Submitted:
30 June 2024
Posted:
01 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Background
2. Glycogen Storage Disorders (GSDs) an Overview
3. Mitochondrial Metabolic Dysfunction
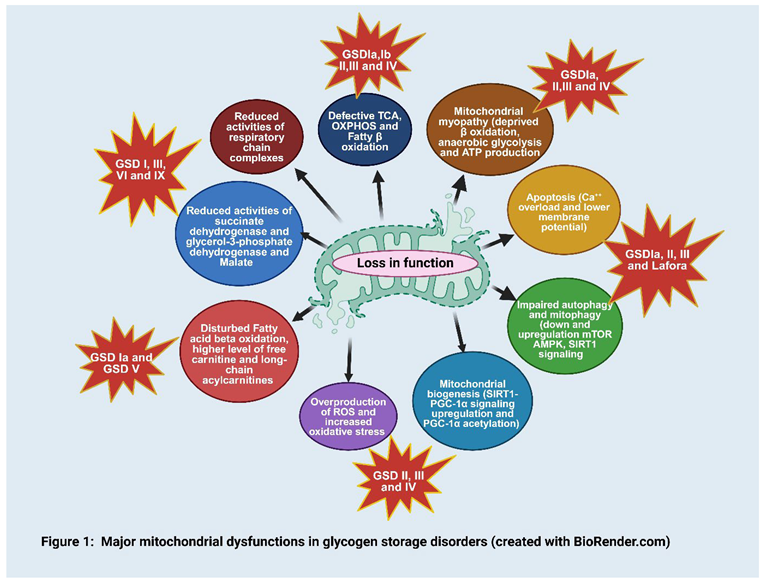
3.1. Overproduction of ROS and Oxidative Stress
3.2. Mitochondrial Biogenesis
3.3. Autophagy and Mitophagy
3.4. Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
3.5. Mitochondrial Myopathy
3.6. Mitochondrial Dysfunction Targeted Diagnosis and Therapeutic Strategies in GSDs
3.6.1. Diagnosis
3.7. Current Treatment Options and Therapies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gümüş, E.; Özen, H. Glycogen storage diseases: An update. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 3932–3963. [CrossRef]
- Kanungo, S.; Wells, K.; Tribett, T.; El-Gharbawy, A. Glycogen metabolism and glycogen storage disorders. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 474–474. [CrossRef]
- Massese, M.; Tagliaferri, F.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Maiorana, A. Glycogen storage diseases with liver involvement: a literature review of GSD type 0, IV, VI, IX and XI. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- de Marchi, R.; Nalin, T.; Sperb-Ludwig, F.; Pinheiro, F.C.; Schwartz, I.V.D.; Steiner, C.E. Glycogen Storage Disease: Expert Opinion on Clinical Diagnosis Revisited after Molecular Testing. Genes 2023, 14, 2219. [CrossRef]
- La Morgia, C.; Maresca, A.; Caporali, L.; Valentino, M.L.; Carelli, V. Mitochondrial diseases in adults. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 287, 592–608. [CrossRef]
- Nsiah-Sefaa, A.; McKenzie, M. Combined defects in oxidative phosphorylation and fatty acid β-oxidation in mitochondrial disease. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36, e00313. [CrossRef]
- Gjorgjieva, M.; Oosterveer, M.H.; Mithieux, G.; Rajas, F. Mechanisms by Which Metabolic Reprogramming in GSD1 Liver Generates a Favorable Tumorigenic Environment. J. Inborn Errors Metab. Screen. 2016, 4. [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhou, R.; Jiang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.; Li, A.; Zhang, Y. Mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in Pompe disease-specific induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Cell Prolif. 2023, 57, e13573. [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, J.S.; Bhatti, G.K.; Reddy, P.H. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in metabolic disorders—A step towards mitochondria based therapeutic strategies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1066–1077. [CrossRef]
- Stepien, K.M.; Roncaroli, F.; Turton, N.; Hendriksz, C.J.; Roberts, M.; Heaton, R.A.; Hargreaves, I. Mechanisms of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Lysosomal Storage Disorders: A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2596. [CrossRef]
- Sentner, C.P.; Hoogeveen, I.J.; Weinstein, D.A.; Santer, R.; Murphy, E.; McKiernan, P.J.; Steuerwald, U.; Beauchamp, N.J.; Taybert, J.; Laforêt, P.; et al. Glycogen storage disease type III: diagnosis, genotype, management, clinical course and outcome. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2016, 39, 697–704. [CrossRef]
- Farah, B.L.; Sinha, R.A.; Wu, Y.; Singh, B.K.; Lim, A.; Hirayama, M.; Landau, D.J.; Bay, B.H.; Koeberl, D.D.; Yen, P.M. Hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction is a feature of Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ia (GSDIa). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep44408. [CrossRef]
- Fiuza-Luces C, Andreu A, Rodríguez-Aguilera J, Martín M, Arenas J, Vissing J, et al. Low aerobic capacity in McArdle disease: A role for mitochondrial network impairment? 2022.
