Submitted:
20 May 2024
Posted:
07 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
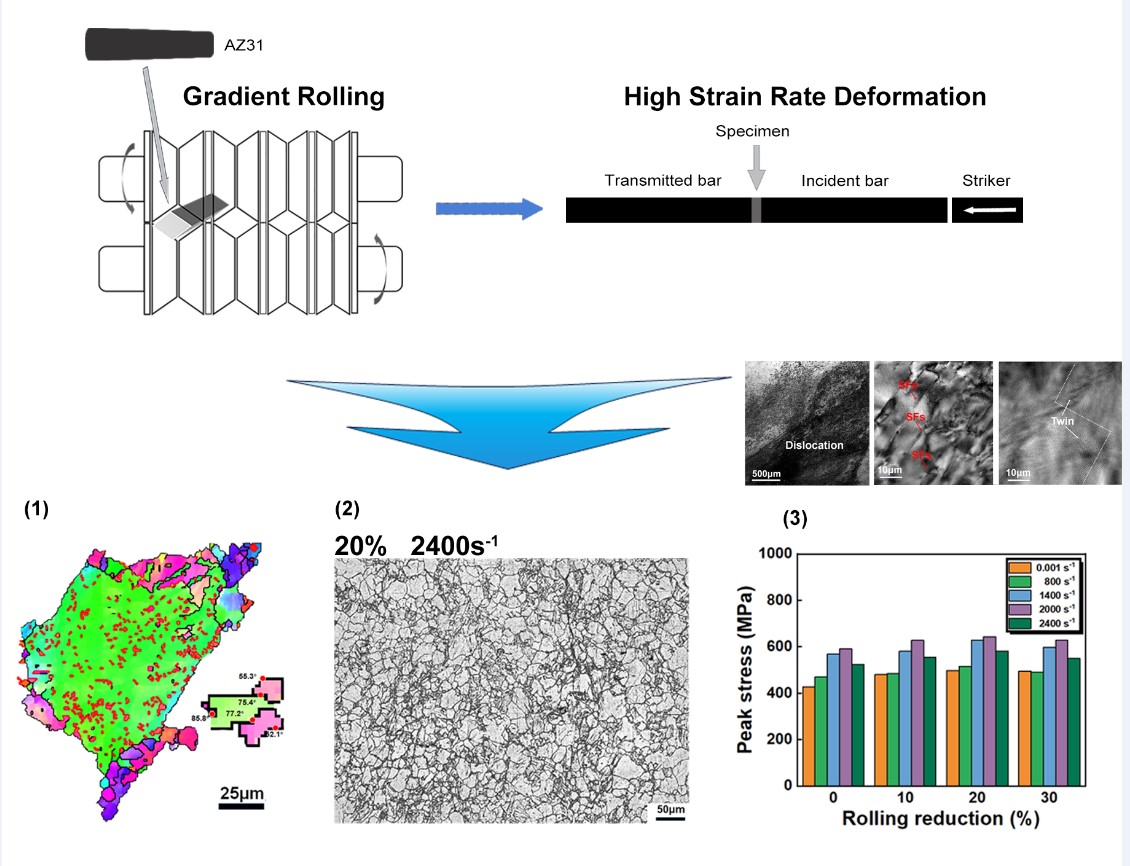
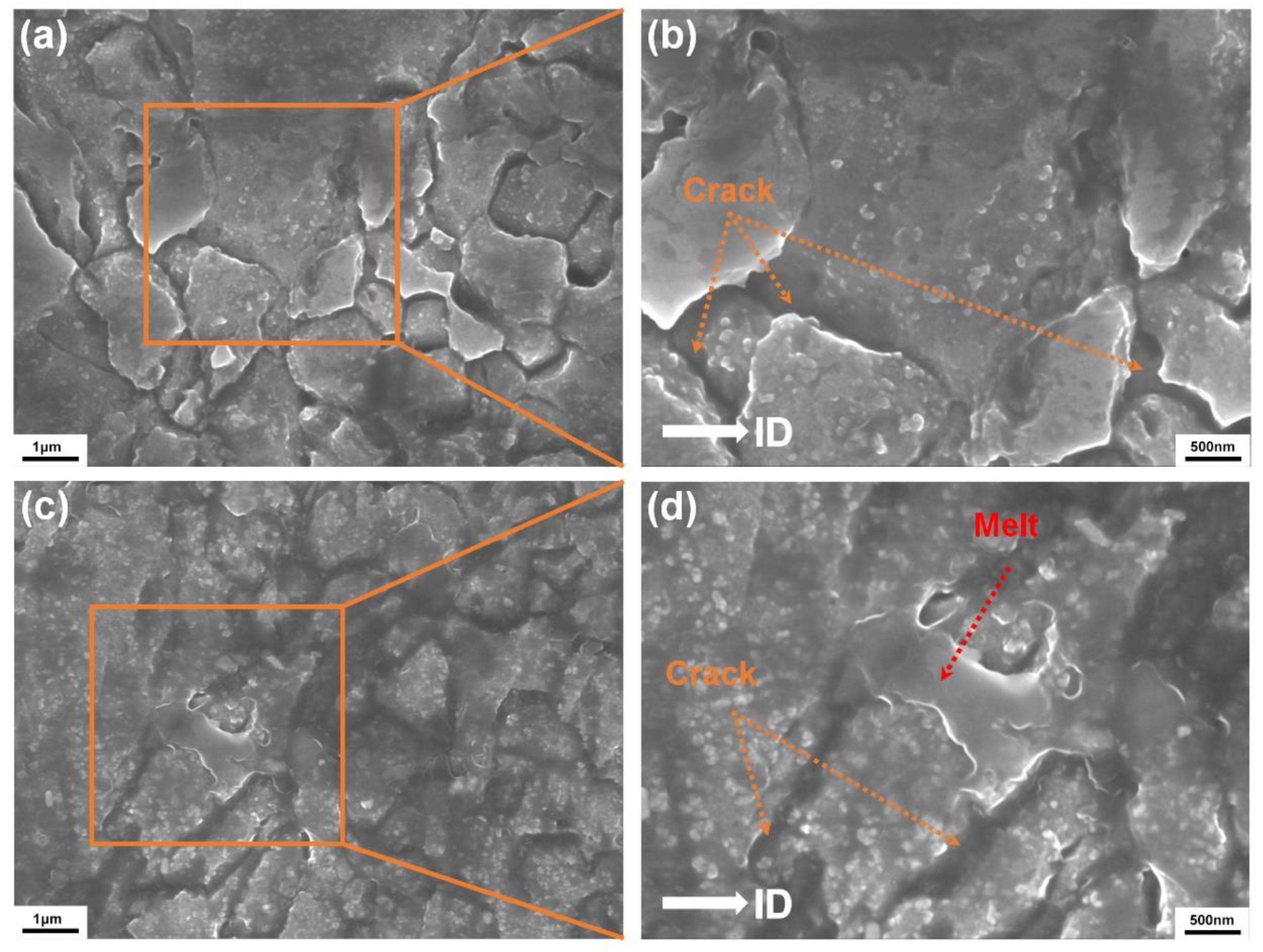
3. Results and Discussion
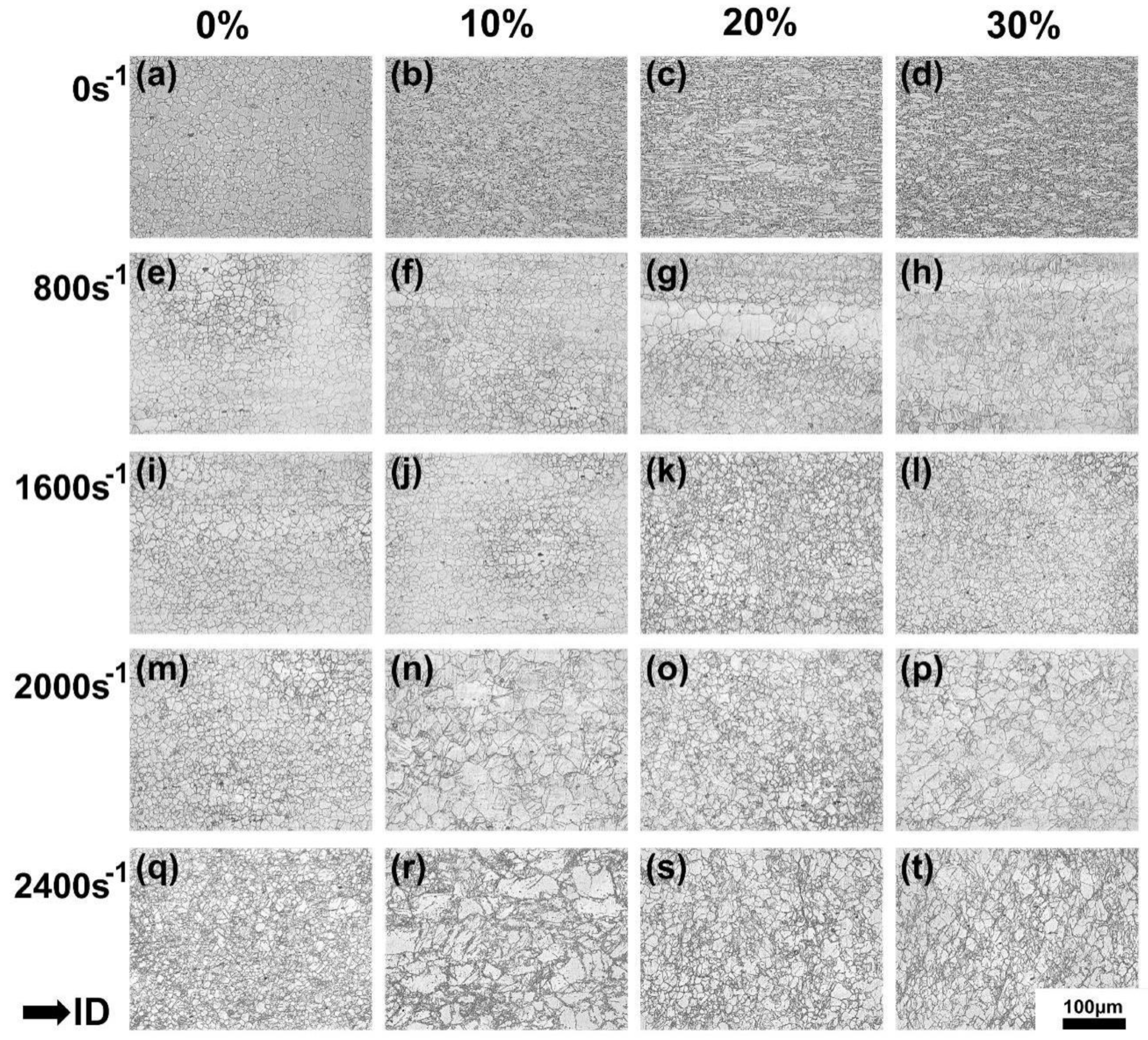
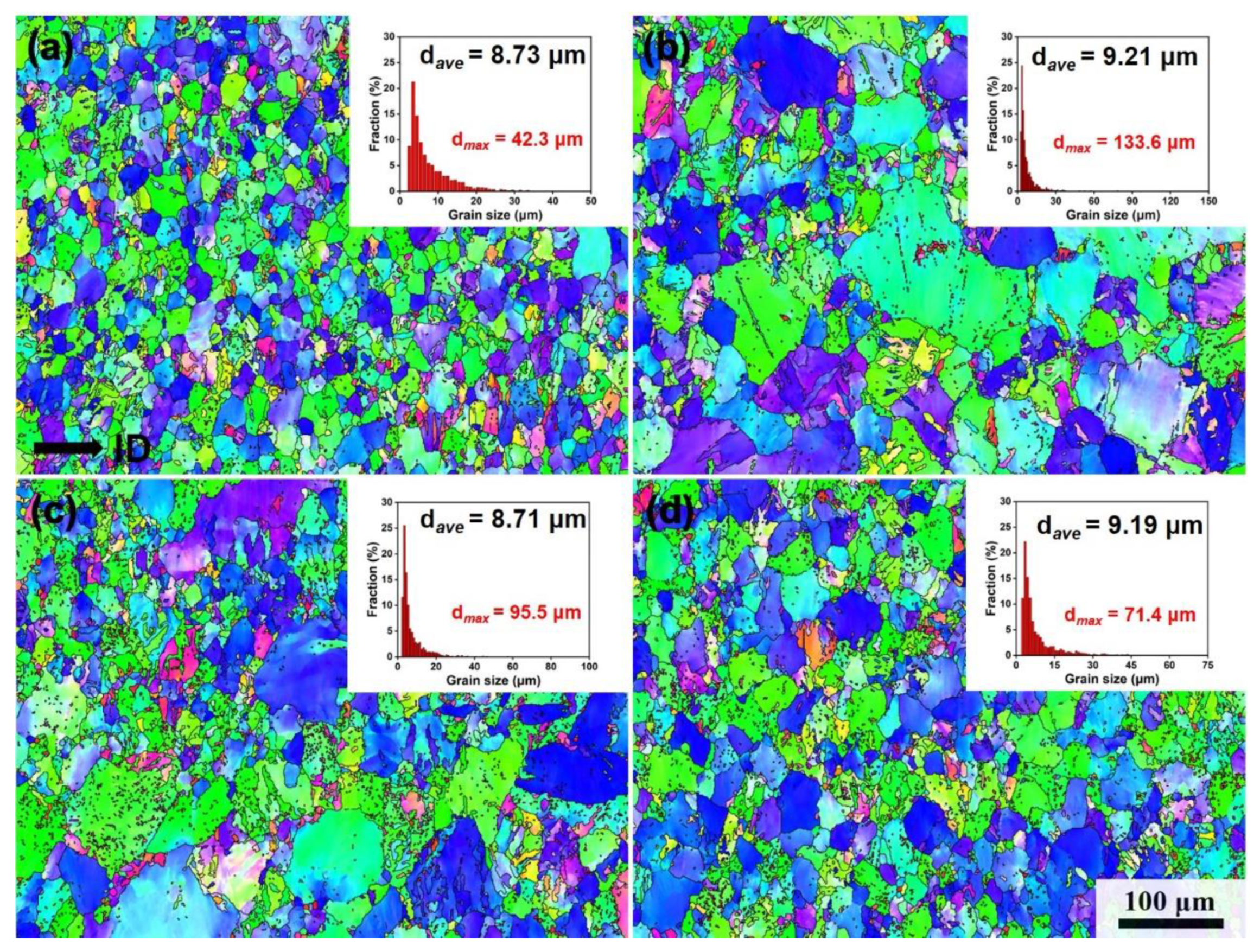
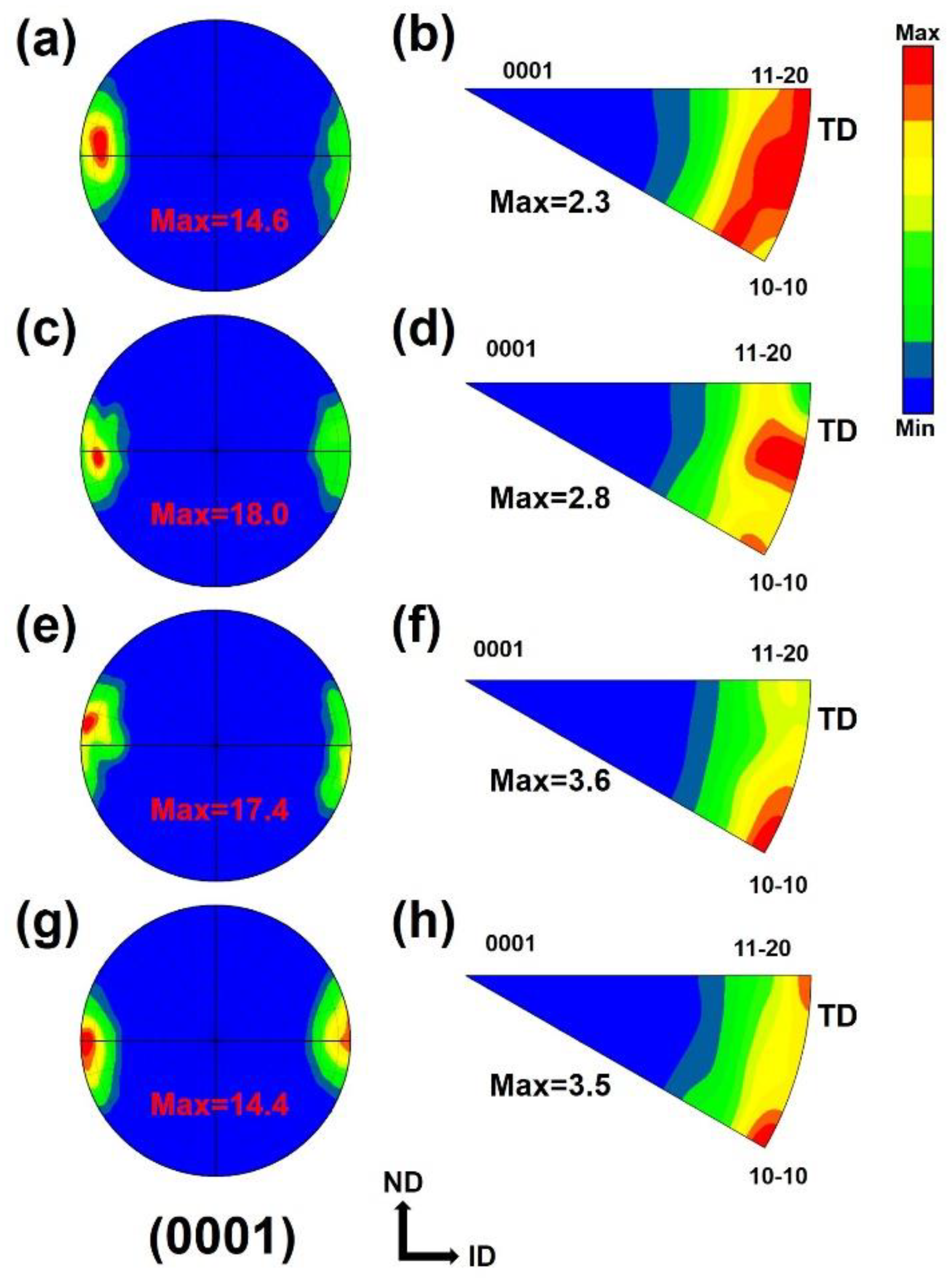
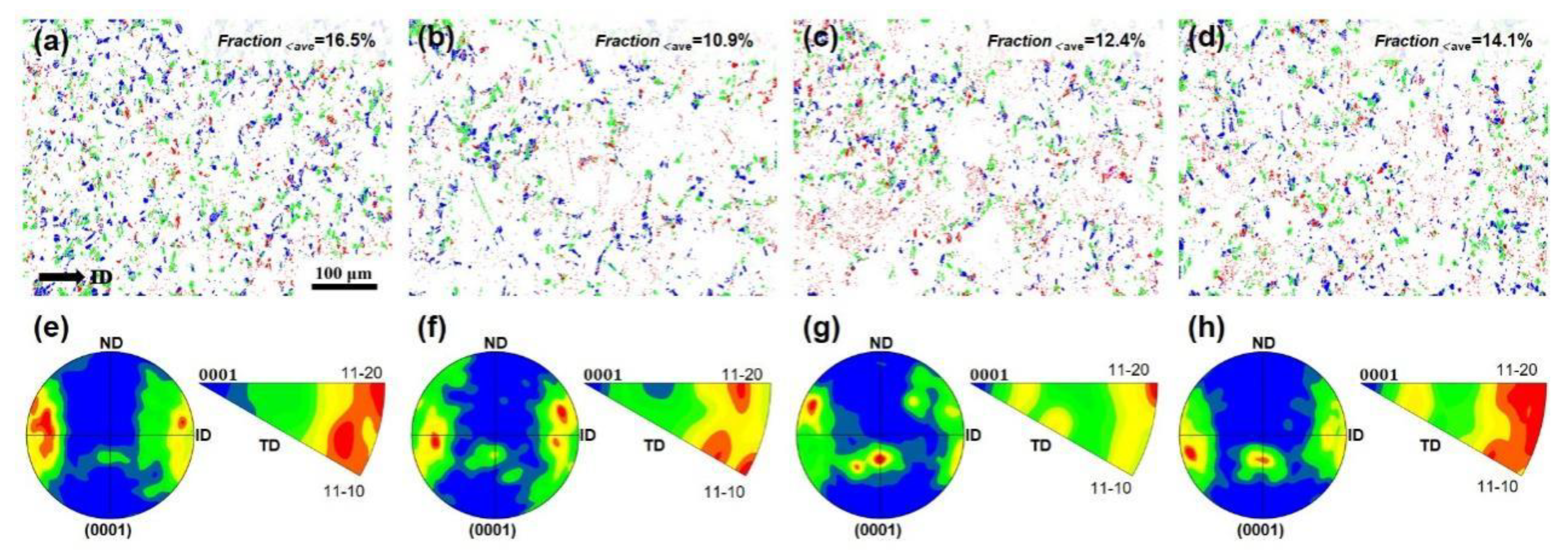
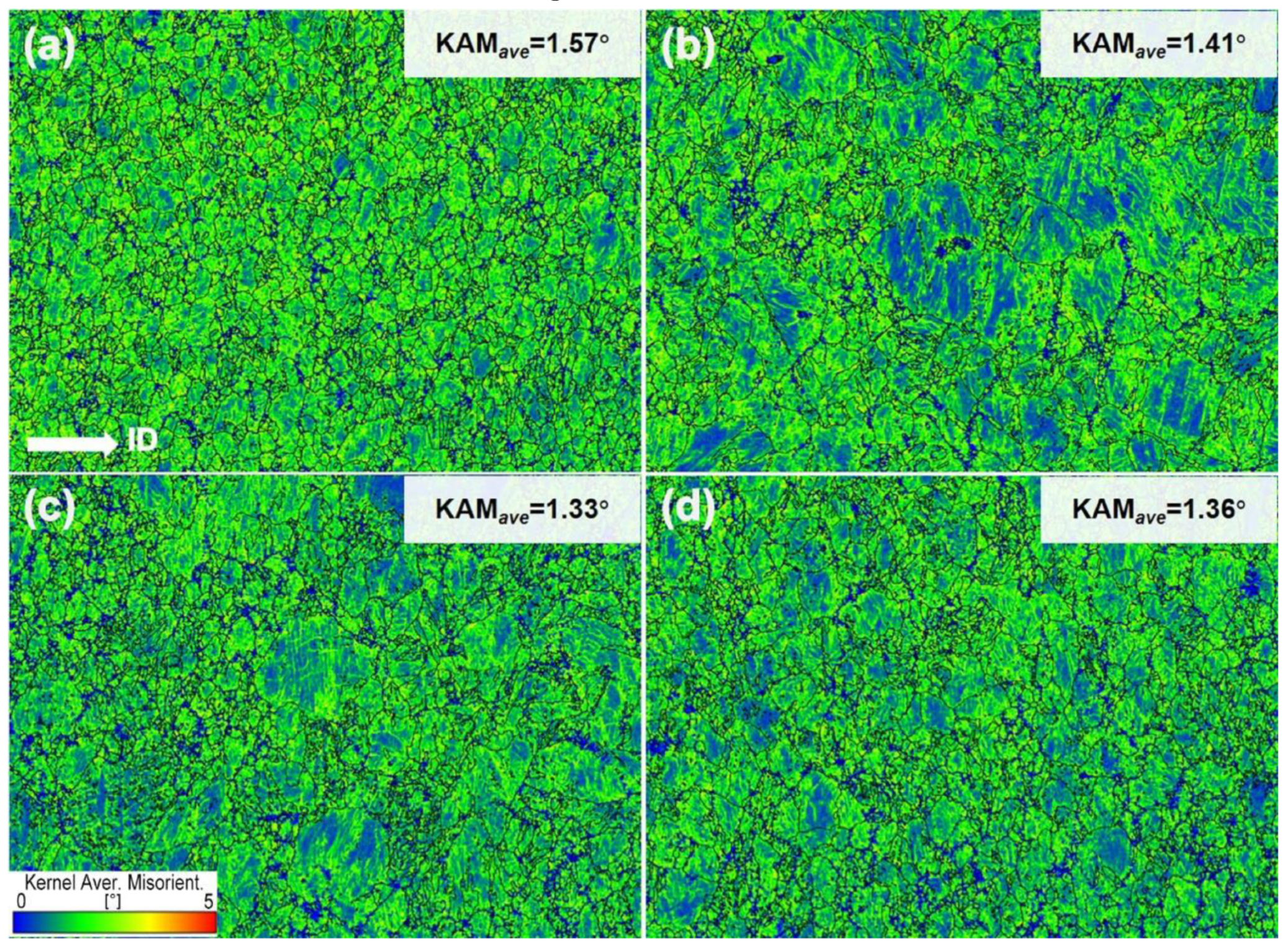
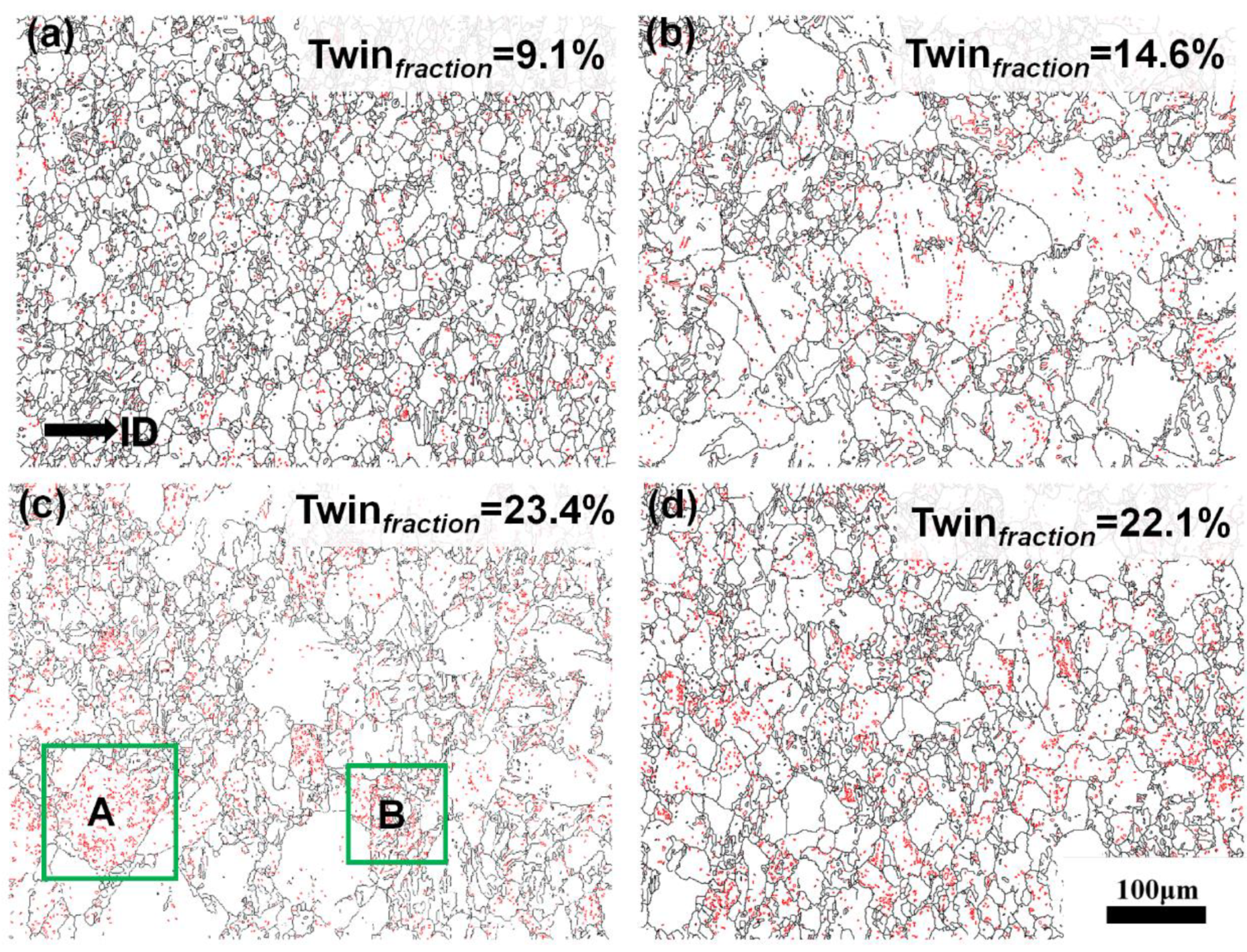
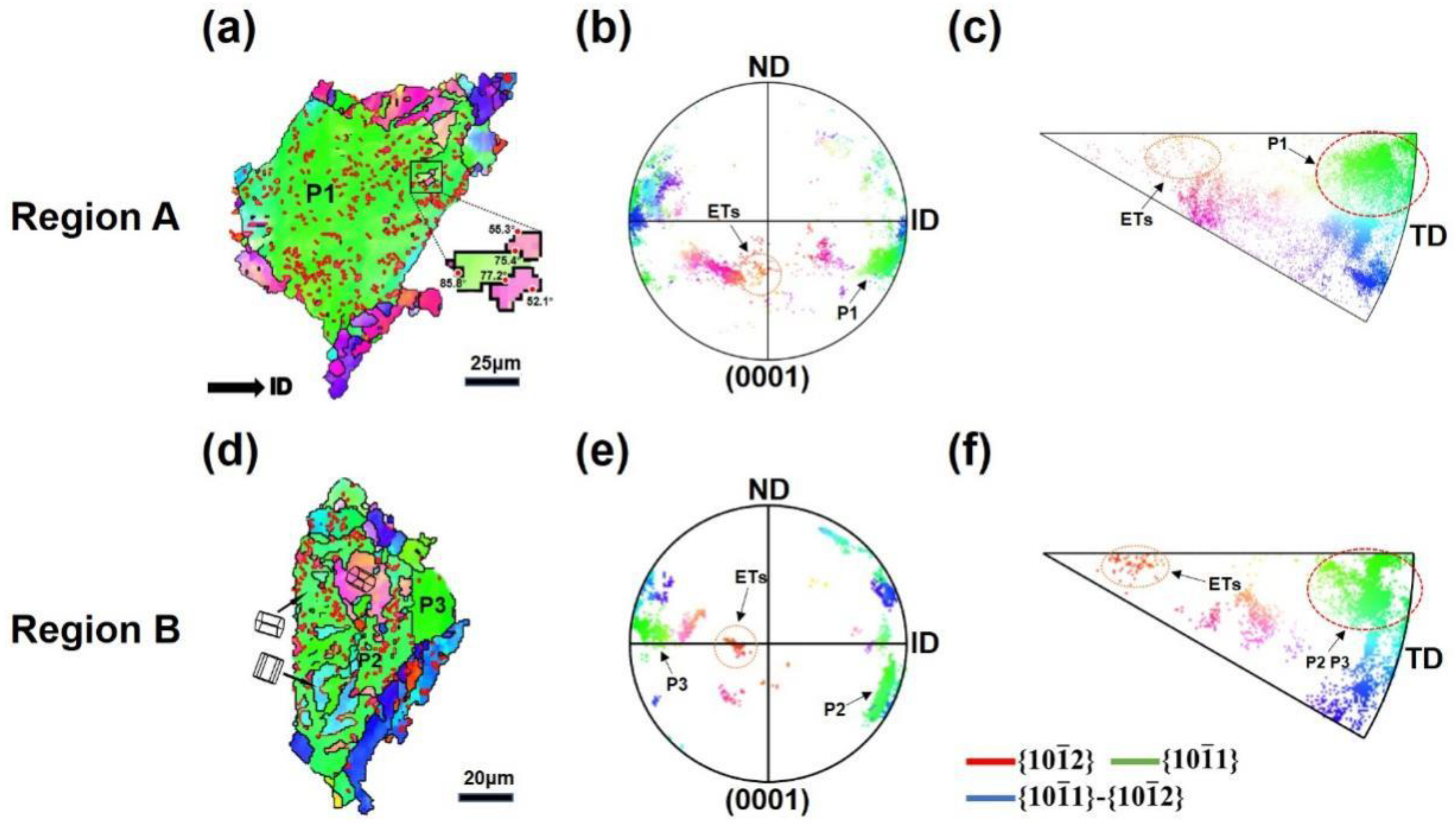
3.1. Microstructural Evolution
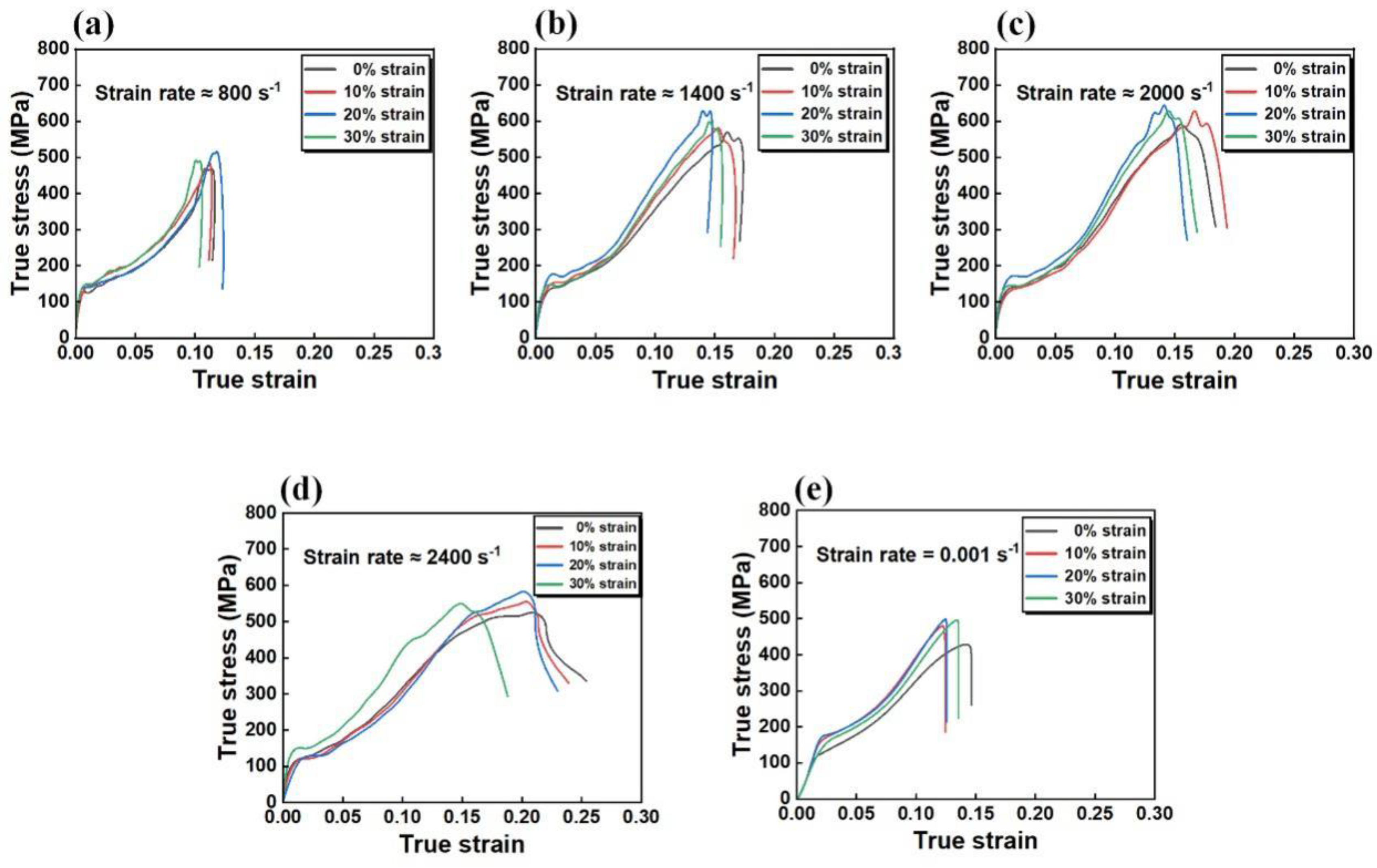
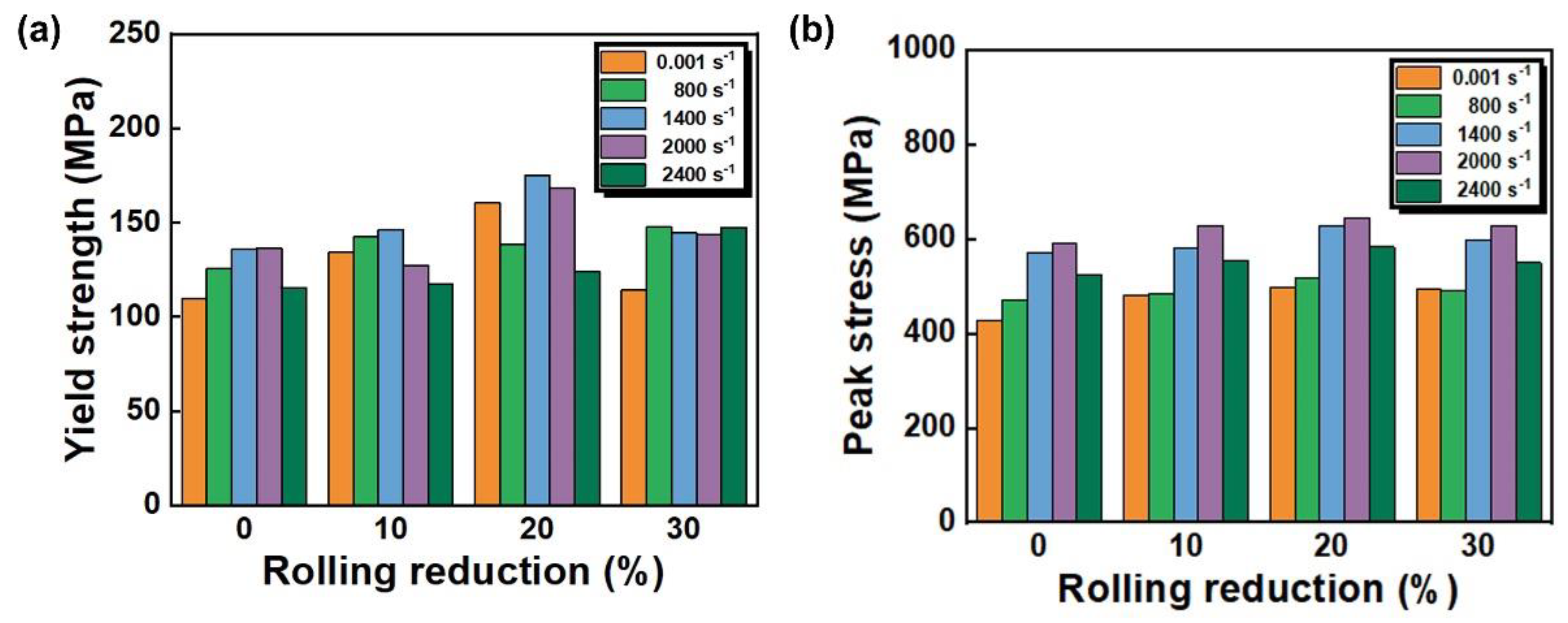
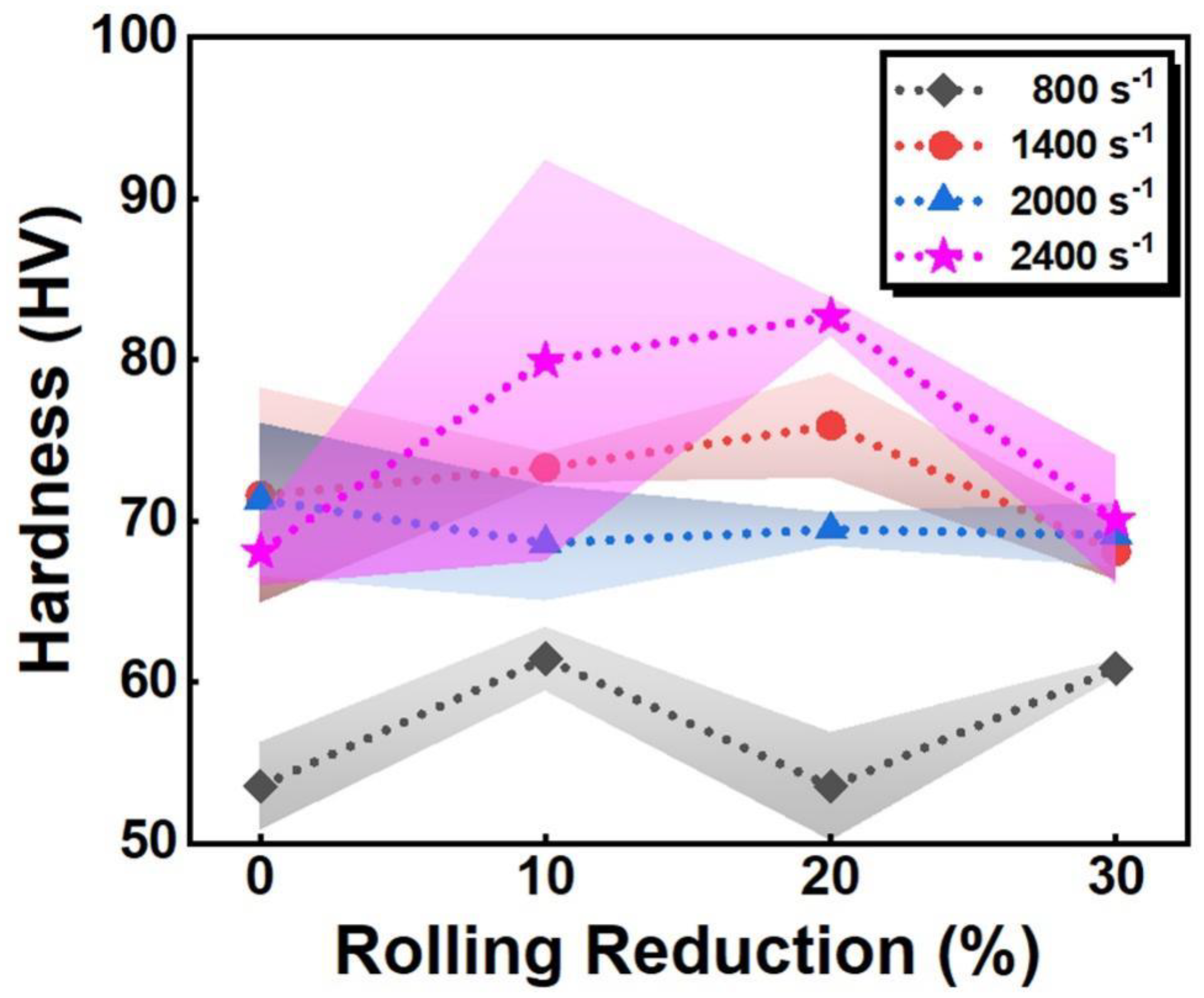
3.2. Mechanical Property
4. Conclusion
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Y. Zhao, G. Dong and B. Zhao, Nonferrous Metals Engineering 5, 23-27,43 (2015). https://doi.org/CSCD:5409879.
- K. Yu, W. Li and Z. Ma, The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals 13, 277-288 (2003). https://doi.org/CSCD:1279225.
- Y. Yang, J. Li, H. Song and P. Liu, Hot Working Technology 42, 24-27 (2013). https://doi.org/CSCD:4840196.
- J. Wang, J. Ju, Z. Huang and Y. Shu, Hot Working Technology 43, 6-9,5 (2014). https://doi.org/CSCD:5319071.
- M. Ruoyu, Z. Daidong and Y. Hongjia, Hot Working Technology 37, 89-92 (2008). https://doi.org/CSCD:3274744.
- Z. Hou, B. Jiang, Y. Wang, J. Song, L. Xiao and F. Pan, Aerospace Shanghai (Chinese/English) 38, 119-133 (2021). https://doi.org/CSCD:7003867.
- H. Deng and B. He, Ordnance Material Science and Engineering 39, 125-129 (2016). https://doi.org/CSCD:5747736.
- W. Chen, M. Zhan, W. Chen, D. Zhang and Y. Li, Special Casting & Non-ferrous Alloys 27, 40-43 (2007). https://doi.org/CSCD:2797413.
