Submitted:
10 June 2024
Posted:
11 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
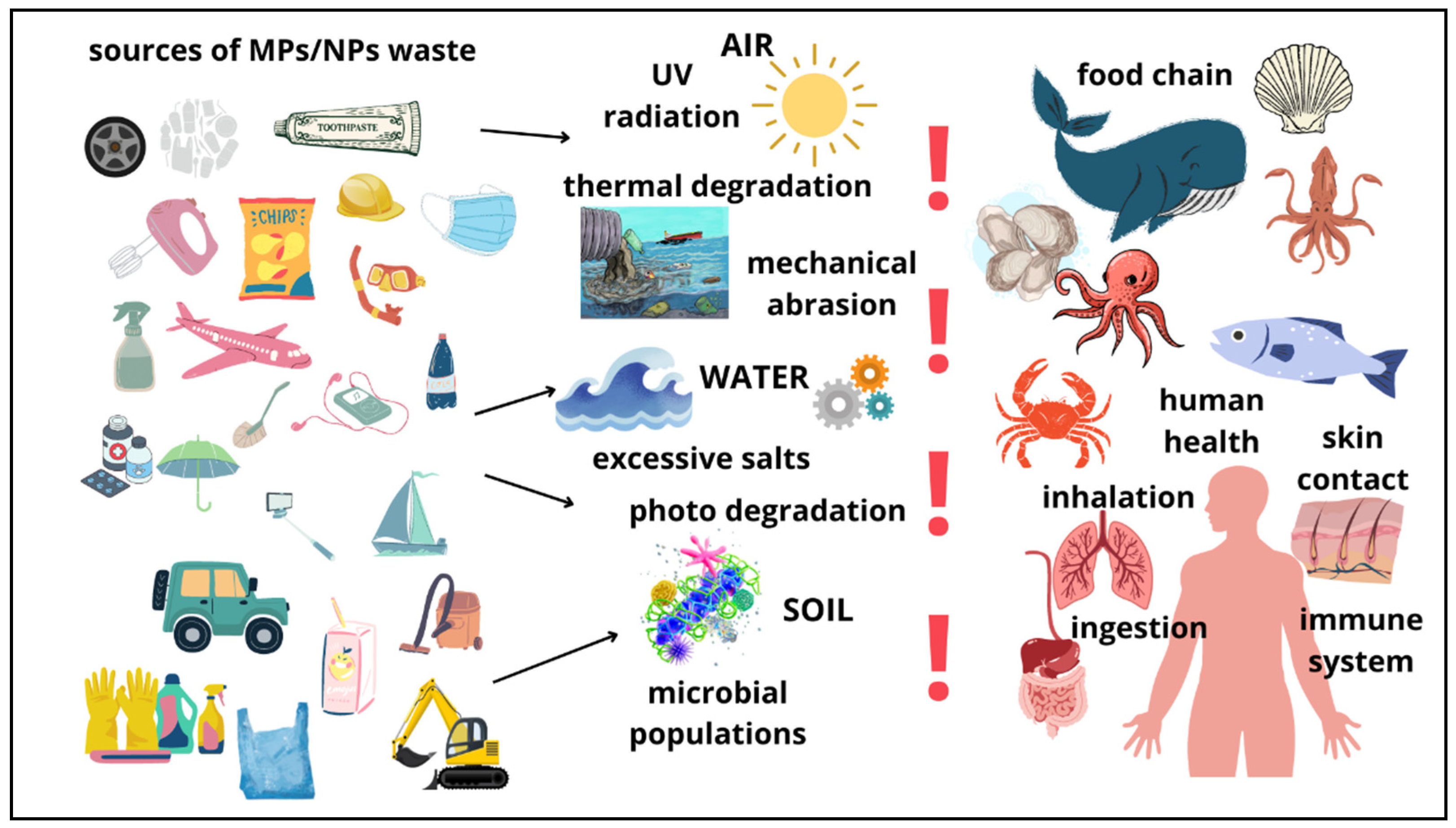
1.1. Sources of Plastic in the Environment
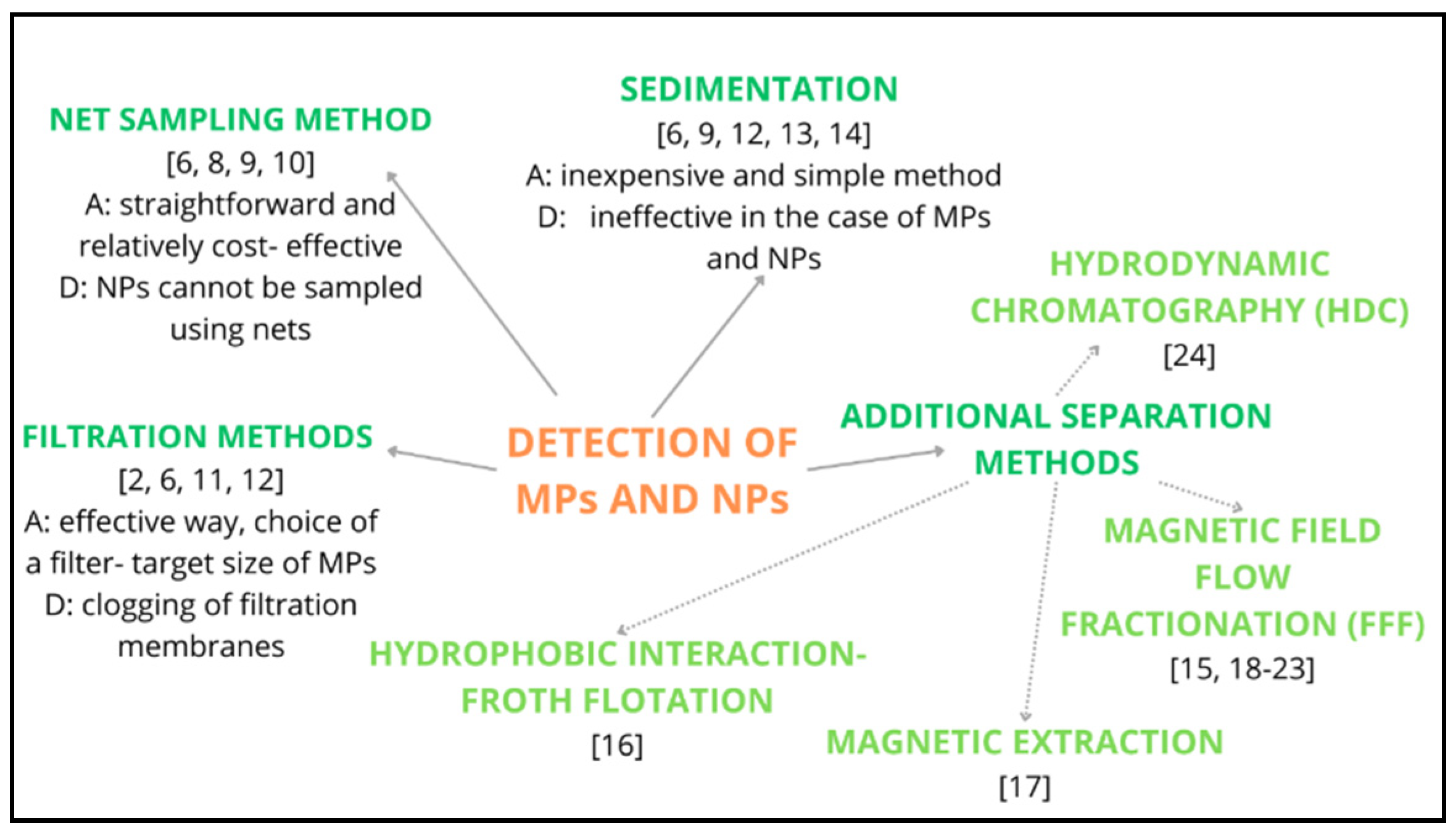
Detection of MPs and NPs
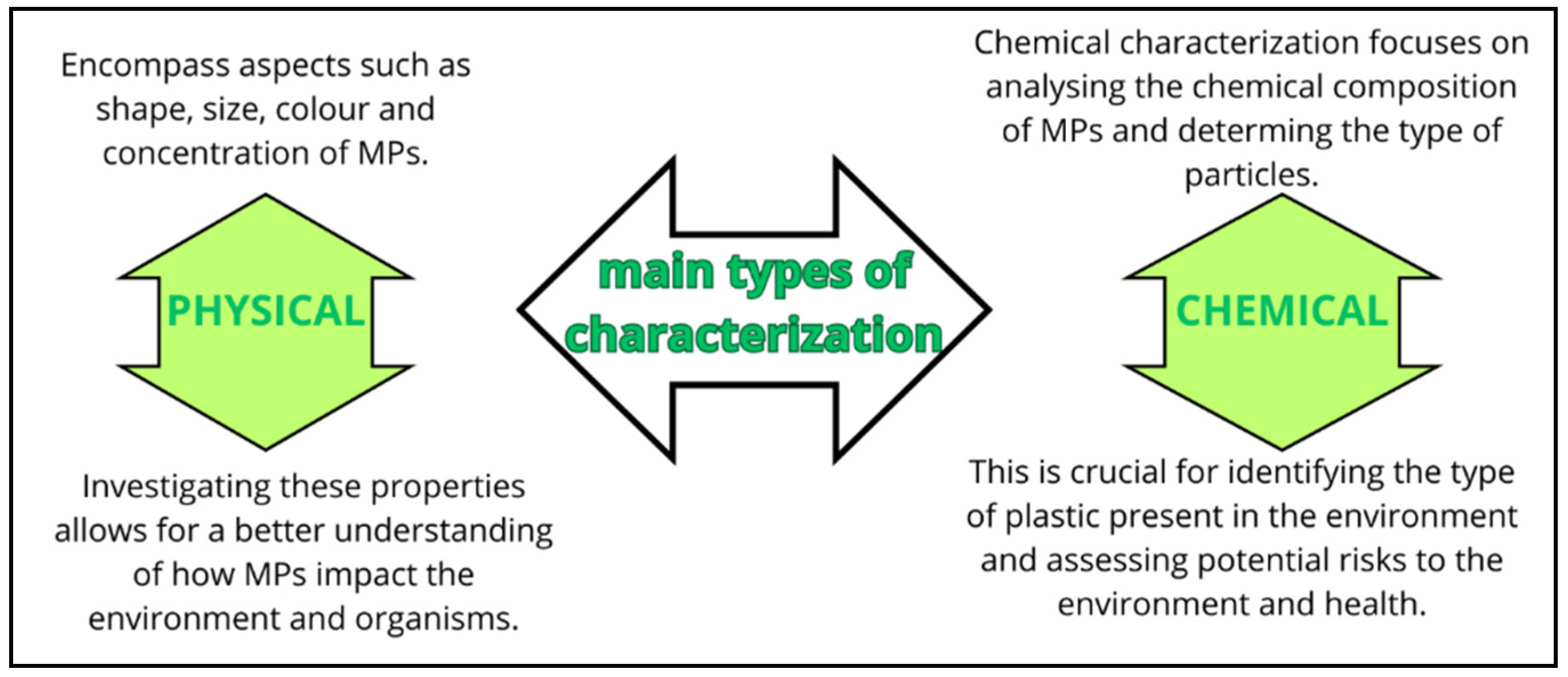
Properties of MPs and NPs
- A wide size range, ranging from 1 μm to 1 mm (and up to 5 mm for larger MPs).
