Submitted:
08 May 2024
Posted:
09 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
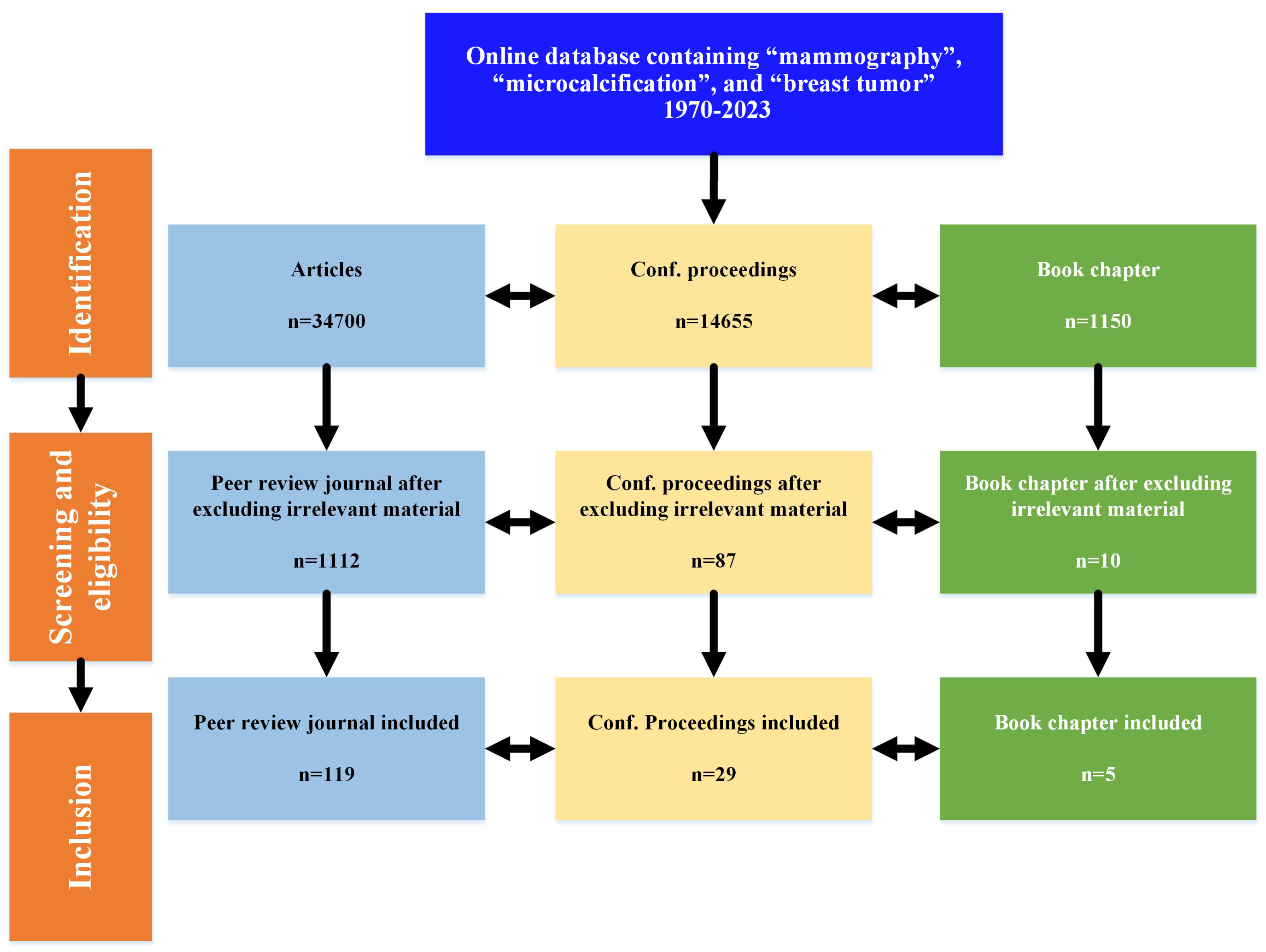
- This work encompasses mammography based on early diagnosis and breast cancer detection, highlighting the significant achievements from 1970 to 2023 using three keywords, namely mammography, microcalcification, and breast tumor.
- The notion is to divide the work into three main basic strategies for early breast cancer detection: image processing-based techniques, ML-based solutions, and DL algorithms.
- Competing algorithms have been briefly discussed in the field of mammography.
- All datasets of mammography have been discussed.
- Recent state-of-the-art techniques have been compared and discussed.
2. Materials and Methods
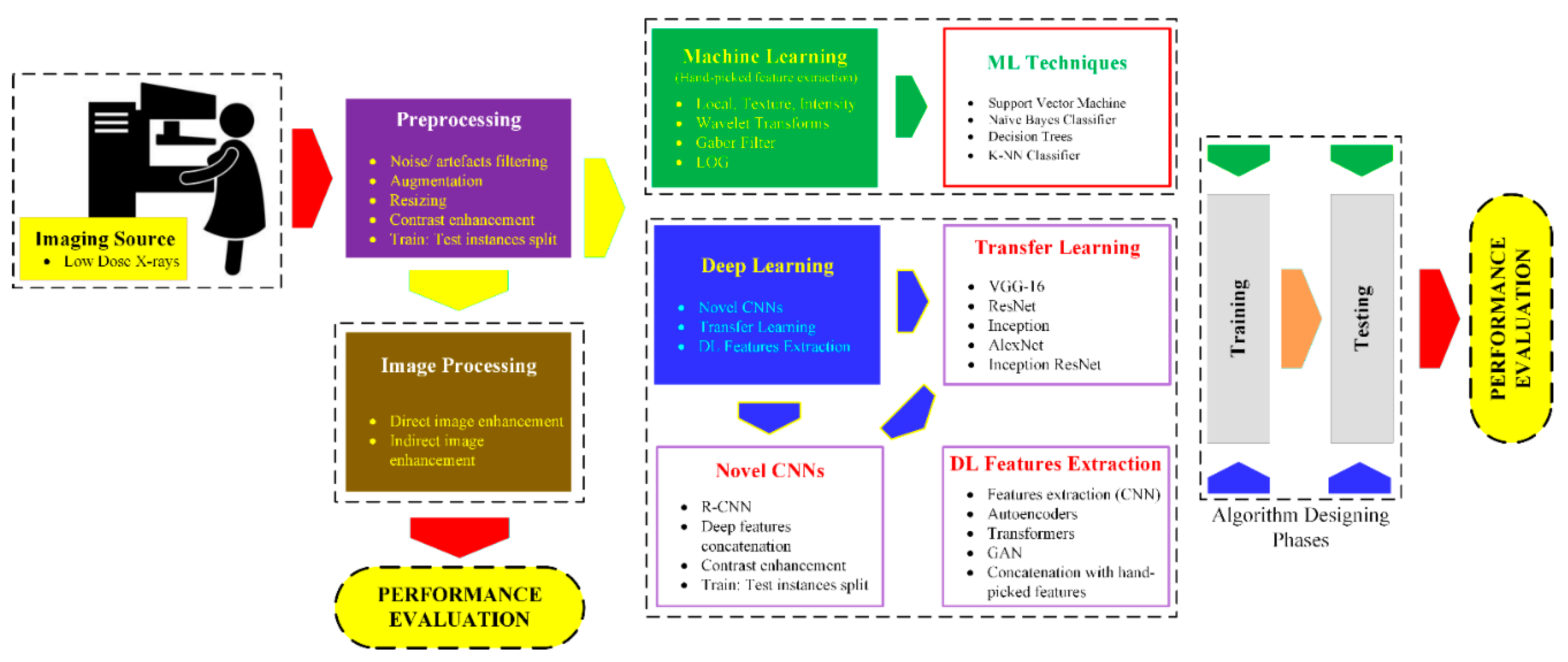
2.1. Preprocessing
2.2. Image Processing Methods
2.3. Classfiication
2.3.1. Feature Extraction for ML
2.3.1.1. Textual Feature Extraction
2.3.1.2. Intensity-based Feature Extraction
2.3.1.3. Multi-scale Feature Extraction
2.3.2. ML Approaches
- k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN) Classifier
- Decision Tree Classifier
- Naïve Bayes (NB) Classifier
- Support Vector Machine
2.3.3. Deep Learning Approaches
- Bayesian Neural Network
- Back Propagation in DL
- Convolutional Neural Network
- Regions with CNN (R-CNN)
- Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Neural Network
3. Results
3.1. Datasets for Mammography
3.2. Image Processing
3.3. Machine Learning
3.4. Deep Learning
3.5. Future Applications of AI in Mammography
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World_Health_Organization. WHO position paper on mammography screening; 2014.
- Ferlay, J.; Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Rosso, S.; Coebergh, J.-W.W.; Comber, H.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. European journal of cancer 2013, 49, 1374–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biermann, F.; Kanie, N.; Kim, R.E. Global governance by goal-setting: the novel approach of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability 2017, 26, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, S.A. Mammographic evaluation of calcifications. RSNA Categorial Course in Breast Imaging 1995, 12, 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Muttarak, M.; Kongmebhol, P.; Sukhamwang, N. Breast calcifications: which are malignant. Singapore Med J 2009, 50, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winchester, D.P.; Jeske, J.M.; Goldschmidt, R.A. The diagnosis and management of ductal carcinoma in-situ of the breast. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 2000, 50, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, J.J.; Taplin, S.H.; Carney, P.A.; Abraham, L.; Sickles, E.A.; D'Orsi, C.; Berns, E.A.; Cutter, G.; Hendrick, R.E.; Barlow, W.E. Influence of computer-aided detection on performance of screening mammography. New England Journal of Medicine 2007, 356, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Cai, H.; Tan, W.; Jin, C.; Li, L. Discrimination of breast cancer with microcalcifications on mammography by deep learning. Scientific reports 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowell, C.F.; Weigelt, B.; Sakr, R.A.; Ng, C.K.; Hicks, J.; King, T.A.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Progression from ductal carcinoma in situ to invasive breast cancer: revisited. Molecular oncology 2013, 7, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, P.; Snyder, R.E.; Foote, F.W.; Wallace, T. Detection of occult carcinoma in the apparently benign breast biopsy through specimen radiography. Cancer 1970, 26, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.A.; Nicholson, B.T.; Cohen, M.A. Finding early invasive breast cancers: a practical approach. Radiology 2008, 248, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabár, L.; Duffy, S.W.; Vitak, B.; Chen, H.H.; Prevost, T.C. The natural history of breast carcinoma: what have we learned from screening? Cancer 1999, 86, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Rashwan, H.A.; Romani, S.; Akram, F.; Pandey, N.; Sarker, M.M.K.; Saleh, A.; Arenas, M.; Arquez, M.; Puig, D. Breast tumor segmentation and shape classification in mammograms using generative adversarial and convolutional neural network. Expert Systems with Applications 2020, 139, 112855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaglan, P.; Dass, R.; Duhan, M. Breast cancer detection techniques: issues and challenges. Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series B 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribli, D.; Horváth, A.; Unger, Z.; Pollner, P.; Csabai, I. Detecting and classifying lesions in mammograms with deep learning. Scientific reports 2018, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeffinger, K.C.; Fontham, E.T.; Etzioni, R.; Herzig, A.; Michaelson, J.S.; Shih, Y.-C.T.; Walter, L.C.; Church, T.R.; Flowers, C.R.; LaMonte, S.J. Breast cancer screening for women at average risk: 2015 guideline update from the American Cancer Society. Jama 2015, 314, 1599–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.S.; Moon, W.K.; Chang, J.M.; Koo, H.R.; Kim, W.H.; Cho, N.; Yi, A.; La Yun, B.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.Y. Breast cancer detected with screening US: reasons for nondetection at mammography. Radiology 2014, 270, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboutalib, S.S.; Mohamed, A.A.; Berg, W.A.; Zuley, M.L.; Sumkin, J.H.; Wu, S. Deep learning to distinguish recalled but benign mammography images in breast cancer screening. Clinical Cancer Research 2018, 24, 5902–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-K.; Kim, H.-E.; Han, K.; Kang, B.J.; Sohn, Y.-M.; Woo, O.H.; Lee, C.W. Applying data-driven imaging biomarker in mammography for breast cancer screening: preliminary study. Scientific reports 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidinekoo, A.; Denton, E.; Rampun, A.; Honnor, K.; Zwiggelaar, R. Deep learning in mammography and breast histology, an overview and future trends. Medical image analysis 2018, 47, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, J.R.; Torosdagli, N.; Khosravan, N.; RaviPrakash, H.; Mortazi, A.; Tissavirasingham, F.; Hussein, S.; Bagci, U. Deep learning beyond cats and dogs: recent advances in diagnosing breast cancer with deep neural networks. The British journal of radiology 2018, 91, 20170545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooi, T.; Litjens, G.; Van Ginneken, B.; Gubern-Mérida, A.; Sánchez, C.I.; Mann, R.; den Heeten, A.; Karssemeijer, N. Large scale deep learning for computer aided detection of mammographic lesions. Medical image analysis 2017, 35, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Diaz, O.; Lladó, X.; Yap, M.H.; Martí, R. Automatic mass detection in mammograms using deep convolutional neural networks. Journal of Medical Imaging 2019, 6, 031409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhafiz, D.; Yang, C.; Ammar, R.; Nabavi, S. Deep convolutional neural networks for mammography: advances, challenges and applications. BMC bioinformatics 2019, 20, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardezi, S.J.S.; Elazab, A.; Lei, B.; Wang, T. Breast cancer detection and diagnosis using mammographic data: Systematic review. Journal of medical Internet research 2019, 21, e14464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geras, K.J.; Mann, R.M.; Moy, L. Artificial intelligence for mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis: current concepts and future perspectives. Radiology 2019, 293, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickman, S.E.; Woitek, R.; Le, E.P.V.; Im, Y.R.; Mouritsen Luxhøj, C.; Aviles-Rivero, A.I.; Baxter, G.C.; MacKay, J.W.; Gilbert, F.J. Machine learning for workflow applications in screening mammography: systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology 2022, 302, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Adam, R.; Huang, P.; Maldjian, T.; Duong, T.Q. Deep Learning Prediction of Pathologic Complete Response in Breast Cancer Using MRI and Other Clinical Data: A Systematic Review. Tomography 2022, 8, 2784–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeek, A.; Holland, R.; Sturmans, F.; Hendriks, J.; Avunac, M.; Day, N. Reduction of breast cancer mortality through mass screening with modern mammography: first results of the Nijmegen project, 1975-1981. The Lancet 1984, 323, 1222–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, J.N.; Saftlas, A.F.; Salane, M. Mammographic parenchymal patterns and quantitative evaluation of mammographic densities: a case-control study. American Journal of Roentgenology 1987, 148, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, P.A.; Miglioretti, D.L.; Yankaskas, B.C.; Kerlikowske, K.; Rosenberg, R.; Rutter, C.M.; Geller, B.M.; Abraham, L.A.; Taplin, S.H.; Dignan, M. Individual and combined