Submitted:
04 June 2024
Posted:
05 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
Survey Population
Data Collection and Sampling Procedure
Sample Processing
Culture, MIC Determination and Identification of Neisseria Species
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Determination
Proportion Resistant
Statistics
Evidence of Transmission of Commensal Neisseria spp. between Family Members
Ethics
Role of the Funding Source
Results
Survey Population Data
Prevalence of Different Species of Oropharyngeal Neisseria spp. in Adults and Children
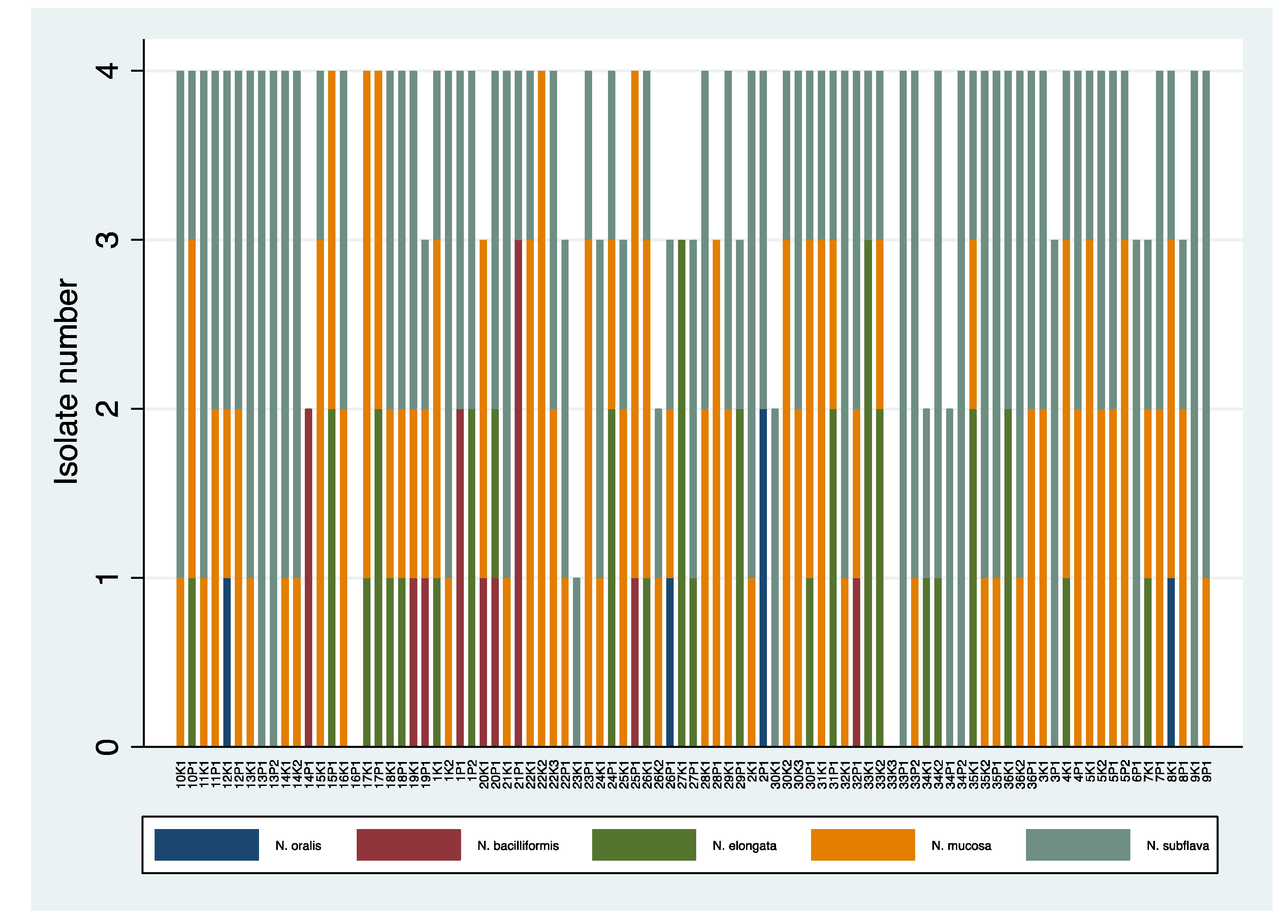
Richness of Neisseria Species
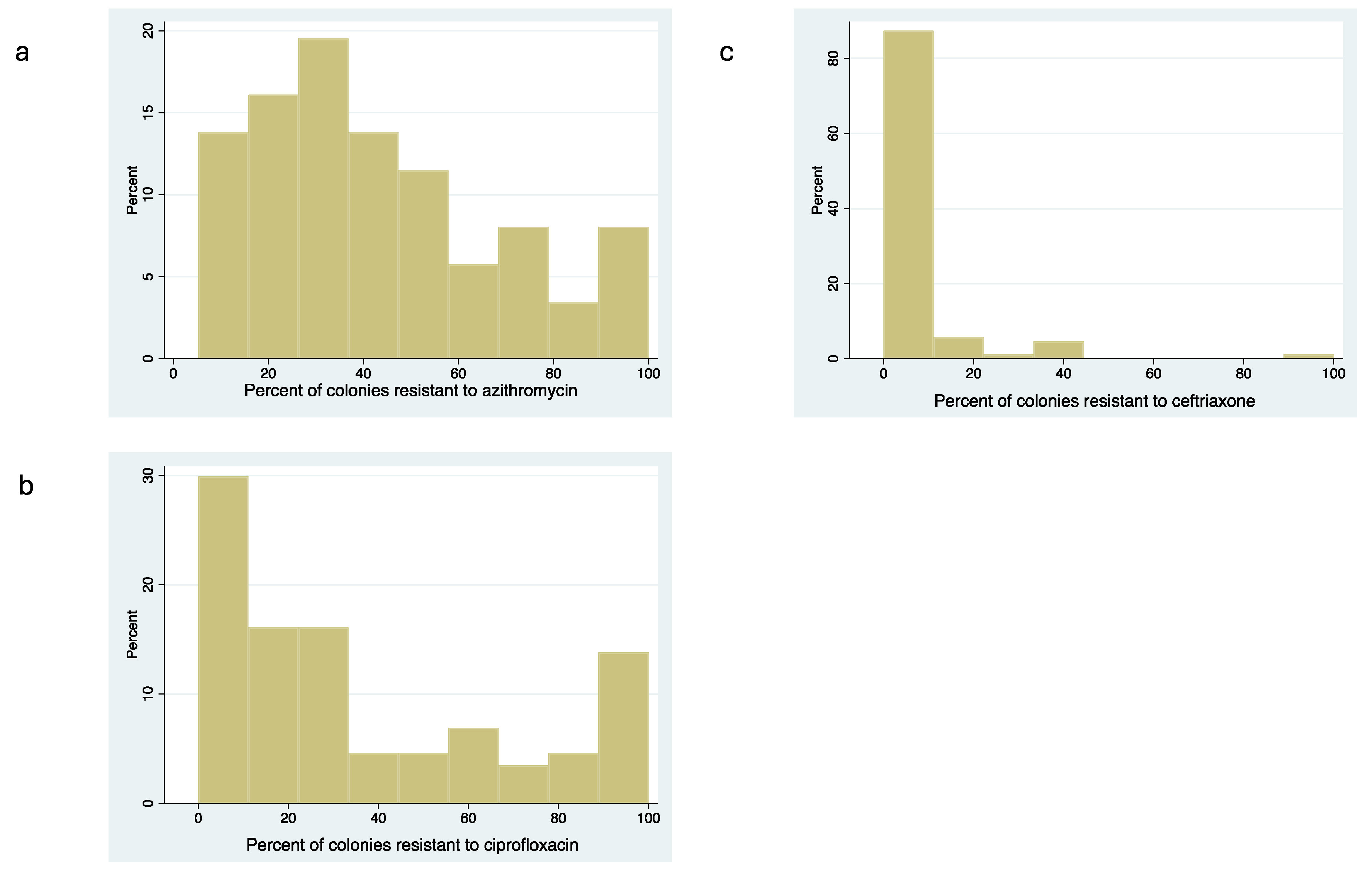
Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Commensal Neisseria spp.
