Submitted:
14 May 2024
Posted:
17 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
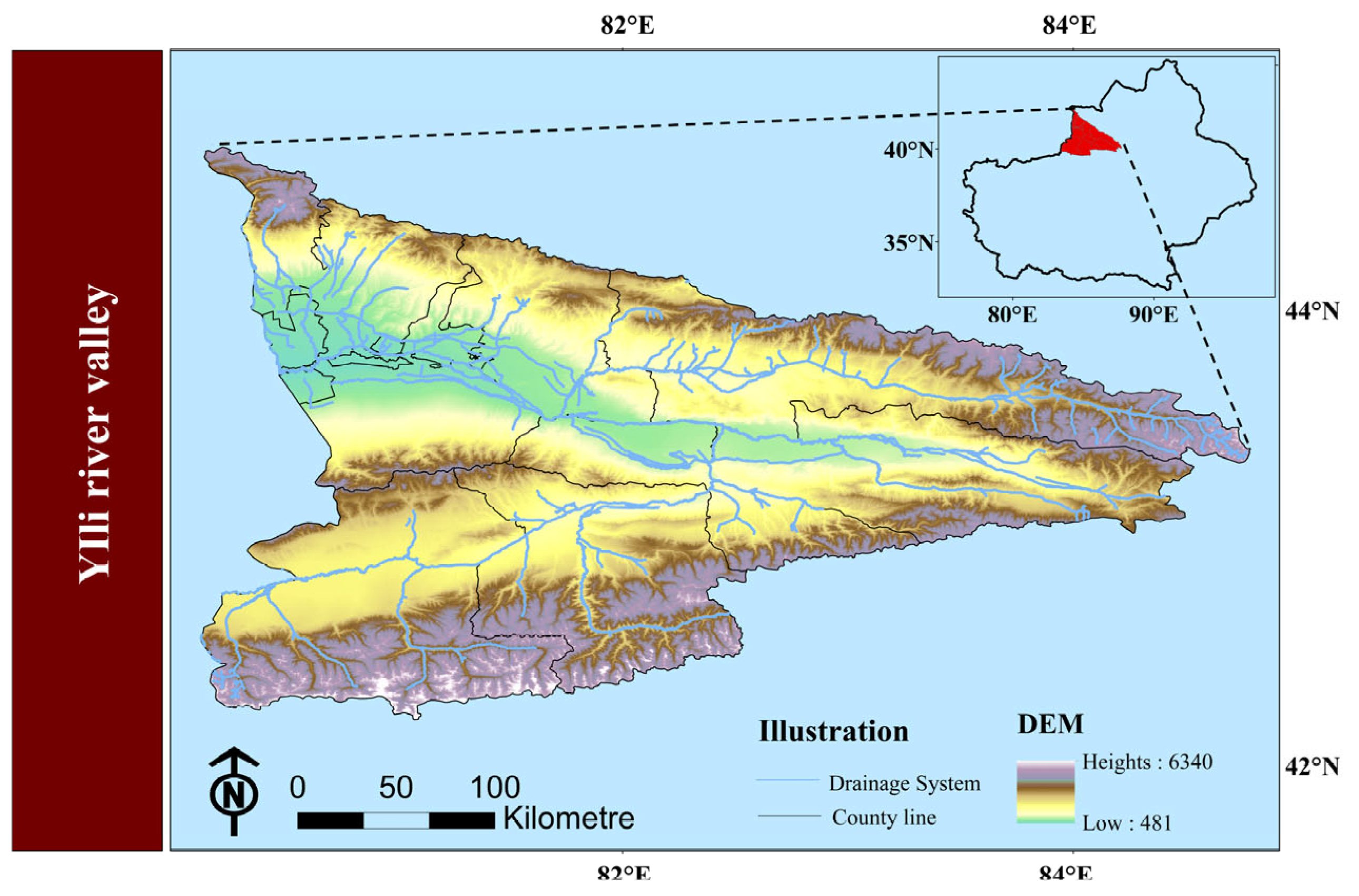
3. Overview of the Research Area
4. Methodology and Data Sources
4.1. Construction of the Indicator System
4.2. The Entropy Weight TOPSIS
4.3. Markov Chain
4.3.1. Traditional Markov chain
4.3.2. Spatial Markov Chain
4.4. Grey Relation Analysis
4.5. Data Sources
5. Results and Analysis
5.1. Characteristics of Spatio-Temporal Differentiation Of Tourism Economic Toughness Level in Yili River Valley
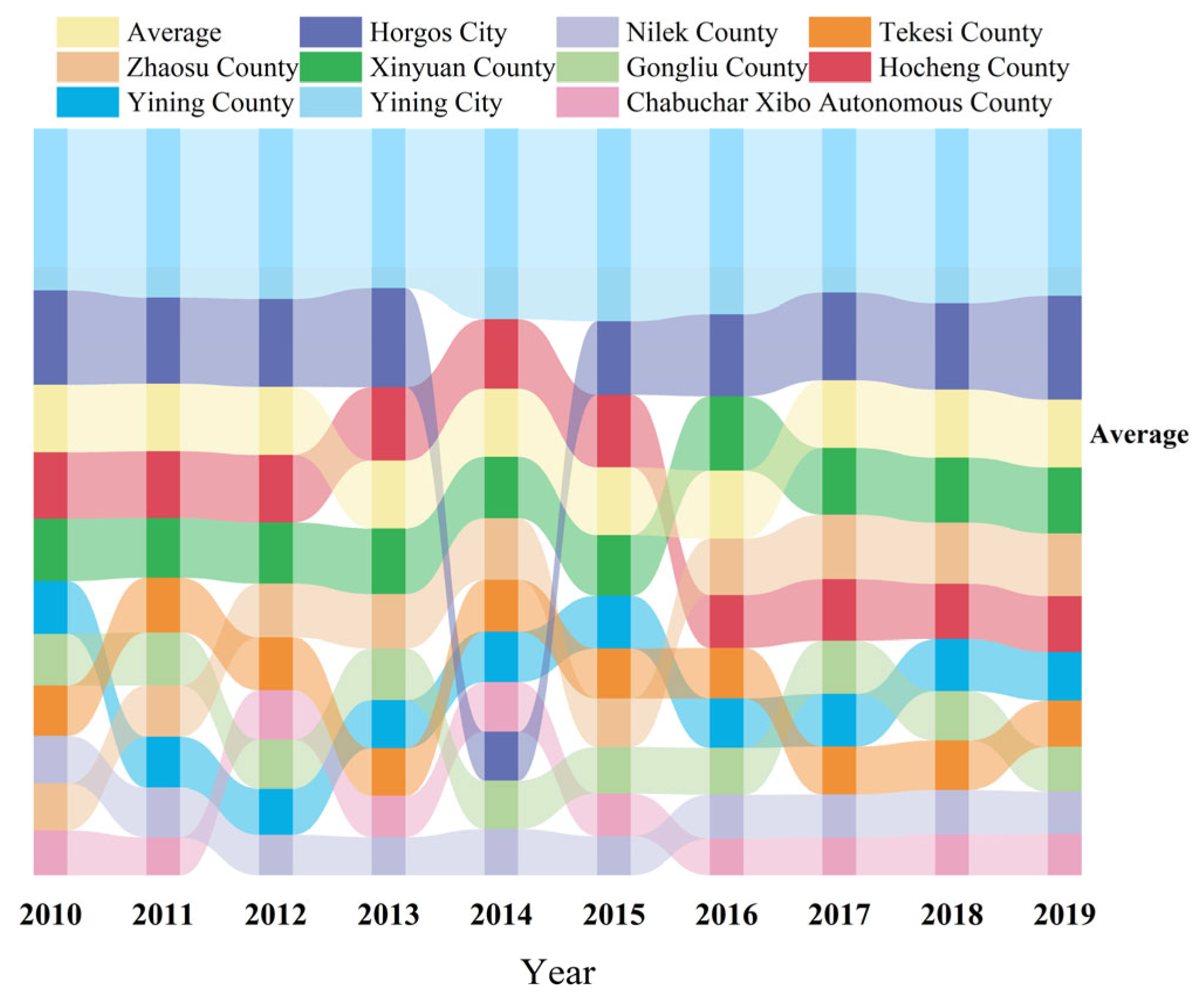
5.1.1. Time-Series Characteristics of Tourism Economic Resilience Level in the Yili River Valley
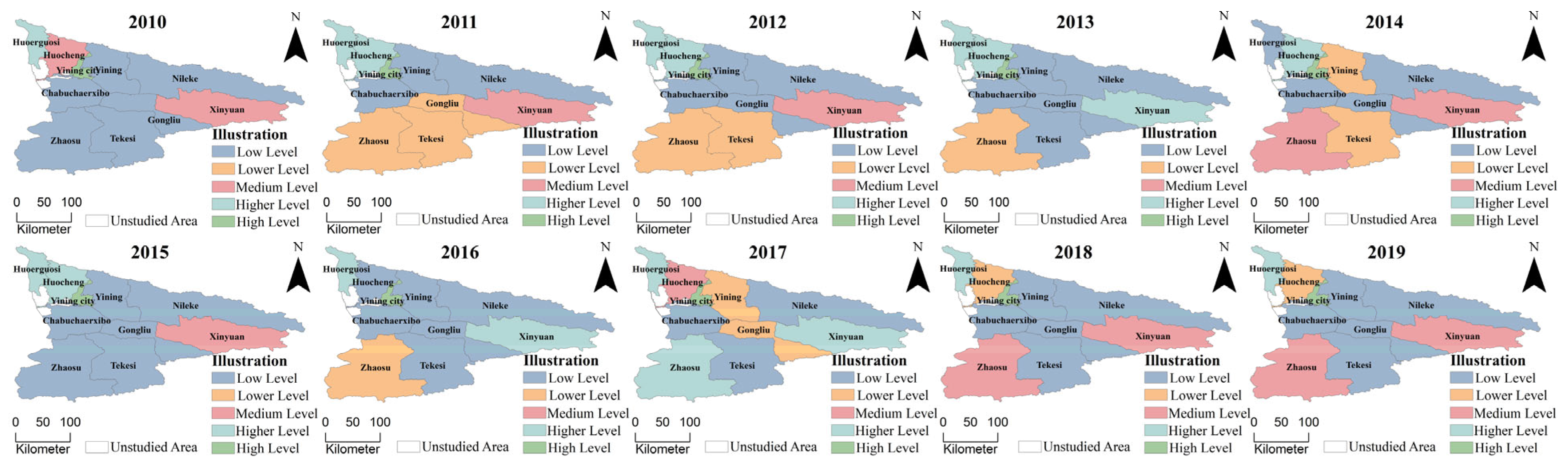
5.1.2. Spatial Characteristics of Tourism Economic Resilience Level in the Yili River Valley
5.2. Characteristics of the Spatio-Temporal Evolution of Tourism Economic Resilience in the Ili River Valley
