Submitted:
13 May 2024
Posted:
13 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
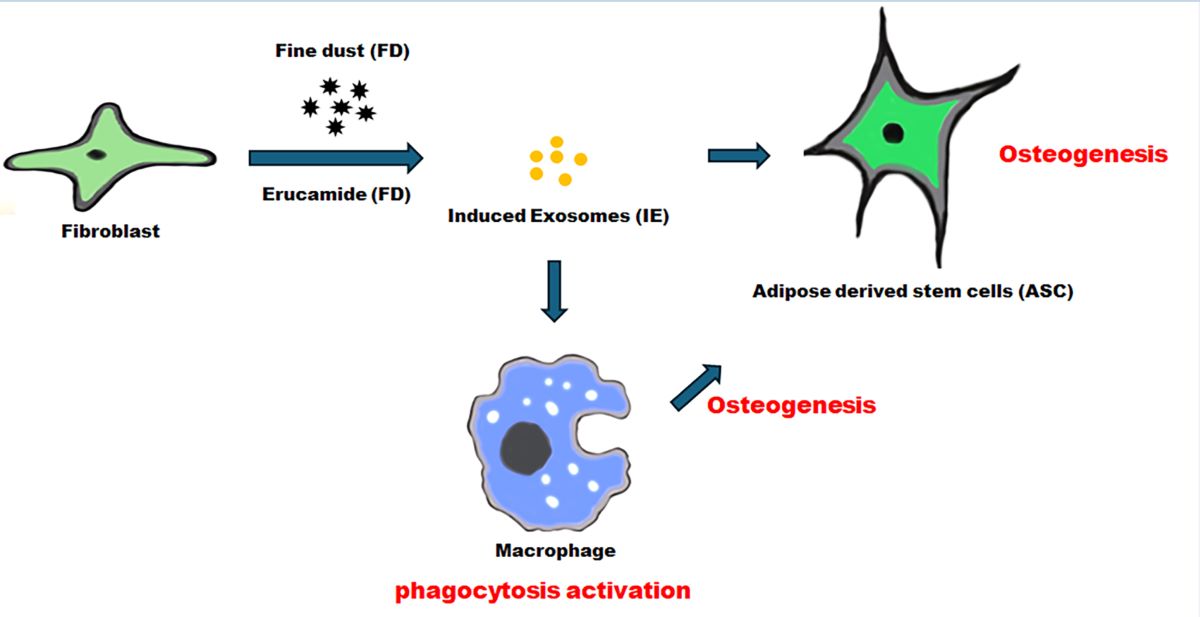
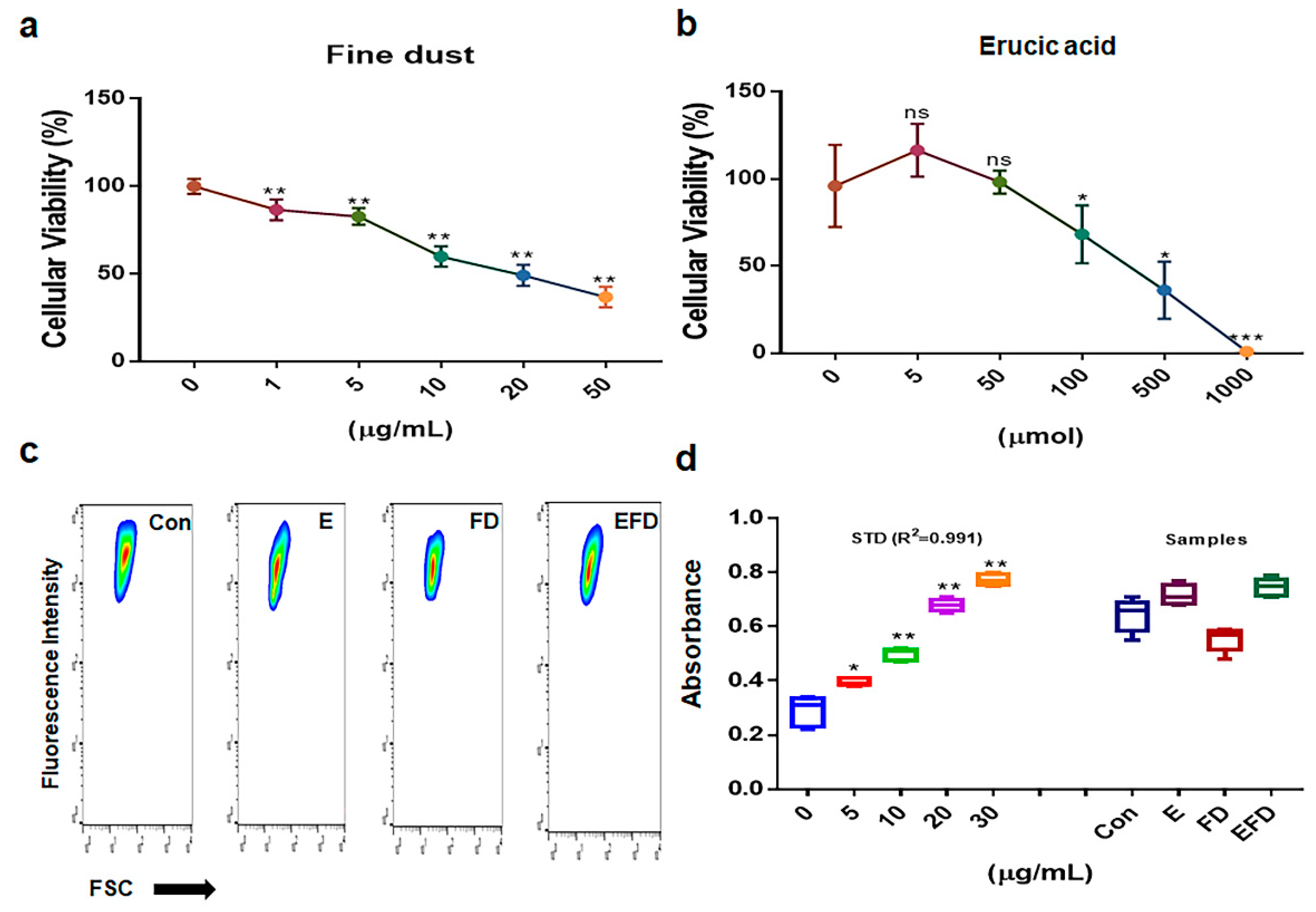
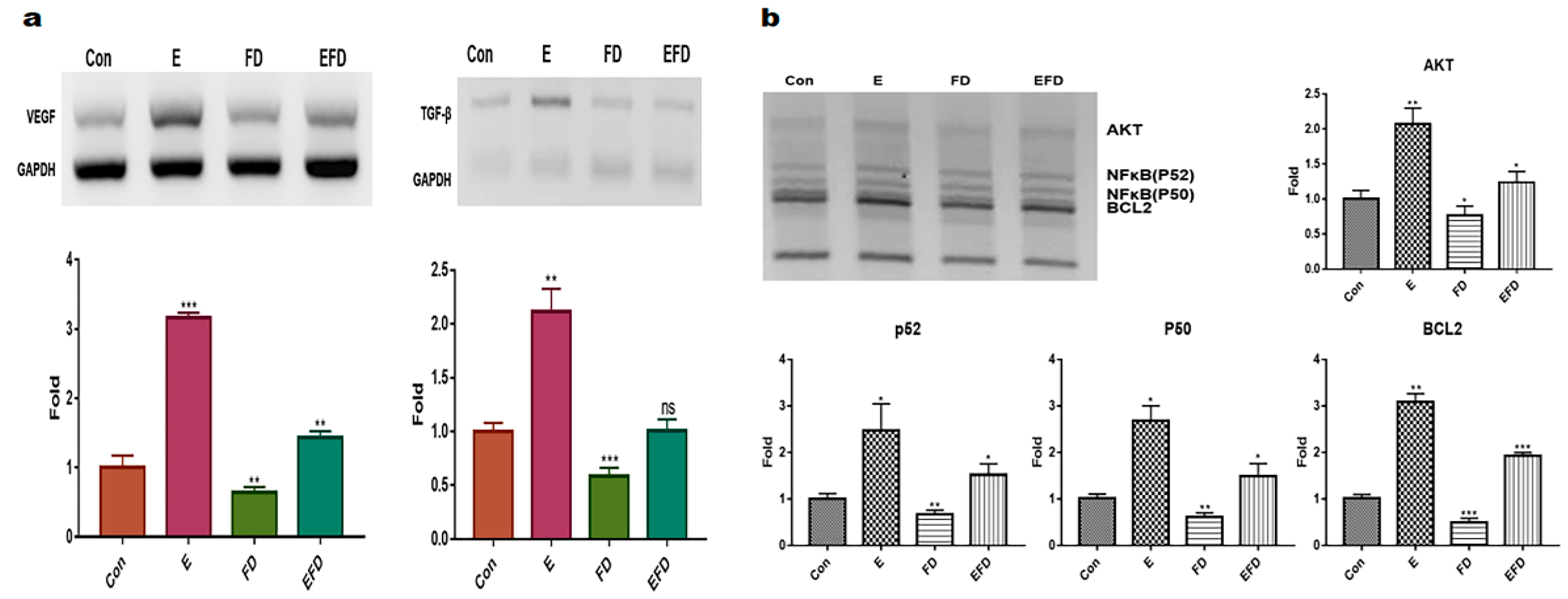
2.1. Antiapoptotic function of erucic acid in fibroblasts exposed to fine dust
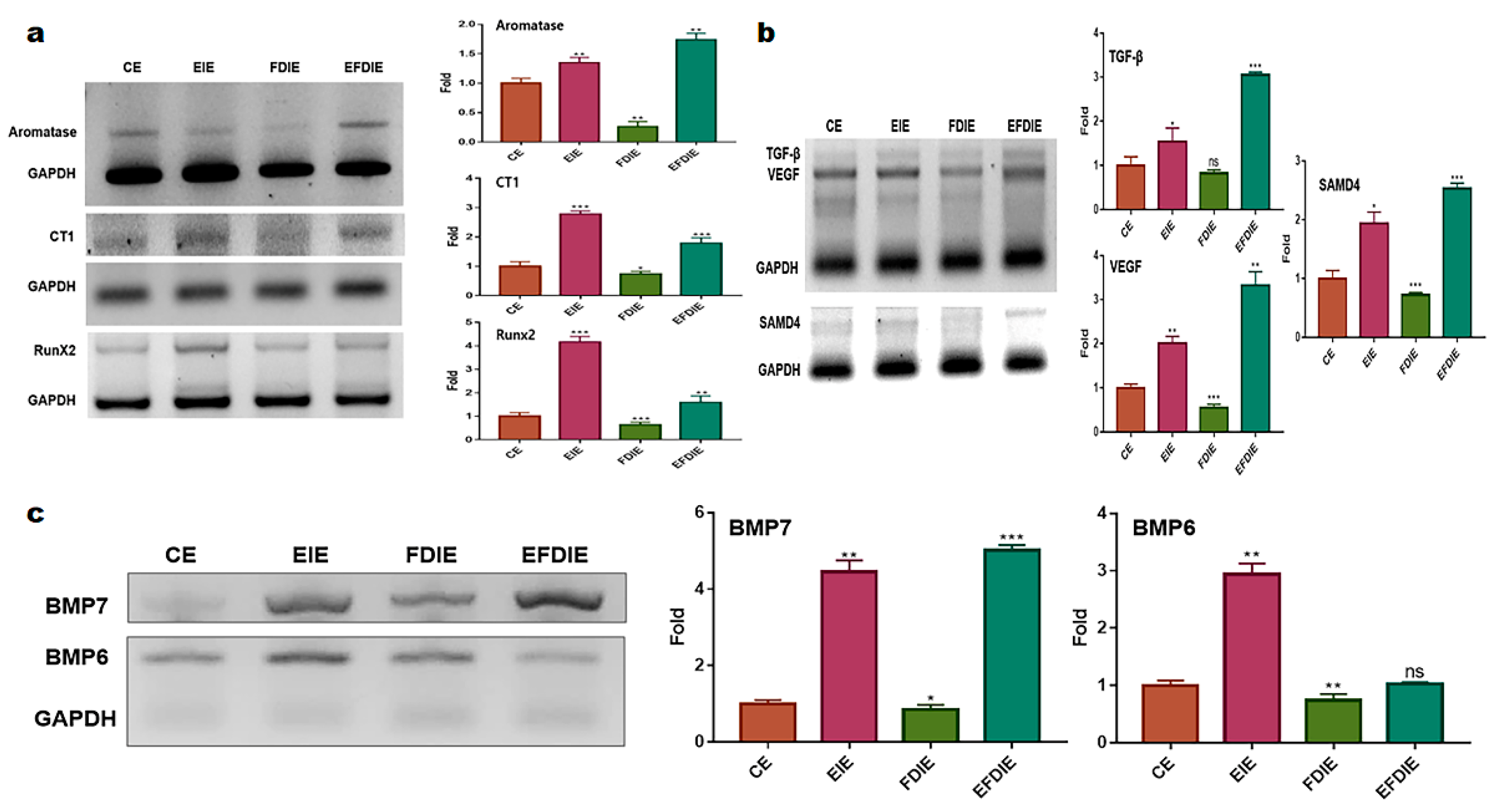
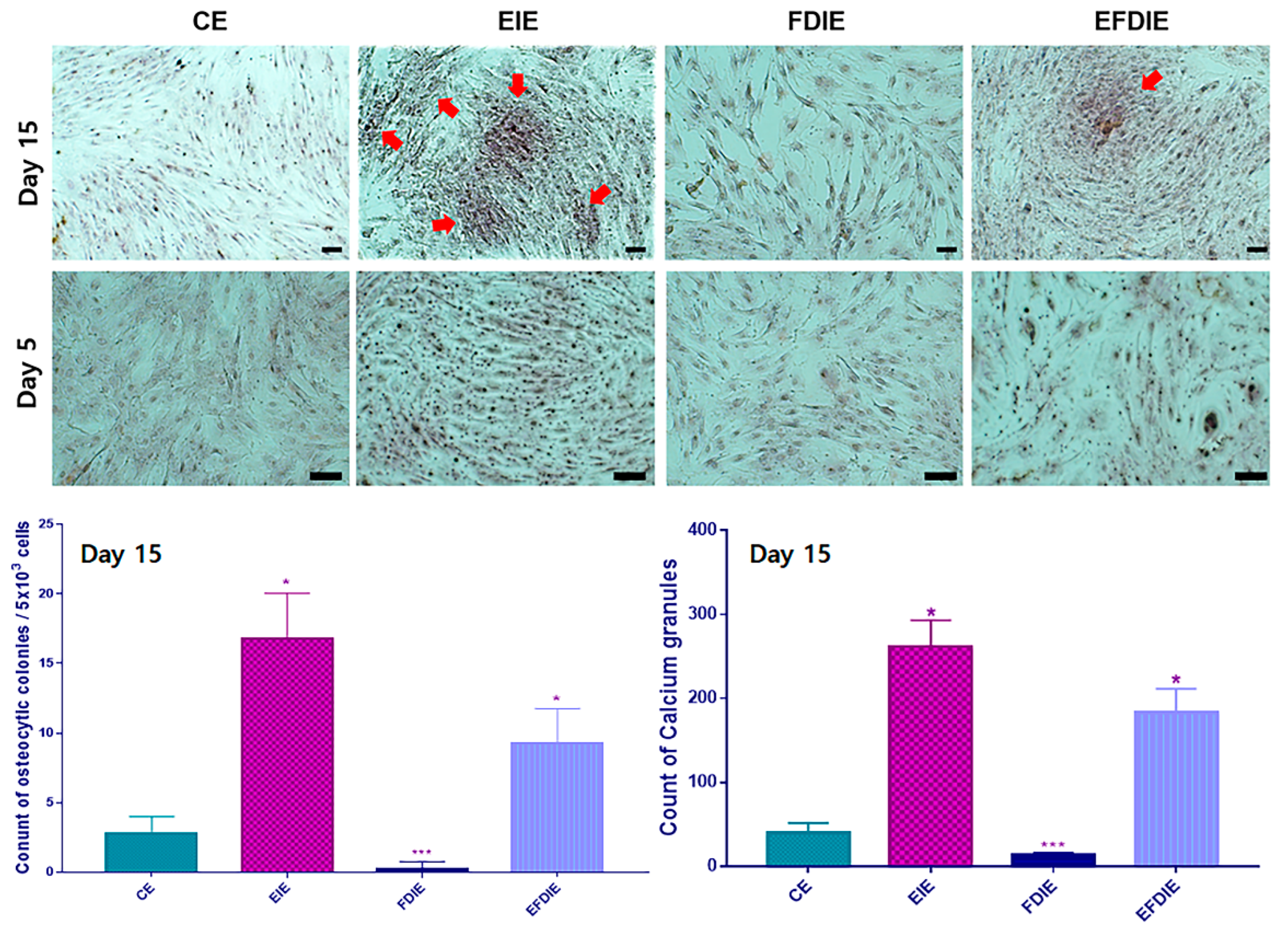
2.2. Protecting and Enhancing of osteocyic differentiation by the induced exosomes
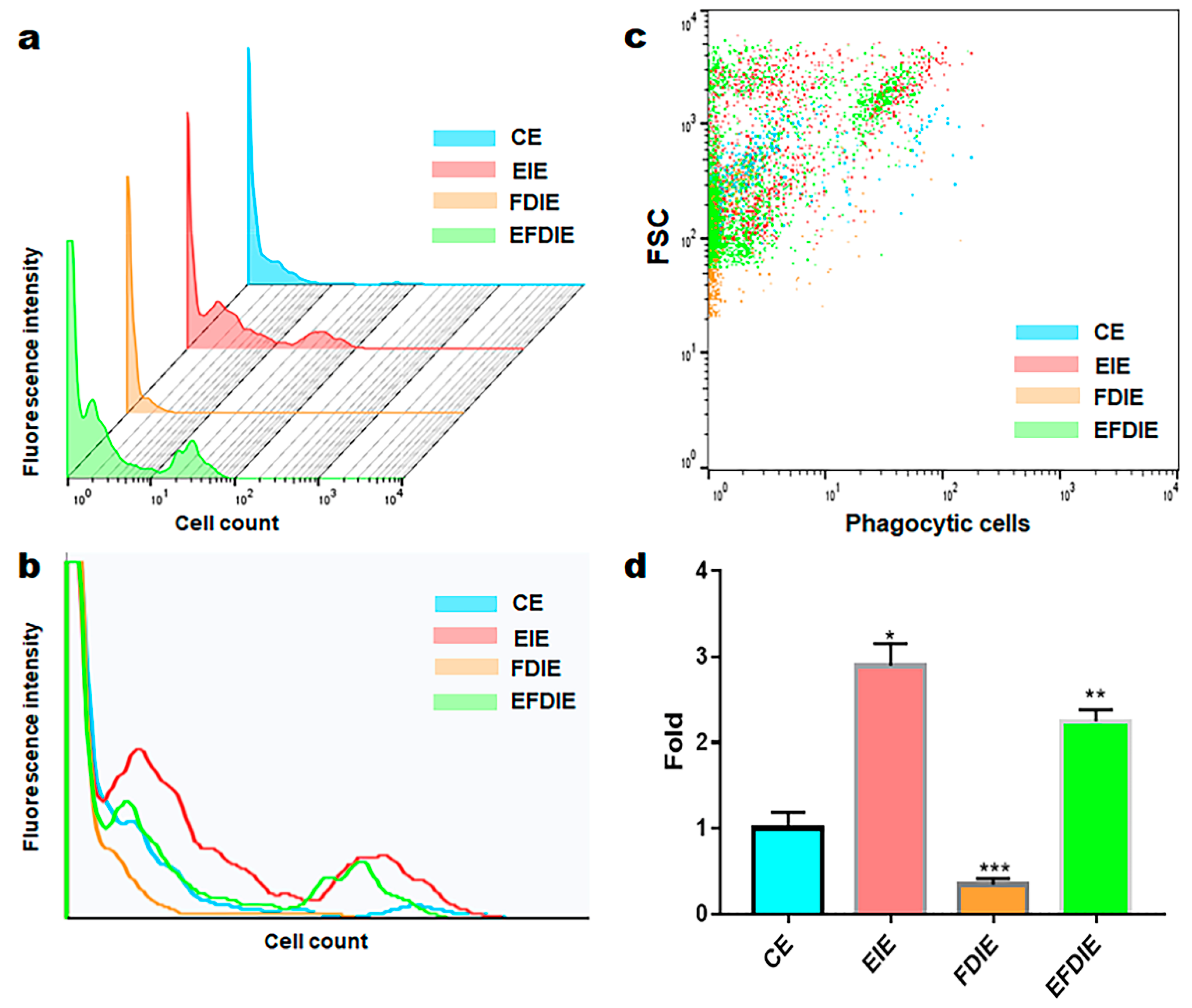
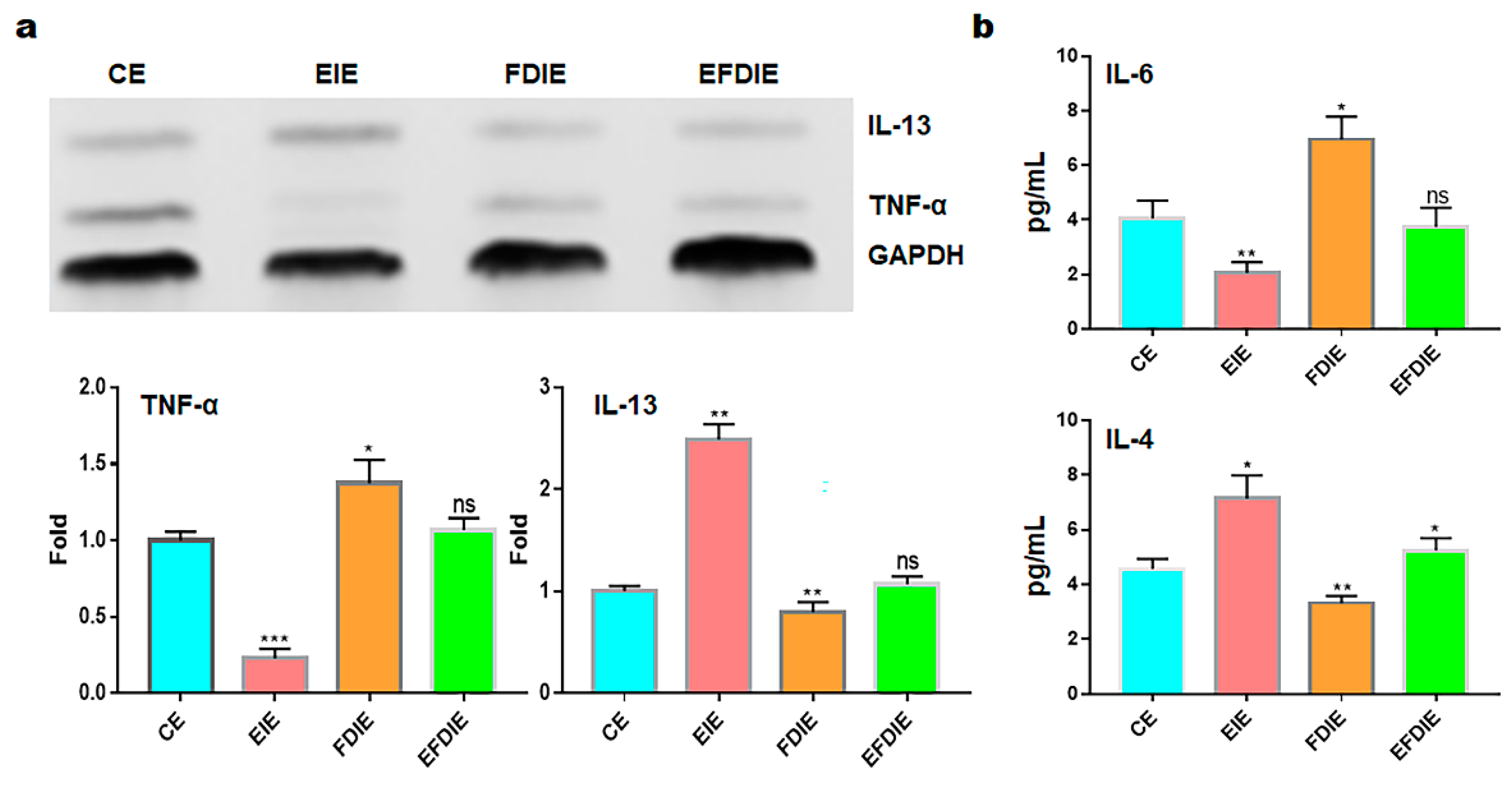
2.3. Activation of immunity in macrophages with induced exosomes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell culture
4.2. Cell viability test
4.3. Evaluation of the concentration of induced exosomes
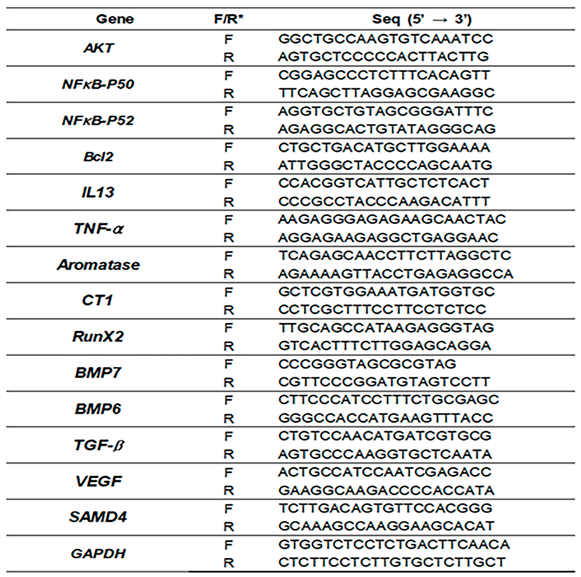
4.4. Quantitative PCR
4.5. Phagocytic activity Test
4.6. Evaluating of cytokine concentration
4.7. Alizarin staining
4.8. Statistical analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sahasrabudhe, M. Crismer values and erucic acid contents of rapeseed oils. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society 1977, 54, 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Dubey, N.; Verma, A.; Agrawal, A. Erucic acid: A possible therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative diseases. Current Molecular Medicine 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, I.A.; ul Ashraf, Z.; Muzzaffar, S. Erucic acid. In Handbook of plant and animal toxins in food; CRC Press: 2022; pp. 169–176.
- Galanty, A.; Grudzińska, M.; Paździora, W.; Paśko, P. Erucic acid—both sides of the story: a concise review on its beneficial and toxic properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Shang, L.; Deng, S.; Li, P.; Chen, K.; Gao, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, J. Peroxisomal oxidation of erucic acid suppresses mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation by stimulating malonyl-CoA formation in the rat liver. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2020, 295, 10168–10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.J.; Khan, S.A. Chemistry and Biological Activity of Mustard Oil: Therapeutic Benefits and Risk to Healthcare. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2024, 34, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendlinger, C.; Hammann, S.; Vetter, W. Various concentrations of erucic acid in mustard oil and mustard. Food chemistry 2014, 153, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Communication by extracellular vesicles: where we are and where we need to go. Cell 2016, 164, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Song, S.; Chen, N.; Liao, J.; Zeng, L. Stem cell-derived exosomes: A supernova in cosmetic dermatology. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology 2021, 20, 3812–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, S.; Du, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chu, L.; Han, X.; Galons, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H. Exosomes from different cells: Characteristics, modifications, and therapeutic applications. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2020, 207, 112784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, M.W.; Kim, B.; Lee, S.G. Effects of induced exosomes from endometrial cancer cells on tumor activity in the presence of Aurea helianthus extract. Molecules 2021, 26, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Shan, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Shu, Y.; Linghu, X.; Wang, B. Adverse effects of exposure to