Submitted:
25 May 2024
Posted:
27 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. CNs Synthesis

2.2. Photocatalytic Experiment
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
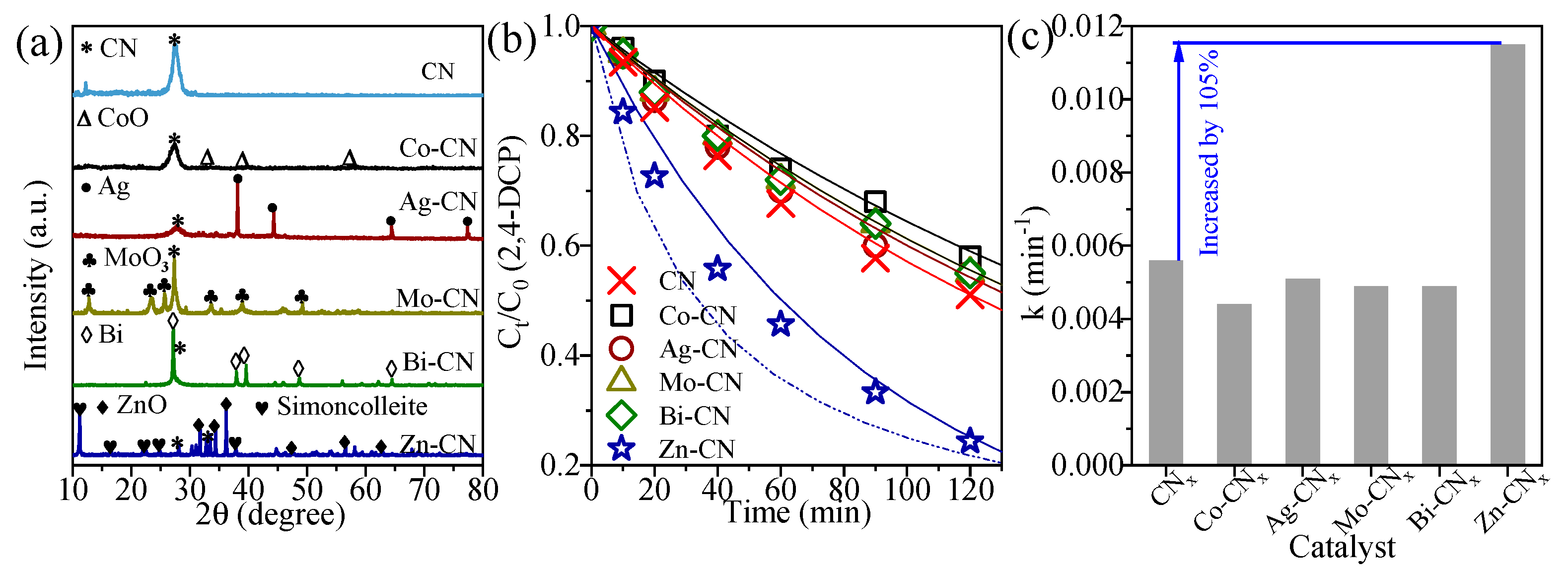
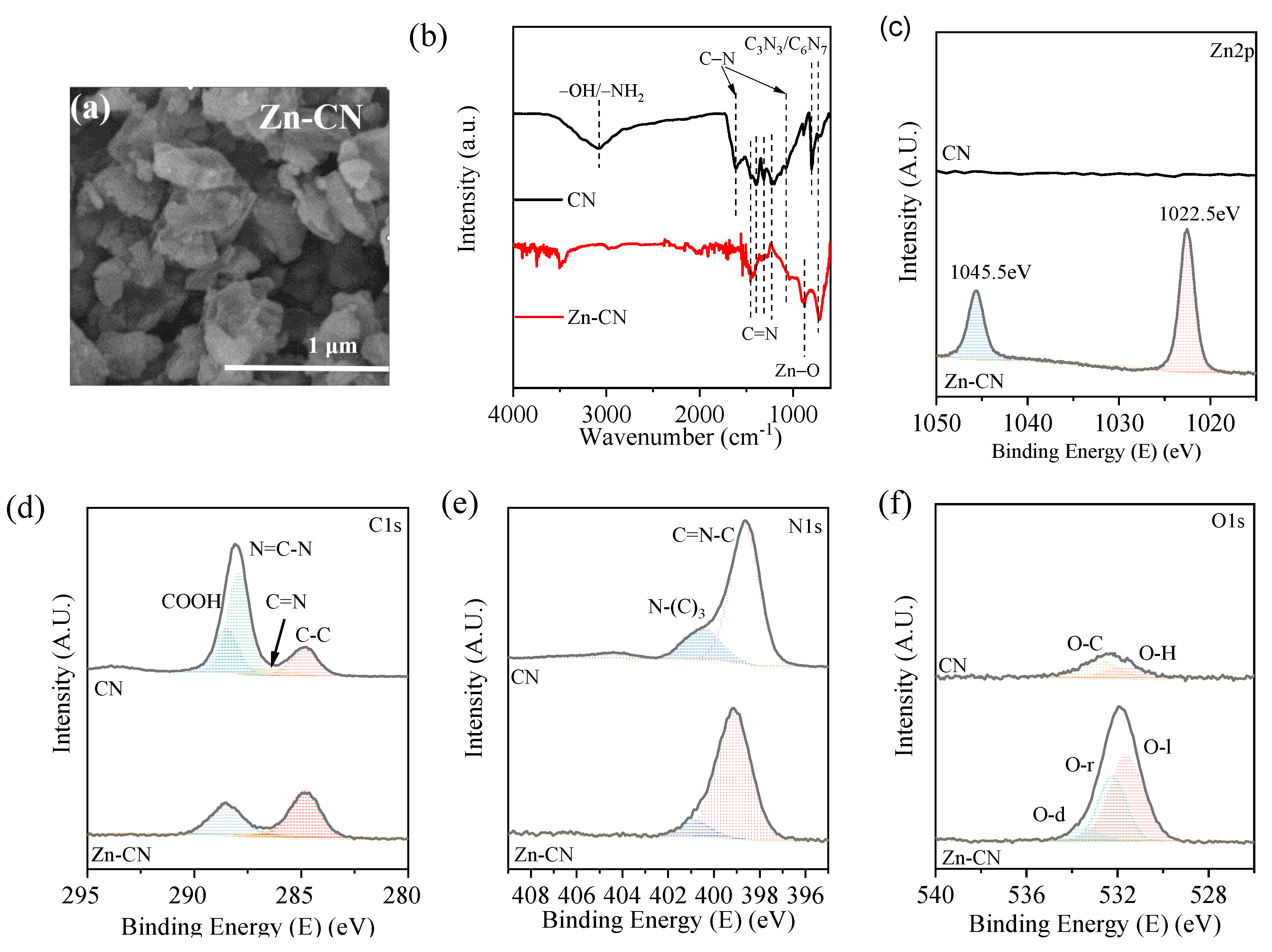
3.1. Metallic CNs Characterization
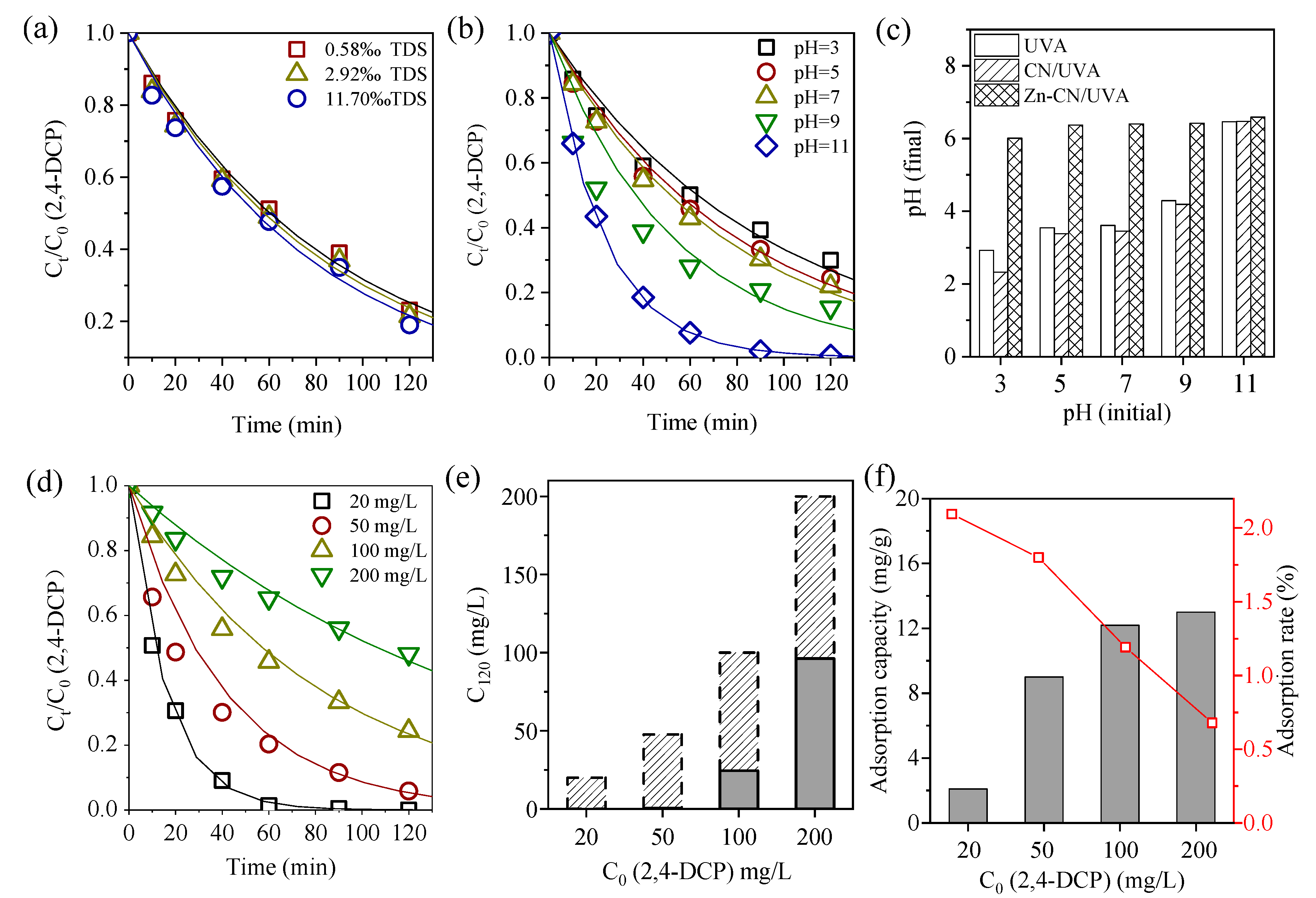
3.2. Photocatalytic Conditions Optimization
3.3. Zn-Rich CNs Materials Characterization
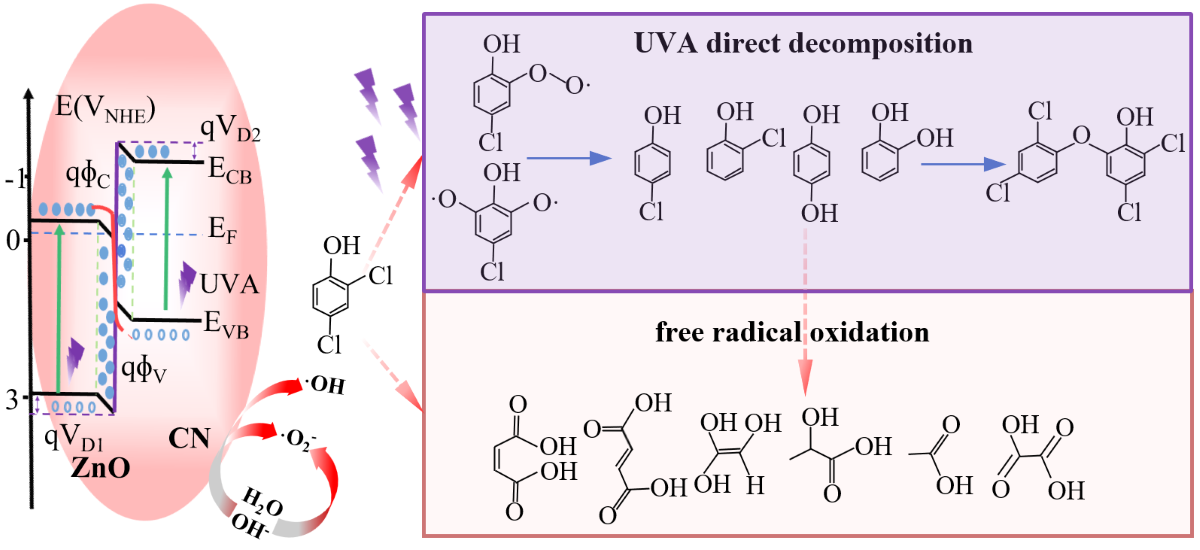
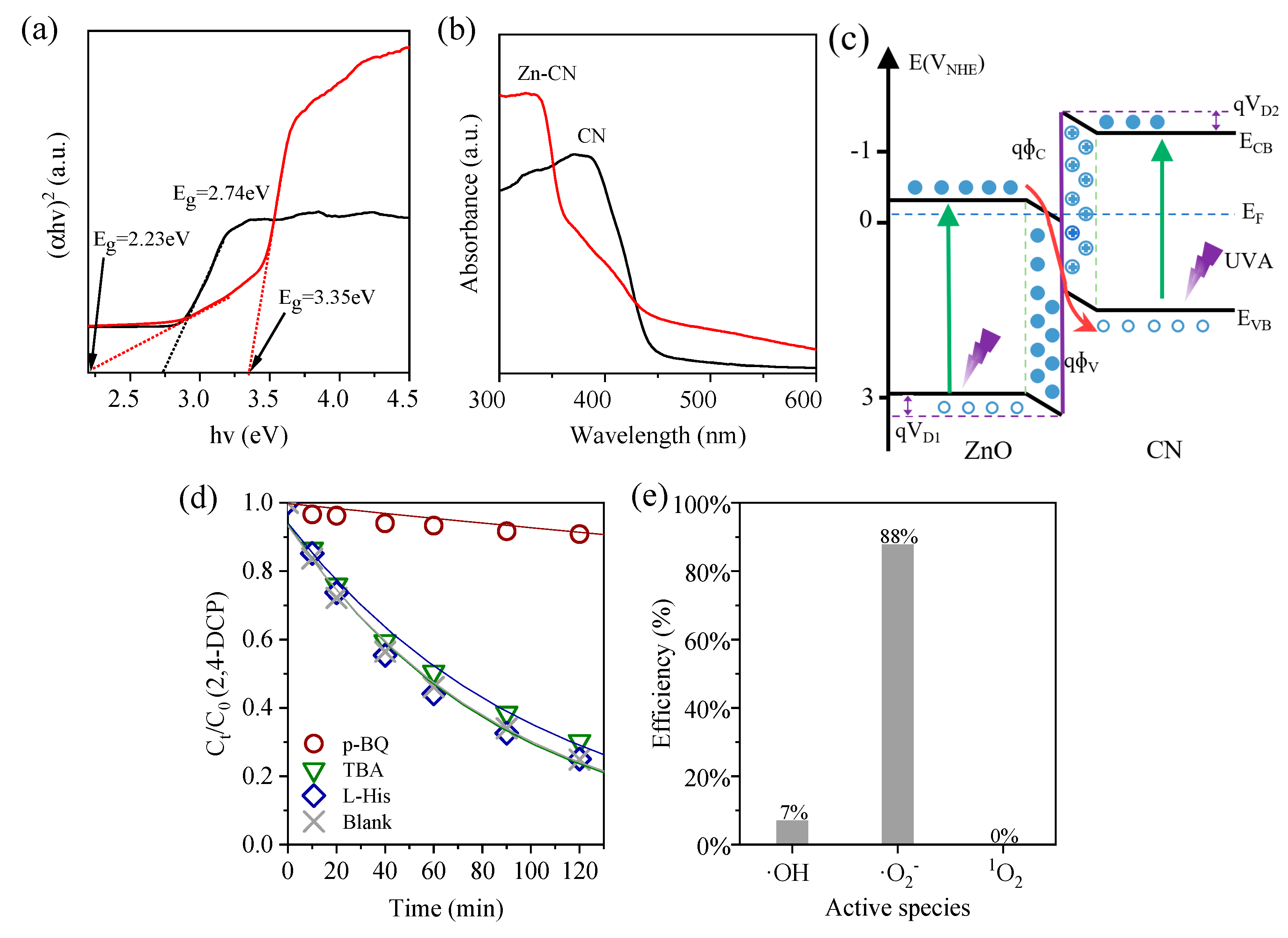
3.4. Photocatalytic Mechanism Analysis
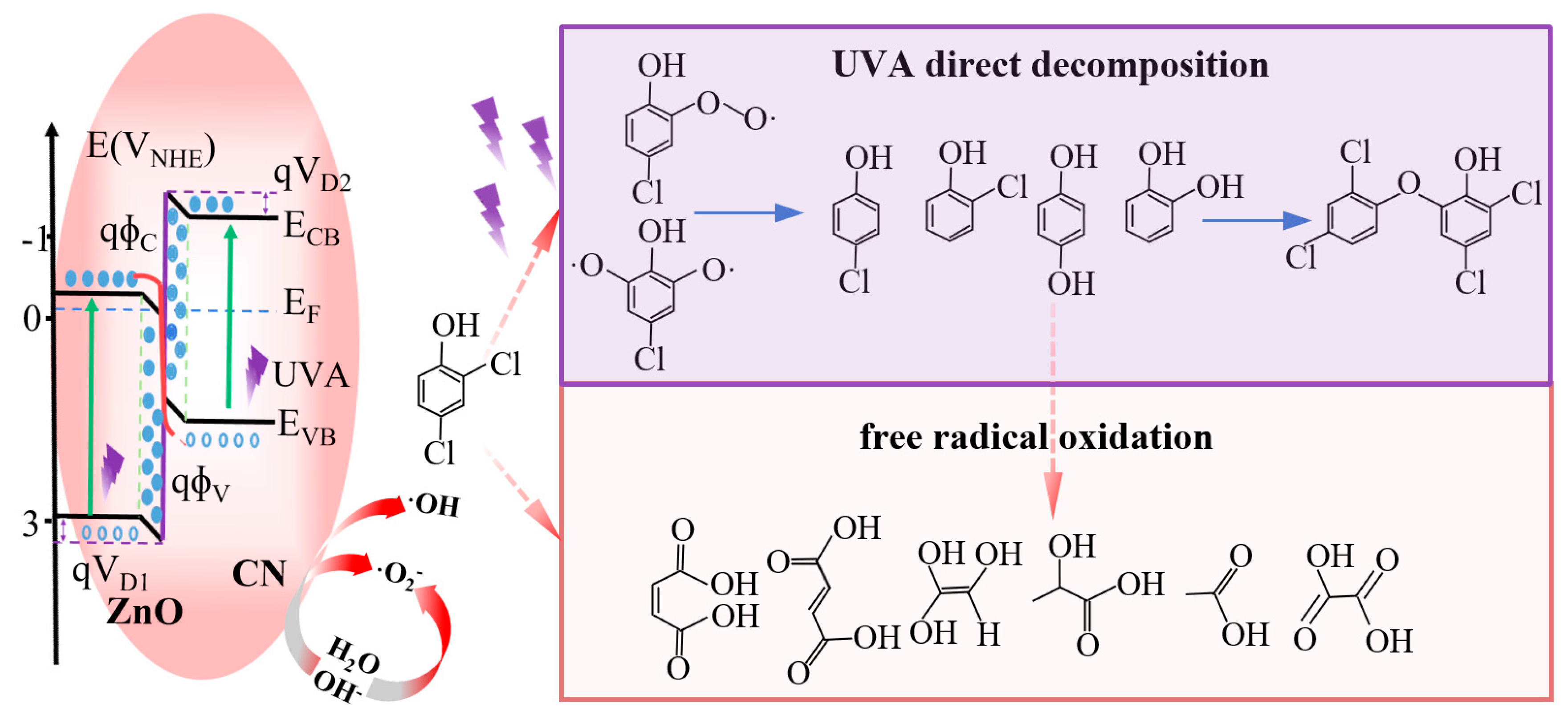
3.5. Prospectives
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Liang, Y, Jiao, C, Pan, L, Zhao, T, Liang, J, Xiong, J, Wang, S, Zhu, H, Chen, G, Lu, L, Song, H, Yang, Q, Zhou, Q. Degradation