Submitted:
13 June 2024
Posted:
14 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Expert Systems
- Knowledge base: Stores expert knowledge and can be divided into short-term and long-term memory. The long-term memory stores rules representing heuristic knowledge of human experts. Whereas the short-term memory corresponds to a database in which the facts used by the rules are stored or removed.
- Inference engine: Emulates the reasoning of human experts by utilizing the knowledge stored in the knowledge base. It matches the facts from the short-term memory with the rules from long-term memory to draw conclusions or solve problems.
- User interface: Serves as the communication environment between the user and the ES.
- Explanation module: Clarifies the reasoning performed by the inference engine to make it comprehensible for the user and thus increase its credibility and acceptance.
- Knowledge acquisition module: Enables updating the knowledge base with new content while the ES is already deployed.
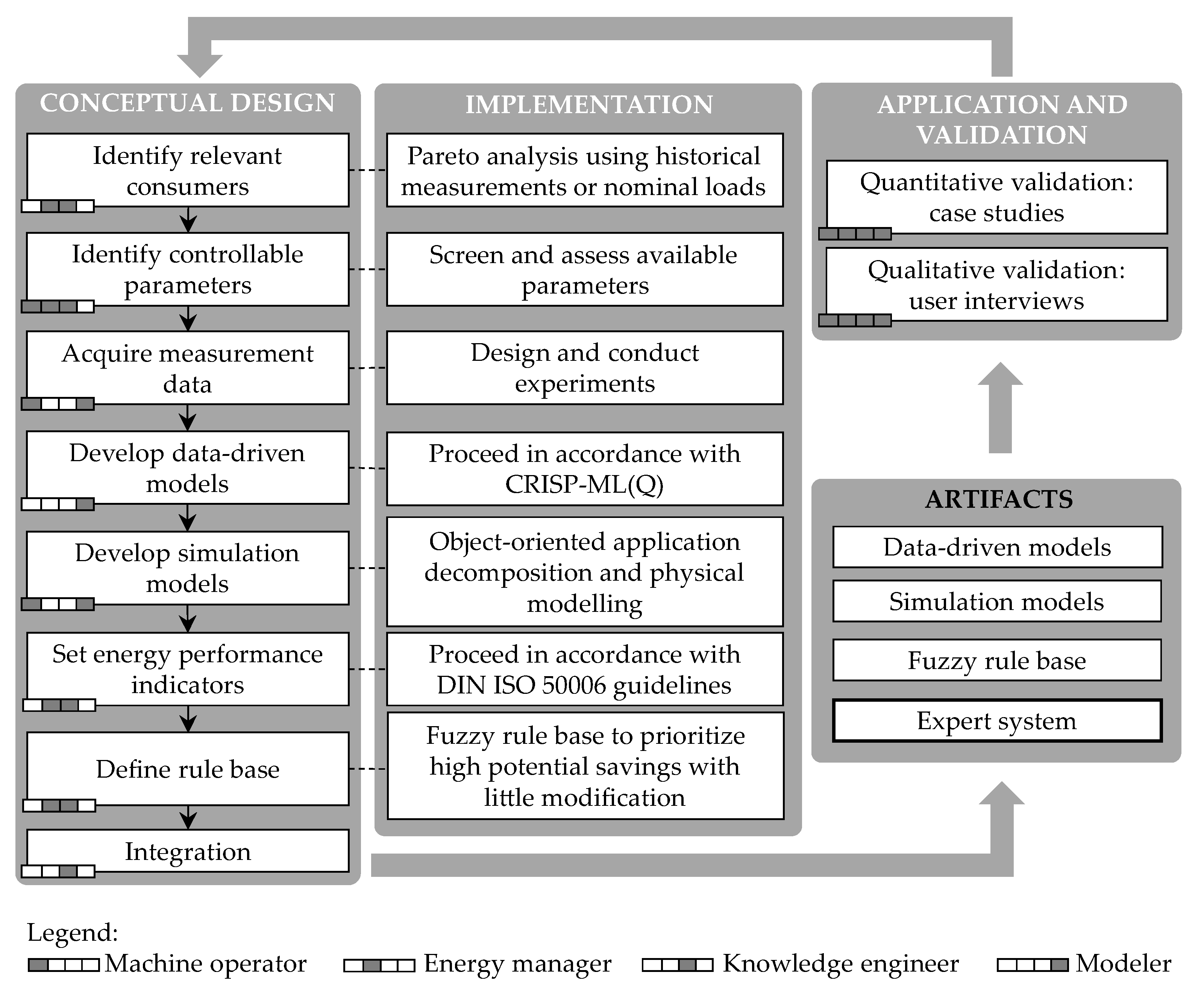
3. Methodology
3.1. Personas and Description
3.2. Methodological Framework
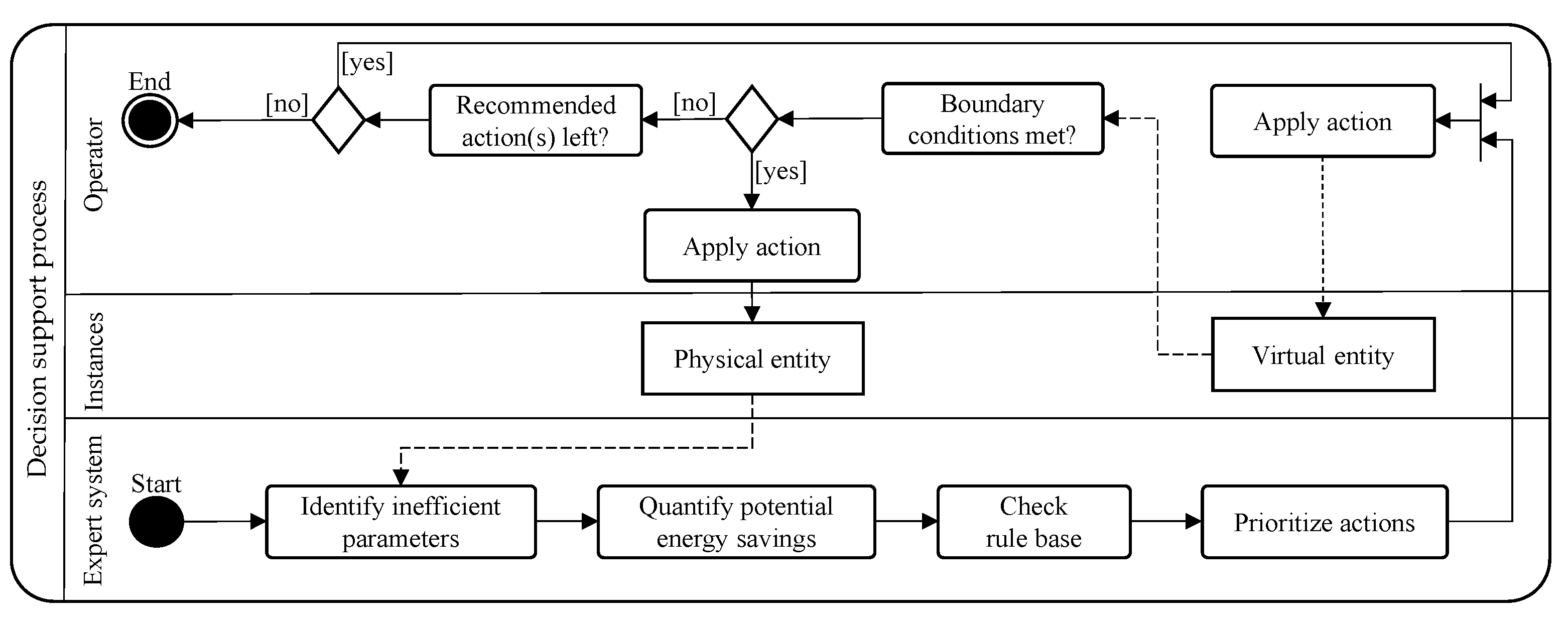
3.3. Decision Support Process
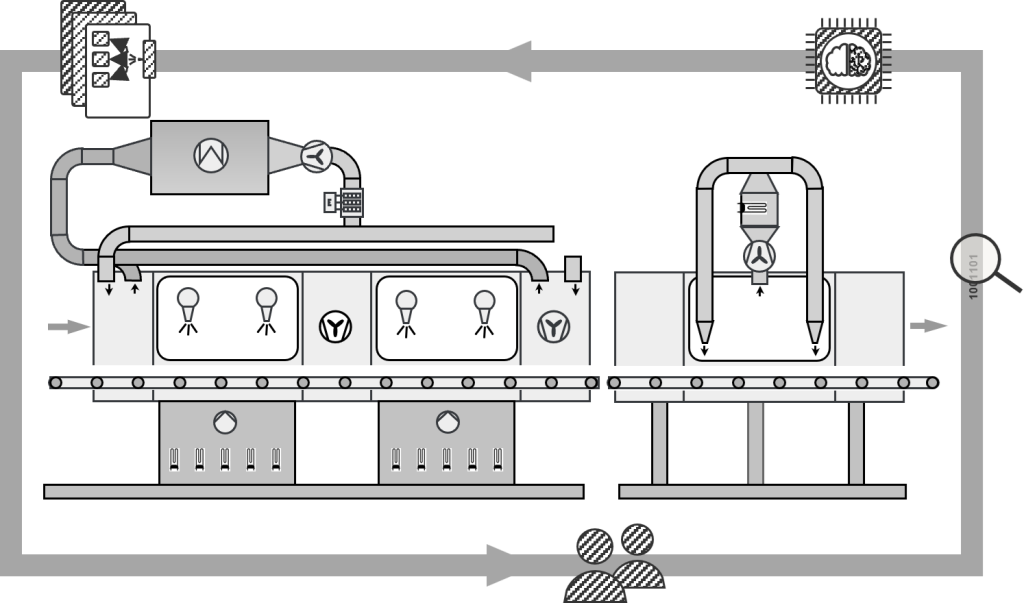
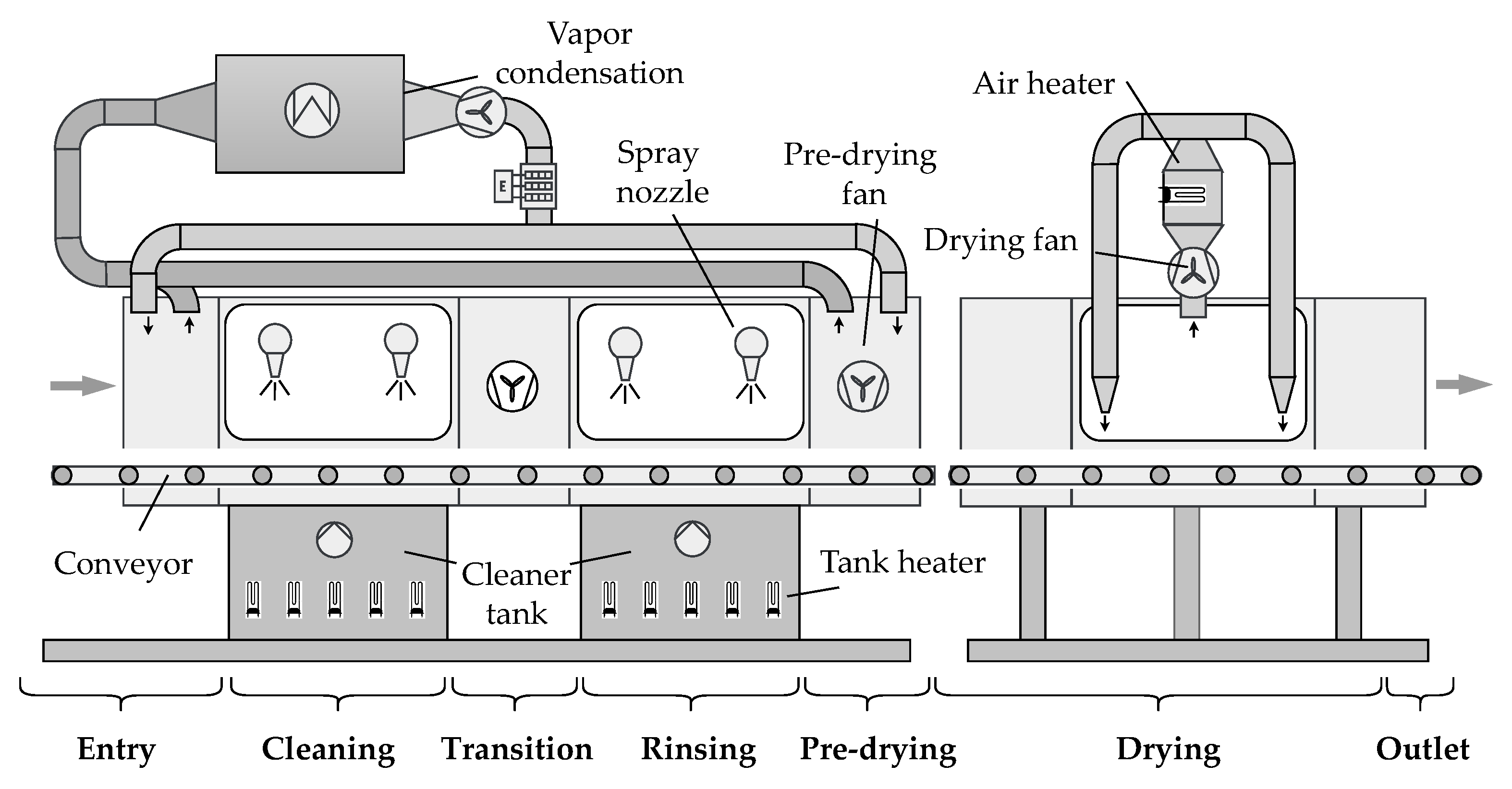
4. Case study: Throughput Cleaning Machine
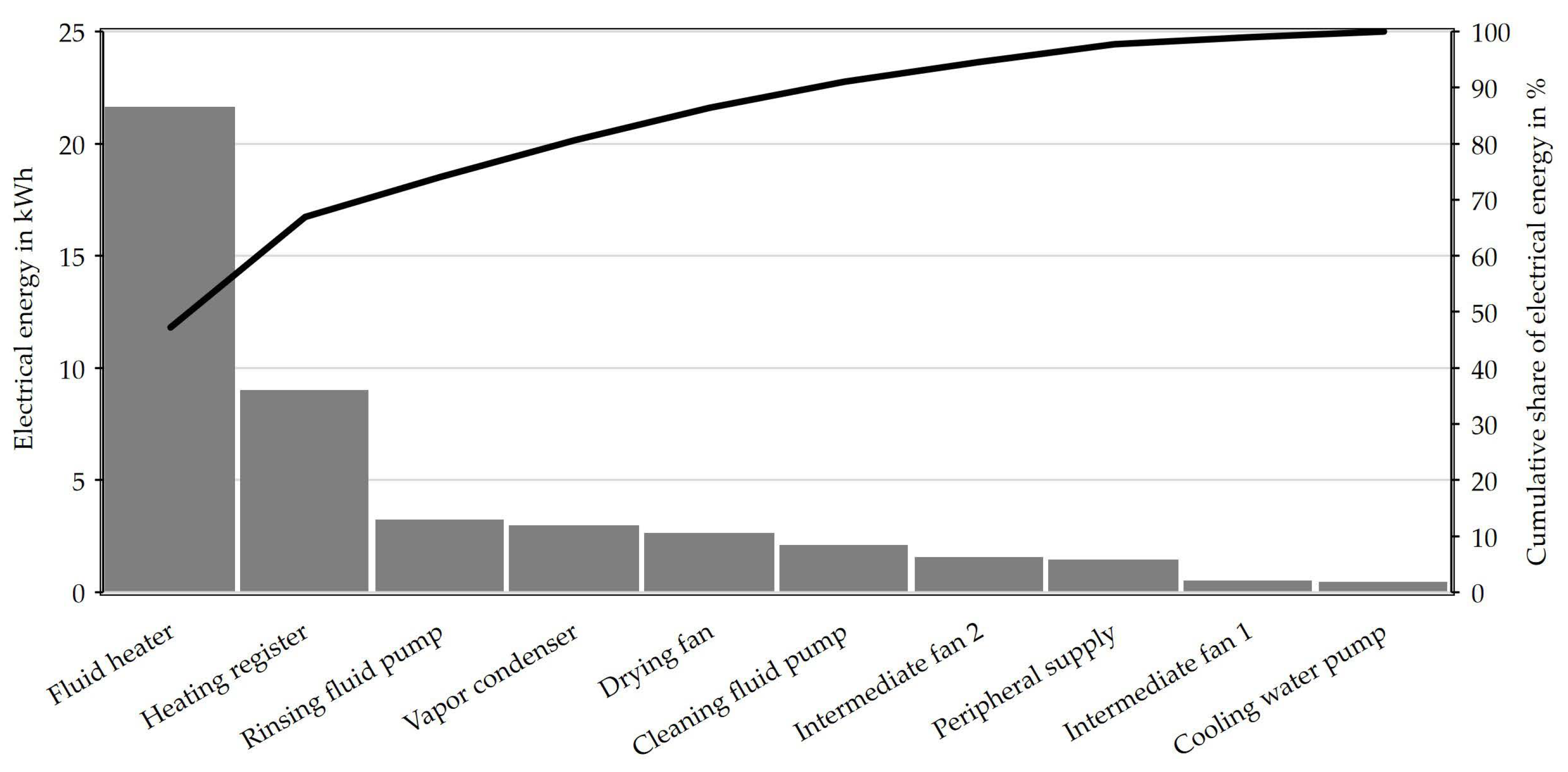
4.1. Relevant Consumers and Controllable Parameters
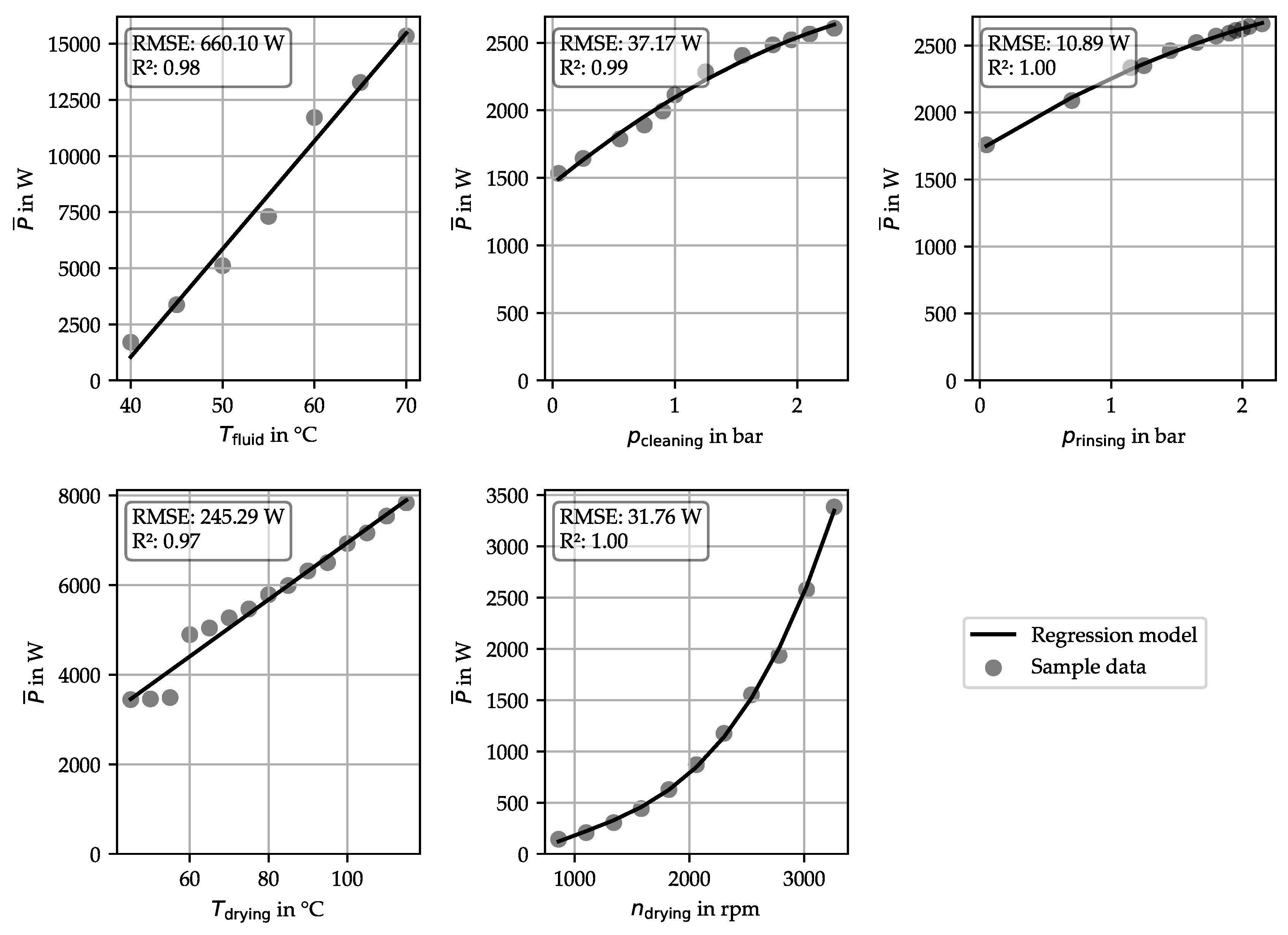
4.2. Data Acquisition and Development of Data-Driven Models
4.3. Development of the Simulation Model
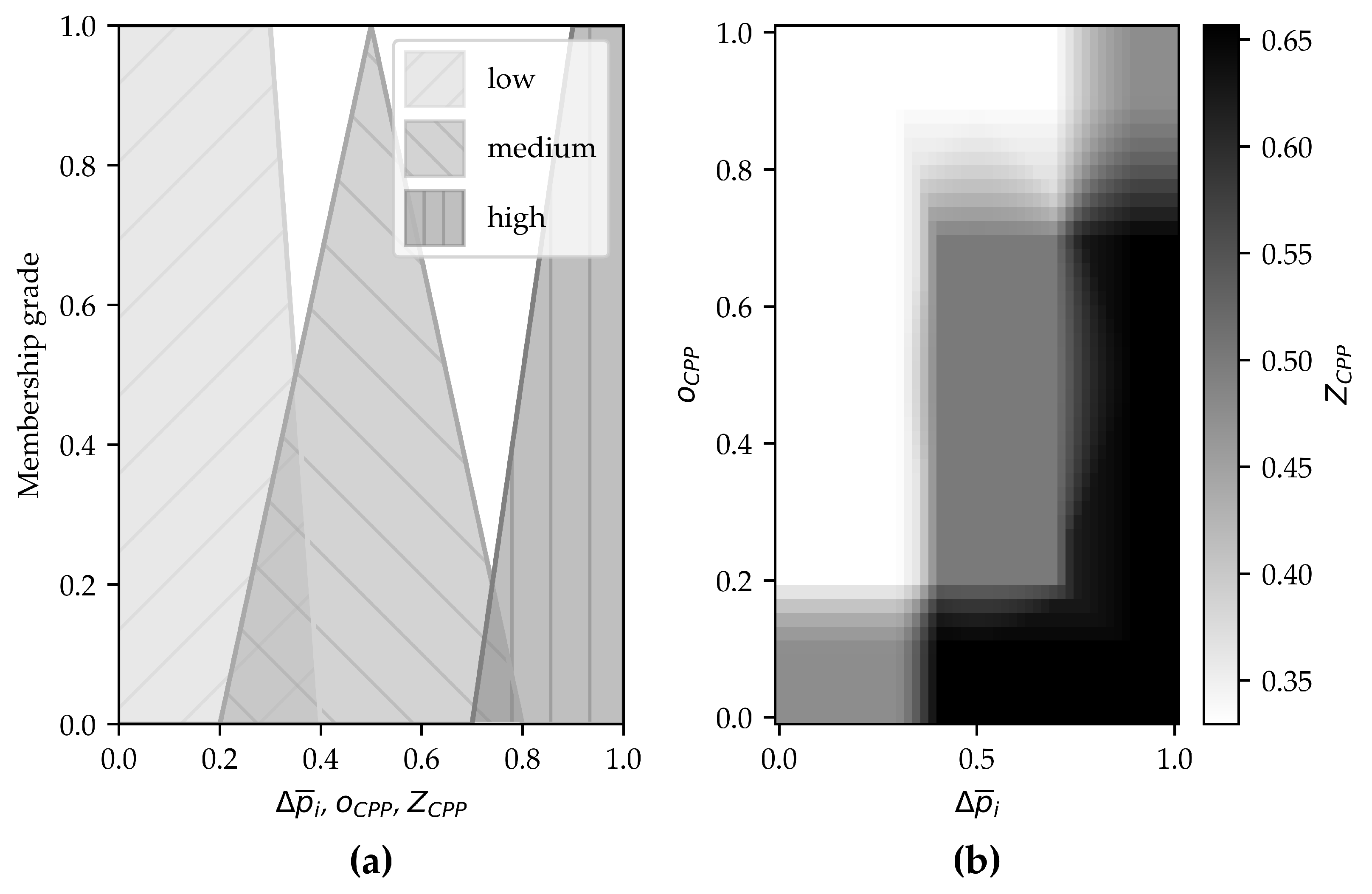
4.4. Energy Performance Indicators and Rule Base