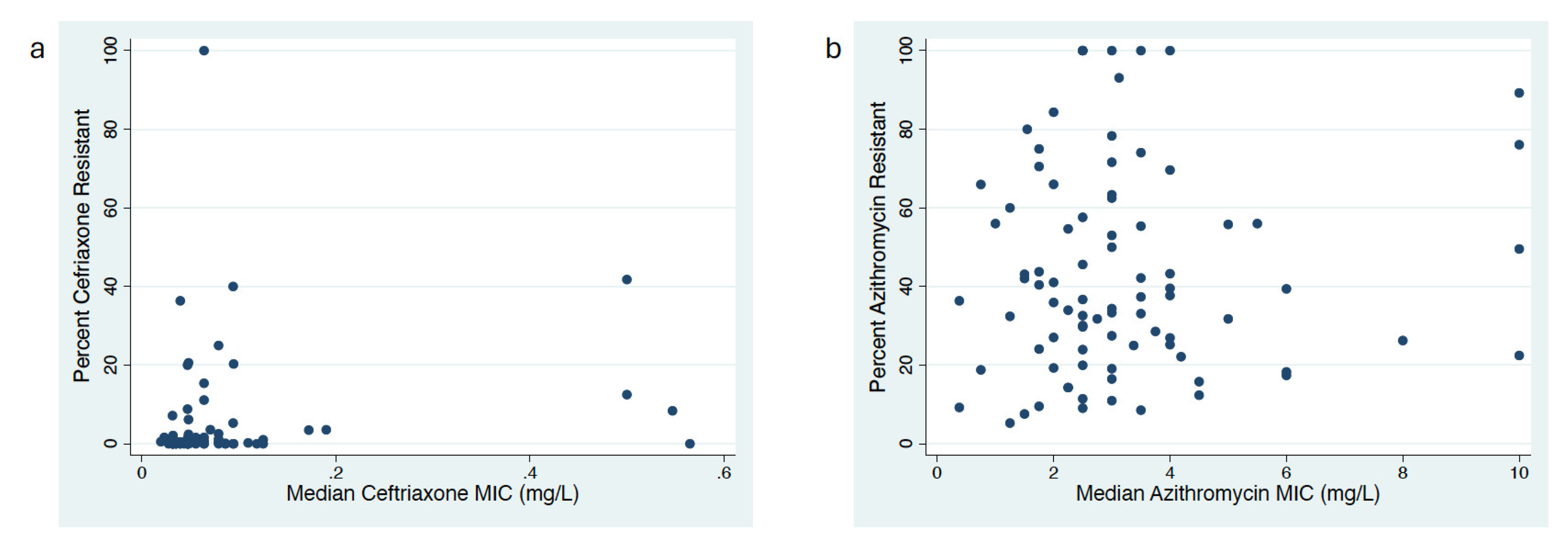
Correlation between MIC Distribution and Proportion Resistant Methods
Predictors of Antimicrobial Susceptibility
Association of MICs of Commensal Neisseria spp. between Family Members
Discussion
Differences in Prevalence of Neisseria spp. by Age Group
Variations of Antimicrobial Susceptibility between Neisseria spp.
Variations in Ceftriaxone MIC by Species and Species by Age Group Explain Variation in MIC by Age Group
Transmission of Neisseria spp.
Proportion versus MIC Distribution to Assess AMR
Data Sharing
References
- Mitjà O, Padovese V, Folch C, Rossoni I, Marks M, i Arias MAR, et al. Epidemiology and determinants of reemerging bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and emerging STIs in Europe. The Lancet Regional Health–Europe. 2023, 34.
- Wi T, Lahra MM, Ndowa F, Bala M, Dillon J-AR, Ramon-Pardo, P, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: global surveillance and a call for international collaborative action. PLoS medicine. 2017, 14, e1002344. [Google Scholar]
- Hanao M, Aoki K, Ishii Y, Shimuta K, Ohnishi M, Tateda, K. Molecular characterization of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates collected through a national surveillance programme in Japan, 2013: evidence of the emergence of a ceftriaxone-resistant strain from a ceftriaxone-susceptible lineage. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2021, 76, 1769–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapun, A., Morlot, C., Taha MK. Resistance to β-Lactams in Due to Chromosomally Encoded Penicillin-Binding Proteins. Antibiotics-Basel. 2016, 5(4). doi: ARTN 35 10.3390/antibiotics5040035. PubMed PMID: WOS:000391620900004. [CrossRef]
- Wadsworth CB, Arnold BJ, Sater MRA, Grad YH. Azithromycin Resistance through Interspecific Acquisition of an Epistasis-Dependent Efflux Pump Component and Transcriptional Regulator in. Mbio. 2018, 9(4). doi: ARTN e01419-18 10.1128/mBio.01419-18. PubMed PMID: WOS:000443884300078. [CrossRef]
- Chen ML, Zhang, C., Zhang, X., Chen, M. Meningococcal Quinolone Resistance Originated from Several Commensal Species. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2020, 64(2). doi: ARTN e01494-19 10.1128/AAC.01494-19. PubMed PMID: WOS:000509748200005. [CrossRef]
- Manoharan-Basil SS, Laumen JGE, Van Dijck C, De Block T, De Baetselier, I., Kenyon, C. Evidence of Horizontal Gene Transfer of 50S Ribosomal Genes rplB, rplD, and rplY in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2021, 12, 1263. [Google Scholar]
- Goytia, M., Wadsworth CB. Canary in the Coal Mine: How Resistance Surveillance in Commensals Could Help Curb the Spread of AMR in Pathogenic Neisseria. Mbio. 2022, 13, e01991–e22. [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C, Laumen J, Manoharan-Basil, S. Choosing new therapies for gonorrhoea: we need to consider the impact on the pan-Neisseria genome: a viewpoint. Antibiotics-Basel. 2021, 10(5). [CrossRef]
- Vanbaelen T, Van Dijck C, Laumen J, Gonzalez N, De Baetselier I, Manoharan-Basil SS, et al. Global epidemiology of antimicrobial resistance in commensal Neisseria species: a systematic review. International Journal of Medical Microbiology. 2022, 312(3). [CrossRef]