of chlorine dioxide bleaching wastewater and response of bacterial community in the intimately coupled system of visible-light photocatalysis and biodegradation. Environmental Research 2021, 195, 110840. [CrossRef]
- Xu, R, Chi, T, Ren, H, Li, F, Tian, J, Chen, L. The occurrence, distribution and removal of adsorbable organic halogens (AOX) in a typical fine chemical industrial park. Environmental Pollution 2022, 312, 120043. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y, Chen, L, Liu, R. AOX contamination status and genotoxicity of AOX-bearing pharmaceutical wastewater. Journal of Environmental Sciences 2017, 52, 170–177. [CrossRef]
- Hu, D, Song, L, Yan, R, Li, Z, Zhang, Z, Sun, J, Bian, J, Qu, Y, Jing, L. Valence-mixed iron phthalocyanines/(100)Bi2MoO6 nanosheet Z-scheme heterojunction catalysts for efficient visible-light degradation of 2-chlorophenol via preferential dechlorination. Chemical Engineering Journal 2022, 440, 135786. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S, Liu, H, Lin, Y, Yang, C, Lou, W, Sun, J, Du, C, Zhang, D, Nie, L, Yin, K, Zhong, Y. Insights into mechanisms of UV/ferrate oxidation for degradation of phenolic pollutants: Role of superoxide radicals. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125490. [CrossRef]
- Erhardt, C S, Basegio, T M, Capela, I, Rodríguez, A L, Machado, Ê L, López, D A R, Tarelho, L, Bergmann, C P. AOX degradation of the pulp and paper industry bleaching wastewater using nZVI in two different agitation processes. Environmental Technology & Innovation 2021, 22, 101420. [CrossRef]