effects of age, breast density, and hormone replacement therapy use on the accuracy of screening mammography. Annals of internal medicine 2003, 138, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, E.; Plewes, D.B.; Hill, K.A.; Causer, P.A.; Zubovits, J.T.; Jong, R.A.; Cutrara, M.R.; DeBoer, G.; Yaffe, M.J.; Messner, S.J. Surveillance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers with magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, mammography, and clinical breast examination. Jama 2004, 292, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarassenko, L.; Hayton, P.; Cerneaz, N.; Brady, M. Novelty detection for the identification of masses in mammograms. 1995. [CrossRef]
- Saslow, D.; Boetes, C.; Burke, W.; Harms, S.; Leach, M.O.; Lehman, C.D.; Morris, E.; Pisano, E.; Schnall, M.; Sener, S. American Cancer Society guidelines for breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 2007, 57, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Metaxas, D.N. Computer-aided diagnosis of mammographic masses using scalable image retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2014, 62, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dheeba, J.; Singh, N.A.; Selvi, S.T. Computer-aided detection of breast cancer on mammograms: A swarm intelligence optimized wavelet neural network approach. Journal of biomedical informatics 2014, 49, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, H.G.; Prorok, P.C.; O’Malley, A.J.; Kramer, B.S. Breast-cancer tumor size, overdiagnosis, and mammography screening effectiveness. New England Journal of Medicine 2016, 375, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y. Breast mass classification in digital mammography based on extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 2016, 173, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangayyan, R.M.; Shen, L.; Shen, Y.; Desautels, J.L.; Bryant, H.; Terry, T.J.; Horeczko, N.; Rose, M.S. Improvement of sensitivity of breast cancer diagnosis with adaptive neighborhood contrast enhancement of mammograms. IEEE transactions on information technology in biomedicine 1997, 1, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, Q. A direct image contrast enhancement algorithm in the wavelet domain for screening mammograms. IEEE Journal of selected topics in signal processing 2009, 3, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ye, Z. Brightness preserving histogram equalization with maximum entropy: a variational perspective. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics 2005, 51, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Georganas, N.D.; Petriu, E.M. Applying contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization and integral projection for facial feature enhancement and detection. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings; 2010; pp. 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.; Rangayyan, R.M. Feature enhancement of film mammograms using fixed and adaptive neighborhoods. Applied optics 1984, 23, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Qian, W.; Sankar, R.; Song, D.; Clark, R. A new false positive reduction method for MCCs detection in digital mammography. 2001, 2, 1033–1036.
- Davies, D.; Dance, D. Automatic computer detection of clustered calcifications in digital mammograms. Physics in Medicine & Biology 1990, 35, 1111. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.K.; Park, H.W. Statistical textural features for detection of microcalcifications in digitized mammograms. IEEE transactions on medical imaging 1999, 18, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I.H. Textural features for image classification. IEEE Transactions on systems, man, and cybernetics 1973, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, M.M. Texture analysis using grey level run lengths. NASA STI/Recon Technical Report N 1974, 75, 18555. [Google Scholar]
- Weszka, J.S.; Dyer, C.R.; Rosenfeld, A. A comparative study of texture measures for terrain classification. IEEE transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics 1976, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltonsy, N.H.; Tourassi, G.D.; Elmaghraby, A.S. A concentric morphology model for the detection of masses in mammography. IEEE transactions on medical imaging 2007, 26, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laws, K.I. Textured image segmentation; University of Southern California Los Angeles Image Processing INST: 1980.
