Submitted:
24 June 2024
Posted:
25 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
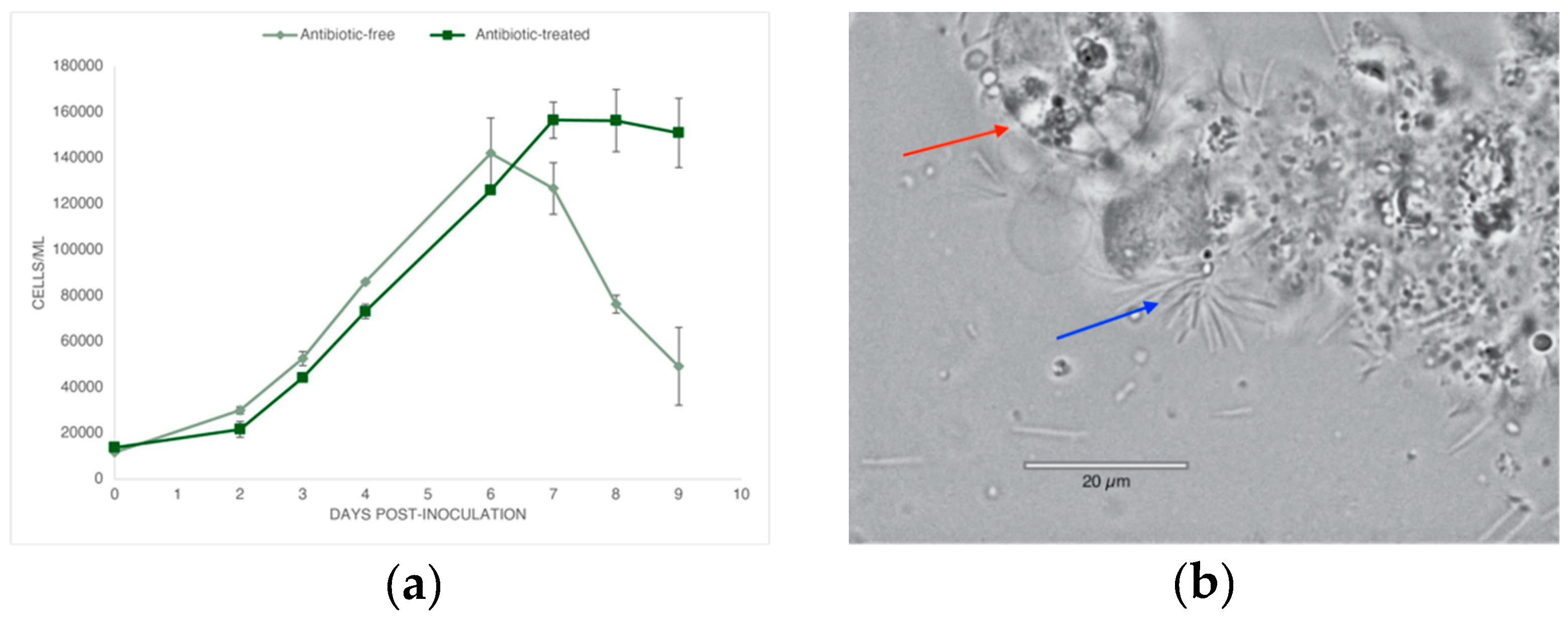
2.1. Bacterial Growth
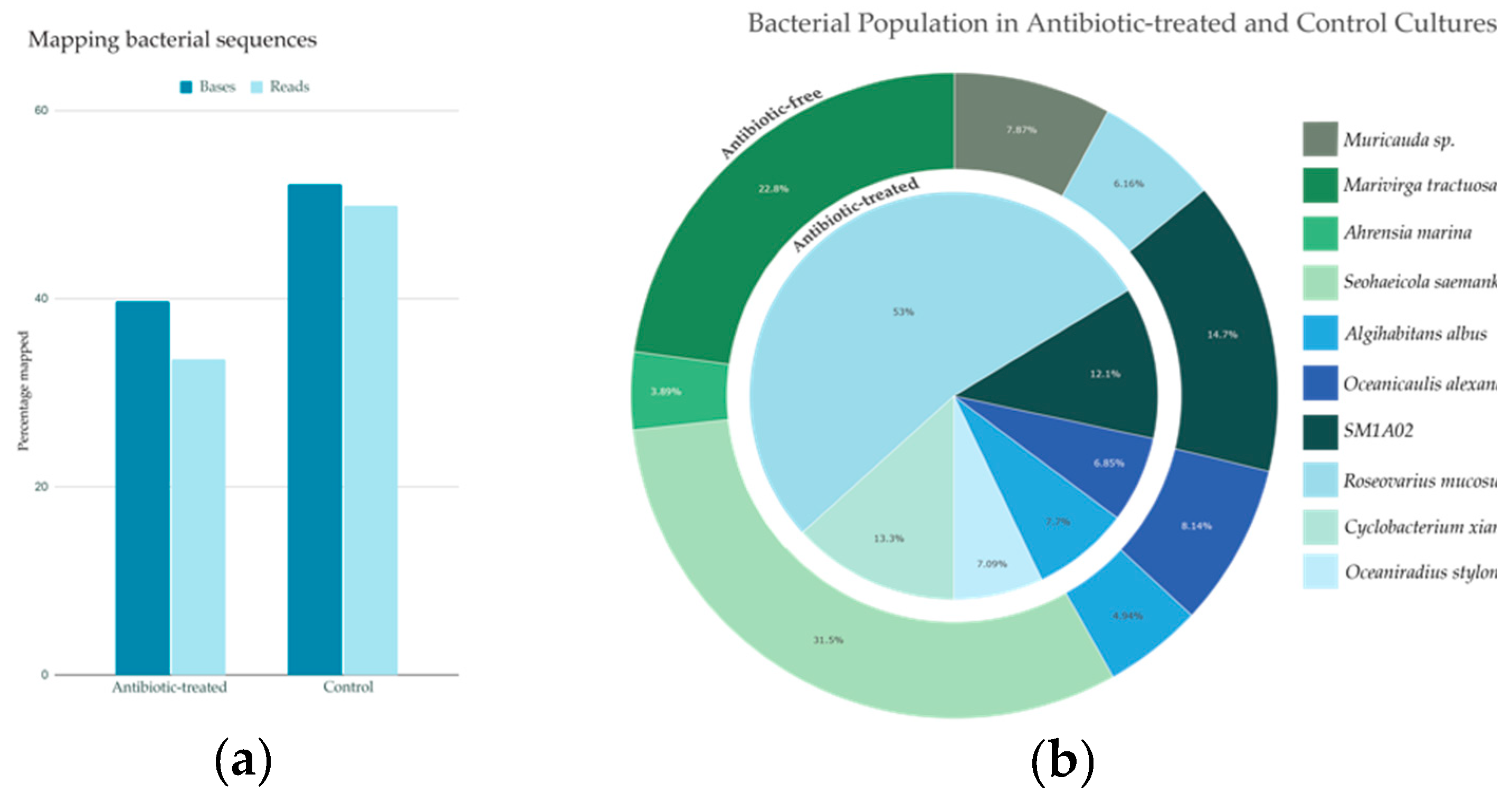
2.2. Bacterial Identification
| NCBI Sample Title | length | AT% |
|---|---|---|
| Labrenzia sp. strain ac12 | 6,053,707 | 40.9 |
| Hoeflea alexandrii strain ac4 | 4,829,646 | 38.4 |
| Algihabitans albus strain ac2 | 4,739,774 | 34.3 |
| Ahrensia marina strain ac1 | 4,424,055 | 42.8 |
| Seohaeicola saemankumensis strain ac14 | 4,275,009 | 36.6 |
| Roseovarius mucosus strain ac13 | 3,969,289 | 38.9 |
| Rhodophyticola porphyridii strain ac11 | 3,902,216 | 35.8 |
| Oceaniradius stylonematis strain ac10 | 3,664,187 | 35.3 |
| Oceanicaulis alexandrii strain ac9 | 2,992,841 | 37.7 |
| Nitratireductor sp. strain ac15 | 2,917,504 | 39.8 |
| Marinobacter adhaerens strain ac5 | 4,424,055 | 42.9 |
| Cyclobacterium xiamenense strain ac3 | 5,806,256 | 51.6 |
| Marivirga tractuosa strain ac6 | 4,787,102 | 65.3 |
| Muricauda sp. strain ac8 | 4,366,883 | 58.0 |
| Phycisphaeraceae SM1A02 strain ac7 | 3,415,114 | 34.9 |
2.2. Bacterial Abundance
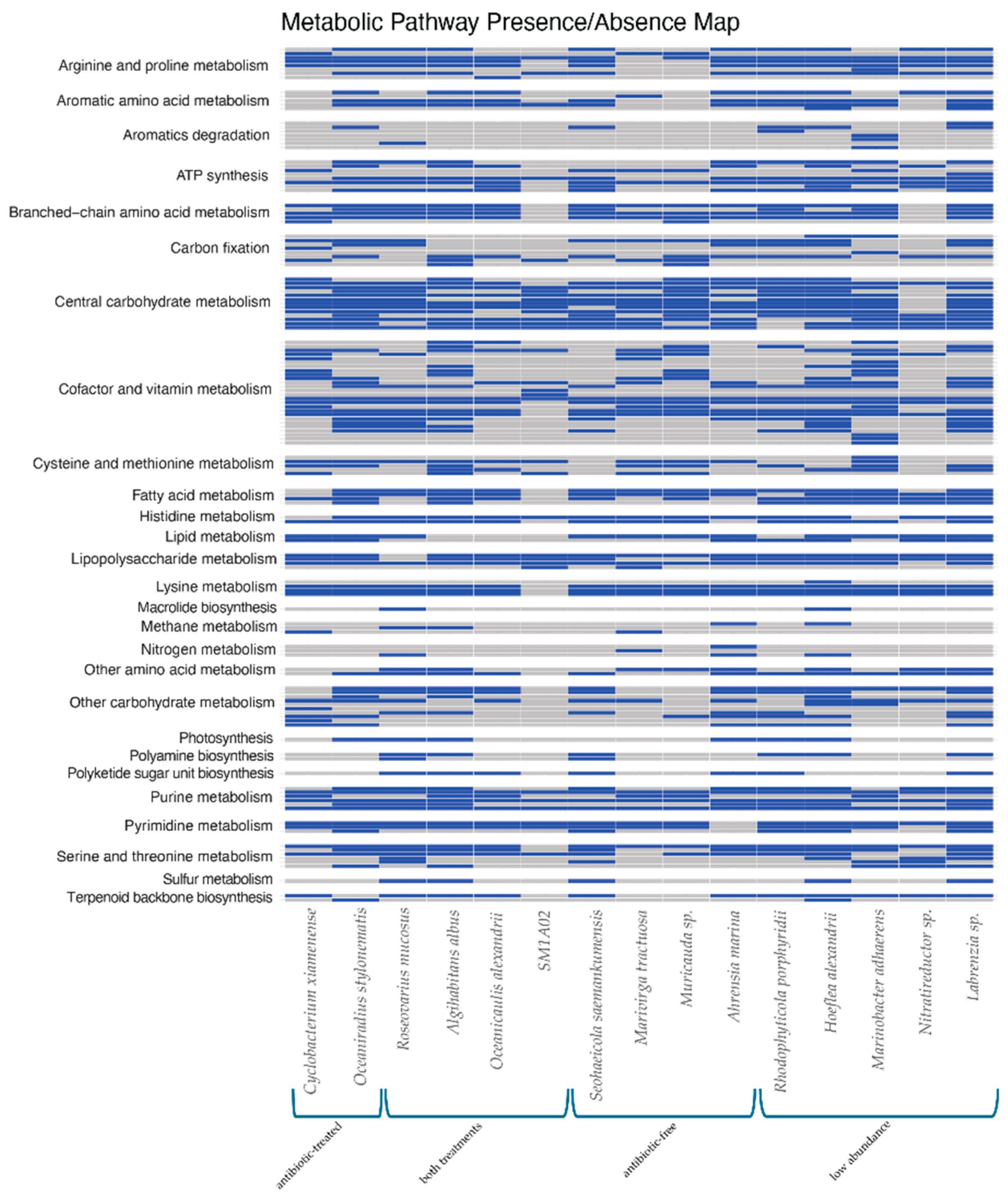
2.3. Bacterial Metabolic Pathways
2.4. Secondary Metabolite Synthesis
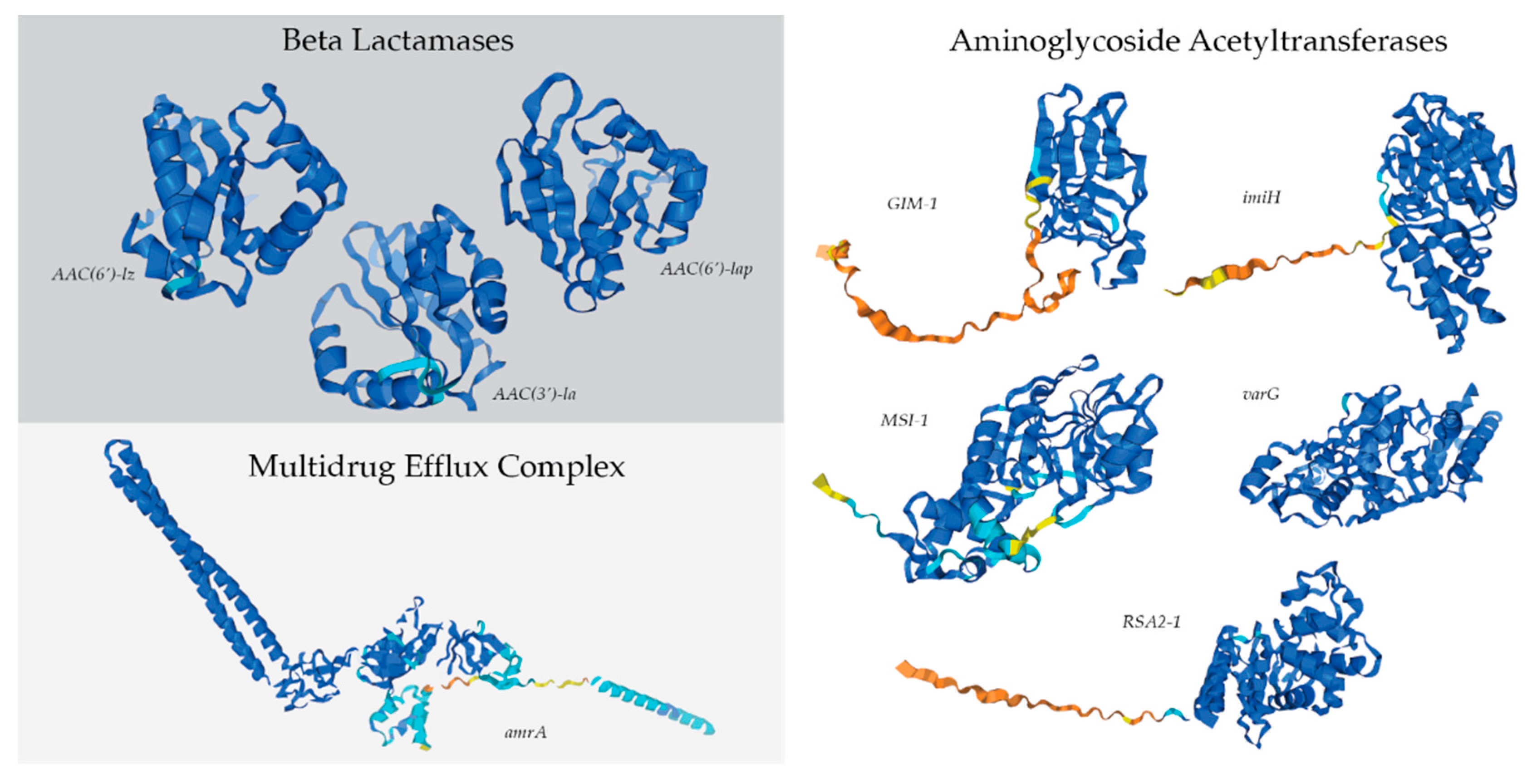
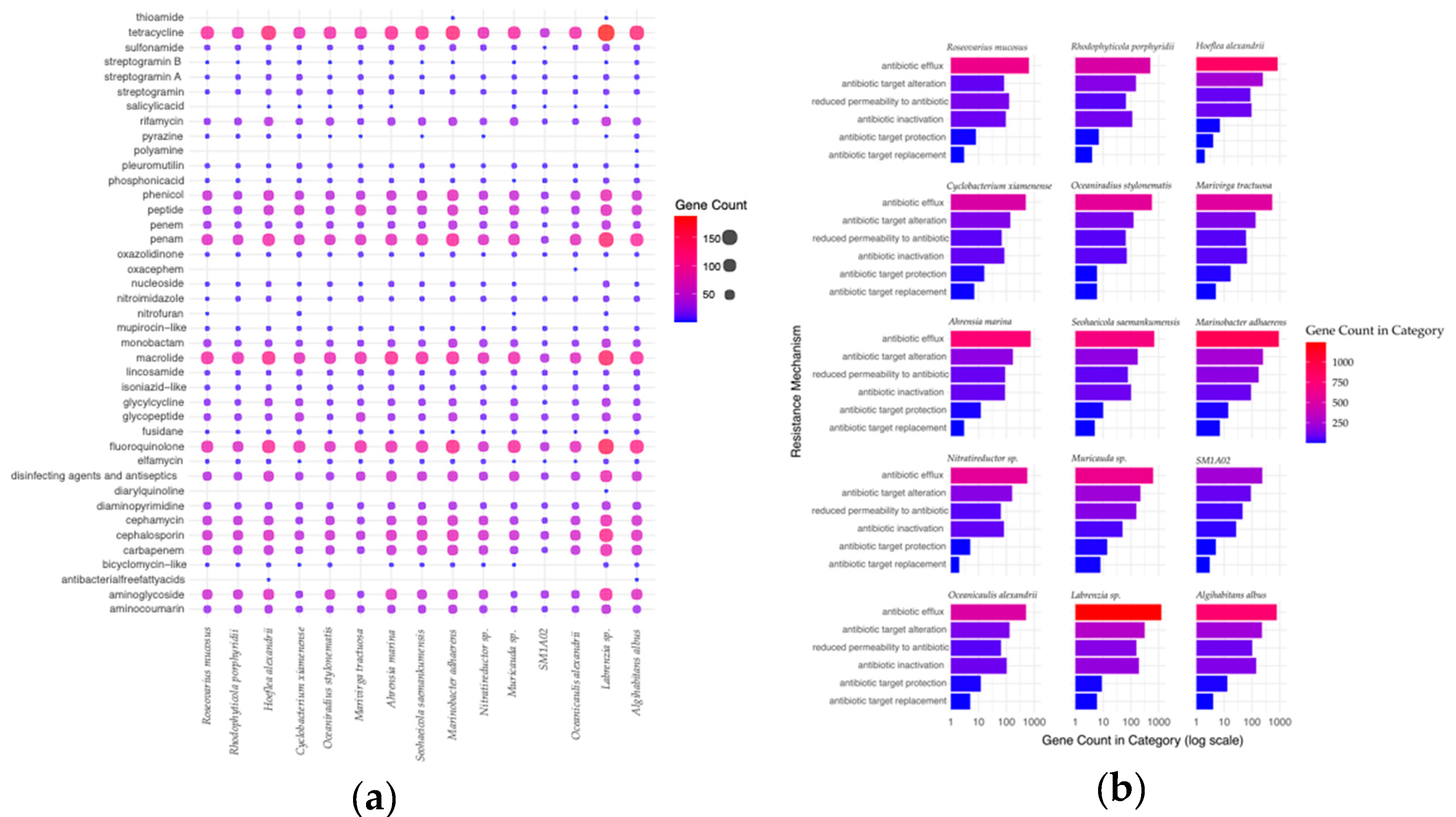
2.5. Antibiotic-Resistance
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culturing
4.2. DNA Extraction and Long-Read Sequencing
4.3. Genome Assembly
4.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.5. Read Abundance Mapping
4.6. Metabolic and Secondary Metabolites Analysis
4.7. Antimicrobial Resistance Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Antibiotic-Free | Antibiotic-Treated | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Reads | Device used | Date | Reads | Device used | |
| 2/1/2024 | 86,499 | GridION | 5/10/2023 | 122,303 | MinION | |
| 2/2/2024 | 62,172 | GridION | 5/12/2023 | 59,113 | MinION | |
| 2/3/2024 | 1,615 | GridION | 5/13/2023 | 180,995 | MinION | |
| 3/15/2024 | 295,191 | GridION | 5/16/2023 | 222,574 | MinION | |
| 3/17/2024 | 188,915 | GridION | 5/17/2023 | 152,303 | MinION | |
| 3/18/2024 | 152,194 | GridION | 10/30/2023 | 3,345,955 | PromethION | |
| Total Reads | 786,585 | 4,083,243 | ||||
| Total Bases | 23,622,147,065 | 151,572,689,672 | ||||

References
- Adolf, J.E.; Stoecker, D.K.; Harding, L.W. The Balance of Autotrophy and Heterotrophy during Mixotrophic Growth of Karlodinium micrum (Dinophyceae). J Plankton Res 2006, 28, 737–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, A.R.; Bowers, H.A.; Bachvaroff, T.R.; Adolf, J.E.; Deeds, J.R.; Sheng, J. Karlodinium veneficum-The Little Dinoflagellate with a Big Bite. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Not, F.; Siano, R.; Kooistra, W.H.C.F.; Simon, N.; Vaulot, D.; Probert, I. Diversity and Ecology of Eukaryotic Marine Phytoplankton; Elsevier, 2012; Vol. 64, ISBN 9780123914996. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, P.J. The Role of Photosynthesis and Food Uptake for the Growth of Marine Mixotrophic Dinoflagellates1. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 2011, 58, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prézelin, B.B.; Alberte, R.S. Photosynthetic Characteristics and Organization of Chlorophyll in Marine Dinoflagellates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1978, 75, 1801–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.Y.B.; Oliveira, C.D.L.; Müller, M.N.; Santos, E.P.; Dantas, D.M.M.; Gálvez, A.O. A Scientometric Overview of Global Dinoflagellate Research. Publications 2020, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botana, L.M. Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Detection, Second Edition. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Detection, Second Edition; 2008; pp. 1–943. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlisch, C.; Shemi, A.; Barak-Gavish, N.; Schatz, D.; Vardi, A. Algal Blooms in the Ocean: Hot Spots for Chemically Mediated Microbial Interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 2024, 22, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.M. Red Tides, 2nd ed. Scientific American, 1994; Vol. 271.
- Alavi, M.; Miller, T.; Erlandson, K.; Schneider, R.; Belas, R. Bacterial Community Associated with Pfiesteria-like Dinoflagellate Cultures. Environ Microbiol 2001, 3, 380–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolch, C.J.S.; Bejoy, T.A.; Green, D.H. Bacterial Associates Modify Growth Dynamics of the Dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum. Front Microbiol 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.H.; Llewellyn, L.E.; Negri, A.P.; Blackburn, S.I.; Bolch, C.J.S. Phylogenetic and Functional Diversity of the Cultivable Bacterial Community Associated with the Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2004, 47, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albinsson, M.E.; Negri, A.P.; Blackburn, S.I.; Bolch, C.J.S. Bacterial Community Affects Toxin Production by Gymnodinium catenatum. PLoS One 2014, 9, e104623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona-Janampa, U.I.; Cembella, A.D.; Pelayo-Zárate, M.C.; Pajares, S.; Márquez-Valdelamar, L.M.; Okolodkov, Y.B.; Tebben, J.; Krock, B.; Durán-Riveroll, L.M. Associated Bacteria and Their Effects on Growth and Toxigenicity of the Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum Lima Species Complex From Epibenthic Substrates Along Mexican Coasts. Front Mar Sci 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, Q.T.N.; Pradhan, B.; Kim, H.-S.; Ki, J.