Submitted:
09 May 2024
Posted:
13 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Survey of the Application of Owas
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Availability
3.2. Participant Selection and Data Observations
3.3. OWAS Analysis
4. Application of Analyses
4.1. Application of OWAS
4.2. Application of Pearson's Correlation Coefficient
5. Discussion
6. Conclusion
References
- Van Der Beek, A., Rings-Dressen, M., Assessment of mechanical exposure in ergonomic epidemiology. Occupational Environment Med.,55: 29-299,1998.
- Valero E. et al., Musculoskeletal disorders in construction: A review and a novel system for activity tracking with body area network, Applied Ergonomics, Volume 54, Pages 120-130,2016.
- Zimmerman, C.L, Cook, T.M., Rosecrance, J.C.,Trade specific trends in self-reported musculoskeletal symptoms and job factor perceptions among unionized construction workers, In proceedings of the 13th Triennial Congress of the IEA, Tampere, Finland, 6. P. Seppäla, T. Luopajärvi, C-H. Nygård, & M. Mattila ,pp.214-216,1997.
- Widanarko, B., Legg, S. et al., Gender differences in work-related risk factors associated with low back symptoms, Ergonomics, 55 (3), 327e342,2012.
- Winkel, J., Mathiassen, S., Assessment of physical work in epidemiology studies: concepts, issues, and operational considerations, Ergonomics,37: 979-988,1994.
- Bongers, W. C., Kompier, M., Hildebrandt, V., Psychosocial factors at work and musculoskeletal disease, Scand J Work Environ Health, 19: 297-312,1993.
- Armstrong, T., Buckle, P., Fine, L. A., Conceptual model for work-related neck and upper limb musculoskeletal disorders, Scand J Work Environ Health, 19: 73-84,1993.
- Mert E. A., Ergonomik Risk Değerlendirme Yöntemlerinin Karşılaştırılması ve Bir Çanta İmalat Atölyesinde Uygulanması, Yayınlanmış Uzmanlık Tezi, T.C. Çalışma ve Sosyal Güvenlik Bakanlığı, İş Sağlığı ve Güvenliği Genel Müdürlüğü, Ankara, 2014.
- Lingard, H., Sublet, A.,Job, family, and individual characteristics associated with professional burnout in the Australian construction industry. In: Rowlinson, S. (Ed.), Construction Safety Management Systems. Spon Press, London,pp. 233–266,2004.
- Punnett, L., Paquet, V., Ergonomic exposures to construction carpenters and carpentry laborers in tunnel construction.In: Mital, A., et al. (Eds.), Advances in Occupational Ergonomics and Safety I (Proceedings of the XIth International Occupational Ergonomics and Safety Conference).IOS Press, Amsterdam, pp.99–104,1996.
- Mirka, G.A. et al., Continuous assessment of back stress (CABS): a new method to quantify low-back stress in jobs with variable biomechanical demands, Human Factors ,42 (2), 209–225,2000.
- Hartmann, B., Kundel, M., Scaffolders profiles of physical load. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Scientific Conference on Prevention of Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders, PREMUS 2001, Amsterdam, p.169,2001.
- Vink, P., Urlings, I., Van der Molen, H.F., A participatory ergonomics approach to redesign work of scaffolders, Saf.Sci., 26 (1–2), 75–85,1997.
- Latza, U., Karmaus, W., Stu¨rmer, T., Steiner, M., Neth, A., Rehder, U., Cohort study of occupational risk factors of low back pain in construction workers, Occup.Environ.Med.,57 (1),28–34,2000.
- Molano, S.M., Burdorf, A., Elders, L.A.M., Factors associated with medical care-seeking due to low-back pain in scaffolders, Am. J.Ind.Med.,40 (3), 275–281,2001.
- Cutlip, R., Hsiao, H., Garcia, R., Becker, E., Mayeux, B., A comparison of different postures for scaffold end-frame disassembly, Appl. Ergon.,31 (5), 507–513,2000.
- Hsiao, H., Stanevich, R., Biomechanical evaluation of scaffolding tasks, Int.J.Ind.Ergon.,18 (5–6), 407–415,1996.