- Yu, S.; Guan, L.; Brown, S. Automatic detection of clustered microcalcifications in digitized mammogram films. Journal of Electronic Imaging 1999, 8, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, A.P.; Chitre, Y.; Kaiser-Bonasso, C. Analysis of mammographic microcalcifications using gray-level image structure features. IEEE Transactions on medical imaging 1996, 15, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, F.R.; Soltanian-Zadeh, H.; Rahmati, M.; Pour-Abdollah, S. Microcalcification classification in mammograms using multiwavelet features. In Proceedings of the Wavelet Applications in Signal and Image Processing VII; 1999; pp. 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogova, G.L.; Stomper, P.C.; Ke, C.-C. Microcalcification texture analysis in a hybrid system for computer-aided mammography. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 1999: Image Processing; 1999; pp. 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netsch, T.; Peitgen, H.-O. Scale-space signatures for the detection of clustered microcalcifications in digital mammograms. IEEE Transactions on medical imaging 1999, 18, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-D.; Cai, X.; Chen, X.; Hu, L.; Lou, X. Computer-aided detection and classification of microcalcifications in mammograms: a survey. Pattern recognition 2003, 36, 2967–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpaslan, N.; Kara, A.; Zenci̇r, B.; Hanbay, D. Classification of breast masses in mammogram images using KNN. In Proceedings of the 2015 23nd Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU); 2015; pp. 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.M.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning; McGraw-hill New York, 1997; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rennie, J.D.; Shih, L.; Teevan, J.; Karger, D.R. Tackling the poor assumptions of naive bayes text classifiers. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 20th international conference on machine learning (ICML-03), 2003; pp. 616–623. [CrossRef]
- Alpaydin, E. Introduction to machine learning; MIT press, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Advances in neural information processing systems 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delphia, A.A.; Kamarasan, M.; Sathiamoorthy, S. Image Processing For Identification of Breast Cancer: A Literature Survey. AJES 2018, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, L. Statistical Problems in Particle Physics, Astrophysics and Cosmology: PHYSTAT05, Oxford, UK, 12-15 September 2005; 2006.
- Specht, D.F. Probabilistic neural networks. Neural networks 1990, 3, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Qian, W.; Clarke, L.P. Digital mammography: mixed feature neural network with spectral entropy decision for detection of microcalcifications. IEEE transactions on medical imaging 1996, 15, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahid, A.-A.; Kong, Y. Involvement of machine learning for breast cancer image classification: a survey. Computational and mathematical methods in medicine 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandare, A.; Bhide, M.; Gokhale, P.; Chandavarkar, R. Applications of convolutional neural networks. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies 2016, 7, 2206–2215. [Google Scholar]
- Sahiner, B.; Chan, H.-P.; Petrick, N.; Wei, D.; Helvie, M.A.; Adler, D.D.; Goodsitt, M.M. Classification of mass and normal breast tissue: a convolution neural network classifier with spatial domain and texture images. IEEE transactions on Medical Imaging 1996, 15, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.-C.B.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Kinnard, L.; Freedman, M.T. A multiple circular path convolution neural network system for detection of mammographic masses. IEEE transactions on medical imaging 2002, 21, 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, P.; Mendoza, J.; Wainer, J.; Ferrer, J.; Pinto, J.; Guerrero, J.; Castaneda, B. Automatic breast density classification using a convolutional neural network architecture search procedure. 2015, 9414, 941428. [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Liu, F.; Xie, Y.; Xing, F.; Meyyappan, S.; Yang, L. Region segmentation in histopathological breast cancer images using deep convolutional neural network. 2015, 55-58. [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. A deep feature based framework for breast masses classification. Neurocomputing 2016, 197, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo, J.; González, F.A.; Ramos-Pollán, R.; Oliveira, J.L.; Lopez, M.A.G. Representation learning for mammography mass lesion classification with convolutional neural networks. Computer methods and programs in biomedicine 2016, 127, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaeilouyeh, H.; Mollahosseini, A.; Mahoor, M.H. Microscopic medical image classification framework via deep learning and shearlet transform. Journal of Medical Imaging 2016, 3, 044501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadoon, M.M.; Zhang, Q.; Haq, I.U.; Butt, S.; Jadoon, A. Three-class mammogram classification based on descriptive CNN features. BioMed research international 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffar, M.A. Deep learning based computer aided diagnosis system for breast mammograms. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 2017, 8, 286–290. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Xiang, X.; Tran, T.D.; Hager, G.D.; Xie, X. Adversarial deep structured nets for mass segmentation from mammograms. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI 2018); 2018; pp. 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Su, H.; Cui, L.; He, H.; Liu, L. Breast mass classification via deeply integrating the contextual information from multi-view data. Pattern Recognition 2018, 80, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastounioti, A.; Oustimov, A.; Hsieh, M.-K.; Pantalone, L.; Conant, E.F.; Kontos, D. Using convolutional neural networks for enhanced capture of breast parenchymal complexity patterns associated with breast cancer risk. Academic radiology 2018, 25, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiao, J.-Y.; Chen, K.-Y.; Liao, K.Y.-K.; Hsieh, P.-H.; Zhang, G.; Huang, T.-C. Detection and classification the breast tumors using mask R-CNN on sonograms. Medicine 2019, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural computation 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahid, A.-A.; Mehrabi, M.A.; Kong, Y. Histopathological breast cancer image classification by deep neural network techniques guided by local clustering. BioMed research international 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suckling, J.; Parker, J.; Dance, D.; Astley, S.; Hutt, I.; Boggis, C.; Ricketts, I.; Stamatakis, E.; Cerneaz, N.; Kok, S. Mammographic image analysis society (mias) database v1. 21. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Suckling, J. The mammographic images analysis society digital mammogram database. In Proceedings of the Exerpta Medica. International Congress Series 1994, 1994, 375–378. [Google Scholar]
- Heath, M.; Bowyer, K.; Kopans, D.; Moore, R.; Kegelmeyer, W. The digital database for screening mammography In: Yaffe. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Digital Mammography, 2000; pp. 212–218.
- Lee, R.S.; Gimenez, F.; Hoogi, A.; Miyake, K.K.; Gorovoy, M.; Rubin, D.L. A curated mammography data set for use in computer-aided detection and diagnosis research. Scientific data 2017, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.E.; Gueld, M.O.; Araújo, A.d.A.; Ott, B.; Deserno, T.M. Toward a standard reference database for computer-aided mammography. In Proceedings of the Medical imaging 2008: Computer-aided diagnosis; 2008; pp. 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheus, B.R.N.; Schiabel, H. Online mammographic images database for development and comparison of CAD schemes. Journal of digital imaging 2011, 24, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, I.C.; Amaral, I.; Domingues, I.; Cardoso, A.; Cardoso, M.J.; Cardoso, J.S. Inbreast: toward a full-field digital mammographic database. Academic radiology 2012, 19, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsolami, A.S.; Shalash, W.; Alsaggaf, W.; Ashoor, S.; Refaat, H.; Elmogy, M. king Abdulaziz university breast cancer mammogram dataset (KAU-BCMD). Data 2021, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Pham, H.H.; Lam, K.; Le, L.T.; Dao, M.; Vu, V. VinDr-Mammo: A large-scale benchmark dataset for computer-aided diagnosis in full-field digital mammography. Scientific Data 2023, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, H.H.; Trung, H.N.; Nguyen, H.Q. Vindr-mammo: A large-scale benchmark dataset for computer-aided detection and diagnosis in full-field digital mammography. Sci Data 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Karale, V.A.; Ebenezer, J.P.; Chakraborty, J.; Singh, T.; Sadhu, A.; Khandelwal, N.; Mukhopadhyay, S. A screening CAD tool for the detection of microcalcification clusters in mammograms. Journal of digital imaging 2019, 32, 728–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Luo, L.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y. Cascaded generative and discriminative learning for microcalcification detection in breast mammograms. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019; pp. 12578–12586. [CrossRef]
- Karale, V.A.; Singh, T.; Sadhu, A.; Khandelwal, N.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Reduction of false positives in the screening CAD tool for microcalcification detection. Sādhanā 2020, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karale, V.A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Singh, T.; Khandelwal, N.; Sadhu, A. Automated detection of microcalcification clusters in mammograms. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2017: Computer-Aided Diagnosis; 2017; p. 101342R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, T. Development of mass detection algorithm based on adaptive thresholding technique in digital mammograms. Digital Mammography'96 1996, 391-396.
