Submitted:
13 June 2024
Posted:
14 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology of FMS
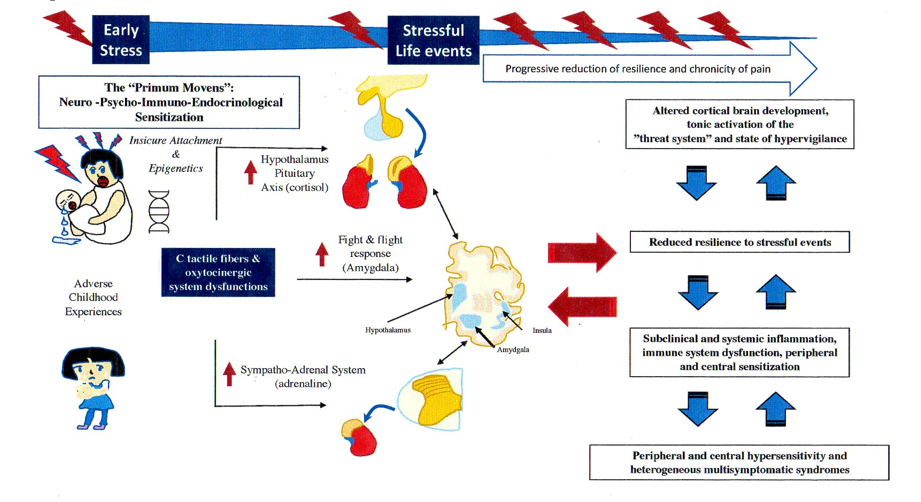
2.1. The Stress Response System in FMS and FSDs
2.2. The BDS and FMS: What Came First?
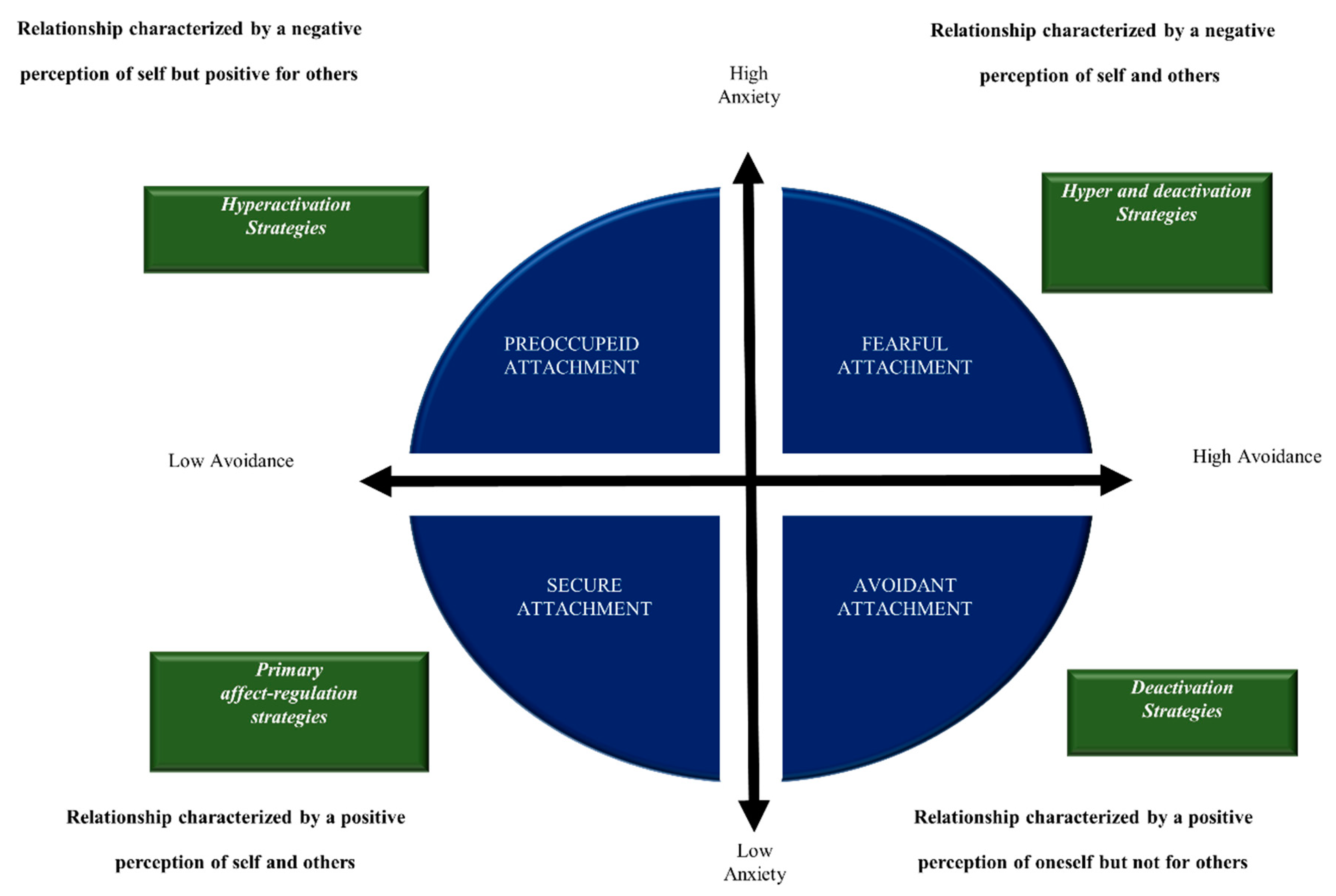
2.3. The Relationship between BSS and the Insecure Attachment in CP and FMS
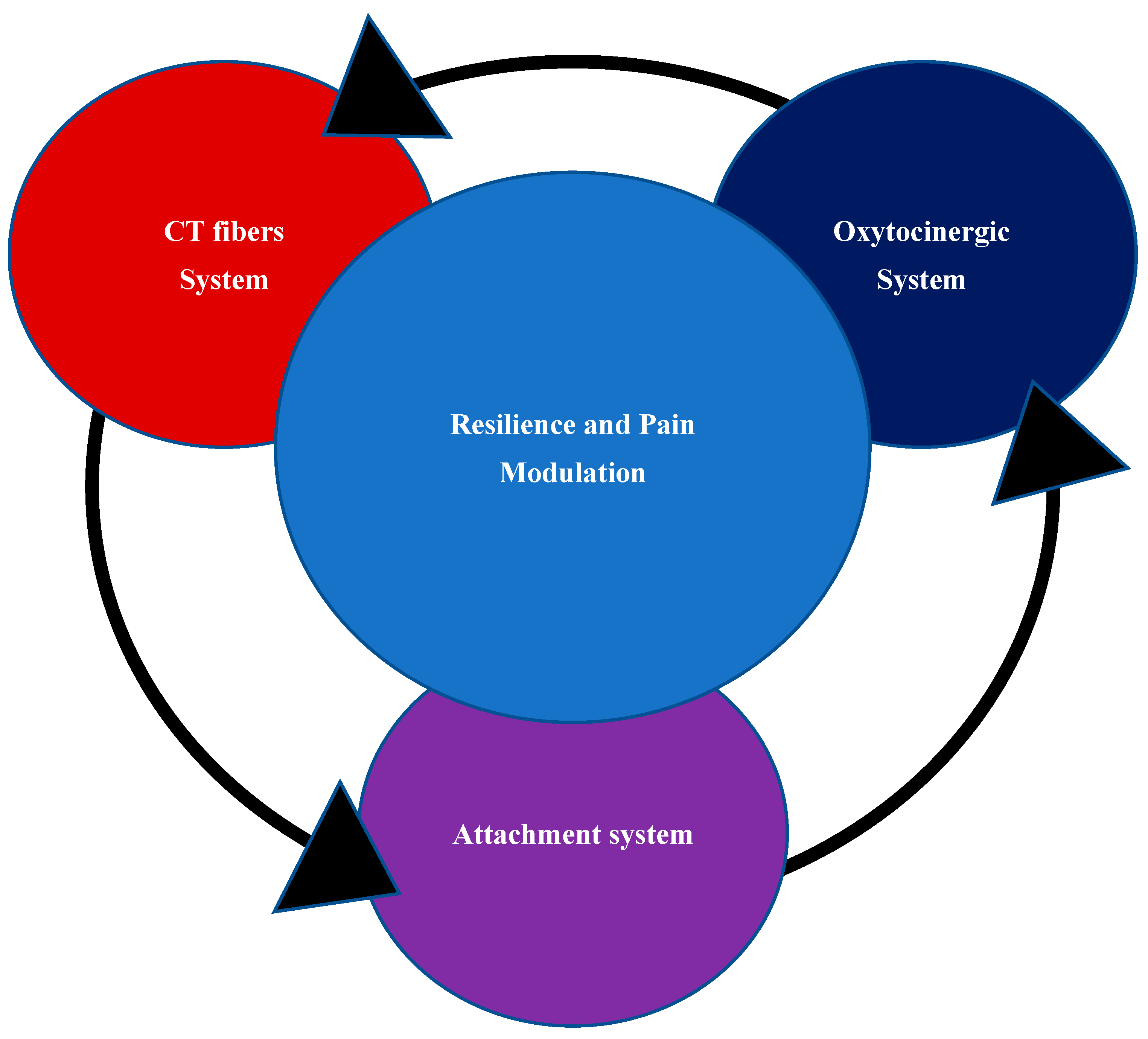
2.4. Role of Oxytocin System in Attachment System and Pain Modulation
2.5. CT Fibers in FMS: from Small Fibers Pathology (SFP) to Oxytocin System
2.6. CT Fibers, Oxytocin System and Brain Development
3. Discussion
Therapeutic Implications and Conclusive Remarks
List of Abbreviations
References
- Wolfe, F.; Clauw, D.J.; Fitzcharles, M. A.; Goldenberg, D. L.; Katz, R. S.; Mease, P.; Russell, A. S.; Russell, I. J.; Winfield, J. B.; Yunus, M. B. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia and measurement of symptom severity. Arthritis Care Res. 2010, 62, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Diseases (ICD). WHO http://www.who.int/ classifications/icd/en/ (2015). 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, C.; Fink, P.; Henningsen, P.; Löwe, B.; Rief, W.; on behalf of the EURONET-SOMA, Group. Functional somatic disorders: discussion paper for a new common classification for research and clinical use. BMC Med. 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, M. B. Central sensitivity syndromes: a new paradigm and group nosology for fibromyalgia and overlapping conditions, and the related issue of disease versus illness. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 37, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veasley, C. in Fibromyalgia Syndrome and Widespread Pain: From Construction to Relevant Recognition (eds Häuser, W. & Perrot, S.) 87–111 (Wolters Kluwer Health, 2018).
