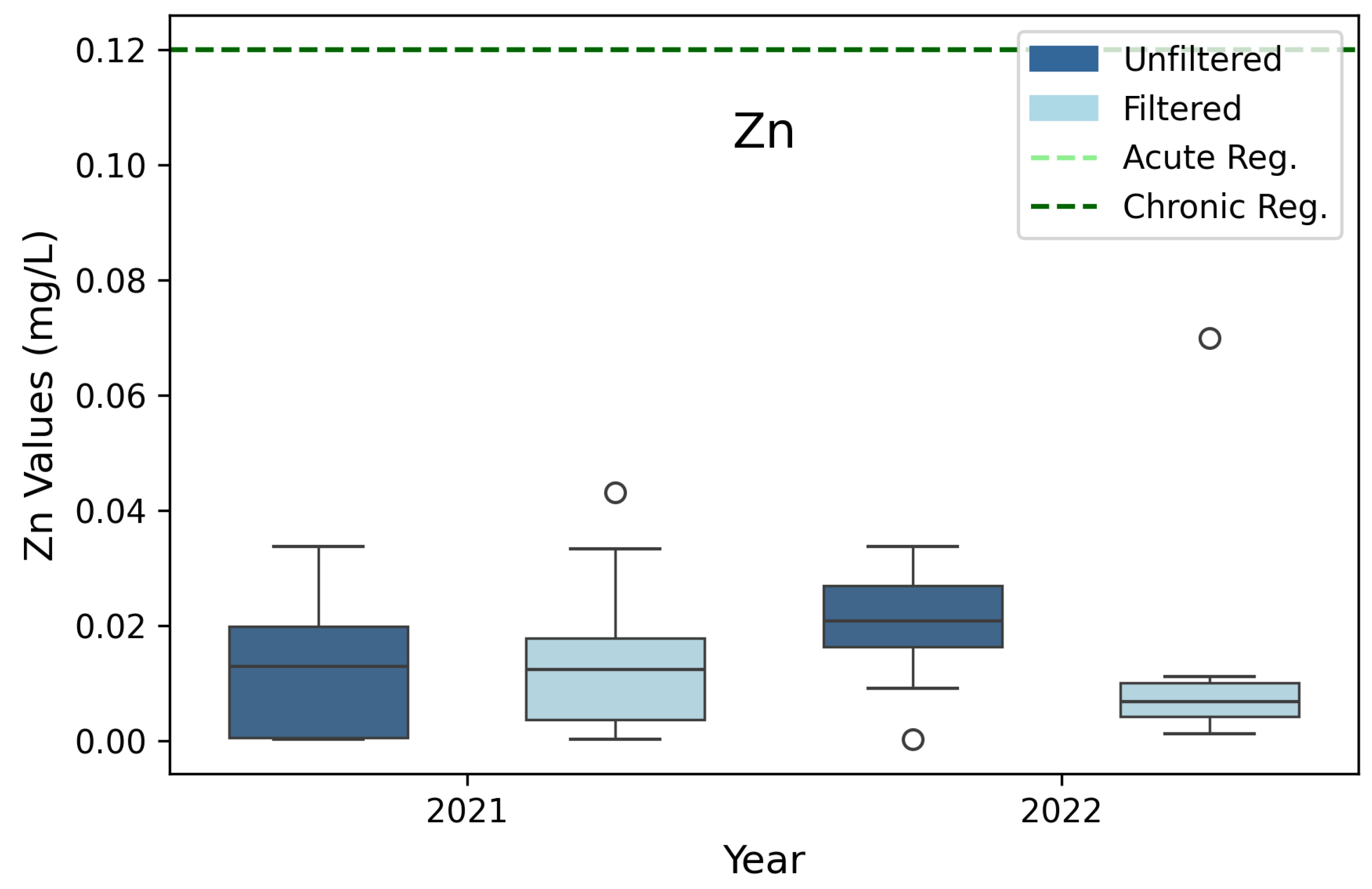
3.4. Zinc (Zn)
3.5. Nickel (Ni)
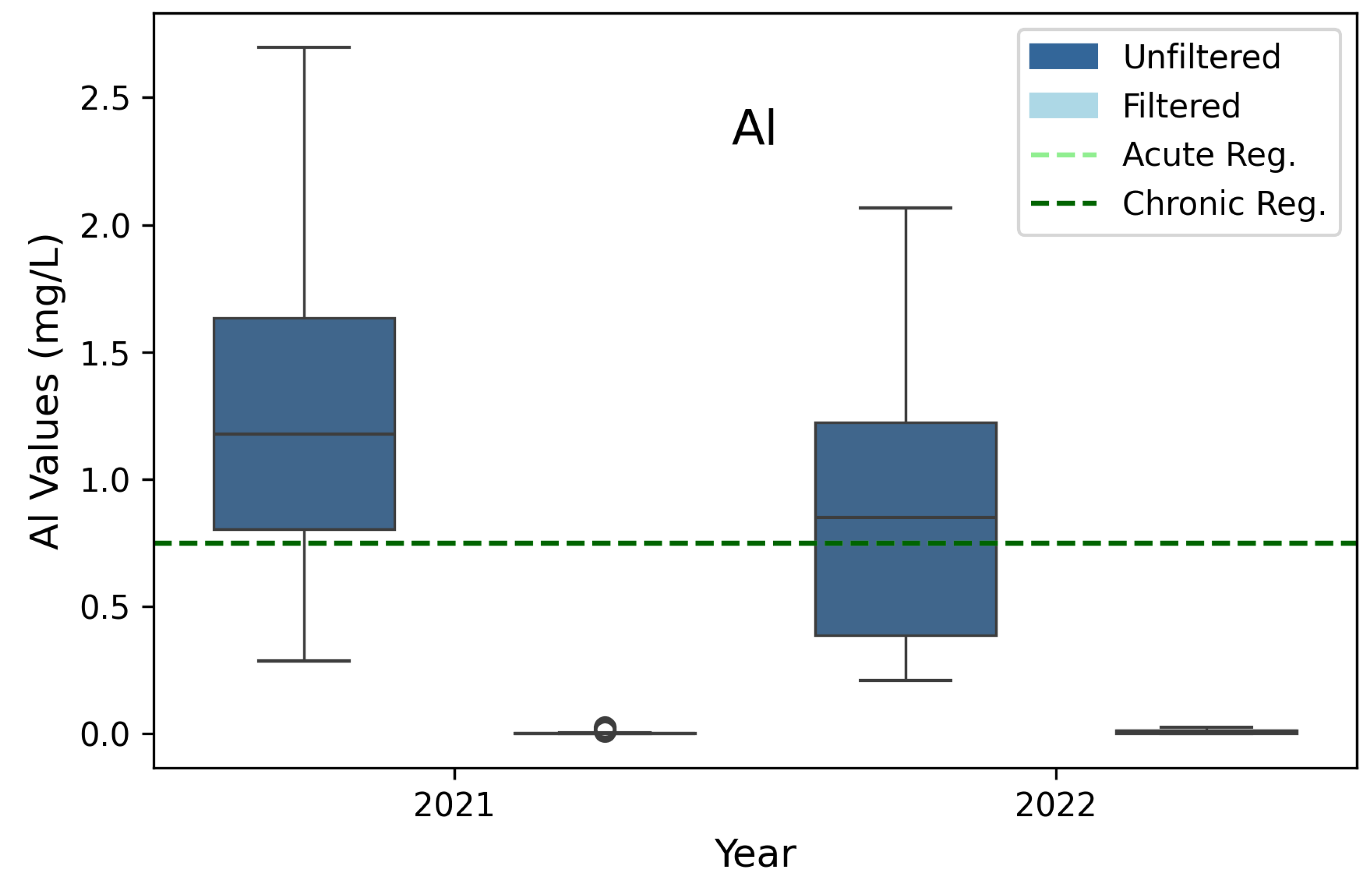
3.6. Aluminum (Al)
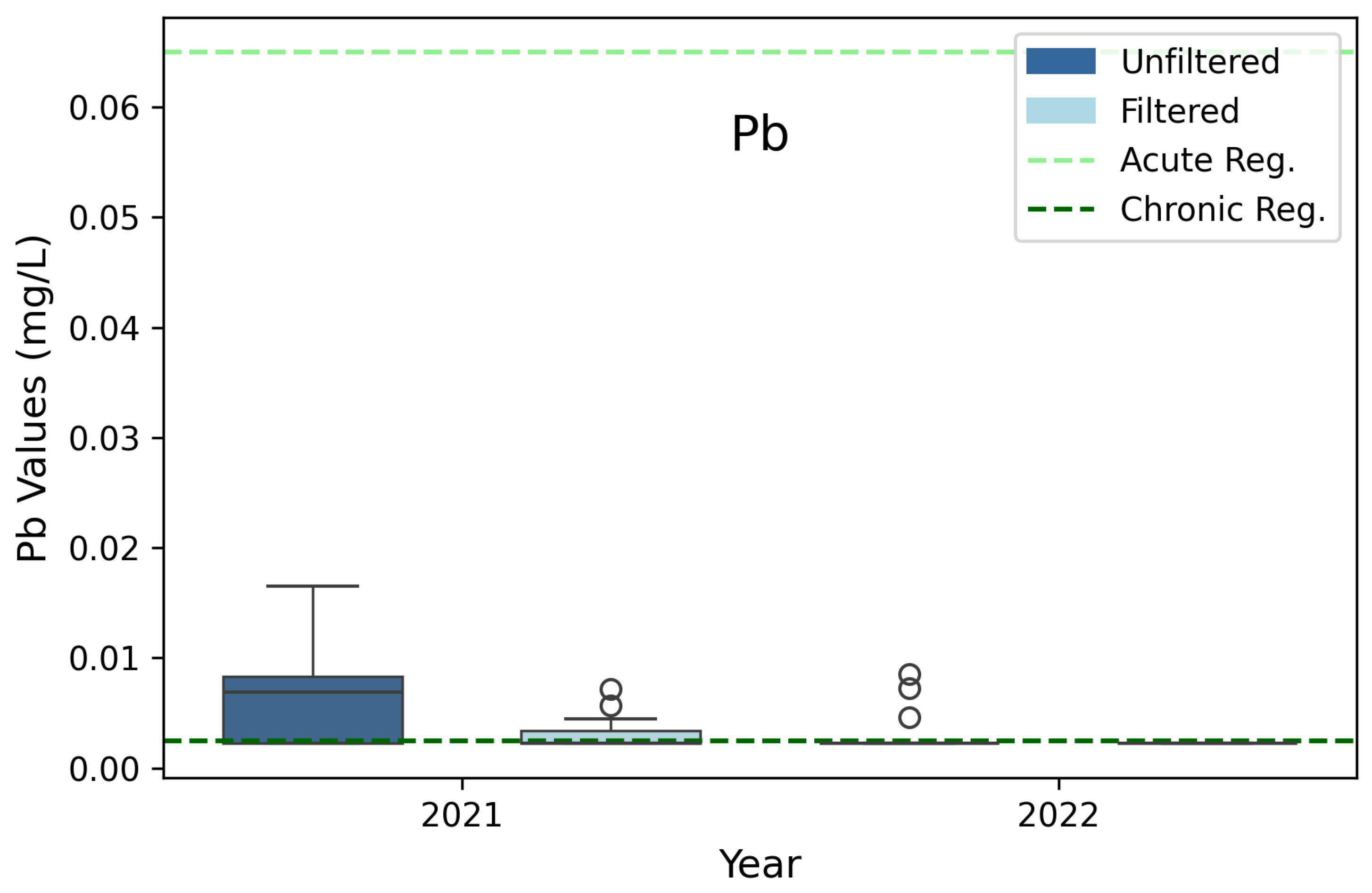
3.7. Lead (Pb)
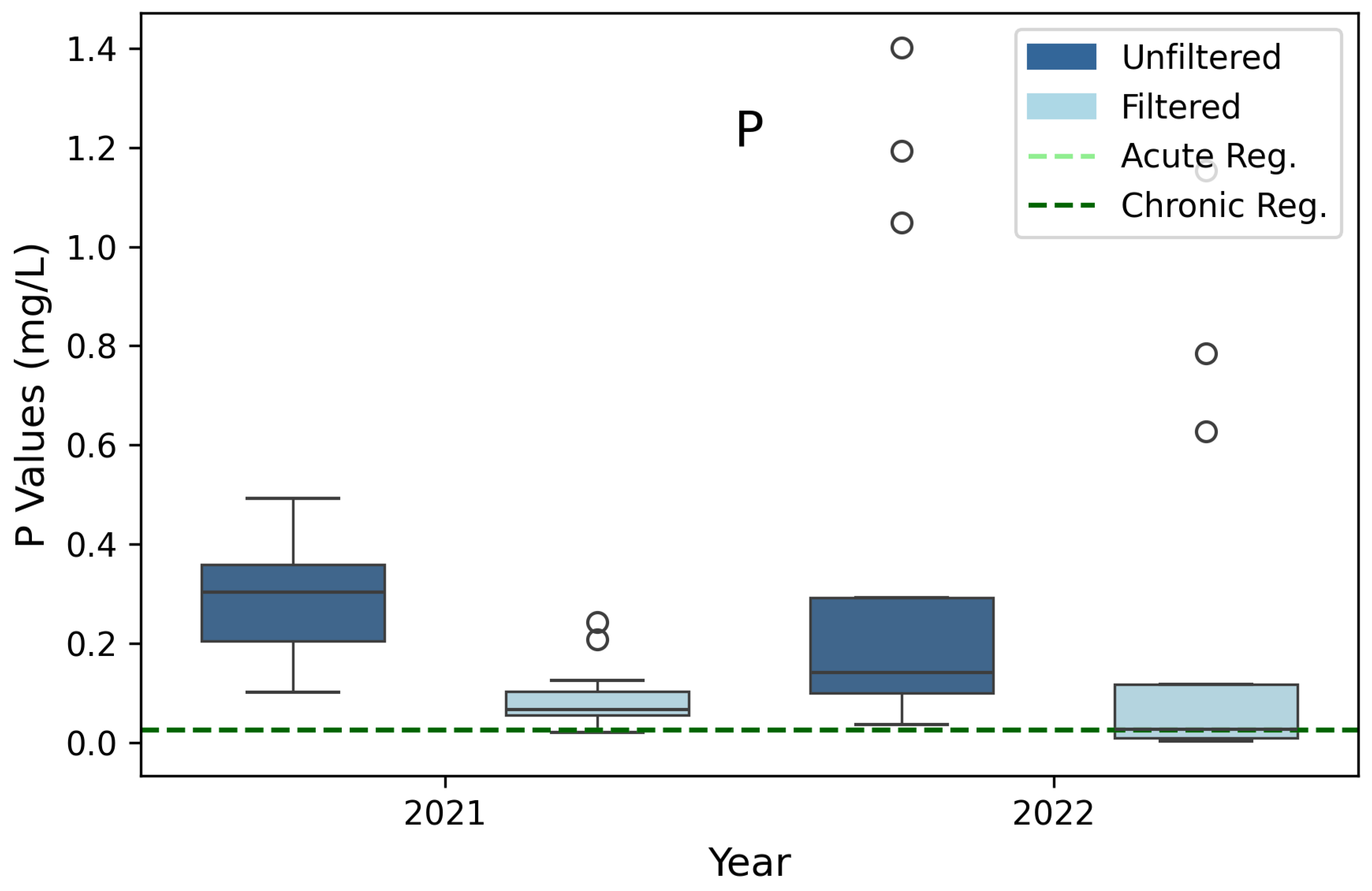
