Submitted:
04 November 2024
Posted:
05 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
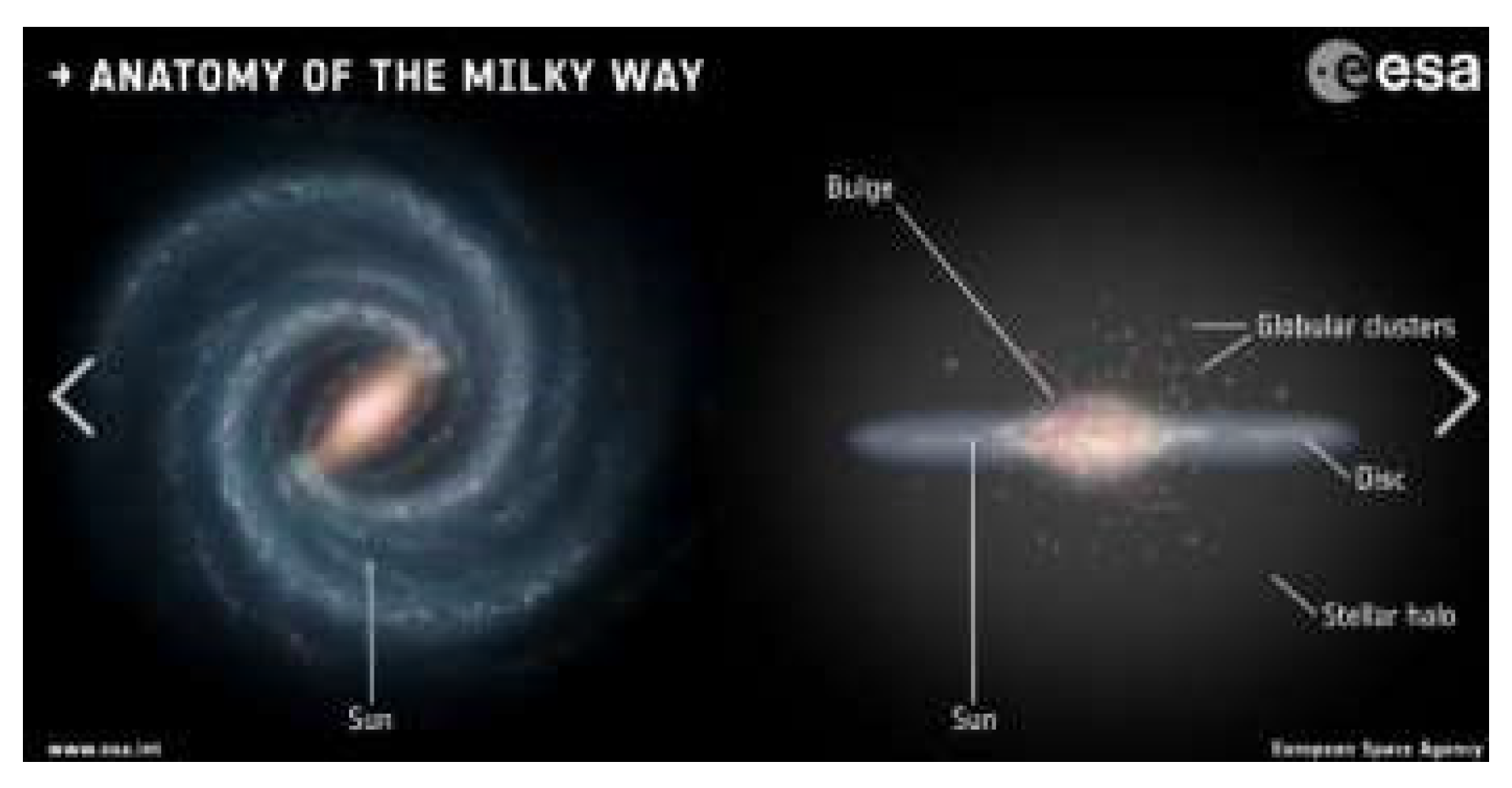
2. The Peanut Shape with the “x-Shaped Structure” or Boxy Core of the Bar: the Possible Another Supermassive Black Hole in the Bar of the Milky Way
2.1. The Possible Structure of the Bar of the Milky Way
2.2. The Galactic Spiral Arms and Hill Sphere
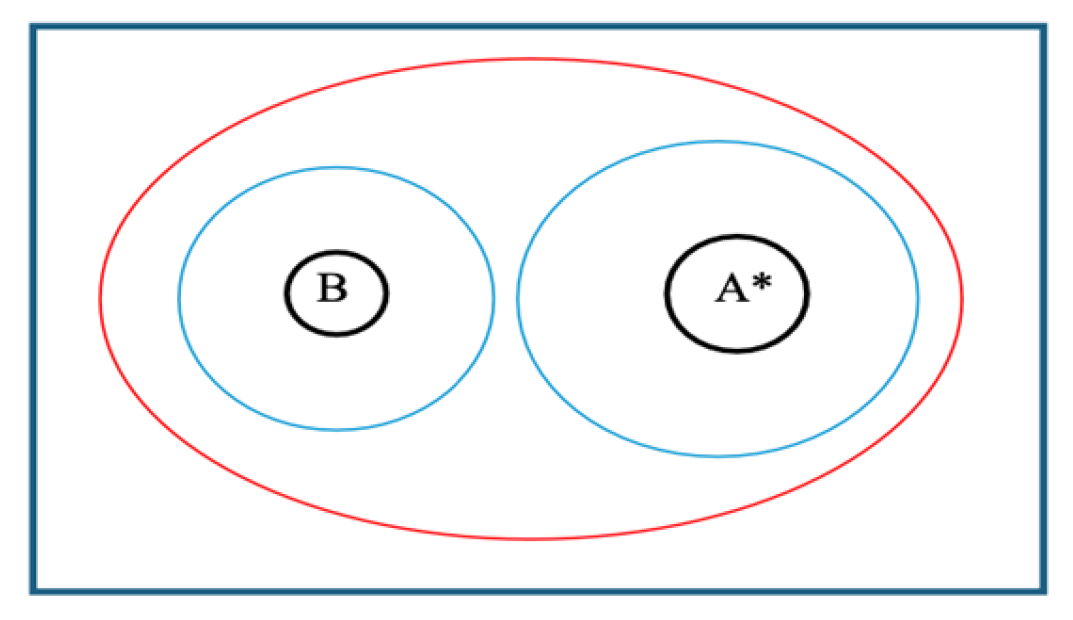
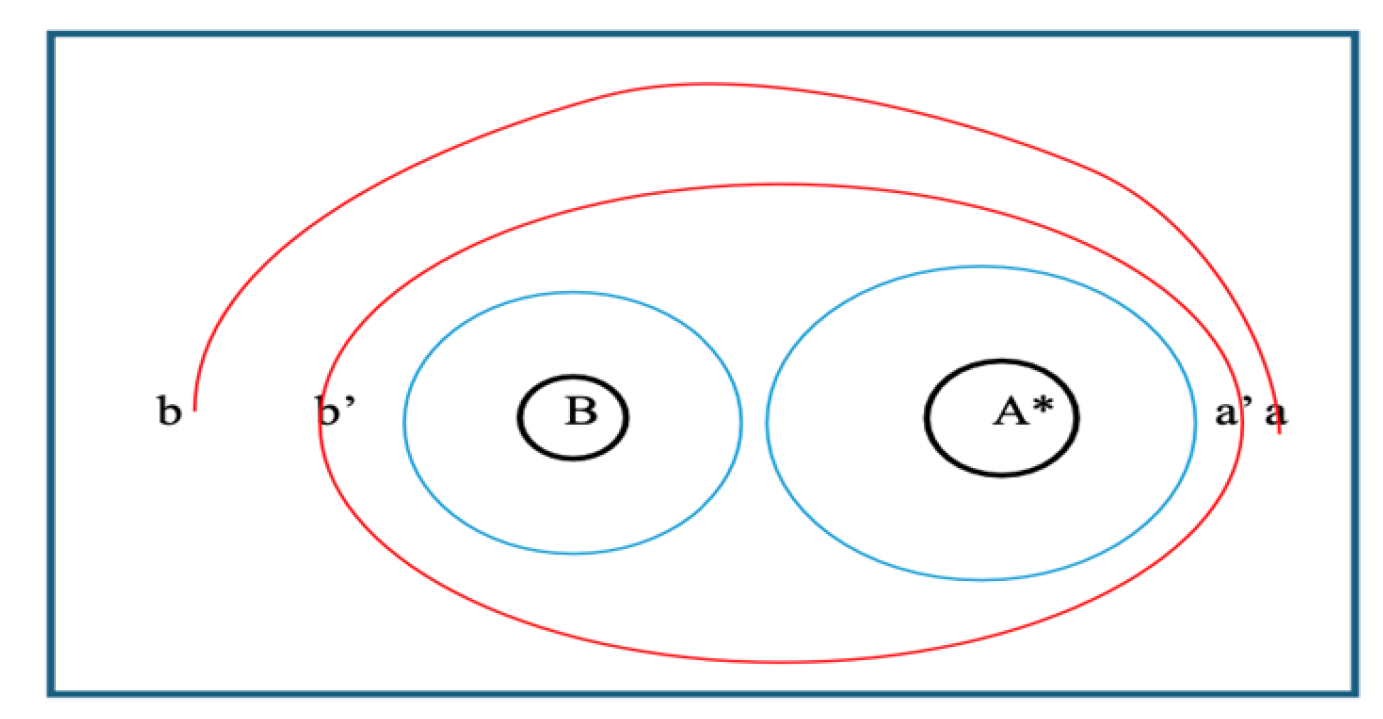
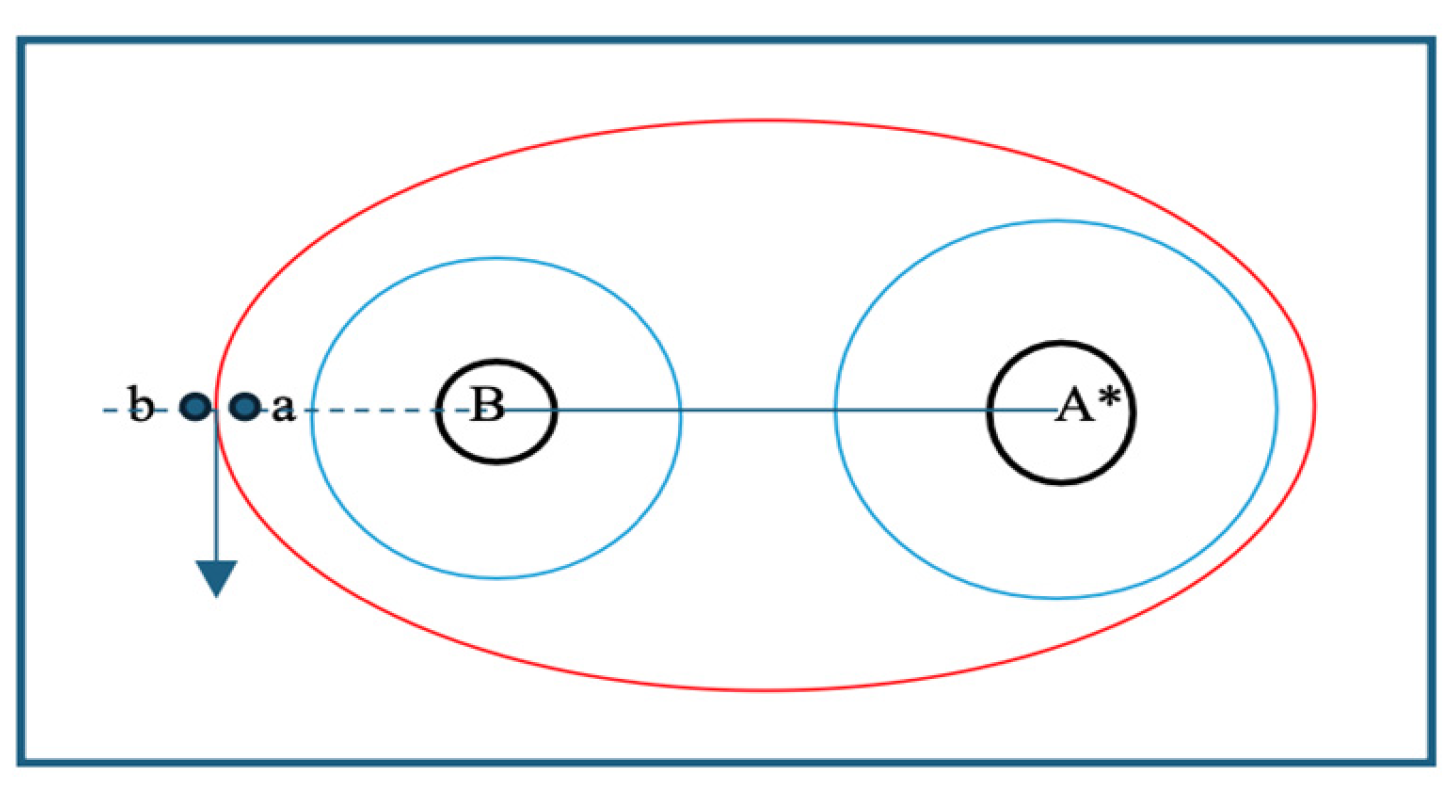
2.3. The Mass and Position of the Black Hole B
3. Discussions
3.1. The Conjectured Supermassive Black Hole May Have Been Observed Through the Rotation of the Bar
