Submitted:
20 January 2025
Posted:
20 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical and Biochemical Characteristics
| Pt | Age of onset | Gender | Family history | Days of onset | Fever | Vomiting | Diarrhea | Poor feeding | Rapid breathing | Seizure | Hepatomegaly | Lethargy/coma | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 5m | M | + | 3.0 | - | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | Shock |
| P2 | 7m | F | + | 1.0 | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | Shock |
| P3 | 14m | M | + | 1.0 | - | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | Shock |
| P4* | - | M | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| P5 | 18m | M | - | 2.0 | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | Shock |
| P6 | 8m | F | - | 1.0 | - | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | Shock |
| P7 | 10d | F | - | 1.0 | - | - | - | + | + | - | NA | + | Jaundice |
| P8 | 28m | M | - | 5.0 | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | Pallor |
| P9 | 13m | M | - | 4.0 | - | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | - |
| P10 | 8m | F | + | 1.0 | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | + | Shock |
| P11* | - | M | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| P12 | 7m | F | - | 3.0 | - | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - |
| P13 | 18m | M | + | 1.0 | - | - | + | + | - | - | + | - | - |
| P14 | 5m | F | + | 0.5 | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| P15 | 6m | F | - | 2.0 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| P16 | 5m | F | + | 2.0 | - | - | - | + | - | + | NA | + | - |
| P17* | - | M | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| P18 | 10m | F | - | 2.0 | - | + | - | + | + | - | NA | + | - |
| P19 | 6m | F | - | 2.0 | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | Loss weight |
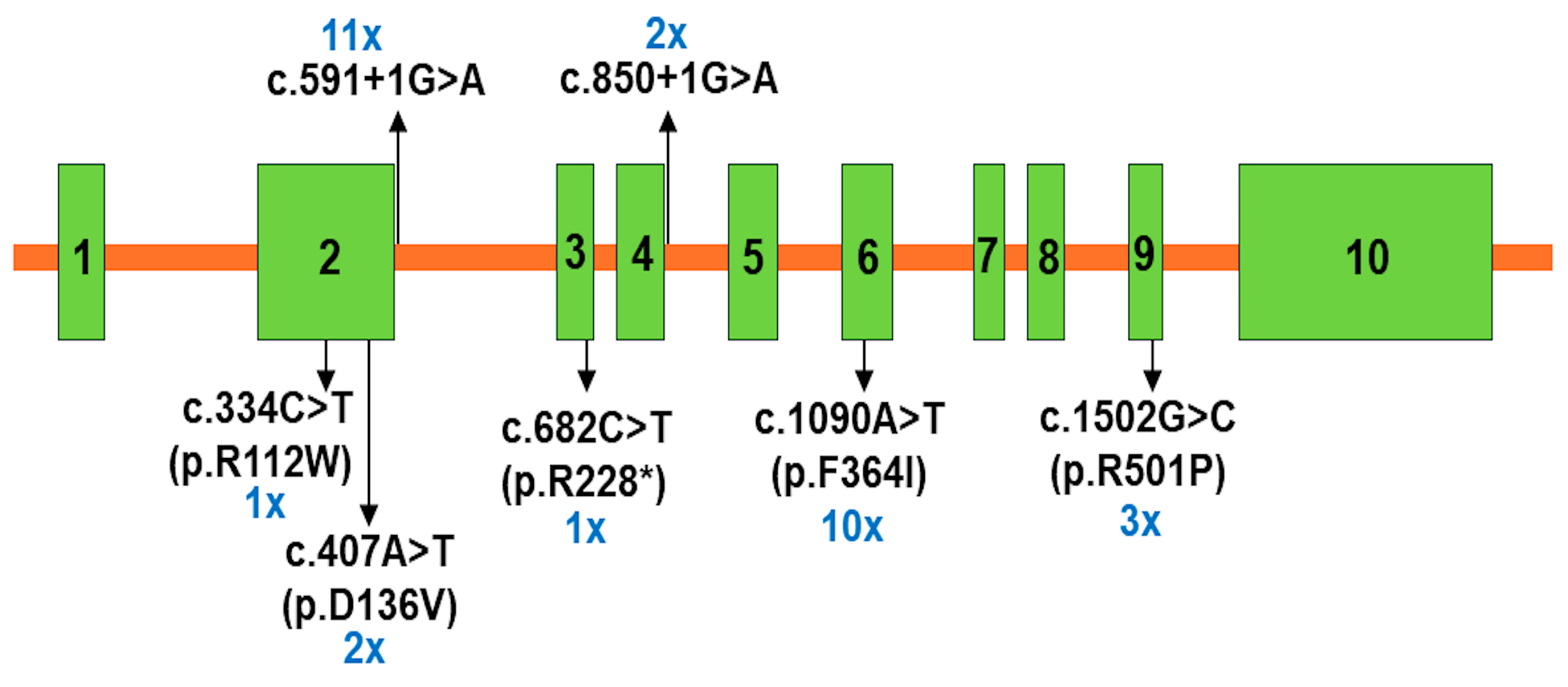
2.2. Molecular Analyses
2.3. Outcomes
| Pt | Initial diagnosis | Management in first crisis | Outcome of first crisis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ventilation (days) | Acidotic correction (hours) | Glucose infusion (days) | CVVH (hours) | Antibiotics (days) | Others | Recovered MA (hours) | Alive | Neurological | ||
| P1 | Organic aciduria | 3 | 34 | 4 | 34 | 13 | L-carnitine, biotin, B12 | 13 | Yes | No |
| P2 | HMGCS2D | 2 | 48 | 2 | 19 | 10 | L-carnitine | 48 | Yes | No |
| P3 | Glutaric acidemia II | 5 | 26 | 3 | 20 | 20 | L-carnitine, B2, coenzyme Q10 | 11 | Yes | Yes |
| P5 | MMA/GA II | 3 | 33 | 6 | 0 | 16 | L-carnitine, B2, B12, biotin | 33 | Yes | No |
| P6 | Myocarditis, # IEM | 4 | 72 | 6 | 82 | 28 | L-carnitine | 72 | Yes | No |
| P7 | Glutaric acidemia II | 2 | 48 | 7 | 0 | 19 | L-carnitine | 48 | Yes | No |
| P8 | Hypoglycemia/IEMs | 0 | 24 | 4 | 0 | 0 | L-carnitine | 24 | Yes | No |
| P9 | IEMs | 6 | 48 | 4 | 0 | 21 | 0 | 48 | Yes | No |
| P10 | Glycogen storage | 2 | 25 | 2 | 32 | 15 | L-carnitine, biotin, B12 | 14 | Yes | No |
| P12 | CUD | 0 | 18 | 2 | 0 | 12 | L-carnitine | 18 | Yes | No |
