1. Introduction
At present, carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) is the main technology used to realize large-scale carbon reduction in China. In the field of oil development, CO
2 flooding technology, as an effective means to improve oil recovery, not only conforms to the concept of effective CCUS but also utilizes the unique advantages of CO
2 during oil recovery enhancement, also known as tertiary recovery[
1,
2,
3]. Supercritical CO
2 (SC-CO
2) can effectively reduce the residual oil saturation of the reservoir by reducing the interfacial tension between oil and water and the extraction effect, maximizing carbon storage while improving the oil displacement efficiency[
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10].
The downhole environment of CO
2 injection well is different from the conventional injection environment, such as waterflooding. When the temperature exceeds 31.26℃ and the critical pressure exceeds 7.2 MPa, CO
2 would be converted into a supercritical state with a density close to liquid and a viscosity close to gas, and its diffusion ability would be further enhanced. Packer is one of the core tools used for CO
2 layered-injection. However, with the increase in injection time and temperature, SC-CO
2 molecules are more likely to diffuse into the rubber matrix, causing the swelling of the rubber cylinder and further expanding the deformation of it, which may lead to tearing failure in extreme cases[
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19]. At present, there are only few studies on the influence of CO
2 diffusion and the consequent rubber swelling on the sealing performance of packer’s rubber cylinders, and also there are lack of appropriate numerical simulation means for the swelling effect. In this study, the simulation software was used to establish the packer’s rubber cylinder model in the SC-CO
2 environment. Based on the thermal analogy method, the gas diffusion and rubber cylinder swelling process was simulated to analyze the deformation and stress of the rubber cylinder caused by temperature, pressure and CO
2 as swelling agent, as well as the change rules between various factors and the maximum contact pressure of the rubber cylinder. This study provides a theoretical basis and technical support for improving the sealing performance of packer’s rubber cylinder in the SC-CO
2 environment.
2. Theoretical Calculation of the Mechanical Properties of the Rubber Cylinder
At present, fluororubber, nitrile rubber and hydrogenated nitrile rubber are mainly used to manufacture packer’s rubber cylinder. According to the large deformation property of rubber and the elastic mechanics theory, the stress situation of the rubber cylinder is investigated. To ensure the convergence of the calculation, the absolute volume of the rubber cylinder is treated as incompressible when not exceeding its elastic limit, meanwhile the radial and circumferential deformations after the contact between the rubber cylinder and the casing are ignored[
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25]. Poisson’s ratio is set as 0.5 according to the incompressibility of rubber. The Mooney–Rivlin two-parameter model was selected as the constitutive model of the rubber cylinder, and the contact pressure between the rubber cylinder and the casing after seating was calculated using the constitutive mode[
26].
The Mooney–Rivlin two-parameter model is expressed as follows:
where
is the strain energy density (J);
and
are material constants;
is the first-order strain invariant; and
is the second-order strain invariant.
The elastic modulus and shear modulus of rubber are expressed in Formula 2 and Formula 3, respectively:
where
E is the elastic modulus (MPa), and
G is the shear modulus (MPa).
Regardless of the friction between the rubber cylinder, the casing and the central pipe, the additional contact pressure generated on the inner wall of the casing caused by the differential pressure between top and bottom during working process can be calculated using Formula (4):
where
is the axial length of the rubber cylinder under the working conditions (m);
is the inner radius of casing (m);
is the radius of metal spacer ring (m);
is the shear stress on the contact surface between the rubber cylinder and the casing wall (MPa); and
is the working pressure difference (MPa).
For incompressible materials, the relationship between the micro-element shear stress and the axial stress can be expressed as follows:
The strain of the rubber cylinder can be expressed as follows:
According to equations (4), (5) and (6), the following equations can be derived:
where
is the axial length of the rubber cylinder under the working conditions (m);
is the inner radius of casing (m);
is the radius of metal spacer ring (m);
is the shear stress on the contact surface between the rubber cylinder and the casing wall (MPa); and
is the working pressure difference (MPa).
3. Establishment of Finite Element Model of Packer’s Rubber Cylinder
3.1. Geometric Model Establishment and Mesh Generation
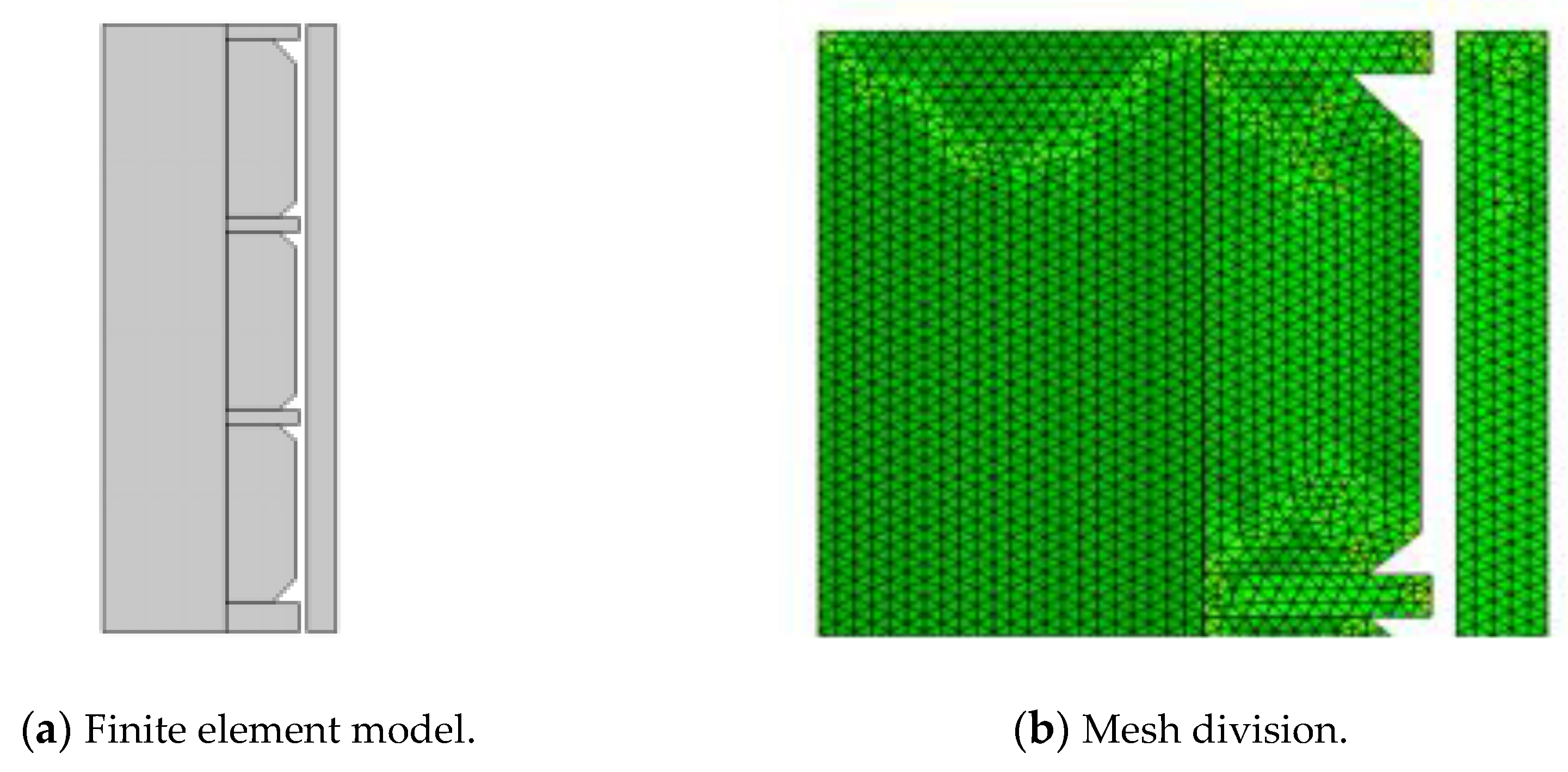
We referred to the conventional rubber cylinder that supporting Y341-114 packer for the overall dimensions of the packer’s rubber cylinder, with an inner diameter of 73 mm and an outer diameter of 114 mm. 40° chamfers were added outside the upper and lower rubber cylinders. The inner diameter of the metal spacer ring of the packer is 73 mm, and the outer diameter is 116 mm. The outer diameter of the central pipe is 73 mm, and the inner diameter of the casing is 121.4 mm. Considering the structural characteristics of the assembly model and reducing the computational intensity, we selected a two-dimensional axisymmetric model in the dimension of the simulation space and established the section geometric model, as shown in
Figure 1. To solve the physical field, the ‘solid mechanics’ solution module was selected. To solve the stress relationship of each part in the seating process, each imported part was used to form an assembly. ‘Free triangular mesh’ was selected for mesh division, with a maximum cell size of 2 mm, a minimum cell size of 0.004 mm, a maximum cell growth rate of 1.2, a curvature factor of 0.2 and a narrow area resolution of 1. The total number of mesh cells was 8,150, and the average element quality was 0.935. The finite element model and mesh division are shown in
Figure 1.