- Elders, L.A.M., Burdorf, A., Interrelations of risk factors and low back pain in scaffolders.Occup.Environ.Med.58 (9), 597–603,2001.
- Karhu, O., Kansi, P., Kuorinka, I., Correcting working postures in industry: a practical method for analysis, Appl. Ergon., 8 (4), 199e201,1977.
- Van der Beek, A.J., Mathiassen, S.E. et al., An evaluation of methods assessing the physical demands of manual lifting in scaffolding, Appl. Ergon.,36 (2), 213e222,2005.
- Joshi M., Deshpande V., An investigative sensitivity study of Ovako working posture analyzing system (OWAS), Theoretical Issues in Ergonomics Science, Volume 24, Issue 1,2023.
- Bachmid Z. A., Andesta D., Analysis of Improvement of Employee Work Posture Using OWAS Method (case study at PT. XYZ), Jurnal Sains, Teknologi dan Industri, Vol. 20, No. 2, pp.603-610,2023.
- Zorlutuna, A., Kılıç, H. S., Evaluation of Ergonomic Risks in the Construction Sector and an Application, International Journal of Advances in Engineering and Pure Sciences 2022, 34 (1) , 14-26. [CrossRef]
- Satapathy S., Workplace discomfort and risk factors for construction site workers, International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, pages 668–680,2022.
- Iqbal M., Angriani L., Hasanuddin I., Erwan F., Soewardi H., Hassan A., Working Posture Analysis of Wall Building Activities in Construction Works Using The OWAS Method, IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering,2021.
- Zengin M. A., Asal Ö., Evaluation of employee postures in building construction with different ergonomic risk assessment methods, Journal of The Faculty of Engineering and Architecture of Gazi University, Volume number: 35 Issue: 3, ss.1615-1630,2020.
- Yan X., Li H., Zhang H., Rose M. T., Personalized method for self-management of trunk postural ergonomic hazards in construction rebar ironwork, Advanced Engineering Informatics, Volume 37, Pages 31-41,2018.
- Joshi M., Deshpande V., A systematic review of comparative studies on ergonomic assessment techniques, International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2019, Volume 74, 102865,2019.
- Kong Y., Lee S., Lee K., Kim D., Comparisons of ergonomic evaluation tools (ALLA, RULA, REBA and OWAS) for farm work, International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics, Volume 24,2018.
- Brandl C., Mertens A., M. Schlick C., Effect of sampling interval on the reliability of ergonomic analysis using the Ovako working posture analysing system (OWAS) ,International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, Volume 57, Pages 68-73,2017.
- Gomez-Galan, M., Perez-Alonso, J., Callejon-Ferre, A. J., Lopez-Martinez, J., Musculoskeletal disorders: OWAS review, Industrial health, 55 (4), 314-337,2017.
- Lee J., Kim T, Cho H., Kang K., Working Posture Analysis Using OWAS method of Core Wall Construction in High-rise Building, Proceedings of the Korean Institute of Building Construction Conference, 05a, pp 72-73,2016.
- Lee, T.H., Han, C.S., Analysis of Working Postures at a Construction Site Using the OWAS Method, International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics, Volume 19, Issue 2,2013.
- Buchholz B., Paquet V., Punnett L., Lee D., Moir S., PATH: A work sampling-based approach to ergonomic job analysis for construction and other non-repetitive work, Applied Ergonomics, Volume 27, Issue 3, Pages 177-187,1996.
- Schneider, S., Susi, P., Ergonomics and Construction: A Review of Potential Hazards in New Construction, American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, 1994, Volume 55, Issue 7,1994.
- Mattila M., Karwowski W., Vilkki M., Analysis of working postures in hammering tasks on building construction sites using the computerized OWAS method, Applied Ergonomics, Volume 24, Issue 6, Pages 405-4121993.
- Kivi P., Mattila M., Analysis and improvement of work postures in the building industry: application of the computerised OWAS method, Applied Ergonomics,Volume 22, Issue 1, Pages 43-48,1991.