- Kamenets, E.A.; Gusarova, E.A.; Milovanova, N.V.; Itkis, Y.S.; Strokova, T.V.; Melikyan, M.A.; Garyaeva, I.V.; Rybkina, I.G.; Nikitina, N.V.; Zakharova, E.Y. Hepatic glycogen synthase (GYS2) deficiency: seven novel patients and seven novel variants. JIMD Rep. 2020, 53, 39–44. [CrossRef]
- Kasapkara, .S.; Aycan, Z.; Açoğlu, E.; Senel, S.; Oguz, M.M.; Ceylaner, S. The variable clinical phenotype of three patients with hepatic glycogen synthase deficiency. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 30. [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, O.; Pugliese, A.; Oteri, R.; Volta, S.; Ciranni, A.; Moggio, M.; Rodolico, C.; Toscano, A. A new phenotype of muscle glycogen synthase deficiency (GSD0B) characterized by an adult onset myopathy without cardiomyopathy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2022, 32, 582–589. [CrossRef]
- Kollberg, G.; Tulinius, M.; Gilljam, T.; Östman-Smith, I.; Forsander, G.; Jotorp, P.; Oldfors, A.; Holme, E. Cardiomyopathy and Exercise Intolerance in Muscle Glycogen Storage Disease 0. New Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1507–1514. [CrossRef]
- Visser, G.; Rake, J.-P.; Fernandes, J.; Labrune, P.; Leonard, J.V.; Moses, S.; Ullrich, K.; Smit, G.A. Neutropenia, neutrophil dysfunction, and inflammatory bowel disease in glycogen storage disease type Ib: Results of the European Study on Glycogen Storage Disease Type I. J. Pediatr. 2000, 137, 187–191. [CrossRef]
- Veiga-Da-Cunha, M.; Wortmann, S.B.; Grünert, S.C.; Van Schaftingen, E. Treatment of the Neutropenia Associated with GSD1b and G6PC3 Deficiency with SGLT2 Inhibitors. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1803. [CrossRef]
- Meena, N.K.; Raben, N. Pompe Disease: New Developments in an Old Lysosomal Storage Disorder. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1339. [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, E.; Szymańska, S.; Truszkowska, G.; Ciara, E.; Pronicki, M.; Shin, Y.S.; Podskarbi, T.; Kępka, A.; Śpiewak, M.; Płoski, R.; et al. Variable clinical presentation of glycogen storage disease type IV: from severe hepatosplenomegaly to cardiac insufficiency. Some discrepancies in genetic and biochemical abnormalities. Arch. Med Sci. 2018, 1, 237–247. [CrossRef]
- Kakhlon, O.; Vaknin, H.; Mishra, K.; D’souza, J.; Marisat, M.; Sprecher, U.; Wald-Altman, S.; Dukhovny, A.; Raviv, Y.; Da’adoosh, B.; et al. Alleviation of a polyglucosan storage disorder by enhancement of autophagic glycogen catabolism. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e14554. [CrossRef]
- Koch, R.L.; Soler-Alfonso, C.; Kiely, B.T.; Asai, A.; Smith, A.L.; Bali, D.S.; Kang, P.B.; Landstrom, A.P.; Akman, H.O.; Burrow, T.A.; et al. Diagnosis and management of glycogen storage disease type IV, including adult polyglucosan body disease: A clinical practice resource. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2023, 138, 107525. [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.D.; Pereira, .; Soares, A.R.; Guimas, A.; Rocha, S.; Cardoso, M.; Garrido, C.; Soares, C.A.; Nunes, I.S.; Fortuna, A.M.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy and the first genotype–phenotype correlation in glycogen storage disease type V. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Labrador E, Weinstein DA. Glycogen storage disease type VI. 2019.
- Aeppli, T.R.; Rymen, D.; Allegri, G.; Bode, P.K.; Häberle, J. Glycogen storage disease type VI: clinical course and molecular background. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 179, 405–413. [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, O.; Bruno, C.; Mongini, T.; Rodolico, C.; Aguennouz, M.; Barca, E.; Amati, A.; Cassandrini, D.; Serlenga, L.; Vita, G.; et al. Clinical features and new molecular findings in muscle phosphofructokinase deficiency (GSD type VII). Neuromuscul. Disord. 2011, 22, 325–330. [CrossRef]
- DiMauro, S.; Spiegel, R. Progress and problems in muscle glycogenoses. 2011, 30, 96–102.
- Fernandes, S.A.; Cooper, G.E.; Gibson, R.A.; Kishnani, P.S. Benign or not benign? Deep phenotyping of liver Glycogen Storage Disease IX. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2020, 131, 299–305. [CrossRef]
- Roscher, A.; Patel, J.; Hewson, S.; Nagy, L.; Feigenbaum, A.; Kronick, J.; Raiman, J.; Schulze, A.; Siriwardena, K.; Mercimek-Mahmutoglu, S. The natural history of glycogen storage disease types VI and IX: Long-term outcome from the largest metabolic center in Canada. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2014, 113, 171–176. [CrossRef]
- Kishnani, P.S.; Goldstein, J.; Austin, S.L.; Arn, P.; Bachrach, B.; Bali, D.S.; Chung, W.K.; El-Gharbawy, A.; Brown, L.M.; Kahler, S.; et al. Diagnosis and management of glycogen storage diseases type VI and IX: a clinical practice resource of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Anesthesia Analg. 2019, 21, 772–789. [CrossRef]
- Bali DS, Goldstein JL, Fredrickson K, Austin S, Pendyal S, Rehder C, et al. Clinical and molecular variability in patients with PHKA2 variants and liver phosphorylase b kinase deficiency. JIMD Reports, Volume 37. 2017:63-72.
