Submitted:
21 June 2024
Posted:
24 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
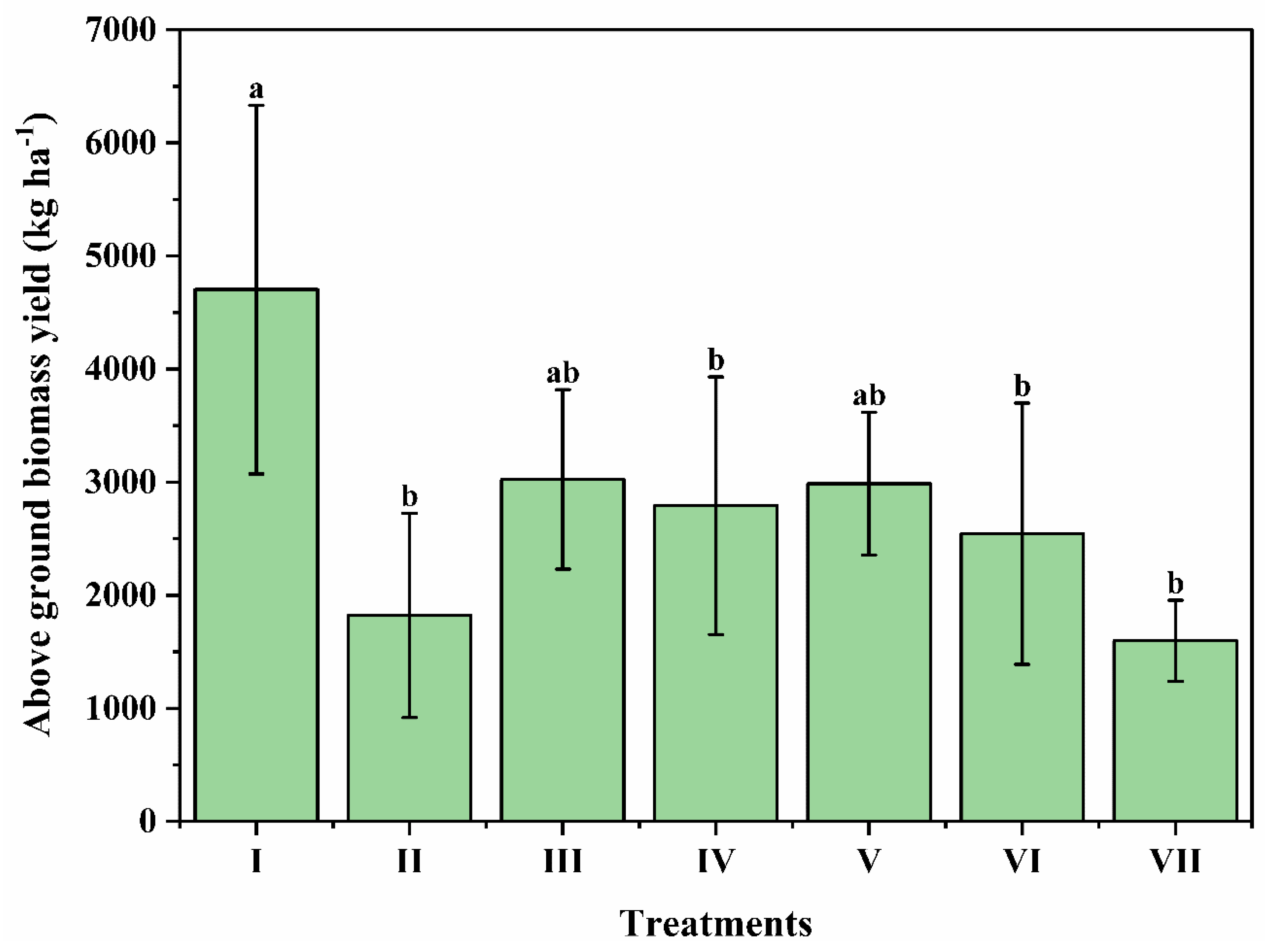
3. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Bian, Z.; Inyang, H.I.; Daniels, J.L.; Otto, F.; Struthers, S. Environmental issues from coal mining and their solutions. Min. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, P.R.; Buonocore, J.J.; Eckerle, K.; Hendryx, M.; Stout, B.M.; Heinberg, R.; Clapp, R.W.; May, B.; Reinhart, N.L.; Ahern, M.M.; et al. Full cost accounting for the life cycle of coal. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1219, 73–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longwell, J. Coal: Energy for the future. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1995, 21, 269–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddick, J.F.; Von Blottnitz, H.; Kothuis, B. Cleaner Production in the South African Coal Mining and Processing Industry: A Case Study Investigation. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2008, 28, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Dong, J.; Lei, S.; Leng, H.; Mu, S.; Wang, H. The impact of disposal and treatment of coal mining wastes on environment and farmland. Environ. Geol. 2009, 58, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, D.M.; Boger, D.V.; Côte, C.M.; Mulligan, D.R. Sustainable development principles for the disposal of mining and mineral processing wastes. Resour. Policy 2011, 36, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lèbre, É.; Corder, G.; Golev, A. The Role of the Mining Industry in a Circular Economy: A Framework for Resource Management at the Mine Site Level. J. Ind. Ecol. 2017, 21, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterham, R.J. The mine of the future – Even more sustainable. Miner. Eng. 2017, 107, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, S.; Kibort, K.; Mioduska, J.; Lieder, M.; Małachowska, A. Waste management in the mining industry of metals ores, coal, oil and natural gas - A review. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 304, 114239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Miao, X.; Lei, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Struthers, S. The Challenges of Reusing Mining and Mineral-Processing Wastes. Science (80-. ). 2012, 337, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komnitsas, K.; Paspaliaris, I.; Zilberchmidt, M.; Groudev, S.N. Environmental impacts at coal waste disposal sites-efficiency of desulfurization technologies. Glob. Nest Int. J 2001, 3, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Kossoff, D.; Dubbin, W.E.; Alfredsson, M.; Edwards, S.J.; Macklin, M.G.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A. Mine tailings dams: Characteristics, failure, environmental impacts, and remediation. Appl. Geochemistry 2014, 51, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, I. Non-energy uses of coal. IEA clean coal Cent. Exec. Summ. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Subba, R.D.V.; Gouricharan, T. Coal Processing and Utilization. 2016.
- Patil, D.P.; Honaker, R.; Parekh, B.K. Paste Thickening of Fine Coal Refuse. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2007, 27, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.W. Coal Preparation; 4th ed.; The American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical and Petroleum Engineers: New York, EUA, 1979;
- Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; Reading, L. Effects of surface coal mining and land reclamation on soil properties: A review. Earth-Science Rev. 2019, 191, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Z.; Fan, J.S.; Qin, P.; Niu, H.Y. Pollution extents of organic substances from a coal gangue dump of Jiulong Coal Mine, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, W.L.; Stewart, B.R. Reclamation of Appalachian Coal Refuse Disposal Areas. In Reclamation of Drastically Disturbed Lands; Barnhisel, R.I., Darmody, R.G., Daniels, W.L., Eds.; 2015; pp. 433–459.
- Ghose, M.K. Soil conservation for rehabilitation and revegetation of mine-degraded land. TIDEE (Teri Inf. Dig. Energy Environ. 2005, 4, 137–150. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, W.; Zipper, C. Creation and management of productive minesoils. Virginia Coop. Ext. Publ. 460-121. 2010, 12.
- IUSS Working Group WRB World reference base for soil resources 2014. International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps; 2014; ISBN 9789251083697.
- Amaral Filho, J.R.; Firpo, B.A.; Broadhurst, J.L.; Harrison, S.T.L. On the feasibility of South African coal waste for production of ‘FabSoil’, a Technosol. Miner. Eng. 2020, 146, 106059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echevarria, G.; Louis Morel, J. Technosols of Mining Areas. Tópicos Ci. Solo 2015, 9, 92–111. [Google Scholar]
- Firpo, B.A.; Amaral Filho, J.R.D.; Schneider, I.A.H. A brief procedure to fabricate soils from coal mine wastes based on mineral processing, agricultural, and environmental concepts. Miner. Eng. 2015, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séré, G.; Schwartz, C.; Ouvrard, S.; Sauvage, C.; Renat, J.-C.; Morel, J.L. Soil construction: A step for ecological reclamation of derelict lands. J. Soils Sediments 2008, 8, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler, J.; Firpo, B.A.; Schneider, I.A.H. Technosol as an integrated management tool for turning urban and coal mining waste into a resource. Miner. Eng. 2020, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firpo, B.A.; Weiler, J.; Schneider, I.A.H. Technosol made from coal waste as a strategy to plant growth and environmental control. Energy Geosci. 2021, 2, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, M.B.; Kirkham, Y.S.O. Spoil to Soil Mine Site Rehabilitation and Revegetation; 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2017;
- Ruiz, F.; Cherubin, M.R.; Ferreira, T.O. Soil quality assessment of constructed Technosols: Towards the validation of a promising strategy for land reclamation, waste management and the recovery of soil functions. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, F.; Andrade, G.R.P.; Sartor, L.R.; dos Santos, J.C.B.; Souza Júnior, V.S. de; Ferreira, T.O. The rhizosphere of tropical grasses as driver of soil weathering in embryonic Technosols (SE-Brazil). Catena 2022, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, R.J.; Higgs, E.; Harris, J.A. Novel ecosystems: implications for conservation and restoration. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiler, J.; da Silva, A.C.; Firpo, B.A.; Fernandes, E.Z.; Schneider, I.A.H. Using static, kinetic and metal mobility procedures to evaluate possibilities of coal waste land disposal at Moatize Mine, Mozambique. REM - Int. Eng. J. 2020, 73, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketema, S.; Research, L.I. of P.G. and C.P. Tef Eragrostis tef (Zucc.) Trotter. 1997.