- Diverse polymer types with varying chemical compositions, including both conventional and biopolymers with different structures and densities.
- Various shapes such as spheres, irregular particles, fibers, films, and foams.
- Incorporation of different additives (antioxidants, light stabilizers, plasticizers, flame retardants, pigments, etc.), weathering byproducts, and adsorbed contaminants (persistent organic pollutants, antibiotics, heavy metals, etc.).
- Different aging states (primary and secondary MPs), biofouling, surface charge, and hydrophobicity [48].
Impact on the Environment and Human Healthy
The Techniques for Removing MPs and NPs from Water
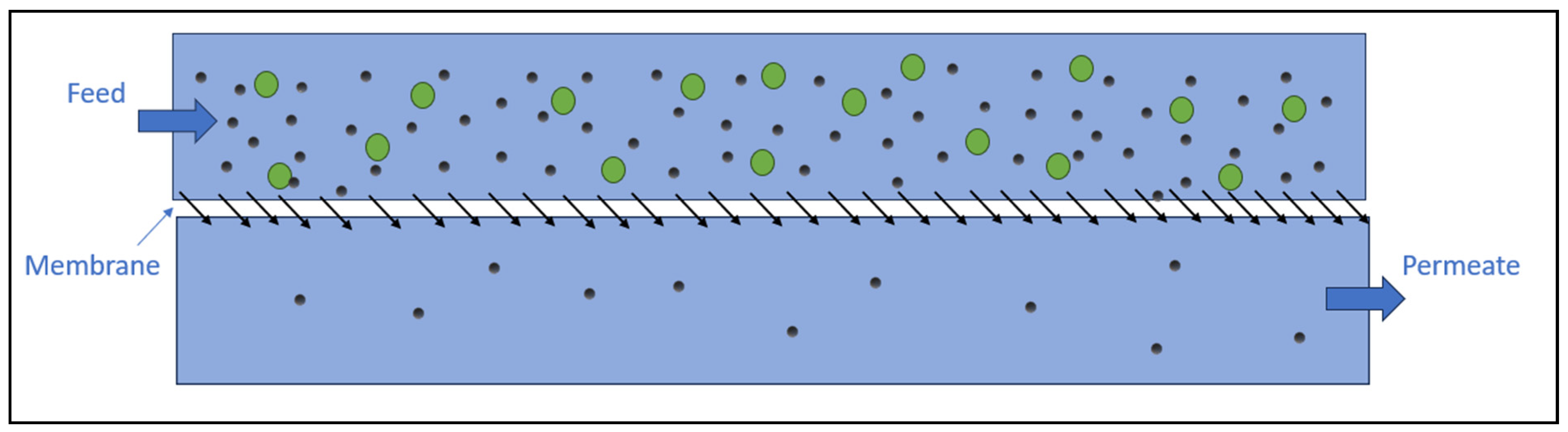
5.1. Membrane Filtration
