Submitted:
13 May 2024
Posted:
13 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
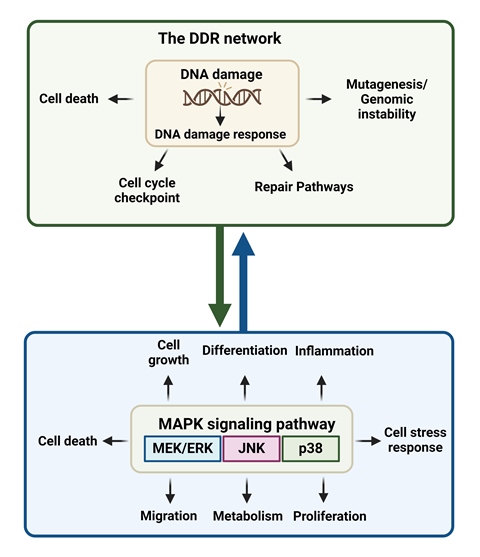
2. The DDR Network
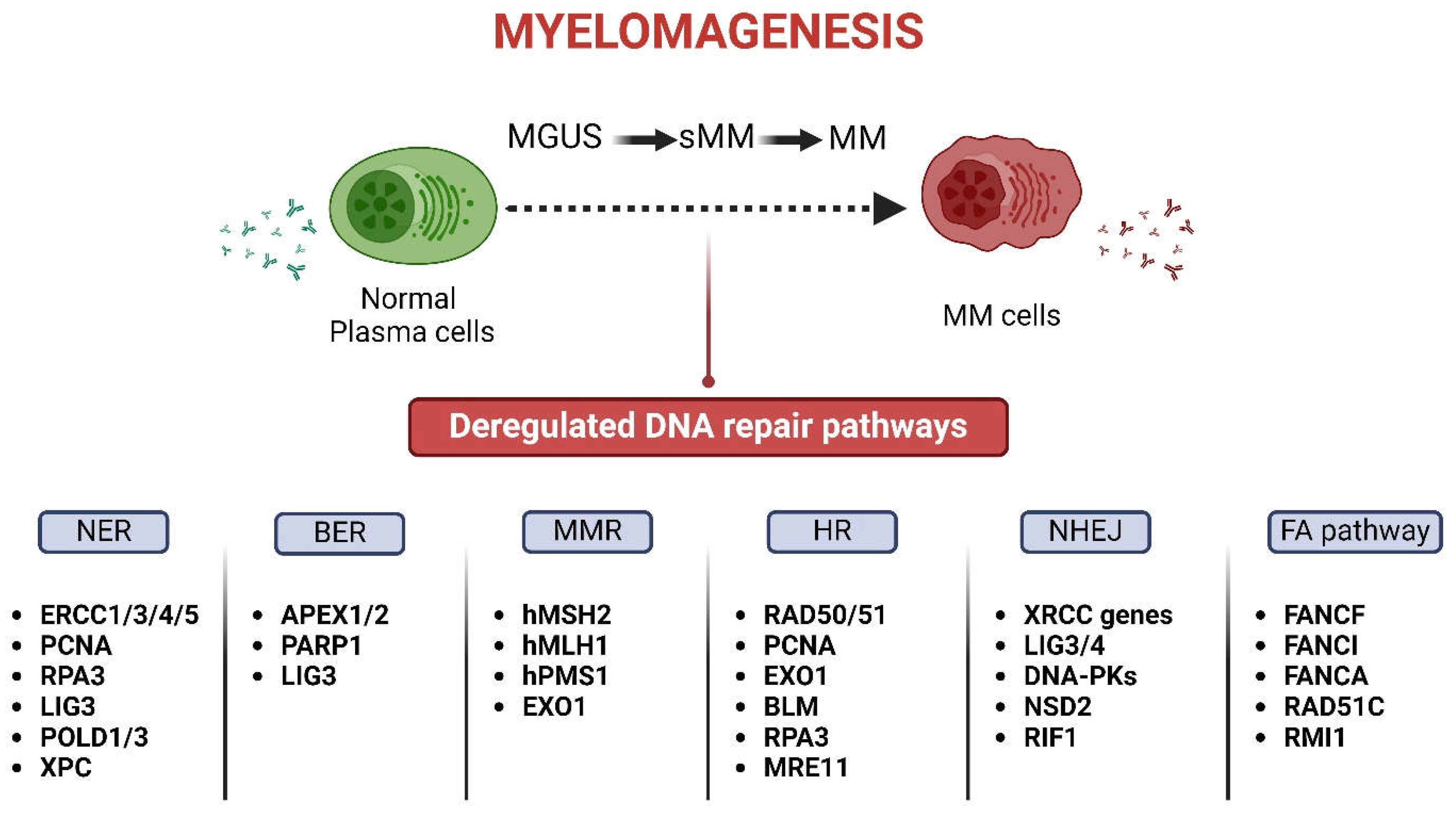
2.1. The DDR Network in the Onset and Progression of MM
2.2. The DDR Network in the Outcome of Anti-Myeloma Therapy
3. The MAPK System
3.1. The MAPK Signaling Pathways in the Onset and Progression of MM
3.2. The MAPK Signaling Pathway in the Outcome of Anti-Myeloma Therapy
4. The DDR Network and the MAPK System Are Coordinately Activated
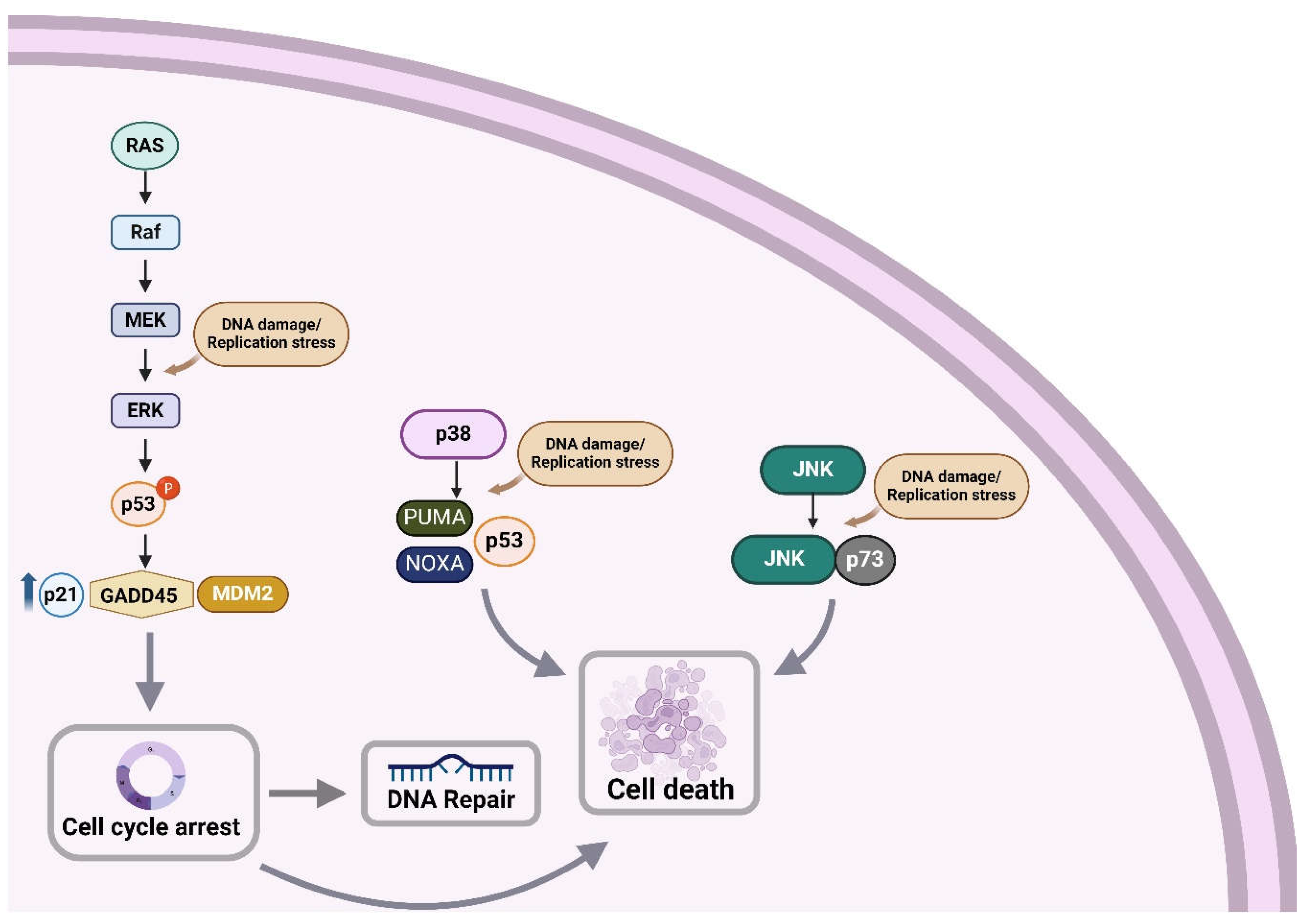
4.1. Induction of DDR Activates MAPK
4.2. Induction of MAPK Activates DDR
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflict of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.K.; Rajkumar, V.; Kyle, R.A.; Van Duin, M.; Sonneveld, P.; Mateos, M.V.; Gay, F.; Anderson, K.C. Multiple Myeloma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2017, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeykoon, J.P.; Tawfiq, R.K.; Kumar, S.; Ansell, S.M. Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance: Evaluation, Risk Assessment, Management, and Beyond. Fac Rev 2022, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thordardottir, M.; Lindqvist, E.K.; Lund, S.H.; Costello, R.; Burton, D.; Korde, N.; Mailankody, S.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Launer, L.J.; Gudnason, V.; et al. Obesity and Risk of Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance and Progression to Multiple Myeloma: A Population-Based Study. Blood Adv 2017, 1, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, J.M.; Hillengass, J.; Tang, L.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Landgren, O.; Usmani, S.Z.; Moysich, K.B.; McCann, S.E.; Shah, U.A. Dietary Risk Factors for Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance in a Racially Diverse Population. Blood Adv 2024, 8, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, A.; Bazou, D.; O’Gorman, P. Smoldering Multiple Myeloma: Prevalence and Current Evidence Guiding Treatment Decisions. Blood Lymphat Cancer 2018, 8, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahiru, W.; Izarra Santamaria, A.; Hultdin, J.; Wu, W.Y.Y.; Späth, F. Progression Patterns in Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance and Multiple Myeloma Outcome: A Cohort Study in 42 Patients. Exp Hematol Oncol 2022, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulla, A.; Anderson, K.C. Multiple Myeloma: The (r)Evolution of Current Therapy and a Glance into Future. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2358–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, S.V. Multiple Myeloma: 2022 Update on Diagnosis, Risk-Stratification and Management. Am J Hematol 2022, 97, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshman, A.; Kumar, S.K. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cells, Bispecific Antibodies, and Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Multiple Myeloma: An Update. Am J Hematol 2022, 97, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raje, N.; Berdeja, J.; Lin, Y.; Siegel, D.; Jagannath, S.; Madduri, D.; Liedtke, M.; Rosenblatt, J.; Maus, M. V.; Turka, A.; et al. Anti-BCMA CAR T-Cell Therapy Bb2121 in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N Engl J Med 2019, 380, 1726–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oben, B.; Froyen, G.; Maclachlan, K.H.; Leongamornlert, D.; Abascal, F.; Zheng-Lin, B.; Yellapantula, V.; Derkach, A.; Geerdens, E.; Diamond, B.T.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals Progressive versus Stable Myeloma Precursor Conditions as Two Distinct Entities. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksenova, A.Y.; Zhuk, A.S.; Lada, A.G.; Zotova, I. V.; Stepchenkova, E.I.; Kostroma, I.I.; Gritsaev, S. V.; Pavlov, Y.I. Genome Instability in Multiple Myeloma: Facts and Factors. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, N.; Walker, G.C. Mechanisms of DNA Damage, Repair and Mutagenesis. Environ Mol Mutagen 2017, 58, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroeidi, D.; Georganta, A.; Panagiotou, E.; Syrigos, K.; Souliotis, V.L. Targeting ATR Pathway in Solid Tumors: Evidence of Improving Therapeutic Outcomes. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Jia, K.