Submitted:
29 May 2024
Posted:
30 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Synthesis and Analyses
3. Status of Available Vaccines
3.1. Early Works on Fish Vaccination
3.2. Properties of Fish Vaccines and Vaccination Process
3.3. Types of Fish Vaccines
3.3.1. Whole Cell Vaccines
3.3.2. Attenuated Vaccines
3.3.3. Recombinant Vaccines
3.3.4. Synthetic Peptide Vaccines
3.3.5. DNA Vaccines
3.3.6. Mucosal Vaccinations
3.3.7. Plant Based Edible Vaccine
3.3.8. Nanoparticles Based Vaccine
3.4. Advancements in Vaccine Development
4. Contemporary Need of Vaccines for Fish, a Growing Field of Research
5. Fish Vaccine Production against Various Pathogens
5.1. Nocardiosis
5.2. Bacterial Hemolytic Jaundice
5.3. Bacterial Cold-Water Disease
5.4. Erythrocyte Inclusion Body Syndrome
5.5. Parasitosis
5.6. Vaccines Other Than Inactivated Vaccine
5.7. Autogenous Vaccines
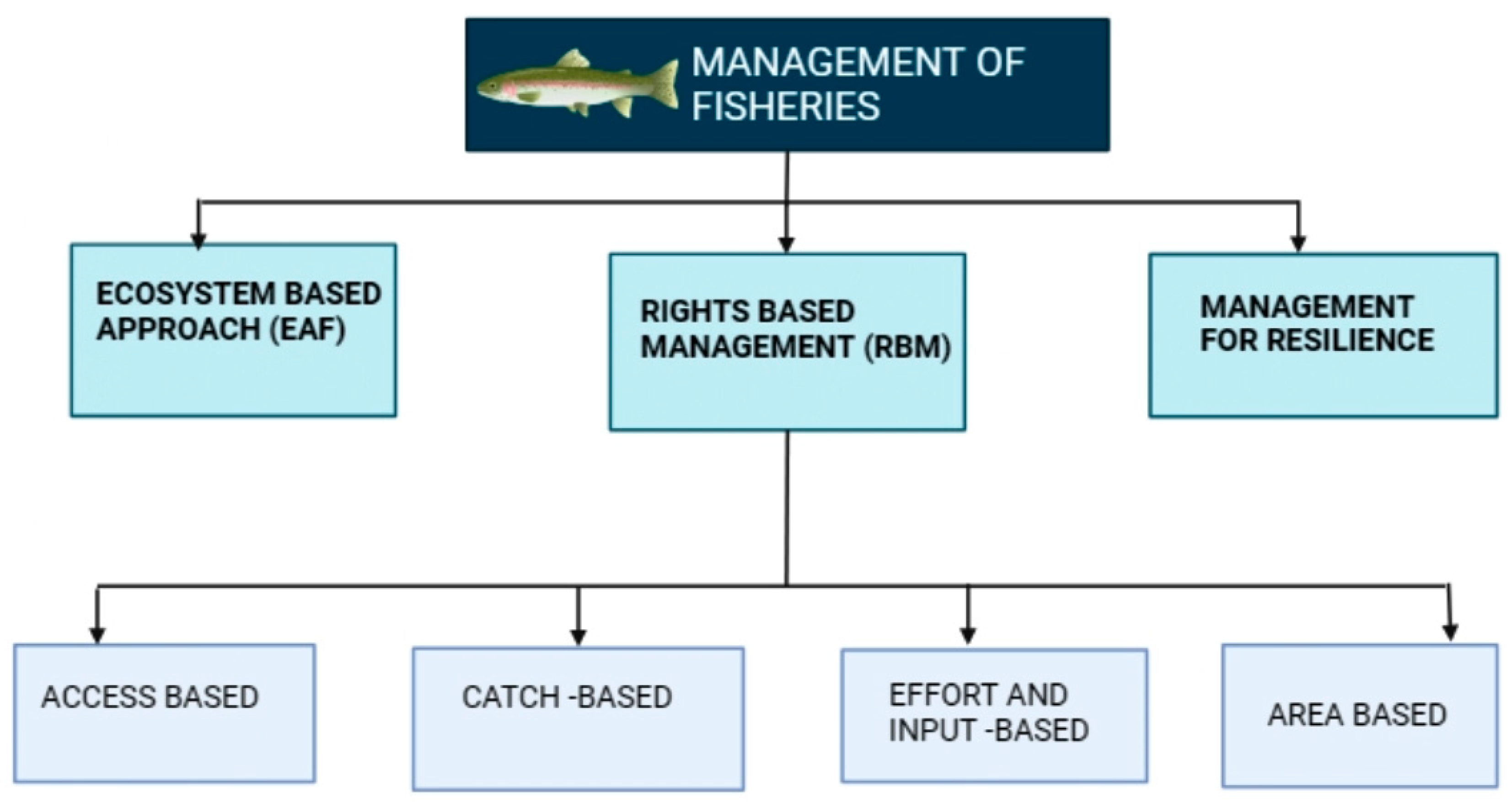
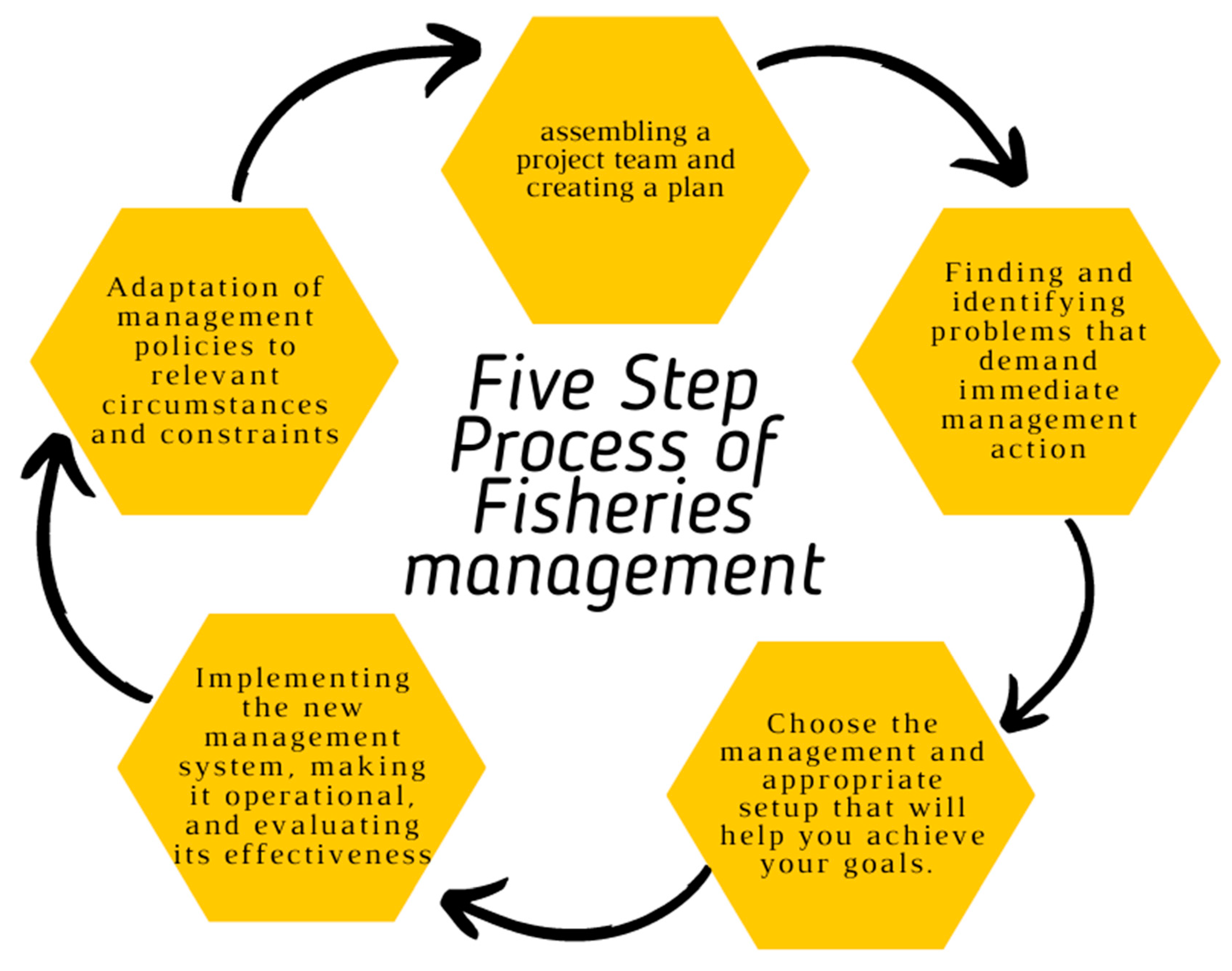
6. Need for Fish Vaccines
6.1. Status of Fisheries Product
6.2. An Emergency Need in Fish Vaccines
7. Plant-Derived Fish Vaccines, a New Perstective in Immunology
7.1. Advantages of Plant Derived Fish Vaccines
7.2. Prospective Plant-Derived Fish Vaccines
8. Updates on Strategies to Develop Fish Vaccines
9. Conclusion
Author’s Contribution
Availability of data and materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Competing Interests
Ethical Approval
Consent to Participate
Consent to Publish
Competitive interest
References
- W.H.O. Immunization, Vaccines and Biologicals. https://www.who.int/teams/immunization-vaccines-and-biologicals. 2023. Accessed on 02.02.2023.
