Submitted:
29 June 2024
Posted:
02 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
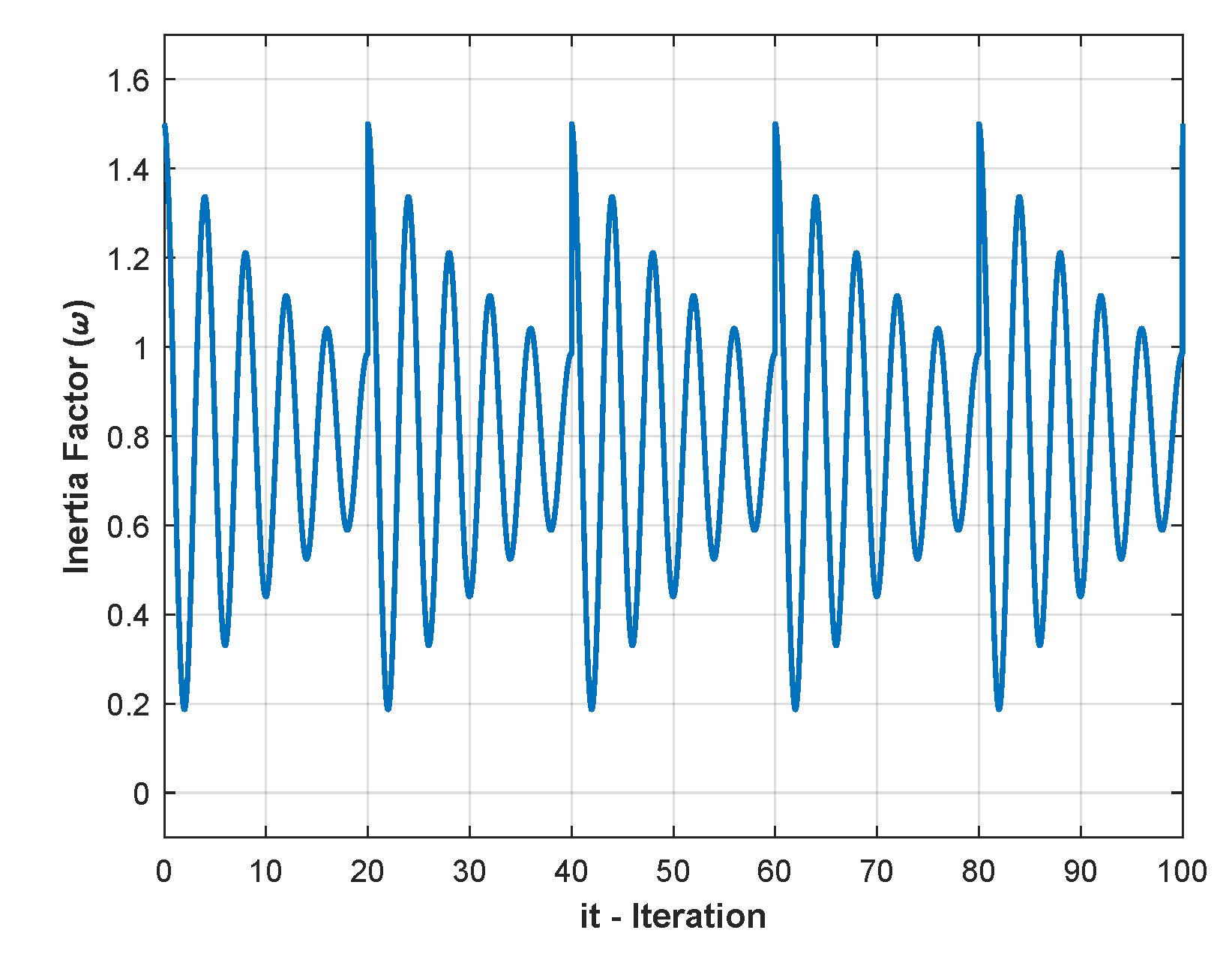
- It presents a new optimization algorithm to improve the Particle Swarm Optimization, introducing a new way to calculate the inertia weight factor . Thus, during the first iterations, the particles of the swarm explore large areas in the search space, and as the number of iterations increases, decreases exponentially over a period of time by using a periodic decaying cosine function, forcing a more condensed temporal search space, then grows to its maximum value and decreases again periodically until the end of the iterations. This cyclic damped oscillation is what characterizes the proposed algorithm.
- An objective function is used that includes four parameters of the Temporal Response Analysis of the controlled power system (Peak overshoot, Steady-state error, Settling time and Rise time), and analyze the effects of the AVR and PSS parameters on several generators simultaneously.