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; He, Y.; Zhou, C. Alterations of DNA Damage Repair in Cancer: From Mechanisms to Applications. Ann Transl Med 2020, 8, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Talluri, S.; Kumar, S.; Buon, L.; Zhao, J.; Potluri, L.B.; Prabhala, R.; Shammas, M.A.; Munshi, N.C. Base Excision Repair and Homologous Recombination Pathway Intermediates Drive Genomic Instability and Evolution in Myeloma. Blood 2020, 136, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushie, C.; Saitoh, T.; Iwasaki, A.; Moriyama, N.; Hattori, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Sawamura, M.; Isoda, J.; Handa, H.; Yokohama, A.; et al. The Polymorphisms of Base Excision Repair Genes Influence the Prognosis of Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2012, 120, 3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Talluri, S.; Pal, J.; Yuan, X.; Lu, R.; Nanjappa, P.; Samur, M.K.; Munshi, N.C.; Shammas, M.A. Role of Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Nucleases in the Regulation of Homologous Recombination in Myeloma: Mechanisms and Translational Significance. Blood Cancer J 2018, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.L.; Ren, E.C. Functional Aspects of PARP1 in DNA Repair and Transcription. Biomolecules 2012, 2, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Li, J.; King, K.; Persaud, A.K.; Duah, E.; Vangundy, Z.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Lamba, J.K.; Tan, A.C.; Fridley, B.L.; et al. PARP1 and POLD2 as Prognostic Biomarkers for Multiple Myeloma in Autologous Stem Cell Transplant. Haematologica 2023, 108, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracciolo, D.; Scionti, F.; Juli, G.; Altomare, E.; Golino, G.; Todoerti, K.; Grillone, K.; Riillo, C.; Arbitrio, M.; Iannone, M.; et al. Exploiting MYC-Induced PARPness to Target Genomic Instability in Multiple Myeloma. Haematologica 2021, 106, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalat, R.; Samur, M.K.; Fulciniti, M.; Lopez, M.; Nanjappa, P.; Cleynen, A.; Wen, K.; Kumar, S.; Perini, T.; Calkins, A.S.; et al. Nucleotide Excision Repair Is a Potential Therapeutic Target in Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2018, 32, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vangsted, A.; Gimsing, P.; Klausen, T.W.; Nexø, B.A.; Wallin, H.; Andersen, P.; Hokland, P.; Lillevang, S.T.; Vogel, U. Polymorphisms in the Genes ERCC2, XRCC3 and CD3EAP Influence Treatment Outcome in Multiple Myeloma Patients Undergoing Autologous Bone Marrow Transplantation. Int J Cancer 2007, 120, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velangi, M.R.; Matheson, E.C.; Morgan, G.J.; Jackson, G.H.; Taylor, P.R.; Hall, A.G.; Irving, J.A.E. DNA Mismatch Repair Pathway Defects in the Pathogenesis and Evolution of Myeloma. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.; Santón, A.; García-Cosio, M.; Bellas, C. HMLH1 and MGMT Inactivation as a Mechanism of Tumorigenesis in Monoclonal Gammopathies. Mod Pathol 2006, 19, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotoula, V.; Hytiroglou, P.; Kaloutsi, V.; Barbanis, S.; Kouidou, S.; Papadimitriou, C.S. Mismatch Repair Gene Expression in Malignant Lymphoproliferative Disorders of B-Cell Origin. Leuk Lymphoma 2002, 43, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branch, P.; Aquilina, G.; Bignami, M.; Karran, P. Defective Mismatch Binding and a Mutator Phenotype in Cells Tolerant to DNA Damage. Nature 1993, 362, 652–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, K.; Fujii, K.; Suehiro, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Uike, N.; Yoshida, M.A.; Oda, S. Heterochronous Occurrence of Microsatellite Instability in Multiple Myeloma - an Implication for a Role of Defective DNA Mismatch Repair in Myelomagenesis. Leuk Lymphoma 2018, 59, 2454–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shammas, M.A.; Reis, R.J.S.; Koley, H.; Batchu, R.B.; Li, C.; Munshi, N.C. Dysfunctional Homologous Recombination Mediates Genomic Instability and Progression in Myeloma. Blood 2009, 113, 2290–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roddam, P.L.; Rollinson, S.; O’Driscoll, M.; Jeggo, P.A.; Jack, A.; Morgan, G.J. Genetic Variants of NHEJ DNA Ligase IV Can Affect the Risk of Developing Multiple Myeloma, a TumourCharacterised by Aberrant Class Switch Recombination. J Med Genet 2002, 39, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.R.; Senyuk, V.; Sweiss, K.; Calip, G.; Oh, A.; Mahmud, N.; Rondelli, D. Overcoming Melphalan Resistance By Targeting Crucial DNA Repair Pathways in Multiple Myeloma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2020, 26, S224–S225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumontet, C.; Landi, S.; Reiman, T.; Perry, T.; Plesa, A.; Bellini, I.; Barale, R.; Pilarski, L.M.; Troncy, J.; Tavtigian, S.; et