- Grace, D.; Gilbert, J.; Randolph, T.; Kang’ethe, E. The multiple burdens of zoonotic disease and an Ecohealth approach to their assessment. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2012, 44, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurie, N.; Manolio, T.; Paterson, A.P.; Collins, F.; Frieden, T. Research as a part of public health emergency response. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monath, T.P. Vaccines against diseases transmitted from animals to humans: a one health paradigm. Vaccine 2013, 31, 5321–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupprecht CE, Hanlon CA, Blanton J, Manangan J, Morrill P, Murphy S, Niezgoda M, Orciari LA, Schumacher CL, Dietzschold B. Oral vaccination of dogs with recombinant rabies virus vaccines. Virus Res. 2005, 111, 101–105. [CrossRef]
- Perkins, S.D.; Smither, S.J.; Atkins, H.S. Towards a Brucella vaccine for humans. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010, 4, 379–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, A. Progress, challenges and opportunities in fish vaccine development. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 90, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.A. Veterinary vaccines and their importance to animal health and public health. Procedia Vaccinol. 2011, 5, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NAOH. National office of animal health, Vaccination for animals: An overview. 2017. http://noah.co.uk, accessed on 02.02.2023.
- Beer, M.; I. Reimann, I.; Hoffmann B.; Depner, K. Novel marker vaccines against classical swine fever. Vaccine 2006, 25, 5665–5670.
- Meeusen, E.N.; Walker. J.; Peters, A.; Pastoret, P.P.; Jungersen, G. Current status of veterinary vaccines. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 489–510. [CrossRef]
- Aida, V.; Pliasas, VC.; Neasham, P.J.; North, J.F.; McWhorter, K.L.; Glover, S.R.; Kyriakis, C.S. Novel technologies in veterinary medicine: A Herald to human medicine vaccines. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 654289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSC. History of New England’s Ground Fish Fishery & Management. 2023. https://northeastseafoodcoalition.org/fishery-101/history/#:~:text=Before%20the%20Magnuson%20was%20implemented,New%20England%20Fishery%20Management%20Council. Accessed on 02.02.2023.
- OWD. Seafood and fish production, World. 2023. https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/seafood-and-fish-production-thousand-tonnes. Accessed on 02.02.2023.
- OECD, Food & Nations, A. O. of the U. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2020-2029. 2020. [CrossRef]
- FAO. 2022. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022-Towards Blue Transformation. Rome, Italy, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.L.; Kishore, A.; Sumaila, U.R.; Issifu, I.; Hunter, B.P.; Belton, B.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Gelcich, S.; Gephart, J.A.; et al. Blue food demand across geographic and temporal scales. Nat. Comm. 2021, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, A.J.; Bijker, E.M. A guide to vaccinology: From basic principles to new developments. Nat Rev. 2021, 21, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, F.; Pati, S.G.; Das, K.; Samanta, L.; Sahoo, D.K.; Paital, B. Biochemical and molecular responses of the freshwater snail Pila sp. To environmental pollutants, abiotic, and biotic stressors. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, A.; Panda, F.; Pati, S.G.; Anwar, T.A.; Das, K.; Paital, B. Influence of anthropogenic activities on redox regulation and oxidative stress responses in different phyla of animals in coastal water via change in salinity. Water 2022, 14(24), 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabria, S.; Mathur, S.; Vadakan, S.; Sahoo, D.K.; Mishra, P.; Paital, B. A review on Phytochemical and Pharmacological Facets of Tropical Ethnomedicinal Plants as Reformed DPP-IV Inhibitors to Regulate Incretin Activity. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1027237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, S.; Mathur, S.; Patel, S.; Paital, B. Microplastic accumulation and degradation in environment via biotechnological approaches. Water 2022, 14, 4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paital, B. Modulation of redox regulatory molecules and electron transport chain activity in muscle of air breathing fish Heteropneustes fossilis under air exposure stress. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2014, 184, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paital, B. Antioxidant and oxidative stress parameters in brain of Heteropneustes fossilis under air exposure condition; Role of mitochondrial electron transport chain. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 95, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paital, B.; Panda, S.K.; Hati, A.K.; Mohanty, B.; Mohapatra, M.K.; Kanungo, S.; Chainy, G.B.N. Longevity of animals under reactive oxygen species stress and disease susceptibility due to global warming. World J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 7, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paital, B.; Guru, D.; Mohapatra, P.; Panda, B.; Parida, N.; Rath, S.; Kumar, V.; Saxena, P.S.; Srivastava, A. Ecotoxic impact assessment of graphene oxide on lipid peroxidation at mitochondrial level and redox modulation in fresh water fish Anabas testudineus. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, S.; Bal, A.; Paital, B. Heavy metal and organic load in Haripur creek of Gopalpur along the Bay of Bengal, east coast of India. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2021, 28, 28275–28288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, A.; Pati, S.G.; Panda, F.; Mohanty, L.; Paital, B. Low salinity induced challenges in the hardy fish Heteropneustes fossilis; future prospective of aquaculture in near coastal zones. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 737007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paital, B.; Pati, S.G.; Panda, F.; Jally, S.K.; Agrawal, P.K. Changes in physicochemical, heavy metals and air quality linked to spot Aplocheilus panchax along Mahanadi industrial belt of India under COVID-19-induced lockdowns. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, H.; Thomas, J. A Review on the Recent Advances and Application of Vaccines against Fish Pathogens in Aquaculture. Aquacul. Int. 2022, 30, 1971–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, S.K. Current Prospects and Challenges in Fish Vaccine Development in India with Special Reference to Aeromonas hydrophila Vaccine. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 100, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadar, M.; Dhama, K.; Vakharia, V.N.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Karthik, K.; Tiwari, R.; Khandia, R.; Munjal, A.; Salgado-Miranda, C.; Joshi, S.K. Advances in Aquaculture Vaccines Against Fish Pathogens: Global Status and Current Trends. Rev. Fish.s Sci. Aquacul. 2016, 25, 184–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Bruce, T.J.; Jones, E.M.; Cain, K.D. A Review of Fish Vaccine Development Strategies: Conventional Methods and Modern Biotechnological Approaches. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embregts, C.W.E.; Forlenza, M. Oral Vaccination of Fish: Lessons from Humans and Veterinary Species. Develop. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 64, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magadan, S.; Jouneau, L.; Boudinot, P.; Salinas, I. Nasal Vaccination Drives Modifications of Nasal and Systemic Antibody Repertoires in Rainbow Trout. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 1480–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, S.B.; Skalla, D.; Lawton, K. Promoters for Regulation of Gene Expression in Plant Roots. 2023. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20050010974A1/en?oq=US+patent+No+US+2005%2f0010974A1 (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- Su, H.; Yakovlev, I.A.; van Eerde, A.; Su, J.; Clarke, J.L. Plant-Produced Vaccines: Future Applications in Aquaculture. Frontiers in Plant Science 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, V.T. Nanovaccines in Aquaculture. Arch. Nanomed. Open Access J. 2019, 2, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.K.; Manna, S.K.; Thomas Allnutt, F.C. Viral Vaccines for Farmed Finfish. Virus Dis. 2013, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreoni, F., Amagliani, G., Magnani, M. Selection of Vaccine Candidates for Fish Pasteurellosis Using Reverse Vaccinology and an In Vitro Screening Approach. In: Vaccine Design, Book Series- Methods in Molecular Biology, Thomas, S. (eds). Humana, New York, NY, 2016, vol 1404, pp-181–192. [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, R.; Jeyabaskar, S.; Michael, D.; Vincent Paul, A.; Sitharaman, G. Computer-Aided Vaccine Designing Approach against Fish Pathogens Edwardsiella Tarda and Flavobacterium Columnare Using Bioinformatics Softwares. Drug Des. Develop. Ther. 2016, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa A, Abunna F. Maintenance of Fish Health in Aquaculture: Review of Epidemiological Approaches for Prevention and Control of Infectious Disease of Fish. Vet. Med. Int 2018, 5432497. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, M.; Funge-Smith, S.; Subasinghe, R.; Phillips, M. Introductions and movement of Penaeus vannamei and Penaeus stylirostris in Asia and the Pacific. Bangkok: FAO; 2004. RAP Publication 2004/10.
- Mishra, S.S.; Rakesh, D.; Dhiman, M.; Choudhary, P.; Debbarma, J.; Sahoo, S.N.; Barua, A.; Giri, B.S.; Ramesh, R.; Ananda, K.; Mishra, K.; Swain, P. Present status of fish disease management in freshwater aquaculture in India: state-of-the-art-review. J. Aquacul. Fish. 2017, 1, 003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdanowicz, M.; Mudryk, Z.J.; Perlinski, P. Abundance and antibiotic resistance of Aeromonas isolated from the water of three carp ponds. Vet. Res. Commun. 2020, 44, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.M.; Mabrok, M.; Sivaramasamy, E.; Youssef, F.M.; Atwa, M.H.; El-Kholy, A.W.; Hetta, H.F.; Hozzein, W.N. Emerging MDR-Pseudomonas aeruginosa in fish commonly harbor oprL and toxA virulence genes and blaTEM, blaCTX-M, and tetA antibiotic-resistance genes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, e15961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashish, E.; Merwad, A.; Elgaml, S.; Amer, A.; Kamal, H.; Elsadek, A.; Marei, A.; Sitohy, M. Mycobacterium marinum infection in fish and man: epidemiology, pathophysiology and management; a review. Vet. Q. 2018, 38, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IASRI. Fish diseases and management. e-Krishi Shiksha. http://ecoursesonline.iasri.res.in/ Accessed on 02.02.2023.