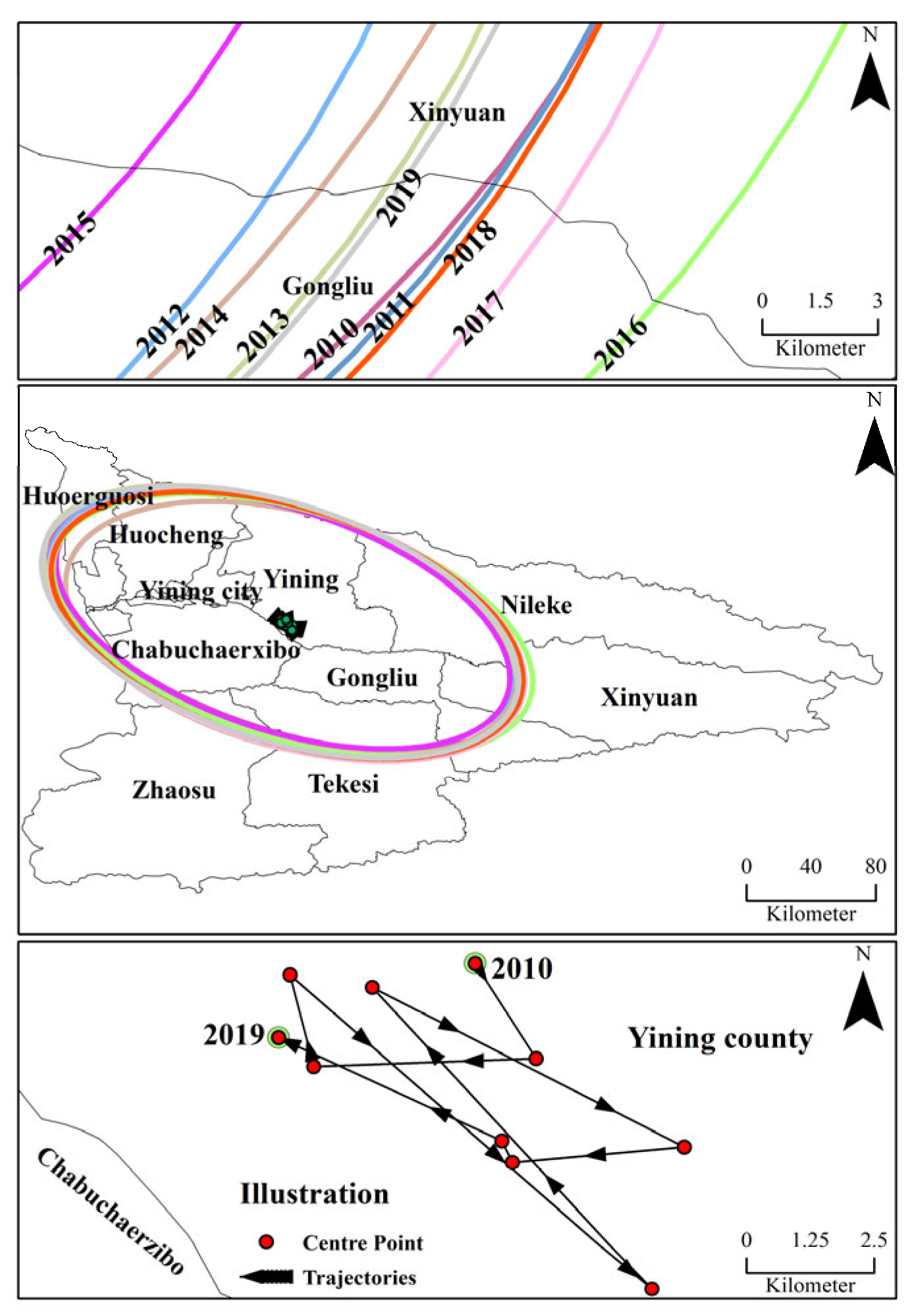
5.2.1. Center of Gravity Evolutionary Trajectory
5.2.2. Characterization of the Evolution of Spatial Dynamics
| t/t+1 | Low level | Lower level | Medium level | Higher level | High level | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low level | 0.834184 | 0.159439 | 0.003827 | 0.002551 | 0 | 784 |
| Lower level | 0.01455 | 0.792328 | 0.189153 | 0.003968 | 0 | 756 |
| Medium level | 0 | 0.016173 | 0.809973 | 0.173854 | 0 | 742 |
| Higher level | 0.001403 | 0.001403 | 0.019635 | 0.887798 | 0.089762 | 713 |
| High level | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.008451 | 0.991549 | 710 |
5.3. Analysis of the Drivers of the Spatial and Temporal Evolutionary Characteristics of Tourism Economic Resilience in the Yili River Valley
6. Conclusion and Discussion