al. Genetic Polymorphisms Associated with Outcome in Multiple Myeloma Patients Receiving High-Dose Melphalan. Bone Marrow Transplant 2010, 45, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Ferguson, D.O.; Xie, W.; Manis, J.P.; Sekiguchi, J.A.; Frank, K.M.; Chaudhuri, J.; Horner, J.; DePinho, R.A.; Alt, F.W. Interplay of P53 and DNA-Repair Protein XRCC4 in Tumorigenesis, Genomic Stability and Development. Nature 2000, 404, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Betti, C.; Singh, S.; Toor, A.; Vaughan, A. Impaired NHEJ Function in Multiple Myeloma. Mutat Res 2009, 660, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roddam, P.L.; Allan, J.M.; Dring, A.M.; Worrillow, L.J.; Davies, F.E.; Morgan, G.J. Non-Homologous End-Joining Gene Profiling Reveals Distinct Expression Patterns Associated with Lymphoma and Multiple Myeloma. Br J Haematol 2010, 149, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, P.J.; Tewari, P.; Morris, D.W.; Staines, A.; Crowley, D.; Nieters, A.; Becker, N.; De sanjosé, S.; Foretova, L.; Maynadié, M.; et al. Variation in DNA Repair Genes XRCC3, XRCC4, XRCC5 and Susceptibility to Myeloma. Hum Mol Genet 2007, 16, 3117–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calimeri, T.; Fulciniti, M.; Lin, J.; Samur, M.K.; Calkins, A.S.; Vahia, A. V; Pal, J.; Cea, M.; Cagnetta, A.; Cottini, F.; et al. Aberrant Non-Homologous End Joining in Multiple Myeloma: A Role in Genomic Instability and As Potential Prognostic Marker. Blood 2012, 120, 2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Peng, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; et al. Targeting NSD2-Mediated SRC-3 Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation Sensitizes Bortezomib Treatment in Multiple Myeloma. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.Y.; Martinez-Garcia, E.; Phillip, J.M.; Chambliss, A.B.; Popovic, R.; Ezponda, T.; Small, E.C.; Will, C.; Phillip, M.P.; Neri, P.; et al. MMSET/WHSC1 Enhances DNA Damage Repair Leading to an Increase in Resistance to Chemotherapeutic Agents. Oncogene 2016, 35, 5905–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, T.; Oda, T. DNA Damage Response in Multiple Myeloma: The Role of the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, J.D.; Noguchi, E. Fanconi Anemia: Current Insights Regarding Epidemiology, Cancer, and DNA Repair. Hum Genet 2022, 141, 1811–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Van Der Sluis, P.C.; Boulware, D.; Hazlehurst, L.A.; Dalton, W.S. The FA/BRCA Pathway Is Involved in Melphalan-Induced DNA Interstrand Cross-Link Repair and Accounts for Melphalan Resistance in Multiple Myeloma Cells. Blood 2005, 106, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A.A.; Gourzones-Dmitriev, C.; Sahota, S.; Rème, T.; Moreaux, J.; Goldschmidt, H.; Constantinou, A.; Pasero, P.; Hose, D.; Klein, B. A DNA Repair Pathway Score Predicts Survival in Human Multiple Myeloma: The Potential for Therapeutic Strategy. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poczta, A.; Rogalska, A.; Marczak, A. Treatment of Multiple Myeloma and the Role of Melphalan in the Era of Modern Therapies—Current Research and Clinical Approaches. J Clin Med 2021, 10, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanswick, V.J.; Craddock, C.; Sekhar, M.; Mahendra, P.; Shankaranarayana, P.; George Hughes, R.; Hochhauser, D.; Hartley, J.A. Repair of DNA Interstrand Crosslinks as a Mechanism of Clinical Resistance to Melphalan in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2002, 100, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Souliotis, V.L.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Papadimitriou, C.; Sfikakis, P.P. Extent of Damage and Repair in the P53 Tumor-Suppressor Gene after Treatment of Myeloma Patients with High-Dose Melphalan and Autologous Blood Stem-Cell Transplantation Is Individualized and May Predict Clinical Outcome. J Clin Oncol 2005, 23, 4381–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Souliotis, V.L.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Bamia, C.; Pouli, A.; Baltadakis, I.; Terpos, E.; Kyrtopoulos, S.A.; Sfikakis, P.P. Melphalan-Induced DNA Damage in Vitro as a Predictor for Clinical Outcome in Multiple Myeloma. Haematologica 2007, 92, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkotzamanidou, M.; Terpos, E.; Bamia, C.; Munshi, N.C.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Souliotis, V.L. DNA Repair of Myeloma Plasma Cells Correlates with Clinical Outcome: The Effect of the Nonhomologous End-Joining Inhibitor SCR7. Blood 2016, 128, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkotzamanidou, M.