Submitted:
21 June 2024
Posted:
21 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
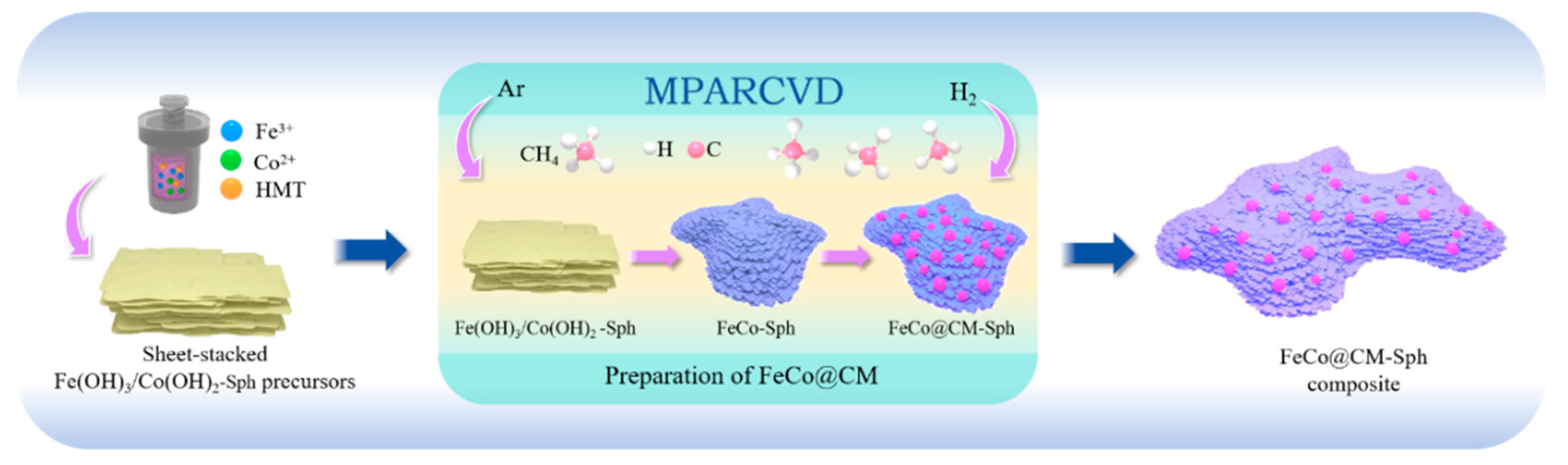
2.2. Preparation of f-Fe(OH)3/Co(OH)2 Precursor
2.3. Preparation of f-FeCo Alloy
2.4. Preparation of f-FeCo@CM and s-FeCo@CM
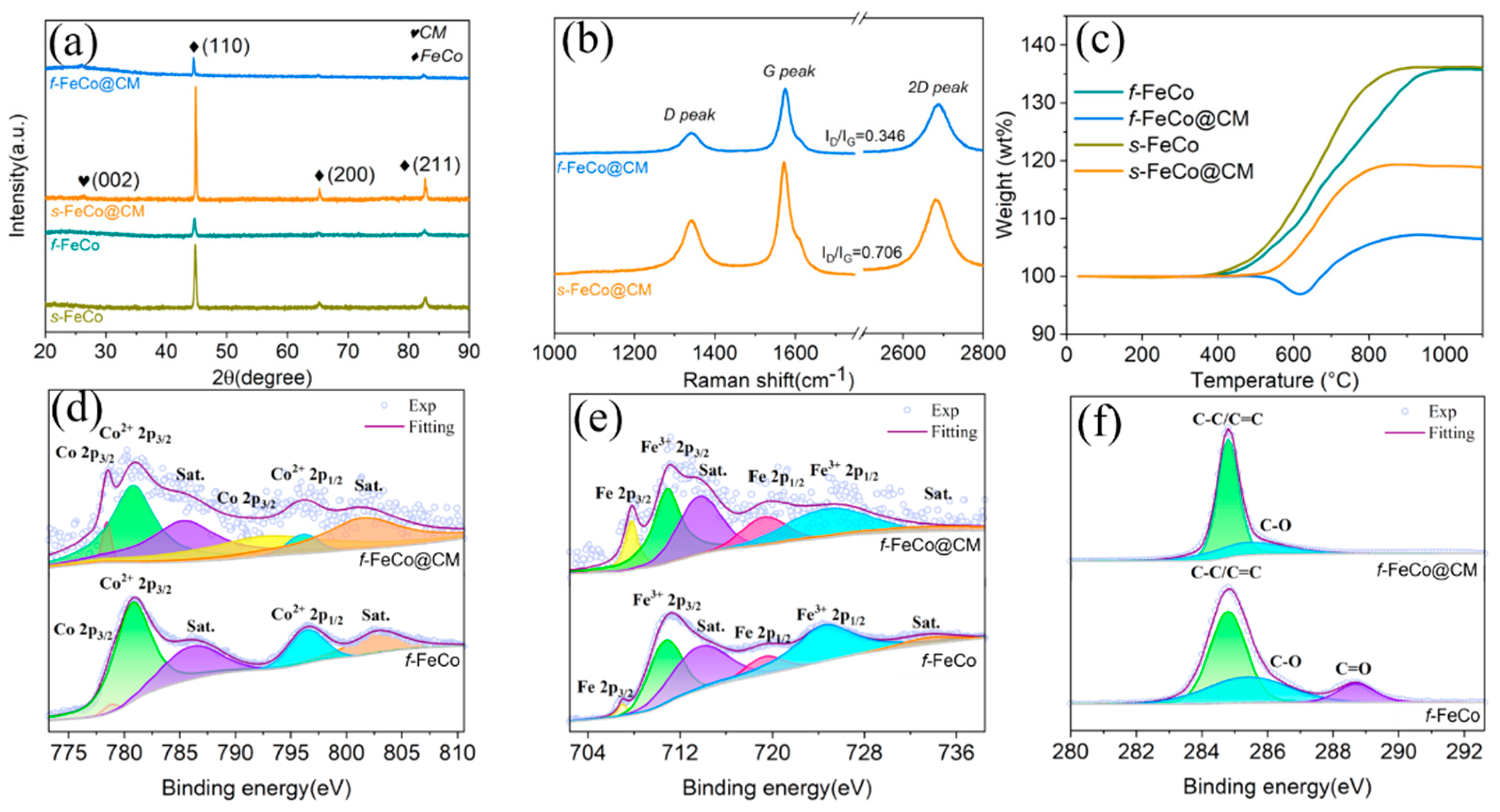
2.5. Characterization
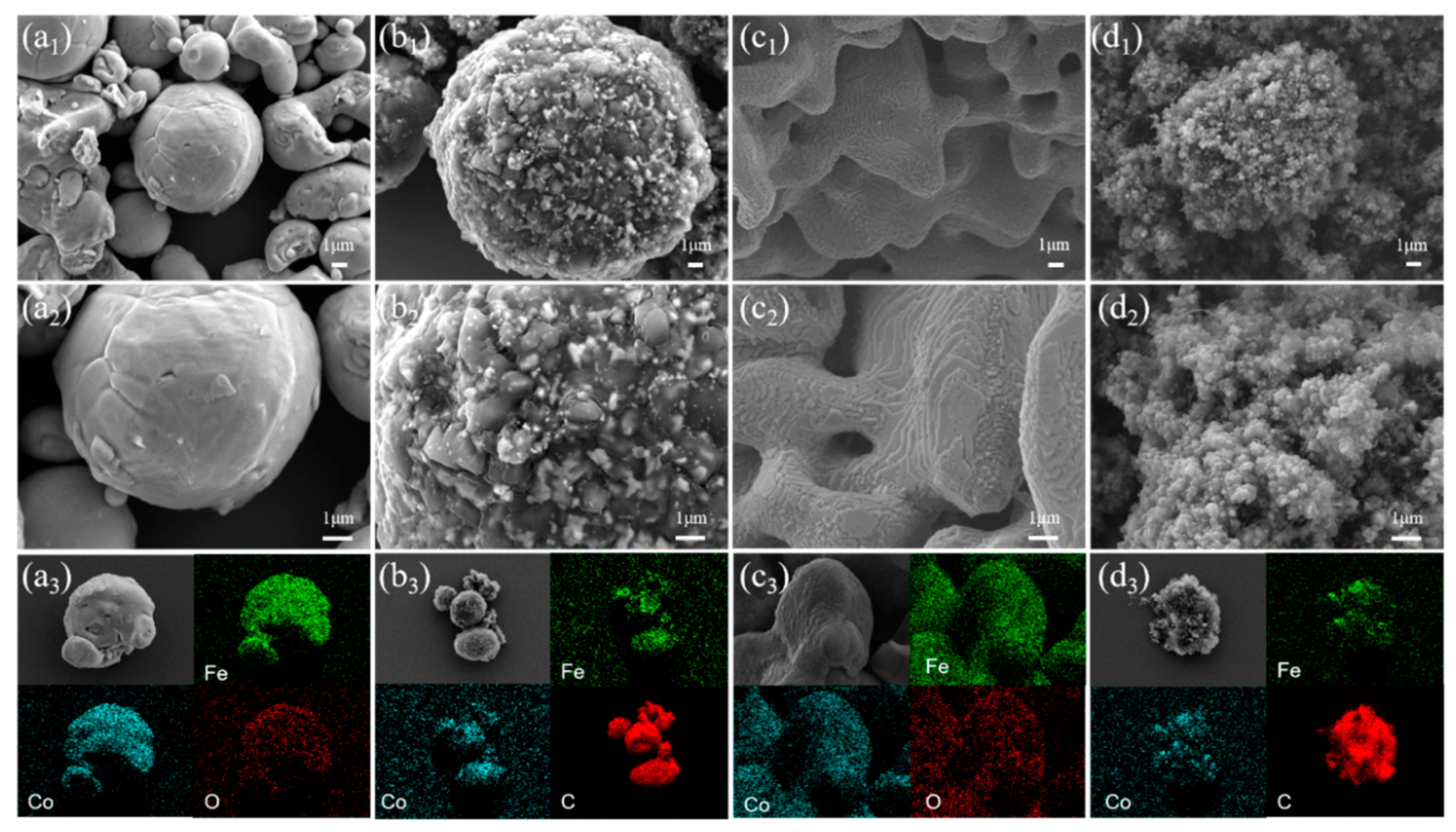
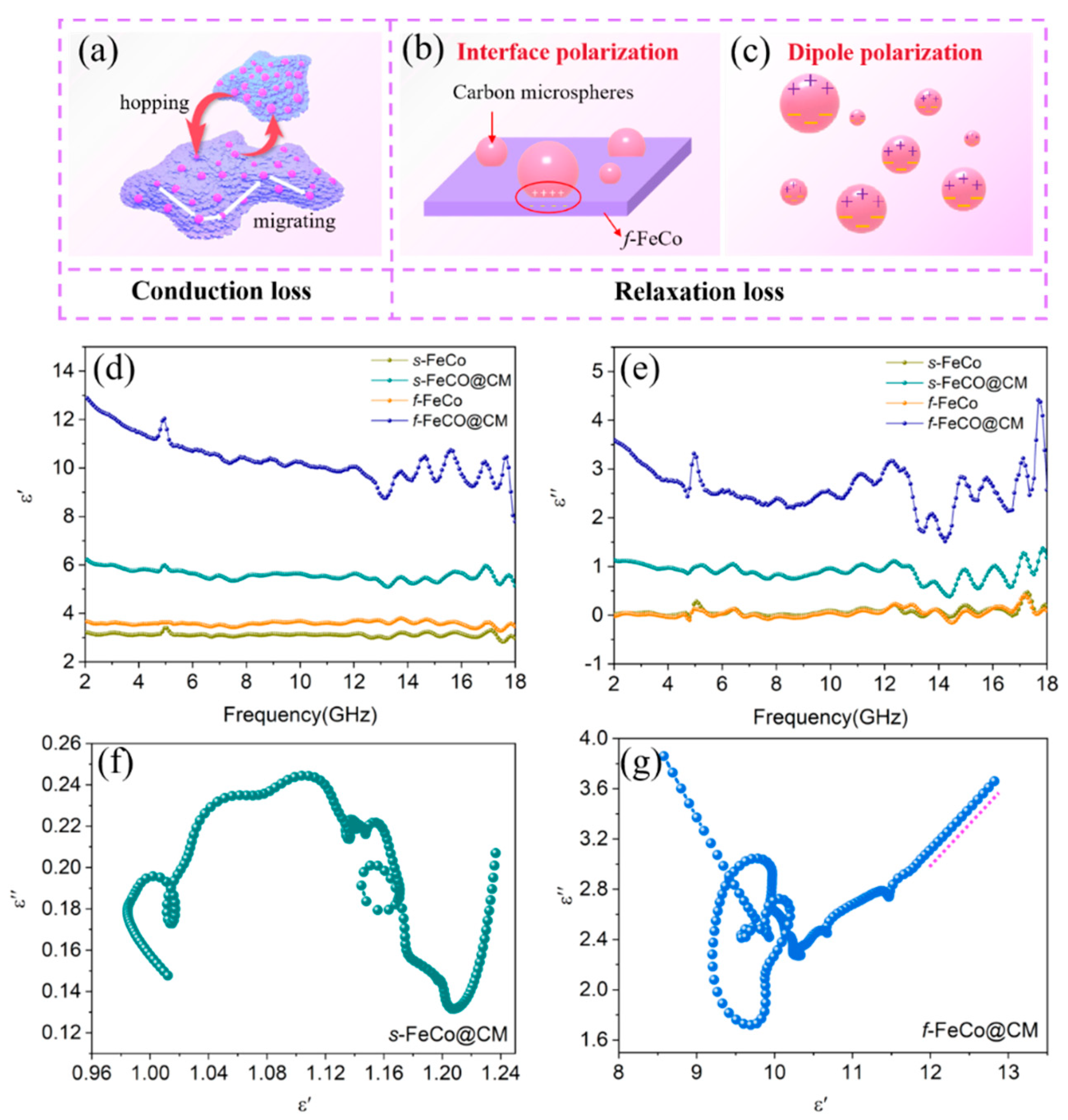
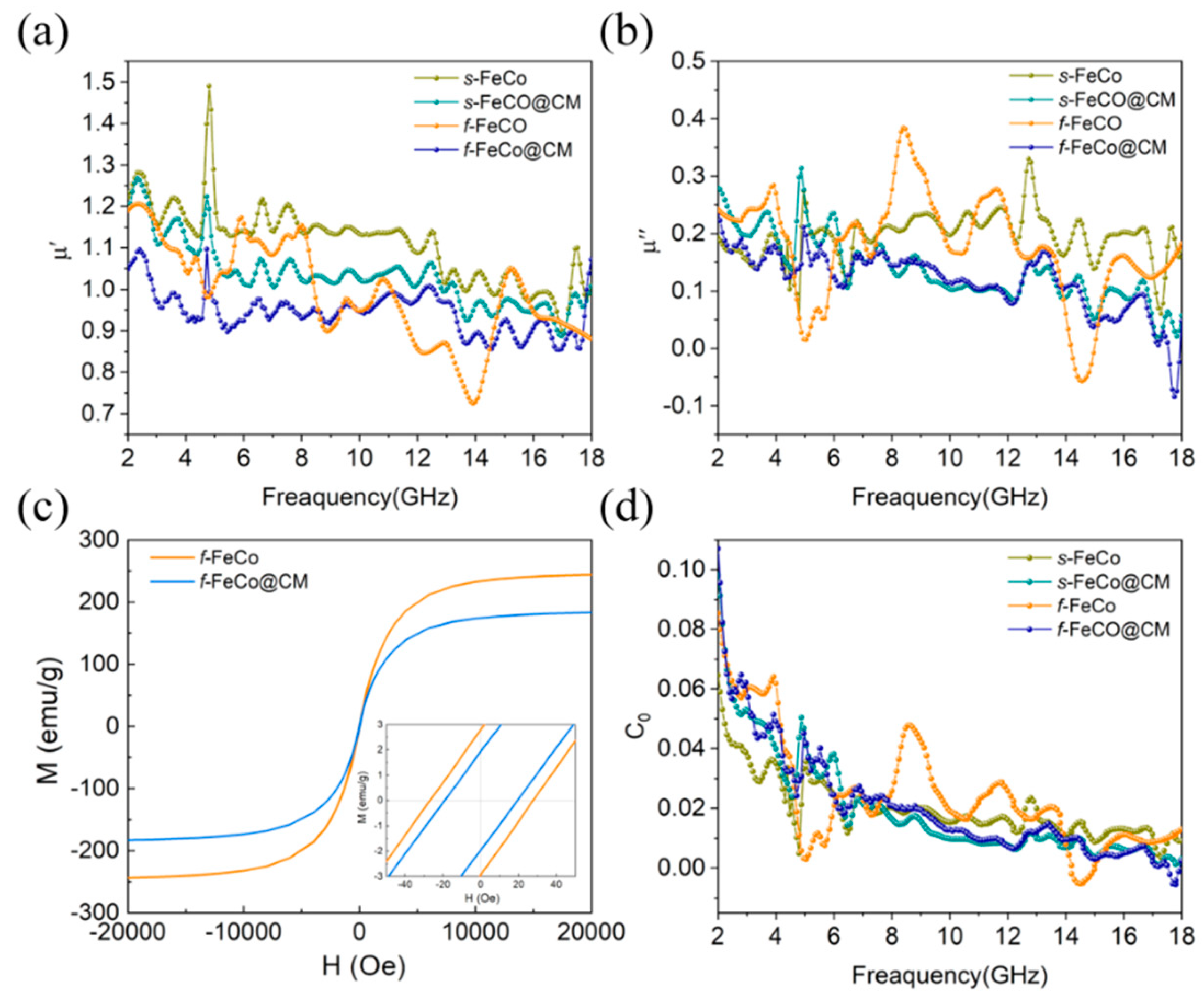
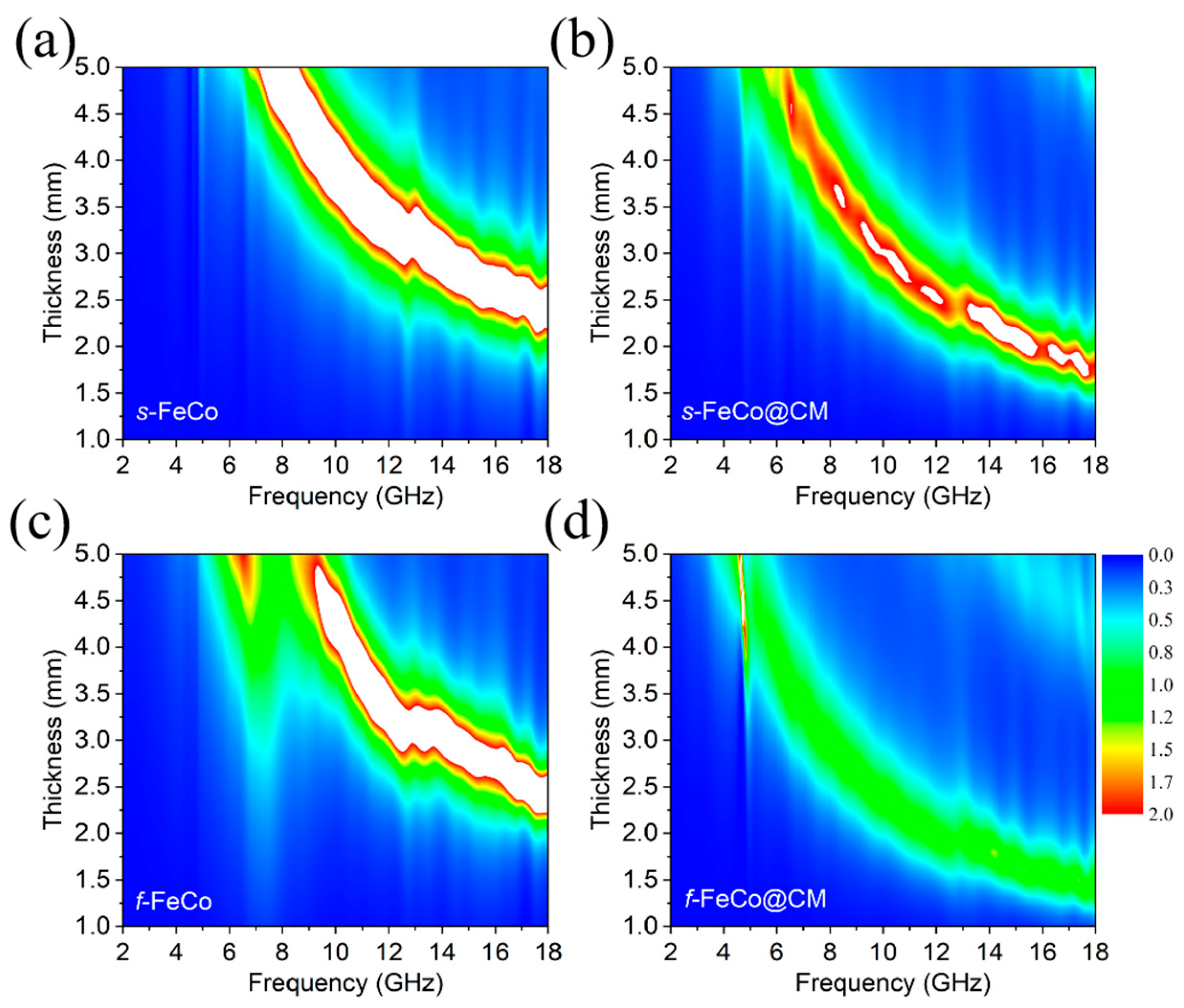
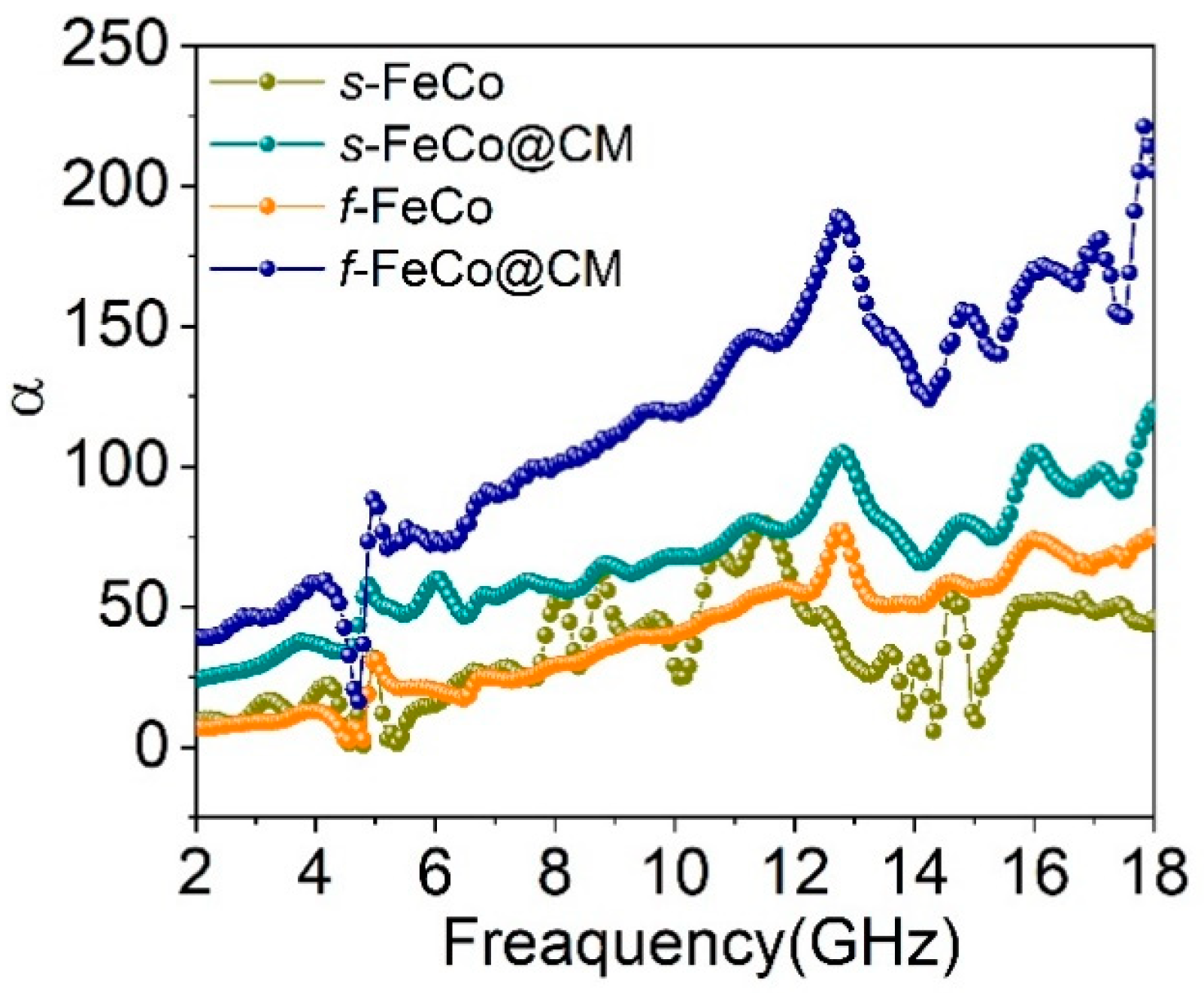
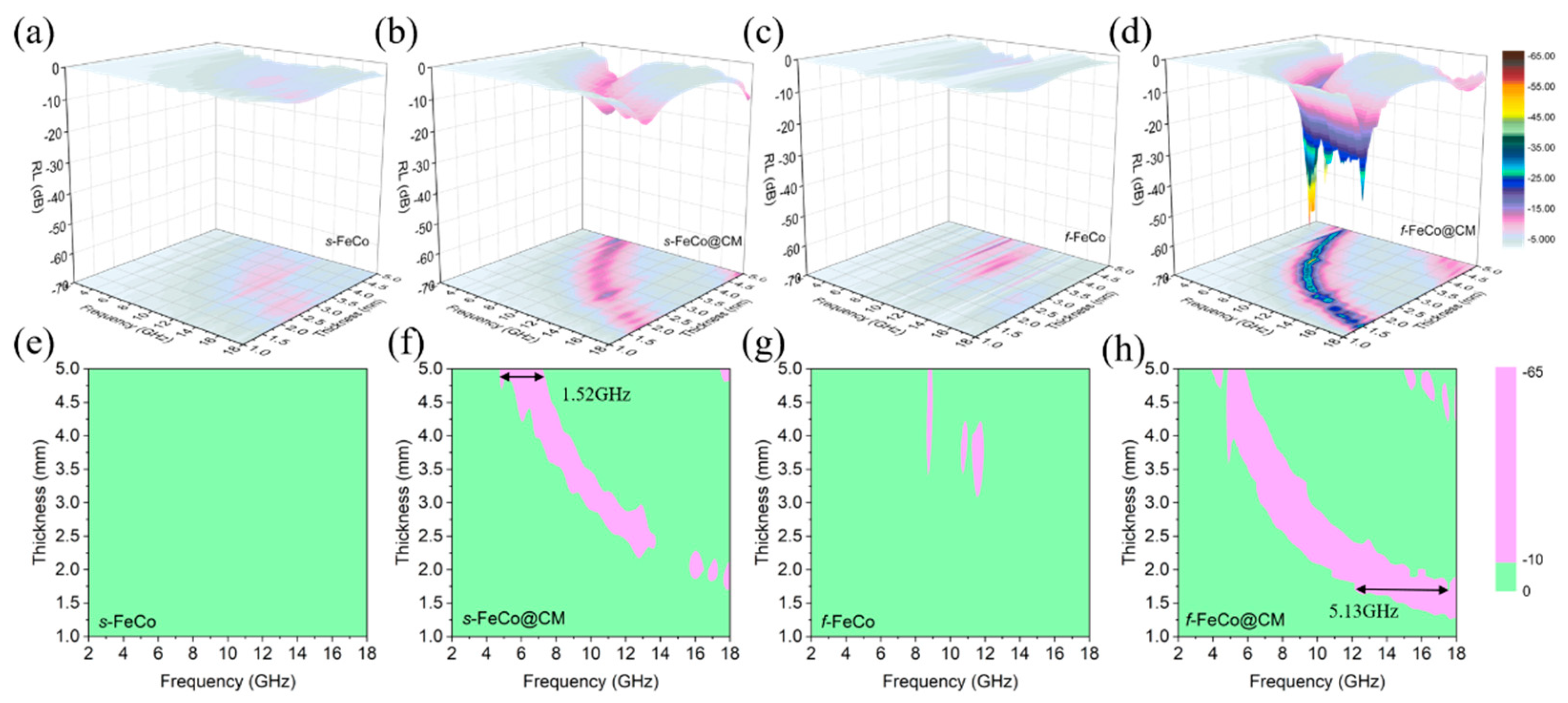
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Han, M.; Liu, W.; Wu, N.; Liu, J. Hydrogel-based composites beyond the porous architectures for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano. Res. 2022, 15(10), 9614–9630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, B.; Han, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, L.; Cao, M. Nature-inspired 3D hierarchical structured “vine” for efficient microwave attenuation and electromagnetic energy conversion device. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Hu, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Min, Z.; Zhang, R. N-doped honeycomb-like Ag@N-Ti3C2Tx foam for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nanomaterials 2022, 12(17), 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Han, L.; Wang, X.; Gao, F.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J. MOF-derived CoNC@rGO/amine-rich@rGO/fluorinated-epoxy nanocomposites with EMI shielding, mechanical robustness, superamphiphobicity and long-term anticorrosion properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cui, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, X.; Wang, X. Polypyrrole chains decorated on CoS spheres: A core-shell like heterostructure for high-performance microwave absorption. Nanomaterials 2020, 10(1), 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Cao, M. VSe2/CNTs nanocomposites toward superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Carbon 2023, 212, 118159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qin, Y.; Peng, L.; Pan, M.; Xu, H. Lightweight and anti-corrosive carbon nanotubes (CNTs)/bamboo fiber/HDPE