Submitted:
17 June 2024
Posted:
17 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
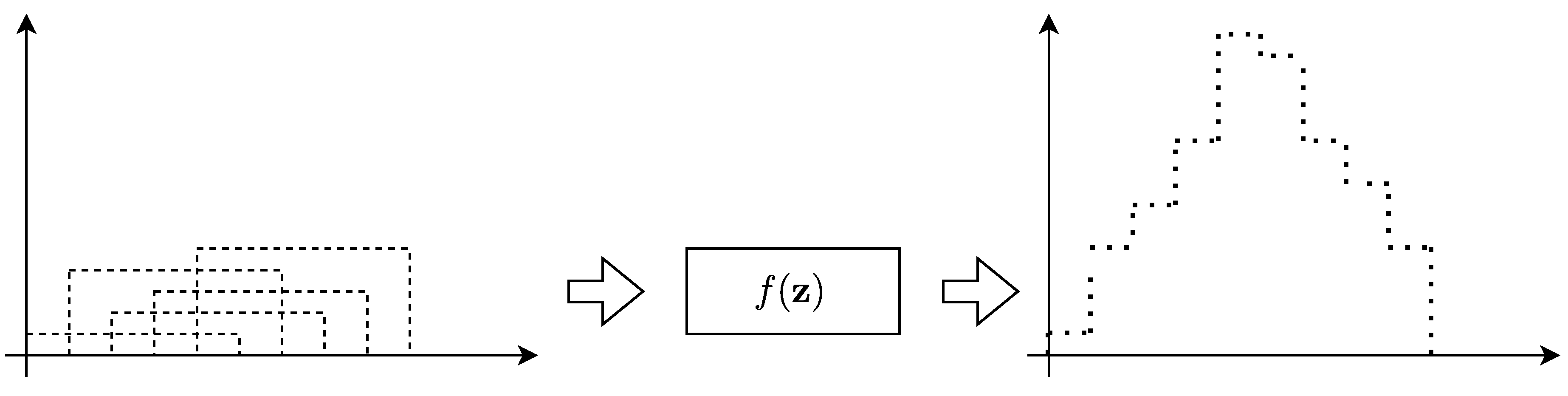
3.1. Nonlinear Optimization Fundamentals (NOPT)
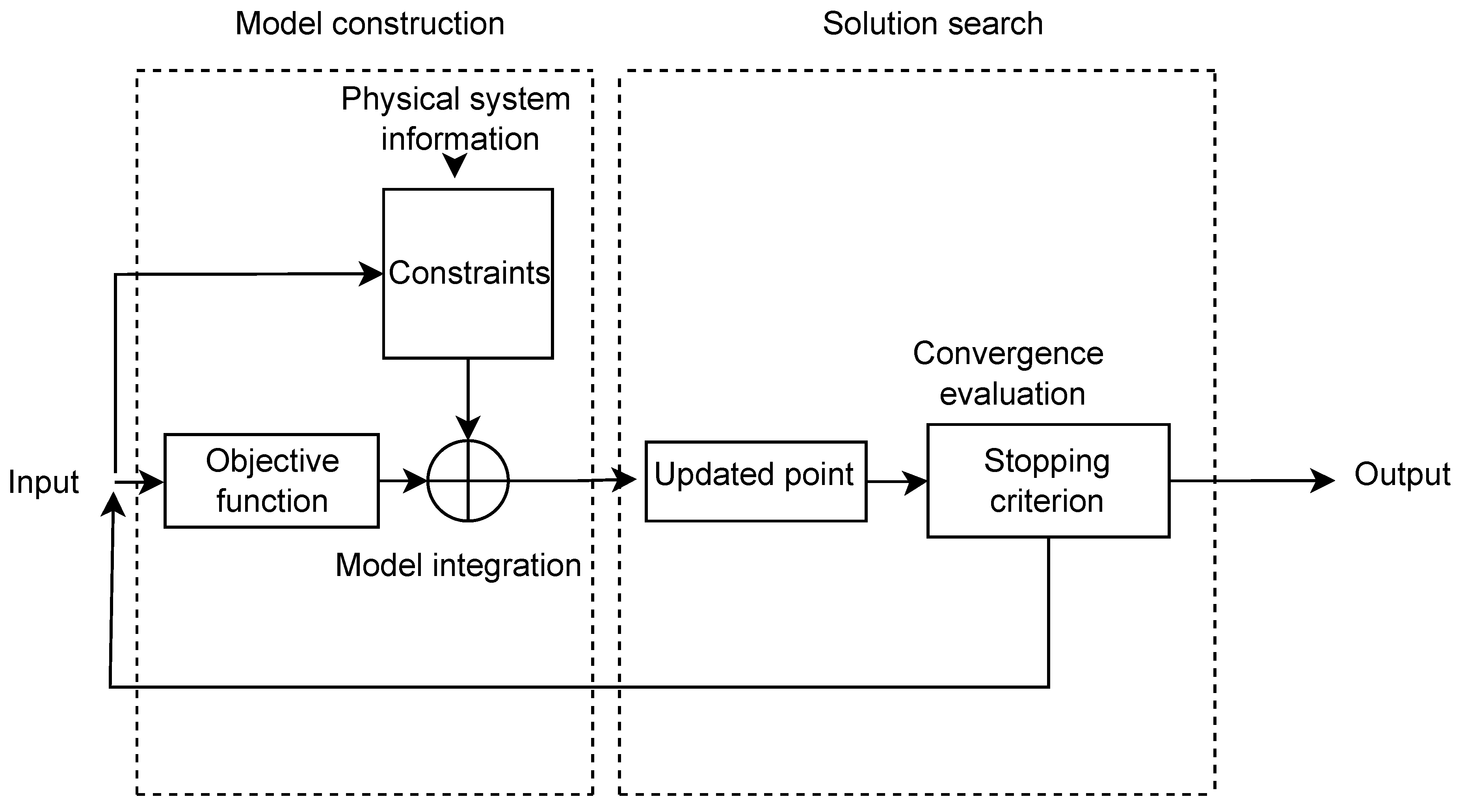
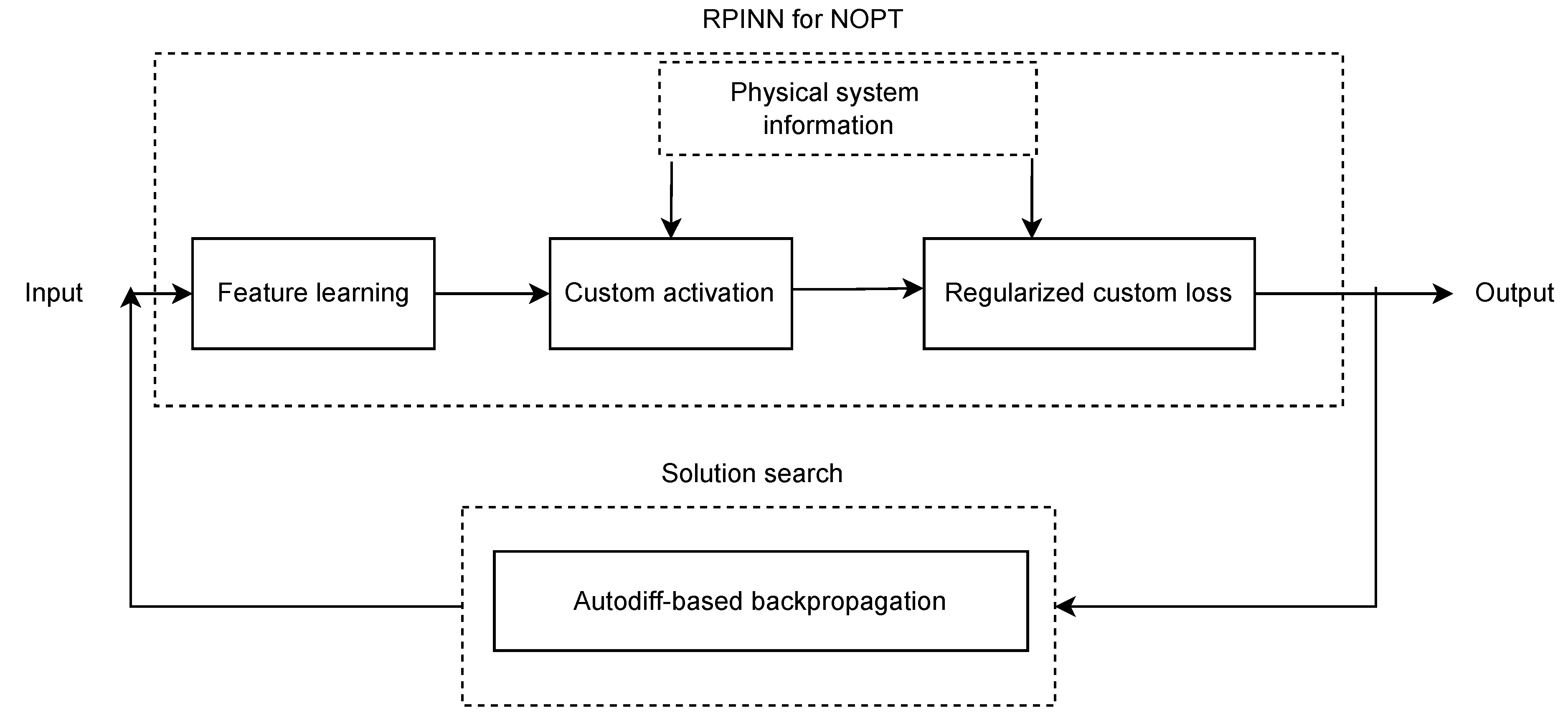
3.2. Regularized Physics-Informed Neural Network (RPINN)
4. Tested Scenarios for NOPT Using RPINN
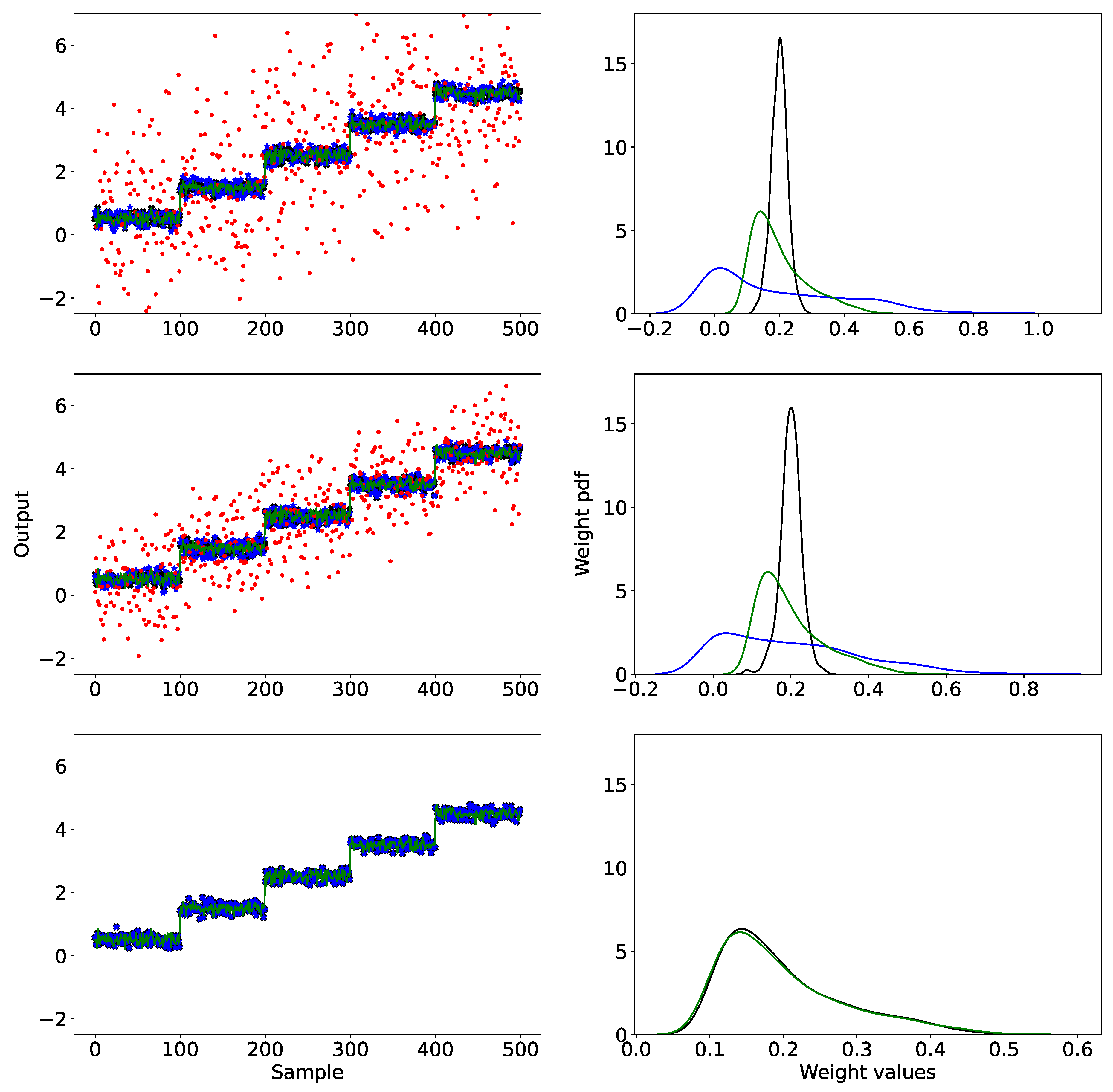
4.1. Supervised Constrained Optimization: Uniform Mixture Model
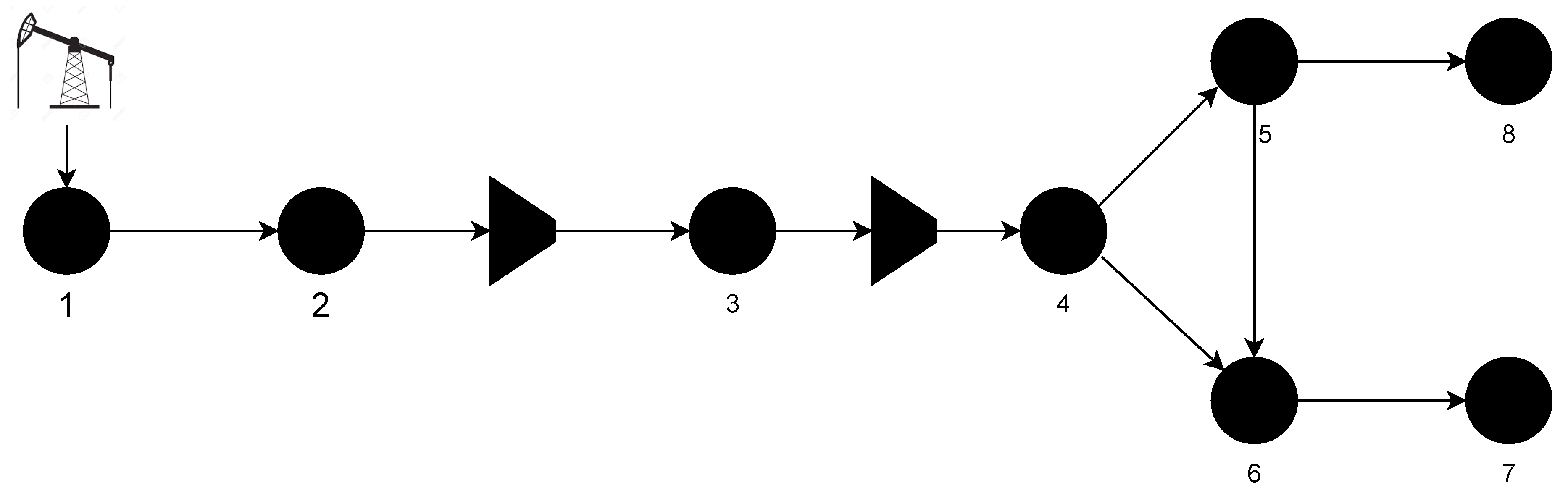
4.2. Unsupervised Constrained Optimization: Gas-Powered System
5. Experimental Set-Up
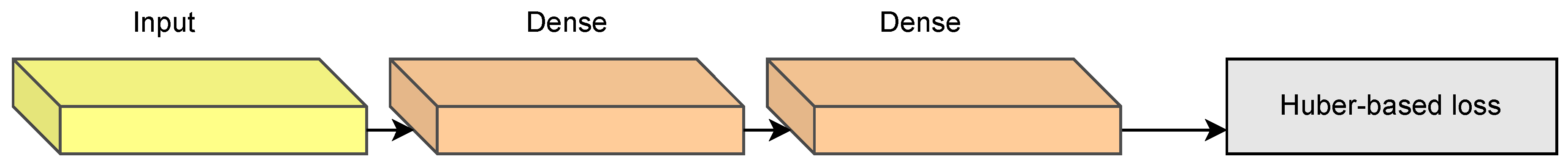
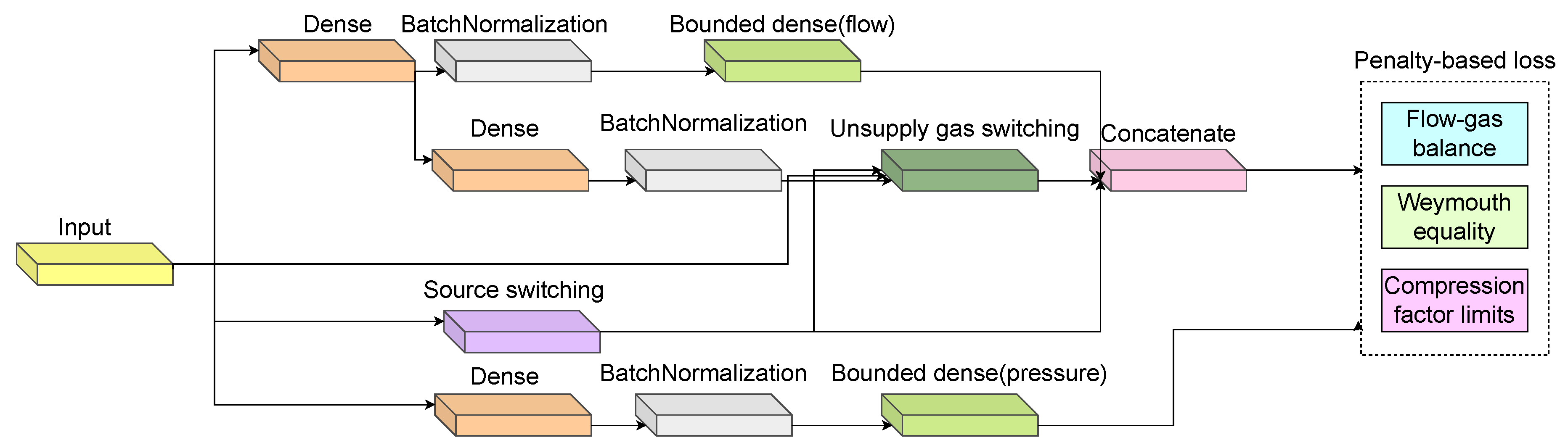
5.1. Deep Learning Architectures
5.2. Training Details and Method Comparison
6. Results and Discussion
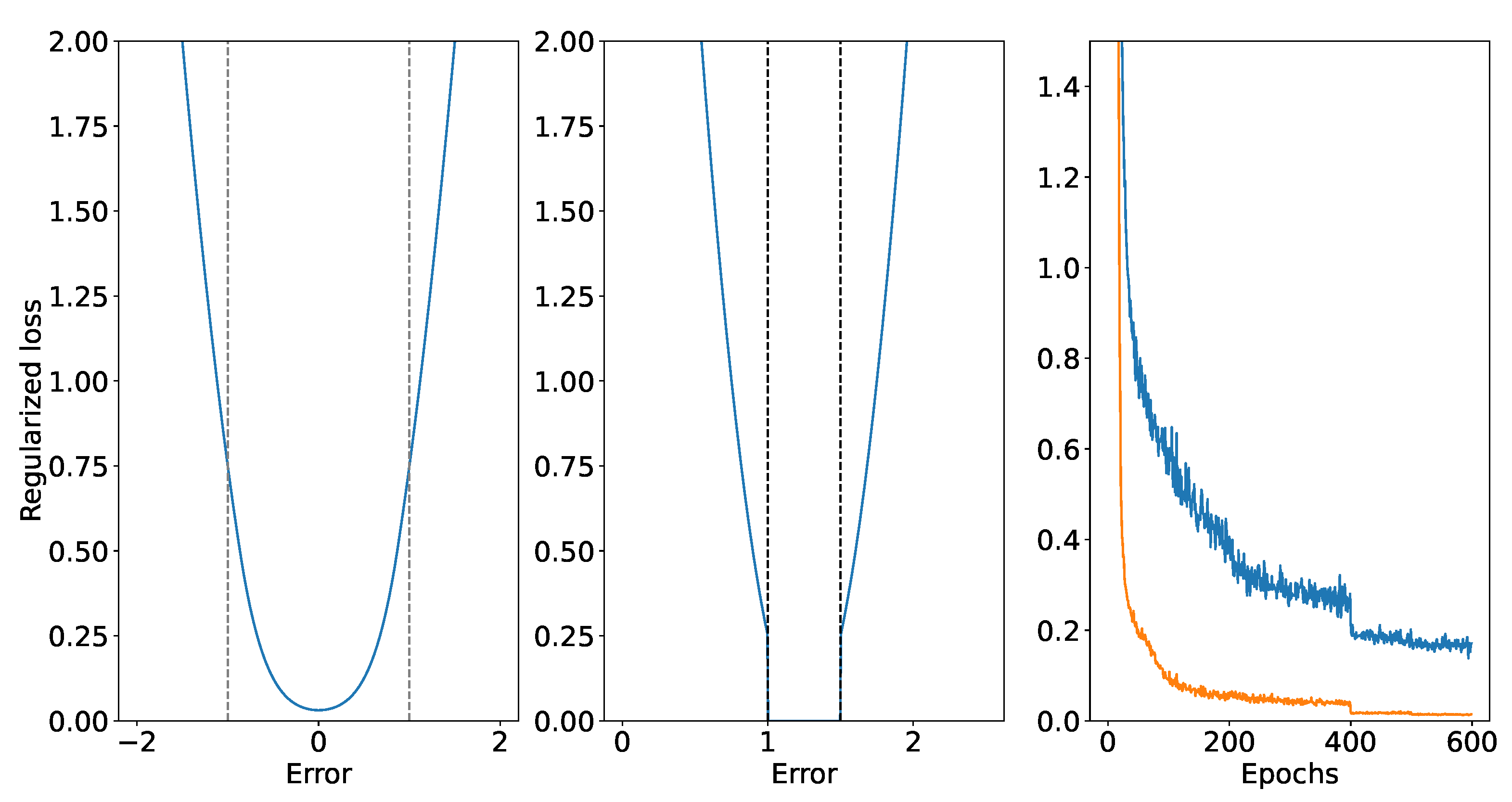