- Kim, C.H.; Leong, J.A. Fish viruses. Encyclop. Virol. 2004, 558–568. [Google Scholar]
- Bajpai, V.; Pragyan, D.; Suman, K.; Mohanty, J.; Sahoo, P.K. Viral diseases in Indian freshwater and marine water pisciculture. Curr. Sci. 2022, 122, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitika, Wei, J.; Hui, A.M. The Development of mRNA Vaccines for Infectious Diseases: Recent Updates. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 5271–5285. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, J.; Han, X.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. mRNA vaccine: a potential therapeutic strategy. Mol, Cancer. 2021, 16, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisini, R.; Poerio, N.; Mariotti, S.; De Santis, F.; Fraziano, M. The Multirole of Liposomes in Therapy and Prevention of Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Y; Wang H. Materials based vaccines for infectious diseases. Wires Nanomedic. Nanobiotech. 2022, 14, e184. [CrossRef]
- Gudding, R.; Van-Muiswinkel, W.B. A history of fish vaccination science-based disease prevention in aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1683–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plant, K.P.; LaPatra, S.E. Advances in fish vaccine delivery. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafalla, C.; Bogwald, J.; Dalmo, R.A. Adjuvants and immunostimulants in fish vaccines: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafalla, C.; Bogwald, J.; Dalmo, R.A.; Munang’andu, H.M.; Evensen, o. Adjuvants in fish vaccines. In Fish Vaccination, 1st ed.; Gudding, R., Lillehaug, A., Evensen, Ø., Eds.; John. Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New. York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holvold, L.B.; Myhr, A.I.; Dalmo, R.A. Strategies and hurdles using DNA vaccines to fish. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perri, S.; Greer, C.E.; Thudium, K.; Doe, B.; Legg, H.; Liu, H.; Romero, R.E.; Tang, Z.; Bin, Q.; Dubensky, T.W.; et al. An alphavirus replicon particle chimera derived from Venezuelan equine encephalitis and sindbis viruses is a potent gene-based vaccine delivery vector. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 10394–10403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, M. The contribution of molecular epidemiology to the understanding and control of viral diseases of salmonid aquaculture. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, M.; Carreras, M.; Ciércoles, C.; Cornax, M.-J.; Gorelli, G.; Morote, E.; Saez, R. Assessing fishing and marine biodiversity changes using fishers’ perceptions: The Spanish Mediterranean and Gulf of Cadiz case study. PLoS ONE, 2014, 9, e85670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugimba, K.K.; Byarugaba, D.K.; Mutoloki, S.; Evensen, O.; Munang’andu, H.M. Challenges and Solutions to Viral Diseases of Finfish in Marine Aquaculture. Pathogen. 2021, 10, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kageyama, A.; Yazawa, K.; Ishikawa, J.; Hotta, K.; Nishimura, K.; Mikami, Y. Nocardial Infections in Japan from 1992 to 2001, Including the First Report of Infection by Nocardia transvalensis. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 19, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Chhina, D.; Soni, R. K.; Kakkar, C.; Sidhu, U. S. Clinical spectrum and outcome of pulmonary nocardiosis: 5-year experience. Lung India: official organ of Ind. Chest Soc. 2016, 33, 398–403. [Google Scholar]
- Vendrell, D.; Balcázar, J. L.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; de Blas, I.; Gironés, O.; & Múzquiz, J. L. Lactococcus garvieae in fish: a review. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infectious Dis. 2006, 29(4), 177–198.
- Shrestha, S.; Kanellis, J.; Korman, T.; Polkinghorne, K. R.; Brown, F.; Yii, M.; Kerr, P. G.; Mulley, W. Different faces of Nocardia infection in renal transplant recipients. Nephrol. (Carlton, Vic.) 2016, 21, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariya, T.; Kubota, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Kira, K. Nocardial infection in cultured yellowtails (Seriola quinqueruiata and S. purpurascens)—I. Bacteriological study. Fish Pathol. 1968, 3, 16–23. (in Japanese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimahara, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Nakamura, A.; Itami, T.; Yoshida, T. Detection of antibody response against Nocardia seriolae by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and a preliminary vaccine trial in yellowtail Seriola quinqueradiata. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2005, 25, 270–275. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, G.; Yamashita, K.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I. Protective efficacy and immune responses induced by a DNA vaccine encoding codonoptimized PPA1 against Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida in Japanese flounder. Vaccine 2015, 33(8), 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorimachi,M.; Maeno, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Inouye,K.; Inui, Y. Causative agent of jaundice of yellowtail. Seriora quinqueradiata, Fish Pathol. 1993, 28, 119–124. (in Japanese).
- Nash, A.A.; Dalziel, R. G.; Fitzgerald, J. R. Mechanisms of Cell and Tissue Damage. Mims’ Pathogen Infectious Dis. 2015, 171–231. [Google Scholar]
- Lampel, K. A.; Formal, S. B.; Maurelli, A. T. A Brief History of Shigella. EcoSal. Plus. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, T.; Fukuda, Y.; Sakai, T.; Tanimoto, N.; Nakanishi, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Takano, T.; Nakayasu, C. Clonal structure in Ichthyobacterium seriolicida, the causative agent of bacterial haemolytic jaundice in yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata, inferred from molecular epidemiological analysis. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelsalam, M.; Asheg, A.; Eissa, A. E. Streptococcus dysgalactiae: An emerging pathogen of fishes and mammals. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2013, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Matsuyama, T.; Sakai, T.; Shigenobu, Y.; Sugaya, T.; Yasuike, M.; Fujiwara, A.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I.; Fukuda, Y.; Nakayasu, C. Complete Genome Sequence of Ichthyobacterium seriolicida JBKA-6T, Isolated from Yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata) Affected by Bacterial Hemolytic Jaundice. Genome Announcements 2017, 5, e01574-16. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, D.; Higuera, G.; Villa, M.; Middelboe, M.; Dalsgaard, I.; Madsen, L.; Espejo, R. T. Diversity of Flavobacterium psychrophilum and the potential use of its phages for protection against bacterial cold water disease in salmonids. J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35(3), 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Pozet, F.; Michel, C. Standardization of experimental infection with Flavobacterium psychrophilum, the agent of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss fry syndrome. Dis. Aquatic. Organisms 2000, 42(3), 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, H.; Horiuchi, M.; Bunya, T.; Hoshiai, G. Outbreaks of cold-water disease in coho salmon in Japan. Fish Pathol. 1991, 26, 211–212. (in Japanese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, Y.; Mizokami, A. Outbreaks of coldwater disease in wild ayu and pale chub. Fish Pathol. 1996, 31, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochat, T.; Calvez, S.; Dalsgaard, I.; Madsen, L.; Calteau, A.; Lunazzi, A.; Nicolas, P.; Wiklund, T.; Bernardet, J.; Duchaud, E. Genomic Characterization of Flavobacterium psychrophilum Serotypes and Development of a Multiplex PCR-Based Serotyping Scheme. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchaud, E.; Rochat, T.; Habib, C.; Barbier, P.; Loux, V.; Guérin, C.; Dalsgaard, I.; Madsen, L.; Nilsen, H.; Sundell, K.; Wiklund, T.; Strepparava, N.; Wahli, T.; Caburlotto, G.; Manfrin, A.; Wiens, G. D.; Fujiwara-Nagata, E.; Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Bernardet, F. . Nicolas, P. Genomic Diversity and Evolution of the Fish Pathogen Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, M. A.; Stiehm, E. R. Passive Immunity in Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravningen, K.; Sakai, M.; Mishiba, T.; Fujimoto, T. The efficacy and safety of an oil-based vaccine against Photobacterium damsela subsp. piscicida in yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata): A field study. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 24, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awate, S.; Babiuk, L.A.; Mutwiri, G. Mechanisms of Action of Adjuvants. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, I.; Garg, R.; van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk, S. Selection of adjuvants for vaccines targeting specific pathogens. Expert Review Vac. 2019, 18, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Ototake, M.; Nakanishi, T. Water-soluble adjuvants enhance the protective effect of Flavobacterium psychrophilum vaccines in ayu Plecoglossus altivelis. Fish Pathol. 2003, 38, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Lida, Y.; Yoneji, T. Field trials of a vaccine with water-soluble adjuvant for bacterial coldwater disease in ayu Plecoglossus altivelis, Fish Pathol 2003, 38, 63–65. (in Japanese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, J. H. Current and New Approaches for Mucosal Vaccine Delivery. Mucos. Vac. 2020, 325–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, E.; Méndez, J.; Cascales, D.; & Guijarro, J. A. Flavobacterium psychrophilum vaccine development: A difficult task. Microbial. Biotechnol. 2014, 7, 414–423.
- Dumetz, F.; Duchaud, E.; LaPatra, S. E.; Marrec, C. L.; Claverol, S.; Urdaci, C.; & Hénaff, M. L. A Protective Immune Response Is Generated in Rainbow Trout by an OmpH-Like Surface Antigen (P18) of Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4845–4852.
- Fux, R.; Arndt, D.; Langenmayer, M. C.; Schwaiger, J.; Ferling, H.; Fischer, N.; Indenbirken, D.; Grundhoff, A.; Dölken, L.; Adamek, M.; Steinhagen, D.; & Sutter, G. Piscine Orthoreovirus 3 Is Not the Causative Pathogen of Proliferative Darkening Syndrome (PDS) of Brown Trout (Salmo trutta fario). Viruses 2019, 11.
- Takano, T.; Nawata, A.; Sakai, T.; Matsuyama, T.; Ito, T.; Kurita, J.; Terashima, S.; Yasuike, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Fujiwara, A.; Kumagai, A.; & Nakayasu, C. Full-Genome Sequencing and Confirmation of the Causative Agent of Erythrocytic Inclusion Body Syndrome in Coho Salmon Identifies a New Type of Piscine Orthoreovirus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11.
