Submitted:
20 May 2024
Posted:
20 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
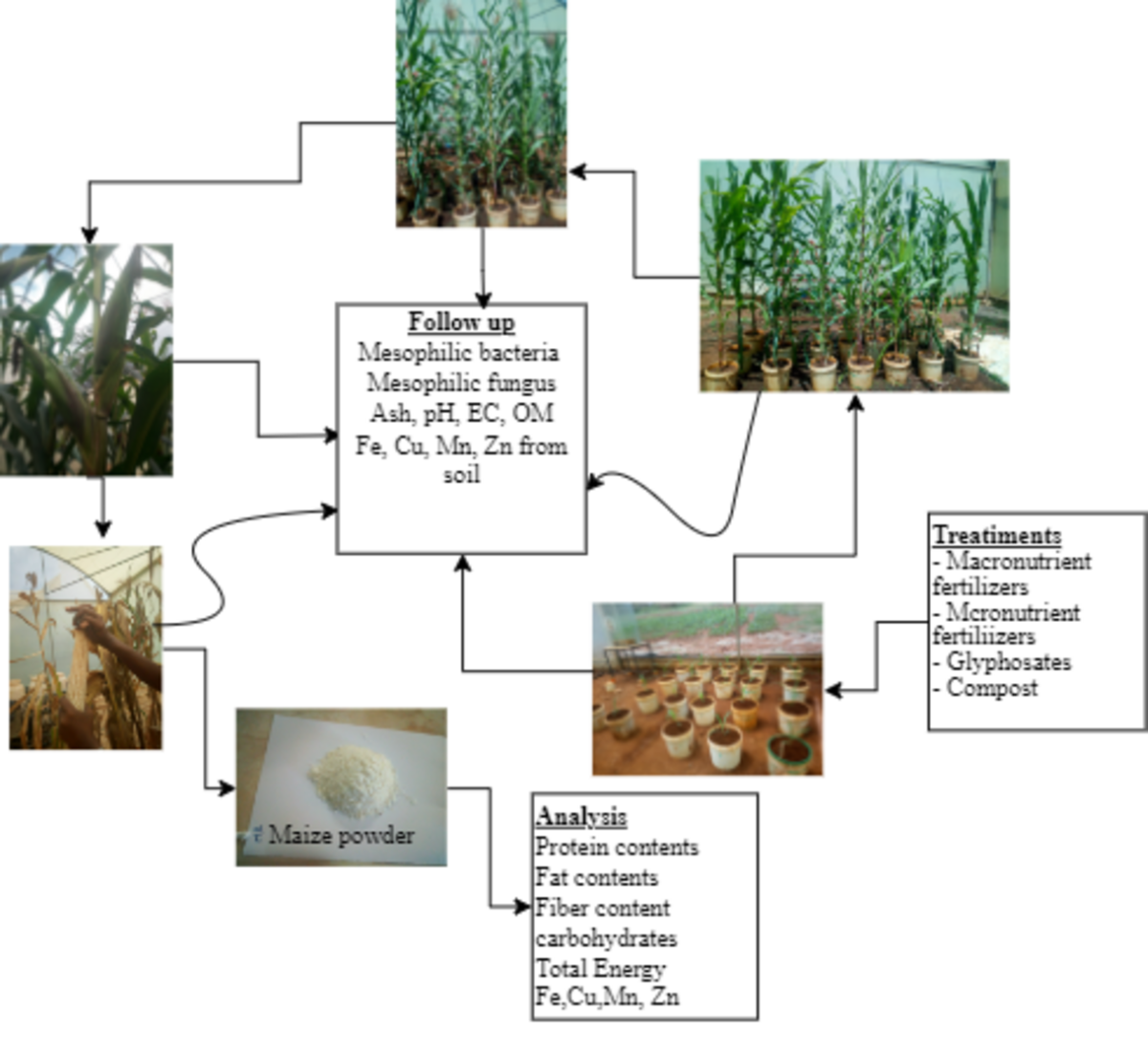
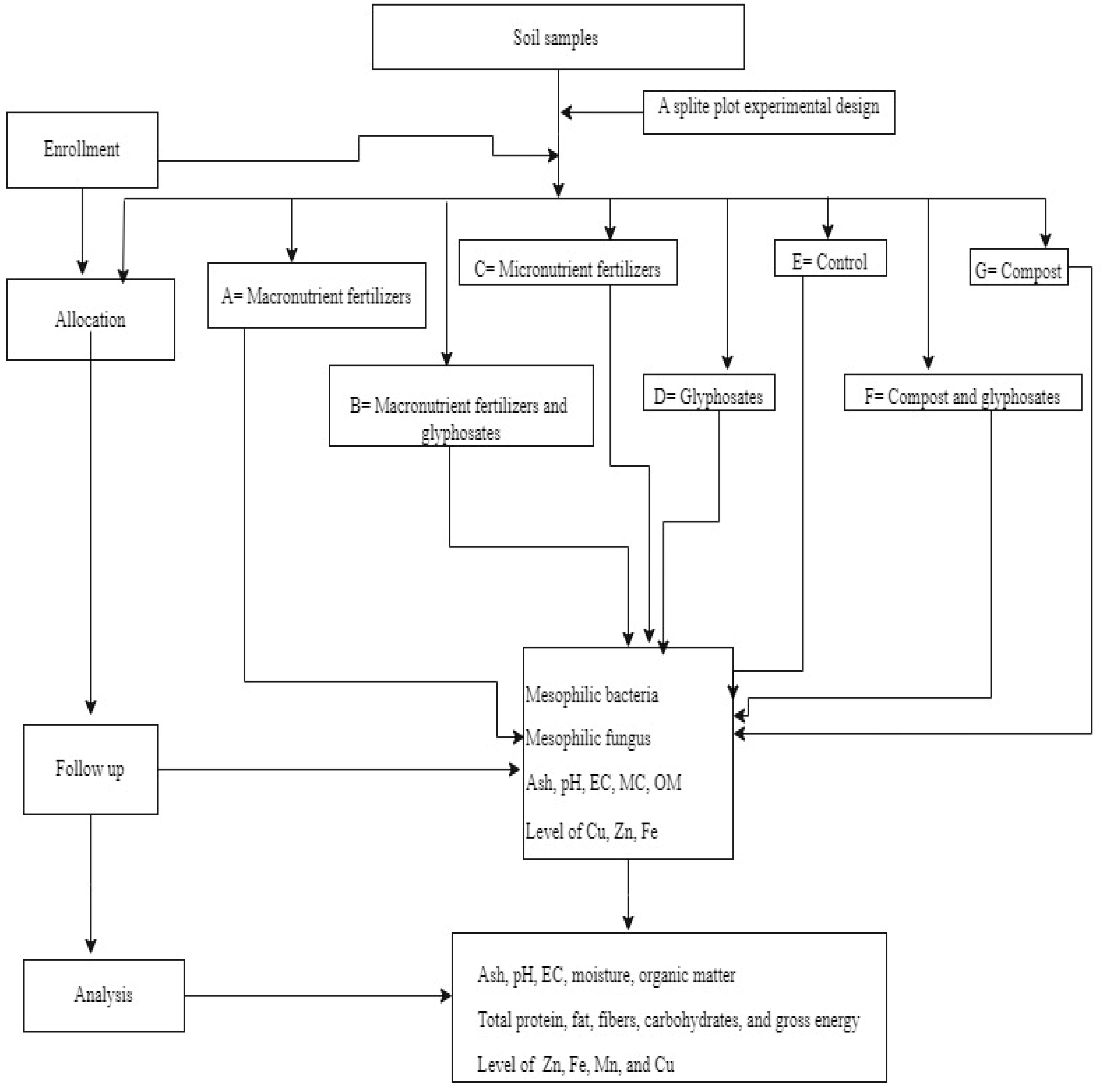
2.1. The Intervention Approach of the Study
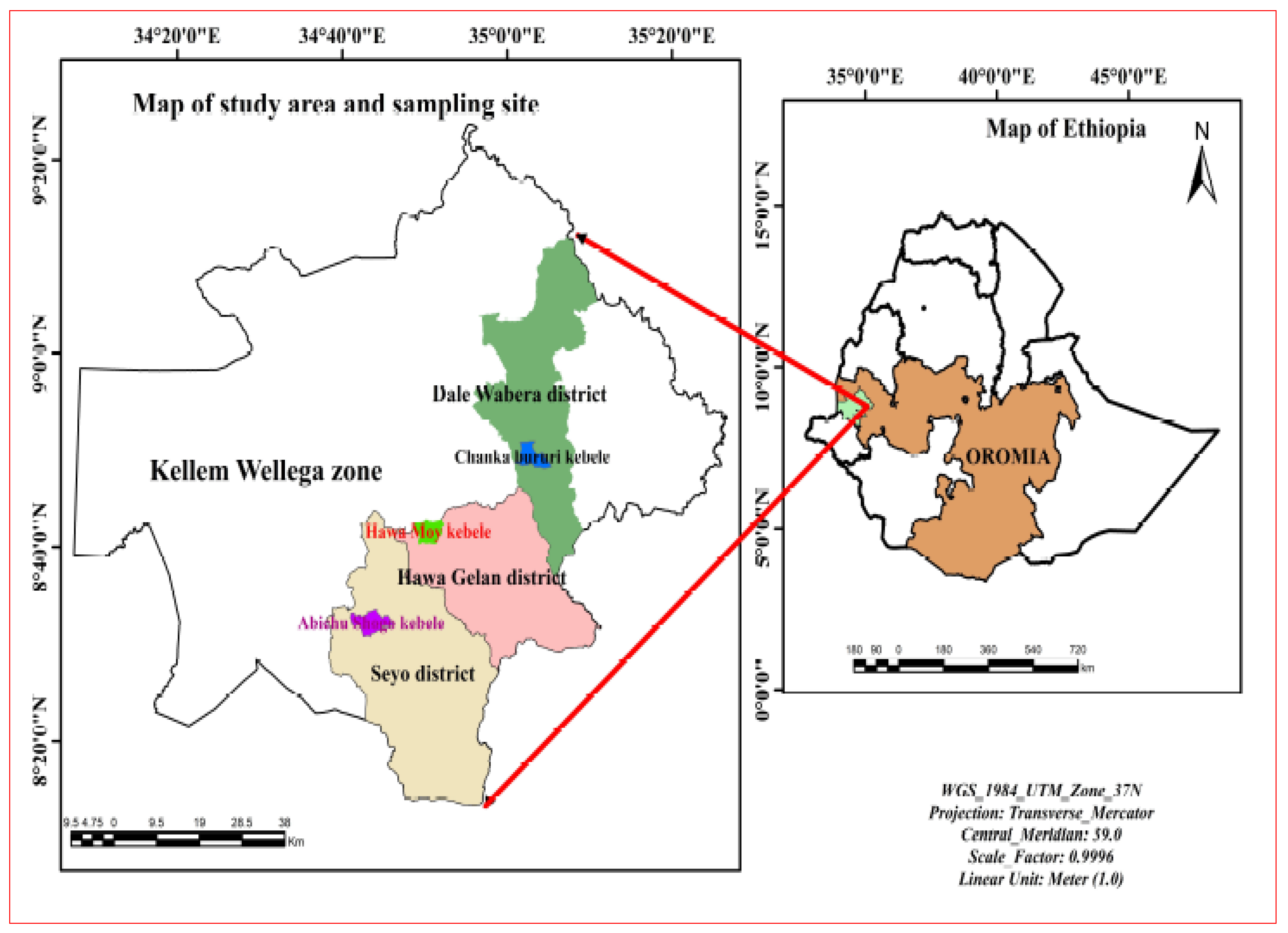
2.2. Study Setting
2.3. Sample Collection from Farming Sites
2.4. Experimental Design and Treatment
2.5. Preparation of Compost Samples
2.6. Moisture Content
2.7. Ash and Organic Matter
2.8. Determination of pH and Electrical Conductivity from Soil Samples