3.8. Phosphorus (P)
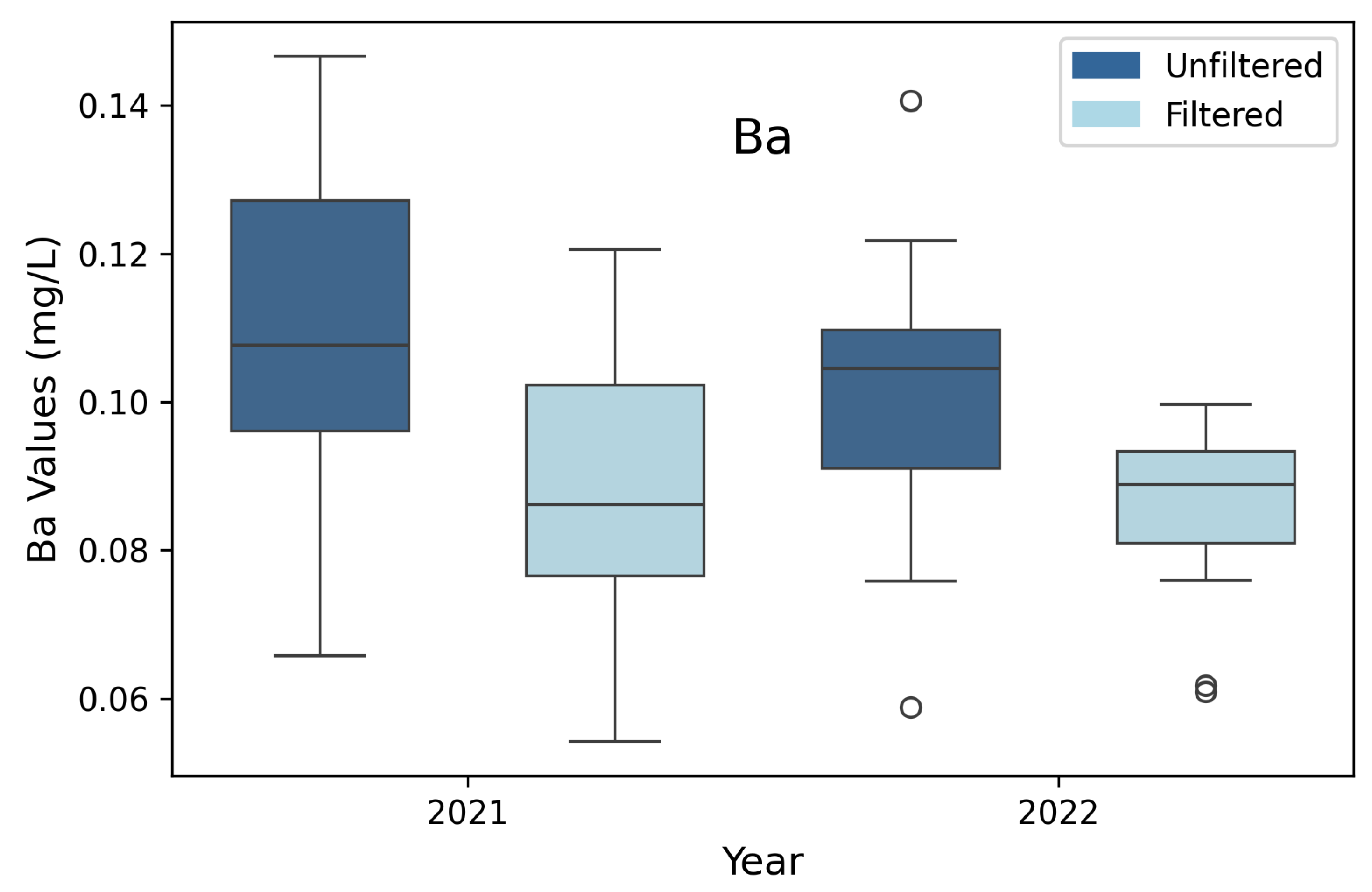
3.9. Barium (Ba)
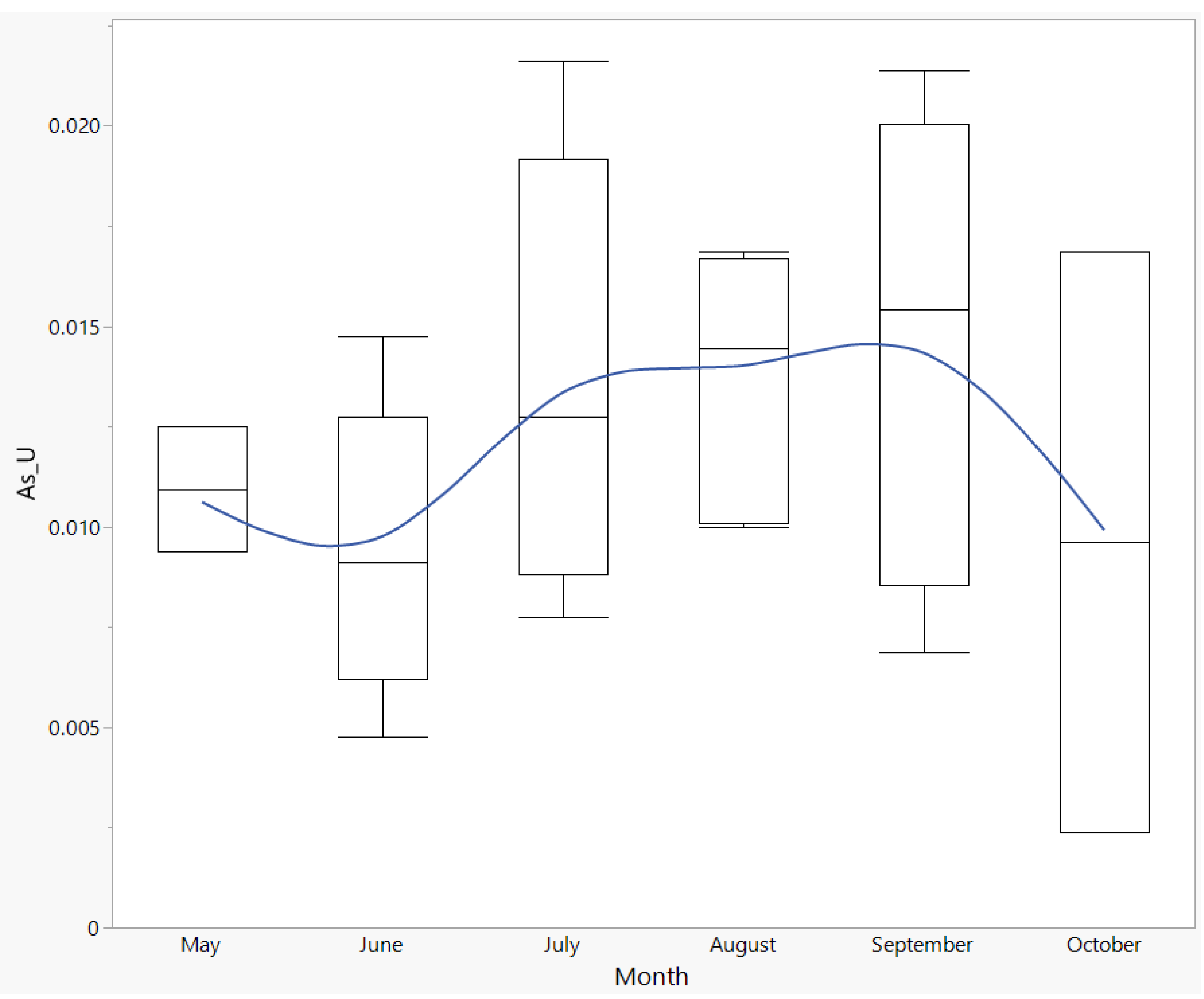
3.10. Arsenic (As)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taggart, J.B.; Ryan, R.L.; Williams, G.P.; Miller, A.W.; Valek, R.A.; Tanner, K.B.; Cardall, A.C. Historical Phosphorus Mass and Concentrations in Utah Lake: A Case Study with Implications for Nutrient Load Management in a Sorption-Dominated Shallow Lake. Water 2024, 16, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, E. A preliminary study of the algae of Utah Lake: Master's thesis. Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah, 84p 1931.