5.1.1. Ultrafiltration
5.1.2. Reverse Osmosis
5.2. Centrifugation
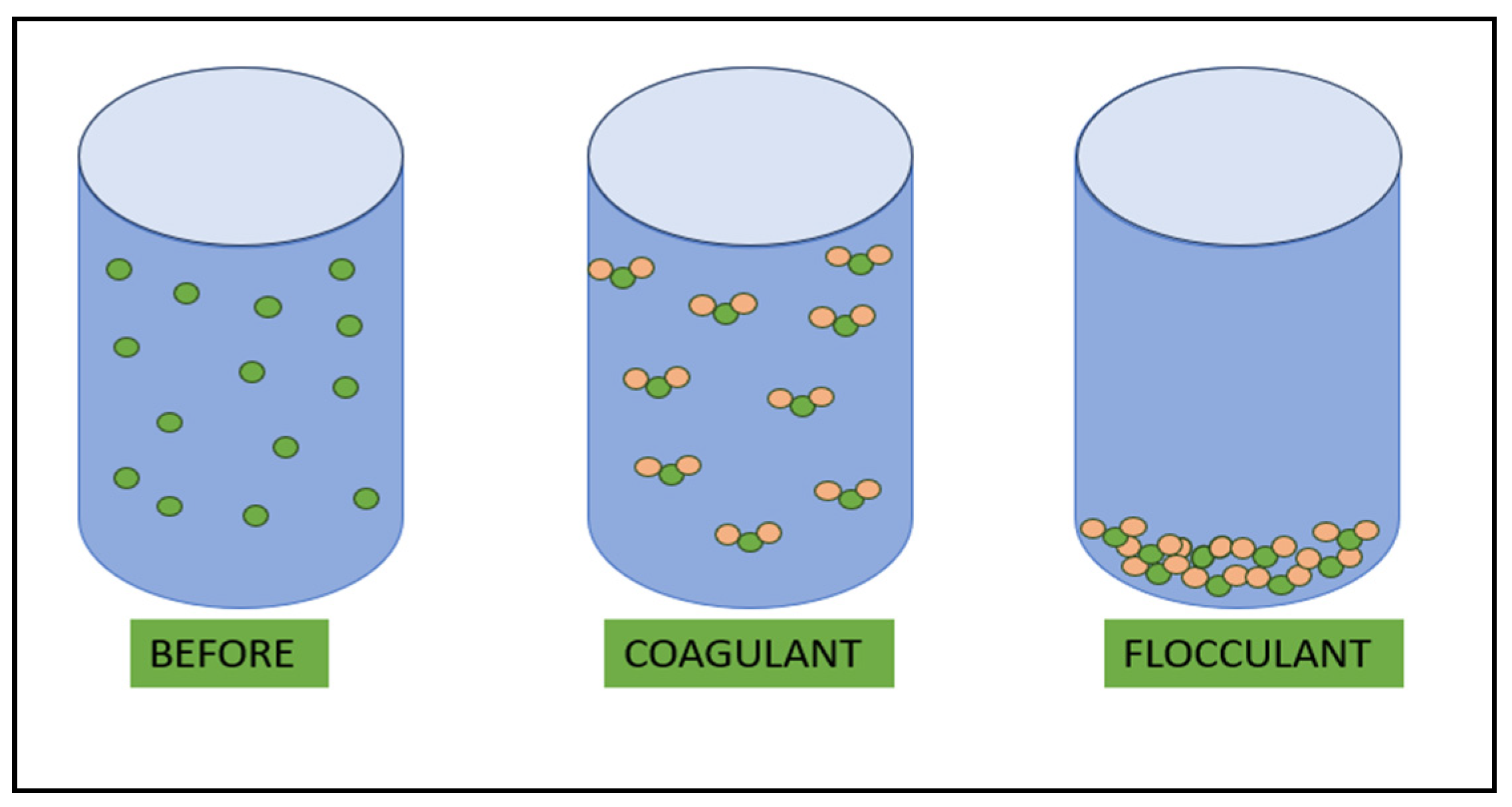
5.3. Flocculation
5.4. Photocatalytic Degradation
5.5. Bioreactors
5.6. Improved Adsorption
5.7. Utilizing Nanomaterials
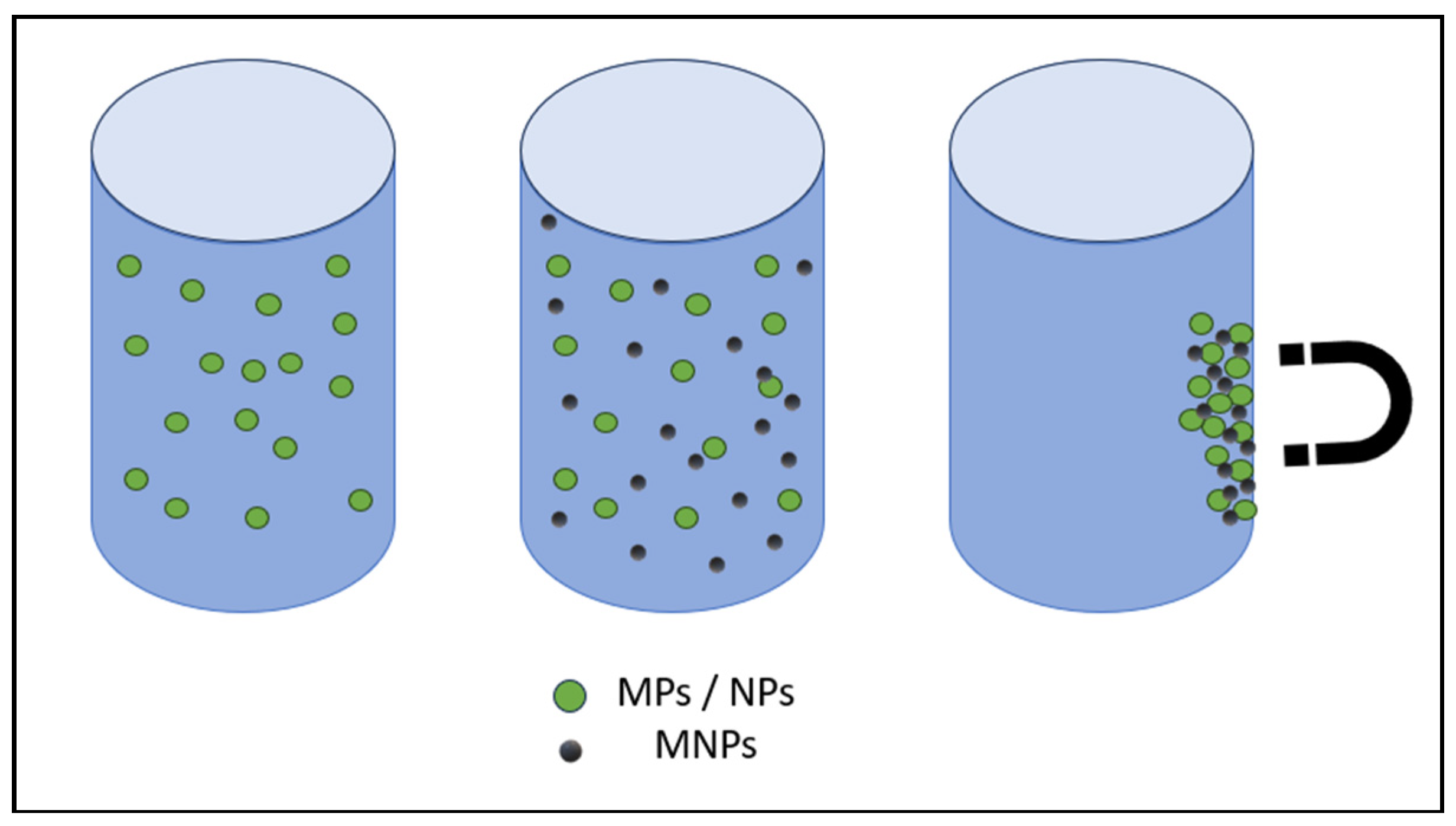
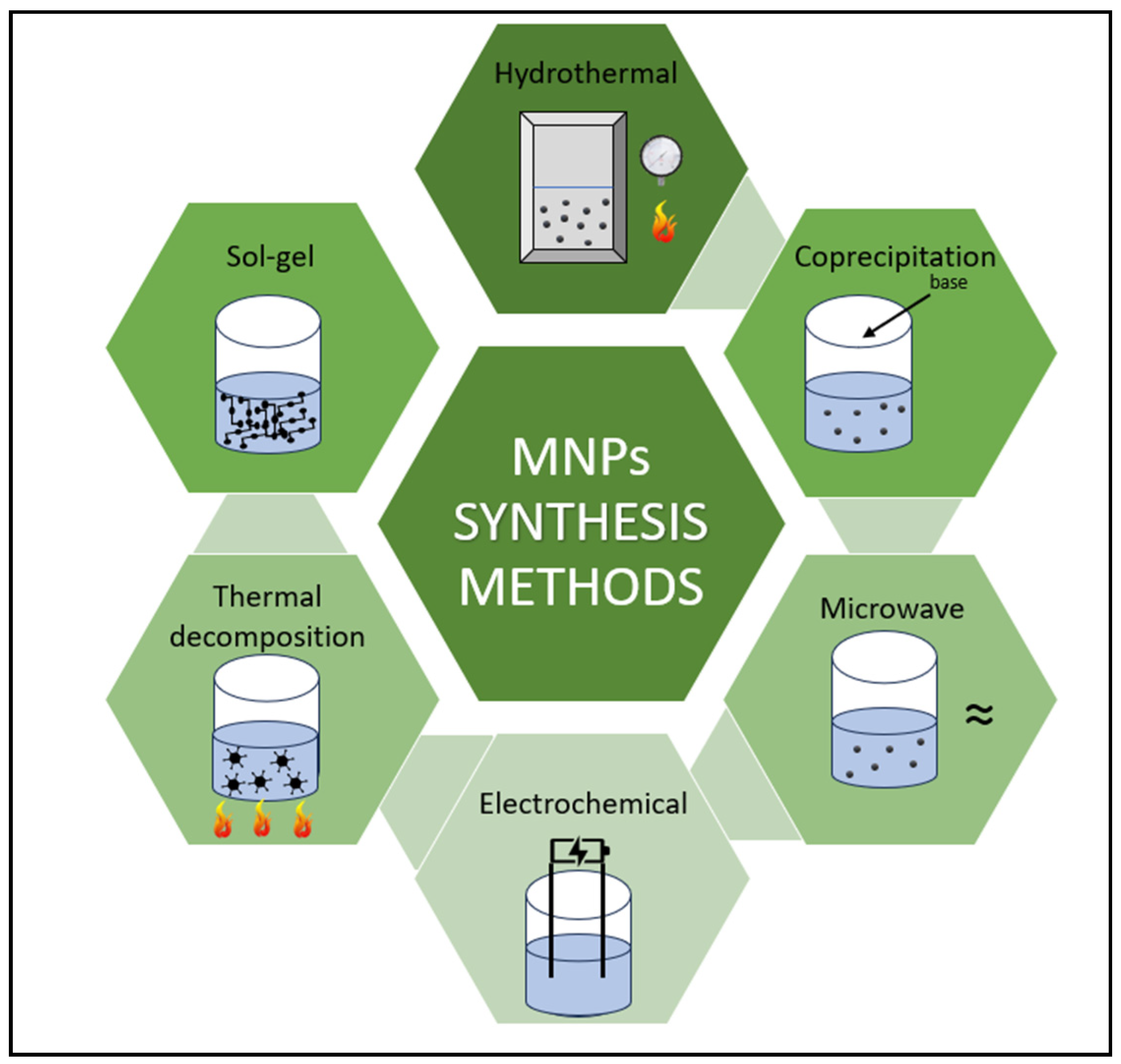
MNPs (Properties, Synthesis Methods, Functionalization)
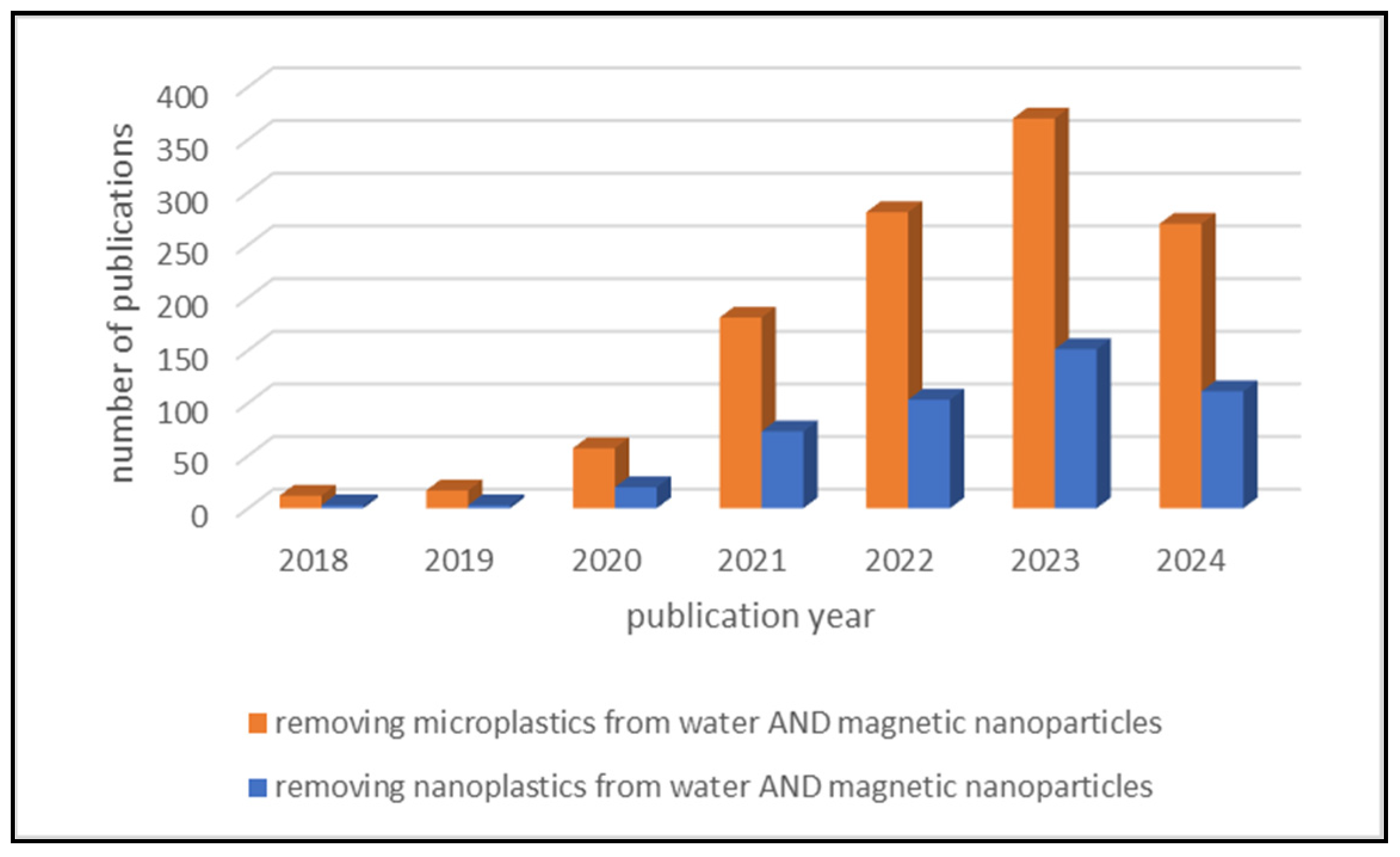
Published Scientific Articles on the Removal of MPs and NPs Using MNPs
Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, S., et al., Micro (nano) plastics in wastewater: A critical review on toxicity risk assessment, behaviour, environmental impact and challenges. Chemosphere, 2022. 290: p. 133169.