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Kyrtopoulos, S.A.; Bamia, C.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Souliotis, V.L. Chromatin Structure, Transcriptional Activity and DNA Repair Efficiency Affect the Outcome of Chemotherapy in Multiple Myeloma. Br J Cancer 2014, 111, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.B.; Gutiérrez, N.C. Targeting Ongoing DNA Damage in Multiple Myeloma: Effects of DNA Damage Response Inhibitors on Plasma Cell Survival. Front Oncol 2017, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, N.A.; Reidy, M.; Natoni, A.; Raab, M.S.; O’Dwyer, M. Targeting the Pim Kinases in Multiple Myeloma. Blood Cancer J 2015, 5, e325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, J.; Santo, L.; Siu, K.T.; Panaroni, C.; Raje, N. Pim2 Is Important for Regulating DNA Damage Response in Multiple Myeloma Cells. Blood Cancer J 2016, 6, e462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, D.; Ye, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sun, T.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, K.; Lu, N. Inhibition of Pim-2 Kinase by LT-171-861 Promotes DNA Damage and Exhibits Enhanced Lethal Effects with PARP Inhibitor in Multiple Myeloma. Biochem Pharmacol 2021, 190, 114648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiso, P.; Carvajal-Vergara, X.; Ocio, E.M.; López-Pérez, R.; Mateo, G.; Gutiérrez, N.; Atadja, P.; Pandiella, A.; San Miguel, J.F. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor LBH589 Is a Potent Antimyeloma Agent That Overcomes Drug Resistance. Cancer Res 2006, 66, 5781–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, E.; Shen, J.; Steinberg, J.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Bonavida, B.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.W.; Berenson, J.R. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor LBH589 Enhances the Anti-Myeloma Effects of Chemotherapy in Vitro and in Vivo. Leuk Res 2011, 35, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkotzamanidou, M.; Terpos, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Souliotis, V.L. The Combination of Panobinostat and Melphalan for the Treatment of Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 15671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junttila, M.R.; Li, S.; Westermarck, J. Phosphatase-Mediated Crosstalk between MAPK Signaling Pathways in the Regulation of Cell Survival. FASEB J 2008, 22, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarpia, L.; Lippman, S.M.; El-Naggar, A.K. Targeting the MAPK-RAS-RAF Signaling Pathway in Cancer Therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2012, 16, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dow, L.E.; Elsum, I.A.; King, C.L.; Kinross, K.M.; Richardson, H.E.; Humbert, P.O. Loss of Human Scribble Cooperates with H-Ras to Promote Cell Invasion through Deregulation of MAPK Signalling. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5988–6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidinia, M.; Sadeghpour, A.; Yousefi, B. The Roles of Signaling Pathways in Bone Repair and Regeneration. J Cell Physiol 2018, 233, 2937–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolli, N.; Genuardi, E.; Ziccheddu, B.; Martello, M.; Oliva, S.; Terragna, C. Next-Generation Sequencing for Clinical Management of Multiple Myeloma: Ready for Prime Time? Front Oncol 2020, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, E.M.; Deshpande, S.; Tytarenko, R.; Ashby, C.; Wang, Y.; Bauer, M.A.; Johnson, S.K.; Wardell, C.P.; Thanendrarajan, S.; Zangari, M.; et al. The Molecular Make up of Smoldering Myeloma Highlights the Evolutionary Pathways Leading to Multiple Myeloma. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maura, F.; Rajanna, A.R.; Ziccheddu, B.; Poos, A.M.; Derkach, A.; Maclachlan, K.; Durante, M.; Diamond, B.; Papadimitriou, M.; Davies, F.; et al. Genomic Classification and Individualized Prognosis in Multiple Myeloma. J Clin Oncol 2024, 42, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohr, J.G.; Stojanov, P.; Carter, S.L.; Cruz-Gordillo, P.; Lawrence, M.S.; Auclair, D.; Sougnez, C.; Knoechel, B.; Gould, J.; Saksena, G.; et al. Widespread Genetic Heterogeneity in Multiple Myeloma: Implications for Targeted Therapy. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolli, N.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Wedge, D.C.; Van Loo, P.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Martincorena, I.; Dawson, K.J.; Iorio, F.; Nik-Zainal, S.; Bignell, G.R.; et al. Heterogeneity of Genomic Evolution and Mutational Profiles in Multiple Myeloma. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, B.A.; Boyle, E.M.; Wardell, C.P.; Murison, A.; Begum, D.B.; Dahir, N.M.; Proszek, P.Z.; Johnson, D.C.; Kaiser, M.F.; Melchor, L.; et al. Mutational Spectrum, Copy Number Changes, and Outcome: Results of a Sequencing Study of Patients With Newly Diagnosed Myeloma. J Clin Oncol 2015, 33, 3911–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, P.H.; Dobbins, S.E.; Cornish, A.J.; Chubb, D.; Law, P.J.; Kaiser, M.; Houlston, R.S. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Multiple Myeloma Reveals Oncogenic Pathways Are Targeted Somatically through Multiple Mechanisms. Leukemia 2018, 32, 2459–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortüm, K.M.; Mai, E.K.; Hanafiah, N.H.; Shi, C.X.; Zhu, Y.X.; Bruins, L.; Barrio, S.; Jedlowski, P.; Merz, M.; Xu, J.; et al. Targeted Sequencing of Refractory Myeloma Reveals a High Incidence of Mutations in CRBN and Ras Pathway Genes. Blood 2016, 128, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.J.; Walker, B.A.; Davies, F.E. The Genetic Architecture of Multiple Myeloma. Nat Rev Cancer 2012, 12, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Targeting the Untargetable KRAS in Cancer Therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B 2019, 9, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, D.; Adjei, A.A. KRAS: From Undruggable to a Druggable Cancer Target. Cancer Treat Rev 2020, 89, 102070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.A.; Mavrommatis, K.; Wardell, C.P.; Cody Ashby, T.; Bauer, M.; Davies, F.E.; Rosenthal, A.; Wang, H.; Qu, P.; Hoering, A.; et al. Identification of Novel Mutational Drivers Reveals Oncogene Dependencies in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2018, 132, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Pfarr, N.; Endris, V.; Mai, E.K.; Md Hanafiah, N.H.; Lehners, N.; Penzel, R.; Weichert, W.; Ho, A.D.; Schirmacher, P.; et al. Molecular Signaling in Multiple Myeloma: Association of RAS/RAF Mutations and MEK/ERK Pathway Activation. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, G.; Lichter, D.I.; Bacco, A. Di; Blakemore, S.J.; Berger, A.; Koenig, E.; Bernard, H.; Trepicchio, W.; Li, B.; Neuwirth, R.; et al. Mutation of NRAS but Not KRAS Significantly Reduces Myeloma Sensitivity to Single-Agent Bortezomib Therapy. Blood 2014, 123, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, E.; Śmiech, M.; Łuczyńska, K.; Bouchard, M.F.; Viger, R.; Kono, H.; Pierzchała, M.; Taniguchi, H. NRF2 DLG Domain Mutations Identified in Japanese Liver Cancer Patients Affect the Transcriptional Activity in HCC Cell Lines. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremolini, C.; Loupakis, F.; Antoniotti, C.; Lonardi, S.; Masi, G.; Salvatore, L.; Cortesi, E.; Tomasello, G.; Spadi, R.; Zaniboni, A.; et al. Early Tumor Shrinkage and Depth of Response Predict Long-Term Outcome in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients Treated with First-Line Chemotherapy plus Bevacizumab: Results from Phase III TRIBE Trial by the Gruppo Oncologico Del Nord Ovest. Ann Oncol 2015, 26, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, E.M.; Ashby, C.; Tytarenko, R.G.; Deshpande, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Rosenthal, A.; Sawyer, J.; Tian, E.; Flynt, E.; et al. BRAF and DIS3 Mutations Associate with Adverse Outcome in a Long-Term Follow-up of Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 2020, 26, 2422–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.; Becker, S.; Strebhardt, K. Stamping out RAF and MEK1/2 to Inhibit the ERK1/2 Pathway: An Emerging Threat to Anticancer Therapy. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2547–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuck, C.J.; Jethava, Y.; Khan, R.; Van Rhee, F.; Zangari, M.; Chavan, S.; Robbins, K.; Miller, S.E.; Matin, A.; Mohan, M.; et al. Inhibiting MEK in MAPK Pathway-Activated Myeloma. Leukemia 2016, 30, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, M.S.; Blakely, C.M.; Riess, J.W. Targeting MEK in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Curr Probl Cancer 2024, 101065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holkova, B.; Zingone, A.; Kmieciak, M.; Bose, P.; Badros, A.Z.; Voorhees, P.M.; Baz, R.; Korde, N.; Lin, H.Y.; Chen, J.Q.; et al. A Phase II Trial of AZD6244 (Selumetinib, ARRY-142886), an Oral MEK1/2 Inhibitor, in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 2016, 22, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schjesvold, F.; Paiva, B.; Ribrag, V.; Rodriguez-Otero, P.; San-Miguel, J.F.; Robak, P.; Hansson, M.; Onishi, M.; Hamidi, H.; Malhi, V.; et al. Cobimetinib Alone and Plus Venetoclax With/Without Atezolizumab in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2023, 23, e59–e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schjesvold, F.; Ribrag, V.; Rodriguez-Otero, P.; Robak, P.J.; Hansson, M.; Hajek, R.; Amor, A.A.; Martinez-López, J.; Onishi, M.; Gallo, J.D.; et al. Safety and Preliminary Efficacy Results from a Phase Ib/II Study of CobimetinibAs a Single Agent and in Combination with Venetoclax with or without Atezolizumab in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2020, 136, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrulis, M.; Lehners, N.; Capper, D.; Penzel, R.; Heining, C.; Huellein, J.; Zenz, T.; von Deimling, A.; Schirmacher, P.; Ho, A.D.; et al. Targeting the BRAF V600E Mutation in Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Discov 2013, 3, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R. Targeting Oncogenic Raf Protein-Serine/Threonine Kinases in Human Cancers. Pharmacol Res 2018, 135, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degirmenci, U.; Yap, J.; Sim, Y.R.M.; Qin, S.; Hu, J. Drug Resistance in Targeted Cancer Therapies with RAF Inhibitors. Cancer Drug Resist 2021, 4, 665–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mey, U.J.M.; Renner, C.; von Moos, R. Vemurafenib in Combination with Cobimetinib in Relapsed and Refractory Extramedullary Multiple Myeloma Harboring the BRAF V600E Mutation. Hematol Oncol 2017, 35, 890–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otieno, S.B.; Nasir, S.; Weir, A.; Johnson, R. Rapid Response in a Patient with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma Treated with BRAF/MEK Inhibitors. Case Rep Hematol 2020, 2020, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesen, N.; Chatterjee, M.; Scheid, C.; Poos, A.M.; Besemer, B.; Miah, K.; Benner, A.; Becker, N.; Moehler, T.; Metzler, I.; et al. A Phase 2 Clinical Trial of Combined BRAF/MEK Inhibition for BRAFV600E-Mutated Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2023, 141, 1685–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Chénard-Poirier, M.; Roda, D.; de Miguel, M.; Harris, S.J.; Candilejo, I.M.; Sriskandarajah, P.; Xu, W.; Scaranti, M.; Constantinidou, A.; et al. Intermittent Schedules of the Oral RAF-MEK Inhibitor CH5126766/VS-6766 in Patients with RAS/RAF-Mutant Solid Tumours and Multiple Myeloma: A Single-Centre, Open-Label, Phase 1 Dose-Escalation and Basket Dose-Expansion Study. Lancet Oncol 2020, 21, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raab, M.S.; Giesen, N.; Scheid, C.; Besemer, B.; Miah, K.; Benner, A.; Metzler, I.; Khandanpour, C.; Seidel-Glaetzer, A.; Trautmann-Grill, K.; et al. Safety and Preliminary Efficacy Results from a Phase II Study Evaluating Combined BRAF and MEK Inhibition in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RrMM) Patients with Activating BRAF V600E Mutations: The GMMG-Birma Trial. Blood 2020, 136, 44–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, V.; Timm, M.; Haug, J.L.; Kimlinger, T.K.; Wellik, L.E.; Witzig, T.E.; Rajkumar, S. V.; Adjei, A.A.; Kumar, S. Sorafenib, a Dual Raf Kinase/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor Has Significant Anti-Myeloma Activity and Synergizes with Common Anti-Myeloma Drugs. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1190–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.K.; Jett, J.; Marks, R.; Richardson, R.; Quevedo, F.; Moynihan, T.; Croghan, G.; Markovic, S.N.; Bible, K.C.; Qin, R.; et al. Phase 1 Study of Sorafenib in Combination with Bortezomib in Patients with Advanced Malignancies. Invest New Drugs 2013, 31, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.; Lauer, R. Phase II Study of Sorafenib and Bortezomib for First-Line Treatment of Metastatic or Unresectable Renal Cell Carcinoma. Oncologist 2015, 20, 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yordanova, A.; Hose, D.; Neben, K.; Witzens-Harig, M.; Gütgemann, I.; Raab, M.S.; Moehler, T.; Goldschmidt, H.; Schmidt-Wolf, I.G. Sorafenib in Patients with Refractory or Recurrent Multiple Myeloma. Hematol Oncol 2013, 31, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, D.S.; Krishnan, A.; Lonial, S.; Chatta, G.; Alsina, M.; Jagannath, S.; Richardson, P.; Hohl, R.J.; Lust, J.A.; Bensinger, W.; et al. Phase II Trial of SCIO-469 as Monotherapy (M) or in Combination with Bortezomib (MB) in Relapsed Refractory