- Martinez-Lavin, M. Fibromyalgia as a sympathetically maintained pain syndrome. Curr. Pain. Headache Rep. 2004, 8, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Lavin, M. Biology and therapy of fibromyalgia. Stress, the stress response system, and fibromyalgia. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosek, E.; Kadetoff, D. Evidence of reduced sympatho-adrenal and hypothalamic-pituitary activity during static muscular work in patients with fibromyalgia. J. Rehabil. Med, 2010, 42, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Martínez, L. A.; Mora, T.; Vargas, A.; Fuentes-Iniestra, M.; Martínez-Lavín, M. Sympathetic Nervous System Dysfunction in Fibromyalgia, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, and Interstitial Cystitis. JCR J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 20, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanriverdi, F.; Karaca, Z.; Unluhizarci, K.; Kelestimur, F. “The hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis in chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia syndrome”. Stress. 2007, 10, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Schweinhardt, P. Dysfunctional neurotransmitter systems in fibromyalgia, their role in central stress circuitry and pharmacological actions on these systems. Pain Res Treat. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.A.; Clauw, D. J. “Understanding fibromyalgia: lessons from the broader pain research community”. Journal of Pain. 2009, 10, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyns, A.; Hendrix, J.; Lahousse, A.; De Bruyne, E.; Nijs, J.; Godderis, L.; Polli, A. The Biology of Stress Intolerance in Patients with Chronic Pain—State of the Art and Future Directions. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, R.; Mork, P.; Westgaard, R.; Rø, M.; Lundberg, U. Fibromyalgia syndrome is associated with hypocortisolism. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2010, 17, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fries, E.; Hesse, J.; Hellhammer, J. and Hellhammer D. H. “A new view on hypocortisolism,” Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2005, 30, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes del Paso, G. A.; Garcia-Hernandez, A.; Contreras-Merino, A. M.; Galvez-Sánchez, C. M.; de la Coba, P.; Montoro, C. I. , & Davydov, D. M. A two-component model of hair cortisol concentration in fibromyalgia: Independent effects of pain chronicity and severity. European Journal of Pain. 2024, 28, 821–830. [Google Scholar]
- Eller-Smith, O. C.; Nicol, A. L. & Christianson, J. A. Potential mechanisms underlying centralized pain and emerging therapeutic interventions. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Koenig, J.; Falvay, D.; Clamor, A.; Wagner, J.; Jarczok, M. N.; Ellis, R. J.; Weber, C.; Thayer, J. F. Pneumogastric (Vagus) Nerve Activity Indexed by Heart Rate Variability in Chronic Pain Patients Compared to Healthy Controls: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain. Physician. 2016, 19, E55–E78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying-Chih, C; Yu-Chen, H; Wei-Lieh H. Heart rate variability in patients with somatic symptom disorders and functional somatic syndromes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020, 112, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, G.; Troisi, G.; Pazzaglia, M.; Pascalis, V.; Casagrande, M. Heart Rate Variability and Pain: A Systematic Review. Brain. Sci. 2022, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, E; Nolty, A. A. T.; Amano, S. S.; Rizzo, A. A.; Buckwalter, J. G.; Rensberger, J. Heart Rate Variability as an Index of Resilience. Mil Med. 2020, 2, 363–369. [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen, T.; Dantoft, T. M.; Petersen, M.W.; Gormsen, L.; Winter-Jensen, M.; Fink, P; Linneberg, A.; Benros, M. E.; Eplov, L. F.; Bjerregaard, A. A.; Schovsbo, S. U.; Brinth, L. S. Is reduced heart rate variability associated with functional somatic disorders? A cross-sectional population-based study; DanFunD. BMJ Open. 2024, 14, e073909. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Martínez, L. A.; Mora, T.; Vargas, A.; Fuentes-Iniestra, M.; Martínez-Lavín, M. Sympathetic nervous system dysfunction in fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, and interstitial cystitis: a review of case-control studies. J Clin Rheumatol. 2014, 20, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes Del Paso, G. A.; Garrido, S.; Pulgar, A.; Martín-Vázquez, M.; & Duschek, S. Aberrances in autonomic cardiovascular regulation in fibromyalgia syndrome and their relevance for clinical pain reports. Psychosomatic medicine. 2010, 72, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeus, M.; Goubert, D.; De Backer, F.; Struyf, F.; Hermans, L.; Coppieters, I.; De Wandele, I.; Da Silva, H.; Calders, P. Heart rate variability in patients with fibromyalgia and patients with chronic fatigue syndrome: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 43, 279–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, L. M.; Ioannou, L.; Baker, K. S.; Gibson, S. J.; Georgiou-Karistianis, N.; Giumarra, M. J. Meta-analytic evidence for decreased heart rate variability in chronic pain implicating parasympathetic nervous system dysregulation. Pain. 2016, 157, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Manzano, C. F.; Lerma, C.; Echeverría, J. C.; Martínez-Lavin, M.; Martínez-Martínez, L. A.; Infante, O. & Guzmán-Vargas, L. Multifractal Analysis Reveals Decreased Non-linearity and Stronger Anticorrelations in Heart Period Fluctuations of Fibromyalgia Patients. Frontiers in physiology. 2018, 9, 1118. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes Del Paso, G. A. & de la Coba, P. Reduced activity, reactivity and functionality of the sympathetic nervous system in fibromyalgia: an electrodermal study. PLoS One. 2020, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Zetterman, T. , Markkula, R., Miettinen, T. et al. Heart rate variability responses to cognitive stress in fibromyalgia are characterised by inadequate autonomous system stress responses: a clinical trial. Sci Rep. 2023, 13, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M. W.; Schröder, A.; Jørgensen, T.; Ørnbøl, E.; Dantoft, T. M.; Eliasen, M.; Thuesen, B. H.; Fink, P. The unifying diagnostic construct of bodily distress syndrome (BDS) was confirmed in the general population. Journal of psychosomatic research. 