- Ellingwood, S.S.; Cheng, A. Biochemical and clinical aspects of glycogen storage diseases. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 238, R131–R141. [CrossRef]
- Kwong, A.K.; Wong, S.S.; Rodenburg, R.J.T.; Smeitink, J.; Chan, G.C.F.; Fung, C. Human d-lactate dehydrogenase deficiency by LDHD mutation in a patient with neurological manifestations and mitochondrial complex IV deficiency. JIMD Rep. 2021, 60, 15–22. [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Lorenzo P, Rabasa M, Esteban J, Hidalgo Mayoral I, Domínguez-González C, Blanco-Echevarría A, et al. Clinical, biochemical, and molecular characterization of two families with novel mutations in the LDHA gene (GSD XI). Genes. 2022;13 [10]:1835.
- Jin, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Ding, J. Lactate dehydrogenase D is a general dehydrogenase for D-2-hydroxyacids and is associated with D-lactic acidosis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Mamoune, A.; Bahuau, M.; Hamel, Y.; Serre, V.; Pelosi, M.; Habarou, F.; Morel, M.-A.N.; Boisson, B.; Vergnaud, S.; Viou, M.T.; et al. A Thermolabile Aldolase A Mutant Causes Fever-Induced Recurrent Rhabdomyolysis without Hemolytic Anemia. PLOS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004711–e1004711. [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, C.; Svingou, M.; Kekou, K.; Vergnaud, S.; Xirou, S.; Niotakis, G.; Papadimas, G. Aldolase A deficiency: Report of new cases and literature review. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2021, 27, 100730. [CrossRef]
- Wigley, R.; Scalco, R.S.; Gardiner, A.R.; Godfrey, R.; Booth, S.; Kirk, R.; Hilton-Jones, D.; Houlden, H.; Heales, S.; Quinlivan, R. The need for biochemical testing in beta-enolase deficiency in the genomic era. JIMD Rep. 2019, 50, 40–43. [CrossRef]
- Buch AE, Musumeci O, Wigley R, Stemmerik MPG, Eisum ASV, Madsen KL, et al. Energy metabolism during exercise in patients with β-enolase deficiency (GSDXIII). JIMD reports. 2021;61 [1]:60-6.
- Malfatti E, Nilsson J, Hedberg-Oldfors C, Hernandez-Lain A, Michel F, Dominguez-Gonzalez C, et al. A new muscle glycogen storage disease associated with glycogenin-1 deficiency. Annals of neurology. 2014;76 [6]:891-8.
- Visuttijai, K.; Hedberg-Oldfors, C.; Thomsen, C.; Glamuzina, E.; Kornblum, C.; Tasca, G.; Hernandez-Lain, A.; Sandstedt, J.; Dellgren, G.; Roach, P.; et al. Glycogenin is Dispensable for Glycogen Synthesis in Human Muscle, and Glycogenin Deficiency Causes Polyglucosan Storage. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 557–566. [CrossRef]
- Conte, F.; Morava, E.; Abu Bakar, N.; Wortmann, S.B.; Poerink, A.J.; Grunewald, S.; Crushell, E.; Al-Gazali, L.; de Vries, M.C.; Mørkrid, L.; et al. Phosphoglucomutase-1 deficiency: Early presentation, metabolic management and detection in neonatal blood spots. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2020, 131, 135–146. [CrossRef]
- Altassan R, Radenkovic S, Edmondson AC, Barone R, Brasil S, Cechova A, et al. International consensus guidelines for phosphoglucomutase 1 deficiency (PGM1-CDG): diagnosis, follow-up, and management. Journal of inherited metabolic disease. 2021;44 [1]:148-63.
- Grünert, S.C.; Schwab, K.O.; Pohl, M.; Sass, J.O.; Santer, R. Fanconi–Bickel syndrome: GLUT2 mutations associated with a mild phenotype. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 105, 433–437. [CrossRef]
- Sharari, S.; Abou-Alloul, M.; Hussain, K.; Khan, F.A. Fanconi–Bickel Syndrome: A Review of the Mechanisms That Lead to Dysglycaemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6286. [CrossRef]
- Matsumaru, S.; Oguni, H.; Ogura, H.; Shimojima, K.; Nagata, S.; Kanno, H.; Yamamoto, T. A novel PGK1 mutation associated with neurological dysfunction and the absence of episodes of hemolytic anemia or myoglobinuria. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2017, 6, 132–136. [CrossRef]
- Echaniz-Laguna, A.; Nadjar, Y.; Béhin, A.; Biancalana, V.; Piraud, M.; Malfatti, E.; Laforêt, P. Phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency: A nationwide multicenter retrospective study. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 803–808. [CrossRef]
- Vega RB, Horton JL, Kelly DP. Maintaining ancient organelles: mitochondrial biogenesis and maturation. Circulation research. 2015;116 [11]:1820-34.