composite for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Colloid Surface A 2023, 672, 131746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, F.; Cui, X.; Sun, S. Electromagnetic radiation-based IC device identification and verification using deep learning. Eurasip J. Wirel. Comm. 2020, 2020, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, R.; Peng, L.; Duan, X.; Chen, Q.; Liang, X. Microwave absorption enhancement and complex permittivity and permeability of Fe encapsulated within carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16(5), 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, P.; J, G.; Song, J.; Zheng, L.; Zeng, H.; Xu, Z. A voltage-boosting strategy enabling a low-frequency, flexible electromagnetic wave absorption device. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30(15), 1706343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cao, Q.; Bi, H.; Liang, C.; Yuan, K.; She, W.; Yang, Y.; Che, R. CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@ Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28(3), 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Wang, X.; Cao, W.; Fang, X.; Wen, B.; Yuan, J. Thermally driven transport and relaxation switching self-powered electromagnetic energy conversion. Small 2018, 14(29), 1800987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sista, Ka.; Dwarapudi, S.; Kumar, D.; Sinha, G.; Moon, A. Carbonyl iron powders as absorption material for microwave interference shielding: A review. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 853, 157251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Ning, M.; Raza, H.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, G.; Zheng, Q.; Che, R. Emerging materials and designs for low- and multi-band electromagnetic wave absorbers: The search for dielectric and magnetic synergy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32(23), 2200123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cao, Q.; Bi, H.; Liang, C.; Yuan, K.; She. W.; Yang, Y.; Che, R. CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 2015, 28(3), 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, J.; Gu, J. New generation electromagnetic materials: harvesting instead of dissipation solo. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67(14), 1413–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Wang, S.; Kuang, D. Facile synthesis and excellent microwave absorption properties of FeCo-C core–shell nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2018, 29(8), 085604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Ji, G; Wang, M. Hexagonal-cone like of Fe50Co50 with broad frequency microwave absorption, Effect of ultrasonic irradiation time. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Jiang, J.; Xu, C. Co7Fe3 and Co7Fe3@SiO2 nanospheres with tunable diameters for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2017, 9(26), 21933–21941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, D.; Hou, L.; Wang, S. Large-scale synthesis and outstanding microwave absorption properties of carbon nanotubes coated by extremely small FeCo-C core-shell nanoparticles. Carbon 2019, 153, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Liu, H.; Cao, Z. Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance of amorphous CoxFe10-x alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 726, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ji, G.; Li, Z. Facile synthesis of FeCo alloys with excellent microwave absorption in the whole Ku-band, Effect of Fe/Co atomic ratio. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 704, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; You, W.; Xiong, X. Morphology-evolved succulent-like FeCo microarchitectures with magnetic configuration regulation for enhanced microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14(28), 32369–32378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zong, Y. Carbon nanofibers supported by FeCo nanocrystals as difunctional magnetic/dielectric composites with broadband microwave absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 824, 153980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ding, M.; Shao, C. Facile synthesis of CoxFey@C nanocomposite fibers derived from pyrolysis of cobalt/iron chelate nanowires for strong broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, D.; Hou, L.; Wang, S. Large-scale synthesis