Submitted:
26 June 2024
Posted:
26 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
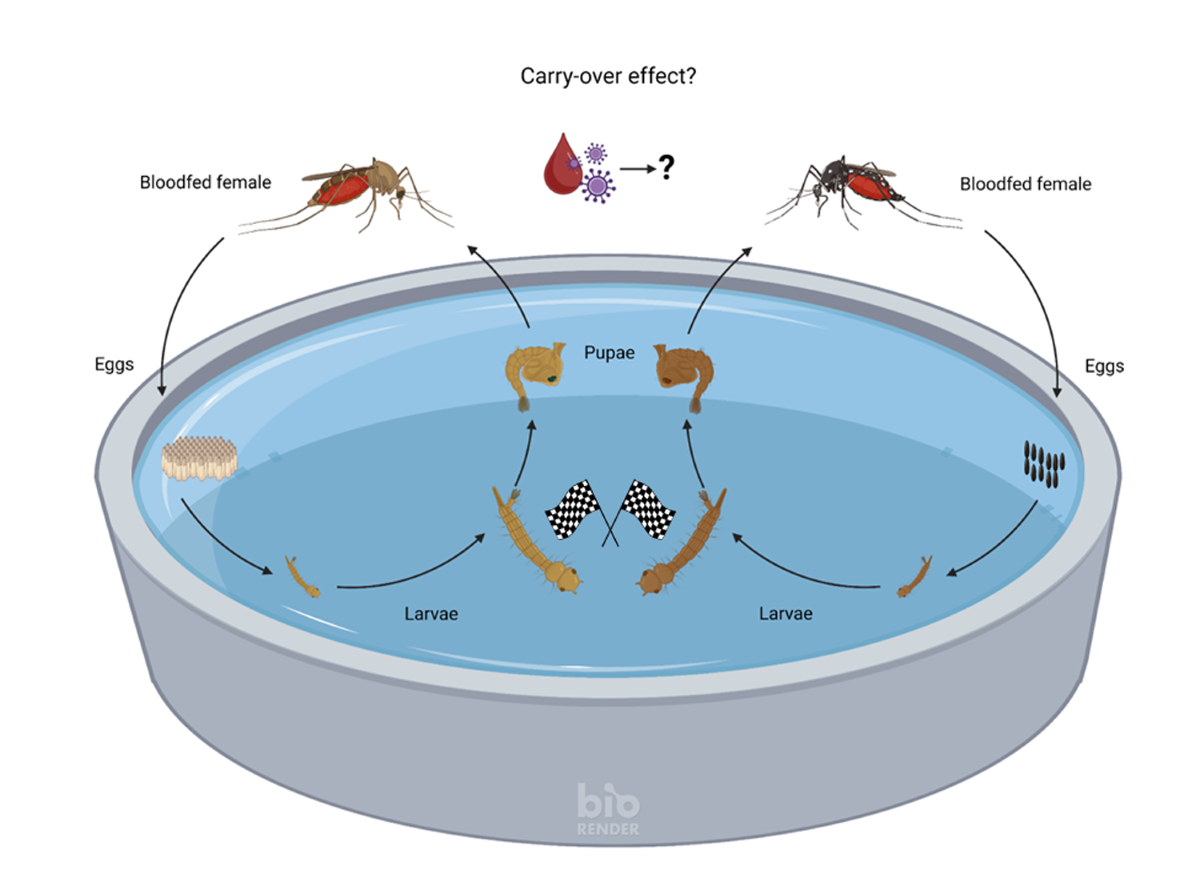
1. Introduction
2. Material & Methods
2.1. Larval Competition Study
2.1.1. Mosquito Material
2.1.2. Larval Replacement-Series Experiments
2.1.3. Video Tracking of Behavioral Variables
2.1.4. Photometric Assays on Pupal Lipid, Glycogen, and Protein Content
2.1.5. Data Analysis
2.2. Infection Study
2.2.1. Infectious Blood Feeding of Mosquitoes Which Experienced Larval Competition
2.2.2. Quantification of Infection Rate
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Competition Study
3.1.1. Mortality
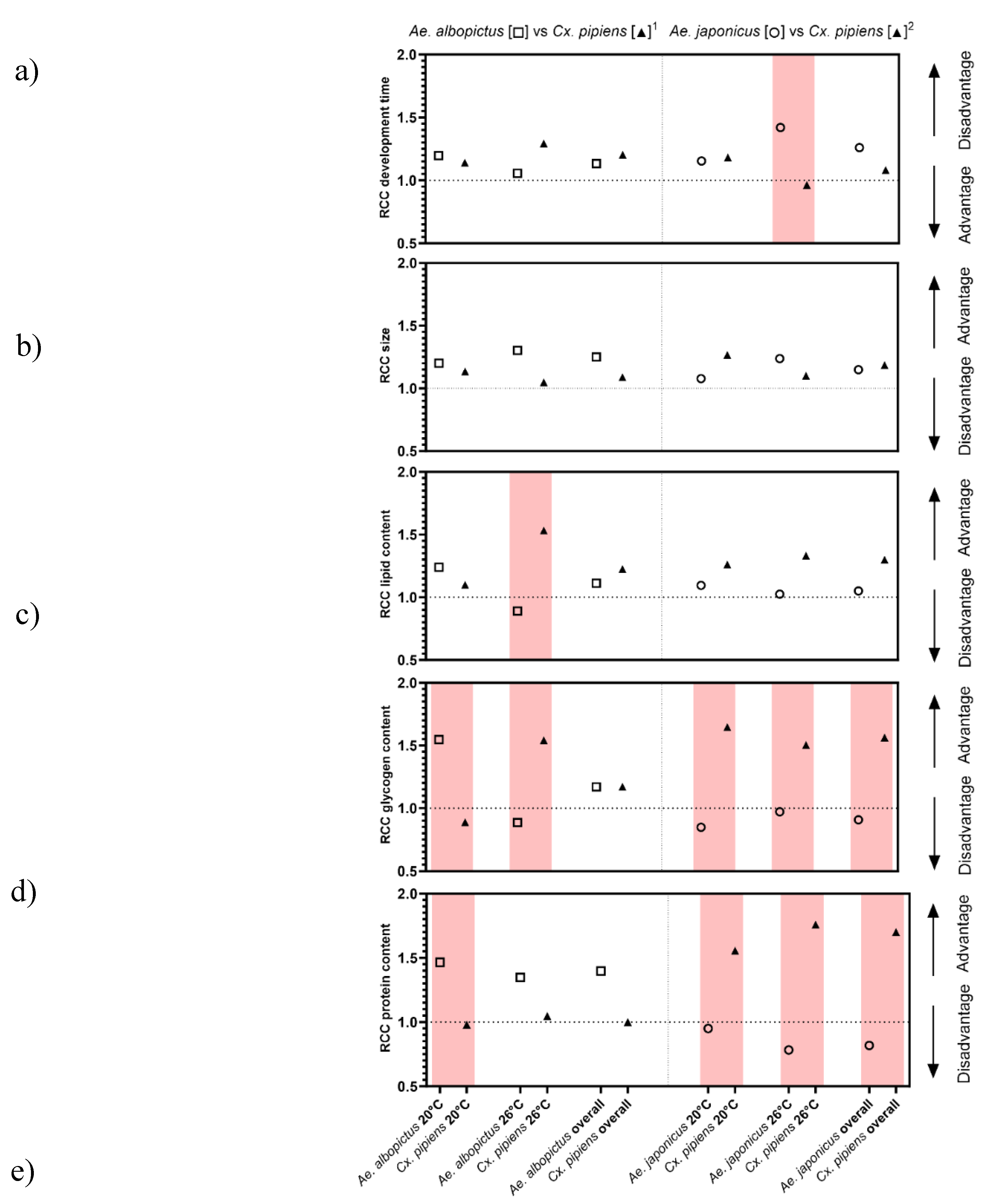
3.1.2. Development Time
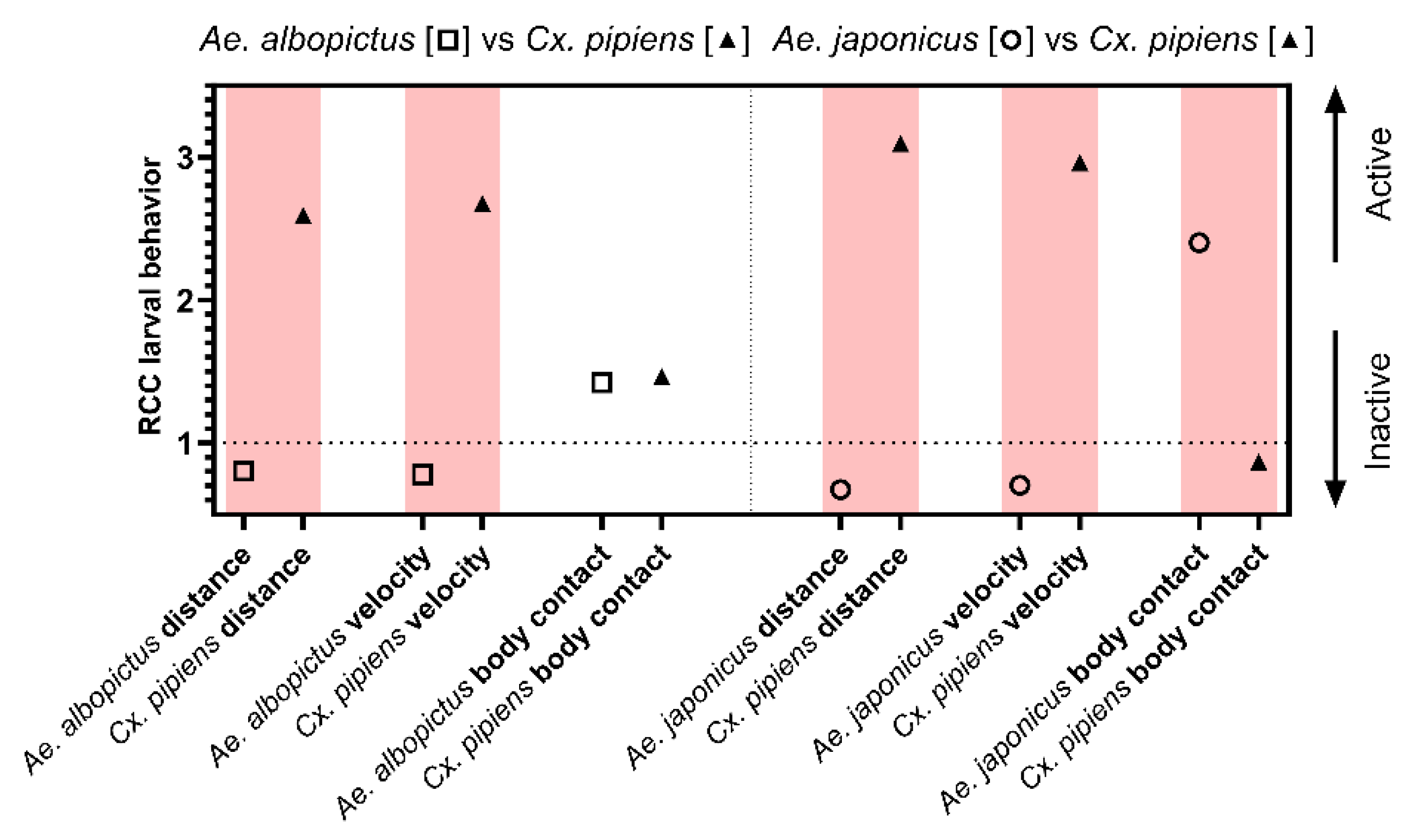
3.1.3. Larval Behavior
3.1.4. Pupal Size
3.1.5. Energy and Protein Storage