- Sturm, G.; Karan, K.R.; Monzel, A.S.; Santhanam, B.; Taivassalo, T.; Bris, C.; Ware, S.A.; Cross, M.; Towheed, A.; Higgins-Chen, A.; et al. OxPhos defects cause hypermetabolism and reduce lifespan in cells and in patients with mitochondrial diseases. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z. Defect of mitochondrial respiratory chain is a mechanism of ROS overproduction in a rat model of alcoholic liver disease: role of zinc deficiency. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G205–G214. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.; Collier, J.J.; Glasgow, R.I.C.; Robertson, F.M.; Pyle, A.; Blakely, E.L.; Alston, C.L.; Oláhová, M.; McFarland, R.; Taylor, R.W. Recent advances in understanding the molecular genetic basis of mitochondrial disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 43, 36–50. [CrossRef]
- Fassone, E.; Rahman, S. Complex I deficiency: clinical features, biochemistry and molecular genetics. J. Med Genet. 2012, 49, 578–590. [CrossRef]
- Rodenburg RJ. Mitochondrial complex I-linked disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics. 2016;1857 [7]:938-45.
- Kurbatova, O.; Izmailova, T.; Surkov, A.; Namazova-Baranova, L.; Polyakova, S.; Miroshkina, L.; Semenova, G.; Samokhina, I.; Kapustiuna, E.; Dukhova, Z.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Children with Hepatic Forms of Glycogen Storage Disease. Ann. Russ. Acad. Med Sci. 2014, 69, 78–84. [CrossRef]
- Wary, C.; Nadaj-Pakleza, A.; Laforêt, P.; Claeys, K.G.; Carlier, R.; Monnet, A.; Fleury, S.; Baligand, C.; Eymard, B.; Labrune, P.; et al. Investigating glycogenosis type III patients with multi-parametric functional NMR imaging and spectroscopy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2010, 20, 548–558. [CrossRef]
- Preisler N, Pradel A, Husu E, Madsen KL, Becquemin M-H, Mollet A, et al. Exercise intolerance in glycogen storage disease type III: weakness or energy deficiency? Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. 2013;109 [1]:14-20.
- Hennis, P.J.; Murphy, E.; Meijer, R.I.; Lachmann, R.H.; Ramachandran, R.; Bordoli, C.; Rayat, G.; Tomlinson, D.J. Aerobic capacity and skeletal muscle characteristics in glycogen storage disease IIIa: an observational study. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Hannibal, L.; Theimer, J.; Wingert, V.; Klotz, K.; Bierschenk, I.; Nitschke, R.; Spiekerkoetter, U.; Grünert, S.C. Metabolic Profiling in Human Fibroblasts Enables Subtype Clustering in Glycogen Storage Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11. [CrossRef]
- Rossi A, Ruoppolo M, Formisano P, Villani G, Albano L, Gallo G, et al. Insulin-resistance in glycogen storage disease type Ia: linking carbohydrates and mitochondria? Journal of inherited metabolic disease. 2018;41 [6]:985-95.
- Saavedra, H.; Yu, A.; Rodriguez-Buritica, D. The use of alanine, free carnitine and IGFBP-1 as potential biomarkers for glycogen storage disease type I. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2022, 136, S18. [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Assunto, A.; Rosano, C.; Tucci, S.; Ruoppolo, M.; Caterino, M.; Pirozzi, F.; Strisciuglio, P.; Parenti, G.; Melis, D. Mitochondrial reprogramming in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with glycogen storage disease type Ia. Genes Nutr. 2023, 18, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R.; Ali, A.H.; Ibdah, J.A. Mitochondrial Dysfunction Plays Central Role in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7280. [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia B, Summers SA. Ceramides–lipotoxic inducers of metabolic disorders. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2015;26 [10]:538-50.
- Milane L, Trivedi M, Singh A, Talekar M, Amiji M. Mitochondrial biology, targets, and drug delivery. Journal of controlled release. 2015;207:40-58.
- Kishnani, P.S.; Steiner, R.D.; Bali, D.; Berger, K.; Byrne, B.J.; Case, L.E.; Crowley, J.F.; Downs, S.; Howell, R.R.; Kravitz, R.M.; et al. Pompe disease diagnosis and management guideline. Anesthesia Analg. 2006, 8, 267–288. [CrossRef]
- Ranjbarvaziri S, Kooiker KB, Ellenberger M, Fajardo G, Zhao M, Vander Roest AS, et al. Altered cardiac energetics and mitochondrial dysfunction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 2021;144 [21]:1714-31. [CrossRef]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Karwi, Q.G.; Tian, R.; Wende, A.R.; Abel, E.D. Cardiac Energy Metabolism in Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1487–1513. [CrossRef]
- Huang H-P, Chen P-H, Hwu W-L, Chuang C-Y, Chien Y-H, Stone L, et al. Human Pompe disease-induced pluripotent stem cells for pathogenesis modeling, drug testing and disease marker identification. Human molecular genetics. 2011;20 [24]:4851-64.