- Melliti, E, Touati, K, Abidi, H, Elfil, H. Iron fouling prevention and membrane cleaning during reverse osmosis process. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 2019, 16(7), 3809–3818.
- Garg, S, Xu, Q, Moss, A B, Mirolo, M, Deng, W, Chorkendorff, I, Drnec, J, Seger, B. How alkali cations affect salt precipitation and CO2 electrolysis performance in membrane electrode assembly electrolyzers. Energy & Environmental Science 2023.
- Ali, S, Humayun, M, Pi, W, Yuan, Y, Wang, M, Khan, A, Yue, P, Shu, L, Zheng, Z, Fu, Q, Luo, W. Fabrication of BiFeO3-g-C3N4-WO3 Z-scheme heterojunction as highly efficient visible-light photocatalyst for water reduction and 2,4-dichlorophenol degradation: Insight mechanism. J Hazard Mater 2020, 397, 122708. [CrossRef]
- Haider, M R, Jiang, W, Han, J, Mahmood, A, Djellabi, R, Liu, H, Asif, M B, Wang, A. Boosting Hydroxyl Radical Yield via Synergistic Activation of Electrogenerated HOCl/H2O2 in Electro-Fenton-like Degradation of Contaminants under Chloride Conditions. Environmental Science & Technology 2023, 57(47), 18668-79. [CrossRef]
- Tang, R, Zeng, H, Gong, D, Deng, Y, Xiong, S, Li, L, Zhou, Z, Wang, J, Feng, C, Tang, L. Thin-walled vesicular Triazole-CN-PDI with electronic n→π* excitation and directional movement for enhanced atrazine photodegradation. Chemical Engineering Journal 2023, 451, 138445. [CrossRef]
- Liang, H, Bai, J, Xu, T, Li, C. Enhancing photocatalytic performance of heterostructure MoS2/g-C3N4 embeded in PAN frameworks by electrospining process. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing 2021.
- Lu, X. Performance study of metal-rich biochar modified TiO2 for photocatalysis and activation of sodium persulfate; Shenyang University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020.
- Sun, J, Ji, X, Jiang, G, Liu, F, Li, F. Photocatalytic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol by Cu-doped ZnS nanomaterials; proceedings of the Chinese Society of Environmental Science 2022 Annual Scientific and Technical Conference - Environmental Engineering Technology Innovation and Application Session, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China, F, 2022.