3.1.6. Relative Crowding Coefficient
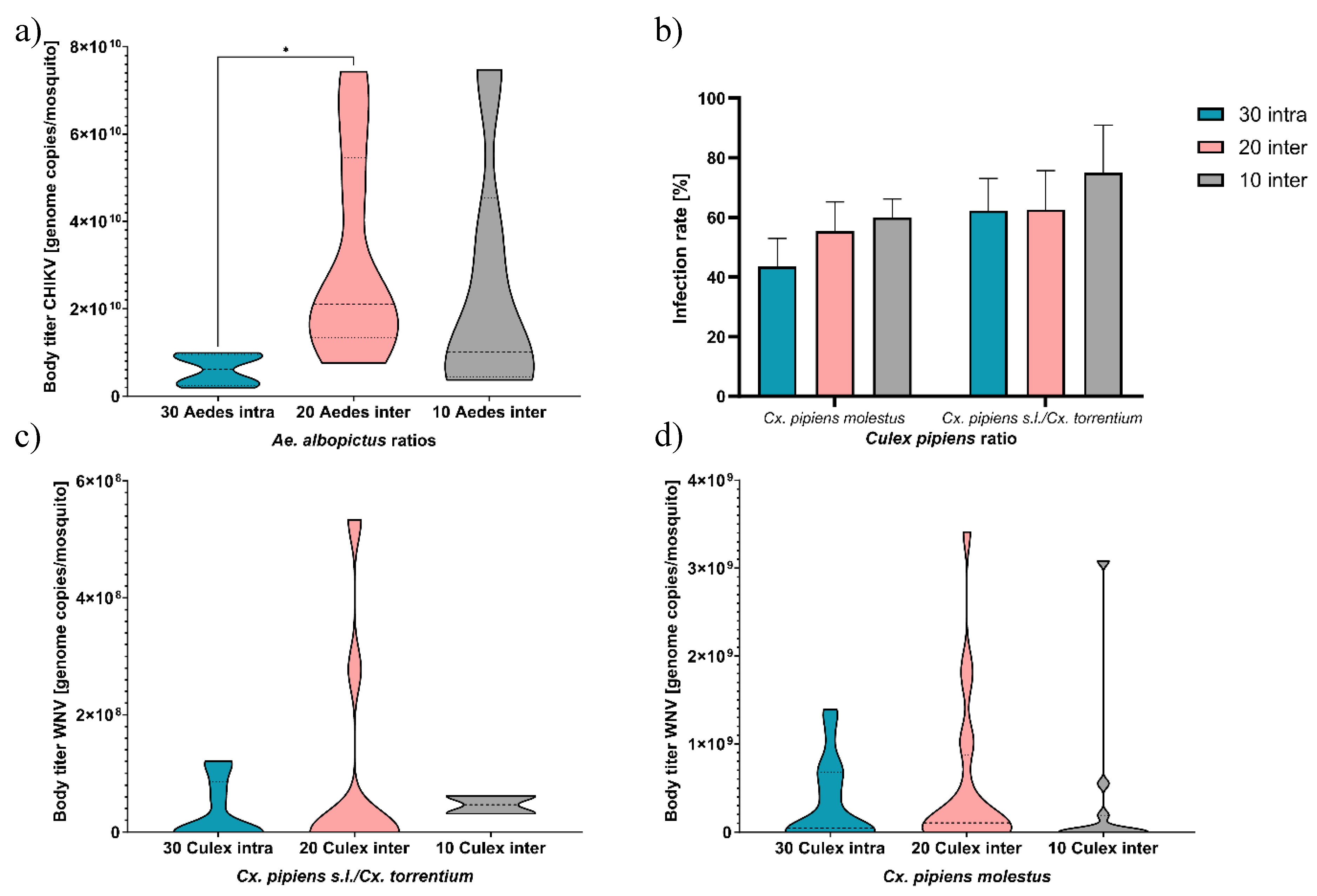
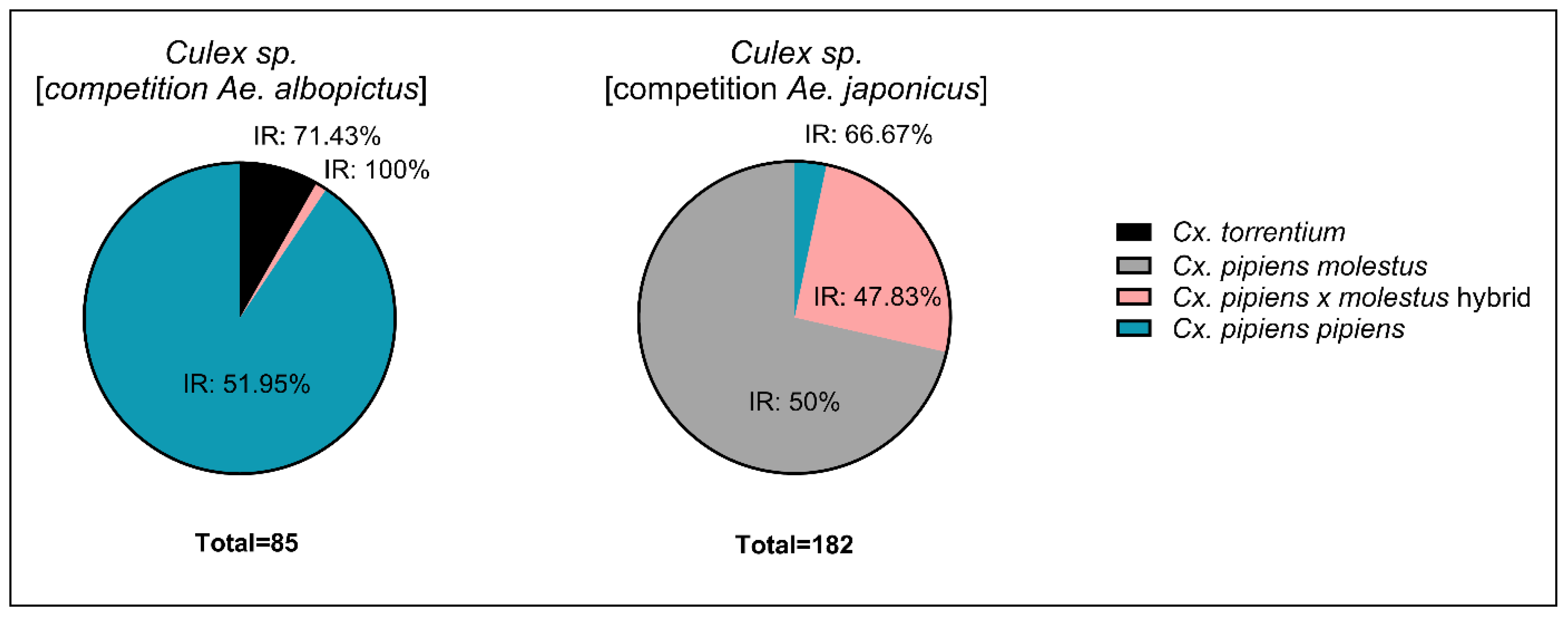
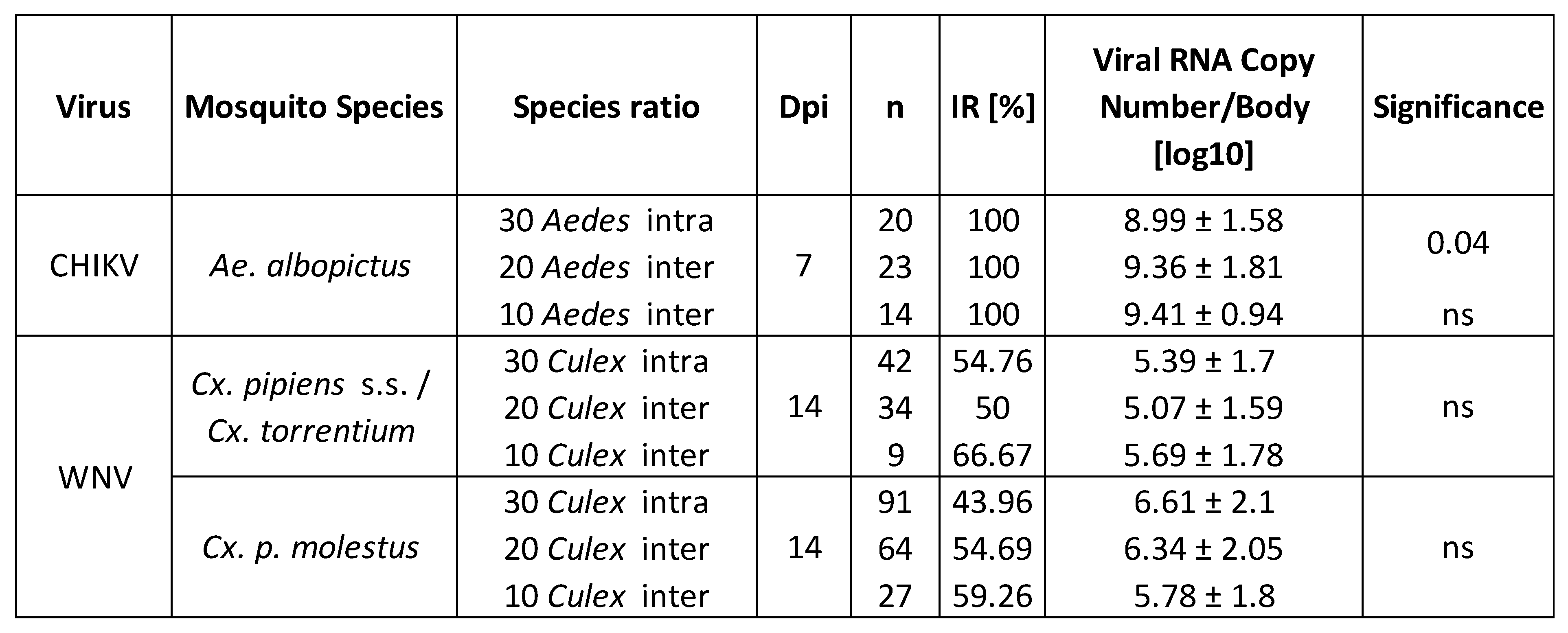
3.2. Infection Study
4. Discussion
4.1. Aedes Albopictus vs Culex pipiens s.s./Cx. Torrentium
4.2. Aedes Japonicus vs Culex Pipiens Bioform Molestus
4.3. Effect of Interspecific Competition On Viral Infection
4.4. Implications on Bigger Scale
4.5. Limitations of the study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Data availability statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publications
Competing interests
Abbreviations
References
- Perrin, A.; Glaizot, O.; Christe, P. Worldwide impacts of landscape anthropization on mosquito abundance and diversity: A meta-analysis. Global Change Biol. 2022, 28, 