- Wessel, O.; Braaen, S.; Alarcon, M.; Haatveit, H.; Roos, N.; Markussen, T.; Tengs, T.; Dahle, M.; Rimstad, E. Infection with purified Piscine orthoreovirus demonstrates a causal relationship with heart and skeletal muscle inflammation in Atlantic salmon. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0183781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, A.; Hjortaas, M.; Tengs, T.; Hellberg, H.; Johansen, R. First description of a new disease in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum)) similar to heart and skeletal muscle inflammation (HSMI) and detection of a gene sequence related to piscine orthoreovirus (PRV). PLoS One 2015, 10, e0131638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcotte, H.; Hammarström, L. Passive Immunization: Toward Magic Bullets. Mucos, Immunol. 2015, 1403-1434.
- Haatveit, H.; Hodneland, K.; Braaen, S.; Hansen, E.; Nyman, I.; Dahle, M.; Frost, P.; Rimstad, E. DNA vaccine expressing the non-structural proteins of Piscine orthoreovirus delay the kinetics of PRV infection and induces moderate protection against heart -and skeletal muscle inflammation in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Vaccine 2018, 36, 7599–7608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, K.; Bondad-Reantaso, M.; Fukudome, M.; Wakabayashi, H. Neobenedenia girellae (Hargis, 1955) Yamaguti, 1963 (Monogenea: Capsalidae) from cultured marine fishes of Japan. J. Parasitol. 1995, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norbury, L. J.; Shirakashi, S.; Power, C.; Nowak, B. F.; & Bott, N. J. (2022). Praziquantel use in aquaculture—Current status and emerging issues. Int. J. Parasitol. Drug Res. 2022, 18, 87–102.
- Jung, S.-J..; Kitamura, S.-I.; Aoyana,M.; Song, J.-Y.; Kim, B.-K.; Oh, M.-J. Immune response of olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus against Miamiensis avidus (Ciliophora: Scuticociliatida). J. Fish Pathol. 2006, 19, 173–181.
- Song, J.Y.; Sasaki, K.; Okada, T.; Sakashita, M.; Kawakami, H.; Matsuoka, S.; Kang, H.S.; Nakayama, K. .; Jung, S.J.; Oh, M.J.. Antigenic differences of the scuticociliate Miamiensis avidus from Japan. J. Fish Dis. 2009, 12, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, S.; Dar, S. A.; Shin, M.; Jeong, J.; Jung, J. Potential Efficacy of Chitosan-Poly (Lactide-Co-Glycolide)-Encapsulated Trivalent Immersion Vaccine in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) Against Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus, Streptococcus parauberis Serotype I, and Miamiensis avidus (Scuticociliate). Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Motokawa, S.; Narasaki, Y.; Song, J.Y.; Yokoyama, Y..; Hirose, E.; Murakami, S.; Jung, S.- J.; Oh, M.J.; Nakayama, K.; Kitamura, S.I. Analysis of genes encoding high antigenicity polypeptides in three serotypes of Miamiensis avidus. Parasitol. Int. 2018, 67, 196–202.
- Nakamura, Y.; Takano, T.; Yasuike, M.; Sakai, T.; Matsuyama, T.; & Sano, M. Comparative genomics reveals that a fish pathogenic bacterium Edwardsiella tarda has acquired the locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) through horizontal gene transfer. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 642.
- Kusuda, R.; Inoue, M.; Sugiura, H.; Kawai, K. Characteristics of a pathogenic Mycobacterium sp. isolated from cultured striped jack, Pseudocaranx dentex. Aquacult. Sci. 1993, 41, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kusuda, R.; Kawakami, K.; Kawai, K. A fish-pathogenic Mycobacterium sp. isolated from an epizootic of cultured yellowtail. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1987, 53, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, S.; Yoshida, T.; Wang, P.; Chen, S. Current knowledge of nocardiosis in teleost fish. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, M.; Kim, H.J.; Kasai, H.; Nishizawa, T.; Yoshimizu, M. Virulence Change of Infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus against Rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss with Viral Molecular Evolution. Fish Pathol. 2009, 44(4), 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, J.; Liu, J. Preclinical Progress of Subunit and Live Attenuated Mycobacterium tuberculosis Vaccines: A Review following the First in Human Efficacy Trial. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redding, L.; Werner, D. B. DNA vaccines in veterinary use. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2009, 8, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Håstein T., Gudding R., Evensen Ø. Bacterial vaccines for fish—an update of the current situation worldwide. Dev. Biol. 2005, 121, 55–74.
- Torres-Corral, Y.; Girons, A.; González-Barreiro, O.; Seoane, R.; Riaza, A.; Santos, Y. Effect of Bivalent Vaccines against Vibrio anguillarum and Aeromonas salmonicida Subspecie achromogenes on Health and Survival of Turbot. Vaccines 2021, 9, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvaraj, S.; Md Yasin, I. S.; A. Karim, M. M.; Saad, M. Z. Elucidating the Efficacy of Vaccination against Vibriosis in Lates calcarifer Using Two Recombinant Protein Vaccines Containing the Outer Membrane Protein K (r-OmpK) of Vibrio alginolyticus and the DNA Chaperone J (r-DnaJ) of Vibrio harveyi. Vaccines, 2020, 8.
- Soler, E.; Houdebine, M. Preparation of recombinant vaccines. Biotechnol. Ann. Rev. 2007, 13, 65–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Lee, A.; Park, Y.; Song, S.; Choi, S.; Lee, B. A review of vaccine development and research for industry animals in Korea. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2012, 1, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, M. A.; Graham, S. P.; & La Ragione, R. M. Challenges in Veterinary Vaccine Development and Immunization. Vaccine. Design. 2016, 1404, 3–35.
- Sommerset, I.; Krossøy, B.; Biering, E.; Frost, P. Vaccines for fish in aquaculture. Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2005, 4, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Yokoyama, H. Parasitic diseases of cultured marine fish in Japan. Fish Pathol. 1998, 33, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentini, S.C.; Rohovec, J.S.; Fryer, J.L. Epizootiology of erythrocytic inclusion body syndrome. J. Aquat. Anim. Health. 1989, 1, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starliper, C. E. Bacterial coldwater disease of fishes caused by Flavobacterium psychrophilum. J. Adv. Res. 2011, 2, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkissian, M. Seven of the Biggest Problems Facing Fish in Our Oceans & raquo; Marine Conservation Institute Available online: https://marine-conservation.org/on-the-tide/seven-of-the-biggest-problems-facing-fish-in-our-oceans/. accessed on 31.01.2023.
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2022. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture towards Blue Transformation. 2022. https://www.fao.org/publications/sofia/2022/en/, accessed on 02.02.2023.
- Snieszko, SF. Columnaris disease of fishes. USFWS Fish Leafl. 1958, 46, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Amend, D.F.; Ross, A.J. Experimental control of columnaris disease with a new nitrofuran drug, P-7138. Prog. Fish-Cult. 1970, 32, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.J. In vitro studies with nifurpirinol (P-7138) and bacterial fish pathogens. Prog. Fish-Cult. 1972, 34, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraki, K.; Miyamoto, F.; Sato, T.; Sonezaki, I.; Yano, K. Studies on a New Chemotherapautic Agent Nifurprazine (HB-115) against Fishinfectious Diseases -Part I. Fish Pathol. 1970, 4, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deufel, J. Prophylactic measures against bacterial diseases of salmonid fry (Prophylaktische Massnahmen gegen bakterielle Erkrankungen der Salmonidenbrut). Osterr Fisch. 1974, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, T.; Ogishima, K.; Hayasaka, H.; Kaneko, S.; Ohshima, S. Application of oxolinic acid as a chemotherapeutic agent against infectious diseases in fishes-I. Antibacterial activity, chemotherapeutic effects and pharmacokinetics of oxolinic acid in fishes. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1973, 39, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Shanker, S.; Munday, B.L. Chemotherapy of Cytophaga/Flexibacter-like bacteria (CFLB) nfections in fish: studies validating clinical efficacies of selected antimicrobials. J. Fish Dis. 1995, 18, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilley, J.H.; Callinan, R.B.; Chinabut, S.; Kanchanakhan, S.; Macrae, I.H.; Phillips, M.J. Epizootic ulcerative syndrome (EUS) technical handbook. 1998, Aquatic Animal Health Research Institute, Bangkok, Thailand.
- Ahne, W.; Bjorklund, H.V.; Essbauer, S.; Fijan, N.; Kurath, G.; Winton, J.R. Spring viremia of carp (SVC). Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2002, 52(3), 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, P.F. Virus diseases of cyprinids. In: Fish Diseases, Vol. 1. Eiras, J.C.; Segner, H.; Wahli, T.; Kapoor, B.G. eds. Science Publishers, Enfield, New Hampshire, USA, 2008. 87‒184.
- Emmenegger, E.J.; Kurath, G. DNA Vaccine Protects Ornamental Koi (Cyprinus Carpio Koi) against North American Spring Viremia of Carp Virus. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6415–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noga, E.J. Lymphocystis In Fish disease: diagnosis and treatment. 2nd edition. Wiley-Blackwell. Ames, Iowa. 2010. Pp. 171–173.
- Wolf, K. Lymphocystis disease. In Fish Viruses and Fish Viral Diseases. Cornell University Press. Ithaca, NY. 1988. Pp. 268–291.
- Cusack, R.; Cone, D.K. A Review of Parasites as Vectors of Viral and Bacterial Diseases of Fish. J. Fish Dis. 1986, 9, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOI. Govt. of India Handbook on Fisheries Statistics, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairy, Government of India. 2021. https://dof.gov.in/sites/default/files/2021-02/Final_Book.pdf, accessed on 02.02.2023.
