Submitted:
30 April 2024
Posted:
01 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
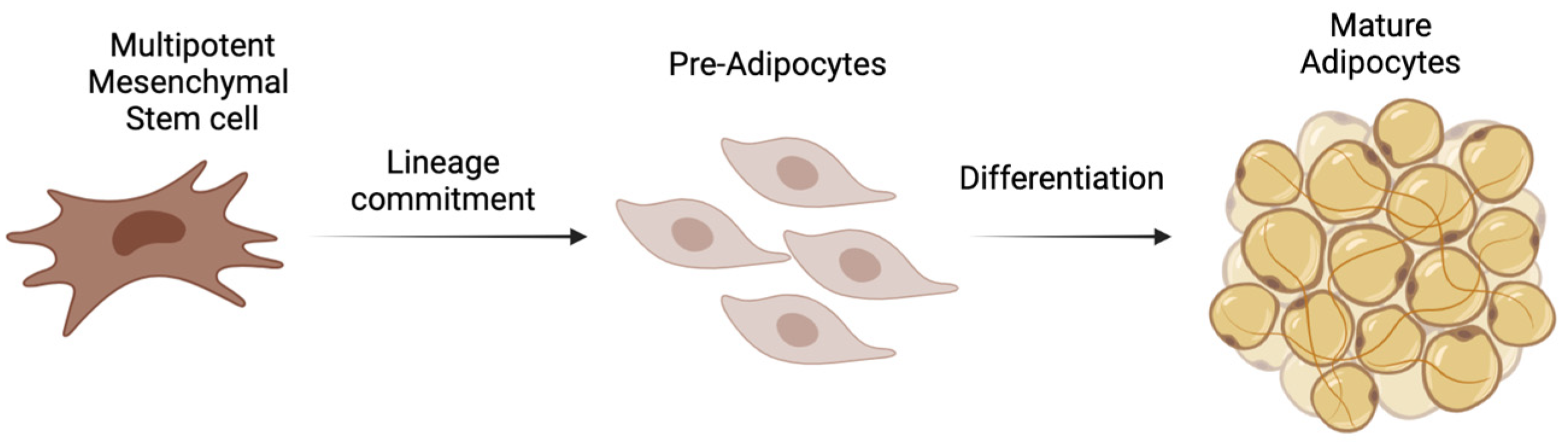
1. Introduction
2. Results
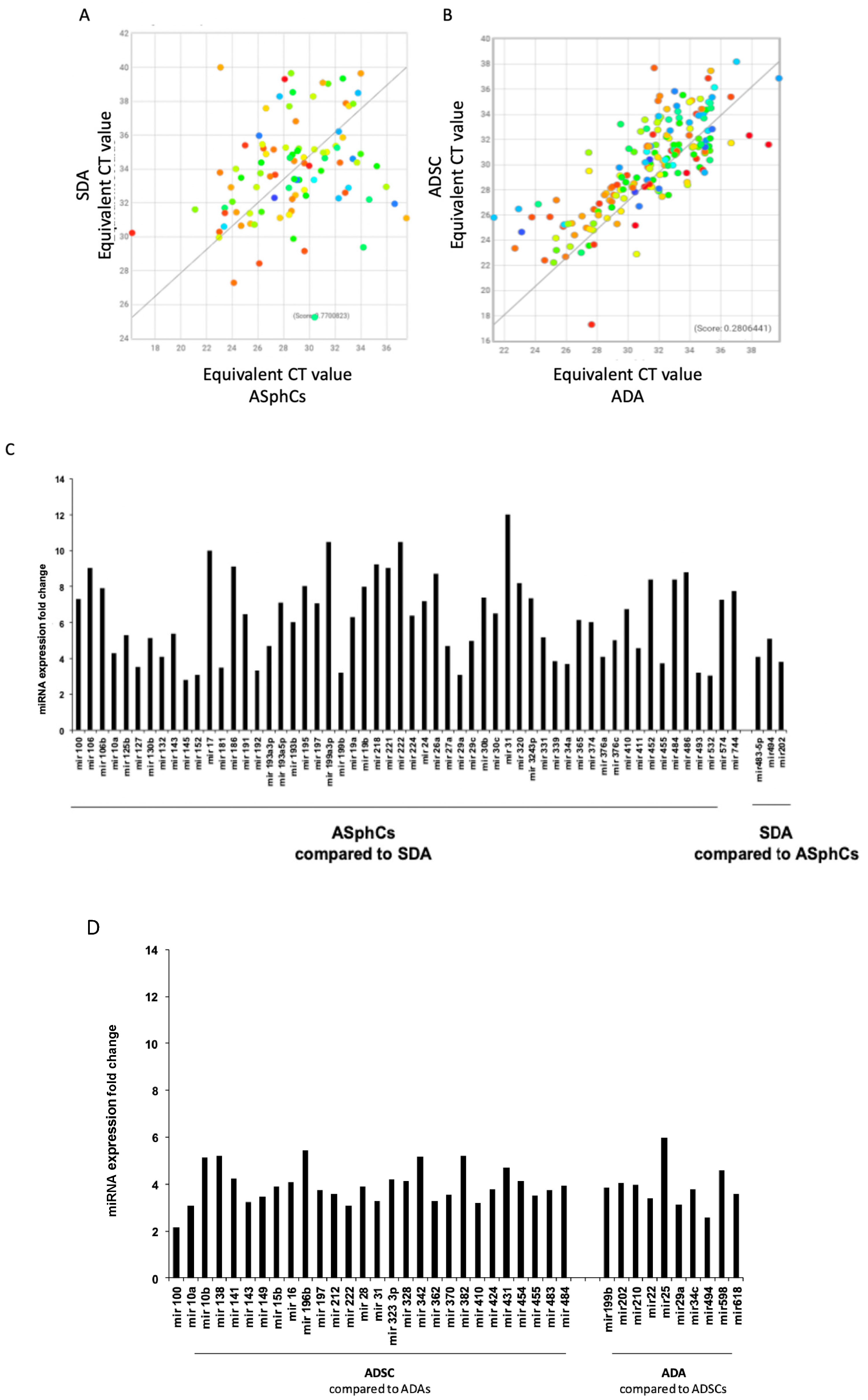
2.1. Different Culture Conditions Affect miRNA Expression
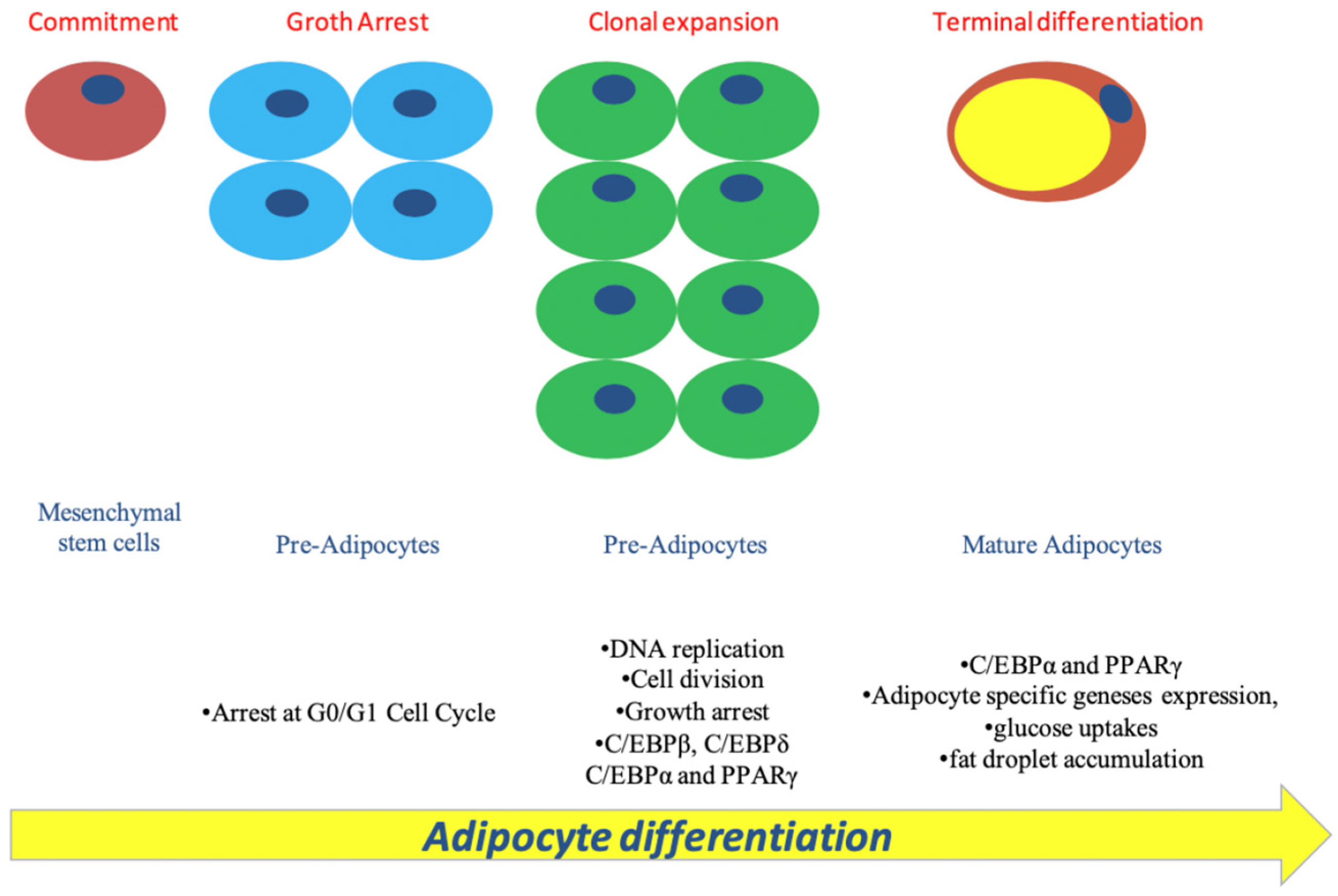
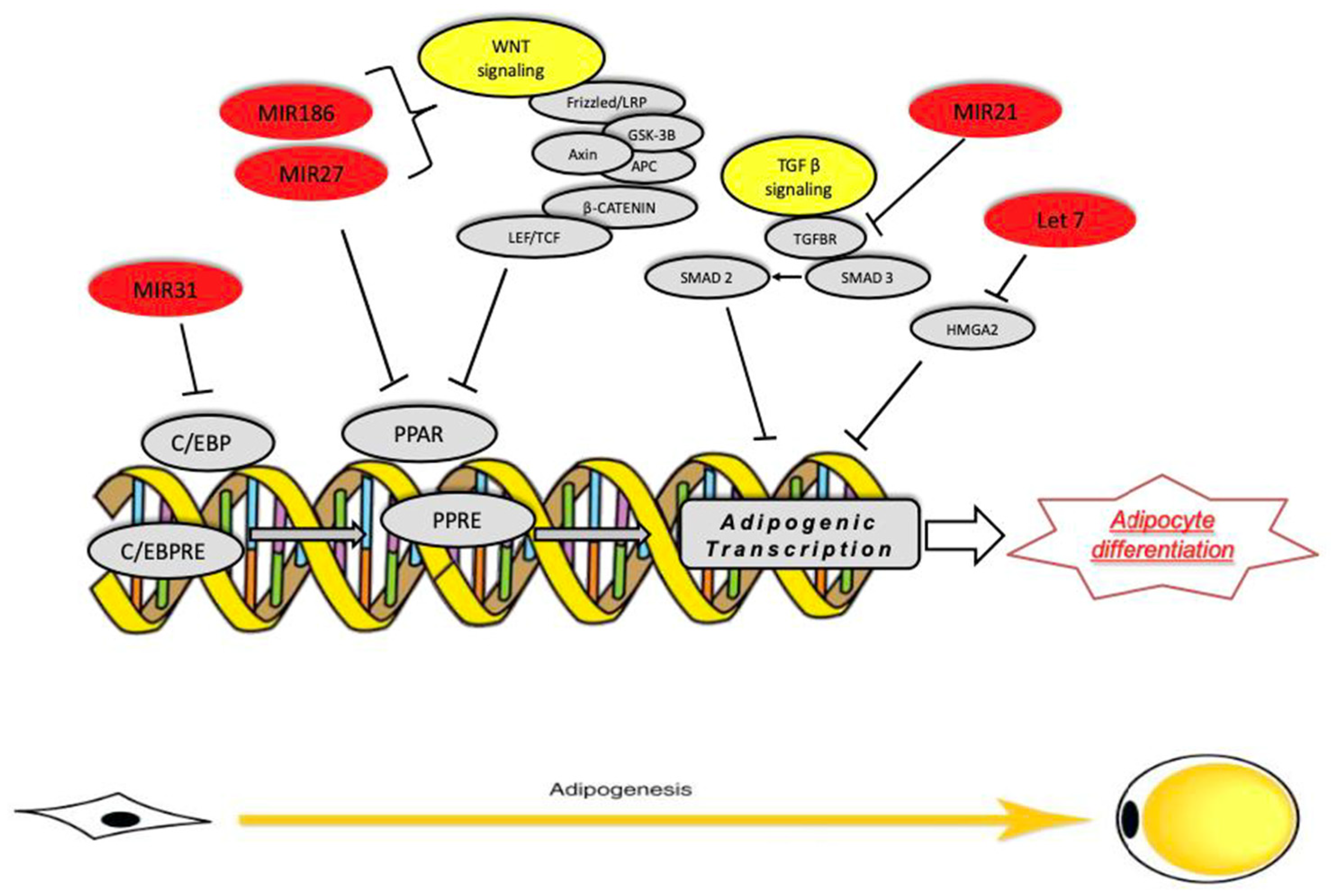
2.2. MicroRNAs Regulate Adipocyte Differentiation
3. Discussion and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Adipose Tissue Samples and Cell Culture
4.2. Adipogenic Differentiation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- R.H. Unger, Lipotoxic diseases, Annu. Rev. Med. 53 (2002) 319–336.
- Cinti S. The adipose organ: morphological perspectives of adipose tissues. Proc Nutr Soc. 2001 Aug;60(3):319-28. