Submitted:
13 June 2024
Posted:
14 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
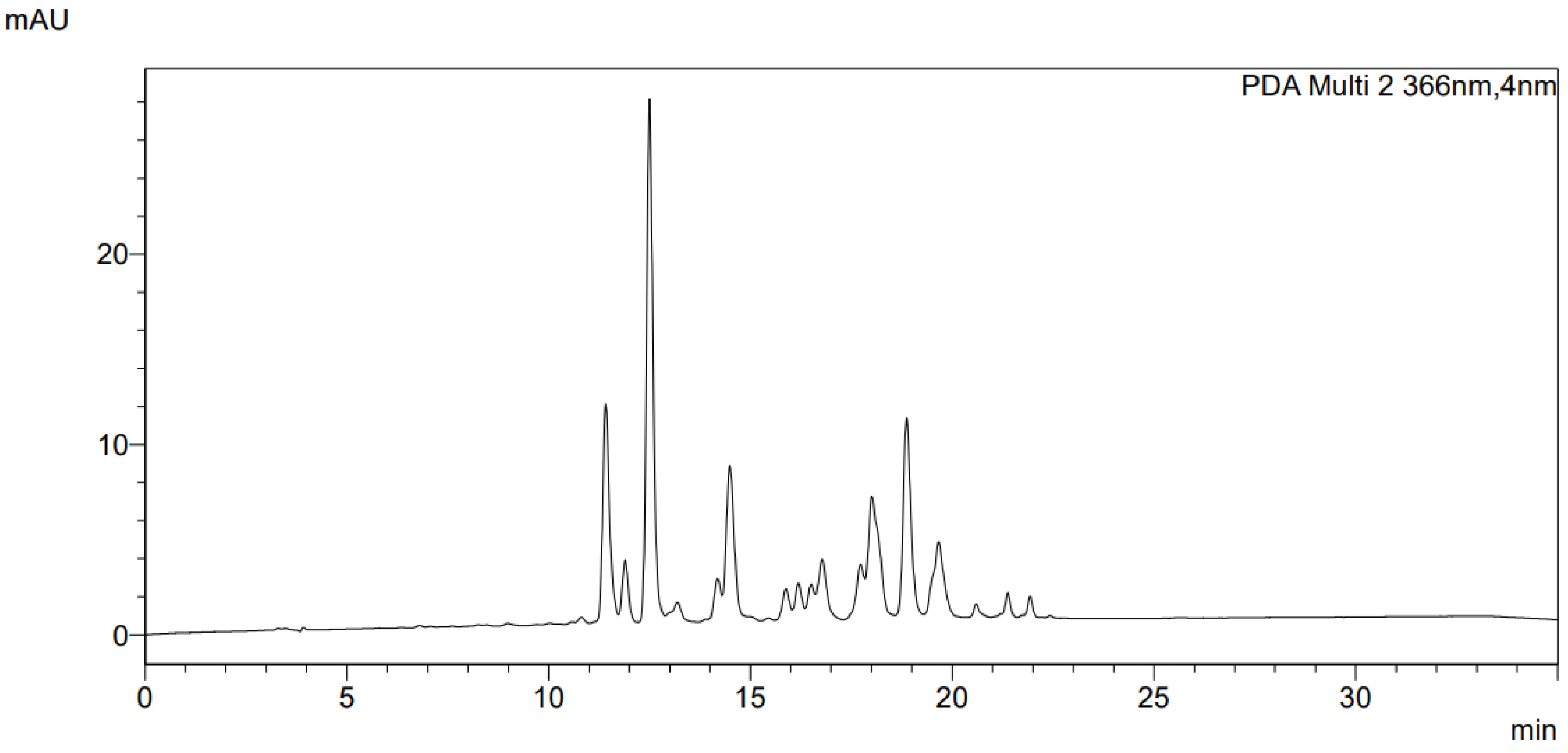
3.1. Chemical characterization of Sedum telephium L. leaves juice
| Chemical class | Content % (m/m) |
| Total polyphenols | 0.08 ± 0.01 |
| Total flavonoids | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| Total proteins | 0.16 ± 0.02 |
| Total polysaccharides | 2.52 ± 0.22 |
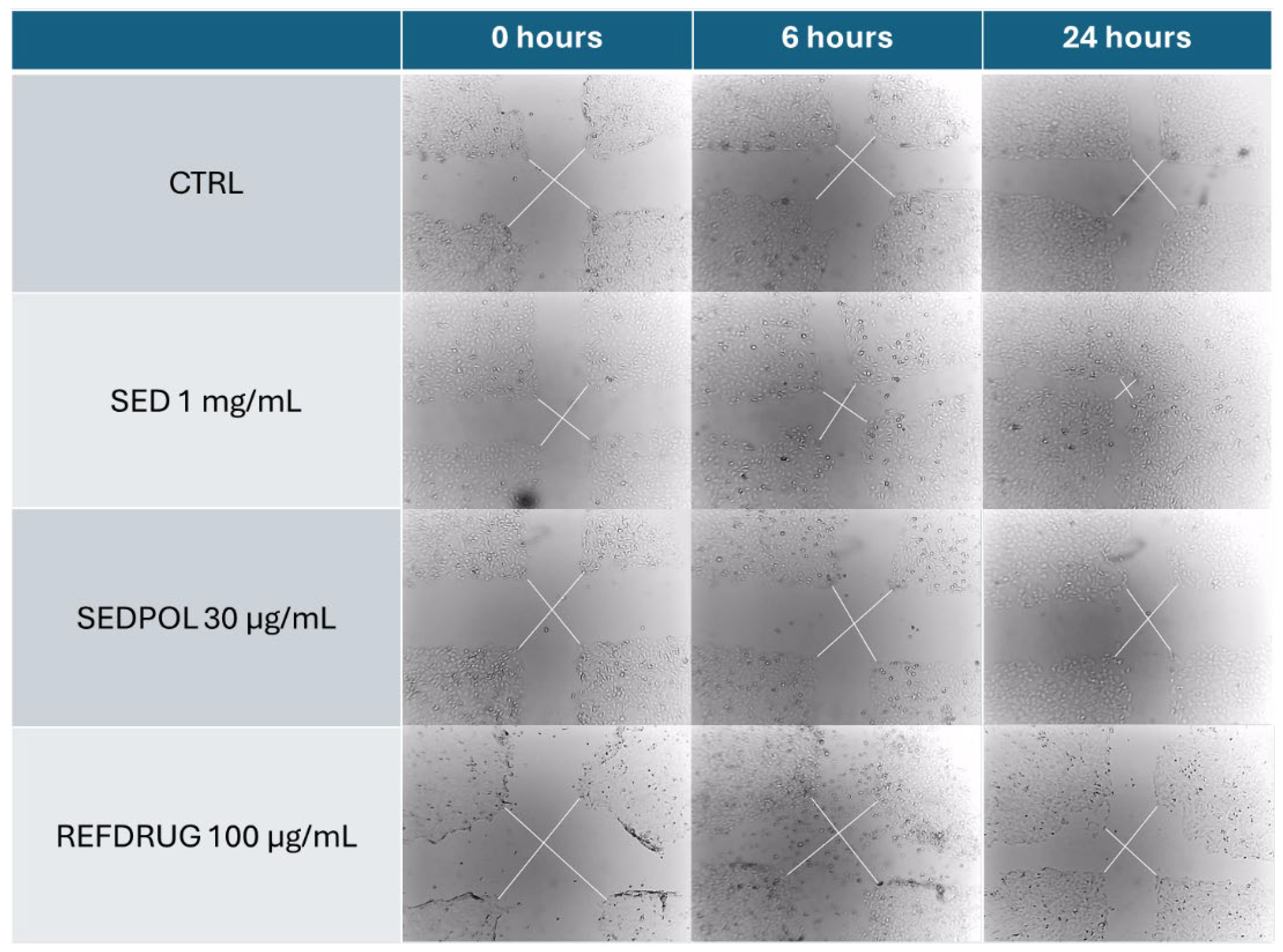
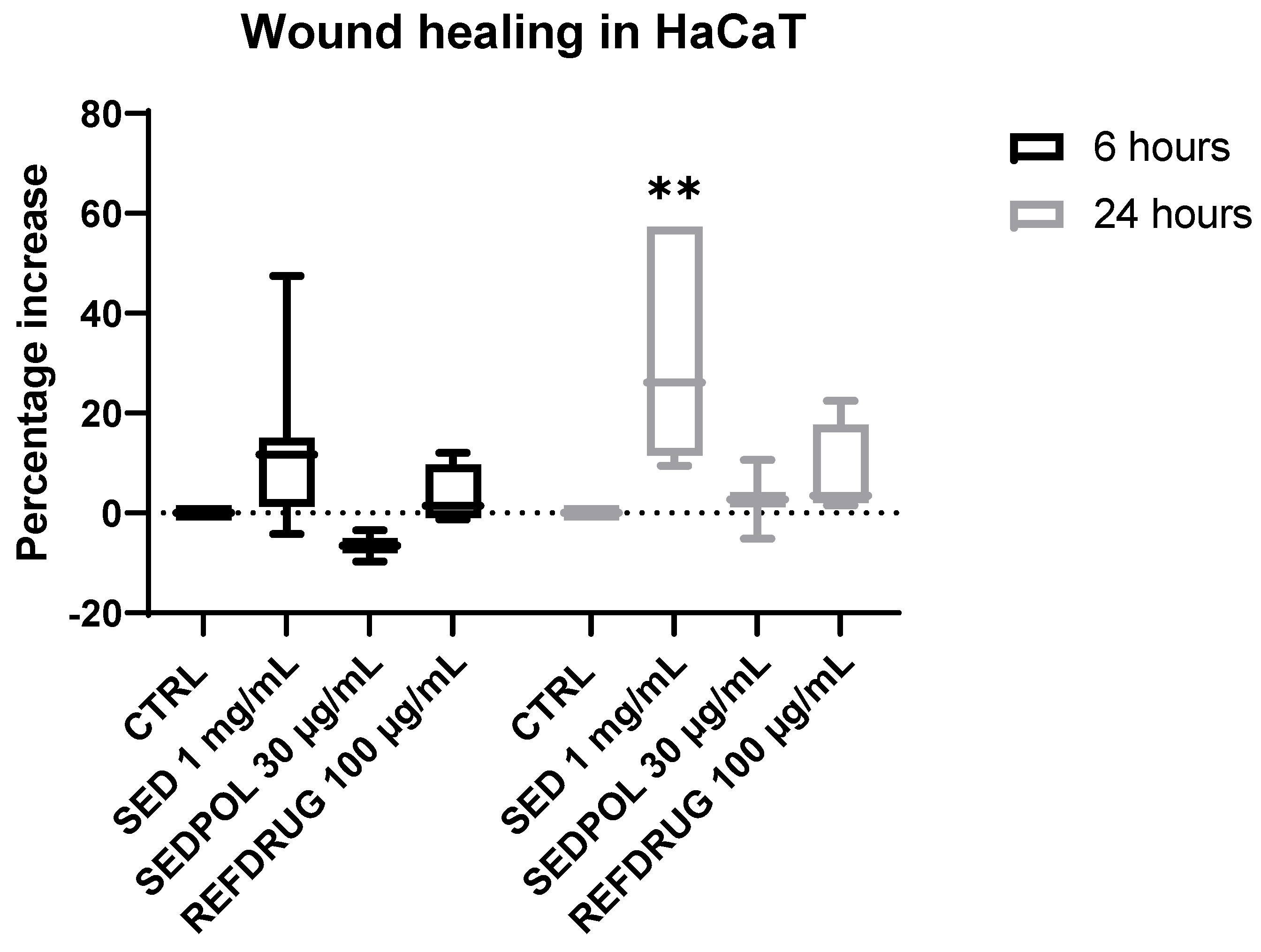
3.2. Wound healing activity of Sedum telephium L. leaves juice in human keratinocytes
3.3. Wound healing mechanism of Sedum telephium L. leaves juice
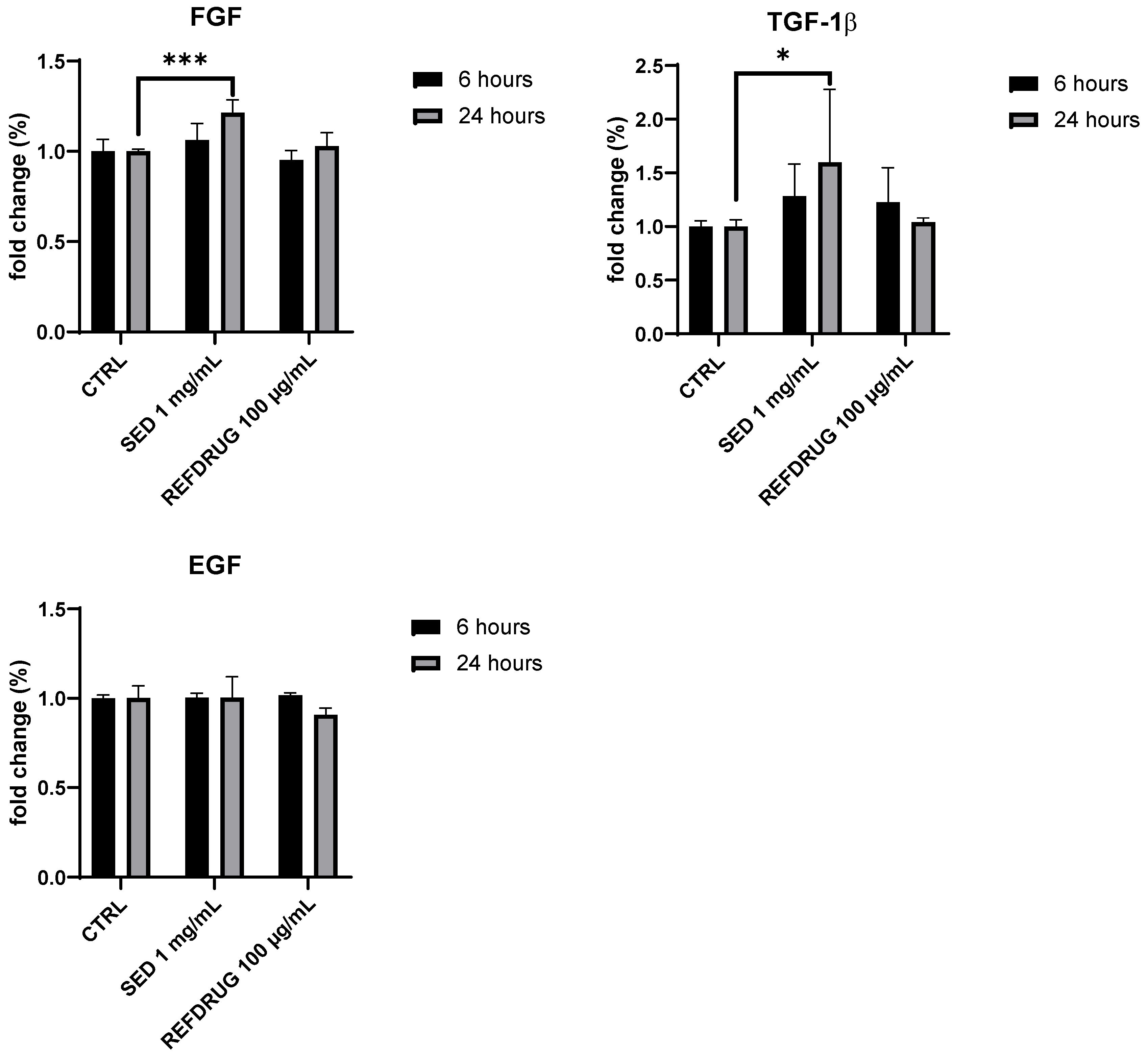
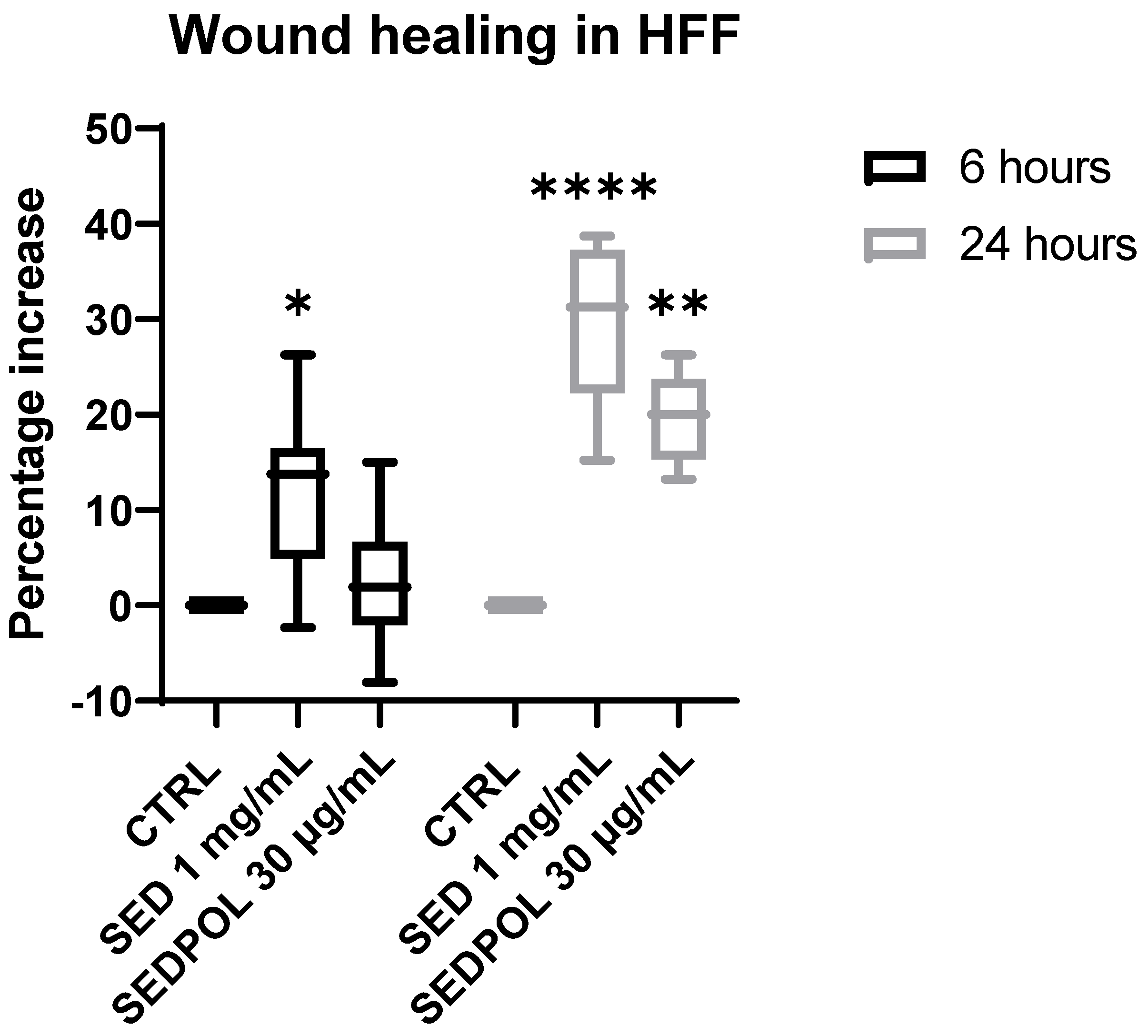
3.4. Wound healing activity of Sedum telephium L. leaves juice and pro-collagen I dosage in human fibroblasts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pazyar, N.; Yaghoobi, R.; Rafiee, E.; Mehrabian, A.; Feily, A. Skin Wound Healing and Phytomedicine: A Review. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 2014, 27, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, M.; Lisboa, C.; Rodrigues, A. Chronic Wounds and Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Br J Community Nurs 2020, 25, S26–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, H.A.; Basehore, B.M.; Zito, P.M. Wound Healing Phases. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ireton, J.E.; Unger, J.G.; Rohrich, R.J. The Role of Wound Healing and Its Everyday Application in Plastic Surgery: A Practical Perspective and Systematic Review. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2013, 1, e10–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholas, M.N.; Yeung, J. Current Status and Future of Skin Substitutes for Chronic Wound Healing. J Cutan Med Surg 2017, 21, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.G.; Higham, C.; Broussard, K.; Phillips, T.J. Wound Healing and Treating Wounds: Chronic Wound Care and Management. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016, 74, 607–625; quiz 625–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaisang, L.; Siyu, W.; Lijun, F.; Daoyan, P.; Xian, C.J.; Jie, S. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Seeded in Pluronic F-127 Hydrogel Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing. Journal of Surgical Research 2017, 217, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Ceilley, R. Chronic Wound Healing: A Review of Current Management and Treatments. Adv Ther 2017, 34, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, M.; Järbrink, K.; Divakar, U.; Bajpai, R.; Upton, Z.; Schmidtchen, A.; Car, J. The Humanistic and Economic Burden of Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review. Wound Repair Regen 2019, 27, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.M.; Andrees, V.; Kirsten, N.; Protz, K.; Augustin, M.; Blome, C. Social Participation of People with Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review. Int Wound J 2021, 18, 287–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gethin, G.; Probst, S.; Stryja, J.; Christiansen, N.; Price, P. Evidence for Person-Centred Care in Chronic Wound Care: A Systematic Review and Recommendations for Practice. J Wound Care 2020, 29, S1–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.; Ielapi, N.; Caprino, F.; Giannotta, N.; Sisinni, A.; Abramo, A.; Ssempijja, L.; Andreucci, M.; Bracale, U.M.; Serra, R. Social Aspects of Diabetic Foot: A Scoping Review. Social Sciences 2022, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, S.R.; Carter, M.J.; Fife, C.E.; DaVanzo, J.; Haught, R.; Nusgart, M.; Cartwright, D. An Economic Evaluation of the Impact, Cost, and Medicare Policy Implications of Chronic Nonhealing Wounds. Value Health 2018, 21, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alma, A.; Marconi, G.D.; Rossi, E.; Magnoni, C.; Paganelli, A. Obesity and Wound Healing: Focus on Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Life (Basel) 2023, 13, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganelli, A.; Naselli, A.G.; Bertoni, L.; Rossi, E.; Azzoni, P.; Pisciotta, A.; Cesinaro, A.M.; Benassi, L.; Kaleci, S.; Garbarino, F.; et al. Wound Healing after Acellular Dermal Substitute Positioning in Dermato-Oncological Surgery: A Prospective Comparative Study. Life (Basel) 2023, 13, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindholm, C.; Searle, R. Wound Management for the 21st Century: Combining Effectiveness and Efficiency. Int Wound J 2016, 13 Suppl 2, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbeni, S.A.; Negm, W.A. The Wound Healing Effect of Botanicals and Pure Natural Substances Used in in Vivo Models. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 755–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pressi, G.; Rigillo, G.; Governa, P.; Borgonetti, V.; Baini, G.; Rizzi, R.; Guarnerio, C.; Bertaiola, O.; Frigo, M.; Merlin, M.; et al. A Novel Perilla Frutescens (L.) Britton Cell-Derived Phytocomplex Regulates Keratinocytes Inflammatory Cascade and Barrier Function and Preserves Vaginal Mucosal Integrity In Vivo. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganelli, A.; Pisciotta, A.; Bertani, G.; Di Tinco, R.; Tagliaferri, N.; Orlandi, G.; Azzoni, P.; Bertoni, L. Food Supplements for Skin Health: In Vitro Efficacy of a Combination of Rhodiola Rosea, Tribulus Terrestris, Moringa Oleifera and Undaria Pinnatifida on UV-Induced Damage. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altavilla, D.; Polito, F.; Bitto, A.; Minutoli, L.; Miraldi, E.; Fiumara, T.; Biagi, M.; Marini, H.; Giachetti, D.; Vaccaro, M.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Methanol Extract of Sedum Telephium Ssp. Maximum in Lipopolysaccharide- Stimulated Rat Peritoneal Macrophages. Pharmacology 2008, 82, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulinacci, N.; Vincieri, F.F.; Baldi, A.; Bambagiotti-Alberti, M.; Sendl, A.; Wagner, H. Flavonol Glycosides from Sedum Telephium Subspecies Maximum Leaves. Phytochemistry 1995, 38, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, L.; Banchelli, G.; Dalmazzi, D.; Mulinacci, N.; Romani, A.; Vincieri, F.F.; Pirisino, R. Sedum Telephium L. Polysaccharide Content Affects MRC5 Cell Adhesion to Laminin and Fibronectin. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2010, 52, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendl, A.; Mulinacci, N.; Vincieri, F.F.; Wagner, H. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunologically Active Polysaccharides of Sedum Telephium. Phytochemistry 1993, 34, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonina, F.; Puglia, C.; Tomaino, A.; Saija, A.; Mulinacci, N.; Romani, A.; Vincieri, F.F. In-Vitro Antioxidant and in-Vivo Photoprotective Effect of Three Lyophilized Extracts of Sedum Telephium L. Leaves. J Pharm Pharmacol 2000, 52, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finetti, F.; Biagi, M.; Ercoli, J.; Macrì, G.; Miraldi, E.; Trabalzini, L. Phaseolus Vulgaris L. Var. Venanzio Grown in Tuscany: Chemical Composition and In Vitro Investigation of Potential Effects on Colorectal Cancer. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Governa, P.; Biagi, M. Copaifera Langsdorffii Desf.: In Vitro Investigation on Anti- Helicobacter Pylori and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Oleoresin and Fruit Methanolic Extract. Plant Biosystems - An International Journal Dealing with all Aspects of Plant Biology 2020, 154, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Di, H.; Yang, S.; Tian, Y.; Tong, Y.; Huang, H.; Escalona, V.H.; Tang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Variation in Nutritional Components and Antioxidant Capacity of Different Cultivars and Organs of Basella Alba. Plants 2024, 13, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Peng, L.