Submitted:
07 July 2024
Posted:
09 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
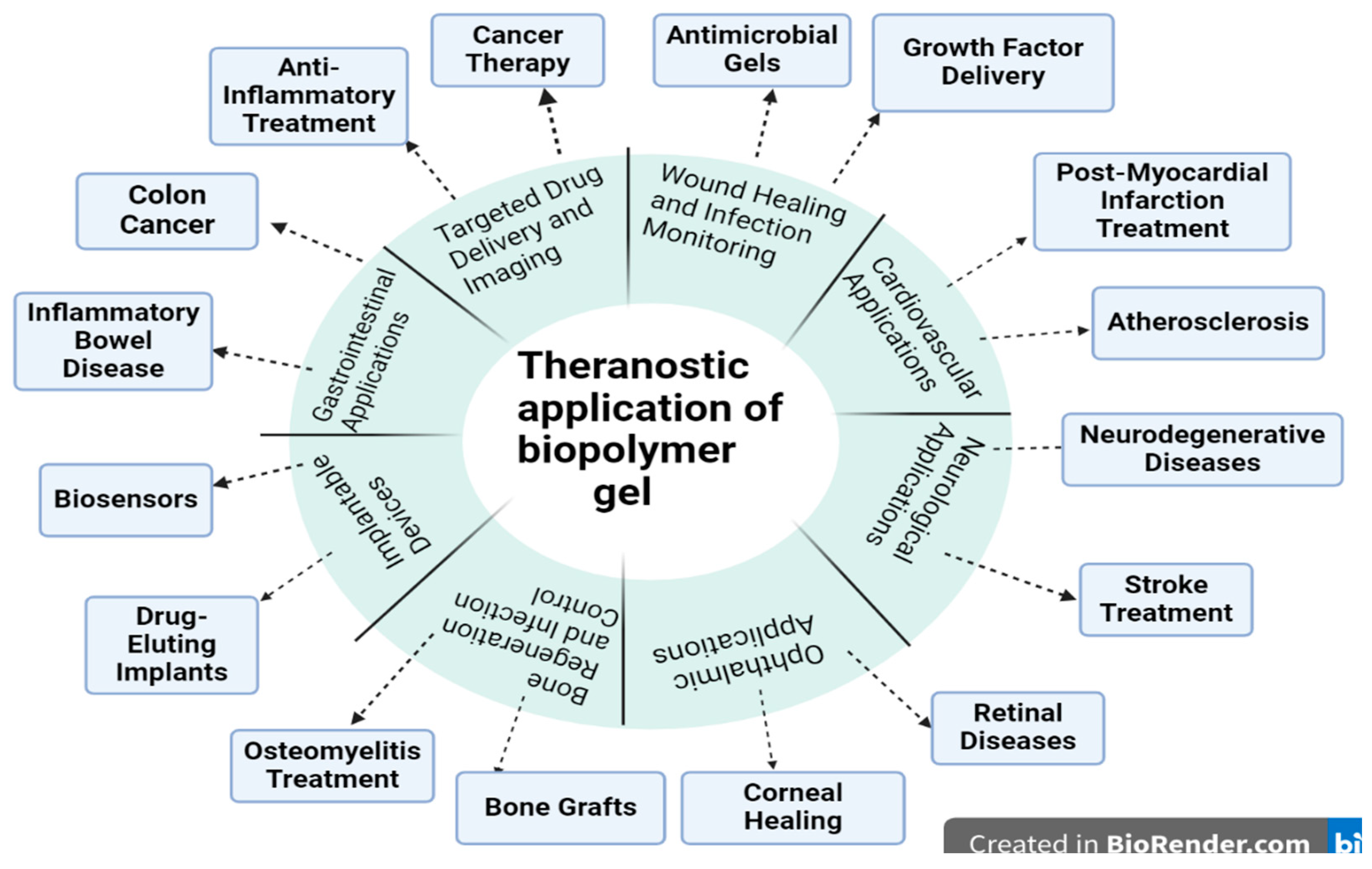
2. Intersecting Diagnosis with Therapy
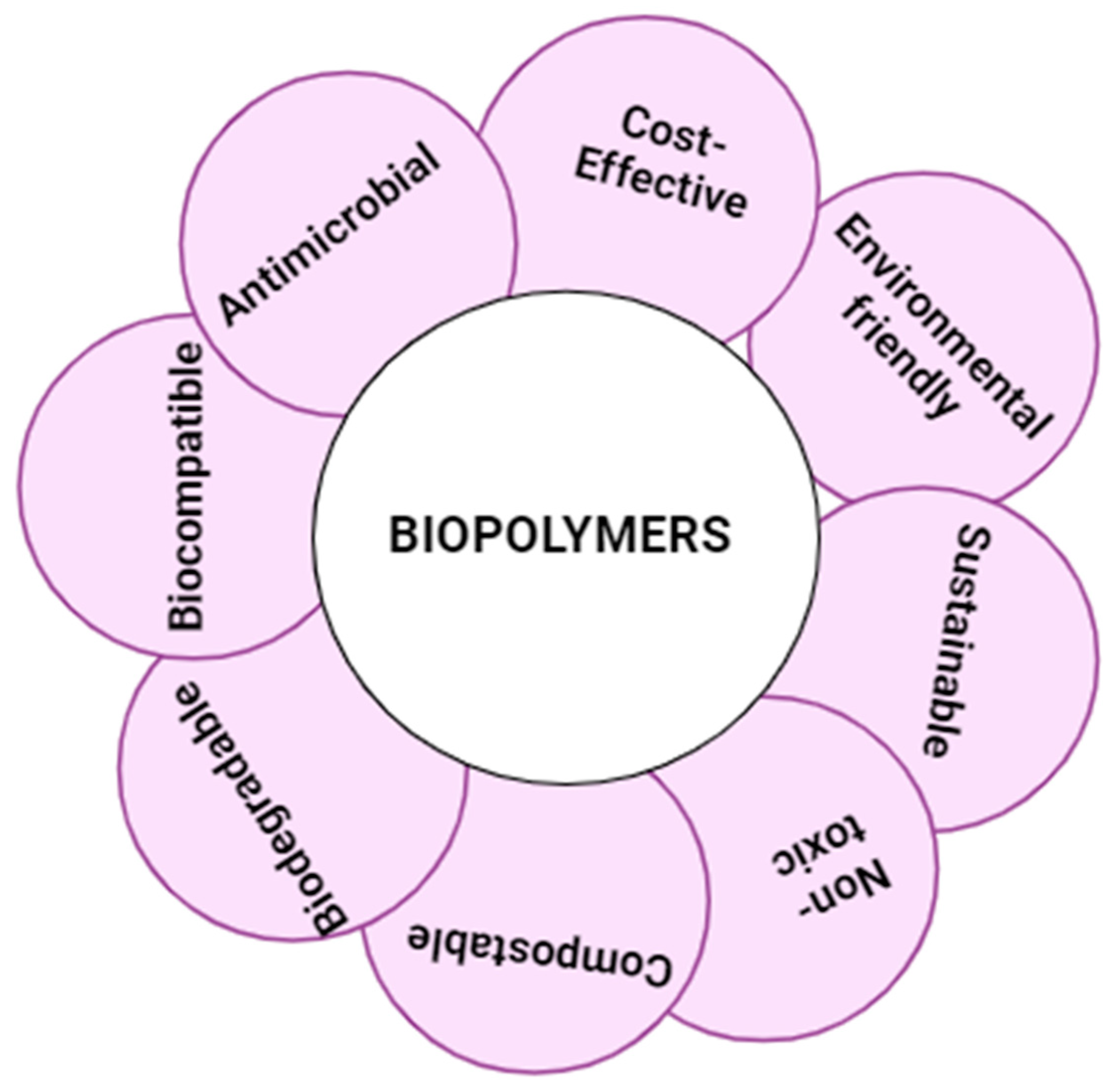
3. Biopolymer Gels as Versatile Platforms
4. Properties and Characteristics of Biopolymer Gels.
5. Imaging Agents in Theranostic Applications
| Imaging Modality | Imaging Agent | Theranostic Application | |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-ray Imaging | Iodine-based contrast agents | Diagnosis of bone fractures, detection of tumors, and monitoring therapeutic interventions | [50] |
| Barium sulfate | Visualization of gastrointestinal tract for diagnosing conditions like ulcers or tumors | ||
|
Ultrasound Imaging |
Microbubble contrast agents | Assessing blood flow, visualizing organs, and guiding interventional procedures | [51] |
| Contrast-enhanced ultrasound | Imaging liver lesions, assessing vascularity in tumors, and diagnosing cardiovascular conditions | ||
|
Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
Gadolinium-based contrast agents | Imaging brain, spinal cord, and musculoskeletal system, detecting tumors, and inflammatory processes | [52] |
| Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles | Targeted drug delivery and imaging of inflammation | ||