- The proposed algorithm resulted in better dynamic performance of the power systems as well as the transient response of the power system because it obtained the best tuned parameters of the AVR and PSS.
- A discussion and a conclusive case-study of simultaneous tuning of the AVR and PSS parameters using different inertia weight factor of Particle Swarm Optimization are shown.
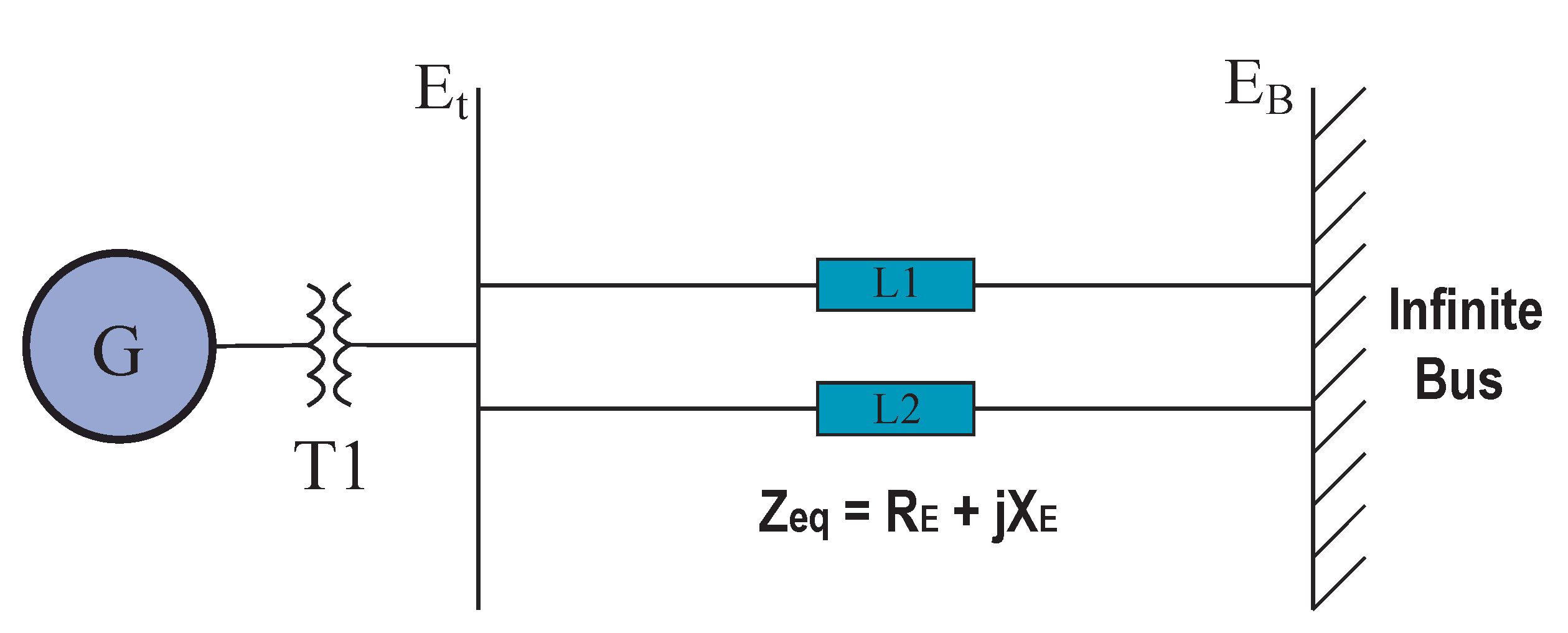
2. Linearized Model of a Single-Machine Infinite-Bus System
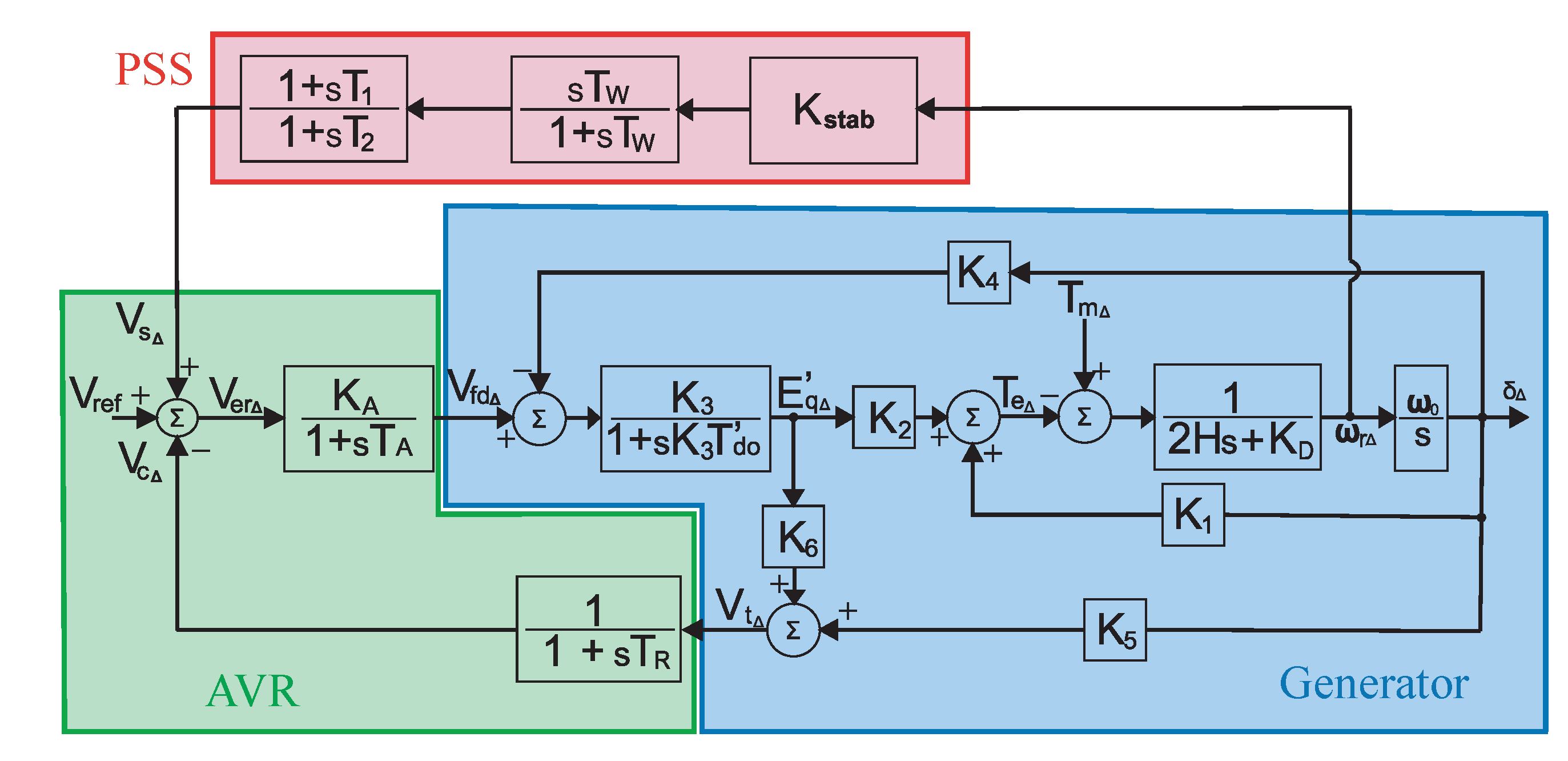
3. Simultaneous Tuning of AVR and PSS Parameters
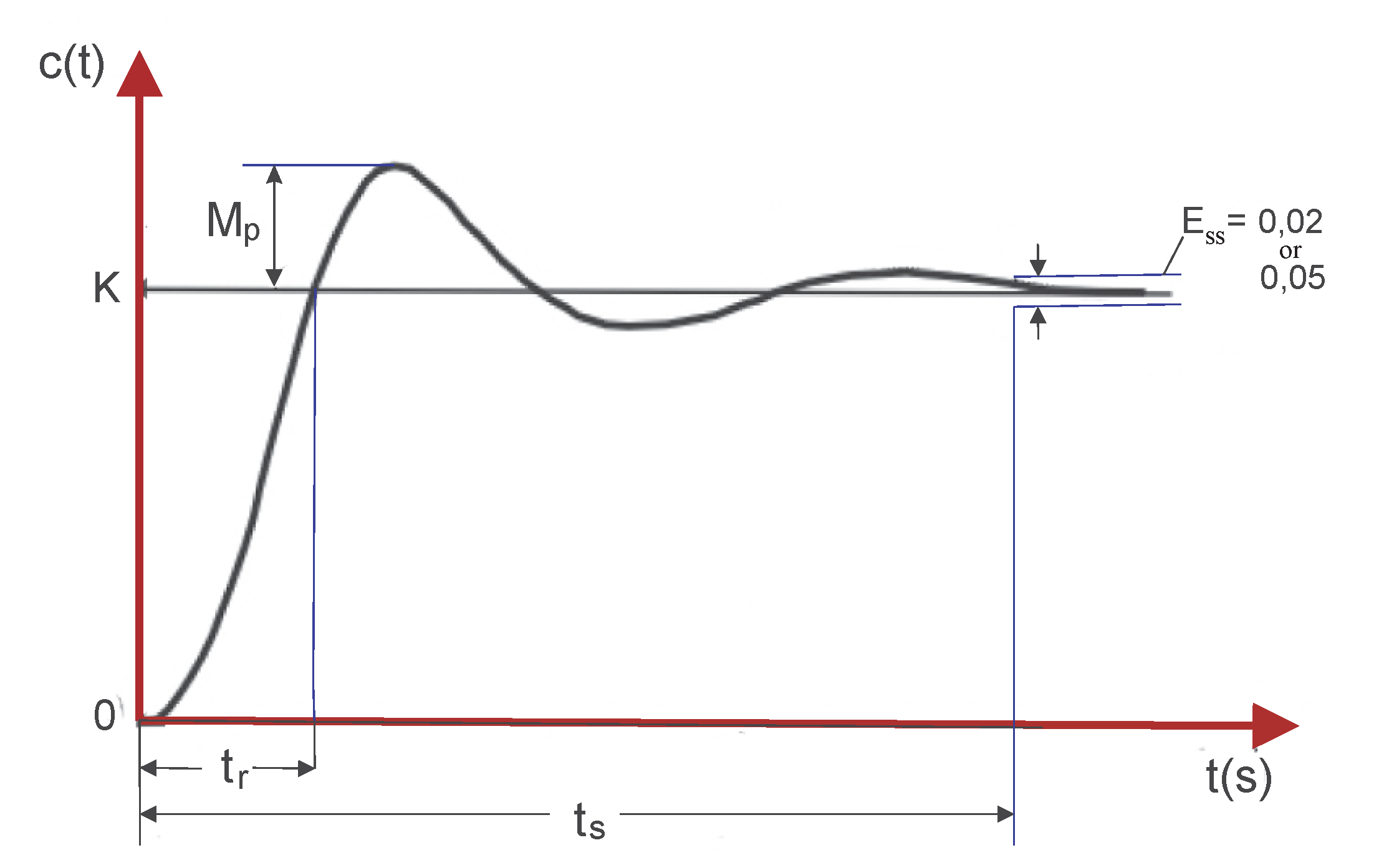
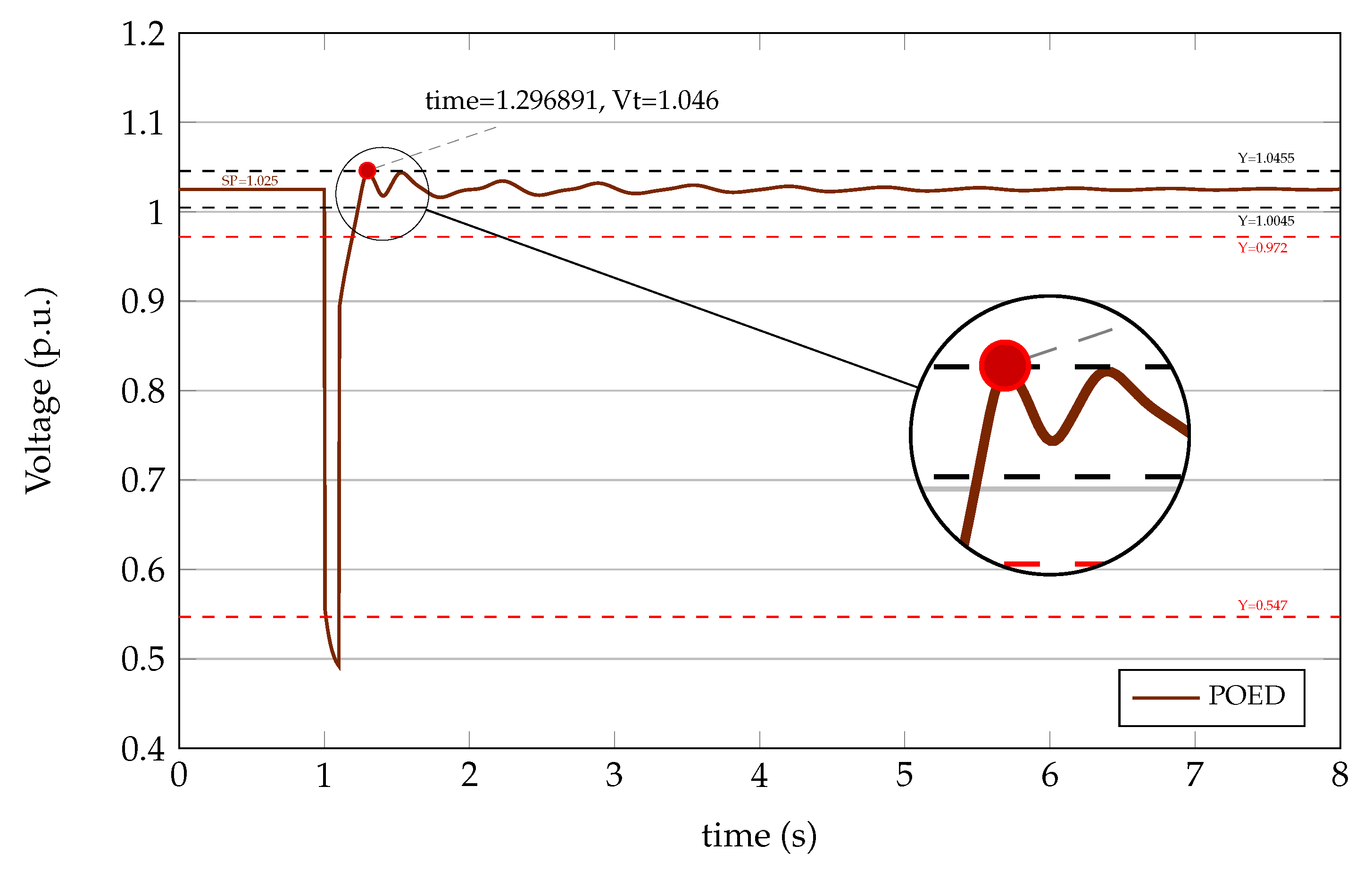
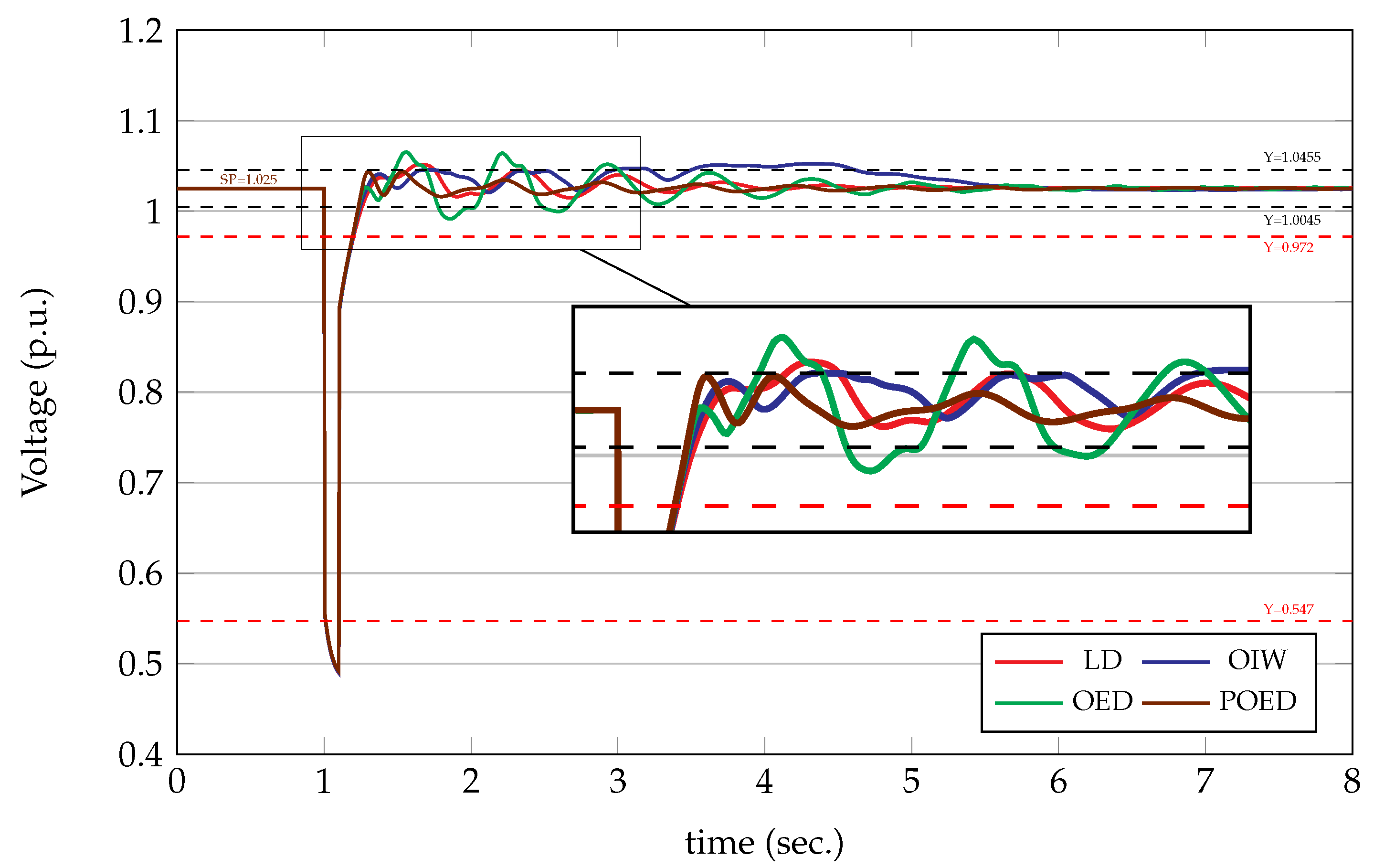
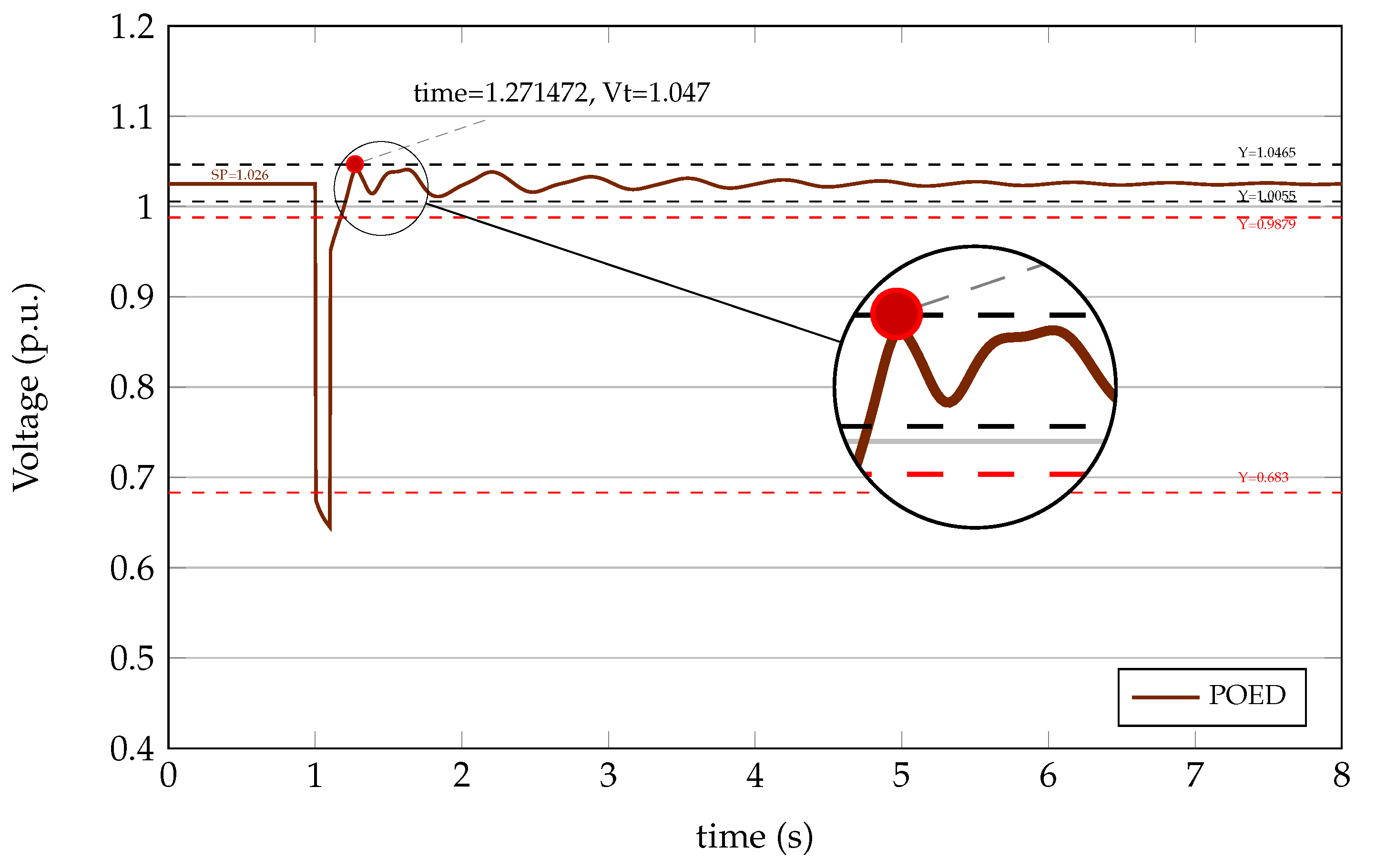
- Peak overshoot (): it is the maximum peak value of the response curve, measured from the gain of the system (K), which in this case is the unity of the step signal.
- Steady - state error (): it is the difference between the desired value and the actual value of a system when the response has reached the steady state. To measure this value, it