Submitted:
21 May 2024
Posted:
22 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Aptamer Selection and Production
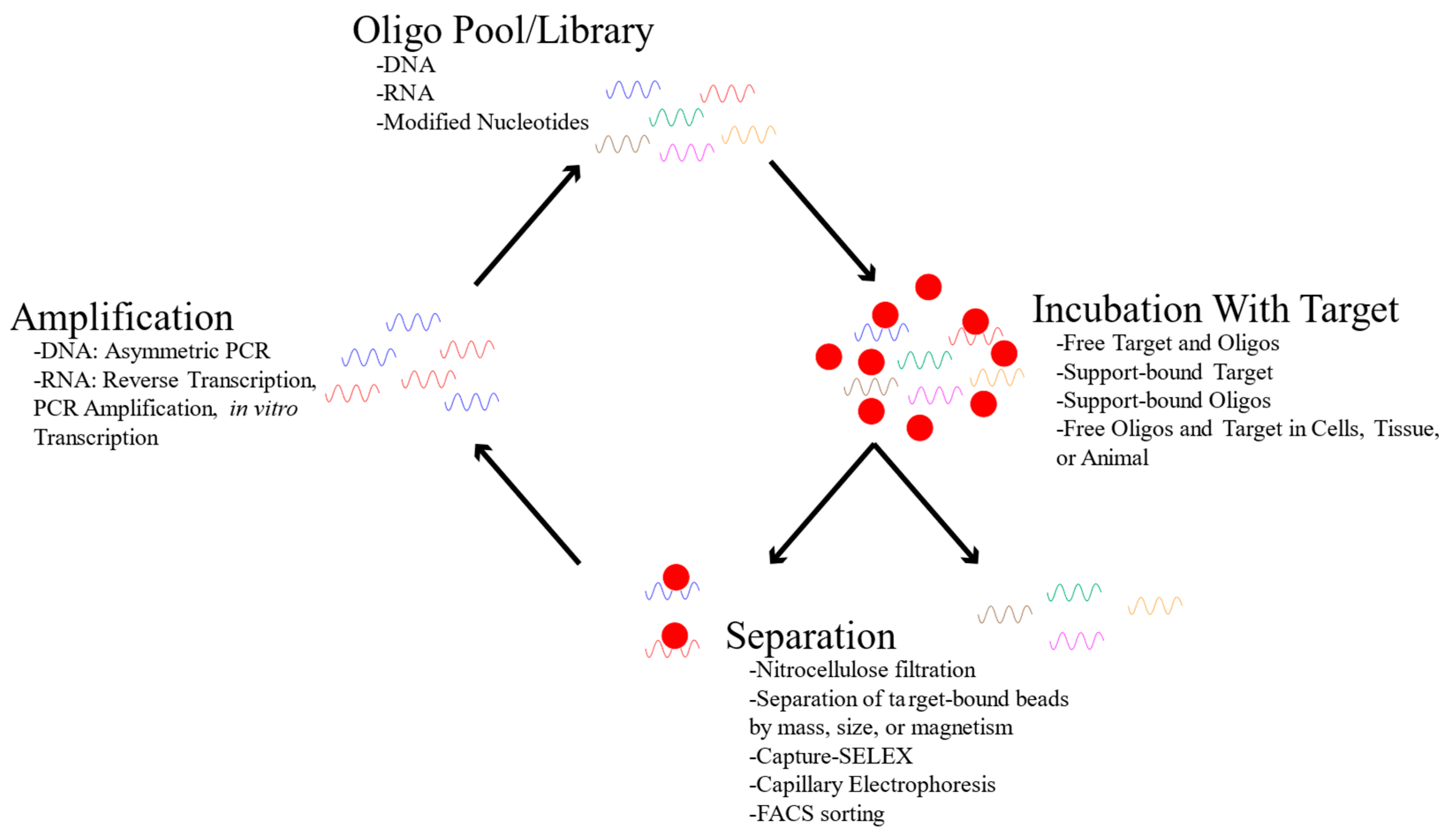
2.1. Aptamer Selection
2.2. Binding Analysis and Optimization
2.3. Methods of Production
3. Comparison to Antibodies
4. Clinical Trials and Approved Drugs
4.1. Therapies for Ocular Diseases
4.2. Autoimmune, Cancer, and Infectious Disease Therapies
4.3. Therapies for Blood Disorders
5. Future Directions
5.1. Therapies for Small Molecule Toxins
5.2. Combinatorial Approaches
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mortimer, S.A.; Kidwell, M.A.; Doudna, J.A. Insights into RNA Structure and Function from Genome-Wide Studies. Nat Rev Genet 2014, 15, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klosterman, P.S.; Tamura, M.; Holbrook, S.R.; Brenner, S.E. SCOR: A Structural Classification of RNA Database. Nucleic Acids Res 2002, 30, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
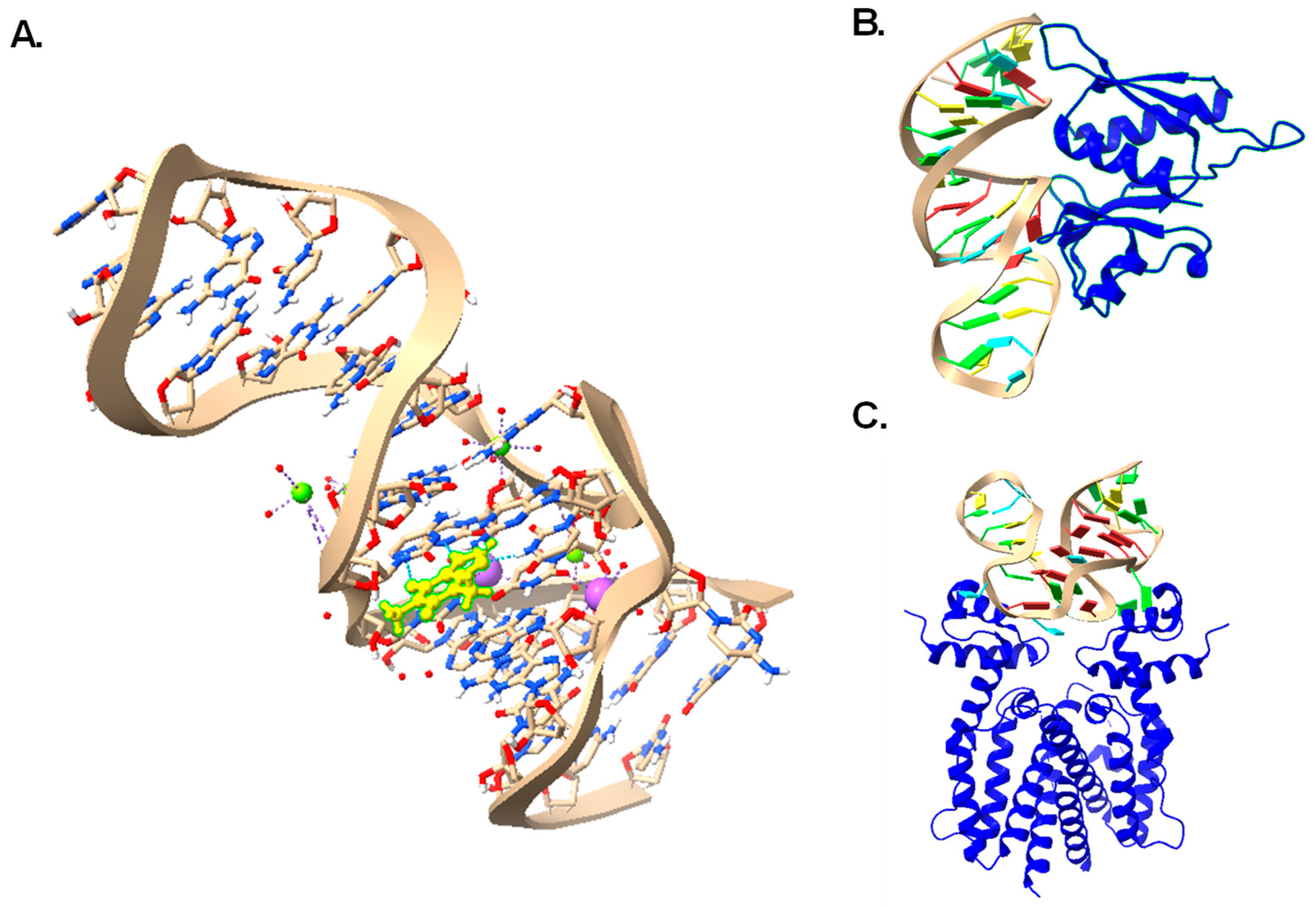
- Lin, C.H.; Pate1, D.J. Structural Basis of DNA Folding and Recognition in an AMP-DNA Aptamer Complex: Distinct Architectures but Common Recognition Motifs for DNA and RNA Aptamers Complexed to AMP;
- Hermann, T.; Westhof, E. Aminoglycoside Binding to the Hammerhead Ribozyme: A General Model for the Interaction of Cationic Antibiotics with RNA. 1998.
- Huizenga, D.E.; Szostak, J.W. A DNA Aptamer That Binds Adenosine and ATP; 1995; Vol. 34;
- Zimmermann, G.R.; Jenison, R.D.; Wick, C.L.; Simorre, J.-P.; Pardi, A. Interlocking Structural Motifs Mediate Molecular Discrimination by a Theophylline-Binding RNA.