and outstanding microwave absorption properties of carbon nanotubes coated by extremely small FeCo-C core-shell nanoparticles. Carbon 2019, 153, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajia, S.; Asa, H; Toyoda, Y. Development of an alternative approach for electromagnetic wave absorbers using Fe–Cr–Co alloy powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 903, 163920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jiao, Q.; Fu, R. Cu/NC@Co/NC composites derived from core-shell Cu-MOF@Co-MOF and their electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2022, 613, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.; Kamkar, M.; Rahmani, F. Multilayer structures of a Zn0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4-reduced graphene oxide/PVDF nanocomposite for tunable and highly efficient microwave absorbers. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021; 3, 12, 5514–5527. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, C.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, R. High-density anisotropy magnetism enhanced microwave absorption performance in Ti3C2Tx MXene@Ni microspheres. ACS Nano 2021, 16(1), 1150–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, R.; Du, Y.; Zhao, H. Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C nanocubes toward efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3(25), 13426–13434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Cao, M.; Chen, Y.; Cao, W.; Liu, J.; Shi, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Yuan, J. Multiscale assembly of grape-like ferroferric oxide and carbon nanotubes: A smart absorber prototype varying temperature to tune intensities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7(34), 19408–19415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Shi, T.; Wu, G.; Lu, Y. One pot green synthesis and EM wave absorption performance of MoS2@nitrogen doped carbon hybrid decorated with ultrasmall cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Carbon 2020, 163, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, M. High efficiency microwave absorption nanocomposites of multiple-phase core-shell CoNi alloy@C loaded on rGO conducting network. Compos. Part A-Appl. S. 2018, 115, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hou, Y.; Li, L. Synthesis of the SiO2@C composites with high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. Powder Technol. 