- Keerthana Devi, M., et al., Removal of nanoplastics in water treatment processes: A review. Science of The Total Environment, 2022. 845: p. 157168.
- Martin, L.M.A., et al., Testing an Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Based Method for Magnetic Separation of Nanoplastics and Microplastics from Water. Nanomaterials, 2022. 12.
- Heo, Y., E.-H. Lee, and S.-W. Lee, Adsorptive removal of micron-sized polystyrene particles using magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Chemosphere, 2022. 307: p. 135672.
- Kiran, B.R., H. Kopperi, and S. Venkata Mohan, Micro/nano-plastics occurrence, identification, risk analysis and mitigation: challenges and perspectives. Re/Views in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 2022. 21: p. 169 - 203.
- Man Thaiba, B., et al., A review on analytical performance of micro- and nanoplastics analysis methods. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2023. 16(5): p. 104686.
- Asamoah, B.O., et al., Towards the Development of Portable and In Situ Optical Devices for Detection of Micro and Nanoplastics in Water: A Review on the Current Status. Polymers (Basel), 2021. 13(5).
- Razeghi, N., et al., Microplastic sampling techniques in freshwaters and sediments: a review. Environ Chem Lett, 2021. 19(6): p. 4225-4252.
- Park, H. and B. Park, Review of Microplastic Distribution, Toxicity, Analysis Methods, and Removal Technologies. Water, 2021. 13(19): p. 2736.
- Campanale, C., et al., A Practical Overview of Methodologies for Sampling and Analysis of Microplastics in Riverine Environments. Sustainability, 2020. 12: p. 6755.
- Zhang, Y., et al., Removal efficiency of micro- and nanoplastics (180 nm-125 μm) during drinking water treatment. Sci Total Environ, 2020. 720: p. 137383.
- Kundu, A., et al., Identification and removal of micro- and nano-plastics: Efficient and cost-effective methods. Chem Eng J, 2021. 421(1).
- Prata, J.C., et al., Methods for sampling and detection of microplastics in water and sediment: A critical review. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2019. 110: p. 150-159.
- Castelvetro, V., et al., New methodologies for the detection, identification, and quantification of microplastics and their environmental degradation by-products. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2021. 28(34): p. 46764-46780.
- Nguyen, B., et al., Separation and Analysis of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Complex Environmental Samples. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2019. 52(4): p. 858-866.
- Crichton, E.M., et al., A novel, density-independent and FTIR-compatible approach for the rapid extraction of microplastics from aquatic sediments. Analytical Methods, 2017. 9(9): p. 1419-1428.
- Grbic, J., et al., Magnetic Extraction of Microplastics from Environmental Samples. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2019. 6(2): p. 68-72.
- Greyling, G. and H. Pasch, Multidetector Thermal Field-Flow Fractionation for the Characterization of Vinyl Polymers in Binary Solvent Systems. Macromolecules, 2017. 50(2): p. 569-579.
- Tadjiki, S., et al., Measurement of the Density of Engineered Silver Nanoparticles Using Centrifugal FFF-TEM and Single Particle ICP-MS. Analytical Chemistry, 2017. 89(11): p. 6056-6064.
- Samanta, A., et al., Operating regimes of a magnetic split-flow thin (SPLITT) fractionation microfluidic device for immunomagnetic separation. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2016. 20(6): p. 87.
- Ornthai, M., A. Siripinyanond, and B.K. Gale, Biased cyclical electrical field-flow fractionation for separation of submicron particles. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2016. 408(3): p. 855-863.
- Podzimek, S., Asymmetric Flow Field Flow Fractionation, in Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistrymistry.
- Contado, C., Field flow fractionation techniques to explore the “nano-world”. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2017. 409(10): p. 2501-2518.
- Fu, W., et al., Separation, characterization and identification of microplastics and nanoplastics in the environment. Science of The Total Environment, 2020. 721: p. 137561.
- Shim, W.J., S.H. Hong, and S.E. Eo, Identification methods in microplastic analysis: a review. Analytical Methods, 2017. 9(9): p. 1384-1391.
- Lee, Y.K., K.R. Murphy, and J. Hur, Fluorescence Signatures of Dissolved Organic Matter Leached from Microplastics: Polymers and Additives. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020. 54(19): p. 11905-11914.
- Auta, H.S., et al., Growth kinetics and biodeterioration of polypropylene microplastics by Bacillus sp. and Rhodococcus sp. isolated from mangrove sediment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018. 127: p. 15-21.
- ter Halle, A., et al., To what extent are microplastics from the open ocean weathered? Environmental Pollution, 2017. 227: p. 167-174.
- Zbyszewski, M., P.L. Corcoran, and A. Hockin, Comparison of the distribution and degradation of plastic debris along shorelines of the Great Lakes, North America. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 2014. 40(2): p. 288-299.
- Ding, J., et al., Detection of microplastics in local marine organisms using a multi-technology system. Analytical Methods, 2019. 11(1): p. 78-87.
- Wang, Z.-M., et al., SEM/EDS and optical microscopy analyses of microplastics in ocean trawl and fish guts. Science of The Total Environment, 2017. 603-604: p. 616-626.
- Sun, X., et al., Toxicities of polystyrene nano- and microplastics toward marine bacterium Halomonas alkaliphila. Science of The Total Environment, 2018. 642: p. 1378-1385.
- Song, C., et al., Different interaction performance between microplastics and microalgae: The bio-elimination potential of Chlorella sp. L38 and Phaeodactylum tricornutum MASCC-0025. Science of The Total Environment, 2020. 723: p. 138146.
- Mariano, S., et al., Micro and Nanoplastics Identification: Classic Methods and Innovative Detection Techniques. Frontiers in Toxicology, 2021. 3.
- Löder, M.G.J., et al., Focal plane array detector-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging for the analysis of microplastics in environmental samples. Environmental Chemistry, 2015. 12(5): p. 563-581.
- Cole, M., et al., Microplastic Ingestion by Zooplankton. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013. 47(12): p. 6646-6655.
- Käppler, A., et al., Analysis of environmental microplastics by vibrational microspectroscopy: FTIR, Raman or both? Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2016. 408(29): p. 8377-8391.
- Araujo, C.F., et al., Identification of microplastics using Raman spectroscopy: Latest developments and future prospects. Water Research, 2018. 142: p. 426-440.
- Majewsky, M., et al., Determination of microplastic polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) in environmental samples using thermal analysis (TGA-DSC). Science of The Total Environment, 2016. 568: p. 507-511.
- Golebiewski, J. and A. Galeski, Thermal stability of nanoclay polypropylene composites by simultaneous DSC and TGA. Composites Science and Technology, 2007. 67(15): p. 3442-3447.
- Fischer, M. and B.M. Scholz-Böttcher, Simultaneous Trace Identification and Quantification of Common Types of Microplastics in Environmental Samples by Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017. 51(9): p. 5052-5060.
- Fries, E., et al., Identification of polymer types and additives in marine microplastic particles using pyrolysis-GC/MS and scanning electron microscopy. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 2013. 15(10): p. 1949-1956.
- Nuelle, M.-T., et al., A new analytical approach for monitoring microplastics in marine sediments. Environmental Pollution, 2014. 184: p. 161-169.
- Gambardella, C., et al., Effects of polystyrene microbeads in marine planktonic crustaceans. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017. 145: p. 250-257.
- Summers, S., T. Henry, and T. Gutierrez, Agglomeration of nano- and microplastic particles in seawater by autochthonous and de novo-produced sources of exopolymeric substances. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018. 130: p. 258-267.
- Gigault, J., et al., Marine plastic litter: the unanalyzed nano-fraction. Environmental Science: Nano, 2016. 3(2): p. 346-350.
- Huang, D., et al., Microplastics and nanoplastics in the environment: Macroscopic transport and effects on creatures. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021. 407: p. 124399.
- Ivleva, N.P. Chemical Analysis of Microplastics and Nanoplastics: Challenges, Advanced Methods, and Perspectives. Chemical Reviews, 2021. 121(19): p. 11886-11936.
- Iyangbe, M.D. Critical Properties of Micro- and Nanoplastics for Potential Health Impact. 2023, North Carolina Central University: United States -- North Carolina. p. 101.
- Bermúdez, J.R. and P.W. Swarzenski, A microplastic size classification scheme aligned with universal plankton survey methods. MethodsX, 2021. 8: p. 101516.
- Syberg, K., et al., Sorption of PCBs to environmental plastic pollution in the North Atlantic Ocean: Importance of size and polymer type. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 2020. 2: p. 100062.
- Alimi, O.S., J.M. Farner, and N. Tufenkji, Exposure of nanoplastics to freeze-thaw leads to aggregation and reduced transport in model groundwater environments. Water Research, 2021. 189: p. 11653.
- Browne, M.A., et al., Accumulation of Microplastic on Shorelines Woldwide: Sources and Sinks. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011. 45(21): p. 9175-9179.