is necessary to identify the size of the signal measured from the instant of time in which the signal enters and no longer leaves an error band located between K ± the Percentage of admissible error, whose value is usually 2% or 5%.
- Rise time (): it is the time elapsed from the emergence of the signal until it crosses the value of the gain K.
- Settling time (): it is the time from the signal’s emergence until it enters and remains within a specific error band.
4. Particle Swarm Optimization - PSO
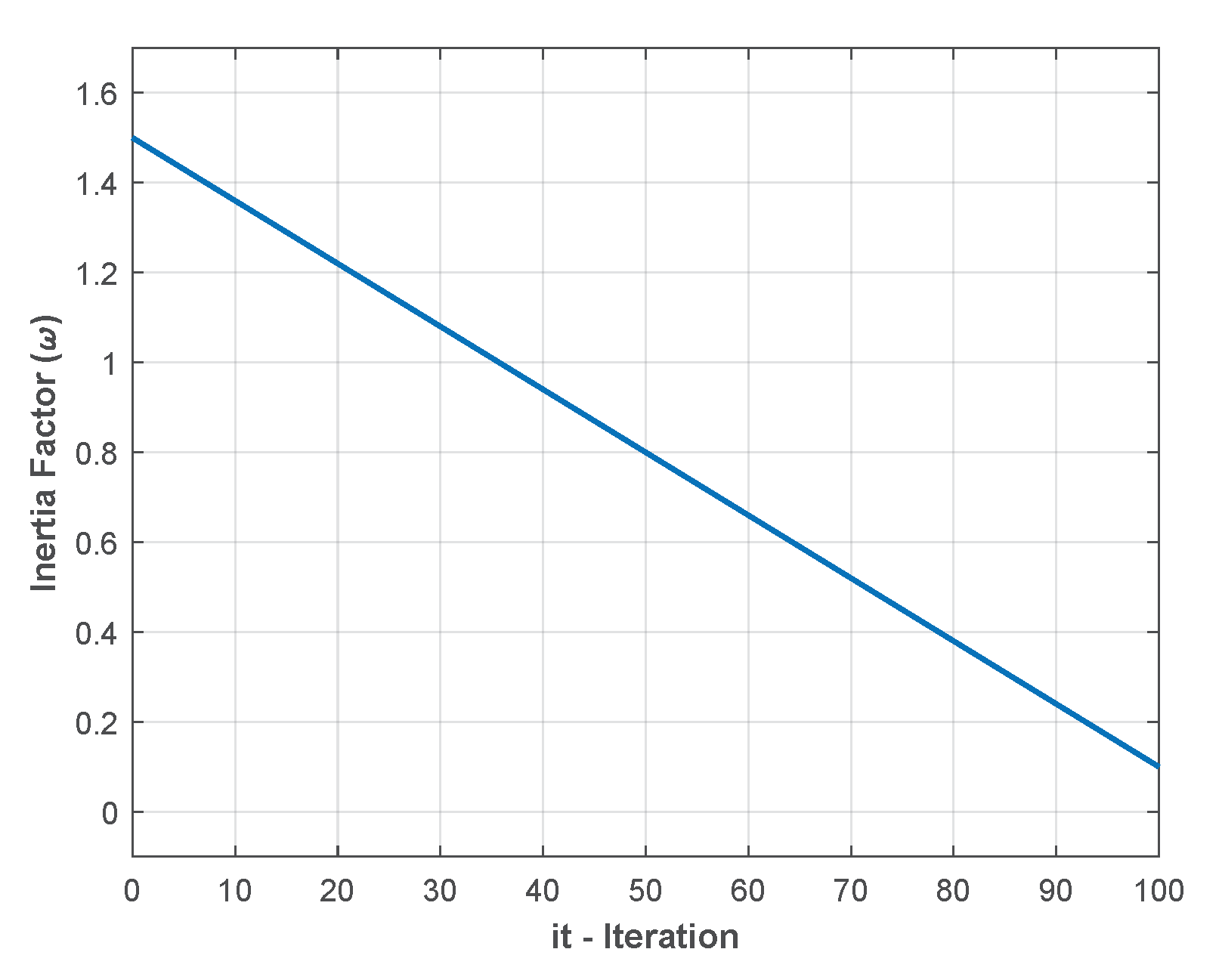
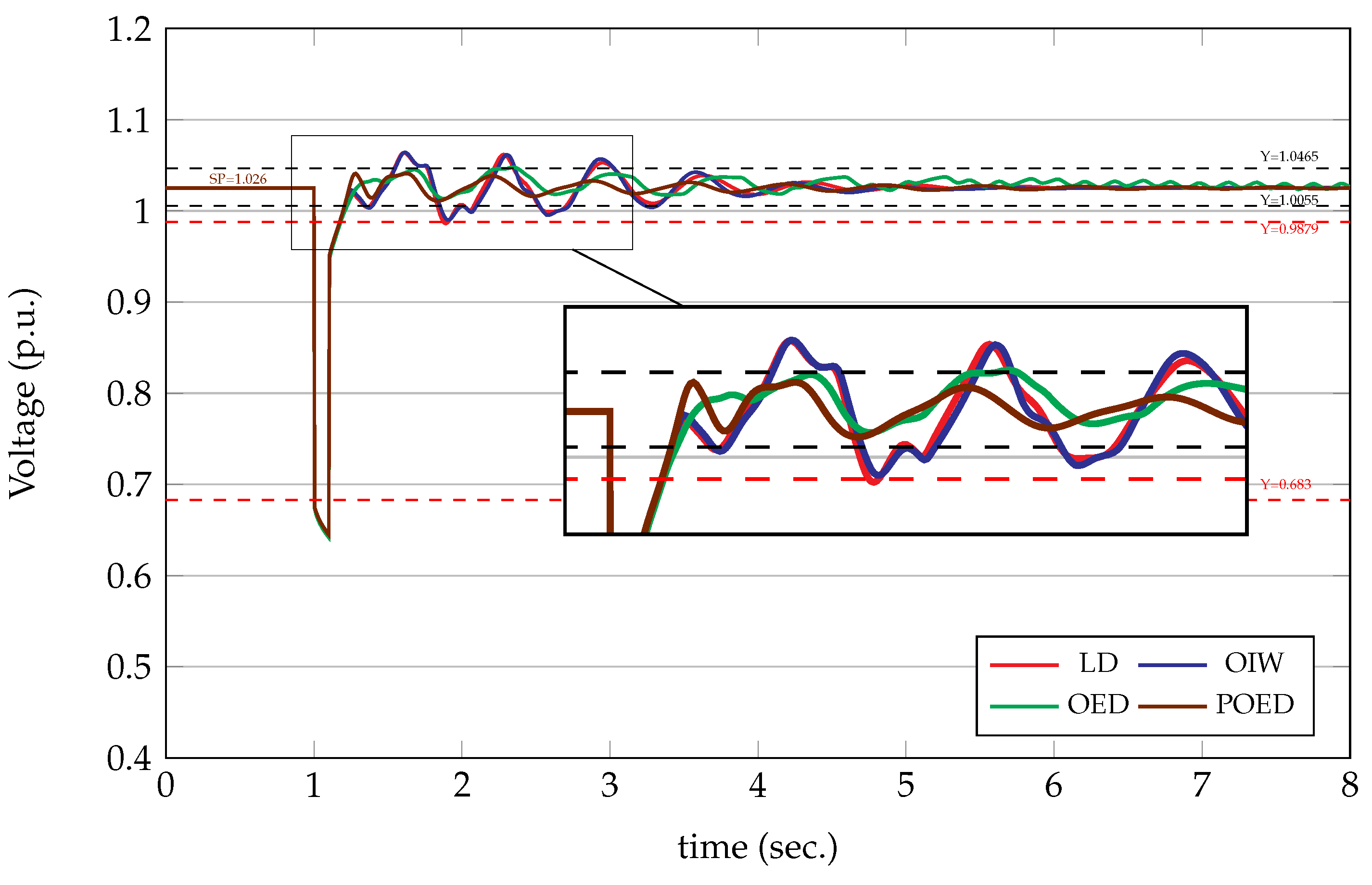
4.1. PSO with Linear Decay (PSO - LD)
4.2. PSO with Oscillating Inertia Weight (PSO - OIW)
4.3. PSO with Oscillating Exponential Decay (PSO - OED)
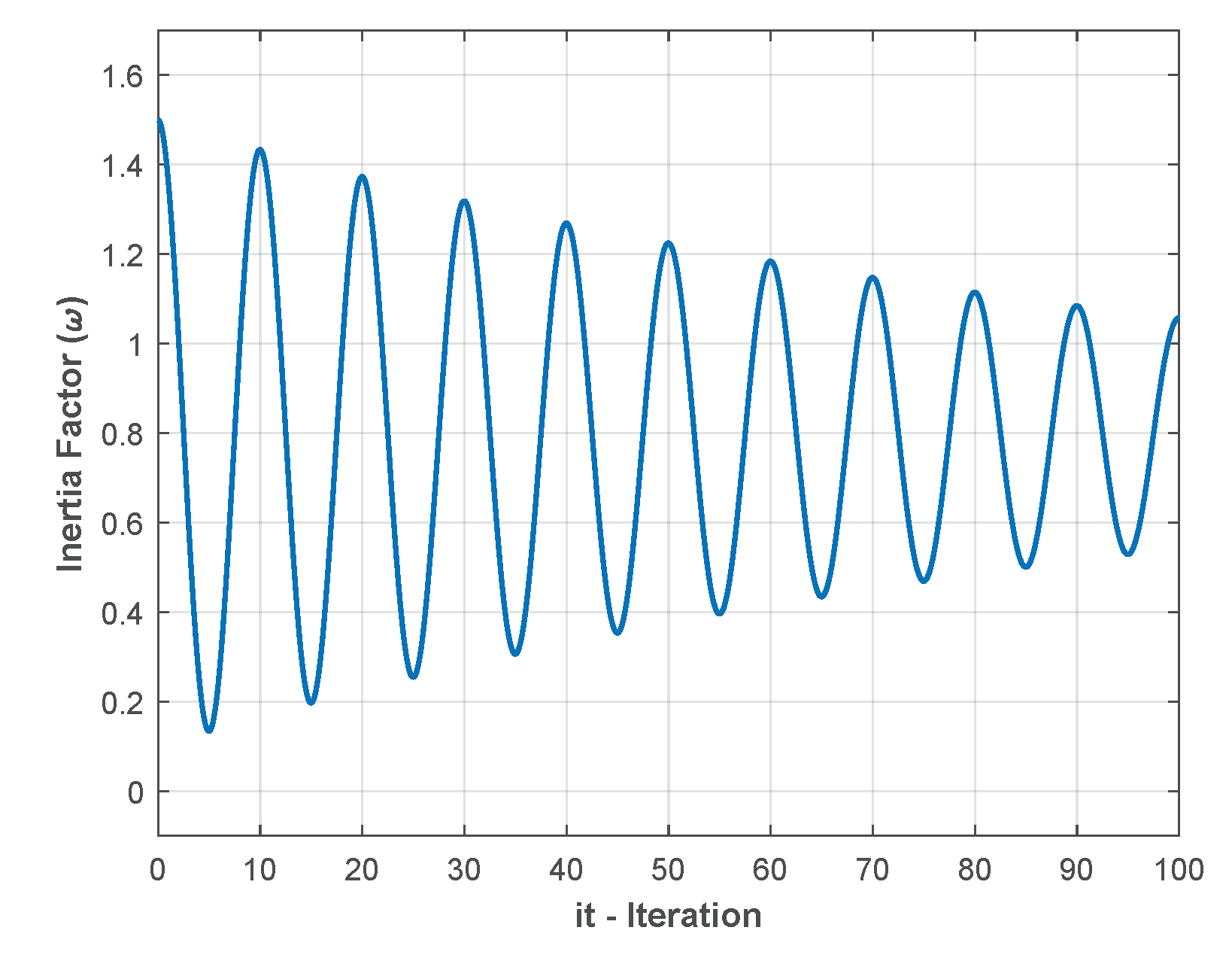
5. Proposed Method
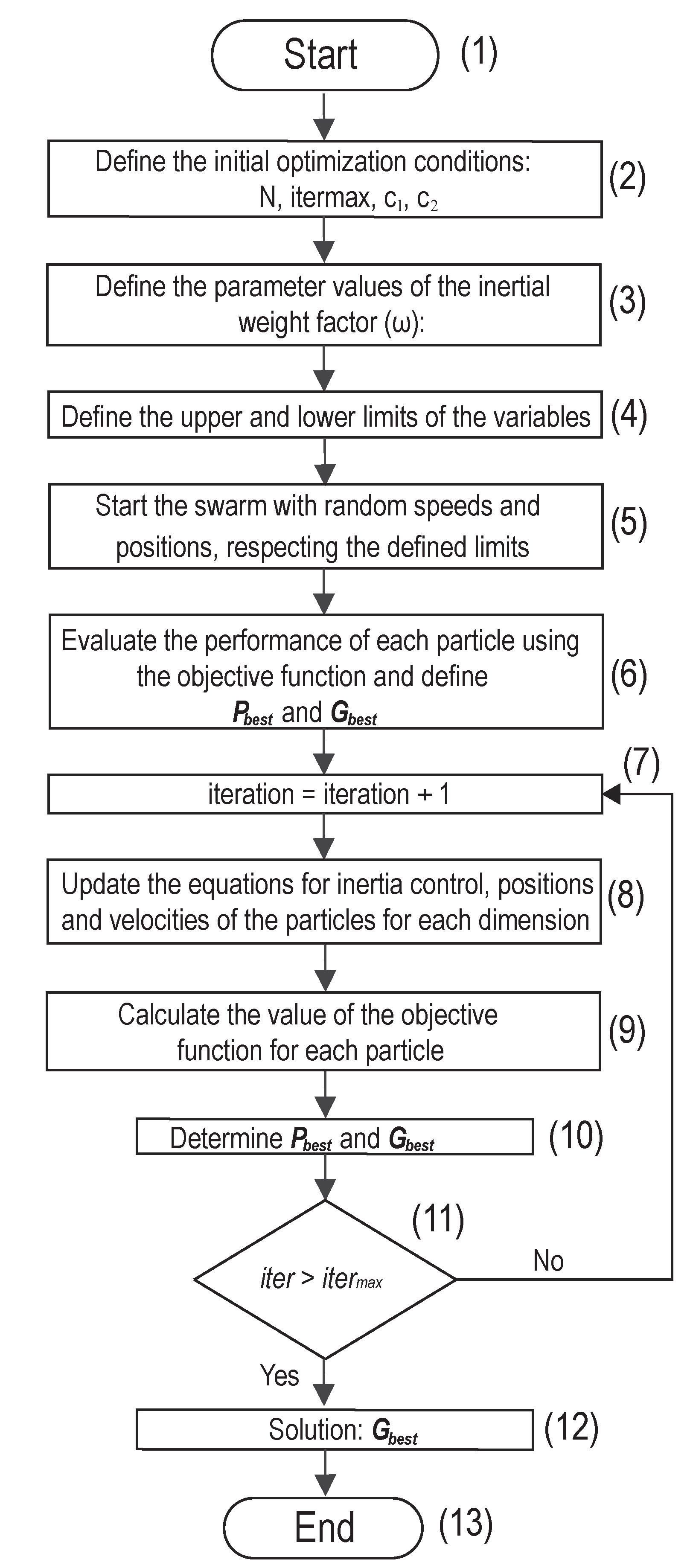
5.1. Algorithm of the Proposed Method PSO - POED
- Start;
- Define the initial optimization conditions: Number of particles (N), Maximum number of iterations (), Value of constants and ;