2020, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M. W.; Schröder, A.; Jørgensen, T.; Ørnbøl, E.; Meinertz Dantoft, T.; Eliasen, M.; Benros, M. E.; Fink, P. Irritable bowel, chronic widespread pain, chronic fatigue and related syndromes are prevalent and highly overlapping in the general population: DanFunD. Sci Rep. 2020, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A. I.; Smyth, N.; Hall, S.J.; Torres, S. J.; Hussein, M.; Jayasinghe, S. U.; Ball, K.; Clow, A. J. Psychological stress reactivity and future health and disease outcomes: A systematic review of prospective evidence. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 114, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, S. N.; Carr, D. B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N. B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F. J.; Mogil, J. S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K. A.; Song, X. J.; Stevens, B.; Sullivan, M. D.; Tutelman, P. R.; Ushida, T.; Vader, K. The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain. 2020, 161, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A. M.; Geenen, R.; Wager, T. D.; Lumley, M. A.; Häuser, W.; Kosek, E.; Ablin, J. N.; Amris, K.; Branco, J.; Buskila, D.; Castelhano, J.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Crofford, L. J.; Fitzcharles, M. A.; López-Solà, M.; Luís, M.; Marques, T. R.; Mease, P. J.; Palavra, F.; Rhudy, J. L.; Uddin, L.Q.; Castilho, P.; Jacobs, J. W. G.; da Silva, J. A. P. Emotion regulation and the salience network: a hypothetical integrative model of fibromyalgia. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generaal, E.; Vogelzangs, N.; Macfarlane, GJ.; Geenen, R.; Smit, J. H.; de Geus, E. J.; Penninx, B. W.; Dekker, J. Biological stress systems, adverse life events and the onset of chronic multisite musculoskeletal pain: a 6-year cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016, 75, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavne, Y.; Amital, D.; Watad, A.; Tiosano, S.; Amital, H. A systematic review of precipitating physical and psychological traumatic events in the development of fibromyalgia. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2018, 48, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K. E.; Pollak, S. D. Early life stress and development: potential mechanisms for adverse outcomes. J Neurodev Disord. 2020, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cay, M.; Gonzalez-Heydrich, J.; Teicher, M. H.; van der Heijden, H.; Ongur, D.; Shinn, A. K.; Upadhyay, J. Childhood maltreatment and its role in the development of pain and psychopathology. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2022, 6, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R. R.; Dworkin, R. H.; Sullivan, M. D.; Turk, D. C.; Wasan, A. D. The Role of Psychosocial Processes in the Development and Maintenance of Chronic Pain. J Pain. 2016, 17, T70–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afari, N.; Ahumada, S. M.; Wright, L. J.; et al. Psychological trauma and functional somatic syndromes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychosom Med. 2014, 76, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holley, A.; Wilson, A.; Noel, M.; Palermo, T. Post-traumatic stress symptoms in children and adolescents with chronic pain: A topical review of the literature and a proposed framework for future research. European journal of pain. 2016, 20, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, S. J.; Kashikar-Zuck, S.; King, C.; Black, W.; Barnes, J.; Noll, J. G. Heightened risk of pain in young adult women with a history of childhood maltreatment: a prospective longitudinal study. Pain. 2020, 161, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S. M.; Cunningham, N. R.; Kashikar-Zuck, S. A conceptual framework for understanding the role of adverse childhood experiences in pediatric chronic pain. The Clinical journal of pain. 2017, 33, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrory, E; De Brito, S. A.; Viding, E. The impact of childhood maltreatment: a review of neurobiological and genetic factors. Front Psychiatry. 2011, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Nardi, A. E.; Karam, E. G.; Carta, M. G. Fibromyalgia patients should always be screened for post-traumatic stress disorder. Expert Rev Neurother. 2020, 20, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKernan, L. C.; Johnson, B. N.; Crofford, L. J.; Lumley, M. A.; Bruehl, S.; Cheavens, J. S. Posttraumatic Stress Symptoms Mediate the Effects of Trauma Exposure on Clinical Indicators of Central Sensitization in Patients With Chronic Pain. Clin J Pain. 2019, 35, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Vives, S.; Díaz-Marsá, M.; De la Vega, I.; Palomares, N.; Vázquez, S.; López-Villatoro, J. M.; Palomo, T. & Carrasco, J. L. Hypothalamic-pituitary axis response to a 0.25-MG dexamethasone test in women with fibromyalgia. Stress (Amsterdam, Netherlands). 2020, 23, 284–289. [Google Scholar]
- Bowlby, J. Attachment and Loss: 1. Attachment. London: Hogarth Press. 1969.
- Bartholomew, K. and Horowitz L. M. “Attachment styles among young adults: a test of a four-category model”. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1991, 61, 226–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrtička, P. , & Vuilleumier, P. Neuroscience of human social interactions and adult attachment style. Frontiers in human neuroscience. 2012, 6, 212. [Google Scholar]
- Gander, M.; Karabatsiakis, A.; Nuderscher, K.; Bernheim, D.; Doyen-Waldecker, C. , & Buchheim, A. Secure Attachment Representation in Adolescence Buffers Heart-Rate Reactivity in Response to Attachment-Related Stressors. Frontiers in human neuroscience. 2022, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, R. What is resilience: an affiliative neuroscience approach. World psychiatry : official journal of the World Psychiatric Association (WPA). 2020, 19, 132–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R. A.; Hutanamon, T. Activating attachments enhances heart rate variability. PLoS One. 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gander, M.; &, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Buchheim, A. Attachment classification, psychophysiology and frontal EEG asymmetry across the lifespan: a review. Frontiers in human neuroscience. 2015, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietromonaco, P. R.; Powers, S. I. Attachment and Health-Related Physiological Stress Processes. Curr Opin Psychol. 