|
Fluorescence Imaging |
Fluorescent dyes | Visualizing specific molecular targets, biomarkers, or cellular processes with high sensitivity | [53] |
| Quantum dots | Multiplexed imaging of molecular targets for personalized medicine | ||
| Nuclear Imaging | Fluorodeoxyglucose | Cancer diagnosis and monitoring response to treatment | [54] |
| Technetium-99m labeled agents | Imaging myocardial perfusion and diagnosing bone metastases | ||
| Copper-64 labeled nanoparticles | Imaging and tracking of stem cell therapy |
6. Importance of Imaging Agents in Theranostic
7. Integration of Imaging Agents with Biopolymer Gels
8. Role of Biopolymer Gels in Real-Time Monitoring
9. Challenges in Conventional Drug Delivery Monitoring
10. Future Outlook and Recommendations
11. Conclusions
References
- Baranwal J, Barse B, Fais A, Delogu GL, Kumar A. Biopolymer: A sustainable material for food and medical applications. Polymers. 2022;14(5):983.
- Mohan A, Santhamoorthy M, Phan TTV, Kim S-C. pNIPAm-Based pH and Thermoresponsive Copolymer Hydrogel for Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Drug Delivery. Gels. 2024;10(3):184.
- Fernandes SC, Aguirre G. Biopolymer micro/nanogel particles as smart drug delivery and theranostic systems. MDPI; 2023. p. 2060. [CrossRef]
- Yuan W, Xu J, Yang N, Wang H, Li J, Zhang M, et al. Engineered Dynamic Hydrogel Niches for the Regulation of Redox Homeostasis in Osteoporosis and Degenerative Endocrine Diseases. Gels. 2023;10(1):31. [CrossRef]
- Altuntaş E, Özkan B, Güngör S, Özsoy Y. Biopolymer-based nanogel approach in drug delivery: basic concept and current developments. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(6):1644. [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.H. Structural and mechanical properties of biopolymer gels. Food polymers, gels and colloids: Elsevier; 1991. p. 322-38.
- Puccetti M, Pariano M, Schoubben A, Giovagnoli S, Ricci M. Biologics, theranostics, and personalized medicine in drug delivery systems. Pharmacological Research. 2024:107086. [CrossRef]
- Zhao L, Kim T-H, Ahn J-C, Kim H-W, Kim SY. Highly efficient “theranostics” system based on surface-modified gold nanocarriers for imaging and photodynamic therapy of cancer. Journal of Materials Chemistry B. 2013;1(42):5806-17. [CrossRef]
- Jeelani S, Reddy RJ, Maheswaran T, Asokan G, Dany A, Anand B. Theranostics: A treasured tailor for tomorrow. Journal of pharmacy and bioallied sciences. 2014;6(Suppl 1):S6-S8.