- Define the parameter values of the inertial weight factor () of the proposed PSO - POED optimization algorithm: Number of iterations necessary to complete the period (cycles), signal period (M) and signal amplitude ().
- Specify the lower and upper bounds of the variables;
- Initialize randomly the position () and velocity () of the particles for each variable, respecting the lower and upper bounds for () and ();
- Calculate the objective function for each particle, the is the objective function for each particle, while will be the best objective function value among the particles.
- iteration = iteration + 1;
- Calculates the value of the objective function for each particle ();
- Define the new and . If the value of . = . If the value of . = ;
- Verify the stopping criteria. If it is satisfied, go to step 12, If not, go back to step 7;
- The solution is obtained, ;
- End.
6. Simulation Results Using the PSO - POED
6.1. Case Study of the Single - Machine Infinite - Bus System
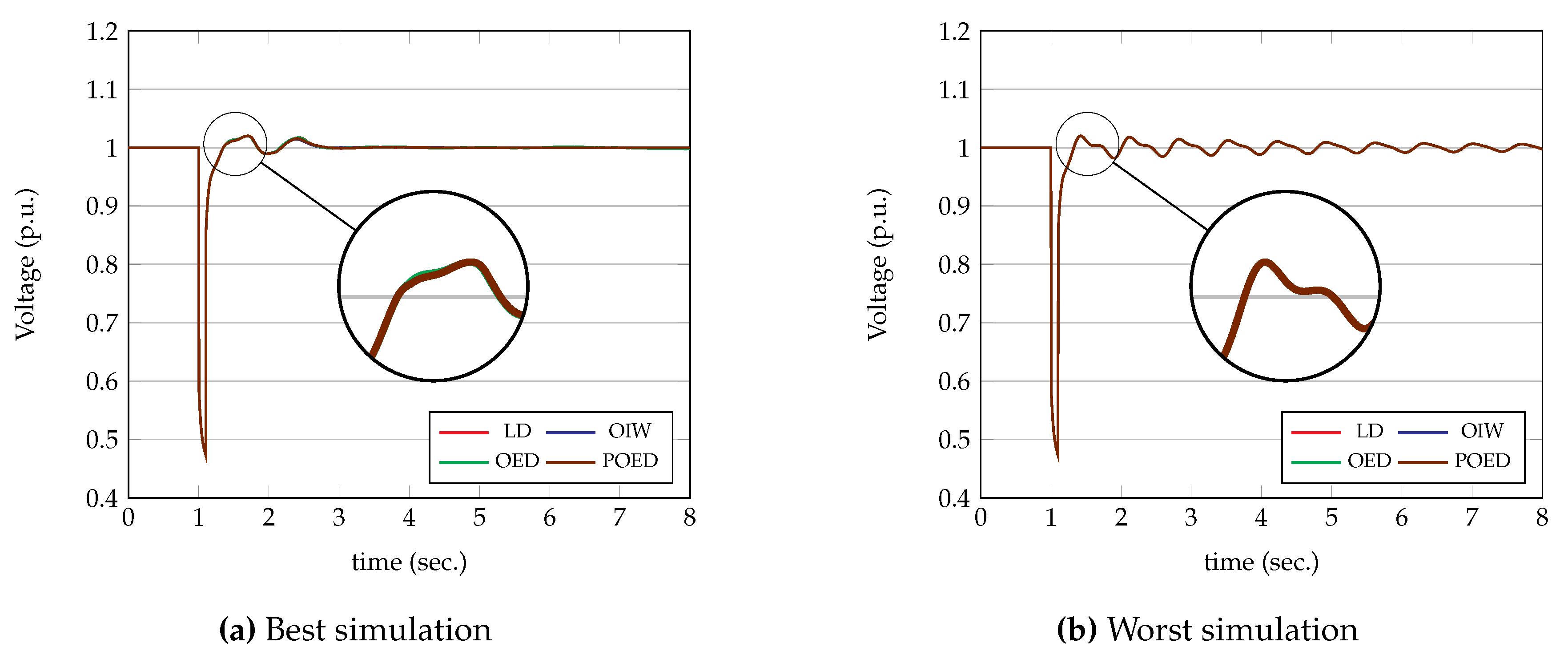
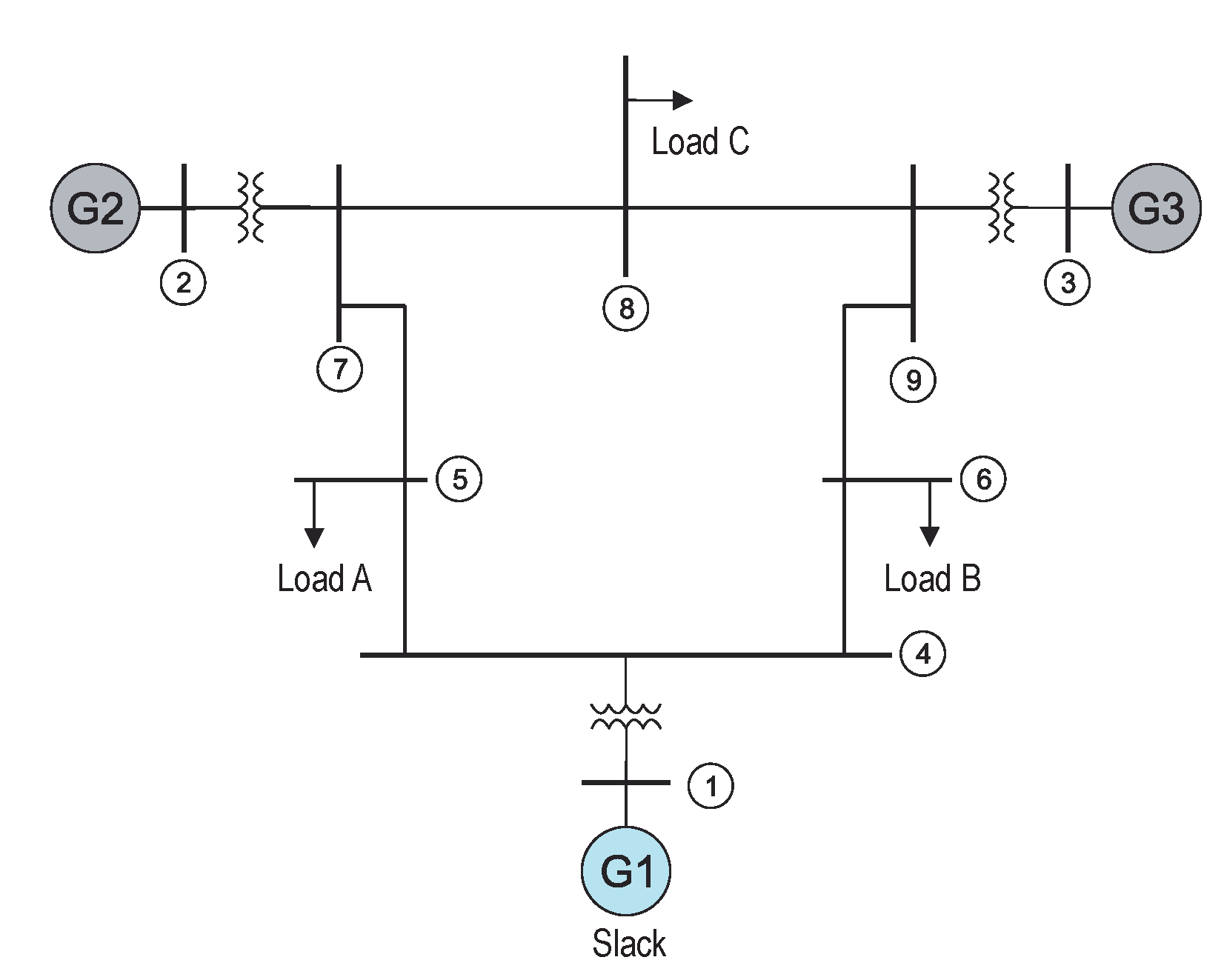