-H.; Li, N.; Li, Q.-M.; Li, P.; Fung, K.-P.; Leung, P.-C.; Gao, J.-Q. The Healing and Anti-Scar Effects of Astragaloside IV on the Wound Repair in Vitro and in Vivo. J Ethnopharmacol 2012, 139, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiocchio, I.; Poli, F.; Governa, P.; Biagi, M.; Lianza, M. Wound Healing and in Vitro Antiradical Activity of Five Sedum Species Grown within Two Sites of Community Importance in Emilia-Romagna (Italy). Plant Biosystems - An International Journal Dealing with all Aspects of Plant Biology 2019, 153, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressi, G.; Bertaiola, O.; Guarnerio, C.; Barbieri, E.; Rigillo, G.; Governa, P.; Biagi, M.; Guzzo, F.; Semenzato, A. In Vitro Cell Culture of Rhus Coriaria L.: A Standardized Phytocomplex Rich of Gallic Acid Derivatives with Antioxidant and Skin Repair Activity. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I.; Lambers, H.; Grant, C.A.; Zhao, F.-J. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi: Key Players in Avoiding Cadmium Accumulation in Food Crops. Plant Soil 2023, 484, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.M.; Proksch, E. The Skin’s Barrier. G Ital Dermatol Venereol 2009, 144, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.; Geyer, S.; Weninger, W.; Guimberteau, J.-C.; Wong, J.K. The Dynamic Anatomy and Patterning of Skin. Exp Dermatol 2016, 25, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.V.; Soulika, A.M. The Dynamics of the Skin’s Immune System. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris-Tryon, T.A.; Grice, E.A. Microbiota and Maintenance of Skin Barrier Function. Science 2022, 376, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomic-Canic, M.; Burgess, J.L.; O’Neill, K.E.; Strbo, N.; Pastar, I. Skin Microbiota and Its Interplay with Wound Healing. Am J Clin Dermatol 2020, 21, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, J.M.; Glatz, M.; Proksch, E. Optimal Support of Wound Healing: New Insights. Dermatology 2020, 236, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E. Minor Traumatic Wounds. Nurs Stand 2016, 31, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, J.H.; Artemi, P.; Benrimoj, S.I. Topical Antimicrobial Prophylaxis in Minor Wounds. Ann Pharmacother 1997, 31, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsioutsiou, E.E.; Miraldi, E.; Governa, P.; Biagi, M.; Giordani, P.; Cornara, L. Skin Wound Healing: From Mediterranean Ethnobotany to Evidence Based Phytotherapy. AJS 2017, 4, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsioutsiou, E.E.; Giordani, P.; Hanlidou, E.; Biagi, M.; De Feo, V.; Cornara, L. Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Used in Central Macedonia, Greece. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2019, 2019, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.H. TGF-Beta1 Regulates TGF-Beta1 and FGF-2 mRNA Expression during Fibroblast Wound Healing. Molecular Pathology 2002, 55, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xie, R.; Luo, Y.; Shi, R.; Ling, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xu, X.; Chu, W.; Wang, X. Cooperation of TGF -β and FGF Signalling Pathways in Skin Development. Cell Proliferation 2023, 56, e13489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hormozi, M.; Assaei, R.; Boroujeni, M.B. The Effect of Aloe Vera on the Expression of Wound Healing Factors (TGFβ1 and bFGF) in Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast Cell: In Vitro Study. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2017, 88, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tito, A.; Minale, M.; Riccio, S.; Grieco, F.; Colucci, M.G.; Apone, F. A Triticum Vulgare Extract Exhibits Regenerating Activity During the Wound Healing Process. CCID 2020, Volume 13, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, L.T.N.; Moon, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C. Antioxidants for Improved Skin Appearance: Intracellular Mechanism, Challenges, and Future Strategies. Int J Cosmet Sci 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftekhari, A.; Dizaj, S.M.; Chodari, L.; Sunar, S.; Hasanzadeh, A.; Ahmadian, E.; Hasanzadeh, M. The Promising Future of Nano-Antioxidant Therapy against Environmental Pollutants Induced-Toxicities. Biomed Pharmacother 2018, 103, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Pintado, M.; Tavaria, F.K. A Systematic Review of Natural Products for Skin Applications: Targeting Inflammation, Wound Healing, and Photo-Aging. Phytomedicine 2023, 115, 154824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