- Laumen JGE, Manoharan-Basil SS, Abdellati S, De Baetselier I, Van Dijck, C., Martiny, D., et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility of commensal Neisseria in the general population and men who have sex with men in Belgium. Scientific Reports. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Dong HV, Pham LQ, Nguyen HT, Nguyen MXB, Nguyen TV, May, F., et al. Decreased Cephalosporin Susceptibility of Oropharyngeal Neisseria Species in Antibiotic-Using Men-who-have-sex-with-men of Hanoi, Vietnam. Clin Infect Dis. 2019. Epub 2019/05/03. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuya R, Onoye Y, Kanayama A, Saika T, Iyoda T, Tatewaki M, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in clinical isolates of Neisseria subflava from the oral cavities of a Japanese population. J Infect Chemother. 2007, 13, 302–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp J, Hook 3rd E. Prevalence and persistence of Neisseria cinerea and other Neisseria spp. in adults. Journal of clinical microbiology. 1988, 26, 896–900.
- Chen ML, Zhang, C., Zhang, X., Chen, M. Meningococcal Quinolone Resistance Originated from Several Commensal Neisseria Species. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2020, 64(2). doi: ARTN e01494-19. 10.1128/AAC.01494-19. PubMed PMID: WOS:000509748200005. [CrossRef]
- Sáez Nieto JA, Marcos, C. , Vindel, A. Multicolonization of human nasopharynx due to Neisseria spp. International Microbiology. 1998, 1, 59–63.
- Shen YF, Chen ML. Prevalence, sequence type, and quinolone resistance of Neisseria lactamica carried in children younger than 15 years in Shanghai, China. Journal of Infection. 2020, 80, 61–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2019.08.020. PubMed PMID: WOS:000507459600008. [CrossRef]
- Van Dijck C, Laumen JG, Manoharan-Basil SS, Kenyon, C. Commensal neisseria are shared between sexual partners: implications for gonococcal and meningococcal antimicrobial resistance. Pathogens. 2020, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspari V, Djusse ME, Morselli S, Rapparini L, Foschi, C., Ambretti, S., et al. Non-pathogenic Neisseria species of the oropharynx as a reservoir of antimicrobial resistance: a cross-sectional study. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 2023, 13.
- Laumen JGE, Abdellati S, Van Dijck C, Martiny D, De Baetselier I, Manoharan-Basil SS, et al. A Novel Method to Assess Antimicrobial Susceptibility in Commensal Oropharyngeal Neisseria—A Pilot Study. Antibiotics. 2022, 11, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Vanbaelen T, Eric F, Christophe VD, Achilleas T, Laumen JGE, Sheeba, M.-BS, et al., editors. Effect on the Resistome of Dual vs Monotherapy for the Treatment of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: Results From a Randomized Controlled Trial (ResistAZM Trial). Open Forum Infectious Diseases; 2023: Oxford University Press US.
- Vanbaelen, T. Self-sampling with oral rinse to detect oropharyngeal Neisseria gonorrhoeae among men who have sex with men: results from an exploratory study in Belgium (the SSONG study). Sex Transm Infec. 2024.
- Bennett JS, Jolley KA, Earle SG, Corton C, Bentley SD, Parkhill, J, et al. A genomic approach to bacterial taxonomy: an examination and proposed reclassification of species within the genus Neisseria. Microbiology. 2012, 158, 1570–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto JAS, Marcos, C. , Vindel, A. Multicolonization of human nasopharynx due to Neisseria spp. International Microbiology. 1998, 1, 59–63.