- Karbalaei, S., et al., Occurrence, sources, human health impacts and mitigation of microplastic pollution. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018. 25(36): p. 36046-36063.
- Jambeck, J.R., et al., Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science, 2015. 347(6223): p. 768-771.
- Horton, A.A., et al., Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Science of The Total Environment, 2017. 586: p. 127-141.
- Amobonye, A., et al., Environmental Impacts of Microplastics and Nanoplastics: A Current Overview. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021. 12.
- Cole, M., et al., Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011. 62(12): p. 2588-2597.
- Cárdenas-Alcaide, M.F., et al., Environmental impact and mitigation of micro(nano)plastics pollution using green catalytic tools and green analytical methods. Green Analytical Chemistry, 2022. 3: p. 100031.
- Yee, M.S., et al., Impact of Microplastics and Nanoplastics on Human Health. Nanomaterials (Basel), 2021. 11(2).
- Lucas, N., et al., Polymer biodegradation: Mechanisms and estimation techniques – A review. Chemosphere, 2008. 73(4): p. 429-442.
- Mattsson, K., et al., Nanofragmentation of Expanded Polystyrene Under Simulated Environmental Weathering (Thermooxidative Degradation and Hydrodynamic Turbulence). Frontiers in Marine Science, 2021. 7.
- Chamas, A., et al., Degradation Rates of Plastics in the Environment. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020. 8(9): p. 3494-3511.
- Roy, R., et al., Isolation of a soil bacterium for remediation of polyurethane and low-density polyethylene: a promising tool towards sustainable cleanup of the environment. 3 Biotech, 2021. 11(1): p. 29.
- Chen, Z., et al., Nanoplastics are significantly different from microplastics in urban waters. Water Research X, 2023. 19: p. 100169.
- Zettler, E.R., T.J. Mincer, and L.A. Amaral-Zettler, Life in the “Plastisphere”: Microbial Communities on Plastic Marine Debris. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013. 47(13): p. 7137-7146.
- Mattsson, K., et al., Chapter 13 - Nanoplastics in the Aquatic Environment, in Microplastic Contamination in Aquatic Environments, E.Y. Zeng, Editor. 2018, Elsevier. p. 379-399.
- Lehner, R., et al., Emergence of Nanoplastic in the Environment and Possible Impact on Human Health. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019. 53(4): p. 1748-1765.
- Ma, Y.-B., et al., Recent advances in micro (nano) plastics in the environment: Distribution, health risks, challenges and future prospects. Aquatic Toxicology, 2023. 261: p. 106597.
- Liu, L., et al., Cellular internalization and release of polystyrene microplastics and nanoplastics. Science of The Total Environment, 2021. 779: p. 146523.
- Zhang, Y., et al., The life cycle of micro-nano plastics in domestic sewage. Science of The Total Environment, 2022. 802: p. 149658.
- Wang, P., et al., Nanotechnology: A New Opportunity in Plant Sciences. Trends in Plant Science, 2016. 21(8): p. 699-712.
- Terepocki, A.K., et al., Size and dynamics of microplastic in gastrointestinal tracts of Northern Fulmars (Fulmarus glacialis) and Sooty Shearwaters (Ardenna grisea). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017. 116(1): p. 143-150.
- Lei, L., et al., Microplastic particles cause intestinal damage and other adverse effects in zebrafish Danio rerio and nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Science of The Total Environment, 2018. 619-620: p. 1-8.
- Santillo, D., K. Miller, and P. Johnston, Microplastics as contaminants in commercially important seafood species. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 2017. 13(3): p. 516-521.
- Dobson, F.S., et al., Plasticity results in delayed breeding in a long-distant migrant seabird. Ecology and Evolution, 2017. 7(9): p. 3100-3109.
- Md Amin, R., et al., Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton in Terengganu coastal waters, southern South China Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020. 150: p. 110616.
- Courtene-Jones, W., et al., Microplastic pollution identified in deep-sea water and ingested by benthic invertebrates in the Rockall Trough, North Atlantic Ocean. Environmental Pollution, 2017. 231: p. 271-280.
- Larue, C., et al., A Critical Review on the Impacts of Nanoplastics and Microplastics on Aquatic and Terrestrial Photosynthetic Organisms. Small, 2021. 17(20): p. 2005834.
- Maity, S. and K. Pramanick, Perspectives and challenges of micro/nanoplastics-induced toxicity with special reference to phytotoxicity. Global Change Biology, 2020. 26(6): p. 3241-3250.
- Yin, L., et al., Interactions between microplastics/nanoplastics and vascular plants. Environmental Pollution, 2021. 290: p. 117999.
- Ali, S.S., et al., Degradation of conventional plastic wastes in the environment: A review on current status of knowledge and future perspectives of disposal. Science of The Total Environment, 2021. 771: p. 144719.
- Stapleton, P.A., Microplastic and nanoplastic transfer, accumulation, and toxicity in humans. Current Opinion in Toxicology, 2021. 28: p. 62-69.
- Kumar, M., et al., Current research trends on micro- and nano-plastics as an emerging threat to global environment: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021. 409: p. 124967.
- Wang, Y.-L., et al., Potent Impact of Plastic Nanomaterials and Micromaterials on the Food Chain and Human Health. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020. 21(5): p. 1727.
- Rahman, A., et al., Potential human health risks due to environmental exposure to nano- and microplastics and knowledge gaps: A scoping review. Science of The Total Environment, 2021. 757: p. 143872.
- Prata, J.C., et al., Environmental exposure to microplastics: An overview on possible human health effects. Science of The Total Environment, 2020. 702: p. 134455.
- Carbery, M., W. O'Connor, and T. Palanisami, Trophic transfer of microplastics and mixed contaminants in the marine food web and implications for human health. Environment International, 2018. 115: p. 400-409.
- Schneider, M., et al., Nanoparticles and their interactions with the dermal barrier. Dermato-Endocrinology, 2009. 1(4): p. 197-206.
- Brennecke, D., et al., Microplastics as vector for heavy metal contamination from the marine environment. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016. 178: p. 189-195.
- Blackburn, K. and D. Green, The potential effects of microplastics on human health: What is known and what is unknown. Ambio, 2022. 51(3): p. 518-530.
- Mason, S.A., V.G. Welch, and J. Neratko, Synthetic Polymer Contamination in Bottled Water. Front Chem, 2018. 6: p. 407.
- Ge, H., et al., Potential role of LINC00996 in colorectal cancer: a study based on data mining and bioinformatics. Onco Targets Ther, 2018. 11: p. 4845-4855.
- Stapleton, P.A. Toxicological considerations of nano-sized plastics. AIMS Environ Sci, 2019. 6(5): p. 367-378.
- Porter, D.W., et al., Mouse pulmonary dose- and time course-responses induced by exposure to multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Toxicology, 2010. 269(2): p. 136-147.
- Ohlwein, S., et al., Health effects of ultrafine particles: a systematic literature review update of epidemiological evidence. Int J Public Health, 2019. 64(4): p. 547-559.
- Hernandez, L.M., N. Yousefi, and N. Tufenkji, Are There Nanoplastics in Your Personal Care Products? Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2017. 4(7): p. 280-285.
- Bouwstra, J., et al., New Aspects of the Skin Barrier Organization. Skin Pharmacology and Applied Skin Physiology, 2004. 14(Suppl. 1): p. 52-62.
- Vogt, A., et al., 40nm, but not 750 or 1,500nm, Nanoparticles Enter Epidermal CD1a+ Cells after Transcutaneous Application on Human Skin. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 2006. 126(6): p. 1316-1322.
- Shen, M., et al., Recent advances in toxicological research of nanoplastics in the environment: A review. Environmental Pollution, 2019. 252: p. 511-521.
- Lv, L., et al., In situ surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for detecting microplastics and nanoplastics in aquatic environments. Science of the Total Environment, 2020. 728: p. 138449.
- Shen, M., et al., Removal of microplastics via drinking water treatment: Current knowledge and future directions. Chemosphere, 2020. 251: p. 126612.
- Park, H.B., et al., Maximizing the right stuff: The trade-off between membrane permeability and selectivity. Science, 2017. 356(6343).
- Enfrin, M., et al., Kinetic and mechanistic aspects of ultrafiltration membrane fouling by nano- and microplastics. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020. 601: p. 117890.
- Enders, K., et al., Abundance, size and polymer composition of marine microplastics ≥10μm in the Atlantic Ocean and their modelled vertical distribution. Mar Pollut Bull, 2015. 100(1): p. 70-81.
- Ramirez Arenas, L., et al., Fate and removal efficiency of polystyrene nanoplastics in a pilot drinking water treatment plant. Science of The Total Environment, 2022. 813: p. 15262.
- McMullen, L.D. Chapter 20 - Remediation at the Water Treatment Plant, in Nitrogen in the Environment (Second Edition), J.L. Hatfield and R.F. Follett, Editors. 2008, Academic Press: San Diego. p. 623-629.
- Yang, Y., et al., Thermal treated amidoxime modified polymer of intrinsic microporosity (AOPIM-1) membranes for high permselectivity reverse osmosis desalination. Desalination, 2023. 551: p. 116413.
- Ziajahromi, S., et al., Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway for microplastics: Development of a new approach to sample wastewater-based microplastics. Water Res, 2017. 112: p. 93-99.
- Ly, Q.V., et al., Characterization of dissolved organic matter for understanding the adsorption on nanomaterials in aquatic environment: A review. Chemosphere, 2021. 269: p. 128690.
- Bannick, C.G., et al., Development and testing of a fractionated filtration for sampling of microplastics in water. Water Res, 2019. 149: p. 650-658.
- Chen, Z., et al., Phase transition of Mg/Al-flocs to Mg/Al-layered double hydroxides during flocculation and polystyrene nanoplastics removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021. 406: p. 124697.