- Gelinas, A.D.; Davies, D.R.; Janjic, N. Embracing Proteins: Structural Themes in Aptamer-Protein Complexes. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2016, 36, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenison, R.D.; Gill, S.C.; Pardi, A.; Polisky, B. High-Resolution Molecular Discrimination by RNA. Science (1979) 1994, 263, 1425–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carothers, J.M.; Oestreich, S.C.; Szostak, J.W. Aptamers Selected for Higher-Affinity Binding Are Not More Specific for the Target Ligand. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Ennifar, E.; Nakamura, Y. Thermodynamic Study of Aptamers Binding to Their Target Proteins. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, J.R. Induced Fit in RNA-Protein Recognition;
- Garst, A.D.; Edwards, A.L.; Batey, R.T. Riboswitches: Structures and Mechanisms. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2011, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombelli, S.; Minunni, M.; Mascini, M. Analytical Applications of Aptamers. Biosens Bioelectron 2005, 20, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.R.; Sullenger, B.A.; Rusconi, C.P. Developing Aptamers into Therapeutics. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2000, 106, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiviyanathan, V.; Gorenstein, D.G. Aptamers and the next Generation of Diagnostic Reagents. Proteomics Clin Appl 2012, 6, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, P.; Nosrati, R.; Alibolandi, M.; Rafatpanah, H.; Abnous, K.; Khedri, M.; Ramezani, M. SELEX Methods on the Road to Protein Targeting with Nucleic Acid Aptamers. Biochimie 2018, 154, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Aguado, J.A.; Penner, G. Determination of Ochratoxin A with a DNA Aptamer. J Agric Food Chem 2008, 56, 10456–10461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamm, J. Characterisation of Antibody-Binding RNAs Selected from Structurally Constrained Libraries; 1996; Vol. 24;
- Szeto, K.; Reinholt, S.J.; Duarte, F.M.; Pagano, J.M.; Ozer, A.; Yao, L.; Lis, J.T.; Craighead, H.G. High-Throughput Binding Characterization of RNA Aptamer Selections Using a Microplate-Based Multiplex Microcolumn Device. Anal Bioanal Chem 2014, 406, 2727–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staii, C. Conformational Changes in Surface-Immobilized Proteins Measured Using Combined Atomic Force and Fluorescence Microscopy. Molecules 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlberger, M.; Gadermaier, G. SELEX: Critical Factors and Optimization Strategies for Successful Aptamer Selection. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 2022, 69, 1771–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.Y.; Lau, H.L.; Kwok, C.K. Capture-SELEX: Selection Strategy, Aptamer Identification, and Biosensing Application. Biosensors (Basel) 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezovski, M.; Musheev, M.; Drabovich, A.; Krylov, S.N. Non-SELEX Selection of Aptamers. J Am Chem Soc 2006, 128, 1410–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sola, M.; Menon, A.P.; Moreno, B.; Meraviglia-Crivelli, D.; Soldevilla, M.M.; Cartón-García, F.; Pastor, F. Aptamers Against Live Targets: Is In Vivo SELEX Finally Coming to the Edge? Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, T.S.; Anna, A.; Tang, T.H.; Citartan, M. Development of an Optimization Pipeline of Asymmetric PCR towards the Generation of DNA Aptamers: A Guide for Beginners. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2022, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, K.; Latulippe, D.R.; Ozer, A.; Pagano, J.M.; White, B.S.; Shalloway, D.; Lis, J.T.; Craighead, H.G. RAPID-SELEX for RNA Aptamers. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margineanu, A.; Chan, J.J.; Kelly, D.J.; Warren, S.C.; Flatters, D.; Kumar, S.; Katan, M.; Dunsby, C.W.; French, P.M.W. Screening for Protein-Protein Interactions Using Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM). Sci Rep 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Hu, B.; Zheng, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, D.; Sun, M.; Jiao, B.; Wang, L. Gonyautoxin 1/4 Aptamers with High-Affinity and High-Specificity: From Efficient Selection to Aptasensor Application. Biosens Bioelectron 2016, 79, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zheng, X.; Jiao, B.; Wang, L. Post-SELEX Optimization of Aptamers. Anal Bioanal Chem 2016, 408, 4567–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieken, W.A.; Olsen, D.B.; Benseler, F.; Aurup, H.; Eckstein, F. Kinetic Characterization of Ribonuclease-Resistant 2′-Modified Hammerhead Ribozymes. Science (1979) 1991, 253, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.P.; Liu, X.-H.; Schumacher, T.N.M.; Lin, H.Y.; Ausiello, D.A.; Kim, P.S.; Bartel, D.P. Bioactive and Nuclease-Resistant L-DNA Ligand of Vasopressin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1997, 94, 11285–11290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veedu, R.N.; Wengel, J. Locked Nucleic Acid Nucleoside Triphosphates and Polymerases: On the Way towards Evolution of LNA Aptamers. Mol Biosyst 2009, 5, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, S.; Chaput, J.C. Darwinian Evolution of an Alternative Genetic System Provides Support for TNA as an RNA Progenitor. Nat Chem 2012, 4, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, K. PEGylation of Therapeutic Oligonucletides: From Linear to Highly Branched PEG Architectures. Nano Res 2018, 11, 5519–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sismour, A.M.; Lutz, S.; Park, J.H.; Lutz, M.J.; Boyer, P.L.; Hughes, S.H.; Benner, S.A. PCR Amplification of DNA Containing Non-Standard Base Pairs by Variants of Reverse Transcriptase from Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1. Nucleic Acids Res 2004, 32, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazier, D.A.; Glazier, D.A.; Liao, J.; Roberts, B.L.; Li, X.; Yang, K.; Stevens, C.M.; Tang, W.; Tang, W. Chemical Synthesis and Biological Application of Modified Oligonucleotides. Bioconjug Chem 2020, 31, 1213–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuri, S.; Church, G.M. Large-Scale de Novo DNA Synthesis: Technologies and Applications. Nat Methods 2014, 11, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurien, B.T.; Scofield, R.H. Western Blotting. Methods 2006, 38, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.Z. Monoclonal Antibodies as Diagnostics; an Appraisal;