- Donati C, Zolfo M, Albanese D, Tin Truong D, Asnicar F, Iebba V, et al. Uncovering oral Neisseria tropism and persistence using metagenomic sequencing. Nature microbiology. 2016, 1, 1–9.
- Masliah-Planchon J, Breton G, Jarlier V, Simon A, Benveniste O, Herson, S. , et al. Endocarditis due to Neisseria bacilliformis in a patient with a bicuspid aortic valve. Journal of clinical microbiology. 2009, 47, 1973–5.
- Abandeh FI, Balada-Llasat J-M, Pancholi P, Risaliti CM, Maher WE, Bazan JA. A rare case of Neisseria bacilliformis native valve endocarditis. Diagnostic microbiology and infectious disease. 2012, 73, 378–9.
- Gavalda M, Vilchez H, Martin M, Ruiz, E. , Ribas, M., Riera, M. Endocarditis caused by Neisseria bacilliformis: a case report and review of literature. IDCases. 2023, 31, e01725.
- Han XY, Hong, T. , Falsen, E. Neisseria bacilliformis sp. nov. isolated from human infections. Journal of clinical microbiology. 2006, 44, 474–9.
- Fiore MA, Raisman JC, Wong NRH, Hudson AO, Wadsworth CB. Exploration of the Neisseria Resistome Reveals Resistance Mechanisms in Commensals That May Be Acquired by N. gonorrhoeae through Horizontal Gene Transfer. Antibiotics-Basel. 2020, 9(10). doi: ARTN 656. 10.3390/antibiotics9100656. PubMed PMID: WOS:000584161000001. [CrossRef]
- Unitt A, Maiden M, Harrison, O. Characterizing the diversity and commensal origins of penA mosaicism in the genus Neisseria. Microbial Genomics. 2024, 10, 001209. [Google Scholar]
- Spratt BG, Bowler LD, Zhang, Q.-Y., Zhou, J., Smith JM. Role of interspecies transfer of chromosomal genes in the evolution of penicillin resistance in pathogenic and commensal Neisseria species. Journal of molecular evolution. 1992, 34, 115–25. [Google Scholar]
- de Block T, Laumen JGE, Van Dijck C, Abdellati S, De Baetselier I, Manoharan-Basil SS, et al. WGS of Commensal Neisseria Reveals Acquisition of a New Ribosomal Protection Protein (MsrD) as a Possible Explanation for High Level Azithromycin Resistance in Belgium. Pathogens. 2021, 10(3). Epub 2021/04/04. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030384. PubMed PMID: 33806962, PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC8005064. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto K, Hohashi N, Sugishita, C. A study on the transmission of MRSA among the family members including clients of visiting nurse and related infection control. [Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi] Japanese Journal of Public Health. 2001, 48, 190–9. [Google Scholar]
- Vanbaelen T, Laumen J, Van Dijck C, De Block T, Manoharan-Basil SS, Kenyon, C. Lack of Association between Antimicrobial Consumption and Antimicrobial Resistance in a HIV Preexposure Prophylaxis Population: A Cross-Sectional Study. Antibiotics. 2024, 13, 188. [Google Scholar]
- Vanbaelen T, Manoharan-Basil S, Kenyon, C. 45 Years of Tetracycline Post Exposure Prophylaxis for STIs and the Risk of Tetracycline Resistance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC infectious diseases. 2024.
- Olesen SW, Torrone EA, Papp JR, Kirkcaldy RD, Lipsitch, M. , Grad YH. Azithromycin Susceptibility Among Neisseria gonorrhoeae Isolates and Seasonal Macrolide Use. J Infect Dis. 2019, 219, 619–23. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kenyon, C. Commentary: Non-pathogenic Neisseria species of the oropharynx as a reservoir of antimicrobial resistance: a cross-sectional study. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 2024, 13, 1343608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenyon, C. Dual azithromycin/ceftriaxone therapy for gonorrhea in PrEP cohorts results in levels of macrolide consumption that exceed resistance thresholds by up to 7-fold. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2021, 224, 1623–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenyon C, Manoharan-Basil SS, Van Dijck, C. Is there a resistance threshold for macrolide consumption? Positive evidence from an ecological analysis of resistance data from Streptococcus pneumoniae, Treponema pallidum, and Mycoplasma genitalium. Microbial Drug Resistance. 2021, 27, 1079–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyndonckx R, Adriaenssens N, Versporten A, Hens N, Monnet DL, Molenberghs, G., et al. Consumption of antibiotics in the community, European union/European economic area, 1997–2017. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2021, 76, ii7–ii13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