4.5. Integration
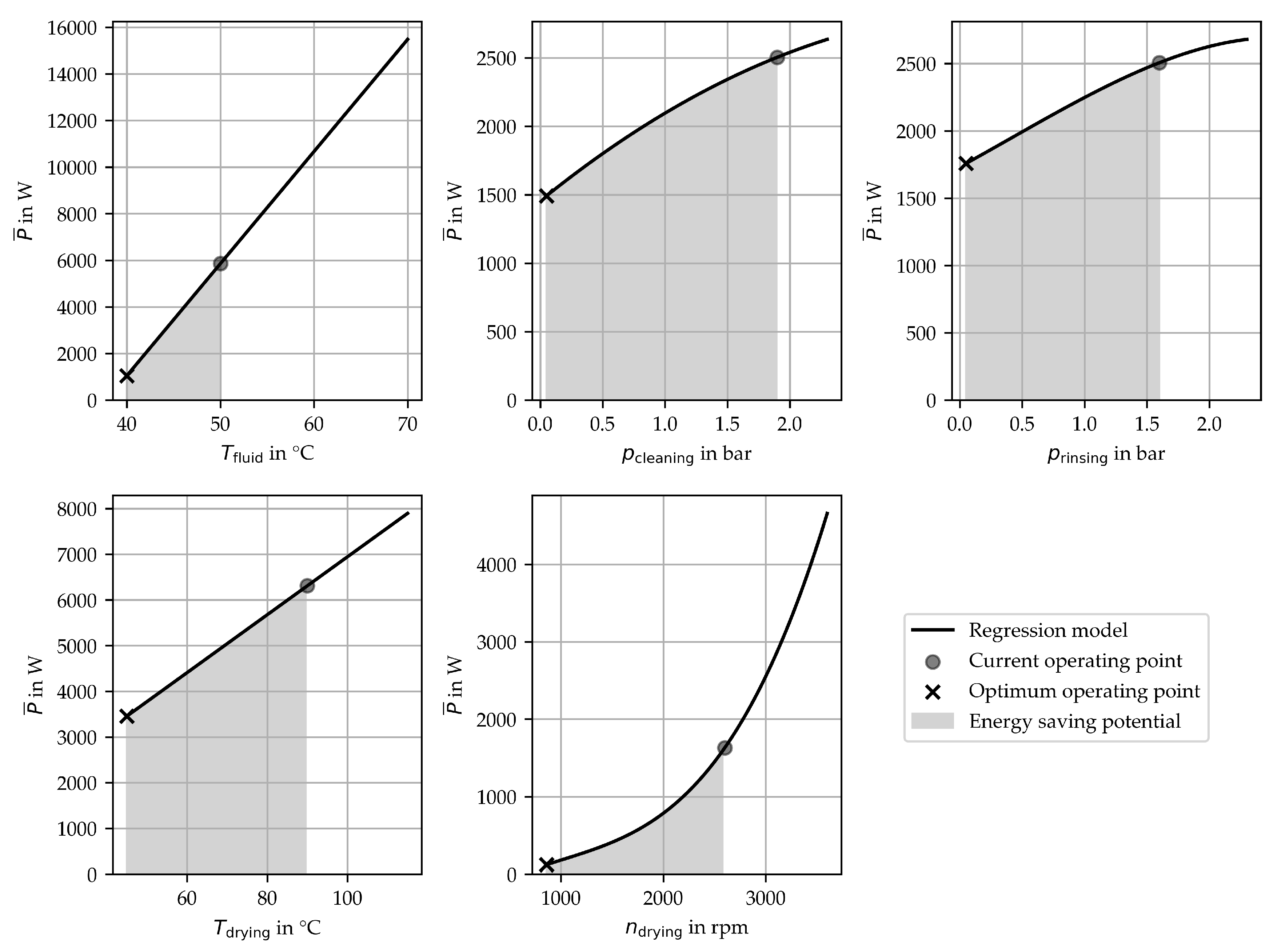
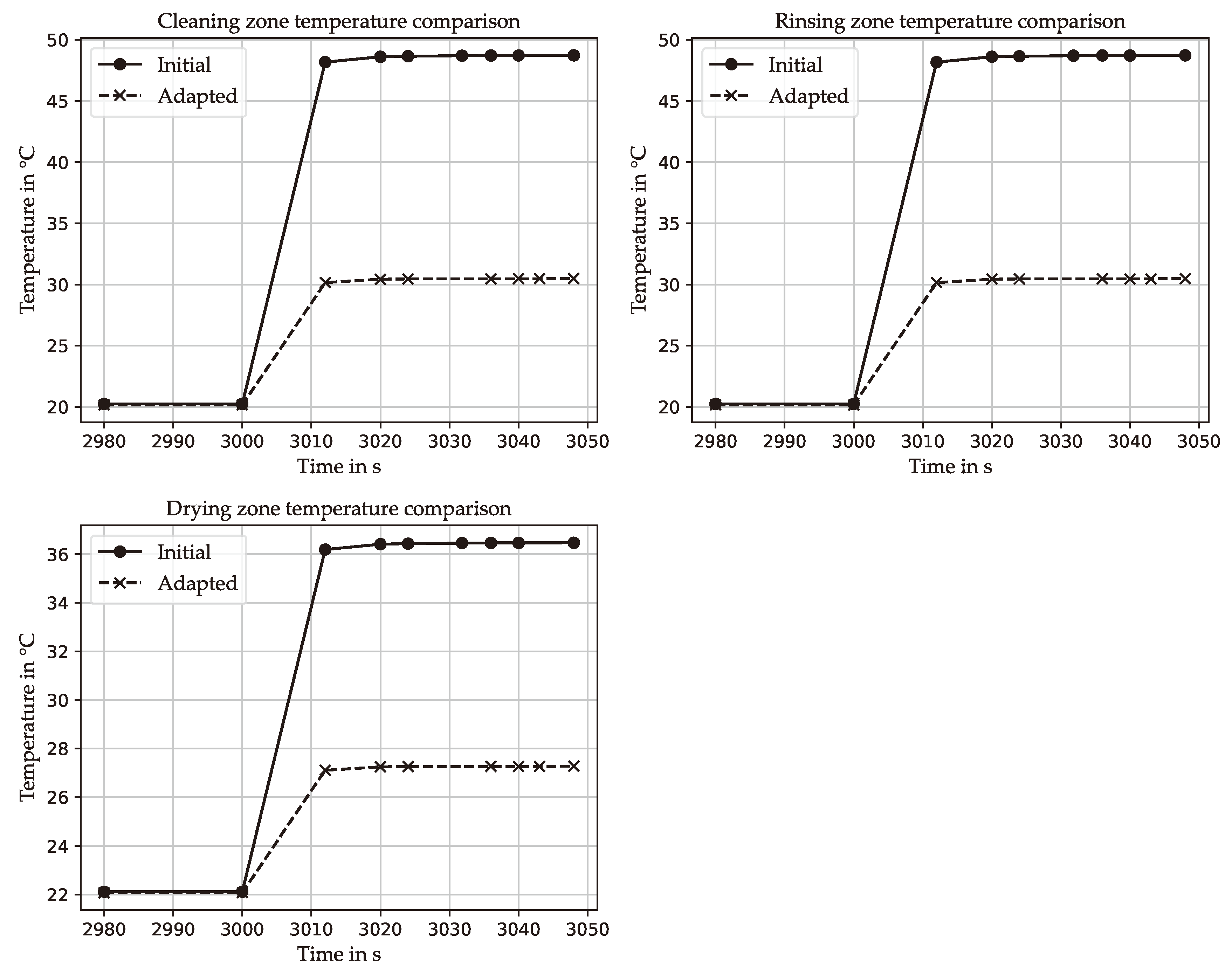
4.6. Application and Validation
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CPP | Controllable Process Parameter |
| CRISP-ML(Q) | CRoss-Industry Standard Process model for the development of |
| Machine Learning applications with Quality assurance methodology | |
| DSM | Design science method |
| EnPIs | Energy performance indicators |
| ES | Expert System |
| OPC UA | Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture |
| PLC | Programmable logic controller |
| TPCM | Throughput cleaning machine |
References
- Rögner, F.H. (Ed.) Markt- und Trendanalyse in der Industriellen Teilereinigung 2020; Fraunhofer-Institut für Organische Elektronik, Elektronenstrahl- und Plasmatechnik: Dresden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin, M.C.; Zisman, A.S. The aqueous cleaning handbook: A guide to critical-cleaning procedures, techniques, and validation, fourth edition ed.; AI Technical Communications: White Plains, NY, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bayerisches Landesamt für Umwelt. Energieeinsparung in Lackierbetrieben - Langfassung: Klima schützen - Kosten senken, 2006.
- Blesl, M.; Kessler, A. Energy Efficiency in Industry; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abele, E.; Beck, M.; Flum, D.; Schraml, P.; Panten, N.; Junge, F.; Bauerdick, C.; Helfert, M.; Sielaff, T.; Daume, C.; Weber, M.; Strobel, N.; Redelberger, A.; Pototzky, L.; Rothenbücher, S.; Landgraf, G.; Rummel, W.; Heimbach, K.; Haase, P.; Stock, S.; Schwarz, J.; Schaal, S.; Kunde, R.; Krönauer, A. Gemeinsamer Schlussbericht zum Projekt ETA-Fabrik: Energieeffiziente Fabrik für interdisziplinäre Technologie- und Anwendungsforschung, 2019.
- LoTuS. LoTuS - Leistungsoptimierte Trocknung und Sauberkeit: Energetische Trockenprozessoptimierung und -vernetzung für eine energieeffiziente Reinigungsanlage, 2023.
- Jaffe, A.B.; Stavins, R.N. The energy-efficiency gap What does it mean? Energy Policy 1994, 22, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioshchikhes, B.; Elserafi, G.; Weigold, M. An Expert System-Based Approach For Improving Energy Efficiency Of Chamber Cleaning Machines. In Proceedings of the Conference on Production Systems and Logistics (CPSL 2023); publish-Ing.: Offenburg; 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, A.; Zhang, H.C.; Kong, L.L.; Hussain, G. A