6857–6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartholomeeusen, K.; Daniel, M.; LaBeaud, D.A.; Gasque, P.; Peeling, R.W.; Stephenson, K.E.; et al. Chikungunya fever. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autochthonous vectorial transmission of dengue virus in mainland EU/EEA, 2010-present [Internet]. ECDC. 2024a [cited 17/06/2024].
- Laverdeur, J.; Desmecht, D.; Hayette, M.P.; Darcis, G. Dengue and chikungunya: future threats for Northern Europe? Front Epidemiol. 2024, 4, 1342723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autochthonous transmission of chikungunya virus in mainland EU/EEA, 2007–present [Internet]. ECDC. 2024b [cited 17/06/2024].
- Historical data by year - West Nile virus seasonal surveillance [Internet]. ECDC. 2024c [cited 18/06/2024]. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/west-nile-fever/surveillance-and-disease-data/historical.
- Ryan, S.J.; Carlson, C.J.; Mordecai, E.A.; Johnson, L.R. Global expansion and redistribution of Aedes-borne virus transmission risk with climate change. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019, 13, e0007213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deblauwe, I.; De Wolf, K.; De Witte, J.; Schneider, A.; Verle, I.; Vanslembrouck, A.; et al. From a long-distance threat to the invasion front: a review of the invasive Aedes mosquito species in Belgium between 2007 and 2020. Parasit Vectors. 2022, 15, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eritja, R.; Ruiz-Arrondo, I.; Delacour-Estrella, S.; Schaffner, F.; Álvarez-Chachero, J.; Bengoa, M.; et al. First detection of Aedes japonicus in Spain: an unexpected finding triggered by citizen science. Parasites & Vectors. 2019, 12, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Sherpa, S.; Blum, M.G.B.; Capblancq, T.; Cumer, T.; Rioux, D.; Despres, L. Unravelling the invasion history of the Asian tiger mosquito in Europe. Mol Ecol. 2019, 28, 2360–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, M.U.G.; Reiner, R.C.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Gilbert, M.; Pigott, D.M.; et al. Past and future spread of the arbovirus vectors Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Nature Microbiology. 2019, 4, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worsening spread of mosquito-borne disease outbreaks in EU/EEA, according to latest ECDC figures [press release]. European Center for Disease Prevention and Control2024d. 2024d.