- Harding, W.J. The algae of Utah Lake. Part II. The Great Basin Naturalist 1971, 31, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Rushforth, S.R.; Squires, L.E. New records and comprehensive list of the algal taxa of Utah Lake, Utah, USA. The Great Basin Naturalist 1985, 237–254. [Google Scholar]
- Squires, L.E.; Rushforth, S.R. Winter phytoplankton communities of Utah Lake, Utah, USA. Hydrobiologia 1986, 131, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, M.C.; Brotherson, J.D.; Rushforth, S.R. Environmental interaction in summer algal communities of Utah Lake. The Great Basin Naturalist 1978, 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Harding, W.J. A preliminary report on the algal species presently found in Utah Lake. The Great Basin Naturalist 1970, 30, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Rushforth, S.R.; St. Clair, L.L.; Grimes, J.A.; Whiting, M.C. Phytoplankton of Utah Lake. Great Basin Naturalist Memoirs 1981, 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Squires, L.E.; Whiting, M.C.; Brotherson, J.D.; Rushforth, S.R. Competitive displacement as a factor influencing phytoplankton distribution in Utah Lake, Utah. The Great Basin Naturalist 1979, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Carozzi, A.V. Observations on algal biostromes in the Great Salt Lake, Utah. The Journal of Geology 1962, 70, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushforth, S.R.; Merkley, G.S. Comprehensive list by habitat of the algae of Utah, USA. The Great Basin Naturalist 1988, 154–179. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R.; Panja, P.; McLennan, J. Integrated workflow for interpretation of satellite imageries using machine learning to assess and monitor algal blooms in Utah Lake, USA. Ecological Informatics 2023, 102033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, K.B.; Cardall, A.C.; Williams, G.P. A Spatial Long-Term Trend Analysis of Estimated Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in Utah Lake Using Earth Observation Data. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.H.; Burian, S.J.; Dennison, P.E.; Williams, G.P. Evaluating historical trends and influences of meteorological and seasonal climate conditions on lake chlorophyll a using remote sensing. Lake and Reservoir Management 2020, 36, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.H.; Williams, G.P.; Adjei, Z.; Barlow, A.; Nelson, E.J.; Miller, A.W. Reservoir water quality monitoring using remote sensing with seasonal models: case study of five central-Utah reservoirs. Lake and Reservoir Management 2015, 31, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrus, S.M.; Williams, G.P.; Miller, A.W.; Borup, M.B.; Merritt, L.B.; Richards, D.C.; Miller, T.G. Nutrient Atmospheric Deposition on Utah Lake: A Comparison of Sampling and Analytical Methods. Hydrology 2021, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telfer, J.T.; Brown, M.M.; Williams, G.P.; Tanner, K.B.; Miller, A.W.; Sowby, R.B.; Miller, T.G. Source Attribution of Atmospheric Dust Deposition to Utah Lake. In Hydrology 2023, Vol. 10.
- Reidhead, J.G. Significance of the Rates of Atmospheric Deposition Around Utah Lake and Phosphorus-Fractionation of Local Soils; Brigham Young University: 2019.
- Abu-Hmeidan, H.Y.; Williams, G.P.; Miller, A.W. Characterizing Total Phosphorus in Current and Geologic Utah Lake Sediments: Implications for Water Quality Management Issues. Hydrology 2018, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.M.; Telfer, J.T.; Williams, G.P.; Miller, A.W.; Sowby, R.B.; Hales, R.C.; Tanner, K.B. Nutrient Loadings to Utah Lake from Precipitation-Related Atmospheric Deposition. Hydrology 2023, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.M.; Williams, G.P.; Miller, A.W.; Merritt, L. Measuring and Calculating Current Atmospheric Phosphorous and Nitrogen Loadings to Utah Lake Using Field Samples and Geostatistical Analysis. Hydrology 2018, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, J.; Sundrud, R.; White, D.; Barton, J.; Fuhriman, D.; Loveridge, E.; Pratt, D. Chemical response of Utah Lake to nutrient inflow. Journal (Water Pollution Control Federation) 1973, 880–887. [Google Scholar]
- Zanazzi, A.; Wang, W.; Peterson, H.; Emerman, S.H. Using Stable Isotopes to Determine the Water Balance of Utah Lake (Utah, USA). Hydrology 2020, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, A.E. Remote sensing of algal blooms by aircraft and satellite in Lake Erie and Utah Lake. Remote sensing of Environment 1974, 3, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, A. ERTS-1 observes algal blooms in Lake Erie and Utah Lake. In Proceedings of NASA. Goddard Space Flight Center Symp. on Significant Results obtained from the ERTS-1, Vol. 1, Sect. A. and B.