6.2. Case Study of the 9-Bus Multi-Machine System
7. Conclusions
References
- Kundur, P. Power system stability. Power system stability and control 2007, 10, 7–1. [Google Scholar]
- Saadat, H.;others. Power systemanalysis; Vol.2,McGraw-hill,1999.
- Costa Filho, R.N.D.; Paucar, V.L. Robust coordinated design of AVR+ PSS using quantum particle swarm optimization. ITEGAM-JETIA 2020, 6, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.; Molina, Y.; Silva, C.; Naupari, Z. Simultaneous tuning of the AVR and PSS parameters using particle swarm optimization with oscillating exponential decay. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2021, 133, 107215. [Google Scholar]
- Marić, P.; Kljajić, R.; Chamorro, H.R.; Glavaš, H. Power system stabilizer tuning algorithm in a multimachine system based on S-domain and time domain system performance measures. Energies 2021, 14, 5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salesi-Mousaabadi, M.; Shahgholian, G. Simultaneous adjustment of AVR and optimized PSS outputs effect in power systems for stability improvement. Journal of Power Technologies 2023, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, F.; Molina, Y.; Araujo, C. Simultaneous tuning of AVR and PSS using particle swarm optimization with two stages. IEEE Latin America Transactions 2020, 18, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvabala, B.; Devaraj, D. Co-ordinated design of AVR-PSS using multi objective genetic algorithm. Swarm, Evolutionary, and Memetic Computing: First International Conference on Swarm, Evolutionary, and Memetic Computing, SEMCCO 2010, Chennai, India, December16-18, 2010. Proceedings 1. Springer, 2010, pp. 481–493. 16 December.
- Selvabala, B.; Devaraj, D. Co-ordinated tuning of AVR-PSS using differential evolution algorithm. 2010 Conference Proceedings IPEC. IEEE, 2010, pp. 439–444.
- Manuaba, I.; Abdillah, M.; Priyadi, A.; Purnomo, M.H. Coordinated tuning of PID-based PSS and AVR using bacterial foraging-PSOTVAC-DE algorithm. Control and Intelligent Systems 2015, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, J.; Mustafa, M.W.; Aliyu, G. Design of AVR and PSS for power system stability based on iteration particle swarm optimization. International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Technology (IJEIT) 2012, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Nirmal, J.F.; Auxillia, D.J. Adaptive PSO based tuning of PID controller for an Automatic Voltage Regulator system. 2013 International Conference on Circuits, Power and Computing Technologies (ICCPCT). IEEE, 2013, pp. 661–666.
- Špoljarić, T.; Pavić, I.; Alinjak, T. Performance Comparison of No-preference and Weighted Sum Objective Methods in Multi-Objective Optimization of AVR-PSS Tuning in Multi-machine Power System. Tehnički vjesnik 2022, 29, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, P.; Chowdhury, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Pal, S.; Crossley, P. Intelligent AVR and PSS with Adaptive hybrid learning algorithm. 2008 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting-Conversion and Delivery of Electrical Energy in the 21st Century. IEEE, 2008, pp. 1–7.