-S. Environmental Factors Modulate Saxitoxins (STXs) Production in Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium: An Updated Review of STXs and Synthesis Gene Aspects. Toxins (Basel) 2024, 16, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, A.; Evans, A.N.; Kulis, D.M.; Hackett, J.D.; Erdner, D.L.; Anderson, D.M.; Bhattacharya, D. Transcriptome Profiling of a Toxic Dinoflagellate Reveals a Gene-Rich Protist and a Potential Impact on Gene Expression Due to Bacterial Presence. PLoS One 2010, 5, e9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stüken, A.; Orr, R.J.S.; Kellmann, R.; Murray, S.A.; Neilan, B.A.; Jakobsen, K.S. Discovery of Nuclear-Encoded Genes for the Neurotoxin Saxitoxin in Dinoflagellates. PLoS One 2011, 6, e20096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.; Bachvaroff, T.; Place, A. Dinoflagellate Phosphopantetheinyl Transferase (PPTase) and Thiolation Domain Interactions Characterized Using a Modified Indigoidine Synthesizing Reporter. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Yang, X.; Zheng, T.; Hong, H. An Efficient Method to Obtain Axenic Cultures of Alexandrium tamarense—a PSP-Producing Dinoflagellate. J Microbiol Methods 2007, 69, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.C.-H.; Chan, P.-L.; Tam, N.F.-Y.; Xu, S.J.-L.; Lee, F.W.-F. Establish Axenic Cultures of Armored and Unarmored Marine Dinoflagellate Species Using Density Separation, Antibacterial Treatments and Stepwise Dilution Selection. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hold, G.L.; Smith, E.A.; Harry Birkbeck, T.; Gallacher, S. Comparison of Paralytic Shellfish Toxin (PST) Production by the Dinoflagellates Alexandrium lusitanicum NEPCC 253 and Alexandrium tamarense NEPCC 407 in the Presence and Absence of Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2001, 36, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Place, A.R.; Jagus, R. Use of Antibiotics for Maintenance of Axenic Cultures of Amphidinium carterae for the Analysis of Translation. Mar Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Holt, K.E. Assembling the Perfect Bacterial Genome Using Oxford Nanopore and Illumina Sequencing. PLoS Comput Biol 2023, 19, e1010905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereika, M.; Kirkegaard, R.H.; Karst, S.M.; Michaelsen, T.Y.; Sørensen, E.A.; Wollenberg, R.D.; Albertsen, M. Oxford Nanopore R10.4 Long-Read Sequencing Enables the Generation of near-Finished Bacterial Genomes from Pure Cultures and Metagenomes without Short-Read or Reference Polishing. Nat Methods 2022, 19, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, S.; Patterson, D.J. The Benthic Dinoflagellate Genus Amphidinium in South-Eastern Australian Waters, Including Three New Species. Eur J Phycol 2002, 37, S0967026202003591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karafas, S.; Teng, S.T.; Leaw, C.P.; Alves-de-Souza, C. An Evaluation of the Genus Amphidinium (Dinophyceae) Combining Evidence from Morphology, Phylogenetics, and Toxin Production, with the Introduction of Six Novel Species. Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 128–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yan, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; Li, K. Acute Toxicity of the Dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae on Early Life Stages of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Toxics 2023, 11, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIXON, G.K.; SYRETT, P.J. The Growth of Dinoflagellates in Laboratory Cultures. New Phytologist 1988, 109, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, H.S.; Saifullah, S.M.; Dar, A. Occurrence and Toxicity of Amphidinium carterae Hulburt in the North Arabian Sea. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.; Flø Jørgensen, M.; Daugbjerg, N.; Rhodes, L. Amphidinium Revisited. II. Resolving Species Boundaries in the Amphidinium operculatum Species Complec (Dinophyceae). J Phycol 2004, 40, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the Quality of Microbial Genomes Recovered from Isolates, Single Cells, and Metagenomes. Genome Res 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, R.; Michoud, G.; Sefrji, F.O.; Fusi, M.; Antony, C.P.; Seferji, K.A.; Barozzi, A.; Merlino, G.; Daffonchio, D. The Identification of the New Species Nitratireductor thuwali sp. Nov. Reveals the Untapped Diversity of Hydrocarbon-Degrading Culturable Bacteria from the Arid Mangrove Sediments of the Red Sea. Front Microbiol 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Tran, P.Q.; Breister, A.M.; Liu, Y.; Kieft, K.; Cowley, E.S.; Karaoz, U.; Anantharaman, K. METABOLIC: High-Throughput Profiling of Microbial Genomes for Functional Traits, Metabolism, Biogeochemistry, and Community-Scale Functional Networks. Microbiome 2022, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medema, M.H.; Blin, K.; Cimermancic, P.; de Jager, V.; Zakrzewski, P.; Fischbach, M.A.; Weber, T.; Takano, E.; Breitling, R. AntiSMASH: Rapid Identification, Annotation and Analysis of Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis Gene Clusters in Bacterial and Fungal Genome Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, W339–W346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, A.G.; Waglechner, N.; Nizam, F.; Yan, A.; Azad, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Bhullar, K.; Canova, M.J.; De Pascale, G.; Ejim, L.; et al. The Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2013, 57, 3348–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadi, M.; Bertoni, D.; Magana, P.; Paramval, U.; Pidruchna, I.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Tsenkov, M.; Nair, S.; Mirdita, M.; Yeo, J.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database in 2024: Providing Structure Coverage for over 214 Million Protein Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 2024, 52, D368–D375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambo, I.M.; Dombrowski, N.; Constant, L.; Erdner, D.; Baker, B.J. Metabolic Relationships of Uncultured Bacteria Associated with the Microalgae Gambierdiscus. Environ Microbiol 2020, 22, 1764–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tizabi, D.; Bachvaroff, T. Nanopore Sequencing of Amoebophrya sp. Reveals Novel Collection of Bacteria Putatively Associated with Karlodinium veneficum. Genome Biol Evol, 2024. (In Review) [Google Scholar]