- Dominguez, A.R.; Nandi, A.K. Detection of masses in mammograms via statistically based enhancement, multilevel-thresholding segmentation, and region selection. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 2008, 32, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Mello-Thoms, C.; Wang, X.-H.; Gur, D. Improvement of visual similarity of similar breast masses selected by computer-aided diagnosis schemes. In Proceedings of the 2007 4th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro; 2007; pp. 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Agyepong, K. Gradient vector flow field and mass region extraction in digital mammograms. In Proceedings of the 2008 21st IEEE International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems; 2008; pp. 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Giger, M.L.; Li, H.; Sennett, C. Correlative feature analysis of FFDM images. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2008: Computer-Aided Diagnosis; 2008; pp. 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, A.E.; Ali, J.M. Digital mammogram segmentation algorithm using pulse coupled neural networks. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Image and Graphics (ICIG'04); 2004; pp. 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, C.B.; Stapleton, S.J.; Holdsworth, D.W.; Jong, R.; Weiser, W.; Cooke, G.; Yaffe, M.J. Characterization of mammographic parenchymal pattern by fractal dimension. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging III: Image Processing; 1989; pp. 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Chang, Y.-H.; Wang, X.H.; Good, W.F.; Gur, D. Application of a Bayesian belief network in a computer-assisted diagnosis scheme for mass detection. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 1999: Image Processing; 1999; pp. 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, D.; Aghdasi, F. Texture analysis techniques for the classification of microcalcifications in digitised mammograms. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Africon. 5th Africon Conference in Africa (Cat. No. 99CH36342); 1999; pp. 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Gao, F.; Long, R.; Zhang, F.-D.; Huang, C.-C.; Cao, M.; Yu, Y.-Z.; Sun, Y.-S. Peri-lesion regions in differentiating suspicious breast calcification-only lesions specifically on contrast enhanced mammography. Journal of X-Ray Science and Technology, 2024; 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Prinzi, F.; Orlando, A.; Gaglio, S.; Vitabile, S. Interpretable Radiomic Signature for Breast Microcalcification Detection and Classification. Journal of Imaging Informatics in Medicine 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoen, H.; Jang, M.-j.; Yi, A.; Moon, W.K.; Chang, J.M. Artificial Intelligence for Breast Cancer Detection on Mammography: Factors Related to Cancer Detection. Academic Radiology 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, A.A.; Alias, M.A.; Razak, F.A.; Noorani, M.S.M.; Mahmud, R.; Zulkepli, N.F.S. Persistent Homology-Based Machine Learning Method for Filtering and Classifying Mammographic Microcalcification Images in Early Cancer Detection. Cancers 2023, 15, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, A.; Mehmood, A.; Alabrah, A.; Alkhamees, B.F.; Amin, F.; AlSalman, H.; Choi, G.S. Breast Cancer Detection and Prevention Using Machine Learning. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Qian, W.; Clarke, L.P.; Clark, R.A.; Thomas, J.A. Improving mass detection by adaptive and multiscale processing in digitized mammograms. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 1999: Image Processing; 1999; pp. 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseri, I.; Oz, C. Computer aided detection of microcalcification clusters in mammogram images with machine learning approach. Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials 2014, 8, 689–695. [Google Scholar]
- Rampun, A.; Wang, H.; Scotney, B.; Morrow, P.; Zwiggelaar, R. Classification of mammographic microcalcification clusters with machine learning confidence levels. In Proceedings of the 14th International workshop on breast imaging (IWBI 2018); 2018; pp. 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanizzi, A.; Basile, T.M.; Losurdo, L.; Bellotti, R.; Bottigli, U.; Dentamaro, R.; Didonna, V.; Fausto, A.; Massafra, R.; Moschetta, M. A machine learning approach on multiscale texture analysis for breast microcalcification diagnosis. BMC bioinformatics 2020, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vy, V.P.T.; Yao, M.M.-S.; Khanh Le, N.Q.; Chan, W.P. Machine learning algorithm for distinguishing ductal carcinoma in situ from invasive breast cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarvestani, Z.M.; Jamali, J.; Taghizadeh, M.; Dindarloo, M.H.F. A novel machine learning approach on texture analysis for automatic breast microcalcification diagnosis classification of mammogram images. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology 2023, 149, 6151–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Tan, W.-M.; Ge, J.-Y.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Jin, Y.-T.; Shao, Z.-M.; Gu, Y.-J.; Yan, B. Artificial intelligence-based diagnosis of breast cancer by mammography microcalcification. Fundamental Research 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Lee, S.; Wong, S.; Yeh, J.; Wang, A.; Wu, H. Image segmentation feature selection and pattern classification for mammographic microcalcifications. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 2005, 29, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golobardes, E.; Martí, J.; Español, J.; Salamó Llorente, M.; Freixenet, J.; Llorà Fàbrega, X.; Maroto, A.; Bernadó Mansilla, E. Classifying Microcalcifications in Digital Mammograms using Machine Learning techniques. 2001.