- Soto, A.; De Coninck, L.; Devlies, A.S.; Van De Wiele, C.; Rosales Rosas, A.L.; Wang, L.; et al. Belgian Culex pipiens pipiens are competent vectors for West Nile virus while Culex modestus are competent vectors for Usutu virus. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023, 17, e0011649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haba, Y.; McBride, L. Origin and status of Culex pipiens mosquito ecotypes. Curr Biol. 2022, 32, R237–R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteirt, V.; Schaffner, F.; Garros, C.; Dekoninck, W.; Coosemans, M.; Van Bortel, W. Introduction and establishment of the exotic mosquito species Aedes japonicus japonicus (Diptera: Culicidae) in Belgium. J Med Entomol. 2009, 46, 1464–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrieri, M.; Bacchi, M.; Bellini, R.; Maini, S. On the competition occuring between Aedes albopictus and Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae) in Italy. Entomological Society of America. 2003, 32, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.; Knautz, T.; Vollroth, S.; Berger, R.; Kress, A.; Reuss, F.; et al. Larval superiority of Culex pipiens to Aedes albopictus in a replacement series experiment: prospects for coexistence in Germany. Parasit Vectors. 2018, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, B.; Montarsi, F.; Huemer, H.P.; Indra, A.; Capelli, G.; Allerberger, F.; et al. First record of the Asian bush mosquito, Aedes japonicus japonicus, in Italy: invasion from an established Austrian population. Parasit Vectors. 2016, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alto, B.W.; Lounibos, L.P.; Higgs, S.; Juliano, S.A. Larval Competition Differentially Affects Arbovirus Infection in Aedes Mosquitoes. Ecology. 2005, 86, 3279–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alto, B.W.; Lounibos, L.P.; Mores, C.N.; Reiskind, M.H. Larval competition alters susceptibility of adult Aedes mosquitoes to dengue infection. Proc Biol Sci. 2008, 275, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bevins, S.N. Invasive mosquitoes, larval competition, and indirect effects on the vector competence of native mosquito species (Diptera: Culicidae). Biol Invasions. 2007, 10, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braks, M.A.H.; Honório, N.A.; Lounibos, L.P.; Lourenço-De-Oliveira, R.; Juliano, S.A. Interspecific Competition Between Two Invasive Species of Container Mosquitoes, Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae), in Brazil. Annals of the Entomological Society of America. 2004, 97, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, K.S.; Mormann, K.M.; Juliano, S.A. Asymmetrical Competition and Patterns of Abundance of Aedes albopictus and Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae). Journal of Medical Entomology. 2005, 42, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armistead, J.S.; Arias, J.R.; Nishimura, N.; Lounibos, L.P. Interspecific larval competition between Aedes albopictus and Aedes japonicus (Diptera: Culicidae) in northern Virginia. J Med Entomol. 2008, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo, K.S.; Muturi, E.J.; Lampman, R.L.; Alto, B.W. The effects of resource type and ratio on competition with Aedes albopictus and Culex pipiens (Diptera:Culicidae). J Med Entomol. 2011, 48, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonizzoni, M.; Gasperi, G.; Chen, X.; James, A.A. The invasive mosquito species Aedes albopictus: current knowledge and future perspectives. Trends Parasitol. 2013, 29, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marini, G.; Guzzetta, G.; Baldacchino, F.; Arnoldi, D.; Montarsi, F.; Capelli, G.; et al. The effect of interspecific competition on the temporal dynamics of Aedes albopictus and Culex pipiens. Parasit Vectors. 2017, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leisnham, P.T.; LaDeau, S.L.; Saunders, M.E.M.; Villena, O.C. Condition-Specific Competitive Effects of the Invasive Mosquito Aedes albopictus on the Resident Culex pipiens among Different Urban Container Habitats May Explain Their Coexistence in the Field. Insects 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giatropoulos, A.; Papachristos, D.; Michaelakis, A.; Kapranas, A.; Emmanouel, N. Laboratory study on larval competition between two related mosquito species: Aedes (Stegomyia) albopictus and Aedes (Stegomyia) cretinus. Acta Trop. 2022, 230, 106389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, J.; Fischer, S.; Werner, D.; Kampen, H. Impact of larvae of the Asian tiger mosquito Aedes albopictus on larvae of the Culex pipiens complex from Germany in laboratory co-breeding studies. Med Vet Entomol. 2023, 37, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreadis, T.G.; Wolfe, R.J. Evidence for reduction of native mosquitoes with increased expansion of invasive Ochlerotatus japonicus japonicus (Diptera: Culicidae) in the northeastern United States. J Med Entomol. 2010, 47, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardstone, M.C.; Andreadis, T.G. Weak larval competition between the invasive mosquito Aedes japonicus japonicus (Diptera: Culicidae) and three resident container-inhabiting mosquitoes in the laboratory. J Med Entomol. 2012, 49, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Donnell, D.L.; Armbruster, P. Comparison of larval foraging behavior of Aedes albopictus and Aedes japonicus (Diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol. 2007, 44, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiskind, M.H.; Lounibos, L.P. Effects of intraspecific larval competition on adult longevity in the mosquitoes Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Med Vet Entomol. 