3.2. Setting the Material Properties
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber was selected as the rubber cylinder material. Compared with fluororubber, hydrogenated nitrile rubber has better heat resistance, oxygen ageing resistance and chemical resistance, it is a common material for packer’s rubber cylinders. The rubber cylinder material model was set as a hyper-elastic material. C10 and C01 in the Mooney–Rivlin model are closely related to the ambient temperature; therefore, different C10 and C01 values were set for the simulation model at different temperatures. The rubber density was set as 1,300 kg/m3. The material model of the central pipe and metal spacer ring was set as a linear elastic material, the material type was set as 3Cr13. The casing material was set as 42MnMo7.
3.3. Boundary Condition Settings
When seated to the casing, the rubber cylinder comes in contact with the central pipe, metal spacer ring and the inner wall of the casing; therefore, 12 contact pairs were set, namely, the rubber cylinder and the central pipe; the rubber cylinder and the upper metal spacer ring; the rubber cylinder and the lower metal spacer ring; and the rubber cylinder and the inner wall of the casing. All contact pairs were set to use the Coulomb friction model, with a friction coefficient of 0.3. The contact method was set as a penalty function, and the penalty factor is controlled by the built-in programme of the software. Given that the central pipe and the lowest metal spacer ring do not move during the entire seating process, so they were set as fixed constraints. Point constraints were set at the upper and lower boundaries of the casing, and the contact surfaces between the remaining metal spacer rings and rubber cylinder were supported by virtual springs to ensure the convergence of the calculation process. Specified displacement was set on the uppermost metal spacer ring, and the displacement parameter could be set through function to gradually add the displacement.
3.4. Finite Element Model Setup of Rubber Swelling process with CO2 as Swelling agent
At present, no relevant calculation model for rubber swelling process with CO2 as swelling agent has been established. We referred to the finite element method for rubber expansion with hydrogen absorption, ignored the CO2 diffusion caused by stress or other factors, and only considered the effect of the concentration gradient on CO2 diffusion in rubber. Then we compared the diffusion process to the heat transfer process of zero heat transfer, replaced the CO2 concentration field in rubber with the temperature field, compared the rubber swelling caused by CO2 diffusion to the thermal expansion of object caused by the heat transfer process, thus established a finite element model of heat conduction and then calculated the stress and strain of rubber cylinder caused by CO2 diffusion through a thermal–mechanical coupling method.
A ‘thermal expansion’ physical reaction interface under the hyper-elastic material node was added, the volume reference temperature was defined as 293.15K and the thermal expansion coefficient was set as tangent coefficient. During the heat transfer calculation, the SC-CO
2 concentration at the boundary of the rubber cylinder where contacting with SC-CO
2 was set as saturated, and the boundary temperature was set as 393.15 K according to a temperature gradient of 100 K. The SC-CO
2 concentration at the boundary of the rubber cylinder where contacting with the central tube was set as 0, and the initial boundary temperature was set as the volume reference temperature. The thermal expansion generated on the rubber cylinder after achieving the steady-state temperature field was obtained through the simulation of the heat transfer process, thus each mechanical parameter of the CO
2 diffusion and rubber swelling process could be calculated [
27,
28]. Through indoor tests, reference [
19] determined the rules of hydrogenated nitrile rubber swelling under high temperature and pressure with CO
2 diffusion, thus set the tangent thermal expansion coefficient of the rubber material as 0.002/K.
4. Analysis of the Simulation Results
4.1. Effect of Seating Distance on Sealing Performance of Rubber Cylinder
Before seating, a reasonable seating distance should be determined for the rubber cylinder to ensure effective sealing of the tubing-casing annulus. A lower seating distance could lead to incomplete seating of the rubber cylinder, resulting in a reduction in the contact area and contact pressure between the rubber cylinder and the inner wall of the casing. A higher seating distance tends to destroy the rubber cylinder and reduce the sealing reliability. For the simulation model, the seating distances were set as 25 mm, 30 mm and 40 mm.
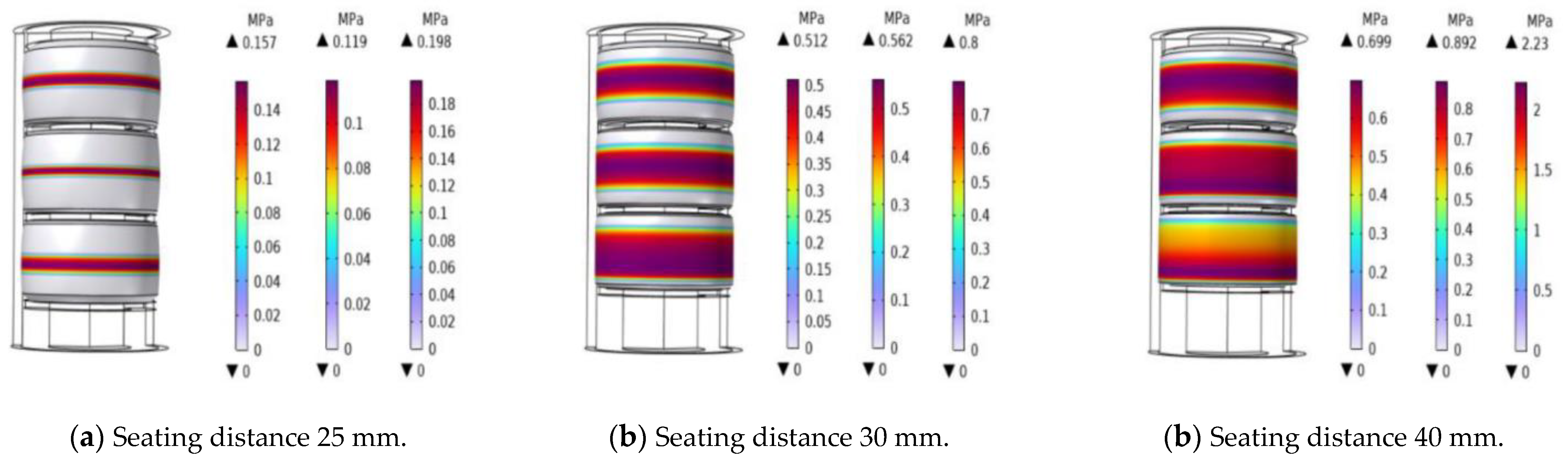
Figure 2 shows the Von mises stress nephogram of the rubber cylinder corresponding to three seating distances at normal temperature without considering the influence of SC-CO
2 diffusion and working pressure difference.
The figure shows that, with an increase of the seating distance, the shape of the rubber cylinder began to produce large deformation, and the increament of deformation and stress decreased from top to bottom. With the seating distance being 25 mm, the rubber cylinder had not been fully compressed. With the seating distance being 30 mm, the Von mises stress in the rubber cylinder began to concentrated, and the deformation was intensified. With the seating distance being 40 mm, the Von mises stress concentration further increased, and the rubber cylinder had completely filled the enclosed space.
Figure 3 shows the contact pressure between the rubber cylinder and the inner wall of the casing at three different seating distances. The Figure shows that with the seating distance being 25 mm, the top rubber cylinder and the bottom rubber cylinder first came into contact with the inner wall of the casing and produce extrusion. With increase in the seating distance, the contact pressure of the middle rubber cylinder increases faster than that of the lower rubber cylinder. The seating mode of the conventional packer is unidirectional compression at the bottom spacer ring, for which uneven deformation of the three rubber cylinders and uneven stress distribution on the contact surface of the upper rubber cylinder are observed. The simulation results were consistent with the actual situation. When the seating distance reached 40 mm, the upper rubber cylinder was fully compressed, and the maximum contact pressure was 2.23 MPa. The simulation showed that continuing to compress would lead to damage and tear to the upper rubber cylinder. Therefore, in the design process of the seating mechanism of the Y441-114 packer, attention should be paid to take the seating distance between 35mm-40mm to prevent the cylinder damage caused by too long distance or the sealing failure caused by too short distance.