- Masifundise. The Importance of Fish to Man: Not Just a Food Source 2016, Available online: https://www.masifundise.org/the-importance-of-fish-to-man-not-just-a-food-source/. Accessed on 31.01.2023.
- McLoughlin, M.F.; Graham, D.A. Alphavirus Infections in Salmonids ? A Review. J. Fish Dis. 2007, 30, 511–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneeringer, S.; Bowman, M.; Clancy, M. The US and EU Animal Pharmaceutical Industries in the Age of Antibiotic Resistance; USDA Economic Research Service Report Number 264; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Assefa, A.; Abunna, F. Maintenance of Fish Health in Aquaculture: Review of Epidemiological Approaches for Prevention and Control of Infectious Disease of Fish. Vet. Med. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horzinek, M.C.; Schijns, V.E.C.J.; Denis, M.; Desmettre, P.; Babiuk, L.A. General description of vaccines. In Veterinary Vaccinology; Pastoret, P.P., Blancou, J., Vannier, P., Verschueren, C., Eds.; Elsevier Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 132–152. [Google Scholar]
- Dadar, M.; Dhama, K.; Vakharia, V. N.; Hoseinifar, S. H.; Karthik, K.; Tiwari, R.; Khandia, R.; Munjal, A.; Salgado-Miranda, C.; Joshi, S. K. Advances in Aquaculture Vaccines Against Fish Pathogens: Global Status and Current Trends. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquacul. 2017, 25, 184–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Bruce, T.J.; Jones, E.M.; Cain, K.D. A Review of Fish Vaccine Development Strategies: Conventional Methods and Modern Biotechnological Approaches. Microorganisms, 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DFO. Efficacy of the APEX vaccine in Atlantic salmon subjected to an IHNV exposure simulating natural and/or elevated field challenges. https://www.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/aquaculture/rp-pr/acrdp-pcrda/projects-projets/P-07-04-010-eng.html. Accessed on 02.02.2023.
- PHARMAQ Seguridad y apoyo. https://www.pharmaq.com/es/pharmaq/, accessed on (19.01.2023).
- HOME—MSD Animal Health Norge (msd-animal-health.no), https://www.msd-animal-health.no/, accessed on (21.01.2023).
- Elanco South Africa, https://www.elanco.no/index, accessed on (24.01.2023).
- Aquavac—Vaccines Against Fish Diseases. Formerly Norvax https://www.aquavac-vaccines.com/, accessed on (16.01.2023).
- PAHC. Review our ESG Report, https://www.pahc.com, accessed on (23.01.2023).
- Tafalla, C.; Bøgwald, J.; Dalmo, R. A. Adjuvants and Immunostimulants in Fish Vaccines: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, A.K.; Manna, S.K.; Thomas Allnutt, F.C. Viral Vaccines for Farmed Finfish. Virus Dis. 2014, 25(1), 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, R.A. Polyvalent vaccines in fish: The interactive effects of multiple antigens. Develop. Biol Standard. 1997, 90, 245–256. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart, N. Treatment of Fish Disease. Veter. Rec. 1983, 112, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shefat, S.H.T. Vaccines for infectious bacterial and viral diseases of fish. J. Bacteriol. Infectious Dis. 2018, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sommerset, I.; Krossøy, B.; Biering, E.; Frost, P. Vaccines for Fish in Aquaculture. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2005, 4(1), 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castells-Graells, R.; Lomonossoff, G. P. Plant-based Production Can Result in Covalent Cross-linking of Proteins. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19(6), 1095–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, A.; Sommergruber, K.; Thompson, D.; Hartmuth, K.; Matzke, M. A.; Matzke, A.J.M. The Expression of a Nopaline Synthase ? Human Growth Hormone Chimaeric Gene in Transformed Tobacco and Sunflower Callus Tissue. Plant Mol. Biol. 1986, 6, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiatt, A.; Caffferkey, R.; Bowdish, K. Production of Antibodies in Transgenic Plants. Nature 1989, 342 6245), 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.M.; Mabrok, M.; Sivaramasamy, E.; Youssef, F.M.; Atwa, M.H.; El-Kholy, A.W.; Hetta, H.F.; Hozzein, W.N. Emerging MDR-Pseudomonas aeruginosa in fish commonly harbor oprL and toxA virulence genes and blaTEM, blaCTX-M, and tetA antibiotic-resistance genes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, e15961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaltiel, Y.; Gingis-Velitski, S.; Tzaban, S.; Fiks, N.; Tekoah, Y.; Aviezer, D. Plant-Based Oral Delivery of β-Glucocerebrosidase as an Enzyme Replacement Therapy for Gaucher’s Disease. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Guo, B.; Huo, Y.; Guan, Z.; Dai, J.; Wei, Y. Recent Advances and Safety Issues of Transgenic Plant-Derived Vaccines. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97(7), 2817–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; van Eerde, A.; Steen, H. S.; Heldal, I.; Haugslien, S.; Ørpetveit, I.; Wüstner, S. C.; Inami, M.; Løvoll, M.; Rimstad, E.; Clarke, J. L. Establishment of a Piscine Myocarditis Virus (PMCV) Challenge Model and Testing of a Plant-Produced Subunit Vaccine Candidate against Cardiomyopathy Syndrome (CMS) in Atlantic Salmon Salmo Salar. Aquaculture 2021, 541, 736806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyel, J. F. Plant Molecular Farming—Integration and Exploitation of Side Streams to Achieve Sustainable Biomanufacturing. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y. J.; Kwon, T. H.; Seo, J. Y.; Kim, T. J. Oral Immunization of Fish against Iridovirus Infection Using Recombinant Antigen Produced from Rice Callus. Vaccine 2013, 31(45), 5210–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelet, L.; Lefebvre-Legendre, L.; Burr, S. E.; Rochaix, J.-D.; Goldschmidt-Clermont, M. Enhanced Chloroplast Transgene Expression in a Nuclear Mutant of Chlamydomonas: Enhanced Chloroplast Transgene Expression. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9(5), 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, R.; Liu, L.; Cao, G.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Zou, Y.; Chen, H.; Gong, C. Oral Vaccination of BacFish-Vp6 against Grass Carp Reovirus Evoking Antibody Response in Grass Carp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34(1), 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsian, J.; Hurdiss, D. L.; Ranson, N. A.; Ritala, A.; Paley, R.; Cano, I.; Lomonossoff, G. P. Plant-Made Nervous Necrosis Virus-Like Particles Protect Fish Against Disease. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, J. L.; Paruch, L.; Dobrica, M.-O.; Caras, I.; Tucureanu, C.; Onu, A.; Ciulean, S.; Stavaru, C.; Eerde, A.; Wang, Y.; Steen, H.; Haugslien, S.; Petrareanu, C.; Lazar, C.; Popescu, C.-I.; Bock, R.; Dubuisson, J.; Branza-Nichita, N. Lettuce-Produced Hepatitis C Virus E1E2 Heterodimer Triggers Immune Responses in Mice and Antibody Production after Oral Vaccination. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15(12), 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisez, L.; Tan, Z. Vaccine development for Asian Aquaculture. Diseases in Asian Aquaculture V Fish health section, Proceedings of the Fifth Symposium in Asian Aquaculture. Edited by: Walker P, Lester R, Bondad-Reantaso MG. Goldcoast, Australia: Asian Fisheries Society 2005, 483-494.
- Brooker, A.J.; Papadopoulou, A.; Gutierrez, C.; Rey, S.; Davie, A.; Migaud, H. Sustainable production and use of cleaner fish for the biological control of sea lice: Recent advances and current challenges. Vet Rec. 2018, 183, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kole, S.; Shin, S.M.; Kwak, I.S.; Cho, S.H.; Jung, S.J. Efficacy of Chitosan-PLGA encapsulated trivalent oral vaccine against viral haemorrhagic septicemia virus, Streptococcus parauberis, and Miamiensis avidus in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 127, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, K. C.; Lamb, A.; Fox, D.; Jegathese, P.S.J. An evaluation of microalgae as a recombinant protein oral delivery platform for fish using green fluorescent protein (GFP). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loera-Muro, A.; Guerrero-Barrera, A.; Tremblay, D.N.Y.; Hathroubi, S.; Angulo, C. Bacterial biofilm-derived antigens: a new strategy for vaccine development against infectious diseases. Expert Rev. Vacc. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaner-Tarbes, S.; Fraile, L.; Montoya, M.; Del Portillo, H. Exosome-Based Vaccines: Pros and Cons in the World of Animal Health. Viruses 2021, 13, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajissa, K.; Zakaria, R.; Suppian, R.; Mohamed, Z. Epitope-based vaccine as a universal vaccination strategy against Toxoplasma gondii infection: A mini-review. J. Adv. Veter. Animal Res. 2019, 6, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Cai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L. ; Strategies for prevention and control of vibriosis in Asian fish culture. Vaccines 2023, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, S.M.; Rosenberg, A.A. Food security and marine capture fisheries: Characteristics, trends, drivers and future perspectives. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol Sci. 2010, 365, 2869–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holsman, K.K.; Haynie, A.C.; Hollowed, A.B.; Reum, J.C.P.; Aydin, K.; Hermann, A.J.; Cheng, W.; Faig, A.; Ianelli, J.N.; Kearney, K.A. Ecosystem-Based Fisheries Management Forestalls Climate-Driven Collapse. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, M.A.; Peterson, J.O.; Lynch, P.D.; Griffis, R.B.; Adams, C.F.; Arnold, W.S.; Barnett, L.A.K.; deReynier, Y.; DiCosimo, J.; Fenske, K.H.; et al. Accounting for Shifting Distributions and Changing Productivity in the Development of Scientific Advice for Fishery Management. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 76, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, N.L.; Evans, L. Approaches and frameworks for management and research in small-scale fisheries. Smallscale fisheries management: frameworks and approaches for the developing world. CAB International, Oxfordshire, 2011, 16-34.