Multiple Myeloma (MM). Blood 2006, 108, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, M.V.; Cibeira, M.T.; Richardson, P.G.; Prosper, F.; Oriol, A.; De La Rubia, J.; Lahuerta, J.J.; García-Sanz, R.; Extremera, S.; Szyldergemajn, S.; et al. Phase II Clinical and Pharmacokinetic Study of Plitidepsin 3-Hour Infusion Every Two Weeks Alone or with Dexamethasone in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 2010, 16, 3260–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Chen, S.; Pei, X.Y.; Almenara, J.A.; Kramer, L.B.; Venditti, C.A.; Dent, P.; Grant, S. Interruption of the Ras/MEK/ERK Signaling Cascade Enhances Chk1 Inhibitor-Induced DNA Damage in Vitro and in Vivo in Human Multiple Myeloma Cells. Blood 2008, 112, 2439–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Yan, J.; Tang, D. Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases Modulate DNA Damage Response - A Contributing Factor to Using MEK Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Curr Med Chem 2011, 18, 5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezatabar, S.; Karimian, A.; Rameshknia, V.; Parsian, H.; Majidinia, M.; Kopi, T.A.; Bishayee, A.; Sadeghinia, A.; Yousefi, M.; Monirialamdari, M.; et al. RAS/MAPK Signaling Functions in Oxidative Stress, DNA Damage Response and Cancer Progression. J Cell Physiol 2019, 234, 14951–14965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Martindale, J.L.; Liu, Y.; Holbrook, N.J. The Cellular Response to Oxidative Stress: Influences of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signalling Pathways on Cell Survival. Biochem J 1998, 333, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, B.; Koppenhoefer, U.; Weinstock, C.; Linderkamp, O.; Lang, F.; Gulbins, E. Fas- or Ceramide-Induced Apoptosis Is Mediated by a Rac1-Regulated Activation of Jun N-Terminal Kinase/P38 Kinases and GADD153. J Biol Chem 1997, 272, 22173–22181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persons, D.L.; Yazlovitskaya, E.M.; Cui, W.; Pelling, J.C. Cisplatin-Induced Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Ovarian Carcinoma Cells: Inhibition of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Activity Increases Sensitivity to Cisplatin. Clin Cancer Res 1999, 5, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Martindale, J.L.; Holbrook, N.J. Requirement for ERK Activation in Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 39435–39443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, G. Cellular Responses to Cisplatin. The Roles of DNA-Binding Proteins and DNA Repair. J Biol Chem 1994, 269, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehaan, R.D.; Yazlovitskaya, E.M.; Persons, D.L. Regulation of P53 Target Gene Expression by Cisplatin-Induced Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2001, 48, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, S.Y.; Ikeda, M.; Taya, Y.; Prives, C. DNA Damage-Induced Phosphorylation of P53 Alleviates Inhibition by MDM2. Cell 1997, 91, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Fang, L.; Igarashi, M.; Ouchi, T.; Lu, K.P.; Aaronson, S.A. Sustained Activation of Ras/Raf/Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Cascade by the Tumor Suppressor P53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97, 8302–8305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Wu, D.; Hirao, A.; Lahti, J.M.; Liu, L.; Mazza, B.; Kidd, V.J.; Mak, T.W.; Ingram, A.J. ERK Activation Mediates Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis after DNA Damage Independently of P53. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 12710–12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch-Presegué, L.; Vaquero, A. Sirtuins in Stress Response: Guardians of the Genome. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3764–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cea, M.; Cagnetta, A.; Adamia, S.; Acharya, C.; Tai, Y.T.; Fulciniti, M.; Ohguchi, H.; Munshi, A.; Acharya, P.; Bhasin, M.K.; et al. Evidence for a Role of the Histone Deacetylase SIRT6 in DNA Damage Response of Multiple Myeloma Cells. Blood 2015, 127, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E. V.; Dickman, M.J.; Whitmarsh, A.J. Regulation of P73-Mediated Apoptosis by c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase. Biochem J 2007, 405, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winograd-Katz, S.E.; Levitzki, A. Cisplatin Induces PKB/Akt Activation and P38(MAPK) Phosphorylation of the EGF Receptor. Oncogene 2006, 25, 7381–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafarga, V.; Cuadrado, A.; Nebreda, A.R. P18(Hamlet) Mediates Different P53-Dependent Responses to DNA-Damage Inducing Agents. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 2319–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozovic, A.; Fritz, G.; Christmann, M.; Zisowsky, J.; Jaehde, U.; Osmak, M.; Kaina, B. Long-Term Activation of SAPK/JNK, P38 Kinase and Fas-L Expression by Cisplatin Is Attenuated in Human Carcinoma Cells That Acquired Drug Resistance. Int J Cancer 2004, 112, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.; Igea, A.; Canovas, B.; Dolado, I.; Nebreda, A.R. Inhibition of P38 MAPK Sensitizes Tumour Cells to Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis Mediated by Reactive Oxygen Species and JNK. EMBO Mol Med 2013, 5, 1759–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-García, M.E.; Quiroga, A.G.; Castro, J.; Ortiz, A.; Aller, P.; Mata, F. Inhibition of P38-MAPK Potentiates Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis via GSH Depletion and Increases Intracellular Drug Accumulation in Growth-Arrested Kidney Tubular Epithelial Cells. Toxicol Sci 2009, 111, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaul, L.; Mandl-Weber, S.; Baumann, P.; Emmerich, B.; Schmidmaier, R. Bendamustine Induces G2 Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Myeloma Cells: The Role of ATM-Chk2-Cdc25A and ATM-P53-P21-Pathways. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2008, 134, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.D.; Raben, D.M.; Phillips, P.J.; Baldassare, J.J. Sustained Activation of Extracellular-Signal-Regulated Kinase 1 (ERK1) Is Required for the Continued Expression of Cyclin D1 in G1 Phase. Biochem J 1997, 326 (Pt 1), 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloche, S.; Seuwen, K.; Pagès, G.; Pouysségur, J. Biphasic and Synergistic Activation of P44mapk (ERK1) by Growth Factors: Correlation between Late Phase Activation and Mitogenicity. Mol Endocrinol 1992, 6, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Ebisuya, M.; Ashida, F.; Okamoto, K.; Yonehara, S.; Nishida, E. Continuous ERK Activation Downregulates Antiproliferative Genes throughout G1 Phase to Allow Cell-Cycle Progression. Curr Biol 2006, 16, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, E.W.; Pratilas, C.A.; Poulikakos, P.I.; Tadi, M.; Wang, W.; Taylor, B.S.; Halilovic, E.; Persaud, Y.; Xing, F.; Viale, A.; et al. The RAF Inhibitor PLX4032 Inhibits ERK Signaling and Tumor Cell Proliferation in a V600E BRAF-Selective Manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 14903–14908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toress-Collado, A.X.; Nazarian, R.; Jazirehi, A.R. Rescue of Cell Cycle Progression in BRAFV600E Inhibitor-Resistant Human Melanoma by a Chromatin Modifier. Tumour Biol 2017, 39, 1010428317721620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phong, M.S.; Horn, R.D. Van; Li, S.; Tucker-Kellogg, G.; Surana, U.; Ye, X.S. P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Promotes Cell Survival in Response to DNA Damage but Is Not Required for the G2 DNA Damage Checkpoint in Human Cancer Cells. Mol Cell Biol 2010, 30, 3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Barakat, B.M.; Qin, S.; Ray, A.; El-Mahdy, M.A.; Wani, G.; Arafa, E.S.; Mir, S.N.; Wang, Q.E.; Wani, A.A. The P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Augments Nucleotide Excision Repair by Mediating DDB2 Degradation and Chromatin Relaxation. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 32553–32561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senderowicz, A.M. Small-Molecule Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Modulators. Oncogene 2003, 22, 6609–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golding, S.E.; Rosenberg, E.; Neill, S.; Dent, P.; Povirk, L.F.; Valerie, K. Extracellular Signal-Related Kinase Positively Regulates Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated, Homologous Recombination Repair, and the DNA Damage Response. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köpper, F.; Bierwirth, C.; Schön, M.; Kunze, M.; Elvers, I.; Kranz, D.; Saini, P.; Menon, M.B.; Walter, D.; Sørensen, C.S.; et al. Damage-Induced DNA Replication Stalling Relies on MAPK-Activated Protein Kinase 2 Activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013, 110, 16856–16861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaestel, M. MAPKAP Kinases - MKs - Two’s Company, Three’s a Crowd. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006, 7, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