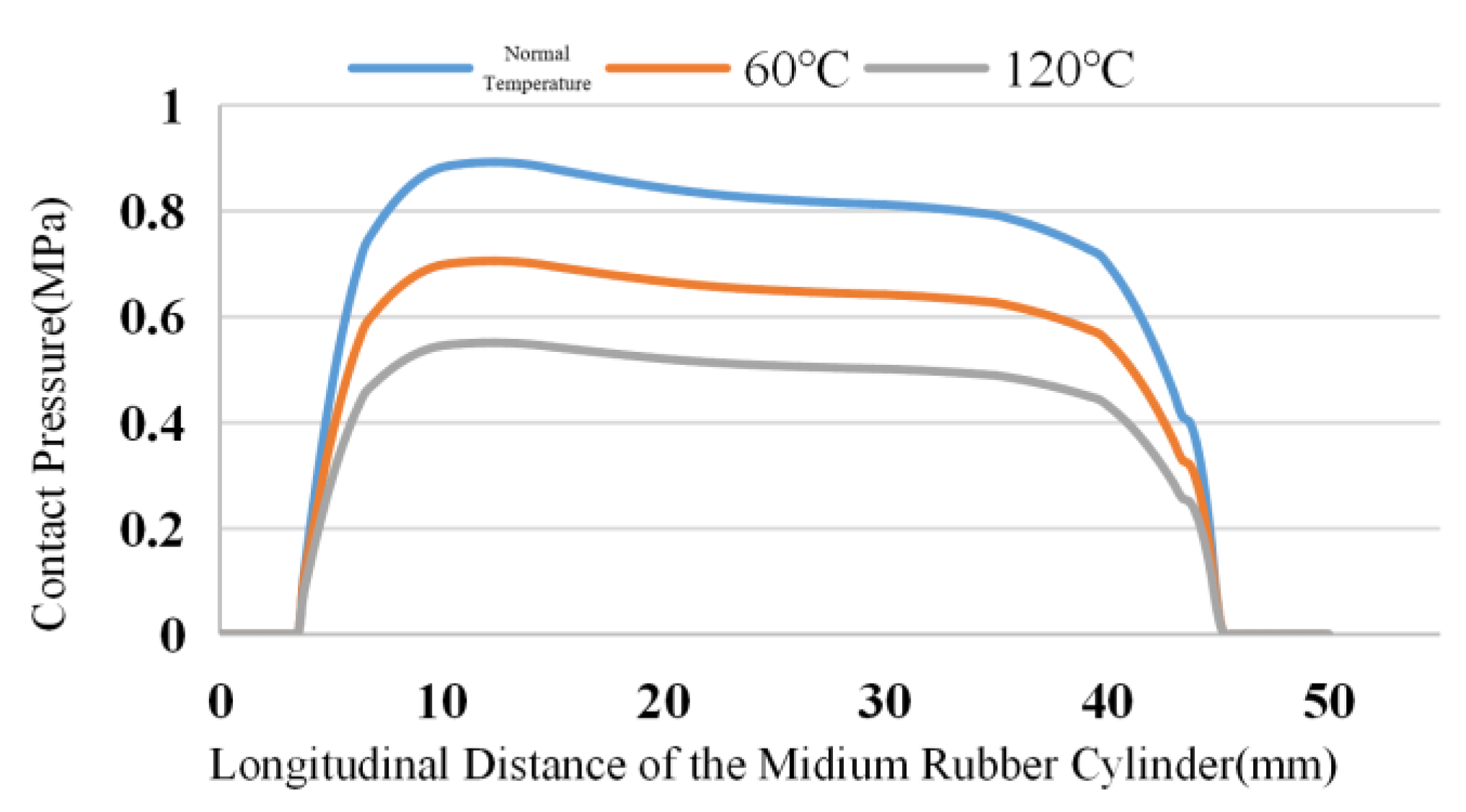
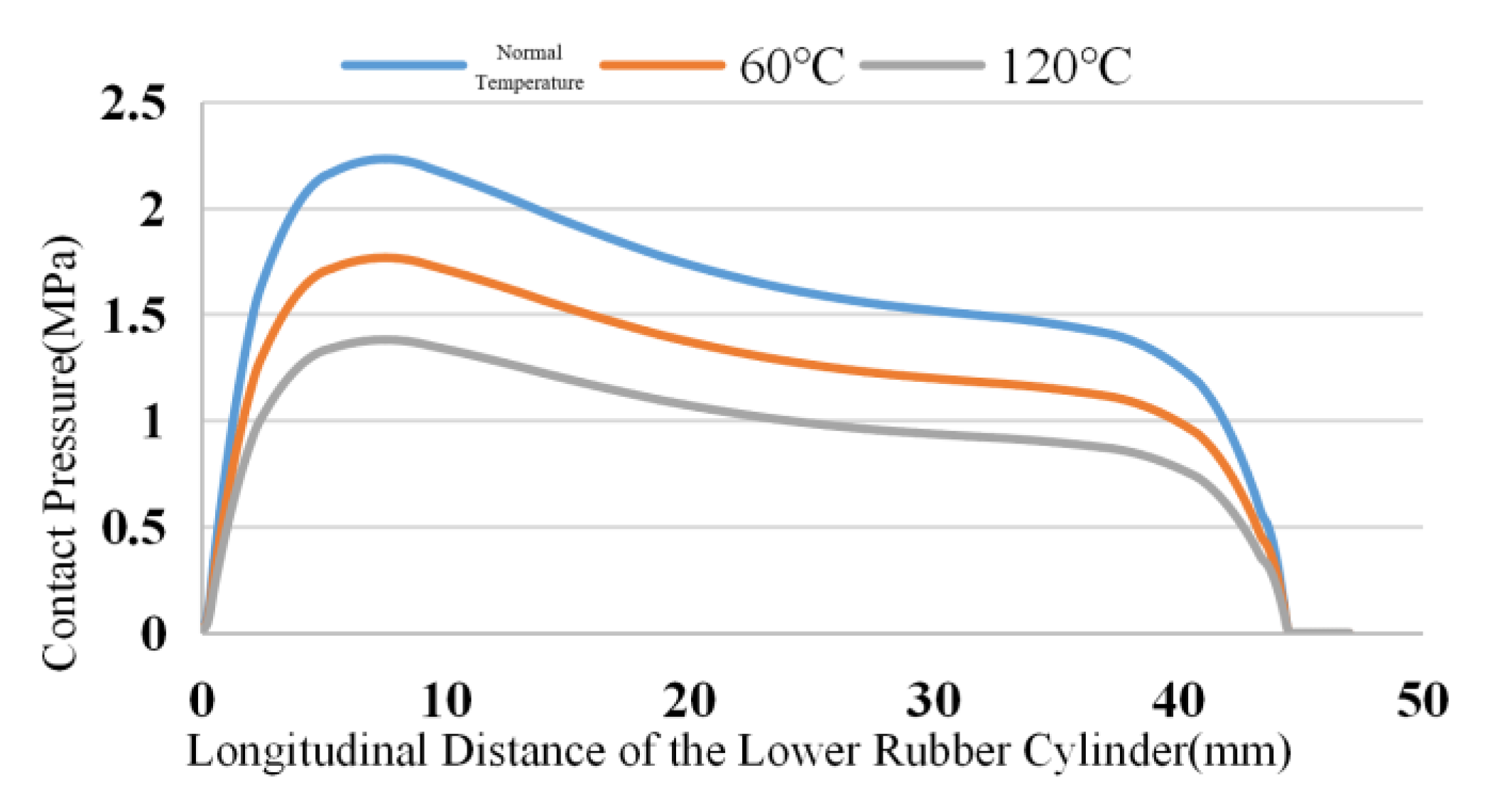
4.2. Effect of Underground Temperature on Sealing Performance of Rubber Cylinder
The downhole temperature of the CO
2 injection wells is generally high, and the maximum temperature is usually close to 120℃. At high temperatures, the ageing rate of the rubber material will further increase, and the stress situation will change. The contact pressure of the rubber cylinder decreases with ageing of the rubber as the downhole working environment temperature increases.