2009, 23, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telang, A.; Qayum, A.A.; Parker, A.; Sacchetta, B.R.; Byrnes, G.R. Larval nutritional stress affects vector immune traits in adult yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti (Stegomyia aegypti). Med Vet Entomol. 2012, 26, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bara, J.; Rapti, Z.; Caceres, C.E.; Muturi, E.J. Effect of Larval Competition on Extrinsic Incubation Period and Vectorial Capacity of Aedes albopictus for Dengue Virus. PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0126703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muturi, E.J.; Kim, C.H.; Alto, B.W.; Berenbaum, M.R.; Schuler, M.A. Larval environmental stress alters Aedes aegypti competence for Sindbis virus. Trop Med Int Health. 2011, 16, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takken, W.; Klowden, M.J.; Chambers, G.M. Effect of body size on host seeking and blood meal utilization in Anopheles gambiae sensu stricto (Diptera: Culicidae): the disadvantage of being small. J Med Entomol. 1998, 35, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnayake, O.C.; Chotiwan, N.; Saavedra-Rodriguez, K.; Perera, R. The buzz in the field: the interaction between viruses, mosquitoes, and metabolism. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1128577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrese, E.L.; Soulages, J.L. Insect fat body: energy, metabolism, and regulation. Annu Rev Entomol. 2010, 55, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimstad, P.R.; Walker, E.D. Aedes triseriatus (Diptera: Culicidae) and La Crosse virus. IV. Nutritional deprivation of larvae affects the adult barriers to infection and transmission. J Med Entomol. 1991, 28, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, G.; Thievent, K.; Koella, J.C. Consequences of larval competition and exposure to permethrin for the development of the rodent malaria Plasmodium berghei in the mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Parasit Vectors. 2020, 13, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolf, M.; Czajka, C.; Borstler, J.; Melaun, C.; Jost, H.; von Thien, H.; et al. First nationwide surveillance of Culex pipiens complex and Culex torrentium mosquitoes demonstrated the presence of Culex pipiens biotype pipiens/molestus hybrids in Germany. PLoS One. 2013, 8, e71832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereecken, S.; Vanslembrouck, A.; Kramer, I.M.; Muller, R. Phenotypic insecticide resistance status of the Culex pipiens complex: a European perspective. Parasit Vectors. 2022, 15, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.; Knautz, T.; Volker, J.; Kress, A.; Kuch, U.; Oehlmann, J. Appropriate larval food quality and quantity for Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol. 2013, 50, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Handel, E. Rapid determination of glycogen and sugars in mosquitoes. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 1985, 1, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Handel, E. Rapid determination of total lipids in mosquitoes. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 1985, 1, 302–304. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, F.; Kuch, U.; Pfenninger, M.; Muller, R. Standardized Laboratory Feeding of Larval Aedes japonicus japonicus (Diptera: Culicidae). J Insect Sci 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, M.G.; Higley, L.G.; Christianssen, C.A.; Rowley, W.A. Evaluating Larval Competition between Aedes-Albopictus and a-Triseriatus (Diptera, Culicidae) through Replacement Series Experiments. Environ Entomol. 1993, 22, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberg, A.L.; Young, L.J.; Higley, L.G. A study of the statistical properties of two measures of competition. Applied statistics in agriculture 1994. [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.L. Population biology of plants; Academic Press: New York, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Heitmann, A.; Jansen, S.; Luhken, R.; Leggewie, M.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Tannich, E. Forced Salivation As a Method to Analyze Vector Competence of Mosquitoes. J Vis Exp 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, K.; Jansen, S.; Leggewie, M.; Badusche, M.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Becker, N.; et al. Aedes japonicus japonicus (Diptera: Culicidae) from Germany have vector competence for Japan encephalitis virus but are refractory to infection with West Nile virus. Parasitol Res. 2014, 113, 3195–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.J.; Lanciotti, R.S. Consensus amplification and novel multiplex sequencing method for S segment species identification of 47 viruses of the Orthobunyavirus, Phlebovirus, and Nairovirus genera of the family Bunyaviridae. J Clin Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2398–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, D.Y.; Davis, B.S.; Chang, G.J. Development of multiplex real-time reverse transcriptase PCR assays for detecting eight medically important flaviviruses in mosquitoes. J Clin Microbiol. 2007, 45, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshoo, M.W.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Zoll, S.T.; Massire, C.; Pennella, T.T.; Blyn, L.B.; et al. Direct broad-range detection of alphaviruses in mosquito extracts. Virology. 2007, 368, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, D.A.; Kesavaraju, B.; Juliano, S.A. Larval feeding behavior of three co-occurring species of container mosquitoes. J Vector Ecol. 2004, 29, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vanslembrouck, A.; Scheers, K.; Vermeersch, X.; Hendrickx, R.; Schneider, A.; De Witte, J.; et al. Exploring the efficacy of predaceous diving beetles as potential nature-based solution for combating the invasive mosquito Aedes albopictus. Neobiota. Under review.