- Loupajarvi, T., Ergonomic analysis of workplace and postural load. In M. I. Bullock (Ed.), Ergonomics, pp. 51-78) UK: Longman Publishers,1990.
- Menegon, L., Campos, Q., Tonin, A., Sticca, G., Souza, J., Volpe, L., Rossi, T., Posture Observer for Ergonomic Observation, Posture Analysis and Reconstruction, USA Patent: US 20120265104 A1,2012.
- Whitford B. A., Correlations, Encyclopaedia of Social Measurement, Pages 523-529,2005.
- Rodgers, J. L., Nicewander, W.A., Thirteen Ways to Look at the Correlation Coefficient, The American Statisticians,42(1), 59-66p,1988.


| No | Study | Field of Activity |
| 1 | Joshi M., Deshpande V.,2023. | An examination of the sensitivity in the OWAS. |
| 2 | Bachmid Z. A., Andesta D.,2023. | Processes of cutting marking, fit up, and packing. |
| 3 | Zorlutuna, A., Kılıç, H. S.,2022. | Mortar preparation, bricklaying, mortar mixing, rebar tying, foundation wrapping, formwork nailing, liquid plaster preparation, plaster application, and mesh pulling. |
| 4 | Satapathy S., 2022. | Using OWAS in Ergo Fellow 3.0 to ascertain the level of discomfort at a construction site. |