rule-based system for trade-off among energy consumption, tool life, and productivity in machining process. JOURNAL OF INTELLIGENT MANUFACTURING 2015, 26, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yahui, F.; Wan, L.; Lv, L. Research on intelligent expert system of green cutting process and its application. JOURNAL OF CLEANER PRODUCTION 2018, 185, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruschke, L.; Elserafi, G.; Ioshchikhes, B.; Weigold, M. Machine learning based identification of energy efficiency measures for machine tools using load profiles and machine specific meta data. MM Science Journal 2021, 2021, 5061–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.; Chandrasekaran, M. Electron Beam Welding Investigation of Inconel 825 and Optimize Energy Consumption Using Integrated Fuzzy Logic-Particle Swarm Optimization Approach. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems 2023, 25, 1377–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Development of grinding intelligent monitoring and big data-driven decision making expert system towards high efficiency and low energy consumption: experimental approach. JOURNAL OF INTELLIGENT MANUFACTURING 2023. [CrossRef]
- Ioshchikhes, B.; Borst, F.; Weigold, M. Assessing Energy Efficiency Measures for Hydraulic Systems using a Digital Twin. Procedia CIRP 2022, 107, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioshchikhes, B.; Weigold, M. Development of Stationary Expert Systems for Improving Energy Efficiency in Manufacturing. In 17th CIRP Conference on Intelligent Computation in Manufacturing Engineering - CIRP ICME ’23; 2023.