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, C.-H.; Wang, W.-C.; Ou, S.-J. Impact of Comparative Climate Change Perceptions on Antecedents of Tourists’ Adaptation Intentions for a Coastal Destination in Taiwan. Journal of Sustainable Tourism 2022, 30, 69–88. [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.; Hall, C.M.; Gössling, S. Global Tourism Vulnerability to Climate Change. Annals of Tourism Research 2019, 77, 49–61. [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Pratt, S.A. Tourism’s Vulnerability and Resilience to Terrorism. Tourism Management 2017, 60, 404–417. [CrossRef]
- Santana-Gallego, M.; Fourie, J. Tourism Falls Apart: How Insecurity Affects African Tourism. Tourism Economics 2022, 28, 995–1008. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z.; Zhang X. Spatio-temporal Differences and Influencing Factors of Resilience of Tourism Svstem in the Yelow River Basin. Geography and Geo-Information Science 2023, 39, 112–121.
- Sun Y.; Song Y. Sustainable tourism development from a resilience perspective. 旅游学刊 2021, 36, 8–10. [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and Stability of Ecological Systems. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 1973, 4, 1–23. [CrossRef]
- Martin, R. Regional Economic Resilience, Hysteresis and Recessionary Shocks. Journal of Economic Geography 2012, 12, 1–32. [CrossRef]
- Sun J.; Sun X. Research Progress of Regional Economic Resilience and Exploration of Its Application in China. Economic Geography 2017, 37, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Sunley, P. On the Notion of Regional Economic Resilience: Conceptualization and Explanation. Journal of Economic Geography 2015, 15, 1–42.