| 5 | Iqbal et al.,2021. | Construction of a brick wall, wall plastering and the casting of a concrete column. |
| 6 | Zengin M. A., Asal Ö.,2020. | Evaluation of employee postures in building construction with REBA, QEC, and OWAS. |
| 7 | Yan X. et al., 2019. | Described OWAS posture scores decreased when personalized recommendations were applied. |
| 8 | Joshi M., Deshpande V.,2019. | Comparisons of REBA, RULA, QEC, OKRA, SI, OWAS and other ergonomic risk assessment methodologies. |
| 9 | Kong et al., 2018. | Comparisons of ALLA, RULA, REBA, and OWAS. |
| 10 | Brandl C. et al., 2017. | Explored the reliability of ergonomic analysis of working postures using the OWAS system. |
| 11 | Gomez-Galan, M. et al., 2017. | Literature review on ‘‘web of science’’. |
| 12 | Lee J. et al.,2016. | OWAS method on wall construction |
| 13 | Lee, T.H. et al.,2013. | Evaluated postures by tying beams with steel bars, assembling column templates, and cement grouting of the ground with OWAS. |
| 14 | Buchholz B. et al.,1996. | Posture codes in the PATH method are derived from the OWAS. |
| 15 | Schneider, S. et al.,1994. | Investigation of health hazards in a new construction |