2.9. Determination of Micronutrients from Soil Samples
2.10. Determination of Total Mesophilic Bacteria and Fungi Counts in Soil Samples
2.11. Quantification and Quality Analysis of Harvested Maize
2.11.1. Sample Preparation for Proximate Composition
2.11.2. Crude Protein Content
2.11.3. Crude Fat Contents
2.11.4. Crude Fiber Contents
2.11.5. Total Carbohydrates and Energy Gross
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.1.1. Soil Moisture (MC), ash (AC), and Organic Matter (OM) Content
3.1.2. Electrical Conductivity (EC) and pH
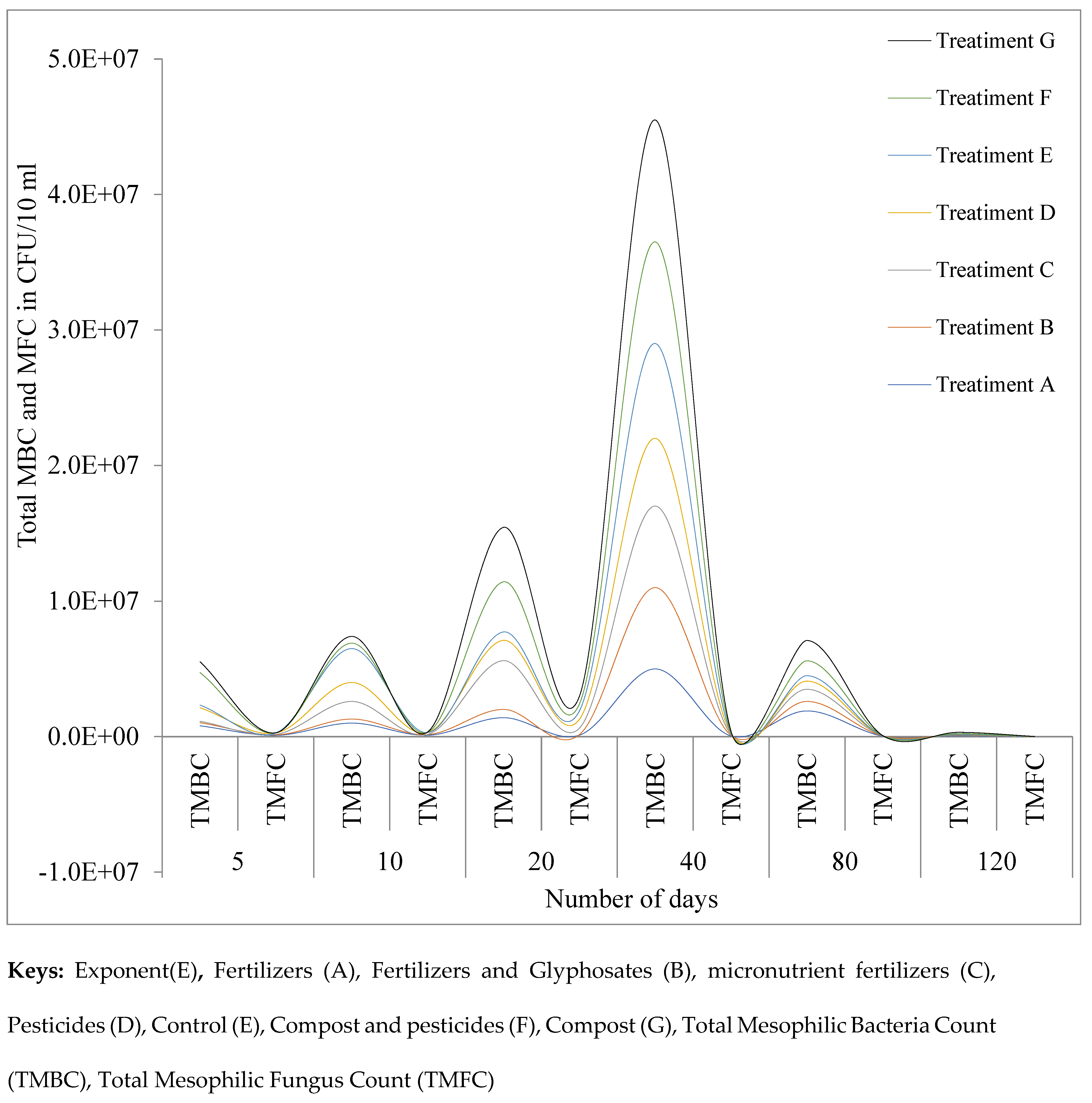
3.1.3. Total Mesophilic Bacterial Count (TMBC) and Fungus (TMFC)
3.1.4. Soil Micronutrient Level Analysed from Pot Experiment
3.2. Maize Yield Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abera Y: Kassa, S. Status of soil micronutrients in Ethiopian soils: a review. Journal of environment and earth science. 2017;7(4):85-90.