- Miller, W.; Rango, A. Using heat capacity mapping mission (hcmm) data to assess lake water quality 1. JAWRA Journal of the American Water Resources Association 1984, 20, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.R.; McGinnis, D.F.; Gatlin, J.A. Use of NOAA/AVHRR visible and near-infrared data for land remote sensing; US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration …: 1981; Vol. 84.
- Hansen, C.H.; Williams, G.P. Evaluating remote sensing model specification methods for estimating water quality in optically diverse lakes throughout the growing season. Hydrology 2018, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.H.; Burian, S.J.; Dennison, P.E.; Williams, G.P. Spatiotemporal variability of lake water quality in the context of remote sensing models. Remote Sensing 2017, 9, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, S.; Landom, K.; Crowl, T. Monitoring macrophytes cover and taxa in Utah Lake by using 2009-2011 Landsat digital imagery. Revista de Teledetección 2013, 39, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Q.; Niu, Z. Construction of the long-term global surface water extent dataset based on water-NDVI spatio-temporal parameter set. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seegers, B.N.; Werdell, P.J.; Vandermeulen, R.A.; Salls, W.; Stumpf, R.P.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Owens, T.J.; Bailey, S.W.; Scott, J.P.; Loftin, K.A. Satellites for long-term monitoring of inland US lakes: The MERIS time series and application for chlorophyll-a. Remote sensing of environment 2021, 266, 112685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Pang, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, Q. Spectral probability distribution of closed connected water and remote sensing statistical inference for yellow substance. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing 2021, 87, 807–819. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, C.H.; Dennison, P.; Burian, S.; Barber, M.; Williams, G. Hindcasting water quality in an optically complex system. WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment 2016, 209, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Page, B.P.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, D.R. A novel cross-satellite based assessment of the spatio-temporal development of a cyanobacterial harmful algal bloom. International journal of applied earth observation and geoinformation 2018, 66, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, R.D.; Falconer, A.; Jensen, J.R. The relationship between NOAA-AVHRR NDVI and ecoregions in Utah. Remote Sensing of Environment 1995, 53, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.; Swain, N.; Munson, K.; Adjei, Z.; Williams, G.P.; Miller, W. Development of sub-seasonal remote sensing chlorophyll-a detection models. American Journal of Plant Sciences 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardall, A.C.; Hales, R.C.; Tanner, K.B.; Williams, G.P.; Markert, K.N. LASSO (L1) Regularization for Development of Sparse Remote-Sensing Models with Applications in Optically Complex Waters Using GEE Tools. Remote Sensing 2023, 15, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Nelson, S.; Rushforth, S.; Rey, K.; Carling, G.; Bickmore, B.; Heathcote, A.; Miller, T.; Meyers, L. Human-Driven Trophic Changes in a Large, Shallow Urban Lake: Changes in Utah Lake, Utah from Pre-European Settlement to the Present. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 2023, 234, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofchissey, S.; Roberts, S.; Hopkinson, J.; McDonald, J.; Emerman, S. Arsenic and other heavy metals in Utah Lake and its tributaries. 2014.
- Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Xu, H.; Wells, M.; Tefsen, B.; Qin, B. Effect of micronutrients on algae in different regions of Taihu, a large, spatially diverse, hypereutrophic lake. Water Research 2019, 151, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, R.A. Algal culturing techniques; Elsevier: 2005.
- Downs, T.M.; Schallenberg, M.; Burns, C.W. Responses of lake phytoplankton to micronutrient enrichment: a study in two New Zealand lakes and an analysis of published data. Aquatic Sciences 2008, 70, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, L.; Cabanesa, D.J.E.; Blanco-Ameijeiras, S.; Moisset, S.A.M.; Hassler, C.S. Iron Biogeochemistry in Aquatic Systems: From Source to Bioavailability. CHIMIA 2014, 68, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivokapić, M. Study on the Evaluation of (Heavy) Metals in Water and Sediment of Skadar Lake (Montenegro), with BCF Assessment and Translocation Ability (TA) by Trapa natans and a Review of SDGs. Water 2021, 13, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueter, J.G.; Petersen, R.R. Micronutrient effects on cyanobacterial growth and physiology. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 1987, 21, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, T.K.; Schallenberg, M.; Martin, C.E. Investigation of nutrient limitation status and nutrient pathways in Lake Hayes, Otago, New Zealand: a case study for integrated lake assessment. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 2008, 42, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengg, M.; Stirling, C.H.; Reid, M.R.; Verburg, P.; Armstrong, E.; Kelly, L.T.; Wood, S.A. Growth at the limits: comparing trace metal limitation of a freshwater cyanobacterium (Dolichospermum lemmermannii) and a freshwater diatom (Fragilaria crotonensis). Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facey, J.A.; Rogers, T.A.; Apte, S.C.; Mitrovic, S.M. Micronutrients as growth limiting factors in cyanobacterial blooms; a survey of freshwaters in South East Australia. Aquatic Sciences 2021, 83, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facey, J.A.; Apte, S.C.; Mitrovic, S.M. A Review of the Effect of Trace Metals on Freshwater Cyanobacterial Growth and Toxin Production. Toxins 2019, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw-Allen, P.; Sutlerm, G.W. Metals. Availabe online: https://www.epa.gov/caddis-vol2/metals (accessed on June 2, 2024).