- Briguglio, L.; Cordina, G.; Farrugia, N.; Vella, S. Economic Vulnerability and Resilience : Concepts and Measurements. Oxford Development Studies 2009, 37, 229–247. [CrossRef]
- Sheng Y.; Tan Z.; Li Q.; Xu L. Can the digital economy promote the resilience of the tourism economy in the Yellow River Basin? Arid Land Geography 2023, 46, 1704–1713.
- Wang Y.; Gao J. Shocks of 2019-nCoV,Economic Resilience and China’s High Quality Development. Business and Management Journal 2020, 42, 5–17. [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Xu, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Tourism Economic Resilience under the Impact of COVID-19—A Case Study of Coastal Cities in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16668. [CrossRef]
- Wang Q.; Zhao L.; Yu W.; Jia J. Spatial-Temporal Evolution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Resilience of Tourism Economic System in China. Geography and Geo-Information Science 2020, 36, 113–118.
- Zhang, P.; Huang, Y.; Pan, S.; Chen, W.; Zhong, H.; Xu, N.; Zhong, M. Does Resilience Exist in China’s Tourism Economy? From the Perspectives of Resistance and Recoverability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10641–10641. [CrossRef]
- Sun H.; Wang Y. Integration research on tourism resources in Baicheng, Xinjiang-YiLi Valley as an exampale. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment 2009, 23, 195–200.
- Ding, C.; Gao, X.; Xie, Z. Analysing the Differential Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Resilience of the Tourism Economy: A Case Study of the Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration in China. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 2024, 102, 104255. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yu, H.; Xu, L.; Guo, W.; Shen, M. Synergistic Relationship or Not? Understanding the Resilience and Efficiency of the Tourism Economy: Evidence from Hainan Province, China. Environ Dev Sustain 2024, 26, 3793–3817. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, S.; Chen, X.; Lei, Z.; Zhou, X. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Resilience of Tourism Environmental Systems in the Yangtze River Economic Belt of China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10527. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhu, G.; Qu, Z.; Ma, G. Earthquake and Tourism Destination Resilience from the Perspective of Regional Economic Resilience. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7766. [CrossRef]
- Hyun, K.; David W, M. Considering Disaster Vulnerability and Resiliency: The Case of Hurricane Effects on Tourism-Based Economies. The Annals of regional science 2015, 54, 945–971.
- Cutter, S.L.; Ash, K.D.; Emrich, C.T. The Geographies of Community Disaster Resilience. Global Environmental Change 2014, 29, 65–77.
- Berrouet, L.M.; Machado, J.; Villegas-Palacio, C. Vulnerability of Socio—Ecological Systems: A Conceptual Framework. Ecological Indicators 2018, C, 632–647. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, J. Is Tourism Development a Catalyst of Economic Recovery Following Natural Disaster? An Analysis of Economic Resilience and Spatial Variability. Current Issues in Tourism 2020, 23, 2602–2623. [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.S.; Rai, S.; Singh, N.K. Organizational Resilience and Social-Economic Sustainability: COVID-19 Perspective. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 12006–12023. [CrossRef]
- Cai C.; Tang J.; He Q. Research on the Relationship Between Tourism Economic Resilience and Tourism Development Quality in China. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University 2024, 47, 42–53.
- Lounis, Z.; McAllister, T.P. Risk-Based Decision Making for Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure Systems. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 142, F4016005. [CrossRef]
- Mononen, L.; Auvinen, A.-P.; Ahokumpu, A.-L.; Ronka, M.; Aarras, N.; Tolvanen, H.; Kamppinen, M.; Viirret, E.; Kumpula, T.; Vihervaara, P. National Ecosystem Service Indicators: Measures of Social-Ecological Sustainability. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 27–37. [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Jiang, R.; Yang, C.; Zhang, F.; Su, M.; Liao, Q. Establishing an Ecological Vulnerability Assessment Indicator System for Spatial Recognition and Management of Ecologically Vulnerable Areas in Highly Urbanized Regions: A Case Study of Shenzhen, China. Ecological Indicators 2016, C, 540–547. [CrossRef]
- He X.; Ren D.; XU H. The Impact of Regional Tourism Industry Agglomeration on Resilience of Tourism Economy and its Spatial Effect: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University 2024, 47, 54–64.