- Afata, T.N.; Mekonen, S.; Shekelifa, M.; Tucho, G.T. Prevalence of Pesticide Use and Occupational Exposure Among Small-Scale Farmers in Western Ethiopia. Environ. Heal. Insights 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husted, S.; Thomsen, M.U.; Mattsson, M.; Schjoerring, J.K. Influence of nitrogen and sulphur form on manganese acquisition by barley (shape Hordeum vulgare). Plant Soil 2005, 268, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogrzeba, M.; Rusinowski, S.; Sitko, K.; Krzyżak, J.; Skalska, A.; Małkowski, E.; Ciszek, D.; Werle, S.; McCalmont, J.P.; Mos, M.; et al. Relationships between soil parameters and physiological status of Miscanthus x giganteus cultivated on soil contaminated with trace elements under NPK fertilisation vs. microbial inoculation. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida SP, Behera BK, Raut MS, Panda MK, Bhattacharjee MS. MICRONUTRIENT DEFICIENCY: Newredmars Education Pvt Ltd; 2023.
- Afata, T.N.; Mekonen, S.; Tucho, G.T. Serum concentration of zinc, copper, iron, and its associated factors among pregnant women of small-scale farming in western Ethiopia. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Akash, S.; Jony, M.H.; alam, N.; Nowrin, F.T.; Rahman, M.; Rauf, A.; Thiruvengadam, M. Exploring the potential function of trace elements in human health: a therapeutic perspective. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2023, 478, 2141–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatav HS, Sharma LD, Sadhukhan R, Singh SK, Singh S, Rajput VD, et al. An overview of micronutrients: prospects and implication in crop production. Plant micronutrients: deficiency and toxicity management. 2020:1-30.
- Kumar D, Patel K, Ramani V, Shukla A, Meena RS. Management of micronutrients in soil for the nutritional security. Nutrient Dynamics for Sustainable Crop Production. 2020:103-34.
- Losak, T.; Hlusek, J.; Martinec, J.; Jandak, J.; Szostkova, M.; Filipcik, R.; Manasek, J.; Prokes, K.; Peterka, J.; Varga, L.; et al. Nitrogen fertilization does not affect micronutrient uptake in grain maize (Zea maysL.). Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B — Soil Plant Sci. 2011, 61, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi KD, Beena S, Abraham C. Effect of 2, 4-D residues on soil microflora. Journal of Tropical Agriculture. 2008;46:76-8.
- Paul N, Sur P, Das D, Mukherjee D. Effect of pesticides on available cationic micronutrients along with viable bacteria and fungi in soil. African Journal of Microbiology Research. 2013;7(22):2764-9.
- Kepler RM, Epp Schmidt DJ, Yarwood SA, Cavigelli MA, Reddy KN, Duke SO, et al. Soil Microbial Communities in Diverse Agroecosystems Exposed to the Herbicide Glyphosate. 2020;86(5).
- Dill GM, Sammons RD, Feng PC, Kohn F, Kretzmer K, Mehrsheikh A, et al. Glyphosate: discovery, development, applications, and properties. Glyphosate resistance in crops and weeds: history, development, and management. 2010;1:344.
- Imfeld, G.; Vuilleumier, S. Measuring the effects of pesticides on bacterial communities in soil: A critical review. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2012, 49, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davet, P. Microbial ecology of soil and plant growth: CRC Press; 2004.
- Tripathi S, Srivastava P, Devi RS, Bhadouria R. Chapter 2 - Influence of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides on soil health and soil microbiology. In: Prasad MNV, editor. Agrochemicals Detection, Treatment and Remediation: Butterworth-Heinemann; 2020. p. 25-54.
- Prashar P, Shah S. Impact of fertilizers and pesticides on soil microflora in agriculture. Sustainable Agriculture Reviews: Volume 19. 2016:331-61.
- Lane, M.; Lorenz, N.; Saxena, J.; Ramsier, C.; Dick, R.P. Microbial activity, community structure and potassium dynamics in rhizosphere soil of soybean plants treated with glyphosate. Pedobiologia 2012, 55, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, M.; Shi, H.; Liu, N.; Bai, H. Influence of long-term fertilization on soil microbial biomass, dehydrogenase activity, and bacterial and fungal community structure in a brown soil of northeast China. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 65, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, T. Effects of continuous cropping Jiashi muskmelon on rhizosphere microbial community. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1086334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, K. Minerals and trace elements in the soil-plant-animal continuum in Ethiopia: A review. African Journal of Food, Agriculture, Nutrition and Development. 2016;16(4):11219-35.
- Laekemariam F, Kibret K, Mamo T, Gebrekidan H. Soil–plant nutrient status and their relations in maize-growing fields of Wolaita Zone, southern Ethiopia. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis. 2016;47(11):1343-56.
- Laekemariam, F.; Kibret, K. Explaining Soil Fertility Heterogeneity in Smallholder Farms of Southern Ethiopia. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2020, 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PSA. Summary and statistical report of the 2007 population and housing census. Population size by age and sex. 2008.
- EDHS. Central Statistical Agency (CSA) [Ethiopia] and ICF. 2016. Ethiopia Demographic and Health Survey 2016.
- Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, and Rockville, Maryland, USA: CSA and ICF.. 2016:1-551.
- Gonfa R, Gadisa T, Habitamu T. The diversity, abundance and habitat association of medium and large-sized mammals of Dati Wolel National Park, Western Ethiopia. International journal of Biodiversity and conservation. 2015;7(2):112-8.
- Smith, KM. How to Build, Maintain, and Use a Compost System: Secrets and Techniques You Need to Know to Grow the Best Vegetables: Atlantic Publishing Company; 2011.
- M.P.C.A. How do I use my compost? 2013.
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis. 2005;18th Edition.
- Carter MR, Gregorich EG. Soil sampling and methods of analysis: CRC press; 2007.