- Schuler, M.S.; Relyea, R.A. A Review of the Combined Threats of Road Salts and Heavy Metals to Freshwater Systems. BioScience 2018, 68, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monchanin, C.; Devaud, J.-M.; Barron, A.B.; Lihoreau, M. Current permissible levels of metal pollutants harm terrestrial invertebrates. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 779, 146398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogren, C.L.; Trumble, J.T. The impacts of metals and metalloids on insect behavior. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata 2010, 135, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainbow, P.S. Trace metal concentrations in aquatic invertebrates: why and so what? Environmental Pollution 2002, 120, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschner, H. Marschner's mineral nutrition of higher plants; Academic press: 2011.
- Gall, J.E.; Boyd, R.S.; Rajakaruna, N. Transfer of heavy metals through terrestrial food webs: a review. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 2015, 187, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.S.; US SA, A.R. Effect of different heavy metal pollution on fish. Res. J. Chem. Environ. Sci 2014, 2, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Amundsen, P.A.; Staldvik, F.J.; Lukin, A.A.; Kashulin, N.A.; Popova, O.A.; Reshetnikov, Y.S. Heavy metal contamination in freshwater fish from the border region between Norway and Russia. Sci Total Environ 1997, 201, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, M.; André, J.-M.; Gontier, K.; Diot, N.; Veiga, J.; Davail, S. Trace element concentrations (mercury, cadmium, copper, zinc, lead, aluminium, nickel, arsenic, and selenium) in some aquatic birds of the Southwest Atlantic Coast of France. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 2010, 58, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.; Gochfeld, M. Behavioral impairments of lead-injected young herring gulls in nature. Toxicological sciences 1994, 23, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuhammer, A. The chronic toxicity of aluminium, cadmium, mercury, and lead in birds: a review. Environmental Pollution 1987, 46, 263–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, E.; Bloom, A.J. Mineral nutrition of plants: principles and perspectives; Sinauer: 1853.
- Cavet, J.S.; Borrelly, G.P.; Robinson, N.J. ; Zn, Cu and Co in cyanobacteria: selective control of metal availability. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 2003, 27, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, P.; Babu, P.R.; Acharyya, T.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Stress and toxicity of biologically important transition metals (Co, Ni, Cu and Zn) on phytoplankton in a tropical freshwater system: An investigation with pigment analysis by HPLC. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Vivián, C.; Cabello, P.n.; Martínez-Luque, M.; Blasco, R.; Castillo, F. Prokaryotic nitrate reduction: molecular properties and functional distinction among bacterial nitrate reductases. Journal of bacteriology 1999, 181, 6573–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axler, R.; Gersberg, R.; Goldman, C. Stimulation of nitrate uptake and photosynthesis by molybdenum in Castle Lake, California. Canadian journal of fisheries and aquatic sciences 1980, 37, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. Journal of Chemistry 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whetten, C.L. “This strange enterprise”: Geneva steel and the American west. M.A., The University of Utah, United States -- Utah, 2011.
- Fuhriman, D.K.; Merritt, L.B.; Miller, A.W.; Stock, H.S. Hydrology and Water Quality of Utah Lake. Great Basin Naturalist Memoirs 1981, 43–67. [Google Scholar]
- Merritt, L.; Miller, W. Nutrient loading to Utah Lake. Utah Lake Studies 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau, U.S.C. US Census Bureau Publications - Census of Population and Housing. Availabe online: https://www.census.gov/prod/www/decennial.html (accessed on October, 2021).
- Schoderboeck, L.; Mühlegger, S.; Losert, A.; Gausterer, C.; Hornek, R. Effects assessment: Boron compounds in the aquatic environment. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norici, A.; Hell, R.; Giordano, M. Sulfur and primary production in aquatic environments: an ecological perspective. Photosynthesis Research 2005, 86, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karjalainen, J.; Hu, X.; Mäkinen, M.; Karjalainen, A.; Järvistö, J.; Järvenpää, K.; Sepponen, M.; Leppänen, M.T. Sulfate sensitivity of aquatic organism in soft freshwaters explored by toxicity tests and species sensitivity distribution. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2023, 258, 114984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodzek, M. The removal of boron from the aquatic environment–state of the art. Desalination and Water Treatment 2016, 57, 1107–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, S.C. Barium. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Third Edition), Wexler, P., Ed. Academic Press: Oxford, 2014; https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-386454-3.00819-8pp. 368-370. O. [CrossRef]
- Casbeer, W.; Williams, G.P.; Borup, M.B. Phosphorus Distribution in Delta Sediments: A Unique Data Set from Deer Creek Reservoir. Hydrology 2018, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constenius, K.N.; Clark, D.L.; King, J.K.; Ehler, J.B. Utah Geological Survey,: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2011.
- Hintze, L.F.; Kowallis, B.J. Geologic History of Utah: A Field Guide to Utah's Rocks, Special Publications 9 ed.; Department of Geological Sciences, Brigham Young University: Provo, UT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Szklarek, S.; Górecka, A.; Wojtal-Frankiewicz, A. The effects of road salt on freshwater ecosystems and solutions for mitigating chloride pollution - A review. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 805, 150289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, K.J.; Knight, A.W. Ecotoxicology of selenium in freshwater systems.