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti S. The adipose organ. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005 Jul;73(1):9-15. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzik TJ , Mangalat D, Korbut R. Adipocytokines - novel link between inflammation and vascular function , J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006 Dec;57(4):505- 28.
- R. Schofield, The relationship between the spleen colony-forming cell and the haemopoietic stem cell, Blood Cells 4 (1978) 7–25.
- V. Greco, S. Guo, Compartmentalized organization: a common and required feature of stem cell niches? Development 137 (2010) 1586–1594.
- K.A. Moore, I.R. Lemischka, Stem cells and their niches, Science 311 (2006) 1880–1885.
- L. Li, H. Clevers, Coexistence of quiescent and active adult stem cells in mammals, Science 327 (2010) 542–545.
- W. Tang, D. Zeve, J.M. Suh, D. Bosnakovski, M. Kyba, R.E. Hammer, M.D. Tallquist, J.M. Graff, White fat progenitor cells reside in the adipose vasculature, Science 322 (2008) 583–586.
- K. Iyama, Electronmicroscopical studies on the genesis of white adipocytes: differentiation of immature pericytes into adipocytes in transplanted preadipose tissue, Virchows Archiv. B, Cell pathology 31 (1979) 143–155.
- S. Cinti, A morphological study of the adipocyte precursor, J. Submicrosc. Cytol. 16 (1984) 243–251.
- H. Eto, H. Suga, D.Matsumoto, K. Inoue, N. Aoi, H. Kato, J. Araki, K. Yoshimura, Characterization of structure and cellular components of aspirated and excised adipose tissue, Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 124 (2009) 1087–1097.
- J.G. Granneman, P. Li, Y. Lu, J. Tilak, Seeing the trees in the forest: selective electroporation of adipocytes within adipose tissue, American Journal of Physiology.
- Y. Cao, Angiogenesis modulates adipogenesis and obesity, J. Clin. Invest. 117 (2007) 2362–2368.
- J. Han, J.-E. Lee, J. Jin, J.S. Lim, N. Oh, K. Kim, S.-I. Chang, M. Shibuya, H. Kim, G.Y. Koh, The spatiotemporal development of adipose tissue, Development 138 (2011) 5027–5037.
- K. Sun, I.W. Asterholm, C.M. Kusminski, A.C. Bueno, Z.V. Wang, J.W. Pollard, R.A. Brekken, P.E. Scherer, Dichotomous effects of VEGF-A on adipose tissue dysfunction, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 109 (2012) 5874–5879.