- Akinyele, I.; Shokunbi, O. Comparative analysis of dry ashing and wet digestion methods for the determination of trace and heavy metals in food samples. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 682–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramer DaS, E.L. . Experimental Soil Microbiology. Burgess Publishing Co, Minneapolis. 1965.
- Thornton, H.G. ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF A STANDARDISED AGAR MEDIUM FOR COUNTING SOIL BACTERIA, WITH ESPECIAL REGARD TO THE REPRESSION OF SPREADING COLONIES1. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1922, 9, 241–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.P. Use of acid, rose bengal, and streptomycin in the plate method for estimating soil fungi. Soil Sci. 1950, 69, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO, editor Food energy-methods of analysis and conversion factors. Report of a technical workshop [Google Scholar]; 2003; Rome, taly.
- Aulakh, C.S.; Sharma, S.; Thakur, M.; Kaur, P. A review of the influences of organic farming on soil quality, crop productivity and produce quality. J. Plant Nutr. 2022, 45, 1884–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somenahally, A.C.; Hollister, E.B.; Loeppert, R.H.; Yan, W.; Gentry, T.J. Microbial communities in rice rhizosphere altered by intermittent and continuous flooding in fields with long-term arsenic application. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1220–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onet, A.; Dincă, L.C.; Grenni, P.; Laslo, V.; Teusdea, A.C.; Vasile, D.L.; Enescu, R.E.; Crisan, V.E. Biological indicators for evaluating soil quality improvement in a soil degraded by erosion processes. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2393–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, A.; DeBruyn, J.; Allen, F.; Radosevich, M.; Owens, P. Microbial community structure is affected by cropping sequences and poultry litter under long-term no-tillage. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 114, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannino, F.; Gianfreda, L. Pesticide influence on soil enzymatic activities. Chemosphere 2001, 45, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govedarica MM, Jarak MN, Milošević NA, Đurić S, Đorđević S, Najdenovska O, et al. Herbicides and microbiological activity in soil under the corn. Letopis naučnih radova Poljoprivrednog fakulteta. 2002;26(1):24-31.
- Wolmarans, K. The effect of glyphosate and glyphosate-resistant maize and soyabeans on soil micro-organisms and the incedence of disease: University of the Free State; 2013.
- Srinivasulu, M.; Ortiz, D.R. Effect of Pesticides on Bacterial and Fungal Populations in Ecuadorian Tomato Cultivated Soils. Environ. Process. 2017, 4, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baboo M, Pasayat M, Samal A, Kujur M, Maharana J, Patel AK. Effect of four herbicides on soil organic carbon, microbial biomass-c, enzyme activity and microbial populations in agricultural soil. Int J Res Environ Sci Te. 2013;3:100-12.
- Chen, F.; Dixon, R.A. Lignin modification improves fermentable sugar yields for biofuel production. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.K.; Ekielski, A. The Self-Assembly of Lignin and Its Application in Nanoparticle Synthesis: A Short Review. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Siddique, T.; Saleem, M.; Arshad, M.; Khalid, A. Impact of pesticides on soil microbial diversity, enzymes, and biochemical reactions. Adv. Agron. 2009, 102, 159–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Kleber, M. The contentious nature of soil organic matter. Nature 2015, 528, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, S.; Concheri, G.; Pizzeghello, D.; Sturaro, A.; Rella, R.; Parvoli, G. Soil organic matter mobilization by root exudates. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassink, J. The capacity of soils to preserve organic C and N by their association with clay and silt particles. Plant Soil 1997, 191, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ramady, H.; Brevik, E.C.; Abowaly, M.; Ali, R.; Moghanm, F.S.; Gharib, M.S.; Mansour, H.; Fawzy, Z.F.; Prokisch, J. Soil Degradation under a Changing Climate: Management from Traditional to Nano-Approaches. Egypt. J. Soil Sci. 2024, 64, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson DW, Sommers LE. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. Methods of soil analysis: Part 3 Chemical methods. 1996;5:961-1010.
- El Bey N, Maazoun AM, Nahdi O, Krima NB, Aounallah M, Mahdy HA, et al. Department of Horticulture & Postharvest Technology, Institute of Agriculture, Visva-Bharati, Sriniketan-731236, West Bengal. Corresponding e-mail: debprld@ yahoo. com. Journal of Applied Horticulture. 2024;26:1.
- Lane, M.; Lorenz, N.; Saxena, J.; Ramsier, C.; Dick, R.P. The effect of glyphosate on soil microbial activity, microbial community structure, and soil potassium. Pedobiologia 2012, 55, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui H, Benjamin JG. Impacts of soil organic carbon on soil physical behavior. Quantifying and modeling soil structure dynamics. 2013;3:11-40.
- Baweja P, Kumar S, Kumar G. Fertilizers and pesticides: Their impact on soil health and environment. Soil health. 2020:265-85.
- Sebiomo A, Ogundero V, Bankole S. Effect of four herbicides on microbial population, soil organic matter and dehydrogenase activity. African journal of biotechnology. 2011;10(5):770-8.
- Shu, X.; He, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xia, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Chu, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Organic amendments enhance soil microbial diversity, microbial functionality and crop yields: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 829, 154627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beek, C.L. (.; Elias, E.; Selassie, Y.G.; Gebresamuel, G.; Tsegaye, A.; Hundessa, F.; Tolla, M.; Mamuye, M.; Yemane, G.; Mengistu, S. Soil organic matter depletion as a major threat to agricultural intensification in the highlands of Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 11, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bàrberi, P. Weed management in organic agriculture: are we addressing the right issues? Weed research. 2002;42(3):177-93.