3.2. The Complicated Orbits in the Bar: The Strong Evidence for the Conjectured Supermassive Black Hole
3.3. The Supermassive Black Holes Binaries in a Galaxy
3.4. The Sgr A* Is the Critical Coordinate to the Observations About the Structure and Orbits of the Milky Way
3.5. The Newtonian Theory of Orbit Perturbation and the Galactic Dynamics
4. Conclusion
References
- Oort J. H., Kerr F. J. & Westerhout G., 1958, The galactic system as a spiral nebula (Council Note), MNRAS, 118, 379.
- Georgelin Y. M. & Georgelin Y. P., 1976, The spiral structure of our Galaxy determined from H II regions, A&A, 49, 57.
- Oort J. H., & Rougoor G. W., 1959, The interstellar gas in the central part of the galaxy, AJ, 64, 130.
- Rougoor G. W. & Oort J. H., 1960, Distribution and Motion of Interstellar Hydrogen in the Galactic System with Particular Reference to the Region Within 3 Kiloparsecs of the Center, Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, 46, 1.
- de Vaucouleurs G., 1964, in IAU Symposium, Vol. 20, The Galaxy and the Magellanic Clouds, ed. F. J. Kerr, 195.
- McWilliam A. & Zoccali M., 2010, Two Red Clumps and the X-shaped Milky Way Bulge, ApJ, 724, 149.
- Li Z.-Y. & Shen J., 2015, Mapping the Three-Dimensional “X-Shaped Structure” in Models of the Galactic Bulg, ApJL, 815, L20.
- Wegg C. & Gerhard O., 2013, Mapping the three-dimensional density of the Galactic bulge with VVV red clump stars, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 435(3), 01, 1874–1887.
- Mattia M. C., Gerhard O., Portail M., Vasiliev E., Clarke J., 2022, The stellar mass distribution of the Milky Way’s bar: an analytical model, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters, 514, L1–L5.
- Skokos Ch., Patsis P. A., Athanassoula E., 2002, Orbital dynamics of three-dimensional bars—I. The backbone of three-dimensional bars. A fiducial case, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 333, 847.
- Genzel R., Eisenhauer F. and Gillessen S., 2010, The Galactic Center Massive Black Hole and Nuclear Star Cluster, Reviews of Modern Physics, 82.4, 3121-3195.
- Shen J. and Zheng X., 2020, The bar and spiral arms in the Milky Way: structure and kinematics, RAA, 20, 159.