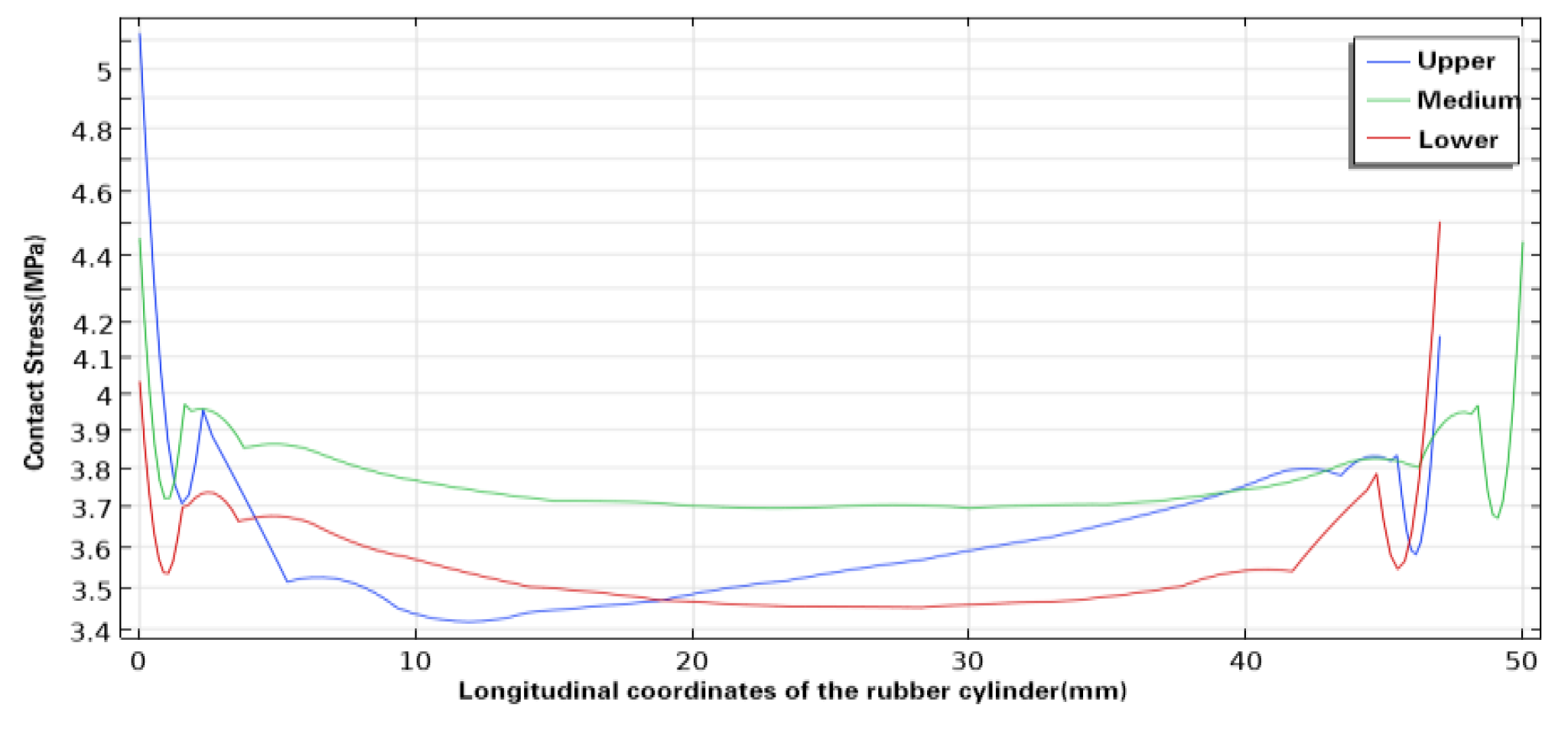
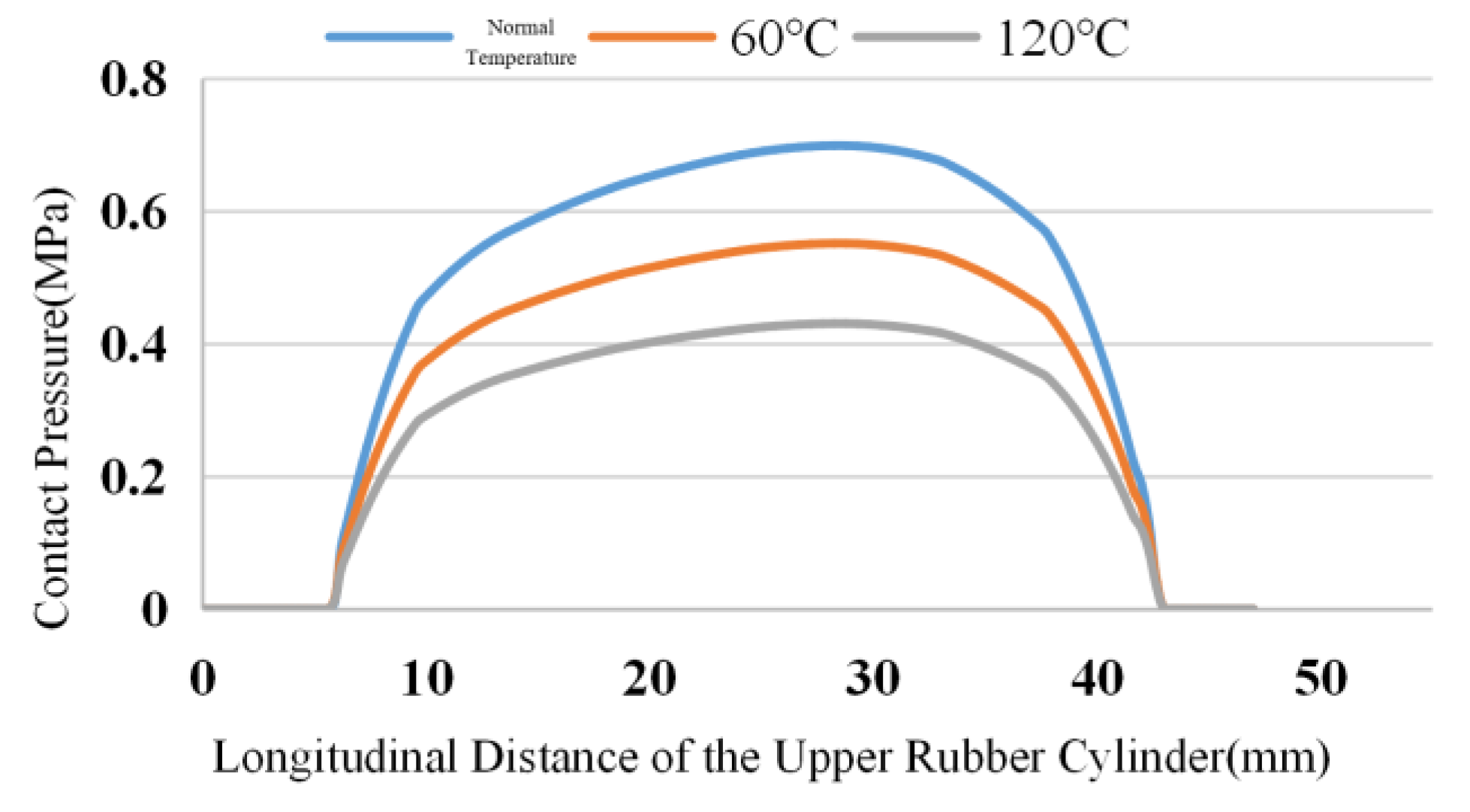
Figure 4,
Figure 5 and
Figure 6 show the simulation results of the contact stress of the lower, middle and upper rubber cylinders after complete seating under steady-state conditions with normal temperature, 60℃ and 120℃, without considering the influence of working pressure difference and swelling by SC-CO
2 diffusion. Seen from the figures, as the temperature rised, the contact stress of the rubber cylinder decreased with the aging of rubber. Under the steady-state condition of 120℃, the contact stress of the rubber cylinder was reduced by about 40% compared with that when it was just seated. In order to ensure a long-term seal at high temperatures, the packer’s rubber cylinder should be made of high-temperature resistant materials to improve the contact stress after seating.