- Lammers T, Aime S, Hennink WE, Storm G, Kiessling F. Theranostic nanomedicine. Accounts of chemical research. 2011;44(10):1029-38. [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal T, Pisulkar SK, Kambala SS. Analysis of Antifungal and Antimicrobial Properties of Functionalized Denture Base Materials Using Chitosan Nanoparticles: A Systematic Review. Journal of Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences University. 2021;16(4):801-5. [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves C, Pereira P, Gama M. Self-assembled hydrogel nanoparticles for drug delivery applications. Materials. 2010;3(2):1420-60. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya T, Preetam S, Ghosh B, Chakrabarti T, Chakrabarti P, Samal SK, et al. Advancement in biopolymer assisted cancer theranostics. ACS Applied Bio Materials. 2023;6(10):3959-83. [CrossRef]
- Ayeldeen MK, Negm AM, El Sawwaf MA. Evaluating the physical characteristics of biopolymer/soil mixtures. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. 2016;9:1-13. [CrossRef]
- Agrawal S, Budhwani D, Gurjar P, Telange D, Lambole V. Pullulan based derivatives: Synthesis, enhanced physicochemical properties, and applications. Drug delivery. 2022;29(1):3328-39.
- Terreno E, Uggeri F, Aime S. Image guided therapy: the advent of theranostic agents. Journal of controlled release. 2012;161(2):328-37. [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava S, Jain S, Kumar D, Soni SL, Sharma M. A review on theranostics: an approach to targeted diagnosis and therapy. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Development. 2019;7(2):63-9. [CrossRef]
- Gunde M, Telange D, Pimpale A, Pethe A. Quality by design driven development of topical gel encompassing papain and bromelain to elicit wound healing. Indian J Pharm Educ Res. 2023;57:s281-91. [CrossRef]
- Burkett BJ, Bartlett DJ, McGarrah PW, Lewis AR, Johnson DR, Berberoğlu K, et al. A review of theranostics: perspectives on emerging approaches and clinical advancements. Radiology: Imaging Cancer. 2023;5(4):e220157. [CrossRef]
- Thakare A, Sedani S, Kriplani S, Patel A, Umre U, Thakare Jr A, et al. Chitosan: A Versatile Biomaterial Revolutionizing Endodontic Therapy. Cureus. 2024;16(6). [CrossRef]
- Islam MM, Shahruzzaman M, Biswas S, Sakib MN, Rashid TU. Chitosan based bioactive materials in tissue engineering applications-A review. Bioactive materials. 2020;5(1):164-83.
- Lazaridou M, Bikiaris DN, Lamprou DA. 3D bioprinted chitosan-based hydrogel scaffolds in tissue engineering and localised drug delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(9):1978. [CrossRef]
- Opriș O, Mormile C, Lung I, Stegarescu A, Soran M-L, Soran A. An overview of biopolymers for drug delivery applications. Applied Sciences. 2024;14(4):1383. [CrossRef]
- Kelkar SS, Reineke TM. Theranostics: combining imaging and therapy. Bioconjugate chemistry. 2011;22(10):1879-903.
- Chavda VP, Balar PC, Nalla LV, Bezbaruah R, Gogoi NR, Gajula SNR, et al. Conjugated Nanoparticles for Solid Tumor Theranostics: Unraveling the Interplay of Known and Unknown Factors. ACS omega. 2023;8(41):37654-84.
- Mahmood A, Patel D, Hickson B, DesRochers J, Hu X. Recent Progress in Biopolymer-Based Hydrogel Materials for Biomedical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3). [CrossRef]
- Panja S, Adams DJ. Stimuli responsive dynamic transformations in supramolecular gels. Chemical Society Reviews. 2021;50(8):5165-200.
- Mercer IG, Italiano AN, Gazaryan IG, Steiner AB, Kazakov SV. Degradation Kinetics of Disulfide Cross-Linked Microgels: Real-Time Monitoring by Confocal Microscopy. Gels. 2023;9(10):782.