- Merritt D. & Ekers R. D., 2002, Tracing Black Hole Mergers Through Radio Lobe Morphology, Science, 297, 1310.
- Roberts D. H., et al., 2015, The Abundance of X-Shaped Radio Sources: Implications for the Gravitational Wave Background, ApJ 810, L6.
- Roberts D. H., et al. 2015. The Abundance of X-Shaped Radio Sources I. VLA Survey of 52 Sources With Off-Axis Distortions. ApJS 220, 7.
- Bansal K., et al., 2017, Constraining the Orbit of the Supermassive Black Hole Binary 0402+379, ApJ 843 14.
- Wang J. and Li Y., 2020, Observational signatures of close binaries of supermassive black holes in active galactic nuclei, Res. Astron. Astrophys. 20 160.
- Komossa S., et al., 2021, Supermassive Binary Black Holes and the Case of OJ 287, arXiv:2104.12901.
- O’Neill S., et al., 2022, The Unanticipated Phenomenology of the Blazar PKS 2131–021: A Unique Supermassive Black Hole Binary Candidate, ApJL 926 L35.
- Gómez J. L., Traianou E., et al., 2022, Probing the innermost regions of AGN jets and their magnetic fields with Radio Astron. V. Space and ground millimeter-VLBI imaging of OJ 287, APJ 924, 122.
- Jiang W., et al. ,2023, Observational Evidence of a Centi-parsec Supermassive Black Hole Binary Existing in the Nearby Galaxy M81, ApJ 959 11.
- Magallanes-Guijón G. & Mendoza S., 2024, A Supermassive Binary Black Hole Candidate in Mrk 501, Galaxies, 2, 30.
- Foord A., Cappelluti N., Liu T. Volonteri M. et al. 2024, Tracking Supermassive Black Hole Mergers from kpc to sub-pc Scales with AXIS, Universe 10(6), 237.
- Goulding A. D., et al., 2019, Discovery of a Close-separation Binary Quasar at the Heart of a z ∼ 0.2 Merging Galaxy and Its Implications for Low-frequency Gravitational Waves, ApJL 879 L21.
- Valtonen M. J., Zola S., Gopakumar A., Lähteenmäki A.,et al, Refining the OJ 287 2022 impact flare arrival epoch, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2023; 521 (4): 6143.
- Busetti F., Beust H. and Harley C., 2018, Stability of planets in triple star systems, A&A619, A91.
- Lee Y., et al., 2018, Assembling the Milky Way Bulge from Globular Clusters: Evidence from the Double Red Clump, ApJL 862 L8.
- Iwanek P., et al. 2023, A Three-dimensional Map of the Milky Way Using 66,000 Mira Variable Stars, ApJS 264 20.
- López-Corredoira M., 2017, Absence of an X-shaped Structure in the Milky Way Bulge Using Mira Variable Stars, ApJ 836 218.
- Nataf D., et al., 2010, The Split Red Clumps of the Galactic Bulge From OGLE-III, ApJL 721 L28.
- 窗体底端Zhou Y., et al., The Circular Velocity Curve of the Milky Way from 5–25 kpc Using Luminous Red Giant Branch Stars, ApJ, 946, 73 (2023).
- Jiao Y., Hammer F., Wang H., Wang J., et al., 2023, Detection of the Keplerian decline in the Milky Way rotation curve, A&A678, A208.
- Eilers A., Hogg D. W., Rix H. and Ness M. K., 2019, The Circular Velocity Curve of the Milky Way from 5 to 25 kpc, ApJ, 871 120.
- Howard D.et al 2008, The Bulge Radial Velocity Assay (BRAVA). I. Sample Selection and a Rotation Curve, ApJ 688 1060.
- Kunder A. et al., 2012, The bulge radial velocity assay (BRAVA). II. Complete sample and data release, AJ 143 57.
- Peißker F., Eckart A. and Parsa M. 2020, S62 on a 9.9 yr Orbit around SgrA*, ApJ, 889, 61.
- Peißker F., Eckart A., Zajaček M. and Britzen S., 2022, Observation of S4716- A star with a 4 year orbit around Sgr A*, ApJ, 933, 49.