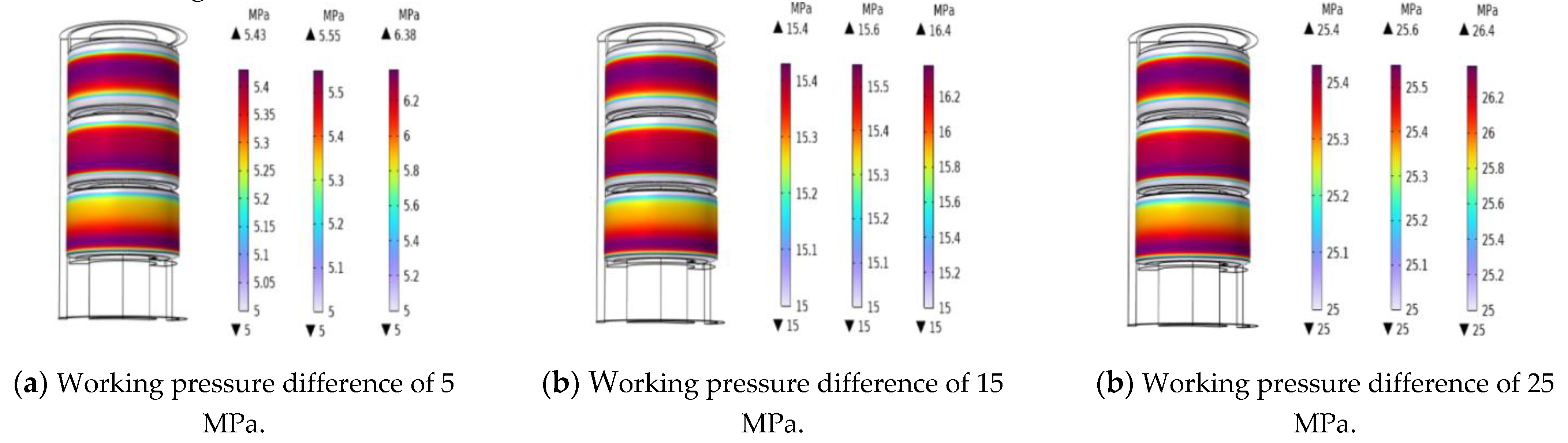
4.3. Effect of Working Pressure Difference on Sealing Performance of Rubber Cylinder
After seating of the packer, the rubber cylinder bears the working pressure difference from the upper and lower injection systems.
Figure 7 shows the contact pressure nephogram of the rubber cylinder under the steady-state condition of 120℃ with the working pressure difference of 5, 15 and 25 MPa, regardless of the influence of swelling by SC-CO
2 diffusion. The Figure shows that, with the increase of the working pressure difference, the contact pressure of the rubber cylinder increased, and the stress distribution of the three rubber cylinders became more uniform. Within the deformation limit of the rubber cylinder, increasing the working pressure difference could increase the contact pressure between the rubber cylinder and the inner wall of the casing thus enhance the sealing effect. The sealing effects of the three rubber cylinders were compared horizontally which showed that the sealing effect of the lower rubber cylinder was the best. Taking the working pressure difference of 5MPa as an example, the maximum contact stress of the upper rubber cylinder was 5.43MPa, with the differences being 0.43MPa, and the maximum contact stress of the lower rubber cylinder was 6.38MPa, with the differences being 1.38MPa, comparing with the working pressure difference 5MPa. Theoretically the sealing effect could be ensured. However, during the actual application, the elasticity of the rubber would be decreased due to long term suffering of high temperature and high pressure, thus there would be risk of leakage and loss of seal for the upper and middle rubber cylinders if the seating mode as lower end compression that similar to the Y441-114 packer was used. Once the upper and middle rubber cylinders leaked and lost their sealing, or had been tore up, the stress of the lower cylinder would be directly changed, which would increase the risk of overall sealing failure. Therefore, in order to improve the contact stress distribution of the rubber cylinder in the seating process, the original unidirectional seating mode at the lower end should be changed, while the bidirectional seating mechanism should be designed to change the overall stress of the rubber cylinder, thus to improve the contact stress distribution and enhance the sealing effect.
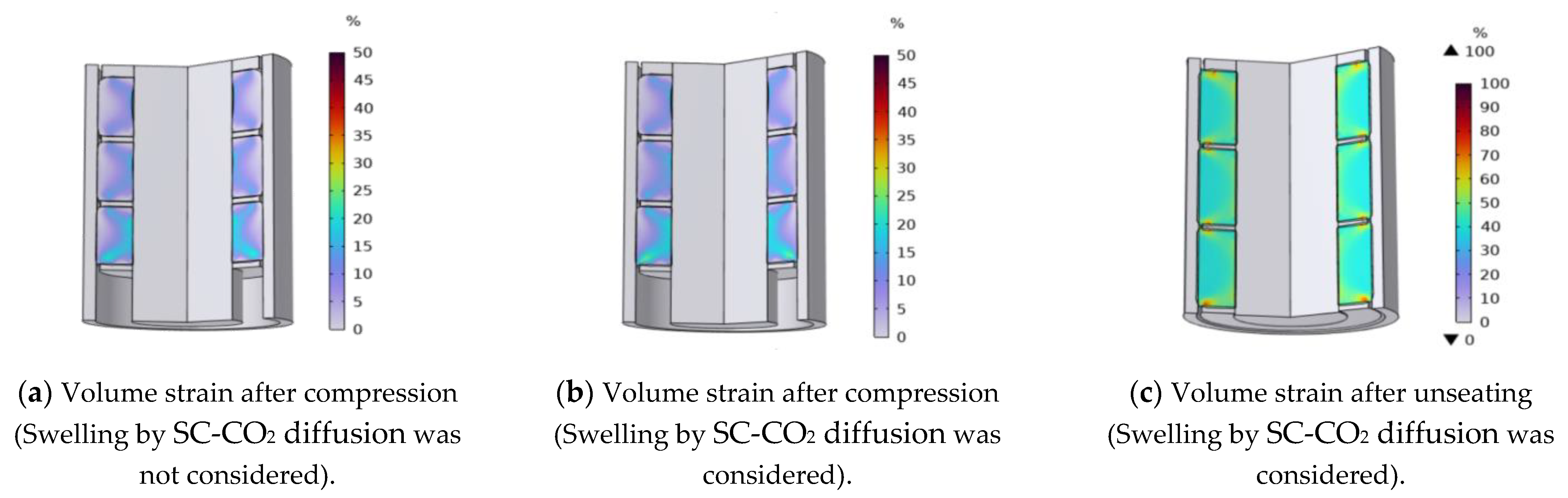
4.4. Effect of SC-CO2 on Sealing Performance of Rubber Cylinder
The influence of SC-CO2 on the seating performance of the rubber cylinder was calculated by thermal analogy method, and the seating distance of 40mm was set as the seating distance of the simulated rubber model. Because of the limited sealing volume of the downhole annulus, when the rubber cylinder was completely seated, the degree of SC-CO2 diffusion into the rubber cylinder body would be less than the results obtained by the indoor sampling experiment.
Therefore, the parameter scanning method was adopted, with the target temperature (SC-CO
2 diffusion percentage) as the variable to carry out a step-by-step scanning, and when the volume of the rubber cylinder expanded to the limit of the wellbore, it was regarded as a complete swelling, and the final expansion coefficient was obtained. The volume strain comparison of the rubber cylinder before and after Swelling by SC-CO
2 diffusion is shown in
Figure 8a,b, respectively. The maximum volume strain in the rubber cylinder was 21.79% when SC-CO
2 was not considered. When SC-CO
2 diffused into the rubber cylinder, the maximum volume strain value increased to 26.52%, and the swelling effect causes the rubber cylinder to further expand to fill the entire sealing space.