- Vico, P.; Iriarte, A.; Bonilla, S.; Piccini, C. Metagenomic Analysis of Raphidiopsis raciborskii Microbiome: Beyond the Individual. Biodivers Data J 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.R.; Belas, R. Dimethylsulfoniopropionate Metabolism by Pfiesteria-Associated Roseobacter spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 2004, 70, 3383–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wang, S.; Qin, P.; Fan, S.; Su, X.; Cai, P.; Lu, J.; Cui, H.; Wang, M.; Shu, Y.; et al. Anaerobic Thiosulfate Oxidation by the Roseobacter Group Is Prevalent in Marine Biofilms. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, G.; Cutignano, A.; Sardo, A.; Fontana, A. Antifungal Amphidinol 18 and Its 7-Sulfate Derivative from the Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae. J Nat Prod 2014, 77, 1524–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, S.; Oyler, B.L.; Williams, E.; Khan, M.M.; Goodlett, D.R.; Bachvaroff, T.; Place, A.R. Investigating A Multi-Domain Polyketide Synthase in Amphidinium carterae. Mar Drugs 2023, 21, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeKieffre, C.; Spero, H.J.; Fehrenbacher, J.S.; Russell, A.D.; Ren, H.; Geslin, E.; Meibom, A. Ammonium Is the Preferred Source of Nitrogen for Planktonic Foraminifer and Their Dinoflagellate Symbionts. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2020, 287, 20200620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, M.; Robertson, E.K.; Edler, L.; Arneborg, L.; Whitehouse, M.J.; Ploug, H. Nitrate and Ammonium Fluxes to Diatoms and Dinoflagellates at a Single Cell Level in Mixed Field Communities in the Sea. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Coyne, K.J. Molecular Insights into the Synergistic Effects of Putrescine and Ammonium on Dinoflagellates. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishibori, N.; Imai, I. Polyamines Control the Growth of the Fish-Killing Dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi in Culture. Harmful Algae 2013, 29, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.H.; Dong, B.; Li, B.; Yang, X.H. Changes in Intracellular and Extracellular Free Polyamines during the Growth Cycle of Prorocentrum donghaiense. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 2019, 344, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biebl, H.; Allgaier, M.; Lünsdorf, H.; Pukall, R.; Tindall, B.J.; Wagner-Döbler, I. Roseovarius mucosus sp. Nov., a Member of the Roseobacter Clade with Trace Amounts of Bacteriochlorophyll a. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2005, 55, 2377–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biebl, H.; Pukall, R.; Lünsdorf, H.; Schulz, S.; Allgaier, M.; Tindall, B.J.; Wagner-Döbler, I. Description of Labrenzia alexandrii Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., a Novel Alphaproteobacterium Containing Bacteriochlorophyll a, and a Proposal for Reclassification of Stappia aggregata as Labrenzia aggregata Comb. Nov., of Stappia marina as Labrenzia marina Comb. Nov. and of Stappia alba as Labrenzia alba Comb. Nov., and Emended Descriptions of the Genera Pannonibacter, Stappia and Roseibium, and of the Species Roseibium denhamense and Roseibium hamelinense. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2007, 57, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, L.; Arahal, D.R.; Reguera, B.; Marín, I. Hoeflea alexandrii sp. Nov., Isolated from the Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum AL1V. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2006, 56, 1991–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strompl, C. Oceanicaulis alexandrii Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., a Novel Stalked Bacterium Isolated from a Culture of the Dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense (Lebour) Balech. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2003, 53, 1901–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Duan, Y.; Yang, X.; Yao, B.; Zeng, T.; Wang, X.; Feng, Q.; Qi, M.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X. Nitratireductor alexandrii Sp. Nov., from Phycosphere Microbiota of Toxic Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2020, 70, 4390–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, G.J.W.L.; Jani, J.; Law, S.V.; Rodrigues, K.F. Whole Genome Sequence Data of a Marine Bacterium, Marinobacter adhaerens PBVC038, Associated with Toxic Harmful Algal Bloom. Data Brief 2023, 46, 108768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Muricauda Amphidinii Sp. Nov., a Novel Marine Bacterium Isolated from the Phycosphere of Dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2019, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.S.; Jeong, S.E.; Chun, B.H.; Quan, Z.-X.; Jeon, C.O. Rhodophyticola porphyridii Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., Isolated from a Red Alga, Porphyridium marinum. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2019, 69, 1656–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernikova, T.N.; Bargiela, R.; Toshchakov, S.V.; Shivaraman, V.; Lunev, E.A.; Yakimov, M.M.; Thomas, D.N.; Golyshin, P.N. Hydrocarbon-Degrading Bacteria Alcanivorax and Marinobacter Associated With Microalgae Pavlova lutheri and Nannochloropsis oculata. Front Microbiol 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Lai, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wei, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, X.; Zheng, W.; Tian, Y.; et al. Cyclobacterium xiamenense Sp. Nov., Isolated from Aggregates of Chlorella autotrophica, and Emended Description of the Genus Cyclobacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2014, 64, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Algihabitans albus Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., Isolated from a Culture of the Green Alga Ulva prolifera. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2019, 69, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.E.; Kim, K.H.; Lhee, D.; Yoon, H.S.; Quan, Z.