- Lim, J.-A.; Li, L.; Kakhlon, O.; Myerowitz, R.; Raben, N. Defects in calcium homeostasis and mitochondria can be reversed in Pompe disease. Autophagy 2015, 11, 385–402. [CrossRef]
- Palma FR, Gantner BN, Sakiyama MJ, Kayzuka C, Shukla S, Lacchini R, et al. ROS production by mitochondria: function or dysfunction? Oncogene. 2024;43 [5]:295-303.
- Napolitano, G.; Fasciolo, G.; Venditti, P. Mitochondrial Management of Reactive Oxygen Species. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1824. [CrossRef]
- Bou-Teen, D.; Kaludercic, N.; Weissman, D.; Turan, B.; Maack, C.; Di Lisa, F.; Ruiz-Meana, M. Mitochondrial ROS and mitochondria-targeted antioxidants in the aged heart. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 167, 109–124. [CrossRef]
- Vujic, A.; Koo, A.N.; Prag, H.A.; Krieg, T. Mitochondrial redox and TCA cycle metabolite signaling in the heart. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 166, 287–296. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Bai, H. Peroxisomal Stress Response and Inter-Organelle Communication in Cellular Homeostasis and Aging. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 192. [CrossRef]
- Betteridge DJ. What is oxidative stress? Metabolism. 2000;49 [2]:3-8.
- Lee, B.-C.; Lee, J. Cellular and molecular players in adipose tissue inflammation in the development of obesity-induced insulin resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2014, 1842, 446–462. [CrossRef]
- Prasun P. Mitochondrial dysfunction in metabolic syndrome. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease. 2020;1866 [10]:165838.
- Wallace, D.C. Mitochondrial genetic medicine. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1642–1649. [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves VF. Mitochondrial genetics. Mitochondria in Health and in Sickness. 2019:247-55.
- Abu Shelbayeh, O.; Arroum, T.; Morris, S.; Busch, K.B. PGC-1α Is a Master Regulator of Mitochondrial Lifecycle and ROS Stress Response. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1075. [CrossRef]
- Islam, H.; Edgett, B.A.; Gurd, B.J. Coordination of mitochondrial biogenesis by PGC-1α in human skeletal muscle: A re-evaluation. Metabolism 2018, 79, 42–51. [CrossRef]
- Jannig, P.R.; Dumesic, P.A.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Ruas, J.L. SnapShot: Regulation and biology of PGC-1α. Cell 2022, 185, 1444–1444.e1. [CrossRef]
- Ruderman NB, Julia Xu X, Nelson L, Cacicedo JM, Saha AK, Lan F, et al. AMPK and SIRT1: a long-standing partnership? American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2010;298 [4]:E751-E60.
- Carling, D.; Viollet, B. Beyond Energy Homeostasis: the Expanding Role of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase in Regulating Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 799–804. [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Kim, G.; Mansfield, B.C.; Chou, J.Y. Sirtuin signaling controls mitochondrial function in glycogen storage disease type Ia. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 997–1006. [CrossRef]
- Majeed, S.T.; Majeed, R.; Andrabi, K.I. Expanding the view of the molecular mechanisms of autophagy pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 3257–3277. [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Tooze, S.A. Autophagy pathway: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Autophagy 2017, 14, 207–215. [CrossRef]
- Deus, C.M.; Yambire, K.F.; Oliveira, P.J.; Raimundo, N. Mitochondria–Lysosome Crosstalk: From Physiology to Neurodegeneration. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 71–88. [CrossRef]
- Audano, M.; Schneider, A.; Mitro, N. Mitochondria, lysosomes, and dysfunction: their meaning in neurodegeneration. J. Neurochem. 2018, 147, 291–309. [CrossRef]
- Narendra, D.P.; Jin, S.M.; Tanaka, A.; Suen, D.-F.; Gautier, C.A.; Shen, J.; Cookson, M.R.; Youle, R.J. PINK1 Is Selectively Stabilized on Impaired Mitochondria to Activate Parkin. PLOS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000298. [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, N.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, T. PINK1-dependent phosphorylation of PINK1 and Parkin is essential for mitochondrial quality control. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2501–e2501. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhu, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, X.; Huang, A.; Huang, Y. Mitophagy in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Roles and Mechanisms. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Miyoshi, T.; Yoshida, M.; Akagi, S.; Saito, Y.; Ejiri, K.; Matsuo, N.; Ichikawa, K.; Iwasaki, K.; Naito, T.; et al. Pathophysiology and Treatment of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy and Heart Failure in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3587. [CrossRef]
- Farah, B.L.; Landau, D.J.; Sinha, R.A.; Brooks, E.D.; Wu, Y.; Fung, S.Y.S.; Tanaka, T.; Hirayama, M.; Bay, B.-H.; Koeberl, D.D.; et al. Induction of autophagy improves hepatic lipid metabolism in glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency. J. Hepatol. 2015, 64, 370–379. [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-H.; Kim, G.-Y.; Pan, C.-J.; Anduaga, J.; Choi, E.-J.; Mansfield, B.C.; Chou, J.Y. Downregulation of SIRT1 signaling underlies hepatic autophagy impairment in glycogen storage disease type Ia. PLOS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006819. [CrossRef]