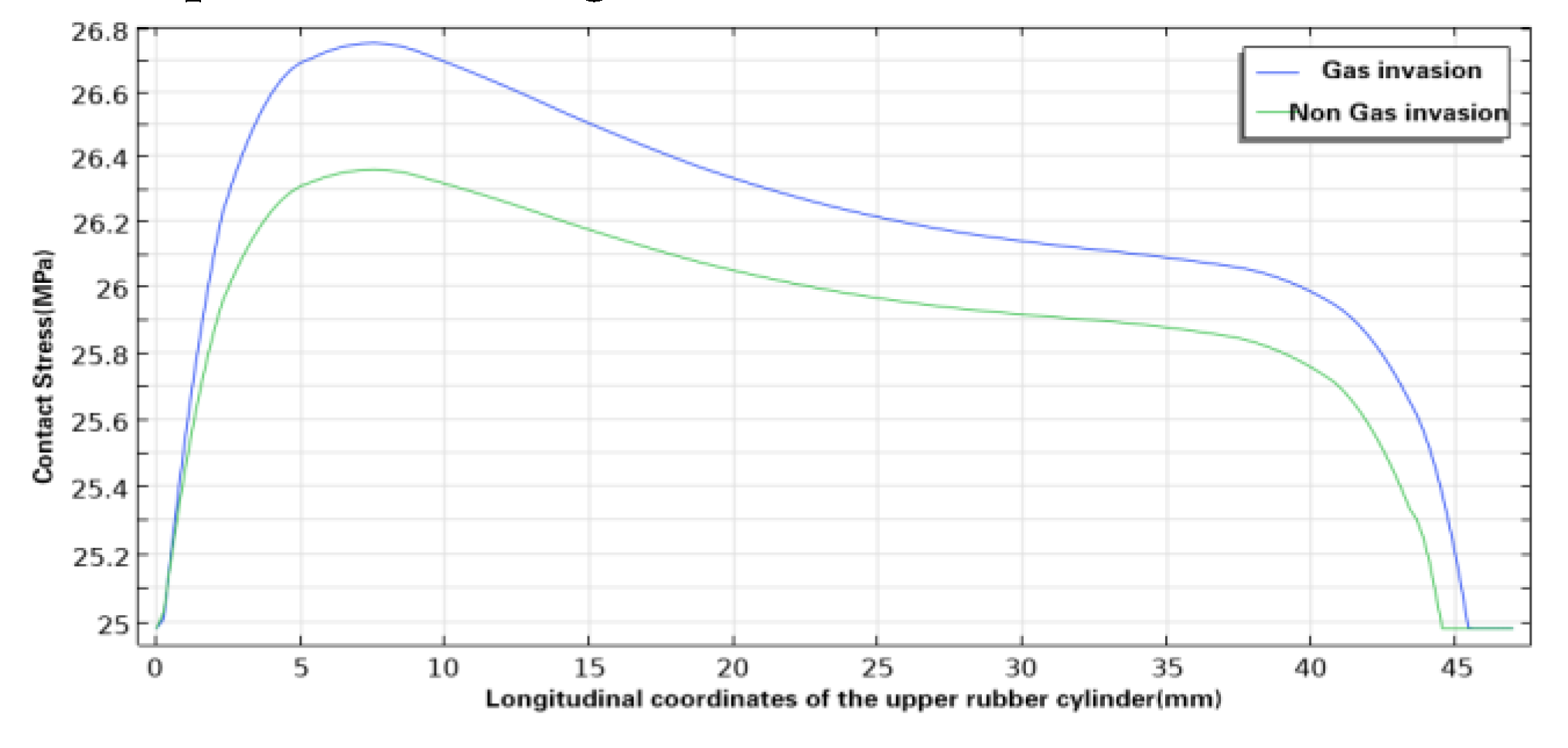
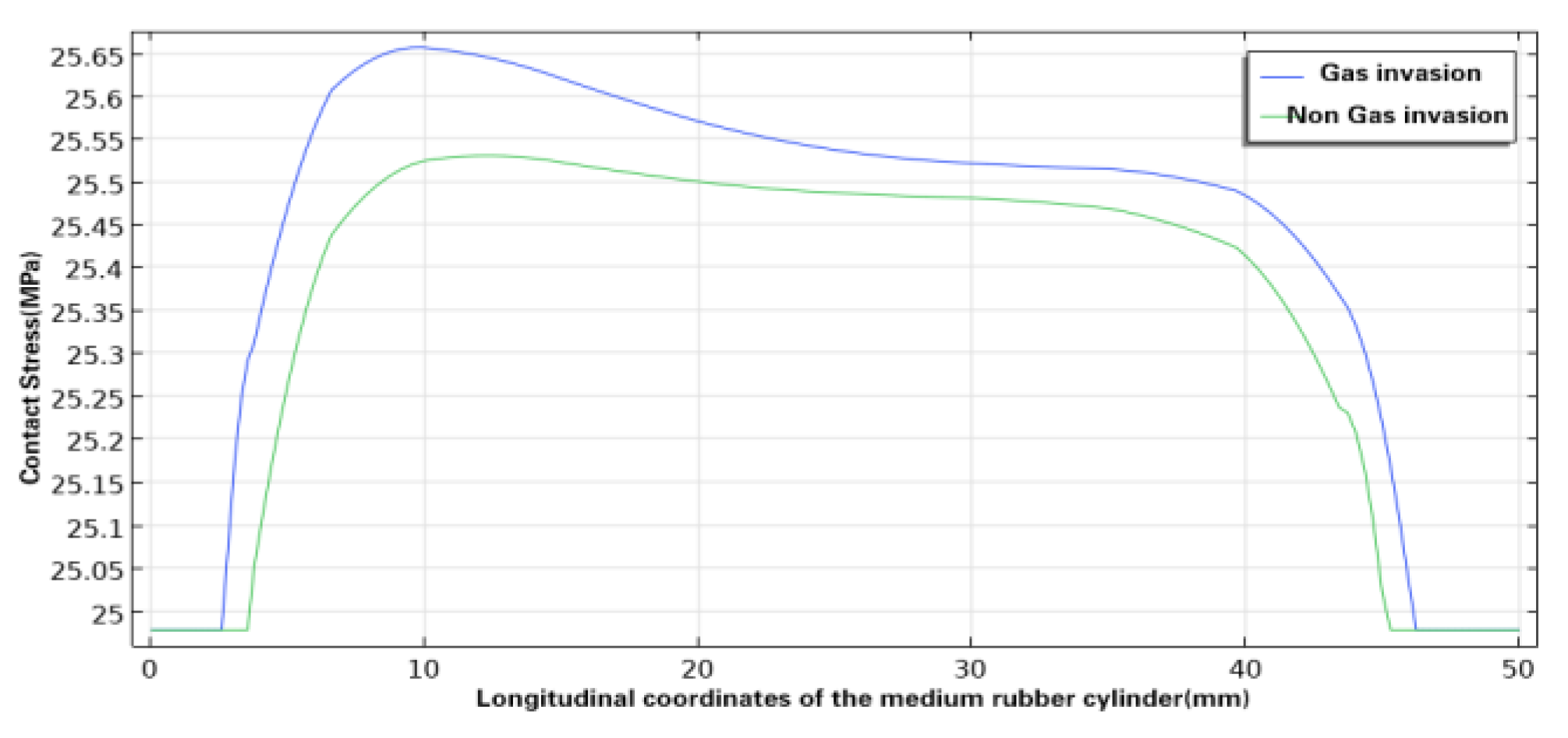
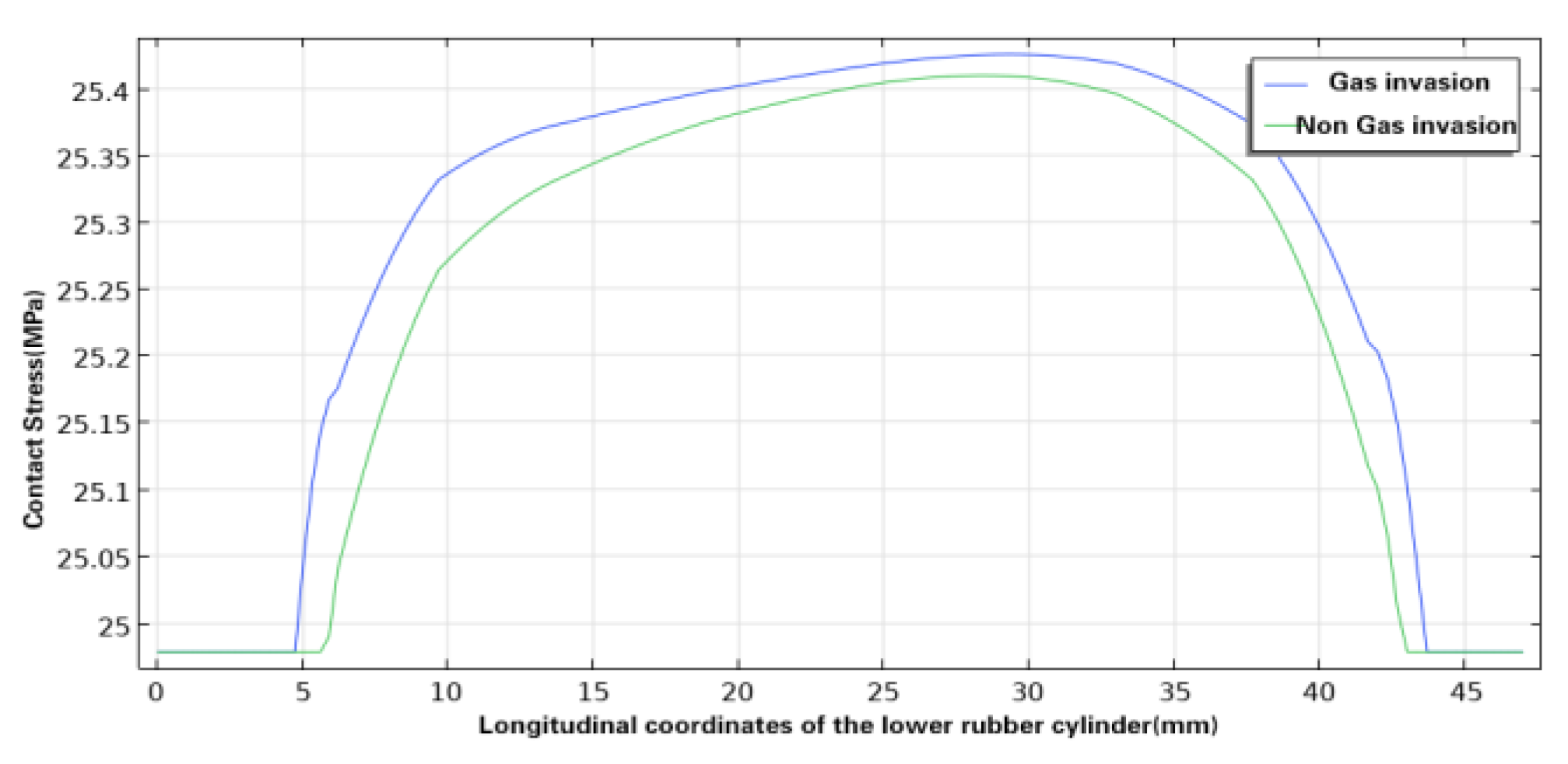
Figure 9,
Figure 10 and
Figure 11 shows the comparison of the contact pressure between the inner wall of the casing and the upper, middle and lower rubber cylinders respectively before and after swelling by SC-CO
2 diffusion. With the swelling by SC-CO
2 diffusion, the contact pressure of the three rubber cylinders increased further, but the increase was small, with that of the upper rubber cylinder increasing from 26.38 MPa to 26.76 MPa, that of the middle rubber cylinder increasing from 25.53 MPa to 25.66 MPa, and that of the lower rubber cylinder increasing from 25.42 MPa to 25.45 MPa. At present, the rubber commonly used in Y441-114 packer for gas injection is hydrogenated nitrile rubber, and its compressive strength is generally about 30MPa, thus the pressure of the packer rubber cylinder was still within the allowable compressive strength after swelling by SC-CO
2 diffusion.