- Balensiefer, M.; Rossi, R.; Ardinghi, N.; Cenni, M.; Ugolini, M. SER international primer on ecological restoration. Soc. Ecol. Restoration, Washingt. 2004.
- Hatton, W.; Fardell, A. New discoveries of coal in Mozambique — Development of the coal resource estimation methodology for International Resource Reporting Standards. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 89, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, C.H.; Ambrós, W.M.; Cazacliu, B.; Moncunill, J.O.; José, D.S.; Miltzarek, G.L.; de Brum, I.A.S.; Petter, C.O.; Fernandes, E.Z.; Oliveira, L.F.S. Destoning the moatize coal seam, mozambique, by dry jigging. Minerals 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobek, A.A.; William, A.S.; Freeman, J.R.; Smith, R.M. Field and Laboratory Methods Applicable to Overburdens and Minesoils 1978.
- Sparks, D.L. Chemistry of Soil Organic Matter. In Environmental Soil Chemistry; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, 2003; pp. 75–113. ISBN 978-0-12-656446-4. [Google Scholar]
- INMET Dados Meteorológicos. Estação: Porto Alegre - Jardim Botânico A801. Available online: https://portal.inmet.gov.br/ (accessed on 13 October 2023).
- Reichardt, K. Capacidade de campo. Rev. Bras. Ciência do Solo 1988, 12, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Darcy, H. Les fontaines publiques de la ville de Dijon: exposition et application des principes à suivre et des formules à employer dans les questions de distribution d’eau; Victor dalmont, 1856; Vol. 1.
- Embrapa Manual de métodos de análise de solo; Teixeira, P.C., Donagemma, G.K., Fontana, A., Teixeira, W.G., Eds.; 3. ed. rev.; Brasília, DF, 2017; ISBN 9788570357717.
- SBCS Manual de Adubação e de Calagem para os estados do Rio Grande so Sul e Santa Catarina; 2016; ISBN 978-85-66301-80-9.
- van Raij, B.; Cantarella, H.; Quaggio, J.A.; Furlani, Â.M.C. Recomendações de adubação e calagem para o Estado de São Paulo; Fundação IAC: Campinas, 1996; Vol. 100. [Google Scholar]
- Indoria, A.K.; Sharma, K.L.; Reddy, K.S. Hydraulic properties of soil under warming climate. In Climate change and soil interactions; Prasad, M.N.V., Pietrzykowski, M., Eds.; Elsevier, 2020; pp. 473–508.
- Brady, N.C.; Weil, R.R. The nature and properties of soils; Pearson Prentice Hall: New Jersey, 2008; Vol. 13, ISBN 978-0-13-227939-0. [Google Scholar]
- Perie, C.; Ouimet, R. Organic carbon, organic matter and bulk density relationships in boreal forest soils. Can. J. soil Sci. 2008, 88, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y.; Ritvo, G.; Meijer, L.E.; Kochba, M. Water content, organic carbon and dry bulk density in flooded sediments. Aquac. Eng. 2001, 25, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakin, E.; Deliboran, A.; Tutar, E. Bulk density of Harran plain soils in relation to other soil properties. African J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 1750–1757. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, V.R.; Reinert, D.J.; Reichert, J.M. Densidade do solo, atributos químicos e sistema radicular do milho afetados pelo pastejo e manejo do solo. Rev. Bras. Ciência do Solo 2000, 24, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabot, E.; Wiesmeier, M.; Schlüter, S.; Vogel, H.-J. Soil structure as an indicator of soil functions: A review. Geoderma 2018, 314, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, W.D.; Drury, C.F.; Tan, C.S.; Fox, C.A.; Yang, X.M. Use of indicators and pore volume-function characteristics to quantify soil physical quality. Geoderma 2009, 152, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.E. Principles and practice of soil science: the soil as a natural resource; John Wiley & Sons, 2005; ISBN 0632064552.