| P13 | Elevated transaminase | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | Yes | No |
| P14 | HMGCS2D | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | L-carnitine | 0 | Yes | No |
| P15 | IEM | 3 | 0 | 3 | 48 | 3 | L-carnitine, | 72 | Yes | No |
| P16 | FAOD | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 | L-carnitine, biotin, B12 | 48 | Yes | No |
| P18 | IEM | 3 | 3 | 3 | 72 | 7 | L-carnitine, B12, arginine, biotin, | 72 | Yes | No |
| P19 | Glutaric aciduria II | 0 | 10 | 5 | 0 | 9 | L-carnitine, B2, coenzyme Q10 | 48 | Yes | No |
| Sum | 11/16 | 13/16 | 15/16 | 7/16 | 14/16 | 14/16 | ||||
| Pt | Age of AD | Time to achieve AD | Management before AD | Crisis numbers before AD | Current age | Crisis numbers after AD | Height (SDS) | Weight (SDS) | DQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 21m | 16m | L-carnitine, Biotin, B12 | 4 (2 times: CVVH) | 7y2m | 1 | -0.2 | -0.4 | Normal |
| P2 | 7m | 10d | L-carnitine | 1 | 1y11m | 0 | -0.2 | 0.2 | Normal |
| P3 | 17m | 3m | L-carnitine | 1 | 4y | 0 | NA | -2.1 | Neurological sequelae |
| P4 | 6y | - | - | 0 | 9y8m | 0 | 0.1 | 0.7 | Normal |
| P5 | 26m | 8m | L-carnitine | 0 | 7y8m | 0 | 1.2 | 1.7 | Normal |
| P6 | 9m | 1m | L-carnitine | 1 | 4y3m | 0 | 1.1 | 0.8 | Normal |
| P7 | 1m | 1m | L-carnitine | 0 | 2y5m | 0 | 0.8 | 1.2 | Normal |
| P8 | 3y3m | 11m | L-carnitine | 2 | 7y3m | 0 | -0.8 | -1.1 | Normal |
| P9 | 17m | 4m | L-carnitine | 0 | 3y | 0 | -0.5 | -1.6 | Normal |
| P10 | 10m | 2m | L-carnitine | 0 | 2y5m | 0 | -1.0 | -0.4 | Normal |
| P11 | 12y | - | - | 14y1m | 0 | 0.2 | -1.2 | Normal | |
| P12 | 8m | 1m | L-carnitine | 0 | 13m | 0 | 1.4 | 0.7 | Normal |
| P13 | 19m | 1m | Arginine, vitamin E, L-carnitine | 0 | 3y4m | 0 | 1.7 | 0.7 | Normal |
| P14 | 5m | - | - | 0 | 5m | 1 | 3.1 | -0.9 | Normal |
| P15 | 10m | 4m | Arginine, L-carnitine | 1 (CVVH) | 18m | 0 | -0.8 | -0.8 | Normal |
| P16 | 8m | 3m | L-carnitine, Biotin, vitamin B12 | 1 | 14m | 0 | 0 | 0 | Normal |
| P17 | 4y6m | - | - | - | 5y | 0 | 0.3 | -0.2 | Normal |
| P18 | 12m | 2m | L-carnitine | 0 | 17m | 0 | -0.9 | -0.2 | Normal |
| P19 | 9m | 3m | L-carnitine, CoQ10, vitamin B2 | 0 | 19m | 0 | 0.1 | -0.8 | Normal |
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Individuals
4.2. Clinical Characteristics
4.3. Genetic Analysis
4.4. Management
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouchard, L.; Robert, M.-F.; Vinarov, D.; Stanley, C.A.; Thompson, G.N.; Morris, A.; Leonard, J.V.; Quant, P.; Hsu, B.Y.L.; Boneh, A.; et al. Mitochondrial 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase Deficiency: Clinical Course and Description of Causal Mutations in Two Patients. Pediatr Res 2001, 49, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegardt, F.G. Mitochondrial 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase: A Control Enzyme in Ketogenesis. Biochemical Journal 1999, 338, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Cogan, K.E.; Egan, B. Metabolism of Ketone Bodies during Exercise and Training: Physiological Basis for Exogenous Supplementation. J Physiol 2017, 595, 