- Barłóg, P.; Grzebisz, W.; Łukowiak, R. Fertilizers and Fertilization Strategies Mitigating Soil Factors Constraining Efficiency of Nitrogen in Plant Production. Plants 2022, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz JE, Mao MK, Sikorski JA. Glyphosate: a unique global herbicide1997.
- Khan, Z.I.; Hussain, A.; Ashraf, M.; McDowell, L.R. Mineral Status of Soils and Forages in Southwestern Punjab-Pakistan: Micro-minerals. Asian-Australasian J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 19, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, BK. Drying and storage of cereal grains: John Wiley & Sons; 2016.
- Ullah, I.; Ali, M.; Farooqi, A. Chemical and Nutritional Properties of Some Maize (Zea mays L.) Varieties Grown in NWFP, Pakistan. Pak. J. Nutr. 2010, 9, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunyemi, A.M.; Otegbayo, B.O.; Fagbenro, J.A. Effects of NPK and biochar fertilized soil on the proximate composition and mineral evaluation of maize flour. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2308–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizhe T, ALONGE SO, IORTSUUN DN, ADEKPE DI, BATTA K. Evaluation of the effect of nicosulfuron at different times of application on the chemical component of maize (Zea mays). Nusantara Bioscience. 2022;14(1).
- Sagbo, F.S.; Aïssi, M.V.; Hounkpatin, W.A.; Houedo, C.; Dansi, A.; Soumanou, M.M. Physicochemical and pasting properties of some local and improved maize varieties cultivated in Benin. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2017, 11, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adugna, G. A review on impact of compost on soil properties, water use and crop productivity. Academic Research Journal of Agricultural Science and Research. 2016;4(3):93-104.
- Ray, K.; Banerjee, H.; Dutta, S.; Sarkar, S.; Murrell, T.S.; Singh, V.K.; Majumdar, K. Macronutrient Management Effects on Nutrient Accumulation, Partitioning, Remobilization, and Yield of Hybrid Maize Cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Restoring Soil Quality to Mitigate Soil Degradation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5875–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyisi IS, Umoh V, Whong C, Alabi O, Abdullahi I. Chemical and nutritional values of maize and maize products obtained from selected markets in Kaduna. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Allied Sciences. 2014;11(2):2106-13.
- Adegbite JA, Lajide L, Aladesanwa RD, Aiyesanmi AF, Abiodun OA, Adepeju AB, et al. Effect of herbicide application on residue content and nutritional composition of maize from a pilot maize farm. American Journal of Agricultural Science. 2016;3(3):35-9.
- Ndukwe OK, Edeoga H, Omosun G. Varietal differences in some nutritional composition of ten maize (Zea mays L.) varieties grown in Nigeria. International journal of academic research and reflection. 2015;3(5):1-11.
- Mohajan, H.K. Food Insecurity and Malnutrition of Africa: A Combined Attempt Can Reduce Them. J. Econ. Dev. Environ. People 2022, 11, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeder, P.; Fliessbach, A.; Dubois, D.; Gunst, L.; Fried, P.; Niggli, U. Soil Fertility and Biodiversity in Organic Farming. Science 2002, 296, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahrurrozi; Muktamar, Z. ; Dwatmadji; Setyowati, N.; Sudjatmiko, S.; Chozin, M. Growth and Yield Responses of Three Sweet Corn (Zea mays L. var. Saccharata) Varieties to Local-based Liquid Organic Fertilizer. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2016, 6, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouis, H.E.; Hotz, C.; McClafferty, B.; Meenakshi, J.V.; Pfeiffer, W.H. Biofortification: A New Tool to Reduce Micronutrient Malnutrition. Food Nutr. Bull. 2011, 32, S31–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- xu X, Wang L, Sun D, Luo L, Banson K. The Impact of Climate Change on Yield Potential of Maize across China. International Journal of Plant Production. 2017;11.
- Kabir, S.; Das, A.; Rahman, M.; Singh, M.; Morshed, M.; Marma, A. Effect of genotype on proximate composition and biological yield of maize (Zea mays L.). Arch. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2019, 4, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, G.S.; Buerkert, A.; Hoffmann, E.M.; Schlecht, E.; Von Cramon-Taubadel, S.; Tscharntke, T. Implications of agricultural transitions and urbanization for ecosystem services. Nature 2014, 515, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar K, Dey P, Tewatia R. Current nutrient management approaches. Indian J Fertil. 2014;10:14-27.