- Natnan, M.E.; Mayalvanan, Y.; Jazamuddin, F.M.; Aizat, W.M.; Low, C.F.; Goh, H.H.; Azizan, K.A.; Bunawan, H.; Baharum, S.N. Omics strategies in current advancements of infectious fish disease management. Biol. 2021, 10(11), 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivam, S.; El-Matbouli, M.; Kumar, G. Development of Fish Parasite Vaccines in the OMICs Era: Progress and Opportunities. Vaccines 2021, 9, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinay, T.N.; Bhat, S.; Gon Choudhury, T.; Paria, A.; Jung, M.-H.; Shivani Kallappa, G.; Jung, S.-J. Recent advances in application of nanoparticles in fish vaccine delivery. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018, 26, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S.; Kim, S.G.; Kang, J.W.; Kwon, J.; Bin Lee, S.; Jung, W.J.; Park, S.C. Applications of carbon nanotubes and polymeric micro-/nanoparticles in fish vaccine delivery: Progress and future perspectives. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13(4), 1844–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.L.; Waheed, M.T.; Lössl, A.G.; Martinussen, I.; Daniell, H. How can plant genetic engineering contribute to cost-effective fish vaccine development for promoting sustainable aquaculture? Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 83, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yakovlev, I.A.; van Eerde, A.; Su, J.; Clarke, J.L. Plant-Produced Vaccines: Future Applications in Aquaculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 718775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
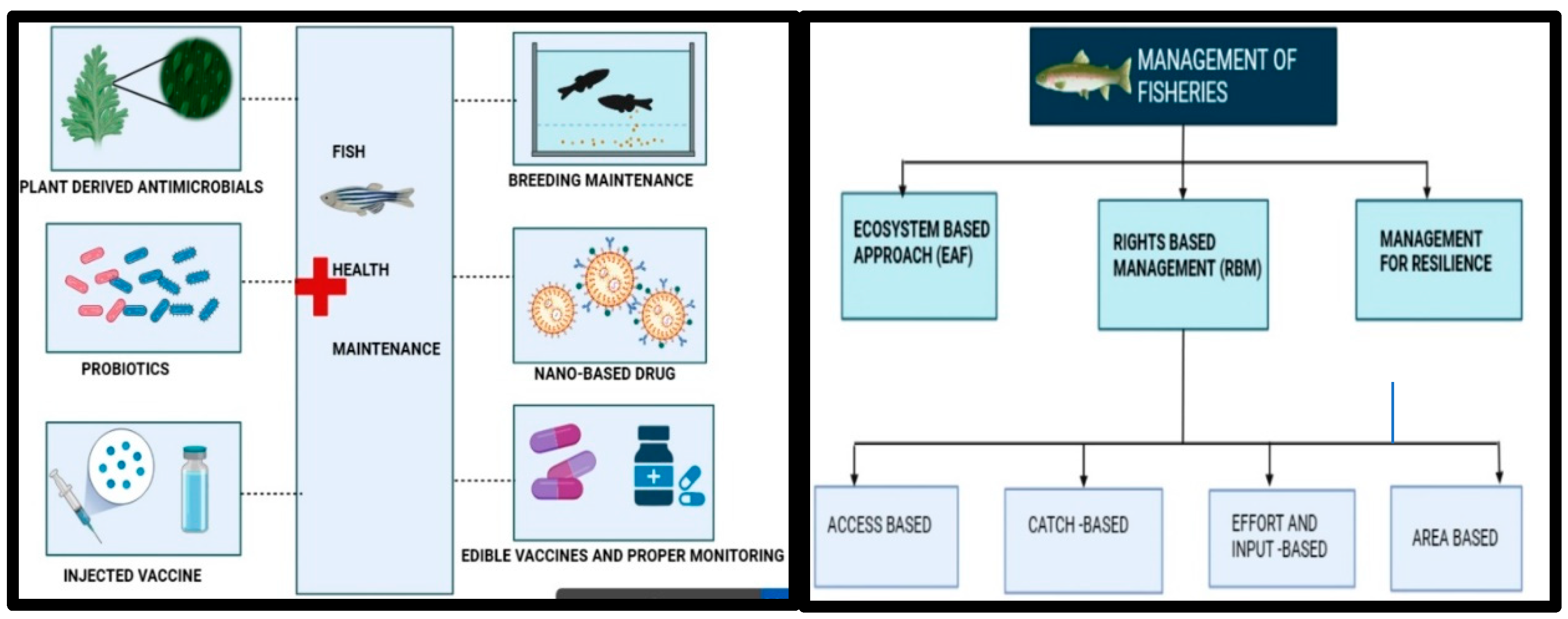
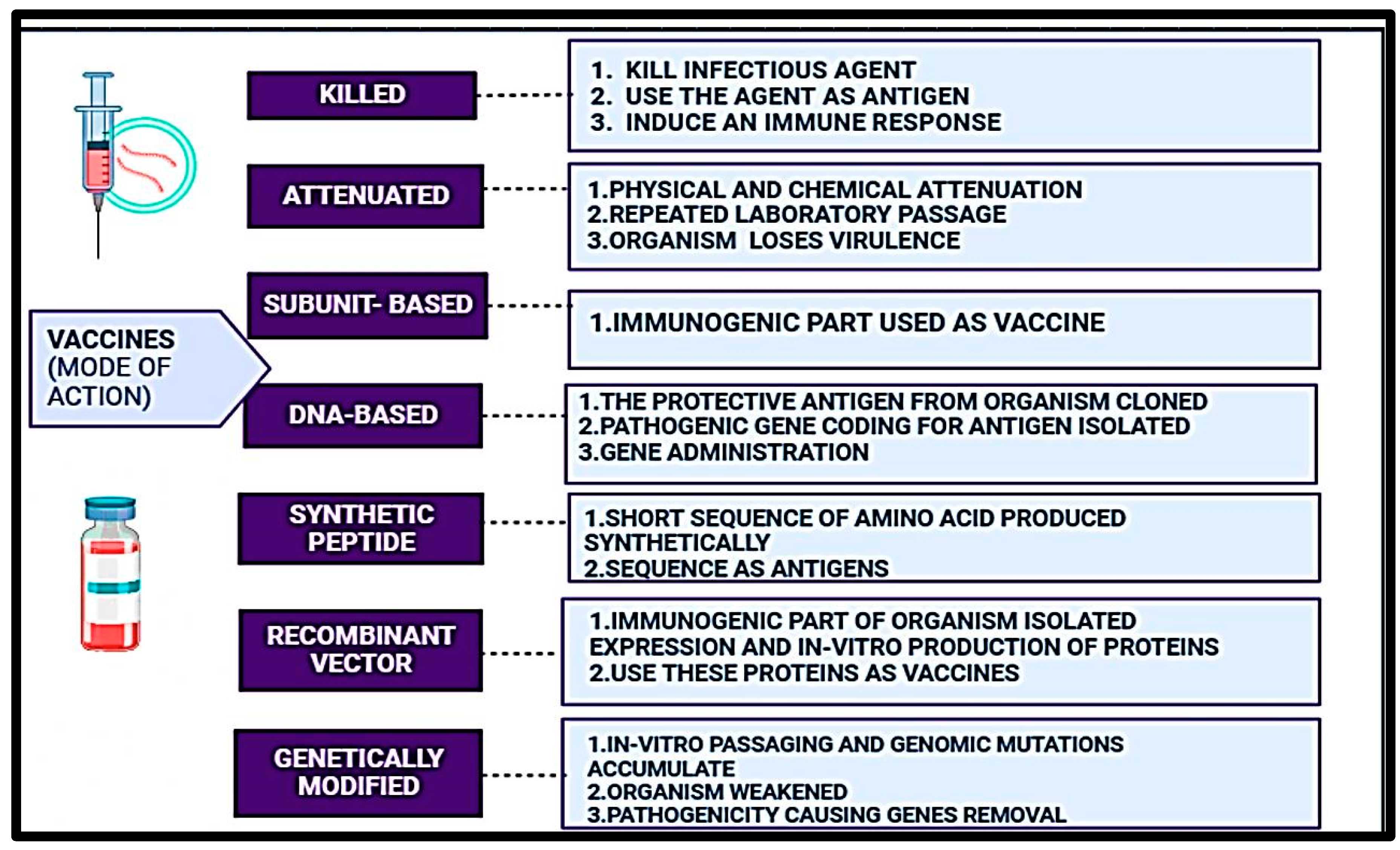
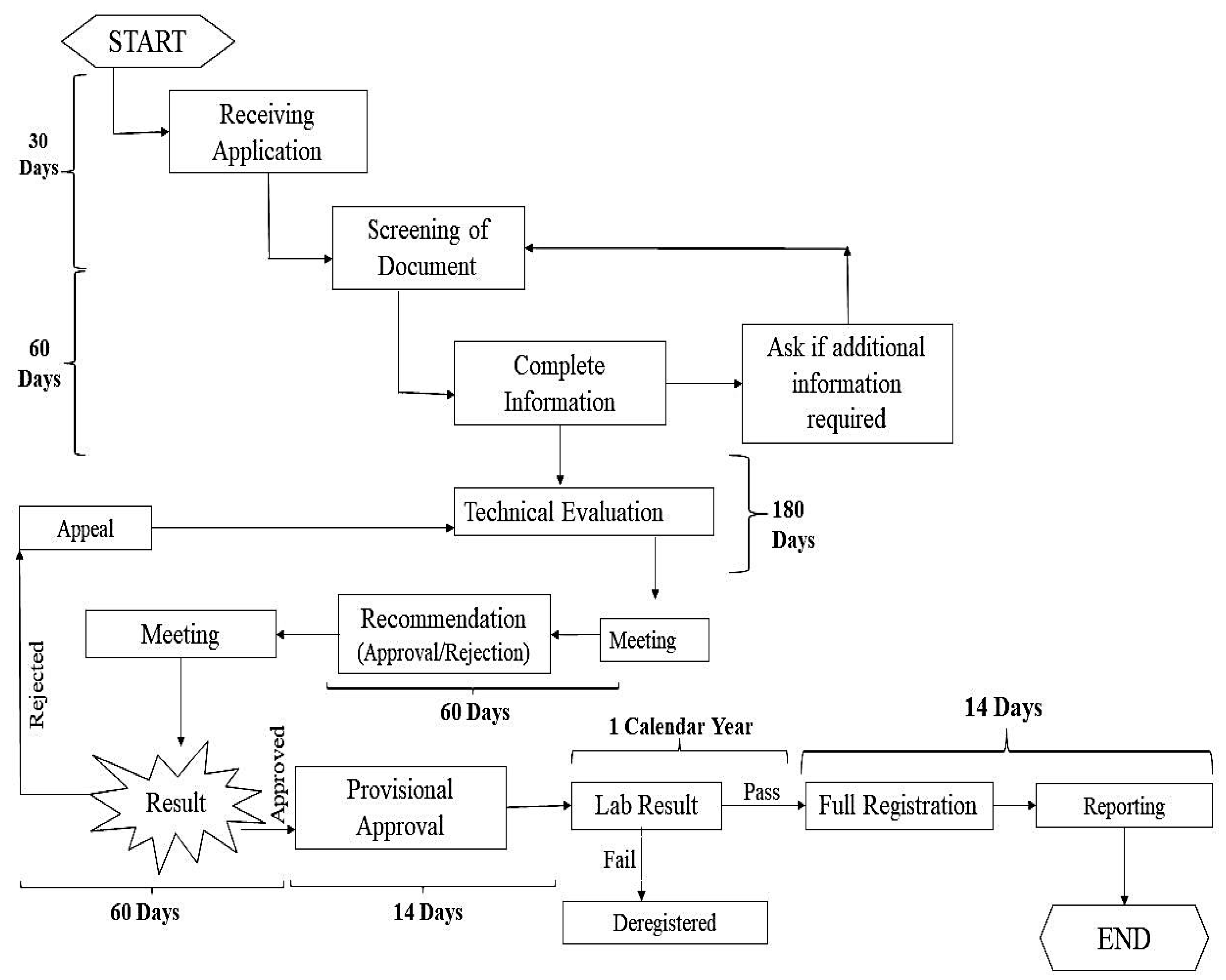
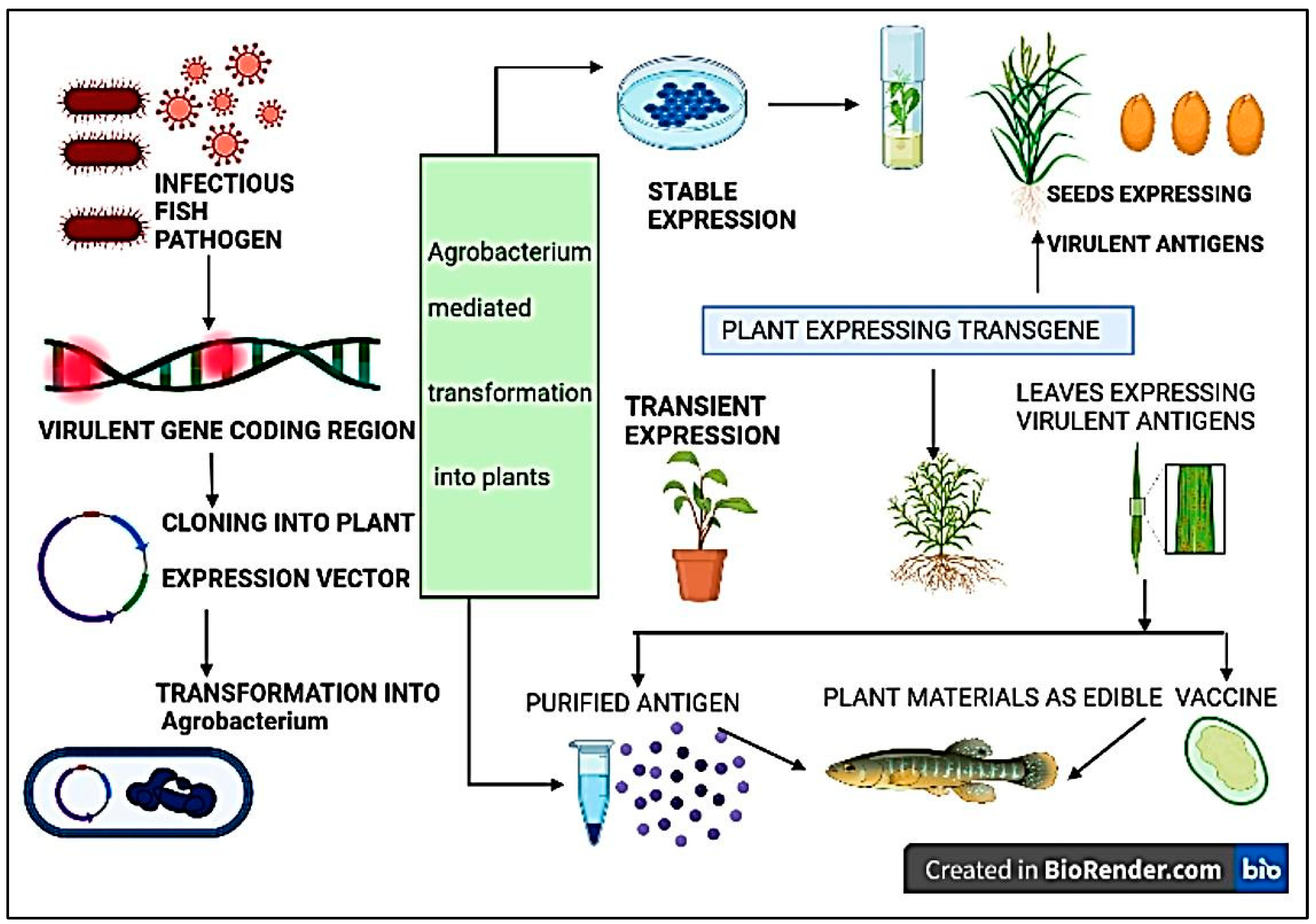

| S. No. | Infectious agent/Etiological agent | Diseases | Animals infected | Vaccines used to prevent the disease (either used in humans or animals) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Avian Influenzae virus | Avian Influenza | Poultry: Chickens, ducks, turkeys, geese | Afluria Quadrivalent, Fluarix Quadrivalent, FluLaval Quadrivalent, and Fluzone Quadrivalent. |
| 2. | Herpes virus, Gallid alphaherpesvirus 2 | Marek’s disease (fowl paralysis) | Poultry-chickens | HSV vaccine candidate (mRNA-1608), herpes zoster |
| 3. | Salmonella sp. | Salmenollosis | Aquatic animals: fishes, tortoises, birds, animals—cattle, pigs, horses | Ty21a, Vivotif (Typhoid Vaccine Live Oral Ty21a), Typbar TCV®, Typhim Vi, Vivotif |
| 4. | Rabies lyssavirus | Rabies | Dogs | HDCV or PCEC, human rabies immune globulin (HRIG) |
| 5. | Bacillus anthracis | Anthrax | Cattle, sheep, goat, camels | Anthrax Vaccine Adsorbed (AVA) or BioThraxTM |
| 6. | Brucella bacteria | Brucellosis | Cattle, sheep, goat, swine, equines | Live attenuated Brucella abortus strain 19 (S19 vaccine), Brucella abortus S19 |
| 7. | Listeria monocytogenes | Listeriosis | birds, crustaceans | Under clinical trials |
| 8. | SARS-Cov | Severe acute respiratory syndrome | Bats, birds, cattle | COMIRNATY®, COMIRNATY®Original/Omicron BA.1, COMIRNATY®Original/Omicron BA.4-5, VAXZEVRIA, COVISHIELD™, COVID-19 Vaccine, SPIKEVAX, Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccine (Vero Cell), CoronaVac, COVAXIN®, COVOVAX™, NUVAXOVID™, CONVIDECIA, |
| 9. | Nipah virus (NiV) | Nipah | Bats, pigs, horses, goats, sheep | The Nipah Virus Vaccine (PHV02) |
| 10. | Monkey pox virus | Monkey pox | Rope squirrels, dormice, non-human primates etc. | ACAM2000®, JYNNEOS™ (Imvamune or Imvanex or MVA-BN) |
| 11. | Clostridium botulinum | Botulism | Fishes mainly trout | Fabrizio Anniballi, Alfonsina Fiore, Charlotta Löfström, Viveca Båverud. |
| 12. | Mycobacterium sp. | Mycobacterial infections | All fishes, | Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) |
| 13. | E. coli | Avian bacterial infections (AVEC) | All avian sp. | Poulvac E. coli, |
| Types of vaccine | Name of vaccine | Fish | Infection | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inactivated or heat killed whole cell Vaccine | Apha Ject® 1000, Norway | Salmon | Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus | monovalent |