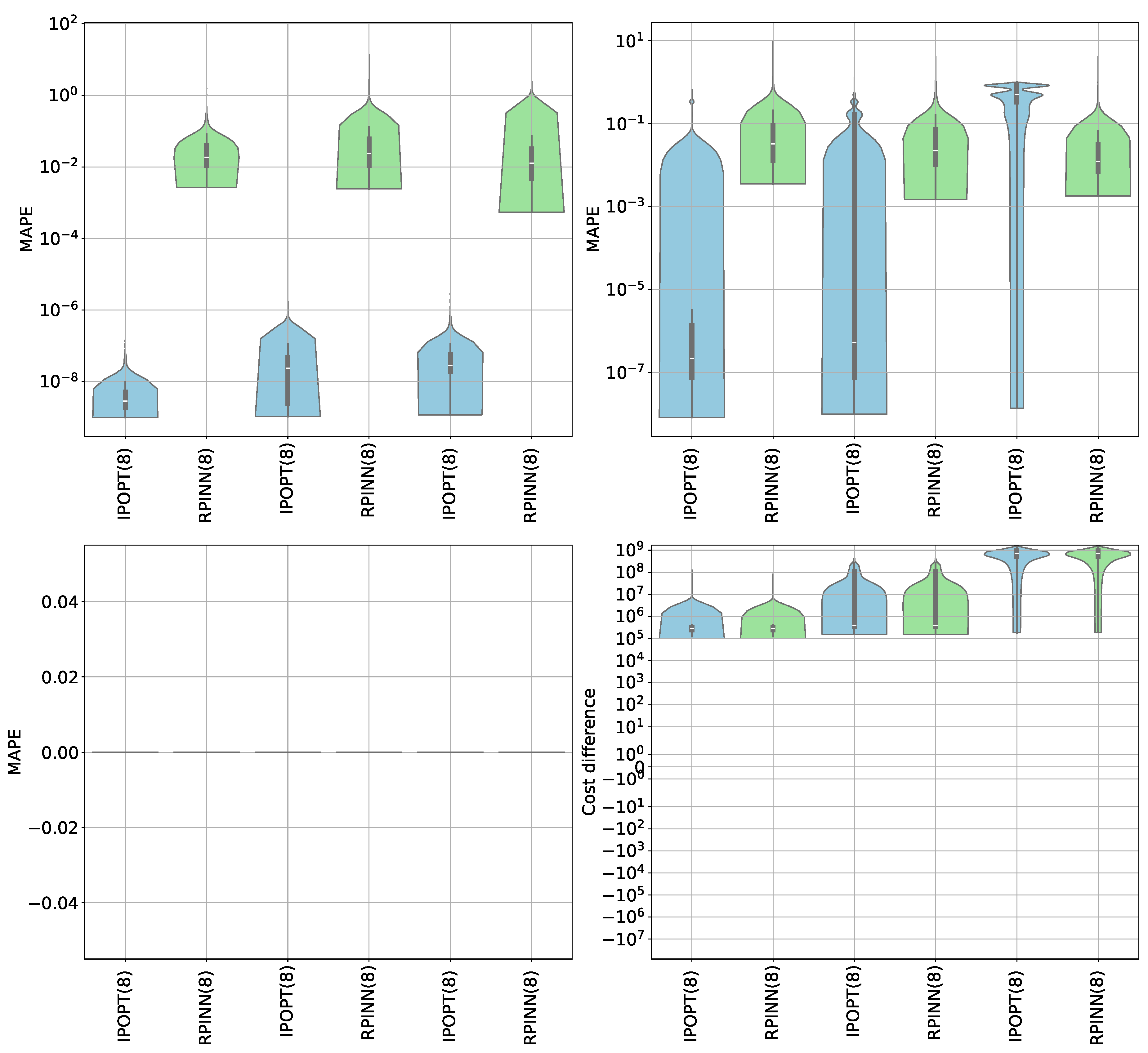
6.1. Supervised Constrained Optimization Results
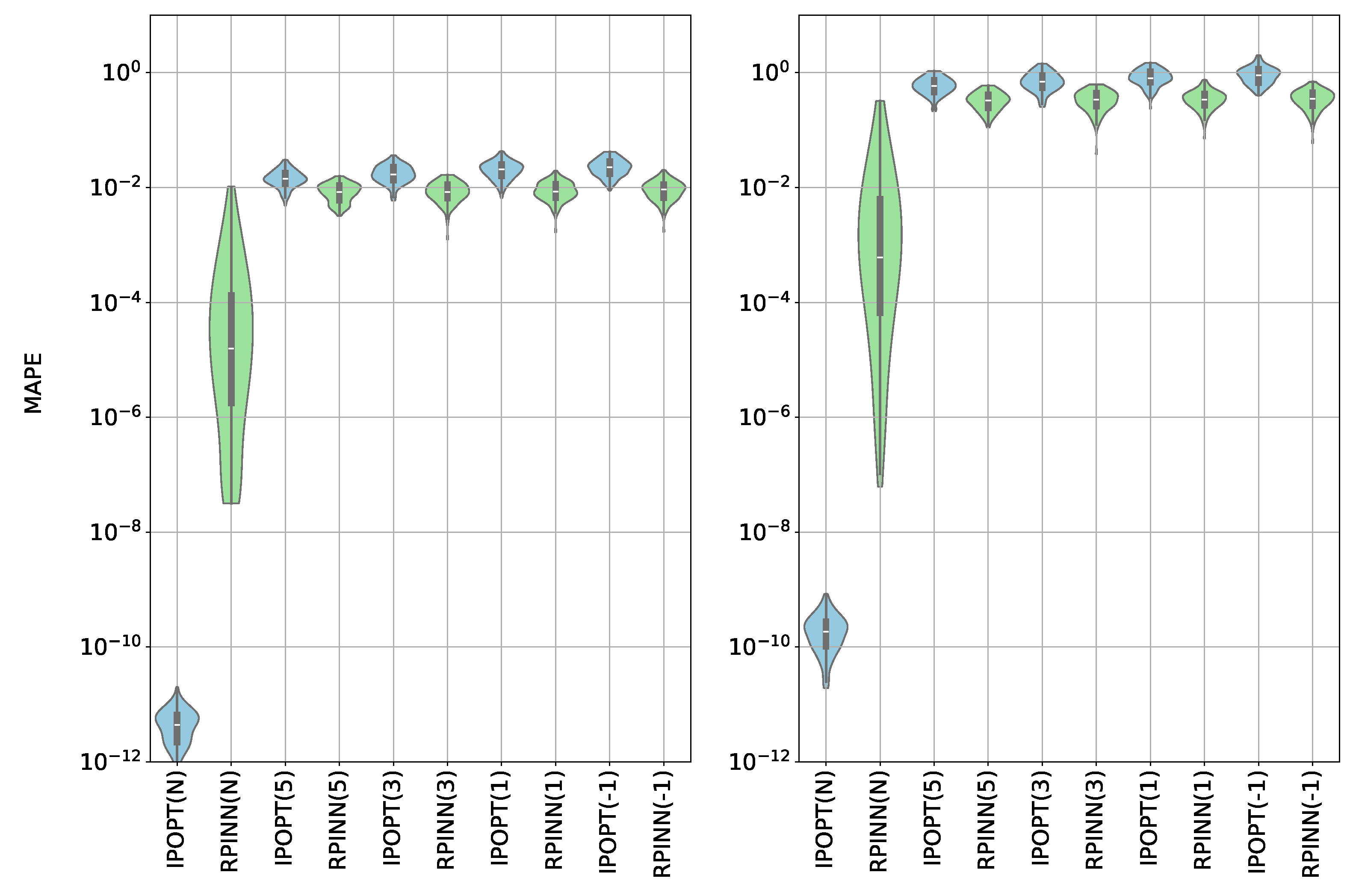
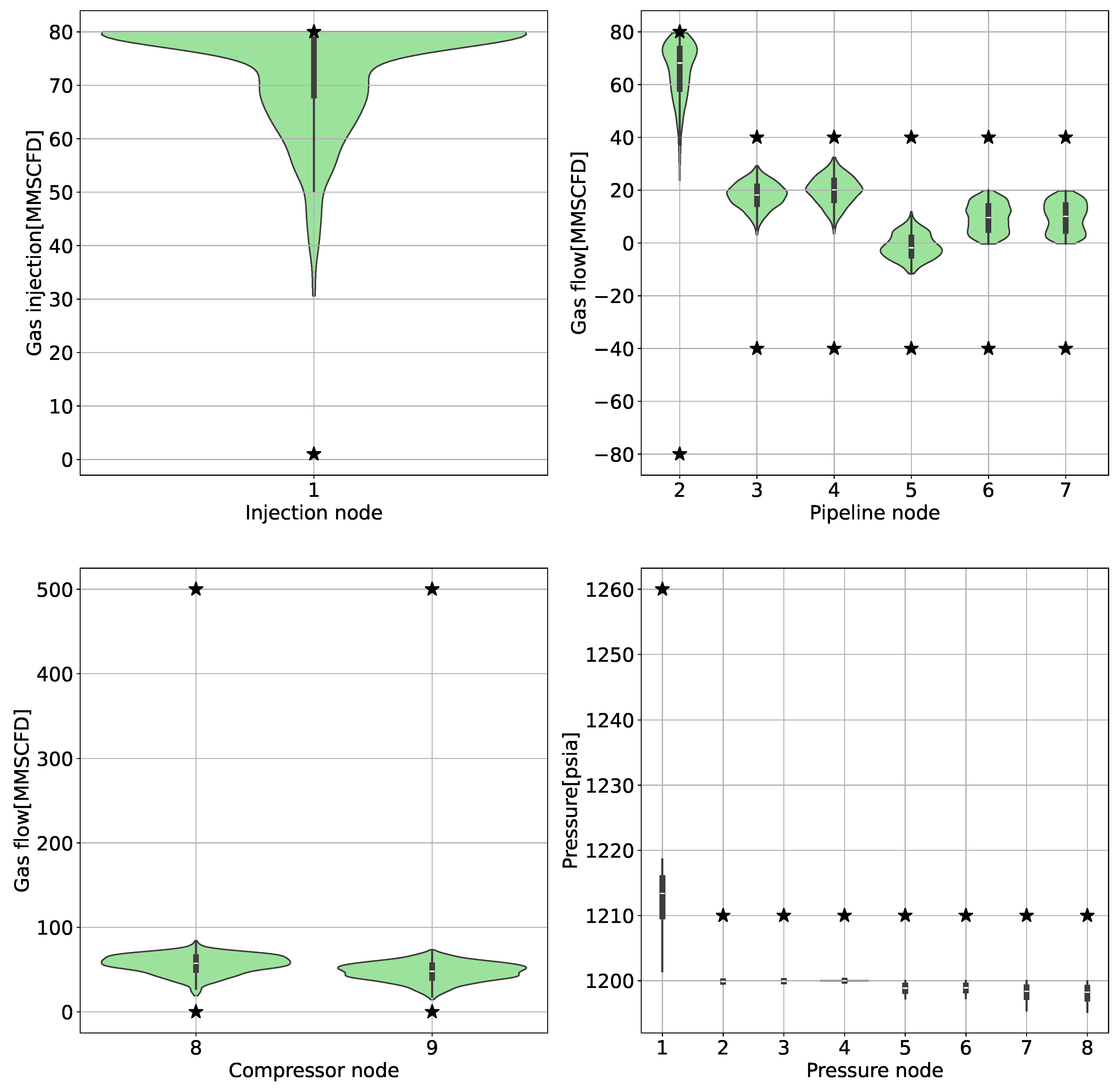
6.2. Unsupervised Constrained Optimization Results
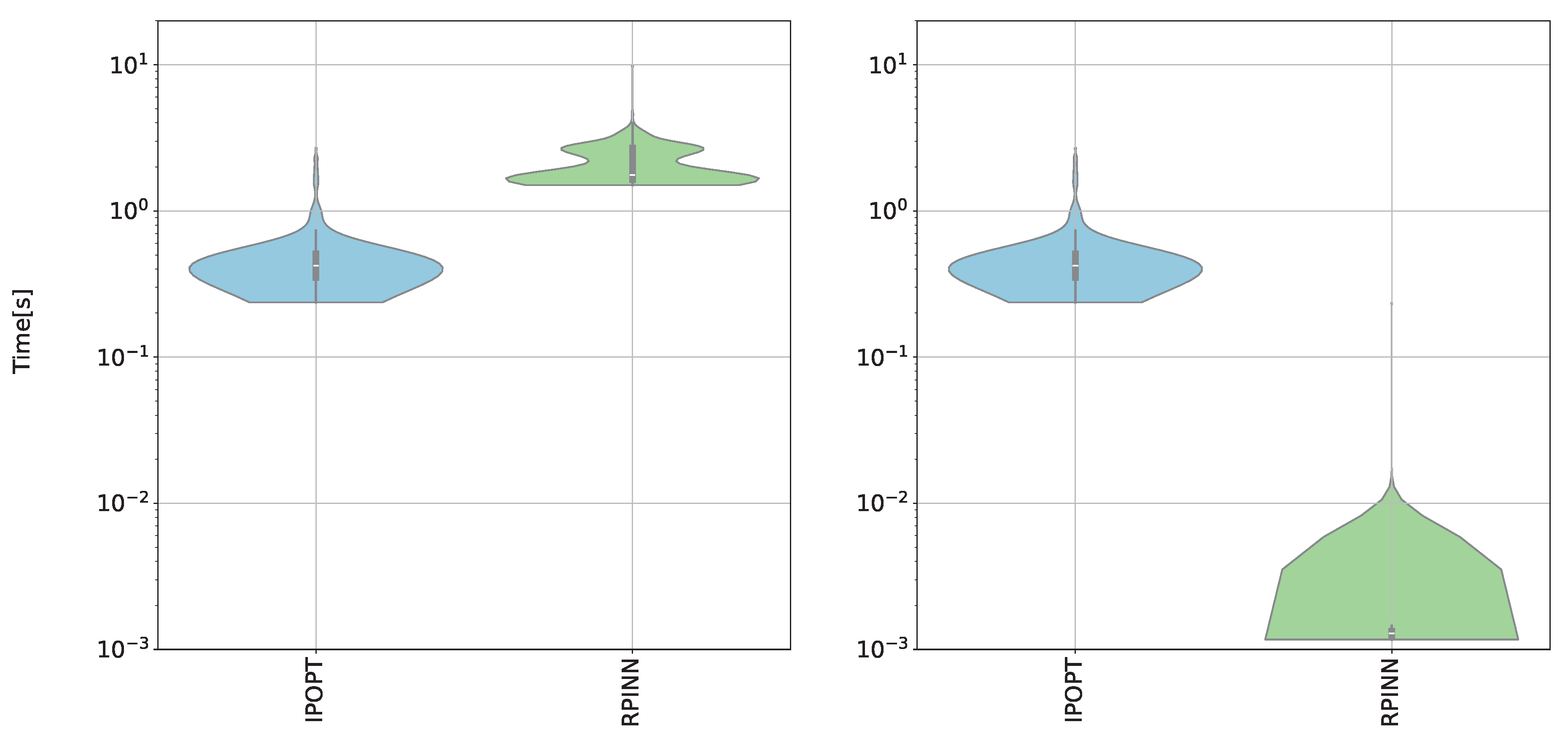
6.3. Computational Cost Results
6.4. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Branislav, I.; Haifeng, M.; Dijana, M.; others. A survey of gradient methods for solving nonlinear optimization. Electronic research archive 2020, 28, 1573–1624. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulkadirov, R.; Lyakhov, P.; Nagornov, N. Survey of optimization algorithms in modern neural networks. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zuo, L.; Wu, C.; Bu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, F. Short-term supply reliability assessment of a gas pipeline system under demand variations. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 2020, 202, 107004. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Huang, W.; Wen, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Wen, K.; Gong, J.; Lu, Y. An integrated gas supply reliability evaluation method of the large-scale and complex natural gas pipeline network based on demand-side analysis. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 2021, 212, 107651. [Google Scholar]
- Kohjitani, H.; Koda, S.; Himeno, Y.; Makiyama, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yoshinaga, D.; Wuriyanghai, Y.; Kashiwa, A.; Toyoda, F.; Zhang, Y.; others. Gradient-based parameter optimization method to determine membrane ionic current composition in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 19110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbakova, G.; Krylov, V.; Qianqi, W.; Rusyn, B.; Sachenko, A.; Bykovyy, P.; Zahorodnia, D.; Kopania, L. Optimization methods on the wavelet transformation base for technical diagnostic information systems. 2021 11th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications (IDAACS). IEEE, 2021, Vol. 2, pp. 767–773.
- Weiner, A.; Semaan, R. Backpropagation and gradient descent for an optimized dynamic mode decomposition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.12928, arXiv:2312.12928 2023.
- Han, M.; Du, Z.; Yuen, K.F.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Q. Walrus optimizer: A novel nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm. Expert Systems with Applications 2024, 239, 122413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhanna, S.; Mancarella, P. An exact sequential linear programming algorithm for the optimal power flow problem. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2021, 37, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Chen, Q.; Lin, R.; Shi, Y.; Xie, L.; Su, H. Controlling Pressure of Gas Pipeline Network Based on Mixed Proximal Policy Optimization. 2022 China Automation Congress (CAC). IEEE, 2022, pp. 4642–4647.
- Wang, G.; Zhao, W.; Qiu, R.; Liao, Q.; Lin, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H. Operational optimization of large-scale thermal constrained natural gas pipeline networks: A novel iterative decomposition approach. Energy 2023, 282, 128856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, O.; Gil-González, W.; Hernández, J.C.; Giral-Ramírez, D.A.; Medina-Quesada, A. A mixed-integer nonlinear programming model for optimal reconfiguration of DC distribution feeders. Energies 2020, 13, 4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robuschi, N.; Zeile, C.; Sager, S.; Braghin, F. Multiphase mixed-integer nonlinear optimal control of hybrid electric vehicles. Automatica 2021, 123, 109325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, A.K.; Jain, R.; Yadav, S.; Bisht, S.; Gautam, S. Recent trends in gas pipeline optimization. Materials Today: Proceedings 2022, 57, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat, S.A.; Sahraei-Ardakani, M. Customized sequential quadratic programming for solving large-scale ac optimal power flow. 2021 North American Power Symposium (NAPS). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–6.