- Abadía, J.; Vázquez, S.; Rellán-Álvarez, R.; El-Jendoubi, H.; Abadía, A.; Álvarez-Fernández, A.; López-Millán, A.F. Towards a knowledge-based correction of iron chlorosis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 49, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, H.A.; Mukherjee, A.B. Trace Elements from Soil to Human; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; ISBN 978-3-540-32714-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatments | Added fertilizers |
|---|---|
| A | Macronutrient fertilizers |
| B | Macronutrient fertilizers and glyphosates |
| C | Micronutrient’s fertilizers |
| D | Glyphosates |
| E | Control (free of any treatments) |
| F | Compost and glyphosates |
| G | Compost |
| Macro and micro fertilizers | Source | rate kg/ha | required for 16kg soil (each pot) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | NH4NO3 | 120 | 0.96 |
| P | P2O5 | 60 | 0.48 |
| K | K2O | 50 | 0.4 |
| Zn | ZnSO4.5H2O | 60 | 0.48 |
| Fe | FeSO4.7H2O | 15 | 0.12 |
| Cu | CuSO4.5H2O | 2 | 0.02 |
| Mn | MnSO4.H2O | 360 | 2.88 |
| sampling days | Parameters | Treatments | ||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | ||
| 5 | Moisture contents | 25.6 | 27.6 | 24.4 | 26.2 | 25.8 | 35.4 | 28.6 |
| Ash contents | 93.2 | 93.2 | 93 | 93.2 | 93 | 91.4 | 89.4 | |
| Organic matter | 6.8 | 6.8 | 7 | 6.8 | 7 | 8.6 | 10.6 | |
| 10 | Moisture contents | 18.8 | 26 | 25.4 | 22 | 21.8 | 23.8 | 23.6 |
| Ash contents | 89.2 | 87.6 | 91.2 | 91 | 91.2 | 91.2 | 85 | |
| Organic matter | 10.8 | 12.4 | 8.8 | 9 | 8.8 | 8.8 | 15 | |
| 20 | Moisture contents | 23 | 24.6 | 24 | 24.4 | 24.4 | 28.2 | 27.6 |
| Ash contents | 91.4 | 91.6 | 91.6 | 92 | 91.8 | 88.6 | 88.4 | |
| Organic matter | 8.6 | 8.4 | 8.4 | 8 | 8.2 | 11.4 | 11.6 | |
| 40 | Moisture contents | 24.51 | 21.34 | 22.57 | 25.1 | 23.55 | 27.06 | 23.21 |
| Ash contents | 91.74 | 91.7 | 91.88 | 92.16 | 92.02 | 89.02 | 89.48 | |
| Organic matter | 8.26 | 8.3 | 8.12 | 7.84 | 7.98 | 10.98 | 10.52 | |
| 80 | Moisture contents | 24.8 | 22.9 | 22.38 | 23.06 | 22.42 | 23.38 | 21.43 |
| Ash contents | 92.26 | 92.59 | 91.88 | 92.25 | 91.67 | 88.98 | 90.08 | |
| Organic matter | 7.74 | 7.41 | 8.12 | 7.75 | 8.33 | 11.02 | 9.92 | |
| 120 | Moisture contents | 17.69 | 23.1 | 20.2 | 24.97 | 15.22 | 18.81 | 16.75 |
| Ash contents | 91.05 | 91.61 | 92.4 | 90.95 | 90.91 | 87.72 | 89.51 | |
| Organic matter | 8.95 | 8.39 | 7.6 | 9.05 | 9.09 | 12.28 | 10.49 | |
| Sampling days | Parameters | Treatments | ||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | ||
|
5 |
pH | 5.32 | 5.45 | 5.72 | 6.21 | 6.28 | 5.95 | 6.55 |
| EC | 80.1 | 68.64 | 90.62 | 78.35 | 78.28 | 68.64 | 328.6 | |
|
10 |
pH | 5.58 | 5.63 | 5.4 | 6.2 | 6.04 | 6.5 | 6.51 |
| EC | 68.08 | 80.37 | 117.6 | 70.55 | 95.8 | 139.8 | 164.1 | |
| 20 | pH | 5.31 | 5.13 | 6.17 | 5.42 | 6.43 | 6.4 | 6.35 |
| EC | 125.5 | 115 | 194.3 | 138.9 | 140.2 | 242.1 | 260.1 | |
|
40 |
pH | 5.47 | 5.04 | 6.42 | 6.23 | 5.84 | 6.39 | 6.42 |
| EC | 83.52 | 78.44 | 89.95 | 86.3 | 93.15 | 152.2 | 152.2 | |
|
80 |
pH | 5.72 | 5.93 | 5.9 | 5.9 | 6.3 | 6.35 | 6.34 |
| EC | 37 | 39.1 | 41.9 | 48.1 | 50.1 | 123.1 | 120.4 | |
|
120 |
pH | 5.82 | 5.5 | 5.89 | 6.26 | 5.96 | 6.36 | 6.45 |
| EC | 91 | 69.7 | 55.9 | 47.9 | 36.2 | 120.4 | 79.7 | |
|
Sampling days |
Microbial Count |
Treatment (cfu/g) | ||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | ||
| 5 | TMBC | 8x105 | 2.3x105 | 1x105 | 1x106 | 2x105 | 2.4 x106 | 8 x105 |
| TMFC | 9.8 x104 | 3.8x104 | 3.5x104 | 1.07x105 | 1x103 | 7x103 | 5x103 | |
| 10 | TMBC | 1x106 | 3x105 | 1.3x106 | 1.4 x106 | 2.5x106 | 4x105 | 5x105 |
| TMFC | 1.02x105 | 5.2x104 | 9x103 | 1.32x105 | 3x103 | 2.9x104 | 2.1x104 | |
| 20 | TMBC | 1.4x106 | 6.1x105 | 3.6x106 | 1.5x106 | 6.2x105 | 3.7x106 | 4x106 |