- Melo BL, Lima-Sousa R, Alves CG, Moreira AF, Correia IJ, de Melo-Diogo D. Chitosan-based injectable in situ forming hydrogels containing dopamine-reduced graphene oxide and resveratrol for breast cancer chemo-photothermal therapy. Biochemical engineering journal. 2022;185:108529. [CrossRef]
- Attama AA, Nnamani PO, Onokala OB, Ugwu AA, Onugwu AL. Nanogels as target drug delivery systems in cancer therapy: A review of the last decade. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 2022;13:874510. [CrossRef]
- Laurent S, Mahmoudi M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: promises for diagnosis and treatment of cancer. International journal of molecular epidemiology and genetics. 2011;2(4):367. [CrossRef]
- Dispinar T, Van Camp W, De Cock LJ, De Geest BG, Du Prez FE. Redox-responsive degradable PEG cryogels as potential cell scaffolds in tissue engineering. Macromolecular bioscience. 2012;12(3):383-94. [CrossRef]
- He Y, Wang C, Wang C, Xiao Y, Lin W. An overview on collagen and gelatin-based cryogels: Fabrication, classification, properties and biomedical applications. Polymers. 2021;13(14):2299. [CrossRef]
- Alshamrani, M. Broad-spectrum theranostics and biomedical application of functionalized nanomaterials. Polymers. 2022;14(6):1221.
- Zhao L, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Liang H, Chen X, Tan H. Natural polymer-based hydrogels: From polymer to biomedical applications. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(10):2514.
- Mazuki N, Saadiah M, Fuzlin A, Khan N, Samsudin A. Basic aspects and properties of biopolymers. 2022. [CrossRef]
- ALSamman MT, Sánchez J. Chitosan-and alginate-based hydrogels for the adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes from water. Polymers. 2022;14(8):1498. [CrossRef]
- Lee EJ, Lee JH, Jin L, Jin OS, Shin YC, Oh SJ, et al. Hyaluronic acid/poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) core/shell fiber meshes loaded with epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate as skin tissue engineering scaffolds. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology. 2014;14(11):8458-63. [CrossRef]
- Huang H, Qi X, Chen Y, Wu Z. Thermo-sensitive hydrogels for delivering biotherapeutic molecules: A review. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 2019;27(7):990-9. [CrossRef]
- Deng H, Dong A, Song J, Chen X. Injectable thermosensitive hydrogel systems based on functional PEG/PCL block polymer for local drug delivery. Journal of Controlled Release. 2019;297:60-70. [CrossRef]
- Alaswad SO, Mahmoud AS, Arunachalam P. Recent advances in biodegradable polymers and their biological applications: a brief review. Polymers. 2022;14(22):4924.
- Hussain S, Mubeen I, Ullah N, Shah SSUD, Khan BA, Zahoor M, et al. Modern diagnostic imaging technique applications and risk factors in the medical field: A review. BioMed Research International. 2022;2022. [CrossRef]
- Kasban H, El-Bendary M, Salama D. A comparative study of medical imaging techniques. International Journal of Information Science and Intelligent System. 2015;4(2):37-58.
- Hsu JC, Nieves LM, Betzer O, Sadan T, Noël PB, Popovtzer R, et al. Nanoparticle contrast agents for X-ray imaging applications. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology. 2020;12(6):e1642.
- Methachan B, Thanapprapasr K. Polymer-based materials in cancer treatment: from therapeutic carrier and ultrasound contrast agent to theranostic applications. Ultrasound in medicine & biology. 2017;43(1):69-82.
- Jeong Y, Hwang HS, Na K. Theranostics and contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials research. 2018;22(1):20.
- Janib SM, Moses AS, MacKay JA. Imaging and drug delivery using theranostic nanoparticles. Advanced drug delivery reviews. 2010;62(11):1052-63.
- Crișan G, Moldovean-Cioroianu NS, Timaru D-G, Andrieș G, Căinap C, Chiș V. Radiopharmaceuticals for PET and SPECT imaging: a literature review over the last decade. International journal of molecular sciences. 2022;23(9):5023.
- Weissleder R, Schwaiger MC, Gambhir SS, Hricak H. Imaging approaches to optimize molecular therapies. Science translational medicine. 2016;8(355):355ps16-ps16.
- Ou X, Chen X, Xu X, Xie L, Chen X, Hong Z, et al. Recent development in x-ray imaging technology: Future and challenges. Research. 2021.