2857–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Tang, Y.; Long, H.; Gu, H.; Zhang, J.; Deng, P.; Zhao, Y.; Cen, X. HMG-CoA Synthase 2 Drives Brain Metabolic Reprogramming in Cocaine Exposure. Neuropharmacology 2019, 148, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sait, H.; Srivastava, S.; Kumar, S.; Varughese, B.; Pandey, M.; Venkatramaiah, M.; Chaudhary, P.; Moirangthem, A.; Mandal, K.; Kapoor, S. Inborn Errors of Ketogenesis: Novel Variants, Clinical Presentation, and Follow-Up in a Series of Four Patients. J Pediatr Genet 2024, 13, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sass, J.O.; Fukao, T.; Mitchell, G.A. Inborn Errors of Ketone Body Metabolism and Transport: An Update for the Clinic and for Clinical Laboratories. J Inborn Errors Metab Screen 2018, 6, 2326409818771101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conboy, E.; Vairo, F.; Schultz, M.; Agre, K.; Ridsdale, R.; Deyle, D.; Oglesbee, D.; Gavrilov, D.; Klee, E.W.; Lanpher, B. Mitochondrial 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase Deficiency: Unique Presenting Laboratory Values and a Review of Biochemical and Clinical Features. JIMD Rep 2018, 40, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yu, D. [Mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA synthase deficiency: a case report and literature review]. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2018, 20, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Miao, J.-K.; Yu, C.-W.; Wan, K.-X.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Z.-J.; Yang, J.; Wang, D.-J.; Zeng, Y.; Zou, L. Severe Clinical Manifestation of Mitochondrial 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase Deficiency Associated with Two Novel Mutations: A Case Report. BMC Pediatr 2019, 19, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, M.; Dorum, S.; Topak, A.; Yazıcı, M.U.; Ezgu, F.S.; Coskun, T. Expanding the Clinical Spectrum of Mitochondrial 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase Deficiency with Turkish Cases Harboring Novel HMGCS2 Gene Mutations and Literature Review. Am J Med Genet A 2020, 182, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Shen, L.; Chen, Q.; Gong, C.; Yang, Y.; Wei, H.; Cao, B.; Chen, Y. Clinical, Biochemical, Molecular, and Outcome Features of Mitochondrial 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase Deficiency in 10 Chinese Patients. Front Genet 2021, 12, 816779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.-L.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.-J.; Li, X.-Q.; Cao, B.-Y.; Gong, C.-X. Clinical, Biochemical, Molecular and Therapeutic Characteristics of Four New Patients of Mitochondrial 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase Deficiency. Clin Chim Acta 2020, 509, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnedo, M.; Ramos, M.; Puisac, B.; Gil-Rodríguez, M.C.; Teresa, E.; Pié, Á.; Bueno, G.; Ramos, F.J.; Gómez-Puertas, P.; Pie, J.; et al. Mitochondrial HMG–CoA Synthase Deficiency. In Advances in the Study of Genetic Disorders; IntechOpen, 2011; pp. 189–204, ISBN 978-953-307-305-7.