- Azoulay, A., P. Garzon, and M.J. Eisenberg, Comparison of the mineral content of tap water and bottled waters. J Gen Intern Med, 2001. 16(3): p. 168-75.
- Batool, A. and S. Valiyaveettil, Surface functionalized cellulose fibers – A renewable adsorbent for removal of plastic nanoparticles from water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021. 413: p. 125301.
- Hu, E., et al., Cotransport of naphthalene with polystyrene nanoplastics (PSNP) in saturated porous media: Effects of PSNP/naphthalene ratio and ionic strength. Chemosphere, 2020. 245: p. 125602.
- Nakata, K. and A. Fujishima, TiO2 photocatalysis: Design and applications. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology C: Photochemistry Reviews, 2012. 13(3): p. 169-189.
- Castelvetro, V., et al., Nylon 6 and nylon 6,6 micro- and nanoplastics: A first example of their accurate quantification, along with polyester (PET), in wastewater treatment plant sludges. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021. 407: p. 124364.
- Kamrannejad, M.M., et al., Photocatalytic degradation of polypropylene/TiO2 nano-composites. Materials Research, 2014. 17: p. 1039-1046.
- Dória, A.R., et al., Ultra-fast synthesis of Ti/Ru0.3Ti0.7O2 anodes with superior electrochemical properties using an ionic liquid and laser calcination. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021. 416: p. 129011.
- Ali, I., et al., Micro- and nanoplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Occurrence, removal, fate, impacts and remediation technologies – A critical review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021. 423: p. 130205.
- Yang, X., et al., Nanoplastics Disturb Nitrogen Removal in Constructed Wetlands: Responses of Microbes and Macrophytes. Environ Sci Technol, 2020. 54(21): p. 14007-14016.
- Jeong, C.B., et al., Nanoplastic Ingestion Enhances Toxicity of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in the Monogonont Rotifer Brachionus koreanus via Multixenobiotic Resistance (MXR) Disruption. Environ Sci Technol, 2018. 52(19): p. 11411-11418.
- Zhou, G., et al., Removal of polystyrene nanoplastics from water by CuNi carbon material: the role of adsorption. Science of The Total Environment, 2022. 820: p. 153190.
- Qu, Y., et al., Magnetic effervescent tablets containing deep eutectic solvent as a green microextraction for removal of polystyrene nanoplastics from water. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2022. 188: p. 736-745.
- Shi, Y., et al., Removal of nanoplastics from aqueous solution by aggregation using reusable magnetic biochar modified with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Environ Pollut, 2023. 318: p. 120897.
- Binandeh, M. Performance of unique magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry Reports, 2022. 6: p. 100072.
- Lu, A.-H., E.L. Salabas, and F. Schüth, Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Protection, Functionalization, and Application. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2007. 46(8): p. 1222-1244.
- Issa, B., et al., Magnetic nanoparticles: surface effects and properties related to biomedicine applications. Int J Mol Sci, 2013. 14(11): p. 21266-305.
- Farinha, P., et al., A Comprehensive Updated Review on Magnetic Nanoparticles in Diagnostics. Nanomaterials (Basel), 2021. 11(12).
- Šafařík, I. and M. Šafaříková, Magnetic Nanoparticles and Biosciences. Monatshefte für Chemie / Chemical Monthly, 2002. 133(6): p. 737-759.
- Kudr, J., et al., Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Design and Synthesis to Real World Applications. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland), 2017. 7(9): p. 243.
- Materón, E.M., et al., Magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications: A review. Applied Surface Science Advances, 2021. 6: p. 100163.
- Anderson, S.D., V.V. Gwenin, and C.D. Gwenin, Magnetic Functionalized Nanoparticles for Biomedical, Drug Delivery and Imaging Applications. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2019. 14(1): p. 188.
- Wu, L., et al., Organic Phase Syntheses of Magnetic Nanoparticles and Their Applications. Chemical Reviews, 2016. 116(18): p. 10473-10512.
- Zhu, N., et al., Surface Modification of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 2018. 8(10): p. 810.
- Gambhir, R.P., S.S. Rohiwal, and A.P. Tiwari, Multifunctional surface functionalized magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications: A review. Applied Surface Science Advances, 2022. 11: p. 100303.
- Nikzamir, M., A. Akbarzadeh, and Y. Panahi, An overview on nanoparticles used in biomedicine and their cytotoxicity. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2021. 61: p. 102316.
- Díez, A.G., et al., Multicomponent magnetic nanoparticle engineering: the role of structure-property relationship in advanced applications. Materials Today Chemistry, 2022. 26: p. 101220.
- Nkurikiyimfura, I., et al., Temperature-dependent magnetic properties of magnetite nanoparticles synthesized via coprecipitation method. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020. 846: p. 156344.
- Ban, I., M. Drofenik, and D. Makovec, The synthesis of iron–nickel alloy nanoparticles using a reverse micelle technique. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2006. 307(2): p. 250-256.
- Setia, A., et al., Theranostic magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, toxicity, and emerging trends for biomedical applications. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2023. 81: p. 104295.
- Stergar, J., et al., The synthesis and characterization of copper–nickel alloy nanoparticles with a therapeutic Curie point using the microemulsion method. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013. 576: p. 220-22.
- Majidi, S., et al., Current methods for synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 2016. 44(2): p. 722-734.
- Kwon, S.G., et al., Kinetics of Monodisperse Iron Oxide Nanocrystal Formation by “Heating-Up” Process. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007. 129(41): p. 12571-12584.
- Dixit, S. and P. Jeevanandam, Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles by Thermal Decomposition Approach. Advanced Materials Research, 2009. 67: p. 221-226.
- Unni, M., et al., Thermal Decomposition Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Diminished Magnetic Dead Layer by Controlled Addition of Oxygen. ACS Nano, 2017. 11(2): p. 2284-2303.
- Laurent, S., et al., Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stabilization, Vectorization, Physicochemical Characterizations, and Biological Applications. Chemical Reviews, 2010. 110(4): p. 2574-2574.
- Byrappa, K. and T. Adschiri, Hydrothermal technology for nanotechnology. Progress in Crystal Growth and Characterization of Materials, 2007. 53(2): p. 117-166.
- Chen, G., et al., A Facile Solvothermal Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of MnFe2O4 Spheres with Tunable Sizes. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012. 95(11): p. 3569-3576.
- Adewunmi, A.A., M.S. Kamal, and T.I. Solling, Application of magnetic nanoparticles in demulsification: A review on synthesis, performance, recyclability, and challenges. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021. 196: p. 107680.
- Arruebo, M., et al., Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today, 2007. 2(3): p. 22-32.
- Chomoucka, J., et al., Magnetic nanoparticles and targeted drug delivering. Pharmacol Res, 2010. 62(2): p. 144-9.
- eng, X.H., et al., Targeted magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for tumor imaging and therapy. Int J Nanomedicine, 2008. 3(3): p. 311-21.
- Qiao, R., et al., Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for brain imaging and drug delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2023. 197: p. 114822.
- Gupta, I., S. Sirohi, and K. Roy, Strategies for functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2023. 72: p. 2757-2767.
- Bohara, R.A., N.D. Thorat, and S.H. Pawar, Role of functionalization: strategies to explore potential nano-bio applications of magnetic nanoparticles. RSC Advances, 2016. 6(50): p. 43989-44012.
- Nguyen, D.T. and K.-S. Kim, Functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2014. 31(8): p. 1289-1305.
- Stergar, J., et al., Synthesis and Characterization of Silica-Coated Cu1-xNix Nanoparticles. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics - IEEE TRANS MAGN, 2012. 48: p. 1344-1347.
- Da, X., et al., Synthesis and characterization of PEG coated hollow Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as a drug carrier. Materials Letters, 2022. 309: p. 131357.
- Ban, I., et al., Synthesis of Poly-Sodium-Acrylate (PSA) Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Use in Forward Osmosis Draw Solutions. 2019.
- Hao, R., et al., Synthesis, Functionalization, and Biomedical Applications of Multifunctional Magnetic Nanoparticles. Advanced Materials, 2010. 22(25): p. 2729-2742.
- Chen, F., et al., Synthesis of magnetite core–shell nanoparticles by surface-initiated ring-opening polymerization of l-lactide. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2008. 320(13): p. 1921-1927.
- Kaman, O., et al., Preparation of Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles and their silica-coated clusters: Magnetic properties and transverse relaxivity. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2017. 427: p. 251-257.
- Villa, S., et al., Functionalization of Fe₃O₄ NPs by Silanization: Use of Amine (APTES) and Thiol (MPTMS) Silanes and Their Physical Characterization. Materials (Basel, Switzerland), 2016. 9(10): p. 826.
- Umut, E., et al., Magnetic, optical and relaxometric properties of organically coated gold–magnetite (Au–Fe3O4) hybrid nanoparticles for potential use in biomedical applications. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2012. 324(15): p. 2373-2379.
- Fakurpur Shirejini, S., S.M. Dehnavi, and M. Jahanfar, Potential of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles coated with carbon dots as a magnetic nanoadsorbent for DNA isolation. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2023. 190: p. 580-589.
- Kaymaz, S.V., et al., Nanomaterial surface modification toolkit: Principles, components, recipes, and applications. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2023. 322: p. 103035.
- Angadi V, J. and M. K, 21 - Present and future applications of magnetic nanoparticles in the field of medicine and biosensors, in Fundamentals and Industrial Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles, C.M. Hussain and K.K. Patankar, Editors. 2022, Woodhead Publishing. p. 655-663.
- Díaz-Hernández, A., et al., Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Chitosan: A Potential Approach for Enzyme Immobilization. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2018. 2018: p. 9468574.
- de Las Nieves Piña, M., et al., Adsorption and Quantification of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) by using Hybrid Magnetic Nanoparticles. Chemistry, 2018. 24(49): p. 12820-12826.