- Chan V, Perlas A. Basics of ultrasound imaging. Atlas of ultrasound-guided procedures in interventional pain management. 2011:13-9.
- Van Geuns R-JM, Wielopolski PA, de Bruin HG, Rensing BJ, Van Ooijen PM, Hulshoff M, et al. Basic principles of magnetic resonance imaging. Progress in cardiovascular diseases. 1999;42(2):149-56.
- Rao J, Dragulescu-Andrasi A, Yao H. Fluorescence imaging in vivo: recent advances. Current opinion in biotechnology. 2007;18(1):17-25.
- Del Vecchio S, Zannetti A, Fonti R, Pace L, Salvatore M. Nuclear imaging in cancer theranostics. The Quarterly Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 2007;51(2):152-63.
- Gomes Marin JF, Nunes RF, Coutinho AM, Zaniboni EC, Costa LB, Barbosa FG, et al. Theranostics in nuclear medicine: emerging and re-emerging integrated imaging and therapies in the era of precision oncology. Radiographics. 2020;40(6):1715-40.
- Ding H, Wu F. Image guided biodistribution and pharmacokinetic studies of theranostics. Theranostics. 2012;2(11):1040.
- De La Vega JC, Häfeli UO. Utilization of nanoparticles as X-ray contrast agents for diagnostic imaging applications. Contrast media & molecular imaging. 2015;10(2):81-95.
- Perera RH, Hernandez C, Zhou H, Kota P, Burke A, Exner AA. Ultrasound imaging beyond the vasculature with new generation contrast agents. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology. 2015;7(4):593-608.
- Arora S, Das G, Alqarni M, Grover V, Manzoor Baba S, Saluja P, et al. Role of chitosan hydrogels in clinical dentistry. Gels. 2023;9(9):698.
- Nathanael AJ, Oh TH. Biopolymer coatings for biomedical applications. Polymers. 2020;12(12):3061.
- Kučuk N, Primožič M, Knez Ž, Leitgeb M. Sustainable biodegradable biopolymer-based nanoparticles for healthcare applications. International journal of molecular sciences. 2023;24(4):3188.
- Pei J, Yan Y, Palanisamy CP, Jayaraman S, Natarajan PM, Umapathy VR, et al. Materials-based drug delivery approaches: Recent advances and future perspectives. Green Processing and Synthesis. 2024;13(1):20230094.
- Vashist A, Raymond AD, Chapagain P, Nair MP, Runowicz CD. Polyols and polyol-based hydrogels with anti-cancer activity. Google Patents; 2024.
- Newman DK, Spero MA, Martins-Green M, Coates JD. Wound prevention and/or treatment and related compounds, matrices, compositions, methods and systems. Google Patents; 2021.
- Loadman P, Falconer R, Gill J, Rao J, Daldrup-Link HE. Tumour-targeted theranostic. Google Patents; 2019.
- Steinmetz, N.F. Polydopamine decorated tobacco mosaic theranostic virus nanoparticles. Google Patents; 2022.
- Dravid VP, Sharma S, Tomita T, Viola KL, Klein WL. Magnetic nanostructures as theranostic agents. Google Patents; 2015.
- Perez Figueroa JM, Santra S. Synthesis of hyperbranched amphiphylic polyester and theranostic nanoparticles thereof. 2013.
- Kumar R, Sridhar S, Wilfred N, Cormack R, Makrigiorgos G. Biopolymer-nanoparticle composite implant for tumor cell tracking. Google Patents; 2020.
- Wu XY, Shalviri A, Cai P. Polymeric nanoparticles useful in theranostics. Google Patents; 2019.
- Körhegyi Z, Rózsa D, Hajdu I, Bodnár M, Kertesz I, Kerekes K, et al. Synthesis of 68Ga-labeled biopolymer-based nanoparticle imaging agents for positron-emission tomography. Anticancer research. 2019;39(5):2415-27.
- Stanisz M, Klapiszewski Ł, Jesionowski T. Recent advances in the fabrication and application of biopolymer-based micro-and nanostructures: A comprehensive review. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2020;397:125409.