- Shi X.; Li L.; Tao Z.; Lai Z.; Li T. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of urban ecotourism development level in the Yangtze River Delta. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2024, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Wang S.; Gao S.; Huang Y.; Shi C. Spatio-temporal evolution and trend prediction of urban carbon emission performance in China based on super-efficiency SBM model. Acta Geographica Sinica 2020, 75, 1316–1330.
- Zeng G.; Shang Y.; Si Y. The convergent evolution of China’s regional economic development models. 地理研究 2015, 34, 2005–2020.
- Wu, Y.; Xie, Q.; Mu, C. Sensitivity Analysis of Factors Influencing the Blast Resistance of Reinforced Concrete Columns Based on Grey Relation Degree. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12285. [CrossRef]
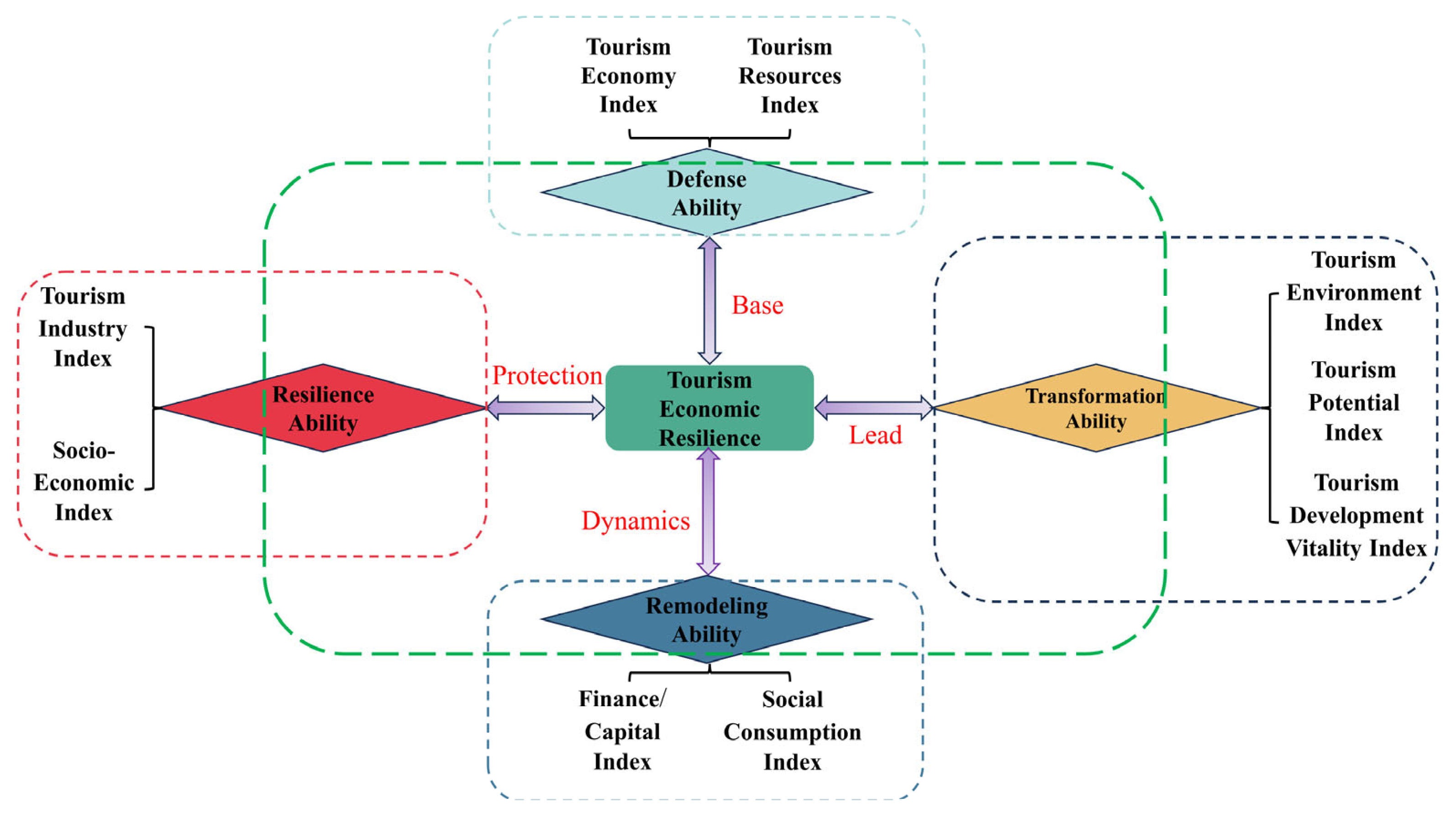
| Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators | Tertiary Indicators | Unit | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Defense Ability | Tourism Economy Index |
Tourism Reception | ten thousand people |
0.048669 |
| Gross Tourism Income | 10K CNY | 0.057321 | ||
| GDP per capita | yuan | 0.04359 | ||
| Tourism Resources Index |
Number of A-grade scenic spots | pcs | 0.031395 | |
| Recovery Ability | Tourism Industry Index |
Number of travel agencies | pcs | 0.112212 |
| Number of rooms in star-rated hotels | pcs | 0.072538 | ||
| Socio-Economic Index | Night Lights | / | 0.119606 | |
| Value Added of Tertiary Industry |
billion | 0.07995 | ||
| Resident Population | ten thousand people | 0.022688 | ||
| Remodeling Ability | Finance/Capital Index | Investment in Social Fixed Assets |
10K CNY | 0.042493 |
| General Public Budget Expenditure |
10K CNY | 0.026415 | ||
| Social Consumption Index | Tertiary Industry Output Value as % of GDP | % | 0.03114 | |
| Total Retail Sales of Consumer Goods | 10K CNY | 0.057466 | ||
| Transformation Ability | Tourism Environment Index | NDVI | % | 0.017156 |
| Waste Gas Emission | Million Nm3 | 0.009544 | ||
| Wastewater Emission | ten thousand t | 0.012967 | ||
| Comprehensive utilisation rate of solid waste | % | 0.015342 | ||
| Tourism Potential Index | Number of students in secondary schools |
people | 0.027383 | |
| Number of employees in tertiary industry | ten thousand people |
0.050973 | ||