- Farah, B.L.; Yen, P.M.; Koeberl, D.D. Links between autophagy and disorders of glycogen metabolism – Perspectives on pathogenesis and possible treatments. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 129, 3–12. [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Gumusgoz, E.; Minassian, B. Lafora disease: Current biology and therapeutic approaches. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 178, 315–325. [CrossRef]
- Lahuerta, M.; Aguado, C.; Sánchez-Martín, P.; Sanz, P.; Knecht, E. Degradation of altered mitochondria by autophagy is impaired in Lafora disease. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 2071–2090. [CrossRef]
- Klemmensen, M.M.; Borrowman, S.H.; Pearce, C.; Pyles, B.; Chandra, B. Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders. Neurotherapeutics 2024, 21, e00292. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Mu, T.; Wang, G.; Jiang, X. Mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in mammals. Protein Cell 2014, 5, 737–749. [CrossRef]
- Orrenius, S.; Gogvadze, V.; Zhivotovsky, B. Calcium and mitochondria in the regulation of cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 72–81. [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, S.; Yang, L.; Damodaran, T.; Desai, D.; Diehl, A.M.; Alzate, O.; Koeberl, D.D. Activation of glycolysis and apoptosis in glycogen storage disease type Ia. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2009, 97, 267–271. [CrossRef]
- Tarnopolsky, M.A. Myopathies Related to Glycogen Metabolism Disorders. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 915–927. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, L.-K.; Hwu, W.-L.; Lee, N.-C.; Huang, P.-H.; Chien, Y.-H. Clinical features of Pompe disease with motor neuronopathy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2019, 29, 903–906. [CrossRef]
- Leslie N, Bailey L. Pompe disease. 2017.
- Leslie N, Bailey L. Pompe Disease. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, et al., editors. GeneReviews(®). Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle.
- Copyright © 1993-2024, University of Washington, Seattle. GeneReviews is a registered trademark of the University of Washington, Seattle. All rights reserved.; 1993.
- De Feo P, Di Loreto C, Lucidi P, Murdolo G, Parlanti N, De Cicco A, et al. Metabolic response to exercise. Journal of endocrinological investigation. 2003;26:851-4.
- Li X-Y, Yang Y-L. Mitochondrial disorders associated with mitochondrial respiratory chain complex V deficiency. Zhongguo Dang dai er ke za zhi= Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics. 2013;15 [7]:596-600.
- De Stefano N, Argov Z, Matthews PM, Karpati G, Arnold DL. Impairment of muscle mitochondrial oxidative metabolism in McArdle’s disease. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine. 1996;19 [6]:764-9.
- Zeviani, M.; Viscomi, C. Mitochondrial Neurodegeneration. Cells 2022, 11, 637. [CrossRef]
- Moslemi, A.-R.; Lindberg, C.; Nilsson, J.; Tajsharghi, H.; Andersson, B.; Oldfors, A. Glycogenin-1 Deficiency and Inactivated Priming of Glycogen Synthesis. New Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1203–1210. [CrossRef]
- Santalla, A.; Valenzuela, P.L.; Rodriguez-Lopez, C.; Rodríguez-Gómez, I.; Nogales-Gadea, G.; Pinós, T.; Arenas, J.; Martín, M.A.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Morán, M.; et al. Long-Term Exercise Intervention in Patients with McArdle Disease: Clinical and Aerobic Fitness Benefits. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2022, 54, 1231–1241. [CrossRef]
- Munguía-Izquierdo, D.; Santalla, A.; Lucia, A. Cardiorespiratory Fitness, Physical Activity, and Quality of Life in Patients with McArdle Disease. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 799–808. [CrossRef]
- Scalco, R.S.; EUROMAC Consortium; Lucia, A.; Santalla, A.; Martinuzzi, A.; Vavla, M.; Reni, G.; Toscano, A.; Musumeci, O.; Voermans, N.C.; et al. Data from the European registry for patients with McArdle disease and other muscle glycogenoses (EUROMAC). Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Santalla, A.; Nogales-Gadea, G.; Encinar, A.B.; Vieitez, I.; González-Quintana, A.; Serrano-Lorenzo, P.; Consuegra, I.G.; Asensio, S.; Ballester-Lopez, A.; Pintos-Morell, G.; et al. Genotypic and phenotypic features of all Spanish patients with McArdle disease: a 2016 update. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 819–819. [CrossRef]
- Pizzamiglio, C.; Mahroo, O.A.; Khan, K.N.; Patasin, M.; Quinlivan, R. Phenotype and genotype of 197 British patients with McArdle disease: An observational single-centre study. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 1409–1418. [CrossRef]
- Kishnani, P.S.; Austin, S.L.; Abdenur, J.E.; Arn, P.; Bali, D.S.; Boney, A.; Chung, W.K.; Dagli, A.I.; Dale, D.; Koeberl, D.; et al. Diagnosis and management of glycogen storage disease type I: a practice guideline of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Anesthesia Analg. 2014, 16, e1–e29. [CrossRef]
- Hannah WB, Derks TG, Drumm ML, Grünert SC, Kishnani PS, Vissing J. Glycogen storage diseases. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. 2023;9 [1]:46.