- Jin M, Yu D-G, Geraldes CF, Williams GR, Bligh SA. Theranostic fibers for simultaneous imaging and drug delivery. Molecular pharmaceutics. 2016;13(7):2457-65.
- Khobragade DS, Potbhare M, Patil A. Evaluation of gum sandarac as a novel release controlling coating polymer for formulation of sustained release pellets. Int J Adv Pharm. 2016;5:39-45.
- Laffleur F, Keckeis V. Advances in drug delivery systems: Work in progress still needed? International journal of pharmaceutics. 2020;590:119912.
- Madej-Kiełbik L, Gzyra-Jagieła K, Jóźwik-Pruska J, Dziuba R, Bednarowicz A. Biopolymer composites with sensors for environmental and medical applications. Materials. 2022;15(21):7493.
- Chiu I, Yang T. Biopolymer-based intelligent packaging integrated with natural colourimetric sensors for food safety and sustainability. Analytical Science Advances. 2024:e202300065.
- Abdullah, Cai J, Hafeez MA, Wang Q, Farooq S, Huang Q, et al. Biopolymer-based functional films for packaging applications: A review. Frontiers in Nutrition. 2022;9:1000116.
- Ezike TC, Okpala US, Onoja UL, Nwike CP, Ezeako EC, Okpara OJ, et al. Advances in drug delivery systems, challenges and future directions. Heliyon. 2023;9(6).
- Phutane P, Telange D, Agrawal S, Gunde M, Kotkar K, Pethe A. Biofunctionalization and applications of polymeric nanofibers in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Polymers. 2023;15(5):1202.

| S. No | Patent Number | Material used | Purpose | Remarks | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | US11969438B1 | vegetable oil-derived polyol. | Anti-cancer activity | Provides compositions and methods for selectively treating a cancer or tumor utilizing an effective amount of a vegetable oil-derived polyol or hydrogel particles comprising a vegetable oil-derived polyol. It provides a method of targeting and imaging various tumors and/or tumor associated macrophages | [63] |
| 2. | US20210322462A1 | Polyvinyl alcohol [PVA], Collagen-chitosan | Wound Prevention and/or Treatment | The composition in embedded in a hydrogel made of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), collagen-chitosan, alginates, carbopol gels, alginate matrices for slow release | [64] |
| 3. | US10201622B2 | Gelatin, Casein, Dextran, PEG, PVP | Theranostic applications | Nanoparticles coated with polymers like Gelatin, Casein, Dextran, PEG, PVP addressed the theranostic applications. | [65] |
| 4. | US11529430B2 | Chitosan, polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid and copolymers | Contrast agent | Gadolinium DOTA nanoparticles decorated with polydopamine and as a photothermal agent to kill cancer cells | [66] |
| 5. | US9095629B2 | PEG and Nitro-DOPA | Magnetic nanoparticles | As contrast agent and Better targeting of the MNPs | [67] |
| 6. | US8372944B1 | Hyperbranched polyester and hyperbranched polyester amine | Polymeric nanoparticles as thenostic agent | Polymeric nanoparticles coated with HBPE for fluroscence and delivery of therapeutic drug | [68] |
| 7. | US10799604B2 | Polyethylene glycol, polyacrylic acid, polyacrylamide, poly[N-isopropylacrylamide], hyaluronic acid, and combinations thereof | Implant for tumor cell tracking | A method of treating cancer is provided by implanting one or more brachytherapy spacers or fiducial markers including the matrix material and an anti-cancer therapeutic agent dispersed within the matrix material. | [69] |
| 8. | US20190233567A1 | Polymethacrylic acid grafted starch | Therapeutics and/or signal molecules | The PMAA-g-St-DTPA-Gd nanoparticle shows promise for detecting pH deviations from the typical physiological pH of 7.4 in tumor tissue or infectious lesions through MR imaging. It has the ability to exhibit different levels of relaxivity at different pH values. To deliver therapeutic agents as the loaded cargo of nanoparticles for the treatment of any of the following: A neuropsychiatric disorder; a neurodegenerative disorder | [70] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