- Alolfe, M.A.; Mohamed, W.A.; Youssef, A.-B.M.; Kadah, Y.M.; Mohamed, A.S. Feature selection in computer aided diagnostic system for microcalcification detection in digital mammograms. In Proceedings of the 2009 National Radio Science Conference; 2009; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, A.; Fotiadis, D.I.; Likas, A. Characterization of clustered microcalcifications in digitized mammograms using neural networks and support vector machines. Artificial intelligence in medicine 2005, 34, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Y.; Lo, S.-C.B.; Freedman, M.T.; Hasegawa, A.; Zuurbier, R.A.; Mun, S.K. Classification of microcalcifications in radiographs of pathological specimen for the diagnosis of breast cancer. 1994, 2167, 630–641. [CrossRef]
- Huynh, B.Q.; Li, H.; Giger, M.L. Digital mammographic tumor classification using transfer learning from deep convolutional neural networks. Journal of Medical Imaging 2016, 3, 034501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, S.S.; Rajaguru, H. Automatic Detection and Classification of Mammograms Using Improved Extreme Learning Machine with Deep Learning. IRBM 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, D.; Yamamoto, A.; Takashima, T.; Onoda, N.; Noda, S.; Kashiwagi, S.; Morisaki, T.; Tsutsumi, S.; Honjo, T.; Shimazaki, A. Visualizing “featureless” regions on mammograms classified as invasive ductal carcinomas by a deep learning algorithm: the promise of AI support in radiology. Japanese Journal of Radiology 2021, 39, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiderski, B.; Gielata, L.; Olszewski, P.; Osowski, S.; Kołodziej, M. Deep neural system for supporting tumor recognition of mammograms using modified GAN. Expert Systems with Applications 2021, 164, 113968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lou, M.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pi, J.; Ma, Y. Multi-Scale Attention-Guided Network for mammograms classification. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2021, 68, 102730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-L.; Lin, T.-Y. Considering breast density for the classification of benign and malignant mammograms. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2021, 67, 102564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebari, D.A.; Ibrahim, D.A.; Zeebaree, D.Q.; Mohammed, M.A.; Haron, H.; Zebari, N.A.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliūnas, R. Breast cancer detection using mammogram images with improved multi-fractal dimension approach and feature fusion. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 12122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomani, A.; Ansari, Y.; Nasirpour, M.H.; Masoumian, A.; Pour, E.S.; Valizadeh, A. PSOWNNs-CNN: a computational radiology for breast cancer diagnosis improvement based on image processing using machine learning methods. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, S.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliūnas, R. TTCNN: A breast cancer detection and classification towards computer-aided diagnosis using digital mammography in early stages. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.-H.; Kujabi, B.K.; Chuang, C.-L.; Lin, C.-S.; Chiu, C.-J. Application of deep learning to construct breast cancer diagnosis model. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.; Muduly, S.; Mohanty, S.; Ravindra, J.; Mohanty, S.N. Evaluation of deep learning models for detecting breast cancer using histopathological mammograms Images. Sustainable Operations and Computers 2022, 3, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tam, R.M.; Al-Hejri, A.M.; Narangale, S.M.; Samee, N.A.; Mahmoud, N.F.; Al-Masni, M.A.; Al-Antari, M.A. A hybrid workflow of residual convolutional transformer encoder for breast cancer classification using digital X-ray mammograms. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Singh, K.; Kumar, S.; Antonakakis, M.; Moirogiorgou, K.; Deep, A.; Kashyap, K.L.; Bajpai, M.K.; Zervakis, M. Deep learning capabilities for the categorization of microcalcification. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsheikhy, A.A.; Said, Y.; Shawly, T.; Alzahrani, A.K.; Lahza, H. Biomedical diagnosis of breast cancer using deep learning and multiple classifiers. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, K.; Marasinou, C.; Li, B.; Nakhaei, N.; Li, B.; Elmore, J.G.; Shapiro, L.; Hsu, W. Automated quantitative assessment of amorphous calcifications: Towards improved malignancy risk stratification. Computers in biology and medicine 2022, 146, 105504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Luo, R.; Wu, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, H.; Tan, W.; Yin, H. A deep learning model integrating mammography and clinical factors facilitates the malignancy prediction of BI-RADS 4 microcalcifications in breast cancer screening. European Radiology 2021, 31, 5902–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, R.; Mutasa, S.; Sant, E.P.V.; Karcich, J.; Chin, C.; Liu, M.Z.; Jambawalikar, S. Accuracy of distinguishing atypical ductal hyperplasia from ductal carcinoma in situ with convolutional neural network–based machine learning approach using mammographic image data. American Journal of Roentgenology 2019, 212, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodan, M.; Paraschiv, E.; Stanciu, A. Applying deep learning methods for mammography analysis and breast cancer detection. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuque, M.P.; Lobbes, M.B.; van Wijk, Y.; Widaatalla, Y.; Primakov, S.; Majer, M.; Balleyguier, C.; Woodruff, H.C.; Lambin, P. Combining deep learning and handcrafted radiomics for classification of suspicious lesions on contrast-enhanced mammograms. Radiology 2023, 307, e221843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesapane, F.; Trentin, C.; Ferrari, F.; Signorelli, G.; Tantrige, P.; Montesano, M.; Cicala, C.; Virgoli, R.; D’Acquisto, S.; Nicosia, L. Deep learning performance for detection and classification of microcalcifications on mammography. European Radiology Experimental 2023, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Bhupati; Bhambu, P.; Pachar, S.; Cotrina-Aliaga, J.C.; Arias-Gonzáles, J.L. Deep Learning-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis Model for the Identification and Classification of Mammography Images. SN Computer Science 2023, 4, 502. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-Y.; Kao, Y.