- Pitt, J.J.; Peters, H.; Boneh, A.; Yaplito-Lee, J.; Wieser, S.; Hinderhofer, K.; Johnson, D.; Zschocke, J. Mitochondrial 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase Deficiency: Urinary Organic Acid Profiles and Expanded Spectrum of Mutations. J Inherit Metab Dis 2015, 38, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puisac, B.; Marcos-Alcalde, I.; Hernández-Marcos, M.; Tobajas Morlana, P.; Levtova, A.; Schwahn, B.C.; DeLaet, C.; Lace, B.; Gómez-Puertas, P.; Pié, J. Human Mitochondrial HMG-CoA Synthase Deficiency: Role of Enzyme Dimerization Surface and Characterization of Three New Patients. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojnueangnit, K.; Maneechai, P.; Thaweekul, P.; Piriyanon, P.; Khositseth, S.; Ittiwut, C.; Chetruengchai, W.; Kamolvisit, W.; Theerapanon, T.; Suphapeetiporn, K.; et al. Expanding Phenotypic and Mutational Spectra of Mitochondrial HMG-CoA Synthase Deficiency. Eur J Med Genet 2020, 63, 104086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, T.A.; Fitzsimons, P.E.; Borovickova, I.; Kirby, F.; Murphy, S.; Knerr, I.; Crushell, E. Hypoglycemia Is Not a Defining Feature of Metabolic Crisis in Mitochondrial 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase Deficiency: Further Evidence of Specific Biochemical Markers Which May Aid Diagnosis. JIMD Rep 2020, 55, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zschocke, J.; Penzien, J.M.; Bielen, R.; Casals, N.; Aledo, R.; Pié, J.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Hegardt, F.G.; Mayatepek, E. The Diagnosis of Mitochondrial HMG-CoA Synthase Deficiency. J Pediatr 2002, 140, 778–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niehaus, A.D.; Cooper, H.; Lee, C.U. Mitochondrial HMG-CoA Synthase Deficiency: A Cyclic Vomiting Mimic Without Reliable Biochemical Markers. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep 2024, 12, 23247096241267154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czempik, P.F.; Pluta, M.P.; Krzych, Ł.J. Sepsis-Associated Brain Dysfunction: A Review of Current Literature. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17, 5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purdie, F.R.; Honigman, B.; Rosen, P. Acute Organic Brain Syndrome: A Review of 100 Cases. Ann Emerg Med 1981, 10, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.; Takami, Y.; Yamada, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Sasai, H.; Otsuka, H.; Takeshima, Y.; Fukao, T. A Japanese Case of Mitochondrial 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase Deficiency Who Presented with Severe Metabolic Acidosis and Fatty Liver without Hypoglycemia. JIMD Rep 2019, 48, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri-Fam, S.; Chen, H.; Wilson, S.; Ayers, K.; Hughes, J.; Sloan-Bena, F.; Calvel, P.; Robevska, G.; Puisac, B.; Kusz-Zamelczyk, K.; et al. The Gene Encoding the Ketogenic Enzyme HMGCS2 Displays a Unique Expression during Gonad Development in Mice. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0227411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.N.; Tran, V.K.; Nguyen, N.L.; Can, T.B.N.; Dang, T.K.G.; Nguyen, T.H.; Do, T.T.M.; Phuong, L.T.; Tran, T.H.; Ta, T.V.; et al. Hyperornithinemia–Hyperammonemia–Homocitrullinuria Syndrome in Vietnamese Patients. Medicina 2024, 60, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, Y.; Hata, I.; Kikawa, Y.; Mayumi, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Sudo, M.; Kado, N. Modifications in Electrospray Tandem Mass Spectrometry for a Neonatal-Screening Pilot Study in Japan. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl 1999, 731, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, Y.; Hirano, S.; Hata, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Sudo, M.; Sakura, N.; Tajima, T.; Yamaguchi, S. Newborn Mass Screening and Selective Screening Using Electrospray Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Japan. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2002, 776, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster2: Mutation Prediction for the Deep-Sequencing Age. Nat Methods 2014, 11, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaganathan, K.; Panagiotopoulou, S.K.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B.; et al. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: An Environment for Comparative Protein Modeling. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pt | Blood glucose mmol/L | metabolic acidosis | Plasma ammoniac μmol/L | ALT UI/L | AST UI/L | CK IU/L | Plasma C0 µmol/L | Plasma C2 µmol/L | Urinary dicarboxylic acid | Ketonuria | Brain MRI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | HCO3 mmol/L | BE | |||||||||||
| P1 | ↓2.0 | 6.96 | 4.2 | -27.0 | 98.4 | ↑88 | ↑138 | NA | 13.2 | 8.5 | - | 1+ | Normal |
| P2 | ↓1.1 | 7.25 | 5.3 | -22.0 | 64.2 | ↑62 | ↑112 | 126.8 | 14.9 | 9.5 | - | Neg | Normal |
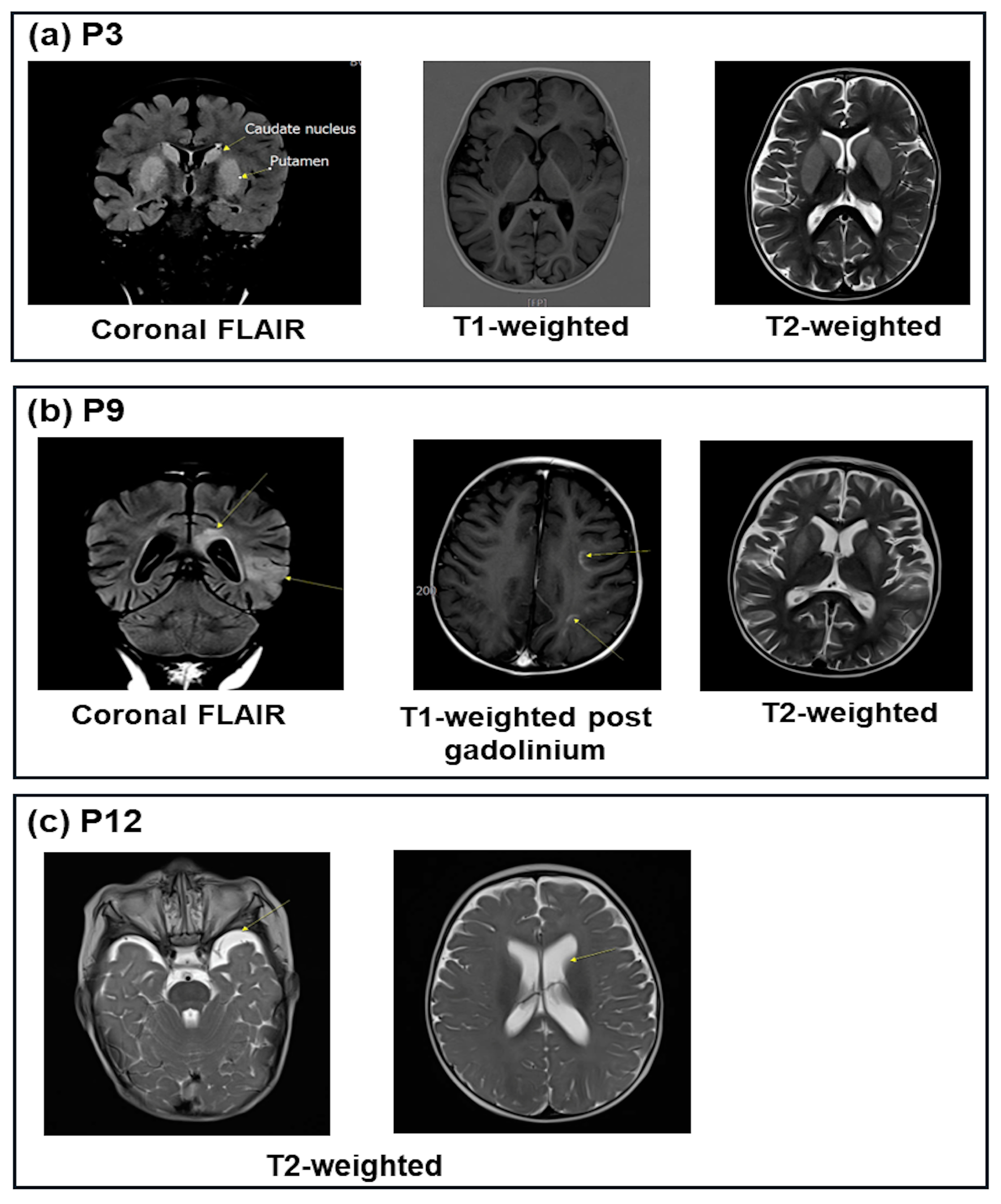
| P3 | ↓0.8 | 7.12 | 9.6 | -21.0 | 51.6 | ↑108 | ↑209 | ↑2287 | ↓4.4 | 27.0 | - | 1+ | Lesions of the bilateral putamen caudate |