- Miller, D. Teff Grass: A new alternative. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2009 California Alfalfa & Forage Symposium and Western Seed Conference, Reno, NV, USA; Citeseer, 2009; pp. 2–4.
- Mihretie, F.A.; Tesfaye, K.; Hoogenboom, G.; Tsunekawa, A.; Molla, A.; Ebabu, K.; Sato, S.; Masutomi, Y. Identifying low risk and profitable crop management practices for irrigated Teff production in northwestern Ethiopia. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 139, 126572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, A.; Stroosnijder, L.; Girmay, G.; Keesstra, S.D. Crop coefficient, yield response to water stress and water productivity of teff (Eragrostis tef (Zucc.). Agric. water Manag. 2011, 98, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihretie, F.A.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Adgo, E.; Tsubo, M.; Masunaga, T.; Meshesha, D.T.; Tsuji, W.; Ebabu, K.; Tassew, A. Tillage and sowing options for enhancing productivity and profitability of teff in a sub-tropical highland environment. F. Crop. Res. 2021, 263, 108050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, D.C.; Weiler, J.; Schneider, I.A.H. Effects of vegetation on erosion in technosols produced from coal waste. In Proceedings of the International Mine Water Association Congress (14.: 2021: online). Mine water management for future generations. Cardiff: International Mine Water Association, 2021.; 2021.
- Lemos, C.M.G.; Ferreira, G.C. Viabilidade do uso de nucleação no auxílio da regularização ambiental das atividades de extração de argila em região de intensa alteração da paisagem. Geosci. Geociências 2017, 36, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, F.C.; Campos Filho, E.M.; Barretto, K.D.; Gabriel, V.A.; Antunes, A.Z.; Reis, A. Unidades demonstrativas de restauração ecológica através de técnicas nucleadoras de biodiversidade. Rev. Bras. Biociências 2007, 5, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Colombini, G.; Watteau, F.; Auclerc, A. Technosol rehabilitation strategies drive soil physico-chemical properties and fauna diversity on a former coking plant area. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 177, 104542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
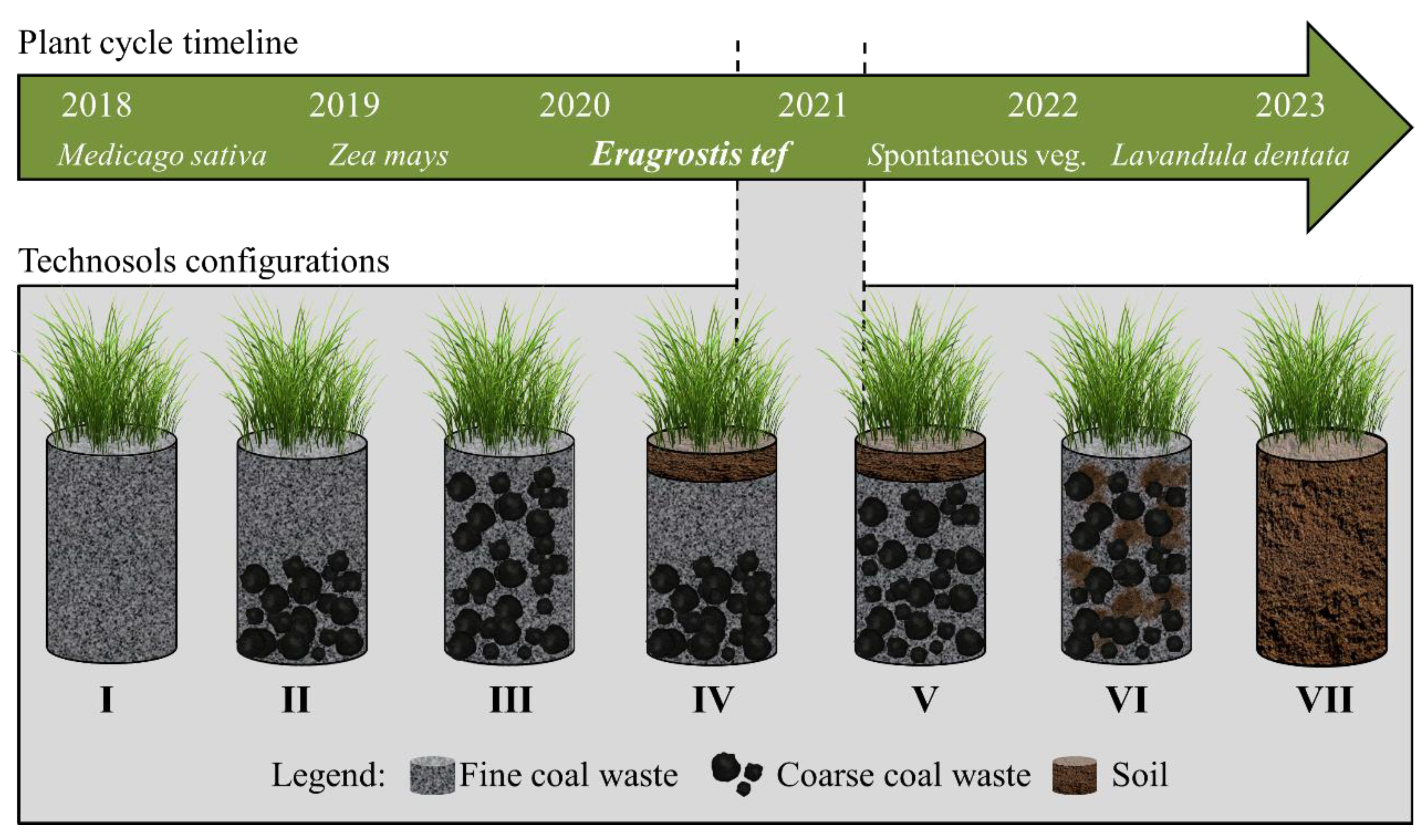