- A.G. Cristancho, M.A. Lazar, Forming functional fat: a growing understanding of adipocyte differentiation, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 12 (2011) 722–734.
- Divoux, K. Clément, Architecture and the extracellular matrix: the stil unappreciated components of the adipose tissue, Obes. Rev. 12 (2011) e494– e503.
- E.M. Mariman, P. Wang, Adipocyte extracellular matrix composition, dynamics and role in obesity, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67 (2010) 1277–1292.
- Nakajima, S. Muroya, R.-i. Tanabe, K. Chikuni, Extracellular matrix development during differentiation into adipocytes with a unique increase in type V and VI collagen, Biol. Cell 94 (2002) 197–203.
- C. Pierleoni, F. Verdenelli, M. Castellucci, S. C., Fibronectins and basal lamina molecole expression in human subcutaneous white adipose tissue, Eur. J. Histochem. 42 (1998) 183–188.
- B.M. Spiegelman, C.A. Ginty, Fibronectin modulation of cell shape and lipogenic gene expression in 3T3-adipocytes, Cell 35 (1983) 657–666.
- Kalebm. Pauley And Edward K.L. Chan MicroRNA in autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun. 2009; 32(3-4): 189–194. [CrossRef]
- Stefani G, Slack FJ: Small Non-Codingrnas In Animal development.Natrevmol Cell Biol 2008, 9:219-230.
- Bartel, D.P. Micrornas: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, And Function. Cell, 116: 281-297, 2004.
- Du, T. & P.D. Zamore. 2005. Microprimer: The Biogenesis and Function Of Microrna. Development 132: 4645–4652.
- Filipowicz,W., S.N. Bhattacharyya&N. Sonenberg. 2008. Mechanisms of Post- Transcriptional Regulationby Micrornas: Are The Answers In Sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 9: 102–114.
- Gesta S, Tseng YH, Kahn CR (2007) Developmental origin of fat:tracking obesity to its source. Cell 131: 242–56.
- Billon N, Monteiro MC, Dani C (2008) Developmental origin of adipocytes: new insights into a pending question. Biol Cell 100: 563–75.
- Considine RV, Nyce MR, Morales LM, Magosin SA, Sinha MK, Bauer TL, Rosato EL, Colberg J, Caro JF (1996) Paracrinestimulation of preadipocyte- enriched cell cultures by mature adipocytes. Am J Physiol 270: 895–99.
- Marques BG, Hausman DB, Martin RJ (1998) Association of fat cell size and paracrine growth factors in development of hyperplastic obesity. Am J Physiol 275: 1898–908.
- Kishida K, Kuriyama H, Funahashi T, Shimomura I, Kihara S,Ouchi N, Nishida M, Nishizawa H, Matsuda M, Takahashi M, Hotta K, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Tochino Y, Matsuzawa Y(2000) Aquaporin Adipose, a Putative Glycerol Channel in Adipocytes. J Biol Chem 275: 20896–902.
- Tang QQ, Otto TC, Lane MD (2003b) CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta is required for mitotic clonal expansion during adipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 850–5.
- Ramji DP, Foka P (2002) CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: structure, function and regulation. Biochem J 365:561–575.
- Wang GL, Shi X, Salisbury E et al (2006) Cyclin D3 maintains growth-inhibitory activity of C/ EBP a by stabilizing C/EBP a -cdk2 and C/EBP a -Brm complexes. Mol Cell Biol 26:2570–2582.
- Huang HJ, Donald JT (2007) Dynamic FoxO transcription factors. J Cell Sci 120:2479–2487.
- Kajimura S, Seale P, Tomaru T et al (2008) Regulation of the brown and white fat gene programs through a PRDM16/CtBP transcriptional complex. Genes Dev 22:1397–1409.
- Morrison RF, Farmer SR (1999) Role of PPARgamma in regulating a cascade expression of cyclindependent kinase inhibitors, p18(INK4c) and p21(Waf1/Cip1), during adipogenesis. J Biol Chem 274:17088–17097.
- Mori T, Sakaue H, Iguchi H et al (2005) Role of Kruppel-like factor 15 (KLF15) in transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. J Biol Chem 280:12867–12875.