| P5 | 4.8 | 7.30 | 5.9 | -20.0 | 38.4 | ↑212 | ↑159 | NA | 9.1 | 9.5 | - | 3+ | Normal |
| P6 | ↓1.8 | 6.99 | 4.6 | -27.0 | ↑109.2 | ↑83 | ↑290 | NA | ↓5.0 | 4.6 | - | Trace | NA |
| P7 | 3.9 | 6.86 | 2.7 | -29.0 | ↑983.0 | ↑56 | ↑139 | NA | ↓5.0 | 4.7 | - | Neg | NA |
| P8 | ↓0.1 | 7.47 | 25.2 | 0.5 | 37.2 | ↑133 | ↑148 | ↑297 | ↓6.0 | 20.4 | - | Neg | Normal |
| P9 | 3.82 | 7.00 | 8.6 | -20.0 | 49.2 | ↑126 | ↑143 | NA | 16.7 | 8.8 | - | Neg | Bilateral cerebrum lesions |
| P10 | ↑25.45 | 6.89 | 1.5 | -31.0 | ↑156.6 | ↑57 | ↑222 | NA | 6.9 | 27.3 | - | Trace | Normal |
| P12 | ↓2.48 | 7.37 | 7.5 | -15.6 | 36.4 | ↑132 | ↑270 | NA | ↓3.8 | 19.7 | - | 1+ | Slight ventilation dilation |
| P13 | 4.5 | 7.40 | 21.0 | -4.0 | 31.8 | ↑465 | ↑691 | ↑1198 | 10.1 | 22.5 | - | Neg | NA |
| P14 | 4.46 | 7.39 | 21.5 | -3.0 | 52.4 | ↑56 | ↑97 | 67 | 26.2 | 11.1 | - | Neg | NA |
| P15 | ↓2.4 | 7.05 | 3.2 | -24.0 | 71.0 | ↑105 | ↑280 | NA | ↓3.3 | 18.5 | - | Neg | NA |
| P16 | ↓0.9 | 7.41 | 23.0 | NA | ↑244.0 | ↑56 | ↑90 | ↑3267 | 8.4 | ↑62.8 | + | Neg | Normal |
| P18 | ↓2.08 | 7.10 | 3.0 | -21.0 | ↑226.0 | 32 | ↑84 | NA | 12.2 | 14.7 | - | Neg | Normal |
| P19 | 3.65 | 7.27 | 4.5 | -21.0 | 43.8 | ↑131 | ↑121 | 59 | ↓3.8 | 22.3 | + | Neg | Normal |
| Patients | Genotype | AA change | Effect |
Mutation Taster | dbSNP | ClinVar | AMCG classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 06 (P1, P2, P7, P9, P16, P17) |
Hom | c.559+1G>A | - | Splicing | Deleterious | rs587603096 | Pathogenic 859738 |
Pathogenic (PVS1, PM1, PM2, PM3, PP1, PP3, PP4, and PP5) |
| 05 (P3, P4, P6, P8, P12) |
CH | c.559+1G>A | - | Splicing | Deleterious | rs587603096 | Pathogenic 859738 |