| Country | Amendments | Vegetation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | Steel slag and sewage sludge | Sorghum bicolor | Firpo et al., 2015 |
| Brazil | Husk ash, steel slag, and sewage sludge | Megathyrsus maximus | Weiler et al., 2018 |
| Mozambique | Organic compost from urban waste | Medicago sativa | Weiler et al., 2020a |
| South Africa | Compost, anaerobic digester sludge and malt residue | Eragrostis tef | Amaral Filho et al., 2020 |
| Brazil | Husk ash, steel slag, and sewage sludge |
Avena strigosa Zea mays |
Firpo et al., 2021 |
| Poland | Sewage sludge, crushed stone (angular sandstone) and fly ash | Trees, shrubs, herbs and grasses |
Halecki and Klatka, 2021 |
| Brazil | Rice processing waste, poultry agroindustry sludge, gypsum | Not measured | Zocche et al., 2023 |
| Property | Fine waste ( < 1.0 mm) |
Coarse waste (1.0 – 50 mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Proximate analysis | ||
| Ashes (%) | 58.4 | 58.9 |
| Volatile material (%) | 16.6 | 16.5 |
| Fixed carbon (%) | 25.0 | 24.6 |
| Sulfur | ||
| Pyritic (%) | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| Sulfate (%) | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Organic (%) | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| Total (%) | 1.3 | 0.9 |
| Crystalline compounds | ||
| Majority | Quartz | Quartz and alumina |
| Minority | Calcite, hematite, and halite |
Calcite and hematite |
| Acid generation according to modified acid-base accounting (ABA) method [38] | ||
| AP (kg CaCO3 t-1) | 19.0 | 14.0 |
| NP (kg CaCO3 t-1) | 25.3 | 23.5 |
| NNP (kg CaCO3 t-1) | + 6.3 | + 9.5 |
| Treatment | Fine coal waste (kg) |
Coarse coal waste (kg) |
Soil (kg) |
Sewage sludge (kg) |
Total (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 18.9 | - | - | 1.1 | 20 |
| II | 7.7 | 11.2 | - | 1.1 | 20 |
| III | 7.7 | 11.2 | - | 1.1 | 20 |
| IV | 5.1 | 7.4 | 6.3 | 1.1 | 20 |
| V | 5.1 | 7.4 | 6.3 | 1.1 | 20 |
| VI | 5.1 | 7.4 | 6.3 | 1.1 | 20 |
| VII | - | - | 18.9 | 1.1 | 20 |
| Treatment | Bulk density dry (kg m-3) |
Bulk density saturated (kg m-3) |
Available water capacity (m3 m-3) |