| Inactivated SVCV | Carp | Spring viremia of carp virus | SVCV emulsified in oil | |
| Formalin-inactivated IHNV | Rainbow Trout | Infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus | ||
| killed VHSV | Rainbow Trout | Viral haemorrohagic septicaemia virus | -- | |
| Attenuated vaccines | Attenuated KHV Israel | Carp | Koi Herpes Virus | |
| Attenuated Flavobacterium columnare |
All fresh water finfish | Flavobacterium columnare | -- | |
| Septicemia due to enterococci | Catfish | Edwardsiella ictaluri | -- | |
| Kidney infection in Fish due to bacteria | Pacific Salmon and Atlantic salmon | Renibacterium salmoninarum | -- | |
| Recombinant vaccines | Recombinant G protein | Carp | SVCV | -- |
| CIBA-Nodavac-R | All types of fishes infected with Nervous necrosis virus (NNV), | Red-spotted grouper NNV | First vaccine indigenously developed in India | |
| Synthetic peptide vaccines | Subunit vaccine IPNV aquabirnavirus | Rainbow trout and Atlantic salmon | Infectious pancreatic necrosis viruses | Target : VP2, VP3 and Capsid proteins |
| DNA vaccines | Apex IHN, Canada | Salmon | Viruses having G antigen | |
| DNA | Salmonids | Infectious hematopoietic necrosis Rhabdovirus | Target : G glycoprotein | |
| Mucosal vaccines | MicroMatrix™ delivery system ( Piscirickettsia salmonis, ISAV and IPNV, Centrovet) | Atlantic salmon | Y. ruckeri V. anguillarum, P. salmonis and IPNV or other similar mucosal infection. | Pathogen killed by heat or inactivated by formalin |
| Plant-based edible vaccines | Under development in plant Nicotiana benthamiana | Salmonids | PMCV and Cardiomyopathy syndrome | -- |
| Nanoparticle-based vaccines | Chitosan-NPs based vaccine formulation NPrgpG, pICrgpG, CSrgpG, NpiV, | Zebrafish | Viral hemorrhagic septicimia virus. | Under experimental trials |
| OCMCS-hyaluronic Acid OCMCS/aerA-NPs, OCMCS-HA/aerA-NPs | European carp | Aeromonas hydrophila | Under experimental trials | |
| Monovalent and polyvalent vaccines | ME-VAC Aqua Strept | Nile tilapia fish, Nile tilapia | Streptococcus infections | Effective against bacterial strains, Streptococcoci, Enterococcoi, and Lactococci |
| Sr. No. | Causative agent | Diseases | Type of fish infected | Loss in production /economic loss (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Aeromonas bacteria | Aeromonas infections | Carps, fresh water fishes | 80-100% | [45] |
| 2. | Pseudomonas sp. | Strawberry disease | Carps, rainbow trout, tench | 50% | [46] |
| 3. | Shewanella putrefaciens | Shewanellosis | Carps, rainbow trout, zebra fish | - | [45,46] |
| 4. | Mycobacterium sp. | Mycobacteriosis | All fresh water and marine fishes | 50% | [47] |
| 5. | Flavobacterium flavobacter | Bacterial gill diseases | All fishes | 60-70% | [48] |
| 6. | Birnavirus | Necrosis | Freshwater fishes like salmonids | 50% | [16] |
| 7. | Retrovirus | Anaemia | Walley pike | 50% | [49] |
| 8. | Ranavirus | Anaemia | Carp | 50% | [50] |
| 9. | Megalocytivirus | Anaemia | Carp and other fresh water fishes | 60-70% | [50] |
| S. No. | Species | Vaccination against | Reference |
| 1 | cold-water vibriosis, classical vibriosis, | Listonella anguillarum, Vibrio ordalii | [111] |
| 2 | furunculosis | Aeromonas salmonicida subspecies achromogenes | [112] |
| 3 | Vibriosis |
Vibrio salmonicida Vibrio anguillarum |
[112] |
| 4 | yersiniosis | Yersinia ruckeri | [111] |
| 5 | pasteurellosis | Photobacterium damselae subspecie piscicida | [111] |
| 6 | edwardsiellosis | Edwardsiella ictaluri | [111] |
| 7 | winter ulcer | Moritella viscosa | [111] |
| 8 | Streptococcosis/Lactococcosis | Streptococcus iniae, Lactococcus garviae | [111] |
| S. No. | Disease | Pathogen | Symptoms | Treatment | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Columnaries Disease | Flavobacterium columnare | Lesions in skin, finerosion, nacrosis in gill | Amphenicol. Nifurpirinol, Nifurprazine, Oxolinic acid |
[123,124,125,126,127,128,129] |
| 2. | Epizootic ulcerative syndrome (EUS), or ‘red spot disease | Aphanomyces invadens | red lesions (sores) or deep ulcers | No effective treatment but can be treated with different parts of Azadirachta indica | [130] |