- Giunti, G.; Becker, N.; Benelli, G. Invasive mosquito vectors in Europe: From bioecology to surveillance and management. Acta Trop. 2023, 239, 106832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.; Riley, C.; Isaac, G.; Hopf-Jannasch, A.S.; Moore, R.J.; Weitz, K.W.; et al. Dengue virus infection perturbs lipid homeostasis in infected mosquito cells. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chotiwan, N.; Andre, B.G.; Sanchez-Vargas, I.; Islam, M.N.; Grabowski, J.M.; Hopf-Jannasch, A.; et al. Dynamic remodeling of lipids coincides with dengue virus replication in the midgut of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, C.; Islam, M.N.; Ye, Y.H.; Chotiwan, N.; Graham, B.; Belisle, J.T.; et al. Dengue virus dominates lipid metabolism modulations in Wolbachia-coinfected Aedes aegypti. Commun Biol. 2020, 3, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, A.S.; Bellamy, S.K.; Alto, B.W.; Dean, C.L.; Yee, D.A. Linking nutrient stoichiometry to Zika virus transmission in a mosquito. Oecologia. 2019, 191, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
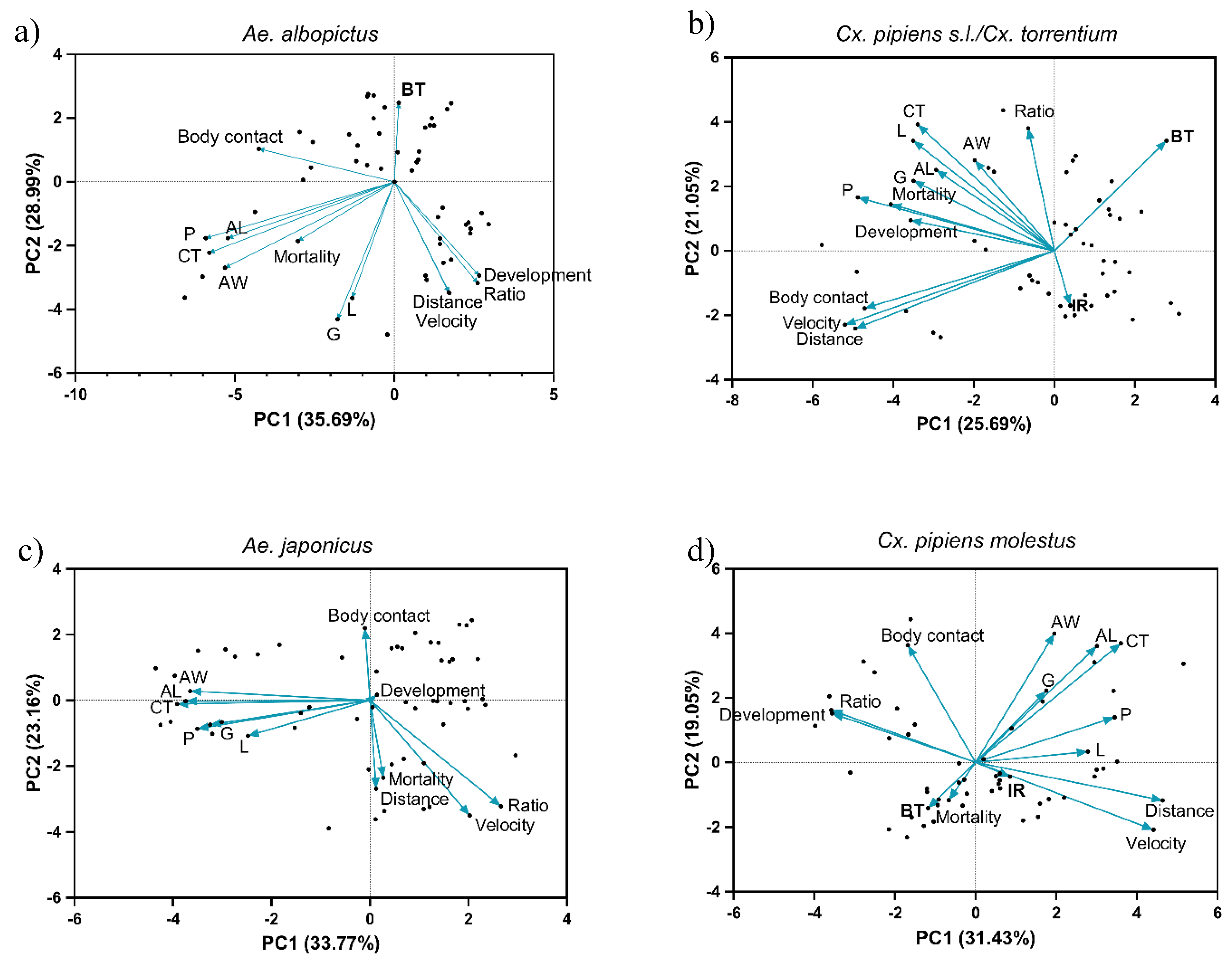
| PC1 | |||||||
| Ae. albopictus | Cx. pipienss.s./Cx. torrentium | Ae. japonicus | Cx. p. molestus | ||||
| Development | 0.78 | Development | -0.51 | L | -0.58 | Distance | 0.81 |
| Ratio | 0.77 | Mortality | -0.58 | G | -0.76 | Velocity | 0.77 |
| AL | -0.71 | Body contact | -0.67 | P | -0.82 | CT | 0.63 |
| AW | -0.73 | P | -0.69 | AW | -0.86 | P | 0.60 |
| CT | -0.79 | Distance | -0.70 | AL | -0.88 | Development | -0.83 |
| P | -0.81 | Velocity | -0.74 | CT | -0.92 | Ratio | -0.84 |
| PC2 | |||||||
| Ae. albopictus | Cx. pipienss.s./Cx. torrentium | Ae. japonicus | Cx. p. molestus | ||||
| BT | 0.58 | CT | 0.57 | Body contact | 0.61 | AW | 0.68 |
| Ratio | -0.59 | Ratio | 0.55 | L | -0.27 | CT | 0.63 |
| Velocity | -0.65 | BT | 0.50 | Mortality | -0.59 | Body contact | 0.62 |
| Distance | -0.65 | L | 0.50 | Distance | -0.68 | AL | 0.62 |
| L | -0.68 | Velocity | -0.63 | Ratio | -0.81 | BT | -0.38 |
| G | -0.80 | Distance | -0.66 | Velocity | -0.88 | Velocity | -0.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