- Li, T., et al., Modified Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for COD removal in oil field produced water and regeneration. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021. 23: p. 101630.
- Yeap, S.P., et al., Electrosteric stabilization and its role in cooperative magnetophoresis of colloidal magnetic nanoparticles. Langmuir, 2012. 28(42): p. 14878-91.
- Yan, R., et al., Effect of aggregation behavior on microplastic removal by magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Science of The Total Environment, 2023. 898: p. 165431.
- Shi, X., et al., Removal of microplastics from water by magnetic nano-Fe(3)O(4). Sci Total Environ, 2022. 802: p. 149838.
- Gaß, H., et al., Magnetic Removal of Micro- and Nanoplastics from Water—from 100 nm to 100 µm Debris Size. Small. n/a(n/a): p. 2305467.
- Li, W., et al., Self-driven magnetorobots for recyclable and scalable micro/nanoplastic removal from nonmarine waters. Science Advances, 2022. 8(45): p. eade1731.
- Li, W., et al., Preparation of magnetic Janus microparticles for the rapid removal of microplastics from water. Sci Total Environ, 2023. 903: p. 166627.
- Wang, H.-P., et al., Modified superhydrophobic magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for removal of microplastics in liquid foods. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023. 476: p. 146562.
- Zhang, Y., et al., Efficient magnetic capture of PE microplastic from water by PEG modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Performance, kinetics, isotherms and influence factors. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2025. 147: p. 677-687.
- Babalar, M., S. Siddiqua, and M.A. Sakr, A novel polymer coated magnetic activated biochar-zeolite composite for adsorption of polystyrene microplastics: Synthesis, characterization, adsorption and regeneration performance. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024. 331: p. 125582.
- Tang, Y., et al., Removal of microplastics from aqueous solutions by magnetic carbon nanotubes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021. 406: p. 126804.
- Li, P., et al., A preliminary study of the interactions between microplastics and citrate-coated silver nanoparticles in aquatic environments. J Hazard Mater, 2020. 385: p. 121601.
- Zhang, Y., et al., Coagulation removal of microplastics from wastewater by magnetic magnesium hydroxide and PAM. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2021. 43: p. 102250.
- Zhang, X., et al., The removal characteristics and mechanisms of polystyrene microplastics with various induced photoaging degrees by CuFe2O4. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023. 322: p. 124245.
- Zhao, H., et al., Removal of polystyrene nanoplastics from aqueous solutions using a novel magnetic material: Adsorbability, mechanism, and reusability. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022. 430: p. 133122.
- Pasanen, F., R.O. Fuller, and F. Maya, Fast and simultaneous removal of microplastics and plastic-derived endocrine disruptors using a magnetic ZIF-8 nanocomposite. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023. 455: p. 140405.
- Surette, M.C., D.M. Mitrano, and K.R. Rogers, Extraction and concentration of nanoplastic particles from aqueous suspensions using functionalized magnetic nanoparticles and a magnetic flow cell. Microplastics and Nanoplastics, 2023. 3(1): p. 2.
- Oliva, J., et al., Using NIR irradiation and magnetic bismuth ferrite microparticles to accelerate the removal of polystyrene microparticles from the drinking water. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023. 345: p. 118784.
- Bakhteeva, Y., et al., Removal of microplastics from water by using magnetic sedimentation. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2023. 20.
- Peng, X., et al., Biohybrid Magnetically Driven Microrobots for Sustainable Removal of Micro/Nanoplastics from the Aquatic Environment. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024. 34(3): p. 2307477.
- Cao, Y., et al., Advances in magnetic materials for microplastic separation and degradation. J Hazard Mater, 2024. 461: p. 132537.
- Munir, N., et al., The potential of zeolite nanocomposites in removing microplastics, ammonia, and trace metals from wastewater and their role in phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2024. 31(2): p. 1695-1718.
- Mahendran, R. and S. Ramaswamy, Nanoplastics as Trojan Horses: Deciphering Complex Connections and Environmental Ramifications: A Review. Chemistry Africa, 2024.
| PLACE | MPs TYPE | MPs SIZE | PROFUSION |
|---|---|---|---|
| Netherlands (tap and surface water) | PS, PE | 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000 nm (PS), 90-106 µm | 260 mg/L |
| Denmark (fish sample) | PS, PE | 100 nm (PS), 200-9900 nm (PE) |
1.3 mg/g fish |
| USA (seawater) | PP, PE, PS, PA | ≤ 5 mm | 0.025 g/mL |
| South Korea (seawater and beach) | expanded polystyrene (EPS) | ≤ 1 mm | 0–0.3 items/L (seawater), 631 items/L (beach) |
| China (surface sediment) | Rayon, PE, PP, PA, PET, PS, PMMA, PU | 34.97–4983.73 μm | 499.76 items/kg |
| Italy (shallow waters) | PE, PP, PS | ≤ 1 mm | 672-2175 items/kg |
| China (sediment) | High-density polyethylene (HDPE), PET, PE, PS | ≤ 5 mm | 5.1-87.1 items/g sediment |
| China (sewage) | PET, PS, PP | 681.46±528.73 μm | 0.59–12 items/L |
| China (freshwater bodies) | PES, rayon, PP, PA, nylon | 20 to 5000 μm | 0.9–2.4 items/L |
| Australia (shrimp) | PS, rayon | 0.190–4.214 mm | 0.40±0.27 items/L |
| China (fishes) | PE, PP, PES | 20–500 μm | 0.3–5.3 items per fish |
| Germany (bottled water) | PET, PP | 1–500 μm | 0–253 items/L |
| Mexico (milk) | PES, polysulfone (PSU) | ≤ 5 mm | 3–11 items/L |
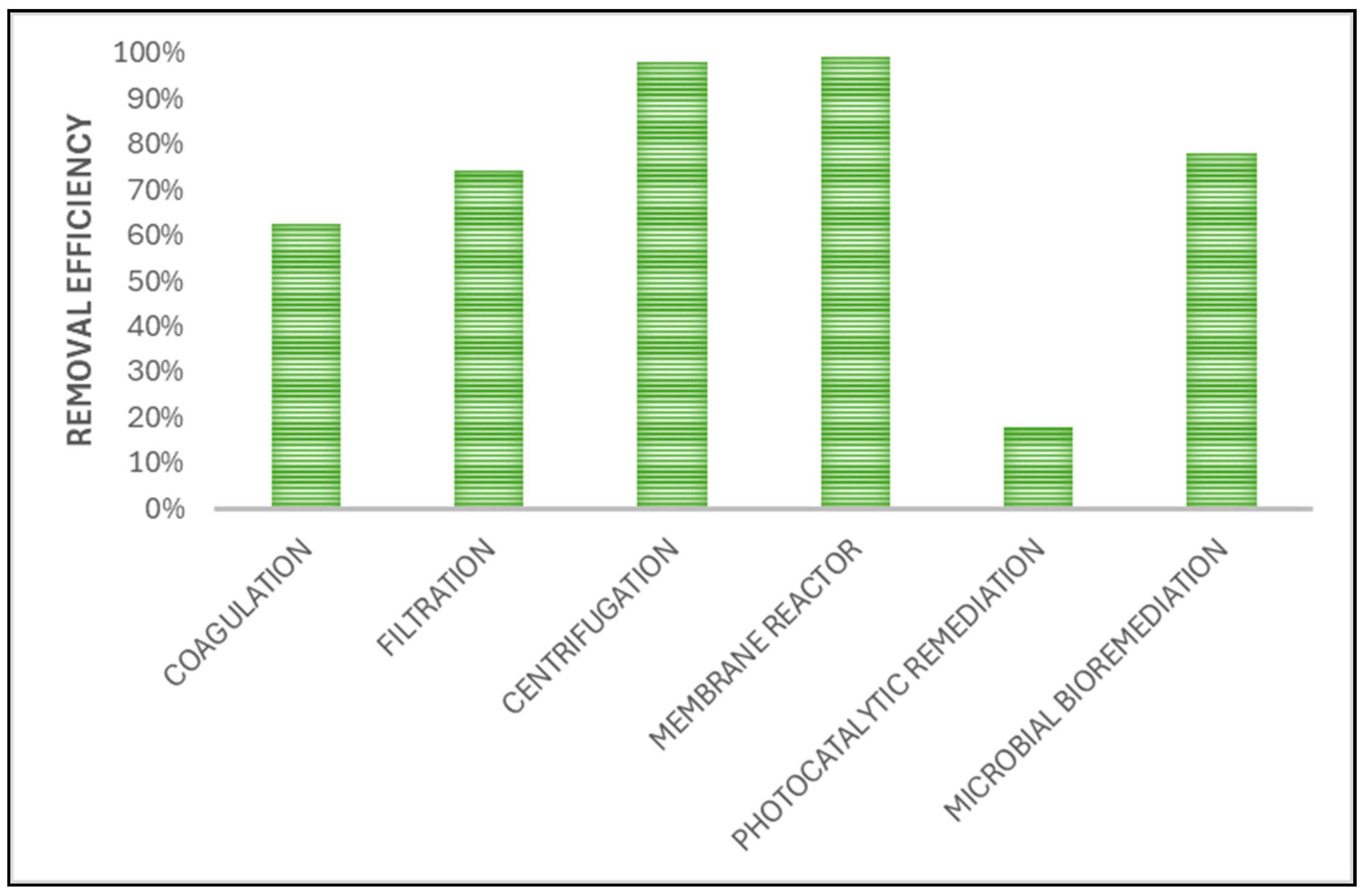
| METHOD | THE SIZE OF REMOVED NP [nm] | REMOVAL EFFICIENCY [%] | LIMITS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filtration | 217-333 | 32-92 | Not suitable for larger particles, as they may remain in the fraction. |
| Ultrafiltration | ≤ 150 | 74 | Particles can evade treatment; the process can be time-consuming. |
| Flocculation | 217 | 77 | More studies are needed to determine the optimal parameters. |
| Centrifugation | 206 | 98 | Time-consuming process. |
| Photocatalytic degradation | ≤ 100 | 17.1 | The phototransformation of NPs can vary and the photo-reactive activity in water can be high. |
| Membrane bioreactor filtration | ≥ 2 | 99 | Proper hydraulic retention time. |
| Sample types | MNPs | characterization | method | Particles size of MPs, NPs | Removal efficiency/ adsorption capacity | Main findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| solutions of MP (PS) | Fe3O4 | XRD, FTIR, DLS, SEM, TEM | magnetic separation | 100, 500, 1000 nm | 83.1 % - 92.9 % in a 1 h period | Electrostatic attraction between electropositive Fe3O4 MNPs and electronegative MPs led to charge neutralization-induced aggregation and efficient removal MP performance. | [173] |
| solutions of MPs (PE, PP, PS, PET) in pure, artificial, and environmental water samples | magnetic nano-Fe3O4 | FTIR, SEM | surface absorption, magnetic separation | 200-900 μm | 62.83 % - 86.87 % in a max. 240 min | Physicochemical properties of MPs such as crystallinity, hydrophobicity, and density, as well as background solutions influence the removal efficiency. | [174] |