Pathogenic (PVS1, PM1, PM2, PM3, PP1, PP3, PP4, and PP5) |
| c.1090T>A | F364I | Missense | Deleterious | rs1652807016 | Pathogenic 859739 | Likely pathogenic (PM1, PM2, PM3, PP1, PP3, PP4, and PP5) | ||
| 01 (P5) | Hom | c.1090T>A | F364I | Missense | Deleterious | rs1652807016 | Pathogenic 859739 | Likely pathogenic (PM1, PM2, PM3, PP1, PP3, PP4, and PP5) |
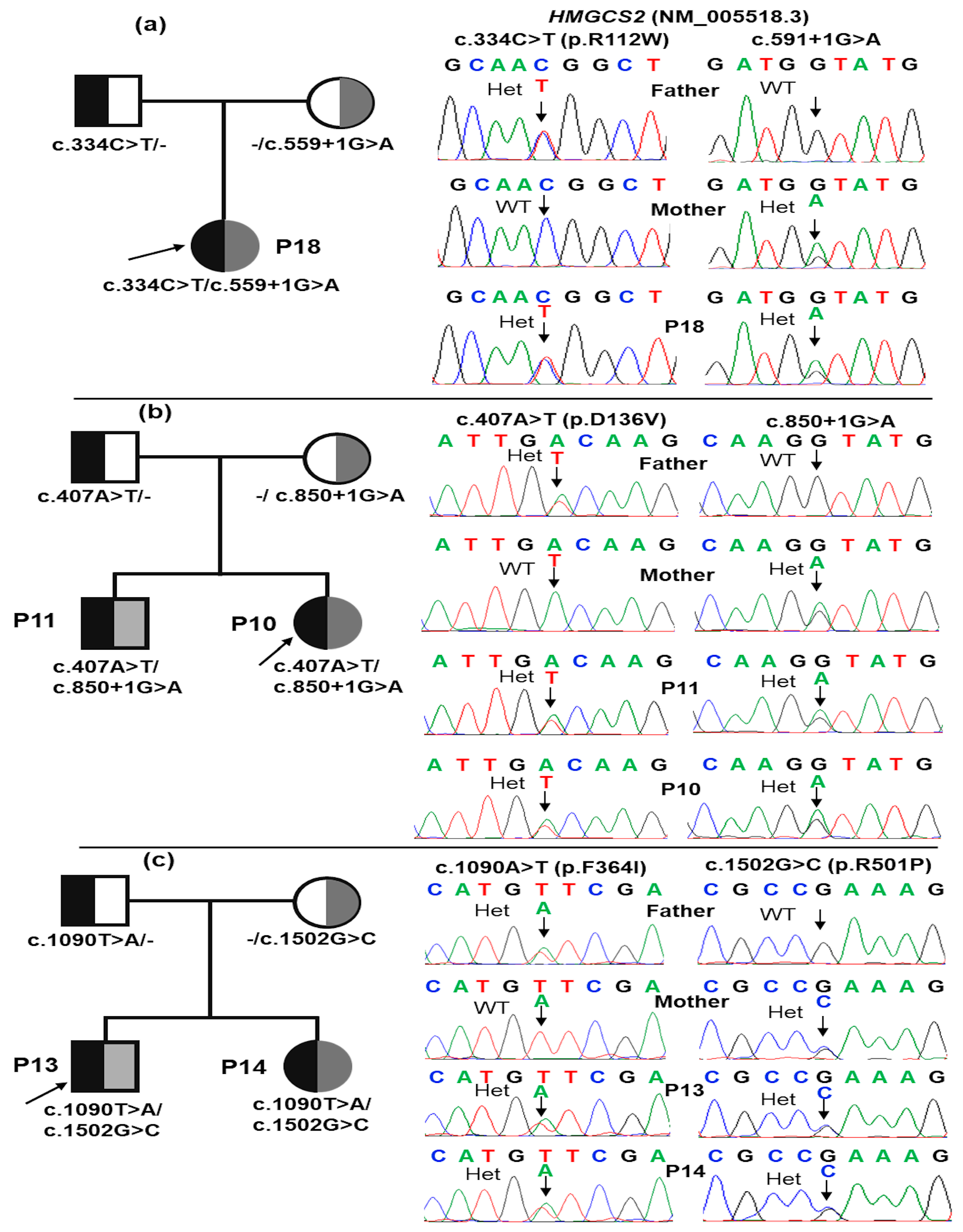
| 02 (P10, P11) |
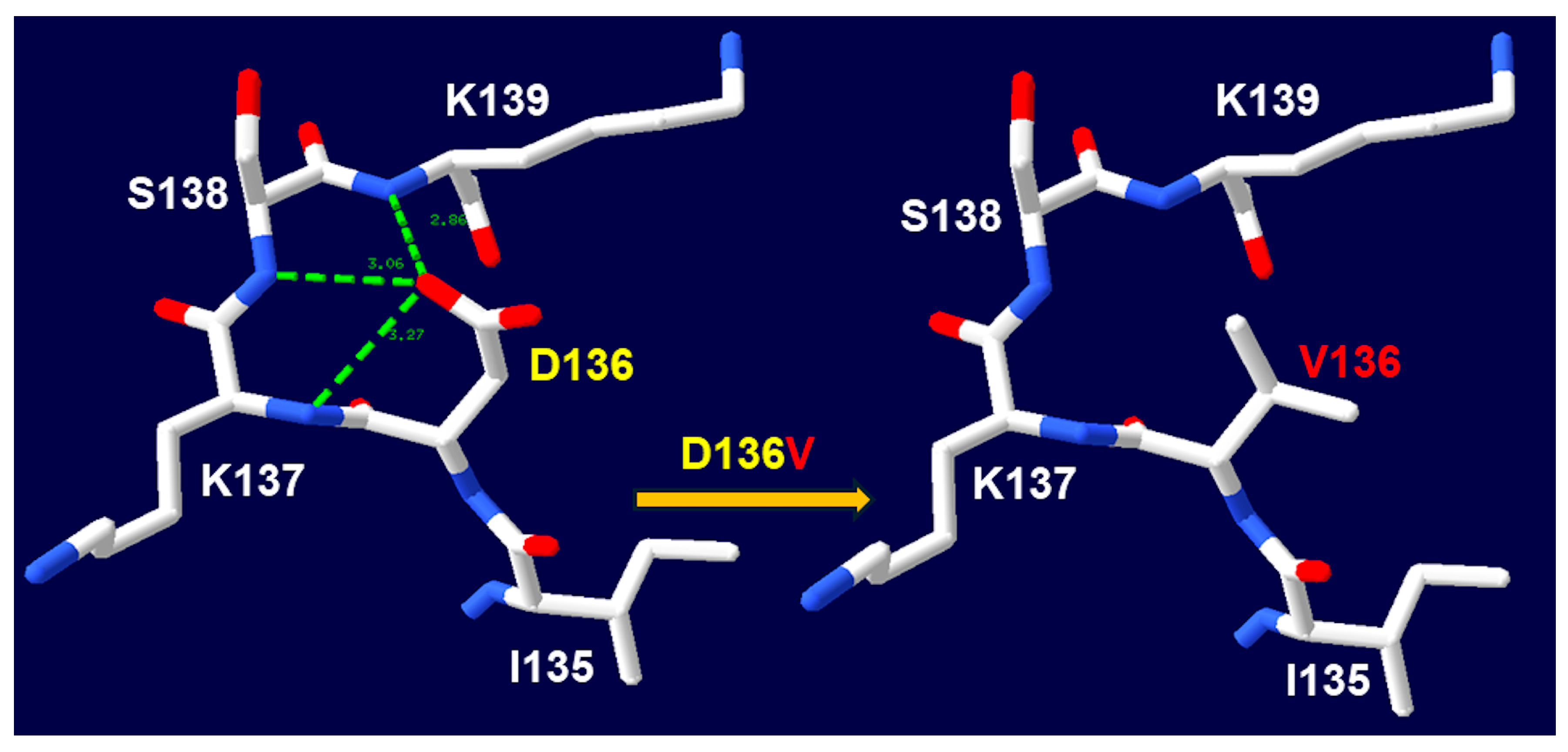
CH | c.407A>T | D136V | Missense | Deleterious | - | - | Likely pathogenic (PM1, PM2, PM5, PP1, PP3, and PP4) |
| c.850+1G>A | - | Splicing | Deleterious | rs112412189 | - | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PM3, PP1, PP3, and PP4) | ||
| 03 (P13, P14, P15) |
CH | c.1090T>A | F364I | Missense | Deleterious | rs1652807016 | Pathogenic 859739 | Likely pathogenic (PM1, PM2, PM3, PP1, PP3, PP4, and PP5) |
| c.1502G>C | R501P | Missense | Deleterious | rs372079931 | Pathogenic 452101 |
Pathogenic (PS3, PM1, PM2, PM3, PP1, PP3, PP4, and PP5) | ||
| 01 (P18) |
CH | c.682C>T | R228* | Nonsense | Deleterious | rs763531478 | Pathogenic 2080601 |
Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PM3, PP3, and PP4) |
| c.1090T>A | F364I | Missense | Deleterious | rs1652807016 | Pathogenic 859739 | Likely pathogenic (PM1, PM2, PM3, PP1, PP3, PP4, and PP5) | ||
| 01 (P19) |
CH | c.334C>T | R112W | Missense | Deleterious | rs768707273 | Likely pathogenic SCV003828997.2 |
Likely pathogenic (PM1, PM2, PM3, PP3, and PP4) |
| c.559+1G>A | - | Splicing | Deleterious | rs587603096 | Pathogenic 859738 |
Pathogenic (PVS1, PM1, PM2, PM3, PP1, PP3, PP4, and PP5) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