Permeability (k) (cm s-1) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| I | 943.6 | 13.7 | 1151.5 | 22.2 | 0.208 | 0.015 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| II | 1166.0 | 22.5 | 1256.1 | 48.0 | 0.090 | 0.033 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| III | 1284.7 | 16,1 | 1440.5 | 0.1 | 0.156 | 0.016 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| IV | 1140.4 | 48.3 | 1288.0 | 53.9 | 0.148 | 0.027 | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| V | 1207.3 | 147.0 | 1388.1 | 8.7 | 0.181 | 0.152 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| VI | 1244.7 | 42.6 | 1408.8 | 67.4 | 0.164 | 0.036 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| VII | 1100.8 | 22.8 | 1324.7 | 16.6 | 0.224 | 0.006 | 0.07 | 0.01 |
| Treat ment |
Macronutrients | Micronutrients | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | SOM | CEC | Al | N | P | K | Ca | Mg | Cu | Zn | Mn | Fe | B | |
| % | cmolc dm-³ | % | mg.dm-3 | cmolc dm-³ | mg dm-³ | |||||||||
| I | 6.1 | 3.5 | 7.24 | 0 | 0.42 | 145.8 | 17.2 | 3.1 | 2.7 | 9.5 | 25.6 | 4.6 | > 5.0 | 0.30 |
| II | 6.0 | 3.5 | 6.96 | 0 | 0.49 | 136.1 | 22.6 | 3.2 | 2.1 | 10.8 | 26.0 | 5.1 | > 5.0 | 0.17 |
| III | 60 | 3.5 | 5.56 | 0 | 0.54 | 76.0 | 17.2 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 11.2 | 25.6 | 3.7 | > 5.0 | 0.30 |
| IV | 5.9 | 3.2 | 8.59 | 0 | 0.51 | 113.9 | 33.4 | 4.3 | 1.7 | 7.3 | 23.7 | 6 | > 5.0 | 0.27 |
| V | 6.4 | 3.2 | 15.32 | 0.1 | 0.56 | 98.8 | 71.1 | 10.7 | 2.4 | 5.9 | 24.1 | 16.3 | > 5.0 | 0.23 |
| VI | 5.7 | 4.1 | 8.69 | 0 | 0.61 | 94.5 | 43.1 | 3.9 | 2.7 | 7.5 | 23.8 | 15.9 | > 5.0 | 0.40 |
| VII | 6.5 | 2.0 | 16.45 | 0 | 0.16 | 71.9 | 303.6 | 11.1 | 2.8 | 3.4 | 23.9 | 23.4 | > 5.0 | 0.27 |
| Ref. | 5-6 | 2.6-5 | 5.0-15 | - | - | 10-60 | 31-180 | 2.1- 4 | 0.6-1 | 0.2-0.4 | 0.2-5 | 2.5- 5 | - | 0.2- 0.3 |
| Treatment | Macronutrients (g kg-1) | Micronutrients (mg kg-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | Ca | Mg | Fe | Mn | Cu | B | |
| I | 21 | 3.8 | 8.2 | 8.6 | 3.2 | 174.4 | 169 | 9.6 | 0.7 |
| II | 20.3 | 4.2 | 10.2 | 6.6 | 3.0 | 149.5 | 239.7 | 8.7 | 0.5 |
| III | 17.5 | 3.6 | 10.8 | 7.9 | 3.8 | 116.1 | 249.5 | 6.4 | 0.9 |
| IV | 18.2 | 4.5 | 12.2 | 9.3 | 2.7 | 131 | 117.7 | 5.5 | 0.9 |
| V | 21 | 4.1 | 13.6 | 7.8 | 2.6 | 121.6 | 154.5 | 5.3 | 0.6 |
| VI | 25.9 | 5.1 | 14.6 | 9.8 | 3.2 | 89.1 | 106.1 | 4.0 | 3.2 |
| VII | 25.2 | 6.6 | 22.8 | 8.9 | 1.6 | 134.9 | 69.2 | 4.5 | 8.2 |
| Ref. | 12‒26 | 1‒3 | 12‒30 | 2‒8 | 1.5‒5 | 50‒250 | 20‒300 | 4‒20 | 5 ‒ 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