- Diaz, X.; Johnson, W.P.; Naftz, D.L. Selenium mass balance in the Great Salt Lake, Utah. Science of the Total Environment 2008, 407, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utah Department of Environmental Quality. Standards of Quality for Waters of the State. Availabe online: https://documents.deq.utah.gov/water-quality/standards-technical-services/DWQ-2021-017555.
- Utah Department of Environmental Quality Division of Water Quality. Water Quality Standards - Utah Department of Environmental Quality. Availabe online: https://deq.utah.gov/water-quality/water-quality-standards (accessed on .
- Quality, U.D.o.E. Water Qulaity Assessment and Analysis: Utah Lake Water Quality Study Availabe online: https://deq.utah.gov/water-quality/water-quality-assessment-and-analysis-utah-lake (accessed on.
- Laan, J.V. Question about interpreting R317-2 water quality standards Tanner, K., Ed. 2022.
- Valek, R.; Walmer, E.; Dorrett, C.; Tanner, K.; Cardall, A.; Williams, G. Utah Lake Nutrient Cycling Studies: Limnnocorral Usage and Experiments. In Proceedings of Intermountain Engineering, Technology, and Computing (IETC), Orem, UT, USA.
- Dorrett, C.; Cardall, A.; Tanner, K.; Valek, R.; Williams, G. Data Collection Methods for Utah Lake Nutrient Cycling Study. American Water Works Association Intermountain Section IMS-AWWA Annual Conference, 2021.
- Horowitz, A.J.; Elrick, K.A.; Colberg, M.R. The effect of membrane filtration artifacts on dissolved trace element concentrations. Water Research 1992, 26, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, B. Utah Lake Marina HAB Treatments Evaluation of Treatment Effectiveness 2021 Interim Report Quality, U.D.o.E., Ed. 2021.
- The Utah Lake Authority. Utah Lake Authority FY 2023 Annual Monitoring Report 2023.
- United States, B.O.R. Historic Data. Availabe online: https://www.usbr.gov/rsvrWater/HistoricalApp.html (accessed on 1/15).
- EPA. 2018 Final Aquatic Life Criteria for Aluminum in Freshwater. US EPA 2022.
- Correll, D.L. The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: A review. Journal of environmental quality 1998, 27, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PSOMAS. Utah Lake TMDL: Pollutant Loading Assessment & Designated Beneficial Use Impairment Assessment; Department of Environmental Quality 2007.
- Telfer, J.T.; Brown, M.M.; Williams, G.P.; Tanner, K.B.; Miller, A.W.; Sowby, R.B.; Miller, T.G. Source Attribution of Atmospheric Dust Deposition to Utah Lake. Hydrology 2023, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Consumer Factsheet on: Barium .
- US EPA. National Primary Drinking Water Regulations Availabe online: https://www.epa.gov/ground-water-and-drinking-water/national-primary-drinking-water-regulations (accessed on.
- Welch, A.H.; Westjohn, D.; Helsel, D.R.; Wanty, R.B. Arsenic in ground water of the United States: occurrence and geochemistry. Groundwater 2000, 38, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, M.S., N. E.; Fernando Ph.D., Q. A review of arsenic (III) in groundwater. Critical Reviews in Environmental Control 1991, 21, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| DE | Acute Standard (mg/L) |
Chronic Standard (mg/L) | Designated Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Aluminum (Al) | 0.75 | 0.75 | 3B, 3D |
| **Arsenic (As) | 0.10 | 0.10 | 4 |
| **Boron (B) | 0.75 | 0.75 | 4 |
| Cadmium (Cd) | 0.0018 | 0.00072 | 3B, 3D |
| ***Chromium (Cr) (Hexavalent) | 0.016 | 0.011 | 3B, 3D |
| Copper (Cu) | 0.013 | 0.009 | 3B, 3D |
| **Iron (Fe) | 1 | 1 | 3B, 3D |
| Nickel (Ni) | 0.468 | 0.052 | 3B,3D |
| *Phosphorus (P) | 0.025 | 0.025 | 3B |
| Lead (Pb) | 0.065 | 0.0025 | 3B, 3D |
| Selenium (Se) | 0.0184 | 0.0046 | 3B, 3D |
| Zinc (Zn) | 0.12 | 0.12 | 3B, 3D |
| * Concentration based on total recovery criteria **Measured as maximum not acute and chronic ***We measured elemental Cr, not hexavalent | |||
| Analyte | Model/Method | Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| DE Total (digested) | EPA 3015A | Thermo Scientific™ 7400 ICP-OES |
| DE Dissolved (filtered) | 0.45 µ filter | Thermo Scientific™ 7400 ICP-OES |
| Analyte | Detection Limit (µg/L) | Analyte | Detection Limit (µg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum (Al) | 1.51 | Molybdenum (Mo) | 1.11 |
| Arsenic (As) | 4.74 | Sodium (Na) | 1.80 |
| Boron (B) | 1.26 | Nickel (Ni) | 2.29 |
| Barium (Ba) | 0.17 | Phosphorus (P) | 5.66 |
| Calcium (Ca) | 0.02 | Lead (Pb) | 4.50 |
| Cadmium (Cd) | 0.19 | Sulfur (S) | 2.22 |
| Cobalt (Co) | 1.16 | Selenium (Se) | 7.36 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 0.85 | Silicon (Si) | 7.20 |
| Copper (Cu) | 2.36 | Strontium (Sr) | 0.04 |
| Iron (Fe) | 0.80 | Titanium (Ti) | 0.58 |
| Potassium (K) | 5.10 | Vanadium (V) | 0.80 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 0.04 | Zinc (Zn) | 0.60 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