- Lu, R.M.; Hwang, Y.C.; Liu, I.J.; Lee, C.C.; Tsai, H.Z.; Li, H.J.; Wu, H.C. Development of Therapeutic Antibodies for the Treatment of Diseases. J Biomed Sci 2020, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonberg, N.; Taylor, L.D.; Harding, F.A.; Trounstine, M.; Higgins, K.M.; Schramm, S.R.; Kuo, C.-C.; Mashayekh, R.; Wymore, K.; McCabe, J.G.; et al. Antigen-Specific Human Antibodies from Mice Comprising Four Distinct Genetic Modifications. Nature 1994, 368, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.J. Isolation of Antibodies for Phosphotyrosine by Immunization with a V- Abl Oncogene-Encoded Protein. Mol Cell Biol 1985, 5, 3640–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huygens, S.; Preijers, T.; Swaneveld, F.H.; Kleine Budde, I.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Koch, B.C.P.; Rijnders, B.J.A. Dosing of Convalescent Plasma and Hyperimmune Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Immunoglobulins: A Phase I/II Dose-Finding Study. Clin Pharmacokinet 2024. [CrossRef]
- Zaroff, S.; Tan, G. Hybridoma Technology: The Preferred Method for Monoclonal Antibody Generation for in Vivo Applications. Biotechniques 2019, 67, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.T.; Dear, P.H.; Foote, J.; Neuberger, M.S.; Winter, G. Replacing the Complementarity-Determining Regions in a Human Antibody with Those from a Mouse. Nature 1986, 321, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, R.; Dou, L.; Wu, W.; Yu, W.; Wen, K.; Yu, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. The Influence of Hapten Spacer Arm Length on Antibody Response and Immunoassay Development. Anal Chim Acta 2023, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCafferty, J.; Griffiths, A.D.; Winter, G.; Chiswell, D.J. Phage Antibodies: Filamentous Phage Displaying Antibody Variable Domains. Nature 1990, 348, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbas III, C.F.; Kang, A.S.; Lerner, R.A.; Benkovict, S.J. Assembly of Combinatorial Antibody Libraries on Phage Surfaces: The Gene III Site; 1991; Vol. 88;
- Dong, Y.; Meng, F.; Wang, Z.; Yu, T.; Chen, A.; Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Yin, M.; Tang, L.; Hu, C.; et al. Construction and Application of a Human ScFv Phage Display Library Based on Cre-LoxP Recombination for Anti-PCSK9 Antibody Selection. Int J Mol Med 2021, 47, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggy, I.; Wine, Y.; Shefet-Carasso, L.; Nahary, L.; Georgiou, G.; Benhar, I. Antibody Isolation from Immunized Animals: Comparison of Phage Display and Antibody Discovery via v Gene Repertoire Mining. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection 2012, 25, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Zhuo, Z.; Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Li, D.; Wan, Y.; et al. Recent Progress in Aptamer Discoveries and Modifications for Therapeutic Applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021, 13, 9500–9519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gaza-Bulseco, G.; Sun, J. Characterization of the Stability of a Fully Human Monoclonal IgG after Prolonged Incubation at Elevated Temperature. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2006, 837, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafraz, M.; Nakhjavani, M.; Shigdar, S.; Christo, F.C.; Rolfe, B. Modelling of Mass Transport and Distribution of Aptamer in Blood-Brain Barrier for Tumour Therapy and Cancer Treatment. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2022, 173, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, N.; An, Z. Engineering Antibody and Protein Therapeutics to Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier. Antib Ther 2022, 5, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, M.; Gao, R.; Lu, F.; Liu, J.; Huang, Q. Repurposing of Thermally Stable Nucleic-Acid Aptamers for Targeting Tetrodotoxin (TTX). Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2022, 20, 2134–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Duan, N.; Xia, Y.; Hun, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Magnetic Separation-Based Multiple SELEX for Effectively Selecting Aptamers against Saxitoxin, Domoic Acid, and Tetrodotoxin. J Agric Food Chem 2018, 66, 9801–9809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Huang, A.; Liu, L.; Xiang, S.; Li, X.; Ling, S.; Wang, L.; Lu, T.; Wang, S. Construction of a Single Chain Variable Fragment Antibody (ScFv) against Tetrodotoxin (TTX) and Its Interaction with TTX. Toxicon 2014, 83, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monrat, C.; Jeeraphong, T.; Kunan, B.; Potjanee, S.; Nitat, S.; Hisao, K.; Kiattawee, C.; Wanpen, C. Human Monoclonal ScFv That Blocks Sodium Ion Activity of Tetrodotoxin. Front Immunol 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumbaca, D.; Wong, A.; Drake, E.; Reyes, A.E.; Lin, B.C.; Stephan, J.P.; Desnoyers, L.; Shen, B.Q.; Dennis, M.S. Highly Specific Off-Target Binding Identified and Eliminated during the Humanization of an Antibody against FGF Receptor 4. MAbs 2011, 3, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongartz, T.; Sutton, A.J.; Sweeting, M.J.; Buchan, I.; Matteson, E.L.; Montori, V. Anti-TNF Antibody Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis and the Risk of Serious Infections and Malignancies Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Rare Harmful Effects in Randomized Controlled Trials;