- Keutzer, J.M. Establishing Pompe Disease Newborn Screening: The Role of Industry. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6, 55. [CrossRef]
- Mancuso M, Coppede F, Migliore L, Siciliano G, Murri L. Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. 2006;10 [1]:59-73.
- Rodenburg, R.J.T. Biochemical diagnosis of mitochondrial disorders. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2010, 34, 283–292. [CrossRef]
- Spinazzi, M.; Casarin, A.; Pertegato, V.; Ermani, M.; Salviati, L.; Angelini, C. Optimization of respiratory chain enzymatic assays in muscle for the diagnosis of mitochondrial disorders. Mitochondrion 2011, 11, 893–904. [CrossRef]
- Spinazzi, M.; Casarin, A.; Pertegato, V.; Salviati, L.; Angelini, C. Assessment of mitochondrial respiratory chain enzymatic activities on tissues and cultured cells. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1235–1246. [CrossRef]
- Medja, F.; Allouche, S.; Frachon, P.; Jardel, C.; Malgat, M.; Mousson de Camaret, B.; Slama, A.; Lunardi, J.; Mazat, J.P.; Lombès, A. Development and implementation of standardized respiratory chain spectrophotometric assays for clinical diagnosis. Mitochondrion 2009, 9, 331–339. [CrossRef]
- Winkel LP, Kamphoven JH, Van Den Hout HJ, Severijnen LA, Van Doorn PA, Reuser AJ, et al. Morphological changes in muscle tissue of patients with infantile Pompe’s disease receiving enzyme replacement therapy. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine. 2003;27 [6]:743-51.
- Koeberl, D.D.; Koch, R.L.; Lim, J.; Brooks, E.D.; Arnson, B.D.; Sun, B.; Kishnani, P.S. Gene therapy for glycogen storage diseases. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2023, 47, 93–118. [CrossRef]
- Jauze, L.; Monteillet, L.; Mithieux, G.; Rajas, F.; Ronzitti, G. Challenges of Gene Therapy for the Treatment of Glycogen Storage Diseases Type I and Type III. Hum. Gene Ther. 2019, 30, 1263–1273. [CrossRef]
- Kishnani, P.S.; Sun, B.; Koeberl, D.D. Gene therapy for glycogen storage diseases. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, R31–R41. [CrossRef]
- Polyak, E.; Ostrovsky, J.; Peng, M.; Dingley, S.D.; Tsukikawa, M.; Kwon, Y.J.; McCormack, S.E.; Bennett, M.; Xiao, R.; Seiler, C.; et al. N-acetylcysteine and vitamin E rescue animal longevity and cellular oxidative stress in pre-clinical models of mitochondrial complex I disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 123, 449–462. [CrossRef]
- El-Hattab, A.W.; Zarante, A.M.; Almannai, M.; Scaglia, F. Therapies for mitochondrial diseases and current clinical trials. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 122, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.I.; Crozier, M.; Di Carlo, A.; Xhuti, D.; Manta, K.; Roik, L.J.; Bujak, A.L.; Nederveen, J.P.; Tarnopolsky, M.G.; Hettinga, B.; et al. Nutritional co-therapy with 1,3-butanediol and multi-ingredient antioxidants enhances autophagic clearance in Pompe disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2022, 137, 228–240. [CrossRef]
- Andreadi, A.; Bellia, A.; Di Daniele, N.; Meloni, M.; Lauro, R.; Della-Morte, D.; Lauro, D. The molecular link between oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes: A target for new therapies against cardiovascular diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2021, 62, 85–96. [CrossRef]
- Grünert, S.C.; Elling, R.; Maag, B.; Wortmann, S.B.; Derks, T.G.J.; Hannibal, L.; Schumann, A.; Rosenbaum-Fabian, S.; Spiekerkoetter, U. Improved inflammatory bowel disease, wound healing and normal oxidative burst under treatment with empagliflozin in glycogen storage disease type Ib. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Wortmann SB, Van Hove JL, Derks TG, Chevalier N, Knight V, Koller A, et al. Treating neutropenia and neutrophil dysfunction in glycogen storage disease type Ib with an SGLT2 inhibitor. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology. 2020;136 [9]:1033-43. [CrossRef]
- Maiorana, A.; Tagliaferri, F.; Dionisi-Vici, C. Current understanding on pathogenesis and effective treatment of glycogen storage disease type Ib with empagliflozin: new insights coming from diabetes for its potential implications in other metabolic disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14. [CrossRef]