| Advanced industrial structure | % | 0.03508 | ||
| Urbanisation rate | % | 0.020962 | ||
| Tourism Development Vitality Index | Ratio of tourists to permanent residents | % | 0.06511 |
| Type of field | t/t+1 | Low level | Lower level | Medium level | Higher level | High level | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low level | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0.571429 | 0.428571 | 0 | 28 | |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0.009901 | 0.80198 | 0.188119 | 101 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.009501 | 0.990499 | 421 | |
| Lower level | 1 | 0.837209 | 0.139535 | 0 | 0.023256 | 0 | 43 |
| 2 | 0 | 0.842105 | 0.157895 | 0 | 0 | 38 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0 | 10 | |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Medium level | 1 | 0.917404 | 0.079646 | 0.00295 | 0 | 0 | 339 |
| 2 | 0.021505 | 0.892473 | 0.086022 | 0 | 0 | 93 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | 10 | |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Higher level | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.25 | 24 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 102 | |
| High level | 1 | 0.763682 | 0.228856 | 0.004975 | 0.002488 | 0 | 402 |
| 2 | 0.0144 | 0.7744 | 0.2064 | 0.0048 | 0 | 625 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0.015942 | 0.817391 | 0.166667 | 0 | 690 | |
| 4 | 0.001727 | 0.001727 | 0.022453 | 0.908463 | 0.06563 | 579 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.010695 | 0.989305 | 187 |
| Impact factors | Representative Indicators | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Defense Ability | Tourism Reception (X1) | Forward |
| Gross Tourism Income (X2) | Forward | |
| Resilience Ability | Number of travel agencies (X3) | Forward |
| Night Lights (X4) | Forward | |
| Remodeling Ability | Investment in Social Fixed Assets (X5) | Forward |
| Total Retail Sales of Consumer Goods (X6) | Forward | |
| Transformation Ability | Number of employees in tertiary industry(X7) | Forward |
| Ratio of tourists to permanent residents(X8) | Forward |
| Implicit Variable | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | 0.9029 | 0.8604 | 0.7716 | 0.8189 | 0.8880 | 0.8563 | 0.9111 | 0.8146 |
| p | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