- Awwal, A.M.; Kumam, P.; Abubakar, A.B. A modified conjugate gradient method for monotone nonlinear equations with convex constraints. Applied Numerical Mathematics 2019, 145, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Li, Z. A benders decomposition based algorithm for steady-state dispatch problem in an integrated electricity-gas system. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2021, 36, 3817–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhou, M.; Yu, Y. A multi-layered gravitational search algorithm for function optimization and real-world problems. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica 2020, 8, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillutla, K.; Roulet, V.; Kakade, S.M.; Harchaoui, Z. Modified Gauss-Newton Algorithms under Noise. 2023 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP), 2023, pp. 51–55. [CrossRef]
- Jamii, J.; Trabelsi, M.; Mansouri, M.; Mimouni, M.F.; Shatanawi, W. Non-Linear Programming-Based Energy Management for a Wind Farm Coupled with Pumped Hydro Storage System. Sustainability 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydin, A.G.; Pearlmutter, B.A.; Radul, A.A.; Siskind, J.M. Automatic differentiation in machine learning: A survey. Journal of machine learning research 2018, 18, 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Chen, M.; Zhao, T.; Low, S.H. DeepOPF: A Feasibility-Optimized Deep Neural Network Approach for AC Optimal Power Flow Problems. IEEE Systems Journal 2023, 17, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellikkath, R.; Chatzivasileiadis, S. Physics-informed neural networks for ac optimal power flow. Electric Power Systems Research 2022, 212, 108412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, J. Applications of Physics-Informed Neural Networks in Power Systems - A Review. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2023, 38, 572–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiasny, J.; Chevalier, S.; Chatzivasileiadis, S. Learning without data: Physics-informed neural networks for fast time-domain simulation. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (SmartGridComm). IEEE, 2021, pp. 438–443.
- Strelow, E.L.; Gerisch, A.; Lang, J.; Pfetsch, M.E. Physics informed neural networks: A case study for gas transport problems. Journal of Computational Physics 2023, 481, 112041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applegate, D.; Diaz, M.; Hinder, O.; Lu, H.; Lubin, M.; O’ Donoghue, B.; Schudy, W. Practical Large-Scale Linear Programming using Primal-Dual Hybrid Gradient. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Ranzato, M.; Beygelzimer, A.; Dauphin, Y.; Liang, P.; Vaughan, J.W., Eds. Curran Associates, Inc., 2021, Vol. 34, pp. 20243–20257.
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhou, M.; Abusorrah, A. Dual-objective mixed integer linear program and memetic algorithm for an industrial group scheduling problem. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica 2020, 8, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.Q.T.; Baiou, M.; Nguyen, V.H.; Weng, P. Improving Subtour Elimination Constraint Generation in Branch-and-Cut Algorithms for the TSP with Machine Learning. Learning and Intelligent Optimization; Sellmann, M., Tierney, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2023; pp. 537–551. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ge, L.; Sidorov, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z. Day-ahead optimization schedule for gas-electric integrated energy system based on second-order cone programming. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems 2020, 6, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Shi, D.; Bian, D. Voltage Stability Constrained Optimal Power Flow for Unbalanced Distribution System Based on Semidefinite Programming. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy 2022, 10, 1614–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.M.U.T.; Kamalasadan, S. A new second-order cone programming model for voltage control of power distribution system with inverter-based distributed generation. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2021, 57, 6559–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharieh Ahari, S.; Kocuk, B. A mixed-integer exponential cone programming formulation for feature subset selection in logistic regression. EURO Journal on Computational Optimization 2023, 11, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Rahaman, O. Lower bound limit analysis using power cone programming for solving stability problems in rock mechanics for generalized Hoek–Brown criterion. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering 2020, 53, 3237–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Shi, D.; Bian, D. Voltage Stability Constrained Optimal Power Flow for Unbalanced Distribution System Based on Semidefinite Programming. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy 2022, 10, 1614–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, A.B.; Kumam, P. A descent Dai-Liao conjugate gradient method for nonlinear equations. Numerical Algorithms 2019, 81, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Yao, B.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Y.S. Automatic fracture optimization for shale gas reservoirs based on gradient descent method and reservoir simulation. Advances in Geo-Energy Research 2021, 5, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, D.; Rajan, V. Multi-task learning with user preferences: Gradient descent with controlled ascent in pareto optimization. International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2020, pp. 6597–6607.
- Karimi, M.; Shahriari, A.; Aghamohammadi, M.; Marzooghi, H.; Terzija, V. Application of Newton-based load flow methods for determining steady-state condition of well and ill-conditioned power systems: A review. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2019, 113, 298–309. [Google Scholar]
- Mannel, F.; Rund, A. A hybrid semismooth quasi-Newton method for nonsmooth optimal control with PDEs. Optimization and Engineering 2021, 22, 2087–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, R.B.; Balbo, A.R.; Cabana, T.G.; Nepomuceno, L. Solving Nonsmooth and Discontinuous Optimal Power Flow problems via interior-point ℓp-penalty approach. Computers & Operations Research 2022, 138, 105607. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, J.A.; Baptista, E.C.; Balbo, A.R.; Soler, E.M.; Silva, D.N.; Martins, A.C.; Nepomuceno, L. A primal–dual penalty-interior-point method for solving the reactive optimal power flow problem with discrete control variables. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2022, 138, 107917. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H. An interior-point solver for AC optimal power flow considering variable impedance-based FACTS devices. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 154460–154470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji, S.H.; Abdulazeez, A.M. Comparison of optimization techniques based on gradient descent algorithm: A review. PalArch’s Journal of Archaeology of Egypt/Egyptology 2021, 18, 2715–2743. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, I.A.; Hossain, M.J. Low voltage distribution networks modeling and unbalanced (optimal) power flow: A comprehensive review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 143026–143084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulart, P.; Chen, Y. Clarabel Documentation. https://oxfordcontrol.github.io/ClarabelDocs/stable/, 2024. Último acceso en 2024.
- Gurobi Optimization. https://www.gurobi.com/, 2024. Último acceso en 2024.
- MOSEK. https://www.mosek.com/, 2024. Último acceso en 2024.
- Xpress Optimization. https://www.fico.com/en/products/fico-xpress-optimization, 2024. Último acceso en 2024.
- O’Donoghue, B. Operator Splitting for a Homogeneous Embedding of the Linear Complementarity Problem. SIAM Journal on Optimization 2021, 31, 1999–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipopt Deprecated Features. https://coin-or.github.io/Ipopt/deprecated.html, 2024. Último acceso en 2024.