- Khezri, R.; Bevrani, H. Fuzzy-based coordinated control design for AVR and PSS in multi-machine power systems. 2013 13th Iranian Conference on Fuzzy Systems (IFSC). IEEE, 2013, pp. 1–5.
- Rodrigues, F.W. ; others. Projeto simultâneo do regulador automático de tensão e estabilizador de sistema de potência utilizando otimização por enxame de partículas modificado 2019.
- Silva Junior, J.N.R.d. Sintonia ótima de regulador automático de tensão e estabilizador de sistema de potência utilizando algoritmo de otimização por enxame de partículas 2012.
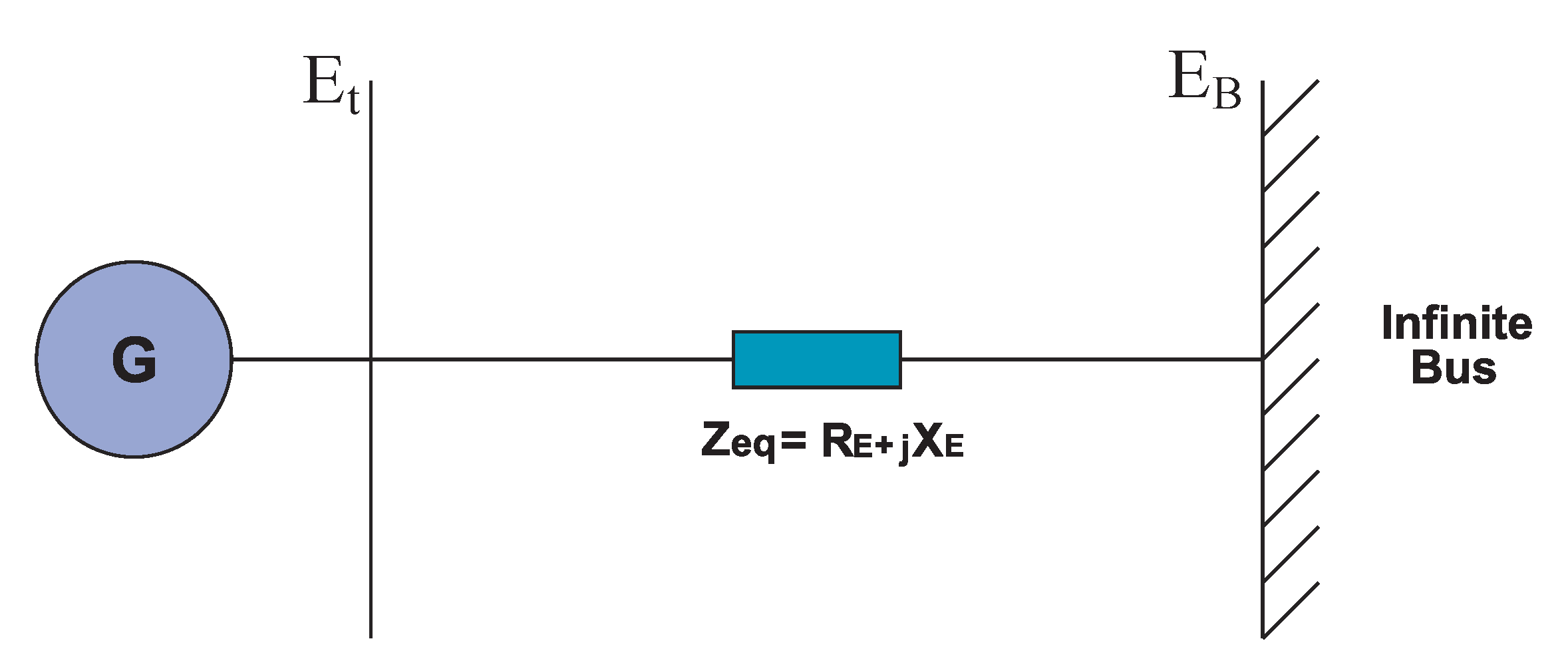

| Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper limit | 400 | 2 | 3 | 0.5 |
| Lower limit | 1 | 0.1 | 1 | 0.0001 |
| Solution | Objective Function | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | (p.u) | (p.u) | (s) | (s) | Stand.Dev. | Average | Best | Worst | |
| PSO-LD | Best | 124.06 | 0.1 | 1 | 0.5 | 2.367 | 5.259 | 9.934 | 2.791 |
| Worst | 100.47 | 2 | 3 | 0.0001 | |||||
| PSO-OIW | Best | 124.06 | 0.1 | 1 | 0.5 | 2.118 | 5.031 | 9.934 | 2.791 |
| Worst | 104.68 | 1.92 | 1 | 0.0001 | |||||
| PSO-OED | Best | 124.06 | 0.1 | 1 | 0.5 | 2.220 | 5.220 | 9.934 | 2.791 |
| Worst | 100.19 | 1.62 | 3 | 0.0001 | |||||
| Proposed | Best | 124.06 | 0.1 | 1 | 0.5 | 2.108 | 5.305 | 9.934 | 2.791 |
| PSO-POED | Worst | 109.36 | 2 | 1.54 | 0.0102 | ||||
| Best Solution | Worst Solution | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | (s) | (s) | (%) | (%) | (s) | (s) | (%) | (%) |
| PSO-LD | 0.332 | 0.422 | 0.229 | 2.0 | 0.352 | 0.702 | 0.0000 | 2.0 |
| PSO-OIW | 0.332 | 0.422 | 0.229 | 2.0 | 0.352 | 0.702 | 0.0002 | 2.0 |
| PSO-OED | 0.332 | 0.422 | 0.229 | 2.0 | 0.352 | 0.702 | 0.0002 | 2.0001 |
| PSO-POED | 0.332 | 0.422 | 0.229 | 2.0 | 0.352 | 0.702 | 0.0004 | 2.0 |
| Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper limit | 400 | 50 | 1 | 0.05 |
| Lower limit | 1 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.005 |
| Best Solution | Objective Function | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | Generator | (p.u) | (p.u) | (s) | (s) | Stand.Dev. | Average | Best | Worst |
| PSO-LD | 37.29 | 1.2197 | 1 | 0.0356 | 0.6917 | 13.9374 | 14.1578 | 12.0357 | |
| 400 | 1 | 1 | 0.0261 | ||||||
| PSO-OIW | 39.75 | 49.1465 | 0.0868 | 0.0489 | 0.4835 | 14.1358 | 14.5754 | 13.7565 | |
| 400 | 1 | 1 | 0.0305 | ||||||
| PSO-OED | 400 | 1 | 0.6001 | 0.0050 | 0.1208 | 14.5941 | 14.7762 | 14.0978 | |
| 34.77 | 50 | 1 | 0.0470 | ||||||
| Proposed | 400 | 0.1038 | 1 | 0.0271 | 4.1126 | 35.9307 | 39.9424 | 20.1955 | |
| PSO-POED | 400 | 0.1457 | 1 | 0.0464 | |||||
| Algorithm | Generator | Terminal Voltage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (s) | (s) | (%) | (%) | ||
| PSO-LD | 1.1417 | 1.2517 | 2.5856 | 4.4956 | |
| PSO-OIW | 1.1517 | 1.2517 | 3.0245 | 4.3509 | |
| PSO-OED | 1.1416 | 1.2417 | 2.5890 | 3.9360 | |
| Proposed PSO-POED | 0.2617 | 0.3017 | 0.0112 | 2.0500 | |
| PSO-LD | 1.1050 | 1.2117 | 2.3702 | 4.0054 | |
| PSO-OIW | 1.1050 | 1.2117 | 2.3655 | 4.0567 | |
| PSO-OED | 1.1050 | 1.2117 | 2.6455 | 3.9099 | |
| Proposed PSO-POED | 0.2417 | 0.2817 | 0.0077 | 2.0500 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