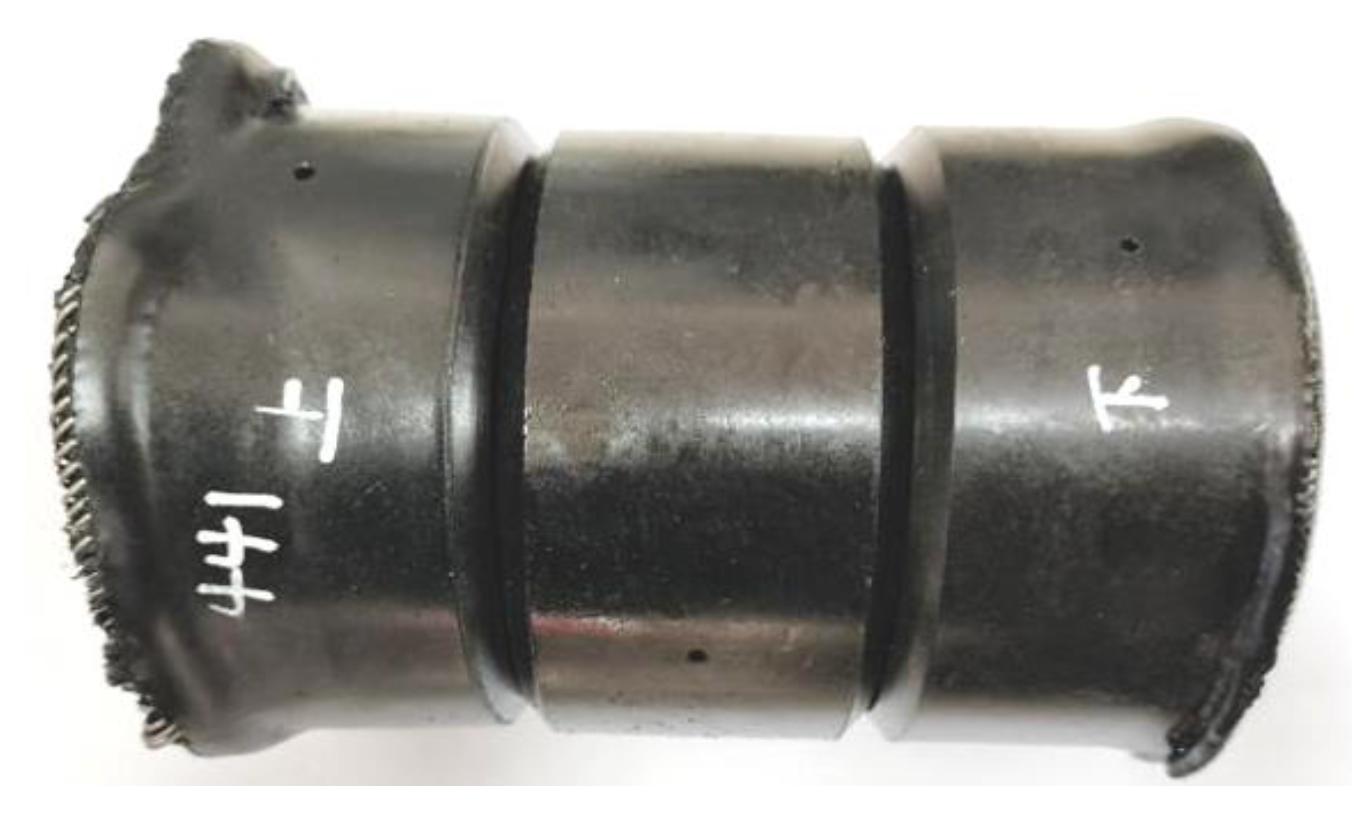
Figure 12 shows the physical picture of the packer’s rubber cylinder taken from the CO
2 layered-injection well site, from which it can be seen that the upper and lower rubber cylinders have undergone large deformation and damage at the edges. It is known that the injection pressure of the well was about 20MPa, and according to the simulation results, the maximum volume strain of the lower rubber cylinder should be lower than 20%, and the maximum contact stress should be lower than 26.76MPa, so it was inferred that the swelling effect by SC-CO
2 diffusion was not the main factor that cause the rubber cylinder to tear due to deformation.
Figure 8(c) shows the volumetric strain cloud diagram of the expansion of the rubber cylinder under the influence of swelling by SC-CO
2 diffusion after the packer unseated. According to the swelling curve under the case of rapid decompression, the volume expansion of the rubber cylinder would be more than 200% of itself. Therefore, even if the packer was completely unsealed, there was still contact stress between the rubber cylinder and the casing wall. Fig. 13 shows the contact stress curve between the rubber cylinder and the inner wall of the casing after unsealing considering the influence of swelling by SC-CO
2 diffusion. It can be seen from the curve that after unsealing, the lower edge of the lower rubber cylinder and the upper edge of the upper rubber cylinder were still affected by the swelling effect, there were still large contact stresses, which is consistent with the actual situation in the field, with the contact stress at the lower edge of the lower rubber cylinder being more than 5MPa, the upper and lower edges of the middle rubber cylinder being close to 4.5MPa, and the upper edge of the upper rubber cylinder being close to 4MPa. According to the simulation results in
Figure 9,
Figure 10 and
Figure 11 when the packer was fully seated, the contact length between the lower rubber cylinder and the casing was about 45mm, the contact length between the middle rubber cylinder and the casing was 40mm, and the contact length between the upper rubber cylinder and the casing was 37mm. The inner diameter of the casing was 124mm. When the packer was unsealed, the space between the rubber cylinder and the casing was filled with injected gas, and the friction coefficient could be set as 0.1. The frictions between the inner wall of the casing and the lower, middle and upper rubber cylinders were 87.61kN, 70.08kN and 57.63kN, respectively. It can be inferred that during the unsealing process, SC-CO
2 diffused into the rubber cylinder and caused the swelling, which enhanced the residual friction between the rubber cylinder and the casing wall. In the operation of pipe string lifting up in the field, deformation damage and tearing of the rubber cylinder usually occured, and the maximum probability of tearing appeared at the lower edge of the lower rubber cylinder and the upper edge of the upper rubber cylinder, it also verified the above conclusions.