- Zimmerman, R.D.; Murillo-Sánchez, C.E. MATPOWER User’s Manual. Zenodo, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Murillo-Sanchez, C.E.; Zimmerman, R.D.; Thomas, R.J. On Computational Issues of Market-Based Optimal Power Flow. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2007, 22, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Marín, S.; González-Vanegas, W.; Murillo-Sánchez, C. MPNG: A MATPOWER-Based Tool for Optimal Power and Natural Gas Flow Analyses. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems. [CrossRef]
- Beal, L.; Hill, D.; Martin, R.; Hedengren, J. GEKKO Optimization Suite. Processes 2018, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugel, S.; Kuchkovsky, C.; Sanchez, E.; Fernandez-Lorenzo, S.; Luis-Hita, J.; Lizaso, E.; Orus, R. Dynamic portfolio optimization with real datasets using quantum processors and quantum-inspired tensor networks. Physical Review Research 2022, 4, 013006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, S.; Boyd, S. CVXPY: A Python-embedded modeling language for convex optimization. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2016, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, A.; Boyd, S. Disciplined quasiconvex programming. Optimization Letters 2020. To appear.
- O’Donoghue, B.; Chu, E.; Parikh, N.; Boyd, S. Conic Optimization via Operator Splitting and Homogeneous Self-Dual Embedding. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications 2016, 169, 1042–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, T.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S. DeepOPF: A Deep Neural Network Approach for Security-Constrained DC Optimal Power Flow. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2021, 36, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, K. A learning-boosted quasi-newton method for ac optimal power flow. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.06074. 2020.
- Zhou, M.; Chen, M.; Low, S.H. DeepOPF-FT: One Deep Neural Network for Multiple AC-OPF Problems With Flexible Topology. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2023, 38, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhao, C. DeepOPF-U: A Unified Deep Neural Network to Solve AC Optimal Power Flow in Multiple Networks, 2023. [arXiv:cs.LG/2309.12849].
- Falconer, T.; Mones, L. Leveraging Power Grid Topology in Machine Learning Assisted Optimal Power Flow. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2023, 38, 2234–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misyris, G.S.; Venzke, A.; Chatzivasileiadis, S. Physics-informed neural networks for power systems. 2020 IEEE power & energy society general meeting (PESGM). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–5.
- Misyris, G.S.; Stiasny, J.; Chatzivasileiadis, S. Capturing power system dynamics by physics-informed neural networks and optimization. 2021 60th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC). IEEE, 2021, pp. 4418–4423.
- Habib, A.; Yildirim, U. Developing a physics-informed and physics-penalized neural network model for preliminary design of multi-stage friction pendulum bearings. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2022, 113, 104953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Meng, X.; Karniadakis, G.E. B-PINNs: Bayesian physics-informed neural networks for forward and inverse PDE problems with noisy data. Journal of Computational Physics 2021, 425, 109913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiassi, E.; De Florio, M.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Mortari, D.; Furfaro, R. Physics-informed neural networks and functional interpolation for data-driven parameters discovery of epidemiological compartmental models. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, G.; Houde, S.; Gosselin, F.P. ModalPINN: An extension of physics-informed Neural Networks with enforced truncated Fourier decomposition for periodic flow reconstruction using a limited number of imperfect sensors. Journal of Computational Physics 2022, 464, 111271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellikkath, R.; Chatzivasileiadis, S. Physics-Informed Neural Networks for AC Optimal Power Flow. Electric Power Systems Research 2022, 212, 108412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.P. Probabilistic machine learning: An introduction; MIT press, 2022.
- González-Vanegas, W.; Álvarez Meza, A.; Hernández-Muriel, J.; Orozco-Gutiérrez, Á. AKL-ABC: An Automatic Approximate Bayesian Computation Approach Based on Kernel Learning. Entropy 2019, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Marín, S.; González-Vanegas, W.; Murillo-Sánchez, C. MPNG: MATPOWER-Natural Gas. https://github.com/MATPOWER/mpng, 2019. [Online; accessed (fecha de acceso)].
- Owerko, D.; Gama, F.; Ribeiro, A. Unsupervised optimal power flow using graph neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.09277, arXiv:2210.09277 2022.
- Mustajab, A.H.; Lyu, H.; Rizvi, Z.; Wuttke, F. Physics-Informed Neural Networks for High-Frequency and Multi-Scale Problems Using Transfer Learning. Applied Sciences 2024, 14, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftheriadis, P.; Leva, S.; Ogliari, E. Bayesian hyperparameter optimization of stacked bidirectional long short-term memory neural network for the state of charge estimation. Sustainable Energy, Grids and Networks 2023, 36, 101160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Romano, S.; Erfani, S.; Bailey, J. Normalized loss functions for deep learning with noisy labels. International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2020, pp. 6543–6553.
- Jeon, H.J.; Van Roy, B. An Information-Theoretic Framework for Deep Learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2022, 35, 3279–3291. [Google Scholar]
- Thangamuthu, A.; Kumar, G.; Bishnoi, S.; Bhattoo, R.; Krishnan, N.; Ranu, S. Unravelling the performance of physics-informed graph neural networks for dynamical systems. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2022, 35, 3691–3702. [Google Scholar]
| Solver | LP | QP | SOCP | SDP | EXP | PCP | MIP | NLP | Strategy | Open source | Software |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clarabel [46] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | x | x | x | IP | ✓ | CVXPY |
| Gurobi [47] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | x | x | x | ✓ | x | IP, Simplex, BC | x | MATPOWER, CVXPY |
| Mosek [48] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓* | x | IP | x | MATPOWER, CVXPY |
| Xpress [49] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | x | x | x | ✓ | ✓** | IP, Simplex, BC | x | CVXPY |
| SCS [50,59] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | x | x | IP | ✓ | CVXPY |
| IPOPT [51] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | IP | ✓ | MATPOWER, GEKKO |
| Layer name | Type | Output shape | Param. # |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | InputLayer | (, 5) | 0 |
| Dense_1 | Dense(SELU) | (, 5) | 25 |
| Dense_2 | Dense(SELU, l1-max-constraint) | (, 1) | 5 |
| Layer name | Type | Output shape | Param. # |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | InputLayer | (, 8) | 0 |
| Dense_1 | Dense(SELU) | (, 236) | 2124 |
| Dense_2 | Dense(SELU) | (, 8) | 1896 |
| Source switching | CustomDense | (, 1) | 1 |
| BatchNormalization_1 | BatchNormalization | (, 236) | 944 |
| BatchNormalization_2 | BatchNormalization | (, 8) | 32 |
| Partial flows | BoundedDense | (, 50) | 1422 |
| Unsupply gas switching | CustomDense | (, 8) | 0 |
| Flow prediction | Concatenate | (, 59) | 0 |
| Dense_3 | Dense(SELU) | (, 236) | 2124 |
| BatchNormalization_3 | BatchNormalization | (, 236) | 944 |
| Pressure prediction | BoundedDense | (, 8) | 1896 |
| Node balance | CustomDense | (, 8) | 472 |
| Weymouth | CustomDense | (, 14) | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