-X.; Lee, E.-Y.; Jeon, C.O. Oceaniradius stylonematis Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., Isolated from a Red Alga, Stylonema cornu-cervi. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2019, 69, 1967–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, T.; Aoyama, K.; Motone, K.; Aburaya, S.; Yamashiro, H.; Miura, N.; Inoue, K. Mutualistic Interactions between Dinoflagellates and Pigmented Bacteria Mitigate Environmental Stress. Microbiol Spectr 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motone, K.; Takagi, T.; Aburaya, S.; Miura, N.; Aoki, W.; Ueda, M. A Zeaxanthin-Producing Bacterium Isolated from the Algal Phycosphere Protects Coral Endosymbionts from Environmental Stress. mBio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska-Krochmal, B.; Dudek-Wicher, R. The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Antibiotics: Methods, Interpretation, Clinical Relevance. Pathogens 2021, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolinson, G. Forty Years of Beta-Lactam Research. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1998, 41, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, C.J.S.; Subramanian, T.A.; Green, D.H. The Toxic Dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum Require Marine Bacteria for Growth. J Phycol 2011, 47, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Kang, S.-J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Oh, K.-H.; Oh, T.-K. Seohaeicola saemankumensis Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., Isolated from a Tidal Flat. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2009, 59, 2675–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedashkovskaya, O.I.; Vancanneyt, M.; Kim, S.B.; Bae, K.S. Reclassification of Flexibacter tractuosus (Lewin 1969) Leadbetter 1974 and ‘Microscilla sericea’ Lewin 1969 in the Genus Marivirga Gen. Nov. as Marivirga tractuosa Comb. Nov. and Marivirga Sericea Nom. Rev., Comb. Nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2010, 60, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, I.; Chertkov, O.; Lapidus, A.; Lucas, S.; Del Rio, T.G.; Tice, H.; Copeland, A.; Cheng, J.-F.; Nolan, M.; Saunders, E.; et al. Complete Genome Sequence of Marivirga tractuosa Type Strain (H-43T). Stand Genomic Sci 2011, 4, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagenais-Bellefeuille, S.; Morse, D. Putting the N in Dinoflagellates. Front Microbiol 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Shang, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z.; Du, H.; Wang, H. Different Dimethylsulphoniopropionate-Producing Ability of Dinoflagellates Could Affect the Structure of Their Associated Bacterial Community. Algal Res 2021, 57, 102359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, E.; Kiene, R.P.; Schwarz, J.; Falck, E.; Dieckmann, G. Methane Cycling in Arctic Shelf Water and Its Relationship with Phytoplankton Biomass and DMSP. Mar Chem 2008, 109, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, S.P.K.; Lee, F.W.F.; Mak, D.Y.L.; Kong, H.K.; Chan, K.K.Y.; Lo, P.Y.; Lo, S.C.L. Production of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins (PSTs) in Toxic Alexandrium catenella Is Intertwined with Photosynthesis and Energy Production. Toxins (Basel) 2020, 12, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, P.; Espejo, R.T. Effect of Associated Bacteria on the Growth and Toxicity of Alexandrium catenella. Appl Environ Microbiol 2003, 69, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Yao, M.; Zhou, J.; Tan, S.; Jin, H.; Zhang, F.; Mak, Y.L.; Wu, J.; Lai Chan, L.; Cai, Z. Growth and Toxin Production of Gambierdiscus spp. Can Be Regulated by Quorum-Sensing Bacteria. Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monroe, E.A.; Johnson, J.G.; Wang, Z.; Pierce, R.K.; Van Dolah, F.M. Characterization and Expression of Nuclear-Encoded Polyketide Synthases in the Brevetoxin-Producing Dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. J Phycol 2010, 46, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, K.S.; Borrone, J. Polyketides from Dinoflagellates: Origins, Pharmacology and Biosynthesis. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 1999, 124, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdai, T.; Matsuoka, S.; Murata, M.; Satake, M.; Ota, S.; Oshima, Y.; Rhodes, L.L. Acetate Labeling Patterns of Dinoflagellate Polyketides, Amphidinols 2, 3 and 4. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 5551–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-López, R.; Maske, H. The Vitamin B1 and B12 Required by the Marine Dinoflagellate Lingulodinium Polyedrum Can Be Provided by Its Associated Bacterial Community in Culture. Front Microbiol 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berges, J.A.; Franklin, D.J.; Harrison, P.J. Evolution of an Artificial Seawater Medium: Improvements in Enriched Seawater, Artificial Water Over the Last Two Decades. J Phycol 2001, 37, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, C.; Gonçalves, P. Multilayered Horizontal Operon Transfers from Bacteria Reconstruct a Thiamine Salvage Pathway in Yeasts. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2019, 116, 22219–22228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Mondo, A.; Smerilli, A.; Sané, E.; Sansone, C.; Brunet, C. Challenging Microalgal Vitamins for Human Health. Microb Cell Fact 2020, 19, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenci, U.; Qiu, H.; Pillonel, T.; Cardol, P.; Remacle, C.; Colleoni, C.; Kadouche, D.; Chabi, M.; Greub, G.; Bhattacharya, D.; et al. Host-Pathogen Biotic Interactions Shaped Vitamin K Metabolism in Archaeplastida. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 15243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of Long, Error-Prone Reads Using Repeat Graphs. Nat Biotechnol 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise Alignment for Nucleotide Sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).