- Gray S, Feinberg MW, Hull S et al (2002) The Kruppel-like factor KLF15 regulates the insulinsensitive glucose transporter GLUT4. J Biol Chem 277:34322–34328.
- Wu J, Srinivasan SV, Neumann JC et al (2005) The KLF2 transcription factor does not affect the formation of preadipocytes but inhibits their differentiation into adipocytes. Biochemistry 44:11098–11105.
- Qian S, Li X, Zhang Y, et al. Characterization of adipocyte differentiation from human mesenchymal stem cells in bone marrow. BMC Dev Biol 2010; 10: 47.
- Esau C, Kang X, Peralta E, et al. MicroRNA-143 regulatesadipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 52361-.
- Ortega FJ, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Pardo G, et al. MiRNA expression profile of human subcutaneous adipose and during adipocyte differentiation. PLoS ONE 2010; 5: e9022.
- Oskowitz A, Lu J, Penfornis P, et al. Human multipotent stromal cells from bone marrow and microRNA: Regulation of differentiation and leukemia inhibitory factor expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 18372.
- Yang Z, Bian C, Zhou H, et al. MicroRNA hsa-miR-138 Inhibits Adipogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose Tissue- Derived Mesenchymal .
- Yang Z, Bian C, Zhou H,Huang S,Wang S, Liao L, Zhao RC (2011) MicroRNA hsa-miR-138 inhibits adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells through adenovirus EID-1. Stem Cells Dev 20: 259–67.
- Xu PZ, Vernooy SY, Guo M, Hay BA (2003) The drosophila MICRORNA Mir- 14 suppresses cell death and is required for normal fat metabolism. Curr Biol 13: 790–95.
- Jordan SD, Krüger M,Willmes DM, Redemann N,Wunderlich FT, Brönneke HS,Merkwirth C, Kashkar H, Olkkonen VM, Böttger T, Braun T, Seibler J, Brüning JC (2011) Obesity-induced overexpression of miRNA-143 inhibits insulin-stimulated AKT activation and impairs glucose metabolism. Nat Cell Biol 13: 434–46.
- Ouaamari AE, Baroukh N, Martens GA, Lebrun P, Pipeleers D, Van OE (2008) miR-375 targets 30-phosphoinositidedependent protein kinase-1 and regulates glucose-induced biological responses in pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes : 2708–17.
- Ross SE, Hemati N, Longo KA, Bennett CN, Lucas PC, Erickson RL, MacDougald OA (2000) Inhibition of adipogenesis by WNT signaling. Science 289: 950–3.
- QinL,ChenY,NiuY,ChenW,WangQ,XiaoS,LiA,XieY,LiJ,ZhaoX,He ZY, Mo DL (2010) A deep investigation into the adipogenesis mechanism: profile of microRNAs regulating adipogenesis by modulating the canonical WNT/beta-catenin signaling pathway. BMC Genomics 11: 320.
- Xie H, Lim B, Lodish HF. MicroRNAs induced during adipogenesis that accelerate fat cell development are downregulated in obesity. Diabetes 2009; 58: 1050-7.
- Sun T, Fu M, Bookout AL, Kliewer SA, Mangelsdorf DJ. MicroRNA let-7 regulates 3T3-L1 adipogenesis. Mol Endocrinol 2009; 23: 925-31.
- Gerin I, Bommer GT, McCoin CS, et al. Roles for miRNA-378/378* in adipocyte gene expression and lipogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2010; 299: E198-206.
- Lund E, Güttinger S, Calado A, Dahlberg JE, Kutay U. Nuclear export of microRNA precursors. Science 2004; 303: 95-8.
- Nakanishi N, Nakagawa Y, Tokushige N, et al. The upregulation of microRNA- 335 is associated with lipid metabolism in liver and white adipose tissue of genetically obese mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 385: 492-6.
- Sun F, Wang J, Pan Q, et al. Characterization of function and regulation of miR- 24-1 and miR-31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 380: 660.
- Esau C, Kang X, Peralta E, et al. MicroRNA-143 regulatesadipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 52361-5.
- Ortega FJ, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Pardo G, et al. MiRNA expression profile of human subcutaneous adipose and during adipocyte differentiation. PLoS ONE 2010; 5: e9022.