| Disorders (Common Name) | Enzyme | Gene/Chromosome/Inheritance | Clinical Manifestation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSD 0a | Glycogen synthase in Liver | GYS2/ 12p12.1/AR | Fasting ketotic hypoglycemia, reactive hyperglycemia and lactate elevation | [14,15] |
| GSD 0b | Glycogen synthase in muscle | GYS1/ 19q13.33/AR | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy exercise intolerance, and adult-onset myopathy without cardiomyopathy |
[16,17] |
| GSD Ia (von Gierke disease) |
Glucose-6-phosphatase | G6PC/17q21.31/ AR | Hypoglycemia, lactic acidosis, hypertriglyceridemia, hepatomegaly, renal dysfunction | [18] |
| GSD Ib |
Glucose-6-phosphate translocase |
SLC37A4/11q23.3/AR | Neutropenia, neutrophil dysfunction and inflammatory bowel disease |
[19] |
| GSD II (Pompe disease) |
alpha-1,4-glucosidase |
GAA /17q25.3/AR | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, hypotonia, and motor delay | [20] |
| GSD III (Cori or Forbes disease) |
Glycogen debranching (amylo-1,6 glucosidase) |
AGL/1p21.2/ AR | Hypoglycemia, elevated ketosis in hyperlipidemia, hepatomegaly, elevated liver enzyme myopathy, variable muscle and cardiac phenotype | [11] |
| GSD IV (Andersen or Adult polyglucosan body disease) |
Glycogen branching enzyme- amylo (1,4 -1,6) transglucosidase |
GBE1/3p12.2/AR | Hepatosplenomegaly, liver dysfunction, progressive cirrhosis, cardiomyopathy, hypotonia, gait difficulty, progressive neurogenic bladder, autonomic dysfunction, sensory loss and variable cognitive difficulty | [21,22,23] |
| GSD 5 (McArdle disease) |
Myophosphorylase | PYGM/11q13.1/ AR | Exercise induces fatigue, cramps, tachypnoea and tachycardia, rhabdomyolysis, myoglobinuria | [24] |
| GSD 6 (Hers disease) |
Liver glycogen phosphorylase |
PYGL/14q22.1/ AR | Hepatomegaly, hypoglycemia, with ketosis, elevated liver transaminases, hyperlipidemia, osteoporosis, liver fibrosis | [25,26] |
| GSD 7 (Tarui disease) |
Muscle phosphofructokinase |
PFKM/12q13.11/ AR | Hemolytic anemia, muscle weakness, exercise-induced muscle cramping, exertional Myopathy, gout/hyperuricemia |
[27,28] |
| GSD 9A1 (formerly GSD 8) |
Alpha-2 subunit of liver phosphorylase kinase |
PHKA2/Xp22.13 XL | Hepatomegaly, growth retardation, motor developmental delay. Hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, elevated liver enzymes; fasting hyperketosis |
[29] |
| GSD 9B (GSD IXb) |
Beta subunit of liver and muscle phosphorylase |
PHKB/16q12.1/ AR | Short stature, hepatomegaly, diarrhea, muscle Weakness, hypotonia |
[3,30] |
| GSD 9C (GSD IXc) |
Hepatic and testis isoform— gamma subunit of phosphorylase kinase |
PHKG2/16p11.2/AR | Growth retardation, hepatomegaly, hypotonia; cognitive delay |
[31,32] |
| GSD 9D (GSD IXd) |
Alpha subunit of muscle phosphorylase kinase |
PHKA1/Xq13.1/XL | Muscle weakness, exercise-induced muscle pain & stiffness, muscle atrophy, elevated CK |
[3,29,31] |
| GSD 10 (GSD X) | Muscle phosphoglycerate mutase |
PGAM2/7p13/AR | Exercise intolerance with cramp or pain, rhabdomyolysis, myoglobinuria, hyperuricemia, coronary arteriosclerosis | [2,33] |
| GSD 11 (GSD XI) |
Lactate dehydrogenase A | LDHA/11p15.1/AR | Exercise-induced muscle cramps & pain, uterine muscle stiffness in pregnancy, psoriatic skin lesions, Elevated serum CK during myoglobinuria, with low serum lactate dehydrogenase | [34,35,36] |
| GSD 12 (GSD XII) |
Fructose-1,6- bisphosphate aldolase |
ALDOA/16p11.2/AR | Short stature dysmorphic face, myopathy; mental retardation; delayed puberty; hemolytic anemia, hepatosplenomegaly; rhabdomyolysis with febrile illness |
[37,38] |
| GSD 13 (GSD XIII) |
Beta-enolase | ENO3/17p13.2/AR | Exercise intolerance, myalgia, rhabdomyolysis with fatty infiltration | [39,40] |
| GSD 15 (GSD XV) |
Glycogenin-1 | GYG1/3q24/AR | Weakness, arrhythmias, skeletal myopathy, cardiomyopathy | [41,42] |
| GSD 14 (Previously GSDXIV) | Phosphoglucomutase-1 | PGM1/1p31.3/AR | Hematological anomalies, hypoglycemia, growth retardation and dilated cardiomyopathy |
[43,44] |
| Fanconi–Bickel syndrome (GSD XI) |
SLC2A2 | GLUT2/3q26.2/AR | Postprandial elevations of glucose and galactose, fasting hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, proximal tubular nephropathy, glucosuria, short stature |
[45,46] |
| PGK deficiency |
PGK1 | PGK/ Xq21.1/ XL | Nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia, myopathy with rhabdomyolysis and neurological features, myopathy, rhabdomyolysis |
[47,48] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