- J. Bao, Q. a. Li, X. Chen, Q. Zhang and Z. Chen, Materials Review 2022, 36). https://doi.org/CSCD:7217131.
- Elambharathi, B.; Kumar, S.D.; Dhanoop, V.; Dinakar, S.; Rajumar, S.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, V.; Li, C.; Eldin, E.M.T.; Wojciechowski, S. Novel insights on different treatment of magnesium alloys: A critical review. Heliyon 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, B.; Lu, L.; Kang, W.; Luo, J.; Ma, M.; Liu, L. Hot deformation behavior and processing map of a new type Mg-6Zn-1Gd-1Er alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, R.B.; Langdon, T.G. Deformation mechanisms in ultrafine-grained metals with an emphasis on the Hall–Petch relationship and strain rate sensitivity. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Qi, X.; Wang, J.; Jin, P.; Zeng, X. Twin recrystallization mechanisms in a high strain rate compressed Mg-Zn alloy. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2020, 9, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Xia, Q.; Xiao, G.; Qin, Y.; Yuan, S. Flow characterization of magnesium alloy ZK61 during hot deformation with improved constitutive equations and using activation energy maps. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 191, 106069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Wang, Y.; Huanwu, C.; Nazeer, F.; Khan, M.A. Dynamic mechanical behavior of magnesium alloys: a review. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 110, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Xu, L.; Tao, T.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; Hong, J.; Li, H.; Chi, Y. Mechanical behavior of multiscale hybrid fiber reinforced recycled aggregate concrete subject to uniaxial compression. Journal of Building Engineering 2023, 71, 106504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.