- Dyke, C.K.; Steinhubl, S.R.; Kleiman, N.S.; Cannon, R.O.; Aberle, L.G.; Lin, M.; Myles, S.K.; Melloni, C.; Harrington, R.A.; Alexander, J.H.; et al. First-in-Human Experience of an Antidote-Controlled Anticoagulant Using RNA Aptamer Technology: A Phase 1a Pharmacodynamic Evaluation of a Drug-Antidote Pair for the Controlled Regulation of Factor IXa Activity. Circulation 2006, 114, 2490–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, K.D.; Gilbert, J.C.; Jilma, B. Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Safety of Aptamers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2018, 134, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintea, I.; Petricau, C.; Dumitrascu, D.; Muntean, A.; Branisteanu, D.; Branisteanu, D.; Deleanu, D. Hypersensitivity Reactions to Monoclonal Antibodies: Classification and Treatment Approach (Review). Exp Ther Med 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougan, H.; Lyster, D.M.; Vo, C. V; Stafford, A.; Weitz, J.I.; Hobbs, J.B. Extending the Lifetime of Anticoagulant Oligodeoxynucleotide Aptamers in Blood; 2000;
- Dass, C.R.; Saravolac, E.G.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.-Q. Cellular Uptake, Distribution, and Stability of 10-23 Deoxyribozymes. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev 2002, 12, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domachowske, J.B.; Khan, A.A.; Esser, M.T.; Jensen, K.; Takas, T.; Villafana, T.; Dubovsky, F.; Griffin, M.P. Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of MEDI8897, an Extended Half-Life Single-Dose Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prefusion F-Targeting Monoclonal Antibody Administered as a Single Dose to Healthy Preterm Infants. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2018, 37, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogesch, P.; Dudek, S.; van Zandbergen, G.; Waibler, Z.; Anzaghe, M. The Role of Fc Receptors on the Effectiveness of Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drolet, D.W.; Green, L.S.; Gold, L.; Janjic, N. Fit for the Eye: Aptamers in Ocular Disorders. Nucleic Acid Ther 2016, 26, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Liu, P.; Shang, K.; Ma, Y. Bin Application and Mechanism of Anti-VEGF Drugs in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storkebaum, E.; Carmeliet, P. VEGF: A Critical Player in Neurodegeneration. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2004, 113, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gragoudas, E.S.; Adamis, A.P.; Cunningham, E.T.; Feinsod, M.; Guyer, D.R. Pegaptanib for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. New England Journal of Medicine 2004, 351, 2805–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, E.W.M.; Shima, D.T.; Calias, P.; Cunningham, E.T.; Guyer, D.R.; Adamis, A.P. Pegaptanib, a Targeted Anti-VEGF Aptamer for Ocular Vascular Disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006, 5, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foy, J.W.-D.; Rittenhouse, K.; Modi, M.; Patel, M. Local Tolerance and Systemic Safety of Pegaptanib Sodium in the Dog and Rabbit. Journal of Ocular Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2007, 23, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, M.; Chiosi, F.; dell’Omo, R.; Romano, M.R.; Parmeggiani, F.; Semeraro, F.; Mastropasqua, R.; Costagliola, C. Intravitreal Pegaptanib Sodium (Macugen®) for Treatment of Diabetic Macular Oedema: A Morphologic and Functional Study. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2012, 74, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.W. PDGF: Ophthalmology’s next Great Target. Expert Rev Ophthalmol 2013, 8, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C. Avacincaptad Pegol: First Approval. Drugs 2023, 83, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shughoury, A.; Sevgi, D.D.; Ciulla, T.A. The Complement System: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2023, 24, 1887–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shah, S.M.; Mangwani-Mordani, S.; Gregori, N.Z. Updates on Emerging Interventions for Autosomal Recessive ABCA4-Associated Stargardt Disease. J Clin Med 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajona, D.; Ortiz-Espinosa, S.; Moreno, H.; Lozano, T.; Pajares, M.J.; Agorreta, J.; Bértolo, C.; Lasarte, J.J.; Vicent, S.; Hoehlig, K.; et al. A Combined PD-1/C5a Blockade Synergistically Protects against Lung Cancer Growth and Metastasis. Cancer Discov 2017, 7, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.-F.; Ward, P.A. ROLE OF C5A IN INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES. Annu Rev Immunol 2005, 23, 821–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.M.; Ferreira, D.; Rodrigues, L.R.; Pereira, M.O. Aptamer-Based Therapy for Fighting Biofilm-Associated Infections. Journal of Controlled Release 2024, 367, 522–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, M.Z.; Lee, H.; Wysoczynski, M.; Wan, W.; Marlicz, W.; Laughlin, M.J.; Kucia, M.; Janowska-Wieczorek, A.; Ratajczak, J. Novel Insight into Stem Cell Mobilization-Plasma Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Is a Major Chemoattractant That Directs the Egress of Hematopoietic Stem Progenitor Cells from the Bone Marrow and Its Level in Peripheral Blood Increases during Mobilization Due to Activation of Complement Cascade and Membrane Attack Complex. Leukemia 2010, 24, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujko, K.; Rzeszotek, S.; Hoehlig, K.; Yan, J.; Vater, A. Mariusz, ·; Ratajczak, Z. Signaling of the Complement Cleavage Product Anaphylatoxin C5a Through C5aR (CD88) Contributes to Pharmacological Hematopoietic Stem Cell Mobilization. 2015, 13, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiuti, A.; Webb, I.J. ; Bleul, ¶ C; Springer, T.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.C. The Chemokine SDF-1 Is a Chemoattractant for Human CD34 Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells and Provides a New Mechanism to Explain the Mobilization of CD34 Progenitors to Peripheral Blood. J. Exp. Med 1997, 185.