| microPS particles from the water | magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles | TEM, FTIR | adsorption process, desorption process | 0.08, 0.43, 0.7 and 1 μm | 42.0 % - 93.7 % depending on the concentration, total surface area and number of PS particles | Hydrophobic interactions are the main interactions involved in the aggregation of Fe3O4 with PS particles. The Fe3O4particles could be recovered from the Fe3O4-PS complexes by desorption process. | [4] |
| Salt and freshwater samples | iron oxide nanoparticles with several polydimethylsiloxane hydrophobic coatings | SEM, TEM, SQUID, DLS, XRD, zeta potential | absorption process | 2-5 mm; 100-1000 nm | 90.0 % - 100 % | They removed 100 % of particles in a range of sizes, from 2-5 mm, and nearly 80 % of NP particles with a size range from 100 nm to 1000 nm using a sample 2-inch permanent NdFeB magnet. | [3] |
| solution of PS, PMMA, ME | modified superparamagnetic γ-Fe2O3, 9.6 nm | ATR-FTIR, TGA, DLS; SEM, | magnetic removal | 100 nm – 100 μm | polymer types of 2.5 – 5 μm for the maximum removal yield in terms of removed MPs and NPs mass (up to 5.38 g/g SPION); MPs and NPs of 100 nm – 1 μm in terms of highest numbers (up to 10 trillion MP and NP fragments per gram SPIONs) | If the size of the MPs is further increased, number as well as mass related efficiency is reduced as the specific surface area decreases rapidly. | [175] |
| nonmarine waters in a recyclable and scalable way | SMR consists of an ion-exchange resin microsphere functionalized by superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles | SEM, EDX, magnetic measurements, DLS, a confocal microscope | dynamic adsorption process; magnetic removal | 0.2 – 40 μm | > 90 % over 100 treatment cycles | As a result of the long-range electrophoretic attraction established by recyclable ion-exchange resin, the magnetorobot shows sustainable removal efficiency of > 90 % over 100 treatment cycles, with verified broad applicability to varying plastic compositions, sizes, and shapes as well as nonmarine water samples. | [176] |
| solutions of MPs (PS, PE) | Magnetic Janus microparticles (MJMs) synthesized via a modified Pickering emulsion method with aminated Fe3O4@SiO2 as the raw material | FTIR, TGA, SEM, contact angle analysis | adsorption process | 10 μm | 92.08 % for PS and 60.67 % for PE in just 20 min | Kinetic and thermodynamic studies confirmed the remarkable rate and capacity of the MJMs (0.759 min-1 and 2.72 mg/mg for PS, 0.539 min-1 and 2.42 mg/mg for PE), underlining their potential as a promising method for the rapid removal of MPs from water. | [177] |
| MPs in five liquid food systems | Fe3O4@Cn (n= 12, 14, 16, 18), modified by different saturated fatty acids (C12, C14, C16, C18) | TEM, AFM, FTIR, XRD, XPS, VSM, BET, TGA, contact angle measurements | nitrogen adsorption measurements | 100 nm | Fe3O4@C12 exhibited 92.89 % adsorption efficiency | A practical and simple method for the adsorption and removal of MPs from various liquid samples, where Fe3O4@C12 showed the desired adsorption efficiency. | [178] |
| PE MPs in water | Fe3O4; PEG/Fe3O4; PEI/Fe3O4; CA/Fe3O4 | FTIR, BET, zeta potential analysis, XRD, | magnetism adsorption | 13-149 μm | 2202.55 mg/g | The PEG/Fe3O4 exhibited a high magnetic capture efficiency of PE MPs in water. | [179] |
| PS MPs | magnetic activated biochar-zeolite composite (MACZ) coated with PEG and PEI (PMACZ) | SEM, EDX, BET, XRD, TGA, VSM | adsorption | 2 and 15 μm | 736 mg/g and 769 mg/g for PMACZ on 2 μm and 15 μm MP | After 4 cycles, the efficiency of the adsorbent decreased by 2.3 % and 2 % for PMACZ and MACZ, respectively, demonstrating the efficiency and high cycling capacity of these adsorbents. | [180] |
| PE, PET, PA | magnetic carbon nanotubes (M-CNTs) | UV-Vis, VSM, XRD, SEM, FTIR, XPS, zeta potential, TGA | magnetic force | 48 μm | 100 % | The mechanism analyses clearly suggested that the adsorption of M-CNTs by PE was caused by the strong hydrophobicity of MPs, the adsorption of M-CNTs by PET was caused by hydrophobic interaction and π-π electron conjugation, and π-π electron interaction, complexation, electrostatic interaction, and hydrogen bonding interaction on the PA surface all contributed to the adsorption of M-CNTs. | [181] |
| PS NPs in water | CuNi carbon material (CuNi@C) | SEM, FTIR, XPS, XRD, BET | adsorption process | 100 nm | 99.18 % | After 4 times cycles, CuNi@C can still remove ~ 75 % of total PS NPs from water. | [123] |
| PE, PP and PS in aquatic environments | Ag nanoparticles | UV-Vis, DLS, TEM, XRD, SEM, EDX | adsorption process | 0.2-0.25 mm | 94.52 % | Results revealed that Ag nanoparticles could be captured on the surface of PS MPs but coexisted with PE and PP MPs in water solutions. | [182] |
| PE in wastewater | magnetic magnesium hydroxide coagulant (MMHC) through the combination of Mg(OH)2 and Fe3O4 | SEM, FTIR, XRD, zeta potential | adsorption process | ≤ 270 μm | 73.4 % - 92.6 % | Among the three kinds of MMHCs, the removal is the highest when the ratio of Mg2+ to OH- reaches 1:1, due to the dense bubble-like structure on its surface. | [183] |
| PS MPs in water | CuFe2O4 | XRD, VSM, BET, FTIR, SEM, EDX, XPS, | remove MPs with different photoaging degrees | 0.96 – 1.59 μm | 98.02 % | Hydrogen bonding played a key role in the removal of pristine PS MPs and the destruction of C=O by Fe-OOH also played an important role in the removal of aged PS MPs. | [184] |
| PS NPs in aqueous solutions | fly ash modified with Fe ions | UV-Vis, FTIR, SEM-EDX, XRD, XPS, VSM | adsorption process | 94.1 % | The adsorption-desorption experiments show that the fly ash modified with Fe ions adsorbents have excellent reusability for PS NPs; they can be used 4 times. | [185] | |
| PS MPs | a zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8) magnetic porous nanocomposite modulated with n-butylamine (nano-Fe@ZIF-8) | SEM, XRD, FESEM, BET, nitrogen adsorption-desorption measurements | magnetic removal | 1.1 μm | ≥ 98 % | The results illustrate the synthesis of a simple, environmentally friendly and high performing material for the fast removal of both soluble organic pollutants and microparticulated organic pollutants. | [186] |
| metal-doped PS NPs in ultrapure water, synthetic freshwater, synthetic freshwater with a model natural organic matter isolate and synthetic marine water | hydrophobically functionalized magnetic nanoparticles | EDX, DLS, SEM, XRD, | magnetic separation flow cell | 229 nm | 56.1 – 84.9 % | MNPs in combination with a flow-through system is a promising technique to extract NPs aqueous suspensions with various compositions. | [187] |
| PS NP/MPs in drinking water | magnetic bismuth ferrite (BiFeO) microparticles | XRD, zeta potential measurements, | 70-11000 nm | ≈ 95.5 % in 90 minutes | The results demonstrated that using photocatalysis + physical-adsorption is a feasible strategy to quickly remove MPs contaminants from the water. | [188] | |
| Polyethylene (PE) and PET MPs from model aqueous suspensions | Composite magnetic Fe-C-NH2 MNPs | DLS, SEM, optical microscopy, XRD, UV-Vis | Magnetic sedimentation | 5-30 μm | > 99 % | PE and PET MPs can be effectively separated from water by adding Fe-C-NH2 MNPs and performing subsequent sedimentation in a gradient magnetic field. | [189] |
| Amino – modified PS in aqueous suspension | Magnetic algae robots (algae cells with Fe3O4 bound on its surface) | SEM, EDX, XRD, zeta potential, magnetic measurements, fluorescence intensity measurements. | Removal under rotating magnetic field | 50 nm and 1.5 μm | 70 – 92 % | Magnetic field driven algae-mased microrobots can be used for effective capture and removal of micro/nanoplastics from the aquatic environment. | [190] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