2019, 343, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Wang, S.; Kuang, D. Facile synthesis and excellent microwave absorption properties of FeCo-C core–shell nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2018, 29(8), 085604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, D.; Hou, L.; Wang, S. Large-scale synthesis and outstanding microwave absorption properties of carbon nanotubes coated by extremely small FeCo-C core-shell nanoparticles. Carbon 2019, 153, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Qiang, R.; Du, Y. Prussian blue analogues derived magnetic FeCo alloy/carbon composites with tunable chemical composition and enhanced microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2018, 514, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, Y.; Yao, Y. Hierarchically porous carbon sheets/Co nanofibers derived from corncobs for enhanced microwave absorbing properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 534, 147510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Miao, P.; Chen, K. Highly effective electromagnetic wave absorbing Prismatic Co/C nanocomposites derived from cubic metal-organic framework. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2020, 182, 107613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wen, B.; Yang, H. Hierarchical nest-like structure of Co/Fe MOF derived CoFe@C composite as wide-bandwidth microwave absorber. Compos. Part A-Appl. S. 2020, 135, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, N.; Han, X. Core-shell FeCo@carbon nanoparticles encapsulated in polydopamine-derived carbon nanocages for efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 2019, 145, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Hu, T.; Yang, L. Facile fabrication of electroactive microporous Co3O4 through microwave plasma etching for supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 771, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, N.; Fonseca, A.; Konya, Z.; Nagy, J. Alumina and silica supported metal catalysts for the production of carbon nanotubes. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 2002; 181, 1-2, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Willems, I.; Kónya, Z.; Colomer, J.; Tendeloo, G.; Nagaraju, N.; Fonseca, A.; Nagy, J. Control of the outer diameter of thin carbon nanotubes synthesized by catalytic decomposition of hydrocarbons. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000; 317, 1-2, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kónya, Z.; Kiss, J.; Oszkó, A.; Siska, A.; Kiricsi, I. XPS characterization of catalysts during production of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3(1), 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Chu, W.; Jiang, C.; Tong, D. Growth of carbon nanotubes on the novel FeCo-Al2O3 catalyst prepared by ultrasonic coprecipitation. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2010, 19(2), 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yu, F.; Ma, C.; Xue, X.; Fu, H.; Yuan, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, G.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L. Effective Oxygen reduction reaction performance of FeCo alloys in situ anchored on nitrogen-doped carbon by the microwave-assistant carbon bath method and subsequent plasma etching. Nanomaterials 2019, 9(9), 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Q.; Zhang, F.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Piao, M. One-step synthesis of cobalt nanosheets depositing with carbon microsphere by microwave plasma assisted reduction chemical vapor deposition technique against electromagnetic pollution. Carbon 2023, 214, 118322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Zou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Dryfe, R.A.W.; Huang, X.; Dou, S.; Dai, L.; Wang, S. Oxygen reduction reaction in a droplet on graphite, direct evidence that the edge is more active than the basal plane. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2014, 53(40), 10804–10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivkov, D.; Petrova, O.; Mingaleva, A.; Ob’edkov, A.; Kaverin, B.; Gusev, S. Vilkov, I.; et al.; The structure and chemical composition of the Cr and Fe pyrolytic coatings on the MWCNTs’ surface according to NEXAFS and XPS Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10(2), 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ding, X.; Liu, Q.; Pang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, T. Safety assessment of graphene oxide and microcystin-LR complex, a toxicological scenario beyond physical mixture. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, D.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Ren, H.; Meng, F. A review of three-dimensional graphene-based aerogels, synthesis, structure and application for microwave absorption. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2021, 211, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, H.; Cheng, J.; Han, C.; Yang, X.; Xu, J. Conductive WS2-NS/CNTs hybrids based 3D ultra-thin mesh electromagnetic wave absorbers with excellent absorption performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 528, 147052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wei, B.; Wang, M.; Yao, Z.; Chen, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, Z. Three dimensional flowerlike ZnFe2O4 ferrite loaded graphene, enhancing microwave absorption performance by constructing microcircuits. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 889, 161734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Guo, F.; Luo, J.; Hao, G.; Liu, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Guo, H.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, W. Mater. Designed 3D heterostructure with 0D/1D/2D hierarchy for low-frequency microwave absorption in the S-band. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2022; 10, 4, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.; Zhao, B.; Which, C.; Pei, K.; Money, L.; Zhang, R.; You, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Che, R. Remarkable magnetic exchange coupling via constructing bi-magnetic interface for broadband lower-frequency microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32(33), 2203161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, W.; Qiang, R.