-W.; Wang, J.-C.; Tsai, T.-Y.; Chung, W.-S.; Hsu, J.-S.; Hou, M.-F.; Weng, S.-F. Multitask deep learning on mammography to predict extensive intraductal component in invasive breast cancer. European Radiology 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, G.; Nascimento, J.; Bradley, A.P. Unregistered multiview mammogram analysis with pre-trained deep learning models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; 2015; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Tseng, T.-L.B.; Zhang, J.; Qian, W. Enhancing deep convolutional neural network scheme for breast cancer diagnosis with unlabeled data. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 2017, 57, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samala, R.K.; Chan, H.-P.; Hadjiiski, L.M.; Cha, K.; Helvie, M.A. Deep-learning convolution neural network for computer-aided detection of microcalcifications in digital breast tomosynthesis. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2016: Computer-Aided Diagnosis; 2016; p. 97850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshamrani, K.; Alshamrani, H.A.; Alqahtani, F.F.; Almutairi, B.S. Enhancement of mammographic images using histogram-based techniques for their classification using CNN. Sensors 2022, 23, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CureMetrix_website. Risk for coronary artery disease. Available online: https://curemetrix.com/cmangio/ (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Rodriguez-Ruiz, A.; Lång, K.; Gubern-Merida, A.; Teuwen, J.; Broeders, M.; Gennaro, G.; Clauser, P.; Helbich, T.H.; Chevalier, M.; Mertelmeier, T. Can we reduce the workload of mammographic screening by automatic identification of normal exams with artificial intelligence? A feasibility study. European radiology 2019, 29, 4825–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartar, M.; Le, L.; Watanabe, A.T.; Enomoto, A.J. Artificial intelligence support for mammography: in-practice clinical experience. Journal of the American College of Radiology 2021, 18, 1510–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Years slab | Methods | Specific Type Basis | Refs. | No. of citations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970-1989 (20) | MA | IP | Mass screening through modern mammography. | [30] | 700 |
| CA | ML | Radiographic appearance of the breast parenchyma-based detection. | [31] | 378 | |
| 1990-2005 (16) | MA | IP | Role of hormone replacement therapy correlated with age and microcalcification density | [32] | 1487 |
| CA | ML | Four methods for surveillance of mutation carriers due to BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation. | [33] | 1493 | |
| DL | Novelty detection for identification of mass mammograms. | [34] | 483 | ||
| 2006-2015 (10) | MA | IP | Breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. | [35] | 3437 |
| CA | ML | Diagnosing mammographic masses using scalable image retrieval and scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT). | [36] | 139 | |
| DL | A swarm intelligence optimized wavelet neural network method for breast cancer detection. | [37] | 474 | ||
| 2016-2023 (8) | MA | IP | Tumor size, overdiagnosis and mammography effectiveness. | [38] | 698 |
| CA | ML | Breast mass classification based on SVM and Extreme Learning Machine (ELM). | [39] | 176 | |
| DL | Detection of radiological lesions in mammograms using DL. | [23] | 1041 | ||
| Dataset | Number of Images |
Classes | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIAS (50 microns) [85] | 322 | B, M, N | 1994 |
| Mini-MIAS (200 microns) [86] | 322 | B, M | 1994 |
| DDSM [87] | 10480 | B, M, N | 1999 |
| CBIS-DDSM [88] | 10239 | B, M, N | 2017 |
| IRMA [89] | 1515 | B, M, N | 2009 |
| BancoWeb LAPIMO [90] | 1400 | B, M, N | 2011 |
| INBreast [91] | 410 | B, M, N | 2010 |
| KAU-BCMD [92] | 5662 | B(2), M(5), N(1) | 2021 |
| VinDr-Mammo [94] | 5000 | B(2), M(5), N(1) | 2022 |
| Microcalcification Method | Acronym | Dataset | Method | Authors | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Multi-Scale 2D NEO Max Multi-Scale and 2D NEO |
MnM2DNEO MxM2DNEO |
DDSM, INbreast and PGIMER-IITKGP databases | Data reduction approach based on data distribution | Karale et al. | [95] |
| Anomaly Separation Network | ASN | INBreast | Hybrid approach (generative plus discriminative) | Zhang et al. | [96] |
| Max Multi-Scale 2D NEO Mean Multi-Scale 2D-NEO |
Modified MxM2DNEO Modified MnM2DNEO |
DDSM, INbreast and PGIMER-IITKGP databases | Computer-aided diagnosis | Karale et al. | [97] |
| Unsharp masking | Unsharp masking | DDSM and private database. | Contrast Enhancement Between Microcalcifications and Background | Karale et al. | [98] |
| Reference | Data | ML Model | Evaluation AUC (ROC) |
Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [46] | 75 images | Automatic detection of clusters for calcifications in digitized mammograms | × | 92.00 |
| [55] | 40 images | Multi-wavelet-based features extraction technique | × | 85.00 |
| [105] | 70 images | Algorithm using Fractal-based Wolfe grade classifier | × | 84.51 |
| [106] | 433 images | Bayesian belief network (BBN) | 0.87 | 80.00 |
| [107] | 180 images | k-NN classifier | × | 80.00 |
| [108] | The mammogram test set included patients between March 2017 and March 2019, while the validation set was collected between April 2019 and October 2019 | Peri-calcification areas in contrast-enhanced mammography | 0.89 | 84.30 |
| [109] | Comprising 380 samples of healthy tissue, 136 samples of benign microcalcifications, and 242 samples of malignant microcalcifications | SVM, RF, and XGBoost | 0.83, 0.85, and 0.87 for healthy, benign, and malignant micro classification, respectively | 74.00, 81.10, and 82.40 for healthy, benign, and malignant micro classification, respectively |
| [110] | A database with consecutive asymptomatic women who underwent breast cancer surgery between (2016-2019) | LunitINSIGHT, MMG, Ver. 1.1.4.0 as a diagnostic tool | × | 72.00 |
| [111] | MIAS)and (DDSM) public mammography datasets | Neural network (NN), SVM, k-NN, and DT models | 0.95 - 0.98 | 94.30 - 96.40 |
| [112] | 3002 merged images from 1501 individuals who underwent digital mammography between February 2007 and May 2015. | RF, DT, k-NN, logistic regression (LR), linear SVM | × | 96.49 |
| [113] | Training part: 30 normal and 47 abnormal images Testing part: 100 normal and 39 abnormal images |
Modified fuzzy decision tree, and committee decision-making method. | > 0.90 | × |