- Peißker F., Eckart A., Zajaček M., Britzen S., Ali B. and Parsa M. 2020, S62 and S4711: Indications of a Population of Faint Fast-moving Stars inside the S2 Orbit—S4711 on a 7.6yr Orbit around Sgr A*, ApJ, 899, 50.
- Peißker F., Eckart A. and Ali B. 2021, Observation of the Apoapsis of S62 in 2019 with NIRC2 and SINFONI, APJ, 918, 25.
- GRAVITY Collaboration, et al., 2022, Deep images of the Galactic center with GRAVITY, A&A 657, A82.
- GRAVITY Collaboration, et al., 2022, Mass distribution in the Galactic Center based on interferometric astrometry of multiple stellar orbits, A&A 657, L12.
- Nishiyama S., et al. 2005, A Distinct Structure inside the Galactic Bar, ApJ, 621, L105.
- Yu S. and Ho L. C. 2020, The Statistical Properties of Spiral Arms in Nearby Disk Galaxies, ApJ, 900, 150.
- Mondal D., Chattopadhyay T., 2021, Role of galactic bars in the formation of spiral arms: a study through orbital and escape dynamics—I. Celest Mech Dyn Astr 133, 43.
- Lindblad P. A. B. & Kristen H., 1996, Hydrodynamical simulations of the barred spiral galaxy NGC 1300. Dynamical interpretation of observations, Astronomy and Astrophysics, 313, 733-749.
- Yoon Y. & Lee M. I., et al., 2019, Observational evidence for bar formation in disk galaxies via cluster–cluster interaction, Nat Astron 3, 844–850.
- Costantin L., Pérez-González, P.G., Guo, Y. et al., 2023, A Milky Way-like barred spiral galaxy at a redshift of 3, Nature 623, 499–501.
- Hey D. R., et al., 2023, The Far Side of the Galactic Bar/Bulge Revealed through Semi-regular Variables, AJ 166 249.
- Zhu Y., 2024, The Mass of the Center of the Milky Way Revalued from the Fastest Orbits around the Center and the Circular Velocity Curve of the Milky Way, doi: 10.20944/preprints202402.1765.v3.
- Aguerri J. A. L., Méndez-Abreu J., Falcón-Barroso J., Amorin A., et al., 2015, Bar pattern speeds in CALIFA galaxies I. Fast bars across the Hubble sequence, A&A,576, A102.
- Cuomo V., Aguerri J. A. L., Corsini E. M., Debattista V. P., et al., 2019, Bar pattern speeds in CALIFA galaxies II. The case of weakly barred galaxies, A&A 632, A51.
- Guo R., Mao S., Athanassoula E., Li H., et al., 2019, SDSS-IV MaNGA: pattern speeds of barred galaxies, MNRAS, 482, 1733.
- Roshan M., Banik I., Ghafourian N., Thies I., et al., 2021, Barred spiral galaxies in modified gravity theories, MNRAS 503, 2833–2860.
- Garma-Oehmichen L., Hernández-Toledo H., Aquino-Ortíz E., Martinez-Medina L., et al., 2022, SDSS IV MaNGA: bar pattern speed in Milky Way analogue galaxies, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 517(4), 5660–5677.
- Naoz S., et al., 2017, The Eccentric Kozai–Lidov Mechanism for Outer Test Particle, AJ 154 18.
- Naoz S., et al., 2020, A Hidden Friend for the Galactic Center Black Hole Sgr A*, ApJL 888 L8.
- Will C. M., et al., 2023, Constraining a companion of the galactic center black hole Sgr A*, ApJ 959 58.
- Gutzwiller M. C., 1998, Moon-Earth-Sun: The oldest three-body problem. Review of Modern Physics, 70(2), 589-639.
- Zhu Y., 2021, Interaction of Gravitational Field and Orbit in Sun-planet-moon system, doi: 10.20944/preprints202105.0203.v1.
- Häberle M., Neumayer, N., Seth A., et al., 2024, Fast-moving stars around an intermediate-mass black hole in ω Centauri, Nature 631, 285–288.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