In the CO2 injection well with two injection sections, generally, two sets of packers are used to protect the casing from corrosion, and another set of packer is used to separate the upper and lower sections. The release force of the three sets of packers was calculated as about 64.59t according to the above method. The rated lifting load of the conventional workover rig is 30t, and the rated lifting load of the workover rig under pressure operation is 60t. It can be seen that the residual friction between the rubber cylinder and the inner wall of the casing is also one of the main reasons for the pipe stuck during the field operation. Therefore, when designing the packer for CO2 injection, it should be considered to set a step-by-step release mechanism to reduce the release force of the string and improve the success rate of the operation.
Figure 13.
Comparison of the contact pressure between the rubber cylinder and the inner wall of the casing after unsealing (Swelling by SC-CO2 diffusion was considered).
Figure 13.
Comparison of the contact pressure between the rubber cylinder and the inner wall of the casing after unsealing (Swelling by SC-CO2 diffusion was considered).
5. Conclusions
(1) Unidirectional compression seating at the lower end is usually used for conventional packers, the simulation results showed that the deformation of the three rubber cylinders was uneven, and if the seating distance was not set reasonably, it will easily lead to tearing and damage of the rubber cylinder. Therefore, when design the seating mechanism of packer, a reasonable seating distance should be retained so as to prevent poor sealing or damage to the rubber cylinder. At the same time, the seating mechanism should be optimized and upgraded, such as bidirectional seating mechanism, to fundamentally change the overall stress of the rubber cylinder and improve the sealing reliability.
(2) The downhole temperature of CO2 injection wells usually exceeds 100℃, and the simulation results showed that the contact stress between the rubber cylinder and the inner wall of the casing decreased significantly with the increase of downhole temperature. Under the steady state condition of 120℃, the contact stress of the rubber cylinder decreased by about 40% compared with that when it is just seated. In order to ensure a long-lasting sealing under high temperature conditions, the packer’s rubber cylinder selected for CO2 injection wells should have the characteristics of high temperature resistance.
(3) Thermal analogy method was used to simulate the effect of SC-CO2 on the sealing performance of rubber cylinder, and the results showed that with the rubber swelling by SC-CO2 diffusion, the deformation of the rubber cylinder was enhanced, and the contact stress between the rubber cylinder and the inner wall of the casing was increased, but the deformation was small which would not result in tearing of the cylinder.
(4) The simulation results showed that in the process of packer unsealing, the swelling effect would greatly increase the contact stress between the rubber cylinder and the inner wall of the casing, thus increase the overall unsealing force of the pipe string. If more than three sets of packers would be applied to a gas injection well, the unsealing force would be more than 60t, which would disable the normal pipe string operation. Therefore, when designing or selecting packers for CO2 injection, attention should be paid to whether they have the function of step-by-step releasing, so as to reduce the difficulty of field operation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Zhenkun Zhu; Methodology, Zhenkun Zhu; Validation, Meng Cai; Formal analysis, Lining Cui; Investigation, Xingliang Song; Resources, Xiaoyu Xu; Data Curation, Chuanbo Cong; Writing-original draft preparation, Haicheng Li; Writing-review and editing, Qiming Gao. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rui Zhenhua, Li Yang, Xue Zhaojie, et al. Development Suggestions on Key Technologies of CO2 Enhanced Oil and Gas Recovery and Geological Storage [J]. Prospect Science and Technology,2023, Volume2(02), pp.145-160.
- Zhu Dajiang, Lin Yuanhua, Zou Dapeng, et al. Study on Corrosion Mechanical Properties of Rubber Material for CO2 Flooding Gas Well Packer [J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2014, Volume42(5), pp.5.
- Zhang Kai, Chen Zhangxing, LAN Haifan, et al. Status and Prospect of Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage Technology [J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs,2023, Volume30(02), pp.1-9.
- Aminu M D, Nabavi S A, Rochelle C A, et al. A Review of Developments in Carbon Dioxide Storage[J]. Applied Energy, 2017; Volume 208, pp.1389-1419.
- Baklid A, Korbol R, Owren G. Sleipner Vest CO2 Disposal, CO2 Injection into a Shallow Underground Aquifer[C]//SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. SPE, 1996: SPE-36600-MS.
- Cook P J. CCS Research Development and Deployment in a Clean Energy Future: Lessons from Australia over the Past two Decades[J]. Engineering, 2017, Volume3(4), pp.477-484.
- Wang Fengshan, Xu Dekui, Li Kuilong, et al. Research on Sealing Mechanism of CO2 Packer Cartridge [J]. Journal of Oil Production Engineering,2018, Volume(03), pp.1-4+84.
- Liu Jianxin, Wang Shijie, Zhang Ruixia, et al. Bidirectional Compression Packer for Stratified Gas Injection in CO2 Flooding [J]. China Petroleum Machinery,2017, Volume45(04), pp.87-89.
- Zhang Xin, Xu Xingping, WANG Lei. Improvement and Advantage Analysis of Packer Rubber Cylinder Structure [J]. Oil Field Machinery, Volume2013(1), pp.5.
- Zhang Zhi, Zhu Xiaohua, Xu Jianbo. Optimization of Structural Parameters of a Compression Packer Casing Based on Orthogonal Tests [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, Volume39(3), pp.5.
- Daou F, de Miranda C R, De Oliveira J L, et al. Swelling of Elastomers in CO2 Environment: Testing Methodology and Experimental Data[C]//SPE Latin America and Caribbean Petroleum Engineering Conference. SPE, 2014: D031S023R002.
- Zhu D, Lin Y, Zhang H, et al. Corrosion Evaluation of Packer Rubber Materials in CO2 Injection Wells under Supercritical Conditions[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2017, Volume151, pp.311-317.
- Davies O M, Arnold J C, Sulley S. The Mechanical Properties of Elastomers in High-pressure CO2[J]. Journal of materials science, 1999, Volume34, pp.417-422.
- Zhong Weiping. Research on Sealing Performance of Packer Rubber Casing [D]. China University of Petroleum (East China).
- Wang Jieli, Gao Baokui, Ma Chao, et al. Effect of Casing Wear on Sealing Performance of Packer [J]. Petroleum Machinery.
- Ge Yuan. Research on Structure Design and Performance of Rubber Cylinder of New Gas Injection Packer [D]. China University of Petroleum (East China).
- Wang Lu, Xu Peng, Tao Jiahui. Finite Element Analysis of Rubber O-ring Static Seal Structure in High-pressure Hydrogen Environment [J]. Manufacturing Automation, 2022, Volume46(7), pp.143-149.
- Wang Weihua. Coupling Simulation of Hydrogen Concentration Field and Stress Field Based on Thermal Analogy [D]. Huazhong University of Science and Technology,2018.
- Liu Mingtai. Study on the Swelling Law of Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber and Fluorine Rubber in Carbon Dioxide [D]. China University of Petroleum (Beijing),2021.
- Huang Xiaomeng, Xiao Guohua, Wang Lei, et al. Design and Development of Plug-in High Temperature and High Pressure Gas Injection Packer [J]. Xinjiang Oil and Gas,2023, Volume19(3), pp.21-25.
- Wang Zhiyong, Liu Junyan, Zhu Shuai, et al. Nonlinear Simulation and Performance Evaluation of Packer Cartridge [J]. Information Technology,2023, Volume52(03), pp.112-116.
- Huang Liang, Guo Zhilong, Wang Xile, et al. Failure Analysis and Improvement Design of Packer Seal Casing Extrusion [J]. Hydraulics and Pneumatics,2023, Volume47(7), pp.177-182.
- Mao Jun, Development of Rubber Casing for High Temperature and High Pressure Test Packer [J]. Oil Drilling and Production Technology,2023, Volume45(5), pp.638-643.
- Sun Yongtao, Wei Anchao, Chen Zongqi, et al. Sealing Structure Design of Rubber Cylinder for High Temperature and High Pressure Packer [J], Lubrication and Sealing,2023, Volume48(9), pp.140-145.
- Yue Qianbei, Wang Gang, Liu Jubao, et al. Simulation and Calculation of Nonlinear Flow in Expansion Packer under High Temperature and Pressure [J], Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics,2023, Volume40(3), pp.411-423.
- Kim B, Lee S B, Lee J, et al. A Comparison Among Neo-Hookean Model, Mooney-Rivlin Model, and Ogden Model for Chloroprene Rubber[J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2012, Volume13, pp.759-764.
- Yamabe J, Nishimura S. Failure Behavior of Rubber O-ring under Cyclic Exposure to High-pressure Hydrogen Gas[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2013, Volume35, pp.193-205.
- Koga A, Uchida K, Yamabe J, et al. Evaluation on High-pressure Hydrogen Decompression Failure of Rubber O-ring Using Design of Experiments[J]. International Journal of Automotive Engineering, 2011, Volume2(4), pp.123-129.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).