- Andersen DC, Jensen CH, Schneider M, et al. MicroRNA-15a fine-tunes the level of Delta-like 1 homolog (DLK1) in proliferating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Exp Cell Res 2010; 316: 1681-91.
- Di Stefano AB, Leto Barone AA, Giammona A, et al (2016) Identifcation and expansion of adipose stem cells with enhanced bone regeneration properties. J Regen Med 5(1):1–11.
- Virzì F, Bianca P, Giammona A, Apuzzo T, Di Franco S, Mangiapane LR, Colorito ML, Catalano D, Scavo E, Nicotra A, Benfante A, Pistone G, Caputo V, Dieli F, Pirrello R, Stassi G. Combined platelet-rich plasma and lipofilling treatment provides great improvement in facial skin-induced lesion regeneration for scleroderma patients. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Oct 23;8(1):236. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
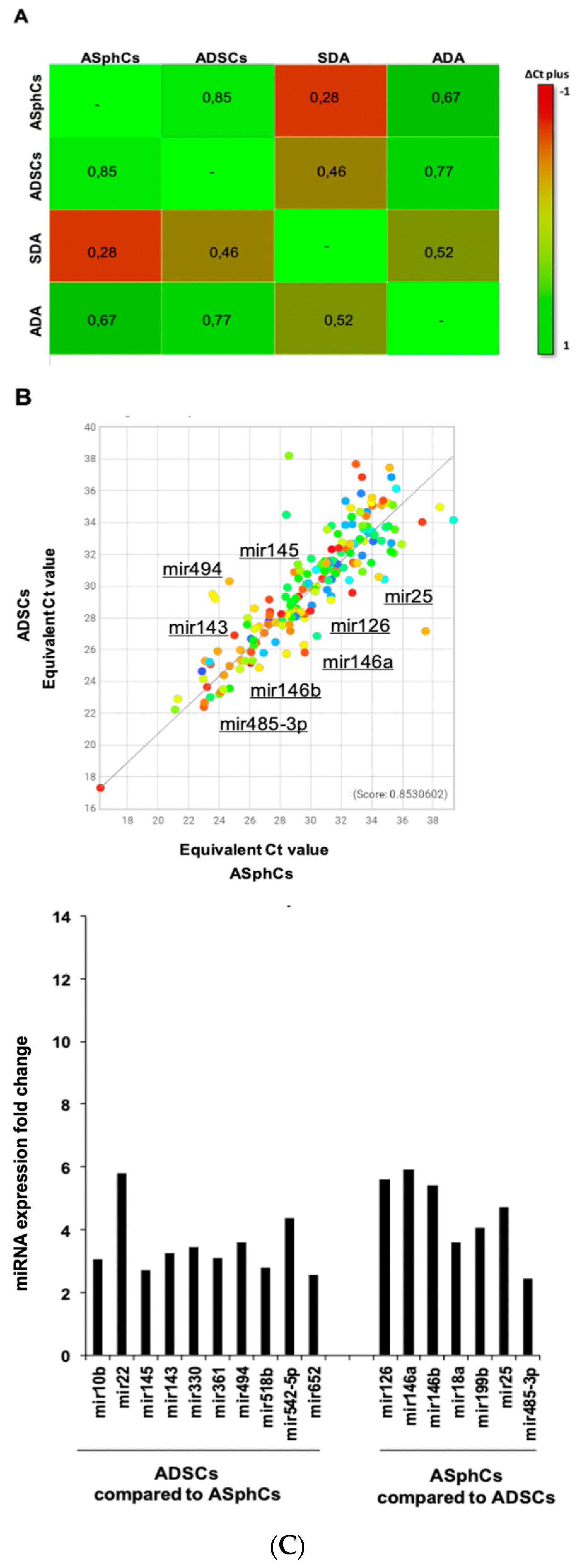
| ASphCs vs ADSCs | |
|---|---|
| miRNA | Fold Change |
| miR-126 | 5,6 |
| miR-146a | 5,9 |
| miR-146b | 5,4 |
| miR-18a | 3,6 |
| miR-199b | 4,05 |
| miR-25 | 4,72 |
| miR-485-3p | 2,43 |
| ADSCs vs ASphCs | |
| miRNA | Fold Change |
| miR-10b | 3,05 |
| miR-22 | 5,8 |
| miR-145 | 2,71 |
| miR-143 | 3,24 |
| miR-330 | 3,45 |
| miR-361 | 3,1 |
| miR-494 | 3,6 |
| miR-518b | 2,79 |
| miR-542-5p | 4,36 |
| miR-652 | 2,55 |
| ASphCs vs SDA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA | Fold Change | ||
| miR-100 | 7,3 | ||
| miR-106 | 9,04 | ||
| miR-106b | 7,9 | ||
| miR-10a | 4,29 | ||
| miR-125b | 5,32 | ||
| miR-130b | 5,15 | ||
| miR-132 | 4,09 | ||
| miR-143 | 5,39 | ||
| miR-17 | 10 | ||
| miR-186 | 9,1 | ||
| miR-191 | 6,48 | ||
| miR-192 | 3,32 | ||
| miR-193A-3p | 4,7 | ||
| miR-193A-5p | 7,1 | ||
| miR-193b | 6,03 | ||
| miR-195 | 8,05 | ||