2015, 1, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, L.; Rossignoli, M.; Delfino-Pereira, P.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; de Lima Umeoka, E. A. Comprehensive Overview on Stress Neurobiology: Basic Concepts and Clinical Implications. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietromonaco, P. R. , Uchino, B., Dunkel Schetter, C. Close relationship processes and health: implications of attachment theory for health and disease. Health Psychol. 2013, 32, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosmans, G.; Borelli, J. L. Attachment and the Development of Psychopathology: Introduction to the Special Issue. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, P.; Ownsworth, T.; Strong, J. A review of the evidence linking adult attachment theory and chronic pain: Presenting a conceptual model. Clin Psychol Rev. 2008, 28, 407–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, L. A. Adult attachment insecurity is positively associated with medically unexplained chronic pain. Eur J Pain. 2017, 21, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, A.; Tesio, V.; Castelnuovo, G.; Castelli, L. Attachment Style and Chronic Pain: Toward an Interpersonal Model of Pain. Front Psychol. 2017, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K. A.; Macfarlane, G. J.; McBeth, J.; Morriss, R.; Dickens, C. Insecure attachment style is associated with chronic widespread pain. Pain. 2009, 143, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, L. A. , & Asmundson, G. J. The relationship of adult attachment dimensions to pain-related fear, hypervigilance, and catastrophizing. Pain. 2007, 127, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Meredith, P. J. A review of the evidence regarding associations between attachment theory and experimentally induced pain. Current pain and headache reports. 2013, 17, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñacoba, C.; Perez-Calvo, S.; Blanco, S. , & Sanroman, L. Attachment styles, pain intensity and emotional variables in women with fibromyalgia. Scandinavian journal of caring sciences. 2018, 32, 535–544. [Google Scholar]
- Romeo, A.; Di Tella, M.; Ghiggia, A.; Tesio, V.; Fusaro, E.; Geminiani, G. C.; Castelli, L. Attachment style and parental bonding: Relationships with fibromyalgia and alexithymia. PLoS One. 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puşuroğlu, M.; Topaloğlu, M. S.; Hocaoğlu, Ç.; Yıldırım, M. Expressing emotions, rejection sensitivity, and attachment in patients with fibromyalgia. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2023, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, C.; Vismara, L.; Brennstuhl, M. J.; Tarquinio, C.; Lucarelli, L. Adult attachment styles, self-esteem, and quality of life in women with fibromyalgia. Health Psychol Open. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, C.; Lucarelli, L.; Vismara, L. Depressive Symptoms and Quality of Life in a Sample of Italian Women with a Diagnosis of Fibromyalgia: The Role of Attachment Styles. Depress Res Treat. 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobloch, H. S.; Grinevich, V. Evolution of oxytocin pathways in the brain of vertebrates. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, R.; Monakhov, M.; Pratt, M. & Ebstein, R. P. Oxytocin Pathway Genes: Evolutionary Ancient System Impacting on Human Affiliation, Sociality, and Psychopathology. Biological psychiatry 2016, 79, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wee, C. L.; Nikitchenko, M.; Wang, W. C.; Luks-Morgan, S. J.; Song, E.; Gagnon, J. A.; Randlett, O.; Bianco, I. H.; Lacoste, A. M. B.; Glushenkova, E.; Barrios, J. P.; Schier, A. F.; Kunes, S.; Engert, F.; Douglass, A. D. Zebrafish oxytocin neurons drive nocifensive behavior via brainstem premotor targets. Nat Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1477–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, R. The adaptive human parental brain: implications for children’s social development. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliava, M.; Melchior, M.; Knobloch-Bollmann, H. S.; Wahis, J.; da Silva Gouveia, M.; Tang, Y.; Ciobanu, A. C.; Triana Del Rio, R.; Roth, L. C.; Althammer, F.; Chavant, V.; Goumon, Y.; Gruber, T.; Petit-Demoulière, N.; Busnelli, M.; Chini, B.; Tan, L. L.; Mitre, M.; Froemke, R. C.; Chao, M. V.; Giese, G.; Sprengel, R.; Kuner, R.; Poisbeau, P.; Seeburg, P. H.; Stoop, R.; Charlet, A.; Grinevich, V. A New Population of Parvocellular Oxytocin Neurons Controlling Magnocellular Neuron Activity and Inflammatory Pain Processing. Neuron. 2016, 16, 1291–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knobloch, H. S.; Charlet, A.; Hoffmann, L. C.; Eliava, M.; Khrulev, S.; Cetin, A. H.; Osten, P.; Schwarz, M. K.; Seeburg, P. H.; Stoop, R. , & Grinevich, V. Evoked axonal oxytocin release in the central amygdala attenuates fear response. Neuron. 2012, 73, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poisbeau, P.; Grinevich, V. & Charlet A. Oxytocin Signaling in Pain: Cellular, Circuit, System, and Behavioral Levels. Chapter in Current topics in behavioral neurosciences 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L. N.; Chen, K.; Yin, X. P.; Liu, D.; Zhu, L. Q. The Comprehensive Neural Mechanism of Oxytocin in Analgesia. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ridder, D.; Adhia, D. & Vanneste, S. The anatomy of pain and suffering in the brain and its clinical implications. Neuroscience and biobehavioral reviews. 2021, 130, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aygün, O.; Mohr, E.; Duff, C.; Matthew, S.; Schoenberg, P. Oxytocin Modulation in Mindfulness-Based Pain Management for Chronic Pain. Life (Basel). 2024, 14, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayanagi, Y.; Onaka, T. Roles of Oxytocin in Stress Responses, Allostasis and Resilience. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 23, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, F. Fibromyalgianess. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 715–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häuser, W.; Schmutzer, G.; Brähler, E. & Glaesmer, H. A cluster within the continuum of biopsychosocial distress can be labeled “fibromyalgia syndrome” — evidence from a representative German population survey. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 2806–2812. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe, F.; Brähler, E.; Hinz, A. & Häuser, W. Fibromyalgia prevalence, somatic symptom reporting, and the dimensionality of polysymptomatic distress: results from a survey of the general population. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 777–785. [Google Scholar]