| 3. | Spring viremia of carp | rhabdovirus, spring viremia of carp virus | destruction of kidney, spleen and liver tissues | DNA vaccination may be protectable in fish |
[131,132,133] |
| 4. | Lymphocystis | Lymphocysti virus or Lymphocystis disease virus | Pebble or wart-like nodules mostly on the fins, skin, gills etc | No effective treatment | [134,135] |
| 5. | Carp Pox | Cyprinid herpesvirus-1 (CyHV-1) | Milky skin lesions, Thickening of fins | No effective treatment | [136,137,138] |
| Species | Disease | Organism | Name of the vaccine | Mode of administration | Type of vaccine | Reference |
| Salmon | Infectious hematopoietic necrosis | Infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus | APEX-IHN® | IM | IHNV plasmid vaccine | [145] |
| Enteric Redmouth disease Yersiniosis | Yersinia ruckeriserotype O1b | Alpha ERM Salar | IP | Inactivated bacterial vaccine | [146] | |
| Aquavac YER knows | IP | Inactivated bacterial vaccine | [147] | |||
| Pancreatic disease | Salmon pancreas disease virus | ALPHA JECT micro 1 PD | IP | Inactivated viral vaccine | [146] | |
| salmonid alphavirus | Clynav | IM. | DNA plasmid | [148] | ||
| Salmon alphaviruses (SAV) | PD Norvax® Compact PD | IP | Inactivated viral vaccine | [147] | ||
| Infectious salmon anemia | Infectious salmon anemia virus (ISAV) | ALPHA JECT® micro 1 ISA | IP | Inactivated viral vaccine | [146] | |
| Tilapia | Streptococcosis | S. agalactiae serotype lb | AQUAVAC® Strep Sa | IP | Inactivated viral vaccine | [149] |
| S. agalactiae serotype Ia & serotype III | AQUAVAC® Strep Sa1 | IP | Inactivated viral vaccine | [149] | ||
| Tilapia, seabass | S. iniae | AQUAVAC® Strep Si | dip immersion/ IP | Inactivated viral vaccine | [149] | |
| Streptococcus agalactiae Ib | ALPHA JECT® micro 1 Tila | IP | Inactivated viral vaccine | [146] | ||
| Koi | Koi herpes virus disease | Koi herpes virus (KHV) | KV-3 | Immersion/ Injection | Attenuated viral vaccine (not used because of its safety issues) | [149] |
| Sea bass | Viral Nervous Necrosis | Nodavirus | ALPHA JECT micro® 1 Noda | IP | Inactivated viral vaccine | [146] |
| Aeromonas veronii infection | Aeromonas veronii | Autogenous Aeromonas veronii vaccine | IP | inactivated bacterial culture | [146] | |
| Vibriosis | Listonella anguillarum | ALPHA DIP® Vib | Dip vaccine | inactivated bacterial vaccine | [146] | |
| Asian seabass | Epizootic Haematopoietic Necrosis | Iridovirus | AQUAVAC® IridoV | IP | Inactivated viral vaccine | [149] |
| Seabass Rainbow trout | Infectious pancreatic necrosis | Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) | AquaVac® IPN Oral | Oral | Inactivated viral vaccine | [147] |
| Alpha Jects® 1000 | IP | Inactivated viral vaccine | [146] | |||
| Pangasius | Enteric Septicaemia disease Motile Aeromonad Septicaemia |
Aeromonas hydrophila and Edwardsiella icataluri | ALPHA JECT® Panga 2 | IP | inactivated bacterial VACCINE | [146] |
| S. no | Protein Expressed | Expression system | Treated animals | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Recombinant major capsid protein (rMCP) of iridovirus | Rice callus | Neoscorpis lithophilus | [156] |
| 2. | Nervous necrosis virus (NNV) coat protein | Tobacco chloroplast | Grouper fish | [152] |
| 3. | AcrV and VapA Antigens from Aeromonas salmonicida | Chloroplasts of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | Salmon | [165] |
| 4. | VP28 from White Spot Syndrome Virus | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | Penaeus monodon | [166] |
| 5. | VP28 from White Spot Syndrome Virus | Dunaliella salina | Cray fish | [167] |
| 6. | Virus-like -particle from Atlantic cod nervous necrosis virus (ACNNV) | Nicotiana benthamiana | Salmonids | [168] |
| 7. | ORF1 from Cardiomyopathy syndrome (PMCV) | Nicotiana benthamiana | Salmonids | [163] |
| World Position number | Country | Total consumption (Million tonnes) |
| 1 | China | 99875 |
| 2 | India | 24601 |
| 3 | United States | 10423 |
| 4 | Mexico | 6061 |
| 5 | Brazil | 5460 |
| 6 | Nigeria | 5359 |
| 7 | France | 3494 |
| 8 | Spain | 2529 |
| 9 | Peru | 23331 |
| 10 | Ghana | 9121 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