- Roccaro, A.M.; Sacco, A.; Klussmann, S.; Ghobrial Correspondence, I.M. SDF-1 Inhibition Targets the Bone Marrow Niche for Cancer Therapy. [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, H.; Weisel, K.; Petrucci, M.T.; Leleu, X.; Cafro, A.M.; Garderet, L.; Leitgeb, C.; Foa, R.; Greil, R.; Yakoub-Agha, I.; et al. Olaptesed Pegol, an Anti-CXCL12/SDF-1 Spiegelmer, Alone and with Bortezomib–Dexamethasone in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma: A Phase IIa Study. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoellenriegel, J.; Zboralski, D.; Maasch, C.; Rosin, N.Y.; Wierda, W.G.; Keating, M.J.; Kruschinski, A.; Burger, J.A. The Spiegelmer NOX-A12, a Novel CXCL12 Inhibitor, Interferes with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cell Motility and Causes Chemosensitization. Blood 2014, 123, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vater, A.; Sahlmann, J.; Kröger, N.; Zöllner, S.; Lioznov, M.; Maasch, C.; Buchner, K.; Vossmeyer, D.; Schwoebel, F.; Purschke, W.G.; et al. Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cell Mobilization in Mice and Humans by a First-in-Class Mirror-Image Oligonucleotide Inhibitor of CXCL12. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2013, 94, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, O.; Pawar, R.D.; Purschke, W.; Eulberg, D.; Selve, N.; Buchner, K.; Ninichuk, V.; Segerer, S.; Vielhauer, V.; Klussmann, S.; et al. Spiegelmer Inhibition of CCL2/MCP-1 Ameliorates Lupus Nephritis in MRL-(Fas)Lpr Mice. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2007, 18, 2350–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panee, J. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1 (MCP-1) in Obesity and Diabetes. [CrossRef]
- Menne, J.; Eulberg, D.; Beyer, D.; Baumann, M.; Saudek, F.; Valkusz, Z.; Rcek, A.W.; Haller, H. C-C Motif-Ligand 2 Inhibition with Emapticap Pegol (NOX-E36) in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Albuminuria. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2017, 32, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Devarapu, S.; Kumar Vr, S.; Rupanagudi, V.; Kulkarni, O.P.; Eulberg, D.; Klussmann, S.; Anders, H.-J. Dual Blockade of the Pro-Inflammatory Chemokine CCL2 and the Homeostatic Chemokine CXCL12 Is as Effective as High Dose Cyclophosphamide in Murine Proliferative Lupus Nephritis. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, A.; Alavizadeh, S.H.; Hosseini, S.A.; Meidany, P.; Doagooyan, M.; Abolhasani, Y.; Saadat, Z.; Amani, F.; Kesharwani, P.; Gheybi, F.; et al. Harnessing Aptamers against COVID-19: A Therapeutic Strategy. Drug Discov Today 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmich, N.N.; Sivak, K. V; Chubarev, V.N.; Porozov, Y.B.; Savateeva-Lyubimova, T.N.; Peri, F. TLR4 Signaling Pathway Modulators as Potential Therapeutics in Inflammation and Sepsis. [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Jiménez, M.; Martín-Vílchez, S.; Ochoa, D.; Mejía-Abril, G.; Román, M.; Camargo-Mamani, P.; Luquero-Bueno, S.; Jilma, B.; Moro, M.A.; Fernández, G.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Clinical Trial of a TLR4-Binding DNA Aptamer, ApTOLL: Safety and Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Volunteers. [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, S.; Wang, L.; Sridharan, V.; Chen, W.; Courtenay-Luck, N.; Jones, D.; Spicer, E.K.; Fernandes, D.J. Plasma Membrane Nucleolin Is a Receptor for the Anticancer Aptamer AS1411 in MV4-11 Leukemia Cells. Mol Pharmacol 2009, 76, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, Y.; Soundararajan, S.; Sengupta, T.K.; Kio, E.A.; Smith, J.C.; Pineda-Roman, M.; Stuart, R.K.; Spicer, E.K.; Fernandes, D.J. Overexpression of Nucleolin in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells Induces Stabilization of Bcl2 MRNA. 2007, 109, 3069–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, Y.; Sengupta, T.K.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Spicer, E.K.; Fernandes, D.J. Retinoid-Induced Apoptosis in HL-60 Cells Is Associated with Nucleolin Down-Regulation and Destabilization of Bcl-2 MRNA. Mol Pharmacol 2005, 67, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Jiménez, M.; Abad-Santos, F.; Cotgreave, I.; Gallego, J.; Jilma, B.; Flores, A.; Jovin, T.G.; Vivancos, J.; Hernández-Pérez, M.; Molina, C.A.