| [114] | 119 images from MIAS and DDSM databases | Multi-window based statistical analysis (MWBSA) for detection of microcalcification clusters, and ANN | × | 97.00 |
| [115] | 1872 micro-calcific cation clusters (1199 benign and 673 malignant) from 753 patients |
C4.5, RF, MLP, LR, NB, BNet, k-NN, ADTree, LMT, AdaBoost, and SVM | 0.82 (ADtree) | 77.80 (C4.5) |
| [116] | 260 ROIs extracted from of BCDR mammograms | RF binary classifier | 0.98 and 0.92 for benign and malignant, respectively | 97.31 and 88.46 for benign and malignant, respectively |
| [117] | Mammographic, clinical, and sonographic features from 420 patients | XGBoost | 0.93 | 84.00 |
| [118] | DDSM dataset | ANN | × | 93.00 |
| [119] | 4810 mammograms with 6663 microcalcification lesions | Resnet50 for feature extraction, and FasterRCNN for microcalcification detection | 0.80 | 72.37 |
| [120] | Nijmegen University Hospital (Netherlands) database | Sequential forward search (SFS) algorithm on General regression neural network (GRNN) and SVM | 0.98 (SVM), 0.97 (GRNN) |
× |
| [121] | 216 mammograms from the database of Girona Health Area | CBR and GA | × | 78.57 (Max) |
| [122] | 322 images of MIAS dataset | wavelet analysis, feature selection method and k-NN and SVM | × | 87.50 (SVM best) 75.00 (k-NN best) |
| [123] | MIAS dataset | SNM, and ANN classifiers | SVM: Nijmegen dataset 0.79 (original) MIAS dataset 0.81 (original) | × |
| Reference | Data | DL Architecture |
Evaluation AUC (ROC) |
Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [70] | Manually extracted ROI’s from 168 mammograms | CNN (4 conv.) with 2 input images, 3 image-groups in the first hidden layer, 2 groups in the second hidden layer, and one real-valued output | 0.87 | × |
| [71] | 200 mammograms selected from MIAS database and BAMC database | MCPCNN | 0.86(mean) | × |
| [72] | Digital images obtained from 1157 subjects (Lima, Peru) | CNN (3 conv.) and SVM classifier | × | 73.05 (mean) |
| [125] | 607 mammography images | An ensemble of SVM1 (TL-features using AlexNet), SVM2 (analytically detected features, TL-based classifier, and analytical feature extraction-based method | 0.81 | × |
| [74] | 600 images from DDSM | CNN (5 conv., 3 fc) | × | 97 |
| [75] | 736 film images | CNN (2 conv., 1 fc and a softmax layer) | 0.82 | × |
| [77] | IRMA dataset: 2796 patches of mammogram images | CNN-discrete wavelet, and CNN-curvelet transforms | × | 81.83 for CNN-DW, and 83.74 for CNN-CT |
| [78] | MIAS: 332 images DDMS: 1800 images |
CNN(3 conv., 1 fc) with SVM | 0.93 | 93.35 |
| [80] | BCDR-F03: 736 film images | CNN with attention mechanism integrating features by LSTM, and classification by multi-view CNN | 0.89 | 85.00 |
| [81] | 424 mammogram images | CNN(2 conv, 1 fc) give five features that are fed to a logistic regressor | 0.90 | × |
| [124] | 80 ROIs selected from digitized radiographs | CNN (1 conv.) with one hidden layer using seven kernels | 0.83 | × |
| [126] | DDMS, MIAS, and INbreast datasets with 570, 322, and 179 mammograms, respectively | ResNet-18 with ICS-ELM | × | 97.19, 98.14, and 98.27 for DDSM, MIAS, and INbreast datasets, respectively |
| [127] | IDC dataset (1119 images) | VGG-16 | × | 61.00-70.00 |
| [128] | 11218 regions of interest of mammographic images from the DDSM | Autoencoder-generative adversarial network (AGAN) plus CNN | 0.94 | 89.71 |
| [129] | DDSM dataset with 2620 cases having four mammograms each | Multi-Scale Attention-Guided Network (MSANet) | 0.94 | × |
| [130] | INbreast dataset | AlexNet, DenseNet, and ShuffleNet | × | 95.46 , 99.72, and 97.84, respectively |
| [131] | Mini-MIAS, DDSM, INbreast, and BCDR contributing:316, 981, 200, and 736 mammograms, repectively |
ANN (Multilayer perceptron) | × | > 96.00 |
| [132] | Mini-MIAS: 1824 images | CNN (3 conv., 3 fc) | × | 95.20 |
| [133] | DDSM: 2620 images INbreast: 410 images MIAS: 326 images |
CNN(3 conv., 2 fc) | 0.97(mean) | 97.49 (mean) |
| [134] | Breast cancer risk factor assessment dataset: 88763 images | CNN (AlexNet, ResNet101, and InceptionV3) | × | 91.30 (InceptionV3) |
| [135] | Mini-DDSM: 9752 mammograms | CNN(AlexNet, VGG16, ResNet50) | 0.86 (AlexNet) | 65.89 (AlexNet) |
| [136] | CBIS-DDSM: 6671 images DDSM: 2620 images |
CNN(12 conv., 4 dropout layers) | 0.98(mean) | 100 (for binary classification), and 95.80 for multiclass problems |
| [137] | CBIS–DDSM | CNN with four different optimizers (ADAM, ADAGrad, ADADelta, and RMSProp) | 0.96 | 94.00 |
| [138] | CBIS-DDSM, and Breast Cancer Wisconsin (BCW) containing 3400 mammographic images | AlexNet, Fuzzy C-Means clustering algorithm and multiple classifiers | × | 98.84 |
| [139] | 168 full-field digital mammography exams (248 images from 168 patients) | Local features with an unsupervised k-means clustering algorithm and training with a light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM) | classifier 0.73 using the clustering | 53.00 |
| [140] | 384 patients with 414 pathologically confirmed microcalcifications (221 malignant and 193 benign) | DL model with mammography and clinical variables | 0.91 | × |
| [141] | 298 mammographic images from 149 patients | CNN (5 residual layers, and 0.25 dropout) | 0.86 | 86.70 |
| [142] | ADMANI dataset (28911 instances) by the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) | CNNs and ViT architectures including data augmentation techniques | 0.88 | 89.00 |
| [143] | Contrast Enhanced Mammography (CEM) images of 1601 patients at Maastricht UMC+, and 283 patients at Gustave Roussy Institute | DL model and handcrafted radiomics-based technique | 0.95 | × |
| [144] | 1000 patients and 1986 mammograms with 389 malignant and 611 benign groups of microcalcification | AlexNet, ResNet18, and ResNet34 | 0.88-0.92 | × |
| [145] | Mini-MIAS dataset | DN-SVM for the detection of breast cancer | 0.99 | 84.45 |
| [146] | 3076 mammograms with 1459 positive breast cancers | Multitask model based on EfficientNet-B0 neural network | 0.76 and 0.78 at the image and breast; 0.92 for mass; 0.88 and 0.82 for mass with calcifications; and 0.63–0.66 for Cell receptor status prediction | × |
| [147] | INbreast: 410 images DDSM: 680 |
CNN (4 conv., 2 fc) | >0.90 | × |
| [148] | FFDM database: 1874 images | CNN (3 conv.) and SVM classifier | 0.88 | 82.43 |
| [149] | 64 breast slice images (University of Michigan) |
CNN (2 conv., 2 locally-connected layers + 1 fc) | 0.93 | × |
| [150] | DDSM and Mini-MIAS datasets | CNN (2 conv., 2local, and 1 fc) | × | 67.00-81.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