- Buccieri, G.P.; Balestieri, J.A.P.; Matelli, J.A. Energy efficiency in Brazilian industrial plants: knowledge management and applications through an expert system. JOURNAL OF THE BRAZILIAN SOCIETY OF MECHANICAL SCIENCES AND ENGINEERING 2020, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lu, Y.; Qian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, W. An explanatory parametric model to predict comprehensive post-commissioning building performances. Building and Environment 2022, 213, 108897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeTore, A.W. An introduction to expert systems. Journal of insurance Medicine 1989, 21, 233–236. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, P. Introduction to Expert Systems, 3rd ed.; Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc: USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hevner, A.R.; March, S.T.; Park, J.; Ram, S. Design Science in Information Systems Research. MIS Q 2004, 28, 75–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsches Institut für Normung, e.V. . Energy management systems – Measuring energy performance using energy baselines (EnB) and energy performance indicators (EnPI) – General principles and guidance (ISO 50006:2014), 2014.
- Deutsches Institut für Normung, e.V. . Energy management systems – Requirements with guidance for use (ISO 50001:2018): German version EN ISO 50001:2018, 2018.
- Blesl, M.; Kessler, A. Energieeffizienz in der Industrie; Springer Vieweg: Berlin and Heidelberg, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Thiede, S. Energy Efficiency in Manufacturing Systems; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Studer, S.; Bui, T.B.; Drescher, C.; Hanuschkin, A.; Winkler, L.; Peters, S.; Müller, K.R. Towards CRISP-ML(Q): A Machine Learning Process Model with Quality Assurance Methodology. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 2021, 3, 392–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posselt, G. Towards Energy Transparent Factories; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelz, P.F.; Groche, P.; Pfetsch, M.E.; Schaeffner, M. (Eds.) Mastering Uncertainty in Mechanical Engineering, 2021 ed., 1st ed.; Springer Tracts in Mechanical Engineering, Springer International Publishing and Imprint Springer: Cham, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzson, P. Principles of object-oriented modeling and simulation with Modelica 3.3 : a cyber-physical approach, second edition ed.; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.H. Expert system methodologies and applications—a decade review from 1995 to 2004. Expert Systems with Applications 2005, 28, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, D.J. Correlation and the coefficient of determination. Psychological Bulletin 1985, 97, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, T.O. Root-mean-square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE): when to use them or not. Geoscientific Model Development 2022, 15, 5481–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. In Journal of Machine Learning Research; 2011; Vol. 12, pp. 2825–2830.
- Modelica Association. Modelica Language Specification 3.5, 2000.
- Modelica Association. Modelica Standard Library: Free library to model mechanical (1D/3D), electrical (analog, digital, machines), magnetic, thermal, fluid, control systems and hierarchical state machines., 2020.
- Ioshchikhes, B.; Frank, M.; Elserafi, G.; Magin, J. Developing Expert Systems for Improving Energy Efficiency in Manufacturing: A case study on parts cleaning. https://github.com/MichaelGeFr/MDPI_Energies_2024_Expert_System.
- Frank, M.; Magin, J. ; TU Darmstadt. Throughput Cleaning Machine YUKON DAD-2 BL. [CrossRef]
- E. H. Mamdani.; S. Assilian. An experiment in linguistic synthesis with a fuzzy logic controller. International Journal of Man-Machine Studies 1975, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F. Loizides.; B. Schmidt.; Thomas Kluyver.; Benjamin Ragan-Kelley.; Fernando Pérez.; Brian Granger.; Matthias Bussonnier.; Jonathan Frederic.; Kyle Kelley.; Jessica Hamrick.; Jason Grout.; Sylvain Corlay.; Paul Ivanov.; Damián Avila.; Safia Abdalla.; Carol Willing., Eds. Jupyter Notebooks – a publishing format for reproducible computational workflows, 2016.
| Persona | Description |
|---|---|
| Machine operator | Responsible for operating the machine and experienced in the manufacturing process |
| Energy manager | Evaluates processes from an energy perspective and assesses current energy utilization |
| Knowledge engineer | Acquires knowledge by experts and research to represent it in a computer system |
| Modeler | Acquires data and builds data-driven or physical models to represent the behavior of complex systems |
| Consumer | Parameter | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid heater | Fluid temperature | (40 – 70) °C |
| Cleaning fluid pump | Cleaning pump pressure | (0.5 - 2.3) bar |
| Rinsing fluid pump | Rinsing pump pressure | (0.05 - 2.3) bar |
| Heating register | Drying air temperature | (45 – 120) °C |
| Drying fan | Drying fan speed | (860 – 3300) rpm |
| Premise (IF) | Consequent (THEN) |
|---|---|
| is high AND is low | is high |
| is medium AND is low | is medium |
| is low AND is low | is medium |
| is high AND is medium | is medium |
| is medium AND is medium | is medium |
| is low AND is medium | is medium |
| is high AND is high | is medium |
| is medium AND is high | is medium |
| is low AND is high | is low |
| CPP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4810.4 | 1.0 | 0.33 | 0.66 | |
| 1012.66 | 0.07 | 0.82 | 0.33 | |
| 748.37 | 0.0 | 0.69 | 0.38 | |
| 2853.59 | 0.52 | 0.64 | 0.44 | |
| 1509.11 | 0.19 | 0.64 | 0.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