fine particles and ultrafine particles in the environment on different organs of organisms. Journal of Environmental Sciences 2024, 135, 449–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combes, A.; Franchineau, G. Fine particle environmental pollution and cardiovascular diseases. Metabolism 2019, 100, 153944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dong, B.; Li, S.; Chen, G.; Yang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Guo, Y. Exposure to ambient particulate matter air pollution, blood pressure and hypertension in children and adolescents: a national cross-sectional study in China. Environment international 2019, 128, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadinejad, S.; Dara, R.; Jafary, F. Health impacts of extreme events. Safety in Extreme Environments 2020, 2, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jia, Y.; Sun, Z.; Su, J.; Liu, Q.S.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, G. Environmental pollution, a hidden culprit for health issues. Eco-Environment & Health 2022, 1, 31–45. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.; Shin, G.H.; Jin, G.S.; Jin, S.; Kim, B.; Lee, S.G. Effects of black jade on osteogenic differentiation of adipose derived stem cells under benzopyrene. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Ikemoto, T.; Morine, Y.; Imura, S.; Saito, Y.; Yamada, S.; Shimada, M. The differences in the characteristics of insulin-producing cells using human adipose-tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells from subcutaneous and visceral tissues. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 13204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzh, M.; Vorontsov, P.; Ashukina, N.; Maltseva, V. Age-related features of bone regeneration (literature review). Orthopaedics, Traumatology and Prosthetics 2021, 3, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velletri, T.; Xie, N.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Shou, P.; Gan, Y.; Cao, G. P53 functional abnormality in mesenchymal stem cells promotes osteosarcoma development. Cell death & disease 2016, 7, e2015–e2015. [Google Scholar]
- Holleville, N.; Matéos, S.; Bontoux, M.; Bollerot, K.; Monsoro-Burq, A.H. Dlx5 drives Runx2 expression and osteogenic differentiation in developing cranial suture mesenchyme. Developmental biology 2007, 304, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IGF, N.S.; but not Length, F.W. Aromatase Inhibition Causes Lower Bone Density Than Ovariectomy in Mice, an Effect Prevented by Bisphosphonates. W. Kozlow1, K.
- Bonewald, L.F. Cell–cell and cell–matrix interactions in bone. Intercellular Signaling in Development and Disease: Cell Signaling Collection.
- Mandal, C.C. Osteolytic metastasis in breast cancer: effective prevention strategies. Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy 2020, 20, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Strategies of macrophages to maintain bone homeostasis and promote bone repair: a narrative review. Journal of Functional Biomaterials 2022, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillon, R. Diabetic bone disease. Calcified tissue international 1991, 49, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.E.; Bouloux, P.-M.G. Metabolic bone disease. Endocrinology in Clinical Practice, ed. by PE Harris, PM Bouloux. CRC Press 2014, 243. [Google Scholar]
- Ritz, B.; Hoffmann, B.; Peters, A. The effects of fine dust, ozone, and nitrogen dioxide on health. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International 2019, 116, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.E.; Cho, D.; Park, H.J. Air pollution and skin diseases: Adverse effects of airborne particulate matter on various skin diseases. Life sciences 2016, 152, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-W.; Chi, M.-C.; Peng, K.-T.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Hsu, L.-F.; Yan, Y.-L.; Li, H.-Y.; Chen, M.-C.; Lee, I.-T.; Lai, C.-H. Water-soluble fullerenol C60 (OH) 36 toward effective anti-air pollution induced by urban particulate matter in HaCaT cell. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirindage, K.G.I.S.; Jayasinghe, A.M.K.; Cho, N.; Cho, S.H.; Yoo, H.M.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Ahn, G. Fine-dust-induced skin inflammation: Low-molecular-weight fucoidan protects keratinocytes and underlying fibroblasts in an integrated culture model. Marine Drugs 2022, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasekara, D.S.; Kim, S.; Rho, J. Regulation of osteoblast differentiation by cytokine networks. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, G.S.; Lian, J.B. Molecular mechanisms mediating proliferation/differentiation interrelationships during progressive development of the osteoblast phenotype. Endocrine reviews 1993, 14, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitkänen, S. In vitro and in vivo osteogenesis and vasculogenesis in synthetic bone grafts. 2020.
- Komori, T. Regulation of proliferation, differentiation and functions of osteoblasts by Runx2. International journal of molecular sciences 2019, 20, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, F.; Córdova, L.A.; Zhang, R.; Pajarinen, J.; Lin, T.-h.; Goodman, S.B.; Yao, Z. The effects of immunomodulation by macrophage subsets on osteogenesis in vitro. Stem cell research & therapy 2016, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Dong, L.; Wang, C. Modulating macrophage activities to promote endogenous bone regeneration: Biological mechanisms and engineering approaches. Bioactive materials 2021, 6, 244–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meo, S.A.; Rasheed, S.; Khan, M.M.; Shujauddin, S.; Al-Tuwaijri, A.S. Effect of cement dust exposure on phagocytic function of polymorphonuclear neutrophils in cement mill workers. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 2008, 21, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