- Limón-Rocha, I, Guzmán-González, C A, Anaya-Esparza, L M, Romero-Toledo, R, Rico, J L, González-Vargas, O A, PérezLarios, A. Effect of the Precursor on the Synthesis of ZnO and Its Photocatalytic Activity. Inorganics 2022, 10, 16. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, H, Lang, S, Wenbo, P, Hui, X, Abbas, K, Zhiping, Z, Qiuyun, F, Yahui, T, Wei, L. Vertically grown CeO2 and TiO2 nanoparticles over the MIL53Fe MOF as proper band alignments for efficient H2 generation and 2,4-DCP degradation. Environmental science and pollution research international 2022, 29(23), 34861-73. [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, S, Thamilselvan, A, Radhika, N, Padmanabhan, D, Durairaj, A, Obadiah, A, Lydia, I S, Vasanthkumar, S. Development of rutin-rGO/TiO2 nanocomposite for electrochemical detection and photocatalytic removal of 2,4-DCP. Journal of the Iranian Chemical Society 2021, 18(9), 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y, Li, J, Guo, C, Cong, S, Yang, X. Preparation and photocatalytic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol by CuPc/g-C3N4. Chemical Engineer 2020, 34(08), 4-6. [CrossRef]
- Ali, S, Li, Z, Ali, W, Zhang, Z, Wei, M, Qu, Y, Jing, L. Synthesis of Au-decorated three-phase-mixed TiO2/phosphate modified active carbon nanocomposites as easily-recycled efficient photocatalysts for degrading high-concentration 2,4-DCP. RSC Advances 2019, 9(66), 38414-21. [CrossRef]
- Humayun, M, Zheng, Z, Fu, Q, Luo, W. Photodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol and rhodamine B over n-type ZnO/p-type BiFeO3 heterojunctions: detailed reaction pathway and mechanism. Environmental science and pollution research international 2019, 26(17), 17696-706. [CrossRef]
- Alalm, M G, Samy, M, Ookawara, S, Ohno, T. Immobilization of S-TiO2 on reusable aluminum plates by polysiloxane for photocatalytic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol in water. Journal of Water Process Engineering 2018, 26, 329–335. [CrossRef]
- Qi, X, Gu, M, Zhu, X, Wu, J, Wu, Q, Long, H, He, K. Controlled synthesis of Ag3PO4/BiVO4 composites with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance for the degradation of RhB and 2, 4-DCP. Materials Research Bulletin 2016, 80, 215–222. [CrossRef]
| No. | Light | Catalyst | Experimental condition | Rate mg/L/min |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 300W HP | 0.1 g/L Pb@BC-20%TiO2 | C0=100 mg/L, 240 min | 0.40 | [13] |
| 3 | 300W HID | 0.4 g/L Cu/ZnS | C0=16 mg/L, pH=4, 150min | 0.07 | [14] |
| 4 | 1 mW/cm2 UV | 0.1 g/L ZnO | C0=80 mg/L, 360min | 0.19 | [15] |
| 5 | 300W HID | 2.5 g/L CeO2/TiO2/MOF | C0=20 mg/L, 150min | 0.12 | [16] |
| 6 | 150 W HW | 0.4 g/L R-rGO/TiO2 |
C0=16.3 mg/L, 60min, pH=6~7 | 0.26 | [17] |
| 7 | HID | 2.5 g/L CuPc/g-C3N4 |
C0=100 mg/L, 240min | 0.33 | [18] |
| 8 | HID | 0.25 g/L Au/TiO2/PO4 | C0=100 mg/L, 240min | 0.42 | [19] |
| 9 | HID | 2.5 g/L Zn/BiFeO | C0=10 mg/L, 60min | 0.10 | [20] |
| 10 | 400w MH,220 μW/cm2 | 0.8 g/L S-TiO2 | C0=25 mg/L, 240 min | 0.09 | [21] |
| 12 | 300W HID | 1 g/L Ag3PO4/BiVO4 | C0=20 mg/L, 180 min | 0.09 | [22] |
| 13 | HP 365nm | 0.1 g/L Zn-CNx | C0=100 mg/L, 120 min | 0.63 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