| 16 | Mattila M. et al.,1993. | Evaluations of various tasks such as roof boarding, concrete form preparation, clamping support braces, assembling roof frames, roof joisting, shelter form preparation and fixing fork clamps using the OWAS method. |
| 17 | Kivi P., Mattila M.,1991. | Use of the OWAS method to analyse work postures in building construction. |
|
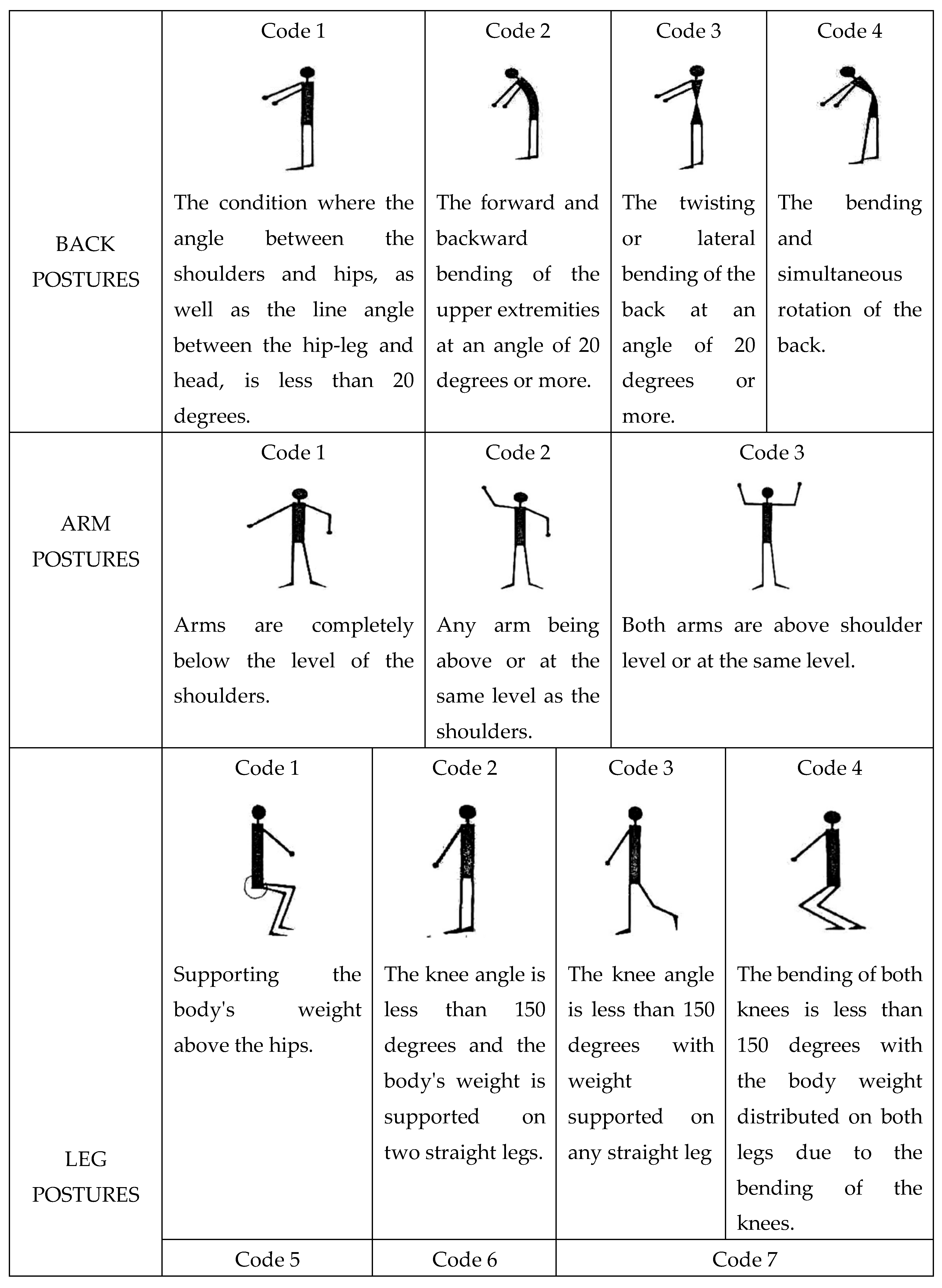
Back |
Arm |
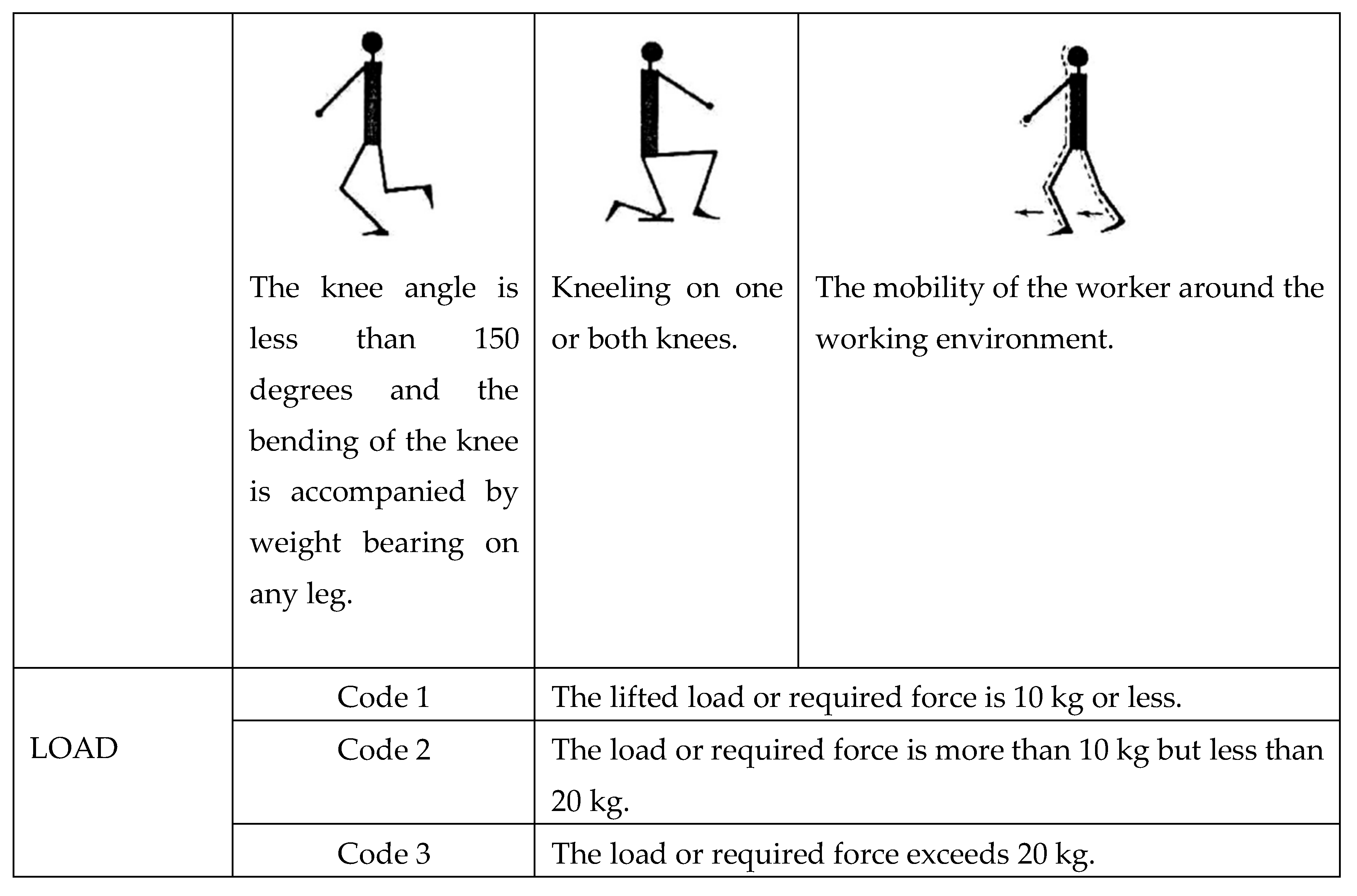
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | Leg | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | Load | ||
| 1 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| Action Code | Action State | Explanation |
| AC1 | Harmless normal posture for the musculoskeletal system. | No action is required. |
| AC2 | Postures with some harmful effects on the musculoskeletal system. | Corrective actions should be taken in the near term. |
| AC3 | Posture with harmful effects on the musculoskeletal system. | Corrective actions should be implemented promptly. |
| AC4 | Postures with severe effects on the musculoskeletal system. | Corrective actions must be applied urgently. |