| miR-197 | 7,08 | ||
| miR-199A-3p | 10,5 | ||
| miR-19a | 6,3 | ||
| miR-19b | 8 | ||
| miR-21 | 2,6 | ||
| miR-218 | 9,25 | ||
| miR-221 | 9,03 | ||
| miR-222 | 10,5 | ||
| miR-224 | 6,4 | ||
| miR-24 | 7,2 | ||
| miR-26a | 8,7 | ||
| miR-27a | 4,7 | ||
| miR-29c | 5 | ||
| miR-30b | 7,4 | ||
| miR-30c | 6,5 | ||
| miR-31 | 12 | ||
| miR-320 | 8,2 | ||
| miR-324-3p | 7,36 | ||
| miR-331 | 5,2 | ||
| miR-365 | 6,16 | ||
| miR-374 | 6,02 | ||
| miR-376c | 5,04 | ||
| miR-410 | 6,75 | ||
| miR-411 | 4,6 | ||
| miR-452 | 8,4 | ||
| miR-455 | 3,75 | ||
| miR-484 | 8,39 | ||
| miR-486 | 8,8 | ||
| miR-574 | 7,27 | ||
| miR-744 | 7,75 | ||
| ADSCs vs ADA | |||
| miRNA | Fold Change | ||
| miR-100 | 2,17 | ||
| miR-10a | 3,1 | ||
| miR-10b | 5,11 | ||
| miR-138 | 5,19 | ||
| miR-141 | 4,23 | ||
| miR-143 | 3,22 | ||
| miR-141 | 3,48 | ||
| miR-149 | 3,89 | ||
| miR-15b | 4,09 | ||
| miR-196b | 5,45 | ||
| miR-197 | 3,74 | ||
| miR-212 | 3,58 | ||
| miR-222 | 3,08 | ||
| miR-28 | 3,9 | ||
| miR-31 | 3,29 | ||
| miR-32-3p | 4,21 | ||
| miR-328 | 4,13 | ||
| miR-342 | 5,17 | ||
| miR-362 | 3,26 | ||
| miR-370 | 3,53 | ||
| miR-382 | 5,22 | ||
| miR-410 | 3,21 | ||
| miR-424 | 3,76 | ||
| miR-431 | 4,69 | ||
| miR-454 | 4,13 | ||
| miR-455 | 3,52 | ||
| miR-483 | 3,74 | ||
| miR-484 | 3,94 | ||
| SDA vs ASphCs | |||
| miRNA | Fold Change | ||
| miR-483-5p | 4,1 | ||
| miR-494 | 5,11 | ||
| miR-202 | 3,82 | ||
| ADA vs ADSCs | |||
| miRNA | Fold Change | ||
| miR-199b | 3,87 | ||
| miR-202 | 4,05 | ||
| miR-210 | 3,99 | ||
| miR-22 | 3,39 | ||
| miR-25 | 5,96 | ||
| miR-29a | 3,14 | ||
| miR-34c | 3,79 | ||
| miR-494 | 2,57 | ||
| miR-59 | 4,6 | ||
| miR-618 | 3,59 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