-Z.; Cheng, X.-M.; Zha, M.; Rong, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.-G.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.-G.; Wang, H.-Y. Effects of Mg17Al12 second phase particles on twinning-induced recrystallization behavior in Mg-Al-Zn alloys during gradient hot rolling. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 2017–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Townsend, D.; Petrinic, N.; Pellegrino, A. Measurement of Pure Shear Constitutive Relationship From Torsion Tests Under Quasi-Static, Medium, and High Strain Rate Conditions. J. Appl. Mech. 2021, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Deng, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, X. Effect of strain rates on mechanical properties, microstructure and texture inside shear bands of pure magnesium. Mater. Charact. 2021, 184, 111686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, L.; Qiao, D.; Feng, D.; Wang, H. Vacuum tribological performance of phosphonium-based ionic liquids as lubricants and lubricant additives of multialkylatedcyclopentanes. Tribol. Int. 2013, 66, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Ren, Y.; Fu, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Meng, X.; Qin, G. Recent developments in rare-earth free wrought magnesium alloys having high strength: A review. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 663, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, L.; Qiao, D.; Feng, D.; Wang, H. Vacuum tribological performance of phosphonium-based ionic liquids as lubricants and lubricant additives of multialkylatedcyclopentanes. Tribol. Int. 2013, 66, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerreta, E.K.; Fensin, S.J.; Perez-Bergquist, S.J.; Trujillo, C.P.; Morrow, B.M.; Lopez, M.F.; Roach, C.J.; Mathaudhu, S.N.; Anghel, V.; Gray, G.T. The High-Strain-Rate Constitutive Behavior and Shear Response of Pure Magnesium and AZ31B Magnesium Alloy. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2021, 52, 3152–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhu, B.; Yang, H.; Xiao, G.; Hu, M. Influence of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties on Formability in High Strain Rate Rolled AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Sheets. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 28, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wan, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhu, B.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.; Tang, C. The Effect of Twins on Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Evolution in AZ31 Magnesium Alloy during High Speed Impact Loading. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 31, 3208–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, L.; Qiao, D.; Feng, D.; Wang, H. Vacuum tribological performance of phosphonium-based ionic liquids as lubricants and lubricant additives of multialkylatedcyclopentanes. Tribol. Int. 2013, 66, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.-F.; Duan, J.-R.; Yuan, H.; Li, H.-Y.; Sun, J.; Ma, L.-F. Effect of variable thickness cross rolling on edge crack and microstructure gradient of AZ31 magnesium alloy. J. Central South Univ. 2022, 29, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Jiang, B.; Park, S.; Yu, W.; Yin, F. Recrystallization mechanisms and texture evolution of AZ31 alloy by gradient caliber rolling. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Tang, Q.; Li, L.; Xie, C.; Liu, W.; Zhu, B.; Liu, X. The deformation mechanism and adiabatic shearing behavior of extruded Mg-8.0Al-0.1Mn alloy in different heat treated states under high-speed impact load. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 11, 2195–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. Mechanical properties and microscopic deformation mechanism of polycrystalline magnesium under high-strain-rate compressive loadings. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 540, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Liu, X.; Xie, C.; Liu, W.; Tang, C.; Lu, L. The flow behavior in as-extruded AZ31 magnesium alloy under impact loading. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2018, 6, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, F.; Naqvi, S.Z.H.; Kalam, A.; Al-Sehemi, A.; Alrobei, H. Texture dependencies on flow stress behavior of magnesium alloy under dynamic compressive loading. Vacuum 2021, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Kang, S.; Mao, P.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z. Microstructure evolution and constitutive relation establishment of Mg–7Gd–5Y–1.2Nd–0.5Zr alloy under high strain rate after severe multi-directional deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 809, 140994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Du, W.; Zhang, D.; Ge, Y.; Jiang, B. Enhancing mechanical properties of an Mg–Zn–Ca alloy via extrusion. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 37, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhai, H.; Xia, H.; Liu, L.; He, J.; Xia, D.; Yang, H.; Jiang, B. Relating Initial Texture to Deformation Behavior During Cold Rolling and Static Recrystallization Upon Subsequent Annealing of an Extruded WE43 Alloy. Acta Met. Sin. English Lett. 2022, 35, 1793–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, L.; Qiao, D.; Feng, D.; Wang, H. Vacuum tribological performance of phosphonium-based ionic liquids as lubricants and lubricant additives of multialkylatedcyclopentanes. Tribol. Int. 2013, 66, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, L.; Qiao, D.; Feng, D.; Wang, H. Vacuum tribological performance of phosphonium-based ionic liquids as lubricants and lubricant additives of multialkylatedcyclopentanes. Tribol. Int. 2013, 66, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.-F.; Tian, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, Y.; Liang, W.; Ma, J. Plastic deformation and fracture mechanisms of rolled Mg-8Gd-4Y-Zn and AZ31 magnesium alloys. Mater. Des. 2022, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mao, P.; Wang, Z.; Cao, G. Tensile twin evolution of Mg–3Al–1Zn magnesium alloy during high-strain rate deformation. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 37, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Cui, Y.; Bian, H.; Li, Q.; Ouyang, L.; Chiba, A. Role of slip and {10-12} twin on the crystal plasticity in Mg-RE alloy during deformation process at room temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 80, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xiao, T.; Yu, Z. Microstructure, Texture Evolution, and Strain Hardening Behaviour of As-extruded Mg-Zn and Mg-Y Alloys under Compression. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Sci. Ed. 2023, 38, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Li, A.; Li, W.; Chang, G.; Liu, Y. Deformation Mechanism and Microstructural Evolution of a Mg–Y–Nd–Zr Alloy under High Strain Rate at Room Temperature. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 33, 3101–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, N.; Xie, K.Y.; Hemker, K.J.; Ramesh, K. Microstructural evolution of pure magnesium under high strain rate loading. Acta Mater. 2015, 87, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, J.; Huang, J.; Lian, X. Difference in adiabatic shear susceptibility between pure copper and Cu–30% Zn solid solution alloy at different strain rate. J. Mater. Res. 2023, 38, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Pan, Q.L.; Bin He, Y.; Bin Li, W.; Liang, W.J.; Yin, Z.M. Flow behavior and microstructural evolution of Al–Cu–Mg–Ag alloy during hot compression deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 500, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Yuan, L.; Shan, D.; Guo, B. Study on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ZK60 magnesium alloy with submicron twins and precipitates obtained by room temperature multi-directional forging. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 13236–13250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottaghian, F.; Taheri, F. Strength and failure mechanism of single-lap magnesium-basalt fiber metal laminate adhesively bonded joints: Experimental and numerical assessments. J. Compos. Mater. 2022, 56, 1941–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, F.; Feng, B.; Liu, L.; Dong, C.; Zhao, Y.; Song, B. Enhancing mechanical properties of friction stir welded AZ31 alloys by post-weld compression. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2023, 28, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Du, W.; Zhu, X.; Dou, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, K.; Li, S. Roles of LPSO phases on dynamic recrystallization of high strain rate multi-directional free forged Mg-Gd-Er-Zn-Zr alloy and its strengthening mechanisms. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaneme, K.K.; Okotete, E.A. Enhancing plastic deformability of Mg and its alloys—A review of traditional and nascent developments. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2017, 5, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ringer, S.P. On the role of twinning and stacking faults on the crystal plasticity and grain refinement in magnesium alloys. Acta Mater. 2018, 144, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, J.; Zhou, Z. Activation Behavior of {10-12}-{10-12} Secondary Twins by Different Strain Variables and Different Loading Directions during Fatigue Deformation of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Metals 2022, 12, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doiphode, R.; Murty, S.N.; Prabhu, N.; Kashyap, B. Grain growth in calibre rolled Mg–3Al–1Zn alloy and its effect on hardness. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2015, 3, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.O.; Børvik, T.; Hopperstad, O.S. Fracture mechanisms of aluminium alloy AA7075-T651 under various loading conditions. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Zhen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, C.; Shao, W.; Pang, B. Deformed microstructure evolution in AM60B Mg alloy under hypervelocity impact at a velocity of 5kms−1. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 3708–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