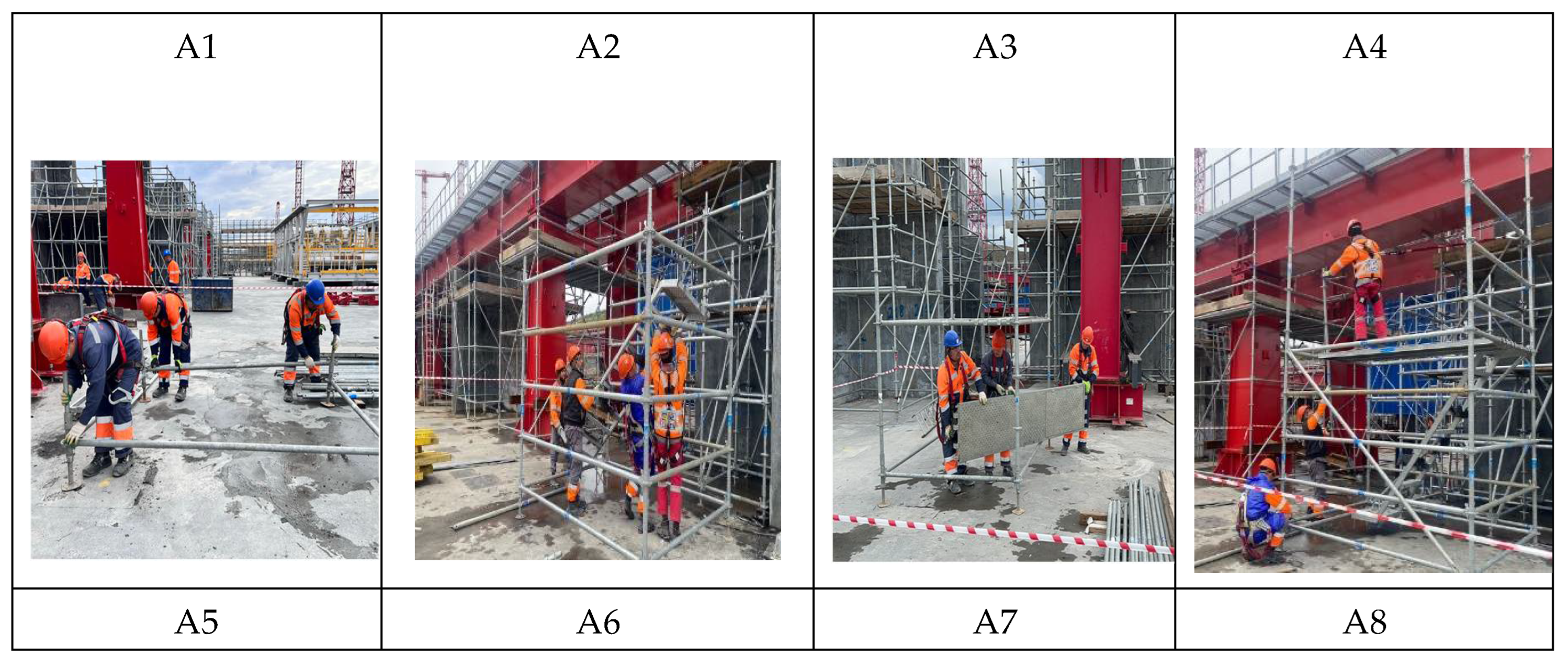
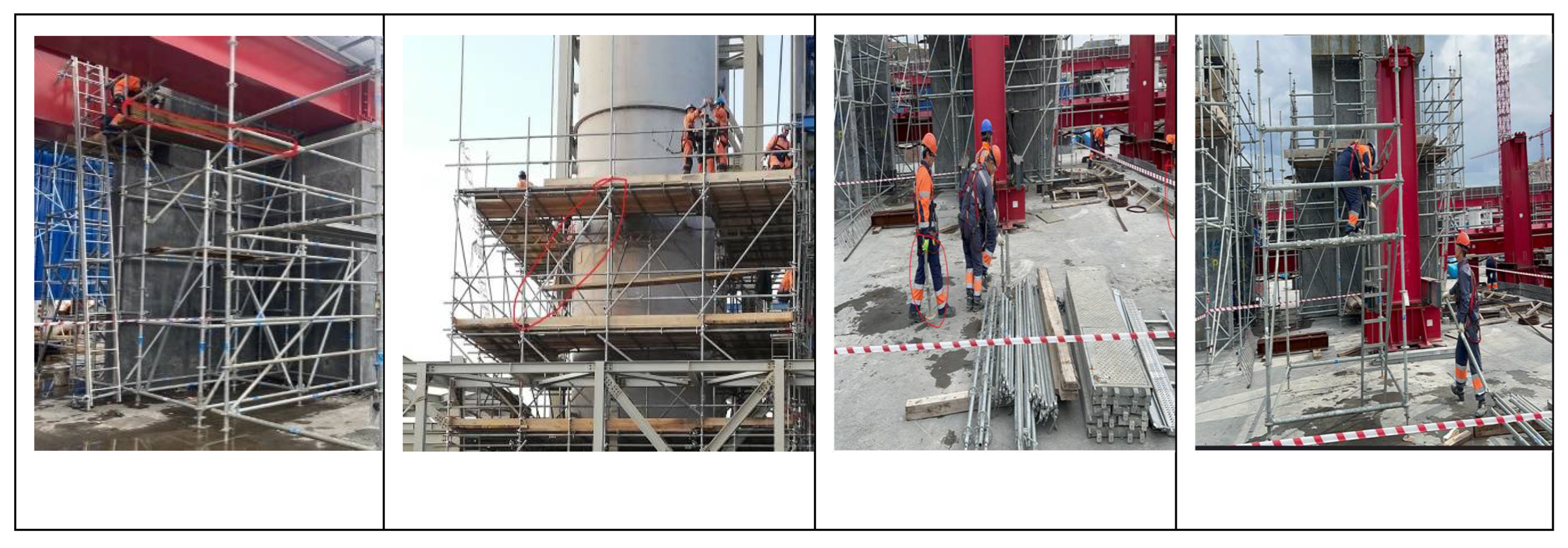
| Equipment | Back Score | Arm Score | Leg Score | Load Score | Action Code |
| A1 | Code 4 | Code 2 | Code 6 | Code 1 | AC4 |
| A2 | Code 2 | Code 3 | Code 7 | Code 3 | AC4 |
| A3 | Code 4 | Code 2 | Code 7 | Code 2 | AC3 |
| A4 | Code 2 | Code 1 | Code 5 | Code 2 | AC3 |
| A5 | Code 4 | Code 1 | Code 6 | Code 1 | AC4 |
| A6 | Code 3 | Code 2 | Code 3 | Code 1 | AC1 |
| A7 | Code 2 | Code 2 | Code 4 | Code 1 | AC4 |
| A8 | Code 4 | Code 2 | Code 7 | Code 1 | AC2 |
| Age Group | Number of workers | Number of workers with MSDs | Absenteeism (days) |
| 18-25 | 125 | 15 | 32 |
| 26-35 | 112 | 13 | 26 |
| 36-45 | 136 | 24 | 56 |
| 46+ | 127 | 31 | 58 |
| Variables | Pearson's Correlation Coefficient (r) | P Value |
| Age Group - MSDs | 0,895 | 0,105 |
| Age Group - Absenteeism (Days) | 0,866 | 0,134 |
| MSDs - Absenteeism (Days) | 0,954 | 0,046 |
| Equipment | Action Code | Action State | Explanation |
| A1 | AC4 | Postures with severe effects on the musculoskeletal system. | Corrective actions must be applied urgently. |
| A2 | AC4 | Postures with severe effects on the musculoskeletal system. | Corrective actions must be applied urgently. |
| A3 | AC3 | Posture with harmful effects on the musculoskeletal system. | Corrective actions should be implemented promptly. |
| A4 | AC3 | Posture with harmful effects on the musculoskeletal system. | Corrective actions should be implemented promptly. |
| A5 | AC4 | Postures with severe effects on the musculoskeletal system. | Corrective actions must be applied urgently. |
| A6 | AC1 | Harmless normal posture for the musculoskeletal system | No action is required. |
| A7 | AC4 | Postures with severe effects on the musculoskeletal system. | Corrective actions must be applied urgently. |
| A8 | AC2 | Postures with some harmful effects on the musculoskeletal system. | Corrective actions should be taken in the near term. |
| Age Group | Number of workers | Number of workers with MSDs | Absenteeism (days) |
| 18-25 | 125 | 8 | 13 |
| 26-35 | 112 | 9 | 15 |
| 36-45 | 136 | 14 | 28 |
| 46+ | 127 | 19 | 33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).