| TMFC | 1.11 x105 | 4.2 x104 | 4.7x105 | 6.5x105 | 6.2x105 | 5.1x105 | 5.7x105 | |
| 40 | TMBC | 5x106 | 6x106 | 6x106 | 5x106 | 7x106 | 7.5x106 | 9x106 |
| TMFC | 5x104 | 4x104 | 5x104 | 7x104 | 2x104 | 8x104 | 7x104 | |
| 80 | TMBC | 1.9 x106 | 7x105 | 9x105 | 6x105 | 4x105 | 1.1x106 | 1.5x106 |
| TMFC | 4x104 | 2x104 | 3x103 | 2x103 | 1x103 | 6x103 | 4x103 | |
| 120 | TMBC | 7x104 | 4x104 | 1x104 | 4x104 | 2x104 | 5x104 | 9x104 |
| TMFC | 2x103 | 2x103 | 1x103 | 2x103 | 2x103 | 3 x103 | 5x103 | |
|
Sampling days |
Parameters | Treatments (PPM) | ||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | ||
| 5 | Fe | 20.38 | 22.99 | 222.49 | 23.57 | 226.56 | 223.94 | 218.85 |
| Mn | 60.95 | 65.69 | 210.67 | 64.22 | 244.62 | 208.76 | 238.18 | |
| Cu | 4.35 | 4.22 | 6.93 | 4.99 | 6.96 | 5.39 | 5.94 | |
| Zn | 2.18 | 2.81 | 23.41 | 2.4 | 25.58 | 30.81 | 29.8 | |
| 10 | Fe | 29.72 | 30.71 | 258.37 | 27.66 | 289.37 | 253.53 | 305.84 |
| Mn | 71.59 | 74.48 | 111.9 | 82.8 | 162.63 | 109.03 | 238.71 | |
| Cu | 4.12 | 3.36 | 2.89 | 1.1 | 1.75 | 3.26 | 4.02 | |
| Zn | 1.45 | 2.1 | 19.21 | 6.5 | 1.33 | 7.96 | 8.65 | |
| 20 | Fe | 23.1 | 21.54 | 300.79 | 20.52 | 257.68 | 273.21 | 270.37 |
| Mn | 121.48 | 204.4 | 127.91 | 88.38 | 114.01 | 222.73 | 170.17 | |
| Cu | 1.75 | 3.09 | 4.74 | 2.44 | 1.99 | 7.49 | 2.41 | |
| Zn | 4.84 | 16.75 | 1.12 | 1.06 | 5.79 | 20.86 | 22.75 | |
| 40 | Fe | 27.22 | 28.13 | 308.89 | 30.51 | 305.89 | 349.26 | 292.95 |
| Mn | 80.67 | 96.53 | 393.38 | 128.49 | 272.51 | 285.57 | 283.72 | |
| Cu | 3.06 | 5.18 | 7.25 | 7.04 | 5.81 | 7.9 | 2.3 | |
| Zn | 1.49 | 2.77 | 40.59 | 3.87 | 29.93 | 37.9 | 54.94 | |
| 80 | Fe | 22.18 | 20.18 | 234.93 | 23.86 | 227.94 | 232.11 | 247.46 |
| Mn | 103.34 | 82.67 | 288.48 | 121.83 | 220.87 | 223.59 | 260.21 | |
| Cu | 6.01 | 4.92 | 7.5 | 4.06 | 4.92 | 5.69 | 5.5 | |
| Zn | 1.53 | 1.74 | 24.67 | 1.11 | 24.36 | 24.12 | 23.63 | |
| 120 | Fe | 23.74 | 21.96 | 235.36 | 22.98 | 226.27 | 232.87 | 233.06 |
| Mn | 122.18 | 20.35 | 305.37 | 118.05 | 203.89 | 237.84 | 234.14 | |
| Cu | 4.79 | 3.71 | 7.06 | 5.05 | 3.61 | 6.04 | 4.79 | |
| Zn | 1.93 | 1.31 | 19.94 | 1.83 | 12.36 | 35.19 | 27.02 | |
| Overall mean | Fe | 24.39 | 24.25 | 260.14 | 24.85 | 255.62 | 255.49 | 261.42 |
| Mn | 93.37 | 90.69 | 239.62 | 100.63 | 203.09 | 214.59 | 237.52 | |
| Cu | 4.01 | 4.08 | 6.06 | 4.11 | 4.17 | 5.97 | 4.16 | |
| Zn | 2.24 | 4.58 | 21.49 | 2.8 | 16.56 | 26.14 | 27.8 | |
| Parameters | A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC(g/100g) | 14.41±0.15** | 12.76±0.05 | 13.23±0.25 | 12.63±0.1 | 14.2±0.25 | 13.25±0.1 | 12.265±0.13* |
| AC(g/100g) | 8.855±0.03 | 7.53±0.1 | 11.2±0.25** | 8.62±0.1 | 8.14±0.25 | 8.51±0.05 | 1.685±0.1* |
| PC(g/100g) | 9.48±0.25 | 11.29±0.8 | 8.569±0.25* | 9.688±0.3 | 10.57±0.3 | 10.825±0.7 | 11.42±0.8** |
| TFC(g/100g) | 2.675±0.1* | 2.21±0.2* | 3.21±0.1 | 3.977±0.01* | 3.22±0.1 | 3.48±0.2 | 3.535±0.13 |
| CF(g/100g) | 6.265±0.1* | 8.195±0.03* | 8.21±0.2 | 7.835±0.03 | 6.585±0.13 | 6.64±0.1 | 6.855±0.03 |
| CHO(g/100g) | 58.915±0.03 | 59.315±0.2 | 66.23±0.1** | 57.34±0.1* | 58.41±0.2 | 58.53±0.15 | 65.49±0.2 |
| Gross energy(kcal/100g) | 308.375±0.13* | 313.265±0.13 | 343.845±0.03 | 320.16±0.1 | 315.37±0.05 | 317.23±0.10 | 348.465±0.08** |
| Fe(ppm) | 48.165±0.1 | 79.495±0.03 | 78.545±0.03 | 19.9875±0.04* | 54.905±0.03 | 45.84±0.05 | 81.4650.13** |
| Mn(ppm) | 6.1±0.05 | 5.9575±0.05 | 9.845±0.03** | 3.13±0.1* | 4.375±0.13 | 6.0125±0.06 | 4.585±0.13 |
| Cu(ppm) | 1.17±0.2 | 0.775±0.01* | 1.425±0.2 | 1.24±0.25 | 0.9675±0.08 | 1.27±0.15 | 1.995±0.14** |
| Zn(ppm) | 38.5±0.05 | 37.095±0.08 | 48.375±0.1 | 36.615±0.08* | 38.435±0.1 | 37.8±0.05 | 50.855±0.03** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