- Grayston, R.; Czanner, G.; Elhadd, K.; Goebel, A.; Frank, B.; Üçeyler, N.; Malik, R. A.; Alam, U. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of small fiber pathology in fibromyalgia: Implications for a new paradigm in fibromyalgia etiopathogenesis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 48, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S. J.; Enders, J.; Kaiser, A.; Rovenstine, L.; Heslop, L.; Hauser, W.; Chadwick, A.; Wright, D. E. Abnormal Intraepidermal Nerve Fiber Density in Disease: A Scoping Review. Front Neurol. 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.; Rapteas, L.; Burgess, J.; Riley, D.; Anson, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Bennett, A.; Kaye, S.; Marshall, A.; Dunham, J.; Fallon, N.; Zhao, S. S.; Pritchard, A.; Goodson, N.; Malik, R. A.; Goebel, A.; Frank, B.; Alam, U. Small fibre pathology, small fibre symptoms and pain in fibromyalgia syndrome. Sci Rep. 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harte, S. E.; Clauw, D. J.; Hayes, J. M.; Feldman, E. L.; St Charles, I. C.; Watson, C. J. Reduced intraepidermal nerve fiber density after a sustained increase in insular glutamate: a proof-of-concept study examining the pathogenesis of small fiber pathology in fibromyalgia. Pain Rep. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Lavín, M. Dorsal root ganglia: fibromyalgia pain factory? Clin Rheumatol. 2021, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, A; Krock, E. ; Gentry, C.; Israel, M. R.; Jurczak, A.; Urbina, C. M.; Sandor, K.; Vastani, N.; Maurer, M.; Cuhadar, U.; Sensi, S.; Nomura, Y.; Menezes, J.; Baharpoor, A.; Brieskorn, L.; Sandström, A.; Tour, J.; Kadetoff, D., Haglund, L.; Kosek, E.; Bevan, S.; Svensson, C. I.; Andersson, D. A. Passive transfer of fibromyalgia symptoms from patients to mice. J Clin Invest. 2021, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Liptan, G. The widespread myofascial pain of fibromyalgia is sympathetically maintained and immune mediated. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2023, 35, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, M.; Guerra-Juárez, A.; Miyake, D. Y.; Sebastian-Arellano, C.; Estrada-Mata, A. G.; González-Moyotl, N. J.; Rodríguez-Aguayo, A. M.; Martínez-Lavin, M.; Martínez-Martínez, L. A. Correlation Between Corneal Nerve Density and Symptoms of Small Fiber Neuropathy in Patients With Fibromyalgia: The Confounding Role of Severe Anxiety or Depression. J Clin Rheumatol. 2021, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänsch, S.; Evdokimov, D.; Egenolf, N.; Meyer Zu Altenschildesche, C.; Kreß, L.; Üçeyler, N. Distinguishing fibromyalgia syndrome from small fiber neuropathy: a clinical guide. Pain Rep. 2024, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üçeyler, N.; Zeller, D.; Kahn, A. K.; Kewenig, S.; Kittel-Schneider, S.; Schmid, A.; Casanova-Molla, J.; Reiners, K.; Sommer, C. Small fibre pathology in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Brain. 2013, 136, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, V. K.; Perl, E. R. Sensory receptors with unmyelinated (C) fibers innervating the skin of the rabbit’s ear. J. Neurophysiol. 1985, 54, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, S. N.; Crepps, B.A.; Perl, E. R. . Relationship of substance P to afferent characteristics of dorsal root ganglion neurones in guinea-pig. J. Physiol. 1997, 505, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, M. Low-threshold mechanoreceptive and nociceptive units with unmyelinated (C) fibres in the human supraorbital nerve. J Physiol. 1990, 426, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallbo, A. B.; Olausson, H.; and Wessberg, J. Unmyelinated afferents constitute a second system coding tactile stimuli of the human hairy skin. J. Neurophysiol. 1999, 81, 2753–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallbo, Å. B.; Olausson, H.; Wessberg, J. Pleasant touch. In: Encyclopedia of neuroscience (Squire LR, ed). Amsterdam: Elsevier. 2009.
- Schirmer, A.; Croy, I.; Ackerley, R. What are C-tactile afferents and how do they relate to “affective touch”? Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerley, R. C-tactile (CT) afferents: Evidence of their function from microneurography studies in humans. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2022, 43, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, L. K.; Čeko, M.; Gracely, J. L.; Richards, E. A.; Olausson, H.; Bushnell, M. C. Touch Perception Altered by Chronic Pain and by Opioid Blockade. eNeuro. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehme, R.; van Ettinger-Veenstra, H.; Olausson.; H, Gerdle, B.; Nagi, S. S. Anhedonia to Gentle Touch in Fibromyalgia: Normal Sensory Processing but Abnormal Evaluation. Brain Sci. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapp, H. S.; Sabatowski, R.; Weidner, K.; Croy, I.; Gossrau, G. C-tactile touch perception in migraineurs - a case-control study. Cephalalgia. 2020, 40, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nees, F.; Usai, K.; Löffler, M.; Flor, H. The evaluation and brain representation of pleasant touch in chronic and subacute back pain. Neurobiol Pain. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossrau, G.; Klimova, A.; Lapp, H. S.; Frost, M.; Peschel, E.; Weidner, K.; Koch, T.; Sabatowski, R.; Croy, I. C-tactile touch perception in patients with chronic pain disorders. Pain Rep. 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, V. F.; Karlsson, P.; Drummond, P. D.; Schaldemose, E. L.; Terkelsen, A. J.; Jensen, T. S.; Knudsen, L. F. Bilaterally Reduced Intraepidermal Nerve Fiber Density in Unilateral CRPS-I. Pain Med. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusaro, M.; Bufacchi, R.J.; Nicolardi, V.; Provenzano, L. The analgesic power of pleasant touch in individuals with chronic pain: Recent findings and new insights. Front Integr Neurosci. 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, M. and Nagi S. S. Role of C-tactile fibers in pain modulation: animal and human perspectives. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences 2022, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Liljencrantz, J.; Strigo, I.; Ellingsen, D. M.; Krämer, H. H.; Lundblad, L. C.; Nagi S., S.; Leknes, S.; Olausson, H. Slow brushing reduces heat pain in humans. Eur J Pain. 2017, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delfini, M. C.; Mantilleri, A.; Gaillard, S.; Hao, J.; Reynders, A.; Malapert, P.; Alonso, S.; François, A.; Barrere, C.; Seal, R.; Landry, M.; Eschallier, A.; Alloui, A.; Bourinet, E.; Delmas, P.; Le Feuvre, Y.; Moqrich, A. TAFA4, a chemokine-like protein, modulates injury-induced mechanical and chemical pain hypersensitivity in mice. Cell Rep. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S. C.; Trotter, P. D.; Swaney, W. T.; Marshall, A. , and Mcglone, F. P. C-tactile afferents: Cutaneous mediators of oxytocin release during affiliative tactile interactions? Neuropeptides. 2017a, 64, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lernia, D.; Cipresso, P.; Pedroli, E. , and Riva, G. Toward an embodied medicine: A portable device with programmable interoceptive stimulation for heart rate variability enhancement. Sensors. 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nummenmaa, L.; Tuominen, L.; Dunbar, R.; Hirvonen, J.; Manninen, S.; Arponen, E.; et al. Social touch modulates endogenous μ-opioid system activity in humans. Neuroimage. 2016, 138, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, L. L.; Ruis, C.; van der Smagt, M. J.; Scherder, E. J. and Dijkerman, H. C. Neural basis of affective touch and pain: A novel model suggests possible targets for pain amelioration. J. Neuropsychol. 2022, 16, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidanza, F.; Polimeni, E.; Pierangeli, V.; Martini, M. A Better Touch: C-tactile Fibers Related Activity is Associated to Pain Reduction During Temporal Summation of Second Pain. J Pain. 2021, 22, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashmi, J. A.; Baliki, M. N.; Huang, L.; Baria, A. T.; Torbey, S.; Hermann, K. M.; Schnitzer, T. J.; Apkarian, A. V. Shape shifting pain: chronification of back pain shifts brain representation from nociceptive to emotional circuits. Brain. 2013, 136, 2751–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habig, K.; Schänzer, A.; Schirner, W.; Lautenschläger, G.; Dassinger, B. , Olausson, H.; Birklein, F.; Gizewski, E. R.; Krämer, H. H. Low threshold unmyelinated mechanoafferents can modulate pain. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habig, K.; Lautenschläger, G.; Maxeiner, H.; Birklein, F.; Krämer, H. H.; Seddigh, S. Low mechano-afferent fibers reduce thermal pain but not pain intensity in CRPS. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lernia, D.; Lacerenza, M.; Ainley, V.; Riva, G. Altered Interoceptive Perception and the Effects of Interoceptive Analgesia in Musculoskeletal, Primary, and Neuropathic Chronic Pain Conditions. J Pers Med. 2020, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsburgh, A.; Summers, S. J.; Lewis, A.; Keegan, R. J.; Flood, A. The Relationship Between Pain and Interoception: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Pain. 2024, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croy, I.; Fairhurst, M. T. , and McGlone, F. The role of C-tactile nerve fibers in human social development. Curr. Op. Behav. Sci. 2022, 43, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, I. ALE meta-analysis reveals dissociable networks for affective and discriminative aspects of touch. Hum Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, W.; Kendrick, K. M. Affective touch in the context of development, oxytocin signaling, and autism. Front Psychol. 2022, 23, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystrova, K. Novel mechanism of human fetal growth regulation: a potential role of lanugo, vernix caseosa and a second tactile system of unmyelinated low-threshold C-afferents. Med Hypotheses. 2009, 72, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, R.; Eidelman, A. I.; Sirota, L., and Weller, A. Comparison of skin-to-skin and traditional care: parenting outcomes and preterm infant development. Pediatrics. 2001, 110, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Jefferies, A. L. Kangaroo care for the preterm infant and family. Paediatr. Child Health. 2012, 17, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bystrova, K.; Widström, A. M.; Matthiesen, A. S.; Ransjö-Arvidson AB, Welles-Nyström B, Wassberg C, Vorontsov I, Uvnäs-Moberg K. Skin-to-skin contact may reduce negative consequences of “the stress of being born”: a study on temperature in newborn infants, subjected to different ward routines in St. Petersburg. Acta Paediatr. 2003, 92, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Puyvelde, M.; Collette, L.; Gorissen, A. S.; Pattyn, N.; McGlone, F. Infants Autonomic Cardio- Respiratory Responses to Nurturing Stroking Touch Delivered by the Mother or the Father. Front Physiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzotti, A.; Cerritelli, F.; Esteves, J. E.; Lista, G.; Lombardi, E.; La Rocca, S.; Gallace, A.; McGlone, F. P.; Walker, S. C. Dynamic touch reduces physiological arousal in preterm infants: A role for c-tactile afferents? Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2019, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gursul, D.; Goksan, S.; Hartley, C.; Schmidt Mellado, G.; Moultrie, F.; Hoskin, A.; Adams, E.; Hathway, G.; Walker, S.; McGlone, F and Slater R. Stroking modulates noxious-evoked brain activity in human infants. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R1380–R1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carozza, S.; Leong, V. The Role of Affectionate Caregiver Touch in Early Neurodevelopment and Parent-Infant Interactional Synchrony. Front Neurosci 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P. Y.; Chiu, Y. M.; Yu, J. H.; Chen, S. K. Mapping Central Projection of Oxytocin Neurons in Unmated Mice Using Cre and Alkaline Phosphatase Reporter. Front Neuroanat. 2020, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvnäs-Moberg, K. , and Petersson, M. Physiological effects induced by stimulation of cutaneous sensory nerves, with a focus on oxytocin. Curr. Op. Behav. Sci. 2022, 43, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Bharadwaj, V. N.; Tzabazis, A. Z.; Klukinov, M.; Manering, N. A.; Yeomans, D. C. Intranasal Administration for Pain: Oxytocin and Other Polypeptides. Pharmaceutics. 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvnäs-Moberg, K.; Handlin, L. , and Petersson, M. Self-soothing behaviors with particular reference to oxytocin release induced by non-noxious sensory stimulation. Front. Psychol. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlone, F.; Wessberg, J.; Olausson, H. Discriminative and affective touch: sensing and feeling. Neuron. 2014, 82, 737–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Funato, H. Physical contact in parent-infant relationship and its effect on fostering a feeling of safety. iScience. 2021, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Miao, W.; Ji, E.; Huang, S.; Jin, S.; Zhu, X.; Liu, M. Z.; Sun, Y. G.; Xu, F.; Yu, X. Social touch-like tactile stimulation activates a tachykinin 1-oxytocin pathway to promote social interactions. Neuron. 2022, 110, 1051–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucsea, O.; Pillai Riddell, R. Non-pharmacological pain management in the neonatal intensive care unit: Managing neonatal pain without drugs. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failo, A.; Giannotti, M.; Venuti, P. Associations between attachment and pain: From infant to adolescent. SAGE Open Med. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Lavín, M. Imbalance of threat and soothing systems in fibromyalgia: rephrasing an established mechanistic model? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuffini, R.; Cofini, V.; Muselli, M.; Necozione, S.; Piroli, A.; Marrelli, A. Emotional arousal and valence in patients with fibromyalgia: a pilot study. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeček, M.; Dabrowska, J. Oxytocin facilitates adaptive fear and attenuates anxiety responses in animal models and human studies-potential interaction with the corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) system in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST). Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 375, 143–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, C. L.; Nikitchenko, M.; Wang, W. C.; Luks-Morgan, S. J.; Song, E.; Gagnon, J. A.; Randlett, O.; Bianco, I. H.; Lacoste, A. M. B.; Glushenkova, E.; Barrios, J. P.; Schier, A. F.; Kunes, S.; Engert, F.; Douglass, A. D. Zebrafish oxytocin neurons drive nocifensive behavior via brainstem premotor targets. Nat Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1477–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinevich, V.; Neumann, I. D. Brain oxytocin: how puzzle stones from animal studies translate into psychiatry. Mol Psychiatry. 2021, 26, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliava, M.; Melchior, M.; Knobloch-Bollmann, H. S.; Wahis, J.; da Silva Gouveia, M.; Tang, Y.; Ciobanu, A. C.; Triana Del Rio, R.; Roth, L. C.; Althammer, F.; Chavant, V.; Goumon, Y.; Gruber, T.; Petit-Demoulière, N.; Busnelli, M.; Chini, B.; Tan, L. L.; Mitre, M.; Froemke, R. C.; Chao, M. V.; Giese, G.; Sprengel, R.; Kuner, R.; Poisbeau, P.; Seeburg, P. H.; Stoop, R.; Charlet, A.; Grinevich, V. A New Population of Parvocellular Oxytocin Neurons Controlling Magnocellular Neuron Activity and Inflammatory Pain Processing. Neuron. 2016, 89, 1291–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friuli, M.; Eramo, B.; Valenza, M.; Scuderi, C.; Provensi, G.; Romano, A. Targeting the Oxytocinergic System: A Possible Pharmacological Strategy for the Treatment of Inflammation Occurring in Different Chronic Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J. H.; Espinera, A. R.; Chen, D.; Choi, K. E.; Caslin, A. Y.; Won, S.; Pecoraro, V.; Xu, G. Y.; Wei, L.; Yu, S. P. Neonatal inflammatory pain and systemic inflammatory responses as possible environmental factors in the development of autism spectrum disorder of juvenile rats. J Neuroinflammation. 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onaka, T.; Takayanagi, Y. The oxytocin system and early-life experience-dependent plastic changes. J Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrory, E.; De Brito, S. A.; Viding, E. The impact of childhood maltreatment: a review of neurobiological and genetic factors. Front Psychiatry. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagi, S. S.; Rubin, T. K.; Chelvanayagam, D. K.; Macefield, V. G.; Mahns, D. A. Allodynia mediated by C-tactile afferents in human hairy skin. J Physiol. 2011, 589, 4065–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagi, S. S.; Mahns, D. A. Mechanical allodynia in human glabrous skin mediated by low-threshold cutaneous mechanoreceptors with unmyelinated fibres. Exp Brain Res. 2013, 231, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodin, B. R.; Ness, T. J.; Robbins, M. T. Oxytocin - a multifunctional analgesic for chronic deep tissue pain. Curr Pharm Des. 2015, 21, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhael, A. A.; Bent, J. E. , Fawcett, J. M., Campbell, T. S., Aguirre-Camacho, A., Farrell, A., & Rash, J. A. Evaluating the efficacy of oxytocin for pain management: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials and observational studies. Canadian journal of pain = Revue canadienne de la douleur 2023, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Mameli, S.; Pisanu, G. M.; Sardo, S.; Marchi, A.; Pili, A.; Carboni, M.; Minerba, L.; Trincas, G.; Carta, M. G.; Melis, M. R.; Agabio, R. Oxytocin nasal spray in fibromyalgic patients. Rheumatol Int. 2014, 34, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porges, S. W.; Davila, M. I.; Lewis, G. F.; et al. Autonomic regulation of preterm infants is enhanced by Family Nurture Intervention. Dev Psychobiol. 2019, 61, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler Iii, G.; Rojas, A. M.; Worts, P. R.; Flynn, H. A. Utilizing Multidisciplinary Medicine in Pain Management: A Narrative Review. Pain Physician. 2021, 24, 369–378. [Google Scholar]
| Organ system | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| The nervous system | depression, thinking or remembering problems, numbness/tingling, nervousness, seizures, hearing difficulties, headache, dizziness, insomnia, blurred vision, ringing in ears |
| The gastrointestinal system | pain/cramps in the abdomen, constipation, pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, diarrhea, loss of appetite, loss of/change in taste, vomiting, oral ulcers, heartburn |
| The immune system | rash, sun sensitivity, easy bruising, dry eyes, fever, dry mouth, Raynaud’s phenomenon, itching, hives/welts |
| The musculoskeletal system | muscle pain, fatigue/tiredness, muscle weakness |
| The urinary system | bladder spasms, painful urination, frequent urination |
| The respiratory system | chest pain, shortness of breath, wheezing |
| The integumentary system | hair loss |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