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of ApTOLL in Patients With Ischemic Stroke Undergoing Endovascular Treatment A Phase 1/2 Randomized Clinical Trial Visual Abstract Supplemental Content. JAMA Neurol 2023, 80, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavalle, J.P.; Cohen, M.G. The REG1 Anticoagulation System: A Novel Actively Controlled Factor IX Inhibitor Using RNA Aptamer Technology for Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndrome. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipe, S.W.; Montgomery, R.R.; Pratt, K.P.; Lenting, P.J.; Lillicrap, D. Life in the Shadow of a Dominant Partner: The FVIII-VWF Association and Its Clinical Implications for Hemophilia A. 2016, 128, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilma, B.; Paulinska, P.; Jilma-Stohlawetz, P.; Gilbert, J.C.; Hutabarat, R.; Knöbl, P. A Randomised Pilot Trial of the Anti-von Willebrand Factor Aptamer ARC1779 in Patients with Type 2b von Willebrand Disease. Thromb Haemost 2010, 104, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilma-Stohlawetz, P.; Knöbl, P.; Gilbert, J.C.; Jilma, B. The Anti-von Willebrand Factor Aptamer ARC1779 Increases von Willebrand Factor Levels and Platelet Counts in Patients with Type 2B von Willebrand Disease. Thromb Haemost 2012, 108, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ay, C.; Kovacevic, K.D.; Kraemmer, D.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Gelbenegger, G.; Firbas, C.; Quehenberger, P.; Jilma-Stohlawetz, P.; Gilbert, J.C.; Zhu, S.; et al. The von Willebrand Factor-Binding Aptamer Rondaptivon Pegol as a Treatment for Severe and Nonsevere Hemophilia A;
- Jilma-Stohlawetz, P.; Gilbert, J.C.; Gorczyca, M.E.; Knöbl, P.; Jilma, B. A Dose Ranging Phase I/II Trial of the von Willebrand Factor Inhibiting Aptamer ARC1779 in Patients with Congenital Thrombotic Thrombo-Cytopenic Purpura. Thromb Haemost 2011, 106, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, K.D.; Grafeneder, J.; Schörgenhofer, C.; Gelbenegger, G.; Gager, G.; Firbas, C.; Quehenberger, P.; Jilma-Stohlawetz, P.; Bileck, A.; Zhu, S.; et al. The von Willebrand Factor A-1 Domain Binding Aptamer BT200 Elevates Plasma Levels of von Willebrand Factor and Factor VIII: A First-in-Human Trial. Haematologica 2022, 107, 2121–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawley, J.T.B.; Lane, D.A. The Haemostatic Role of Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008, 28, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, E.K.; Genga, R.M.; Schwartz, M.C.; Nelson, J.A.; Schaub, R.G.; Olson, K.A.; Kurz, J.C.; Mcginness, K.E. Aptamer ARC19499 Mediates a Procoagulant Hemostatic Effect by Inhibiting Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwoebel, F.; Van Eijk, L.T.; Zboralski, D.; Sell, S.; Buchner, K.; Maasch, C.; Purschke, W.G.; Humphrey, M.; Ollner, S.Z. ¨; Eulberg, D.; et al. The Effects of the Anti-Hepcidin Spiegelmer NOX-H94 on Inflammation-Induced Anemia in Cynomolgus Monkeys. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangat, N.; Wolanskyj, A.P. Anemia of Chronic Disease. [CrossRef]
- Roy, C.N.; Mak, H.H.; Akpan, I.; Losyev, G.; Zurakowski, D.; Andrews, N.C. Hepcidin Antimicrobial Peptide Transgenic Mice Exhibit Features of the Anemia of Inflammation. Blood 2007, 109, 4038–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Eijk, L.; Swinkels, D.W.; Aaron, J.; Schwoebel, F.; Fliegert, F.; Summo, L.; Stéphanie, V.; Laarakkers, C.; Riecke, K.; Pikkers, P. Randomized Double Blind Placebo Controlled PK/PD Study On the Effects of a Single Intravenous Dose of the Anti-Hepcidin Spiegelmer Nox-H94 On Serum Iron During Experimental Human Endotoxemia. Blood 2012, 120, 3452–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.C.; Casewell, N.R.; Elliott, C.T.; Harvey, A.L.; Jamieson, A.G.; Strong, P.N.; Turner, A.D. Friends or Foes? Emerging Impacts of Biological Toxins. Trends Biochem Sci 2019, 44, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omotayo, O.P.; Omotayo, A.O.; Mwanza, M.; Babalola, O.O. Prevalence of Mycotoxins and Their Consequences on Human Health. Toxicol Res 2019, 35, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerssen, A.; Pol-Hofstad, I.E.; Poelman, M.; Mulder, P.P.J.; van den Top, H.J.; Dde Boer, J. Marine Toxins: Chemistry, Toxicity, Occurrence and Detection, with Special Reference to the Dutch Situation. Toxins (Basel) 2010, 2, 878–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.D. Bioterrorism: Toxins as Weapons. J Pharm Pract 2012, 25, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janik, E.; Ceremuga, M.; Bijak, J.S.; Bijak, M. Biological Toxins as the Potential Tools for Bioterrorism. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, K. A Monoclonal Antibody against Tetrodotoxin That Reacts to the Active Group for the Toxicity; 1995; Vol. 293;
- Arakawa, O.; Hwang, D.-F.; Takatani, T. Toxins of Pufferfish That Cause Human Intoxications; 2010;
- Ruscito, A.; DeRosa, M.C. Small-Molecule Binding Aptamers: Selection Strategies, Characterization, and Applications. Front Chem 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascoët, S.; De Waard, M. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Value of Aptamers in Envenomation Cases. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Liu, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, M.; Liu, Z.; Kong, Y.; Liu, S. Marine Toxins Detection by Biosensors Based on Aptamers. Toxins (Basel) 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Aziz, T.M.A.; Ravelet, C.; Molgo, J.; Fiore, E.; Pale, S.; Amar, M.; Al-Khoury, S.; Dejeu, J.; Fadl, M.; Ronjat, M.; et al. Efficient Functional Neutralization of Lethal Peptide Toxins in Vivo by Oligonucleotides. Sci Rep 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.L.; Gan, S.T.; Ho, B. Single-Stranded DNA Oligoaptamers: Molecular Recognition and LPS Antagonism Are Length- and Secondary Structure-Dependent. J Innate Immun 2008, 1, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Chen, Y.H.; Lennox, K.A.; Behlke, M.A.; Davidson, B.L. In Vivo SELEX for Identification of Brain-Penetrating Aptamers. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2013, 2, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, W.H.; Thiel, K.W.; Flenker, K.S.; Bair, T.; Dupuy, A.J.; Mc namara, J.O.; Miller, F.J. H. Giangrande, P. Cell-Internalization SELEX: Method for Identifying Cell- Internalizing RNA Aptamers for Delivering SiRNAs to Target Cells. Methods in Molecular Biology 2015, 1218, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leko, V.; Rosenberg, S.A. Identifying and Targeting Human Tumor Antigens for T Cell-Based Immunotherapy of Solid Tumors. [CrossRef]
- Bates, P.J.; Reyes-Reyes, E.M.; Malik, M.T.; Murphy, E.M.; O’toole, M.G.; Trent, J.O. G-Quadruplex Oligonucleotide AS1411 as a Cancer-Targeting Agent: Uses and Mechanisms ☆. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.T.; O, M.G.; Casson, L.K.; Thomas, S.D.; Bardi, G.T.; Merit Reyes-Reyes, E.; Ng, C.K.; Kang, K.A.; Bates, P.J. AS1411-Conjugated Gold Nanospheres and Their Potential for Breast Cancer Therapy. 6.
- Wheeler, L.A.; Trifonova, R.; Vrbanac, V.; Basar, E.; McKernan, S.; Xu, Z.; Seung, E.; Deruaz, M.; Dudek, T.; Einarsson, J.I.; et al. Inhibition of HIV Transmission in Human Cervicovaginal Explants and Humanized Mice Using CD4 Aptamer-SiRNA Chimeras. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2011, 121, 2401–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.M.; Xiao, Y.; Soh, H.T. Selection Is More Intelligent than Design: Improving the Affinity of a Bivalent Ligand through Directed Evolution. [CrossRef]
- Chi Wong, B.; Shahid, U.; Siew Tan, H. Ribozymes as Therapeutic Agents against Infectious Diseases. In RNA Therapeutics - History, Design, Manufacturing, and Applications; IntechOpen, 2023.
- Thomas, I.B.K.; Gaminda, K.A.P.; Jayasinghe, C.D.; Abeysinghe, D.T.; Senthilnithy, R. DNAzymes, Novel Therapeutic Agents in Cancer Therapy: A Review of Concepts to Applications. J Nucleic Acids 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