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.; Ma, J.; Xu, P. Shell thickness-dependent microwave absorption of core-shell Fe3O4@C composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Liang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, D.; Zhang, B.; Ji, G.; Du, Y. Coin-like α-Fe2O3@CoFe2O4 Core–Shell Composites with Excellent Electromagnetic Absorption Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7(8), 4744–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjipanayis, G.; Kim, A. Domain wall pinning versus nucleation of reversed domains in R-Fe-B magnets (invited). J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 63(8), 3310–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, D.; Geng, D.; An, J.; He, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z. Microwave absorption properties of core double-shell FeCo/C/BaTiO3 nanocomposites. Nanoscale 2014, 6(8), 3967–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Dong, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Lei, J.; Sun, J. Microwave absorption properties of the core/shell-type iron and nickel nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320(6), 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Garg, A.; Ketterson, J. Ferromagnetic resonance modes in the exchange-dominated limit in cylinders of finite length. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2021, 16(6), 064007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Ji, G.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Du, W. Achieving hierarchical hollow carbon@Fe@Fe3O4 nanospheres with superior microwave absorption properties and lightweight features. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2015; 3, 39, 10232–10241. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, P.; Yun, J.; et al. A novel MOF-drived self-decomposition strategy for CoO@N/C-Co/Ni-NiCo2O4 multi-heterostructure composite as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, B.; Yao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Tao, X. Constructing FeCo@C core-shell structure with strong polarization behavior towards excellent microwave absorption performance. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 300, 127553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




