Submitted:
25 June 2024
Posted:
25 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.2. Underpinning Theory
1.2.1. Sustainable Competitive Advantage (SCA)
1.2.2. Eco-Innovation
1.2.3. Eco-Innovation as a Complex Adaptive System
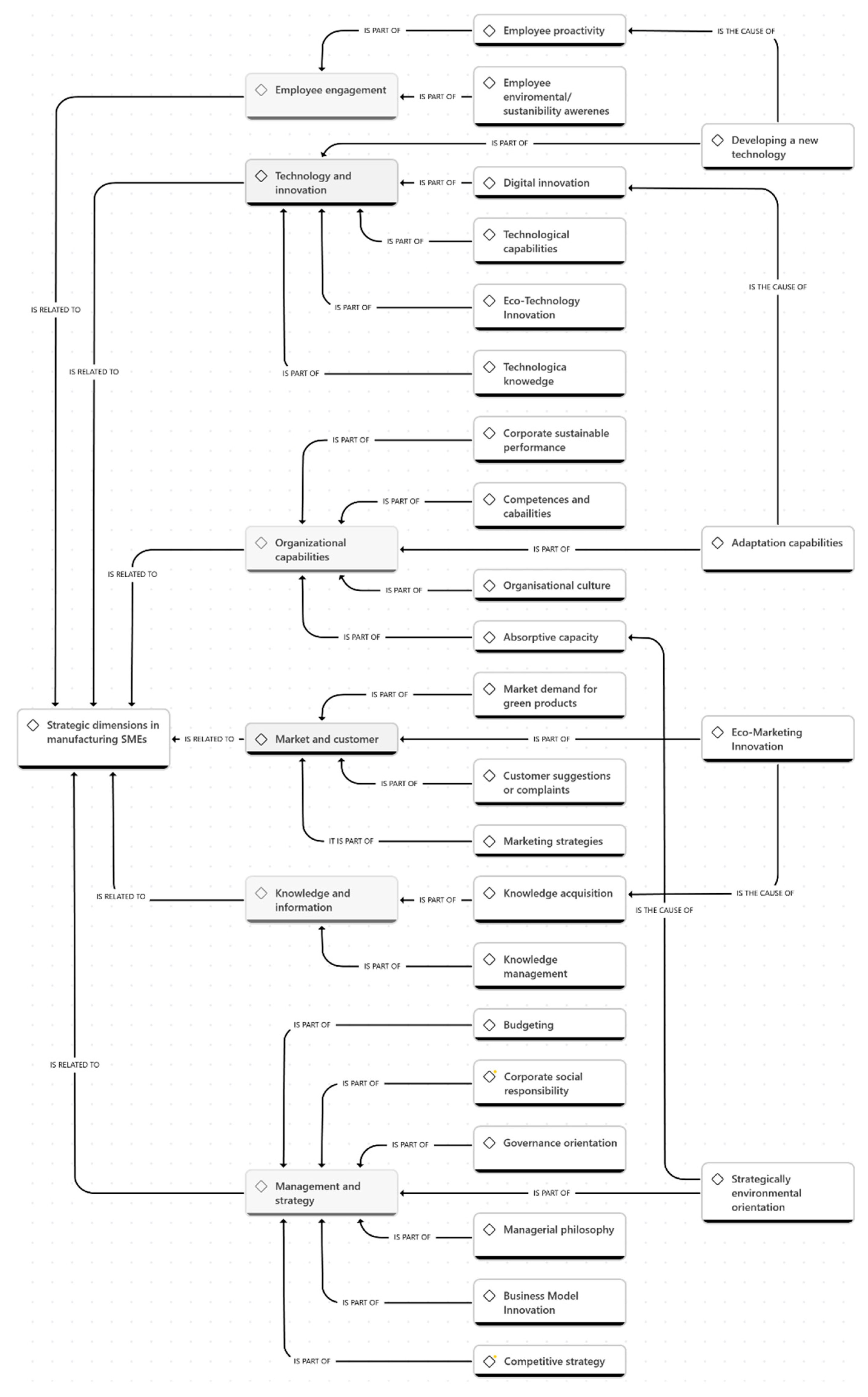
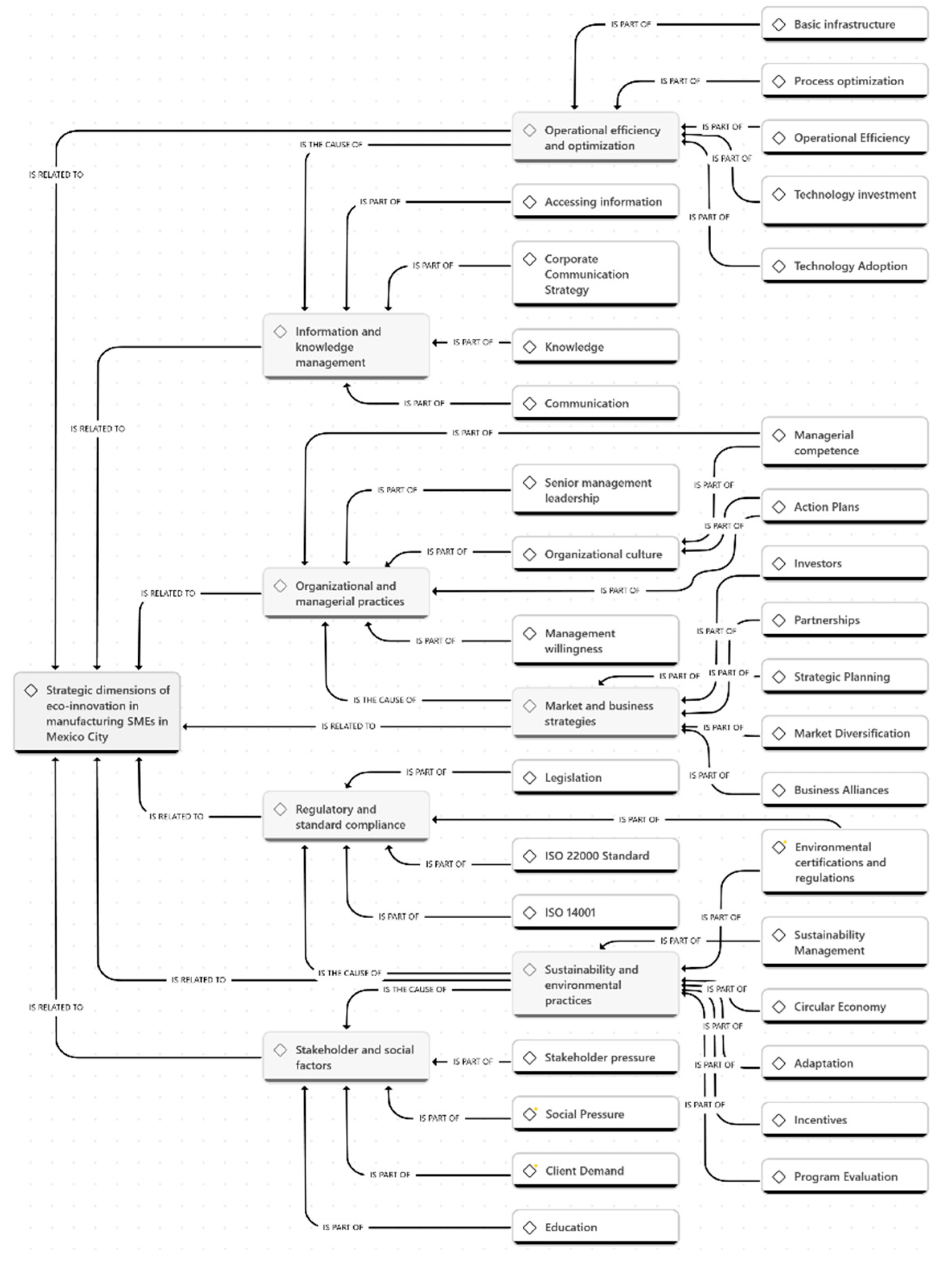
1.2.4. Relationship of eco-innovation to strategic dimensions in manufacturing SMEs
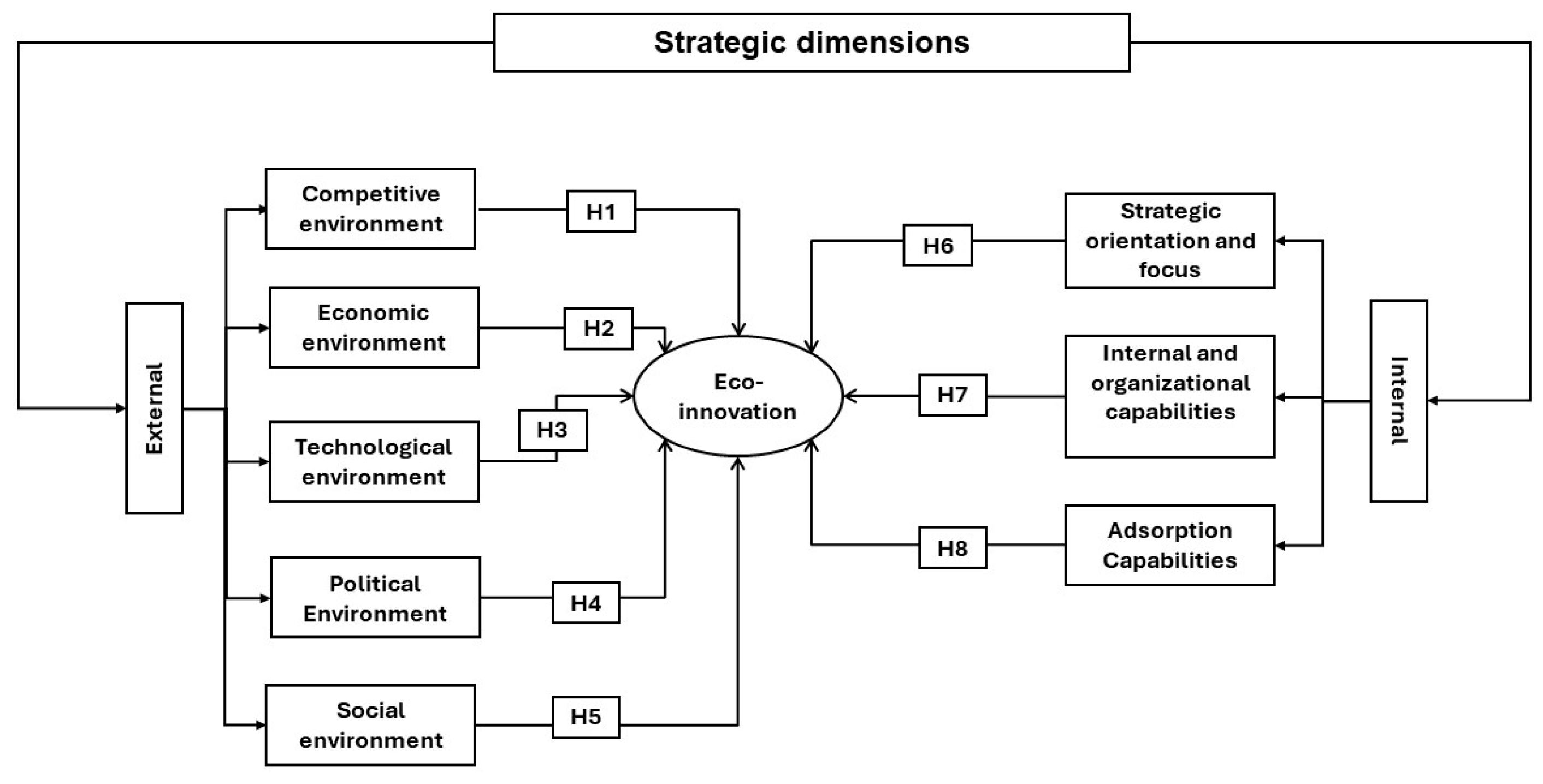
1.3. Research Hypotheses
1.3.1. The Competitive Environment
1.3.2. The economic environment
1.3.3. The Technological Environment
1.3.4. Political Environment
1.3.5. Social environment
1.3.6. Strategic Orientation and Focus
1.3.7. Internal and Organizational Capabilities
1.3.8. Adsorption Capabilities
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Research Design
2.2. Data Collection
- Step 1: formulation of the research question.
- Step 2: location of studies.
- Step 3: selection and evaluation of studies.
- Step 4: analysis and synthesis.
- Step 5: reporting and use of research results.
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Literature Review
| Overall dimensions/categories | Study |
|---|---|
| Social capital and eco-Innovation | Assessing the influence of social capital and innovations on environmental performance of manufacturing SMEs [158]. |
| Knowledge and expertise for eco-Innovation | Ecolabnet service packages as a response to the needs of manufacturing enterprises in the SME sector of the Baltic Sea Region [159]. |
| Eco-innovation of food processing and manufacturing SMEs [160]. | |
| Innovation in manufacturing SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic: How does environmental dynamism reinforce employee proactive behavior [161]. | |
| Manufacturing SMEs doing it for themselves: developing, testing and piloting an online sustainability and eco-innovation toolkit for SMEs [162]. | |
| Internal environmental capabilities | Linking internal environmental capabilities to sustainable competitive advantage in manufacturing SMEs [163]. |
| The role of CSR oriented organisational culture in eco-innovation practices [164]. | |
| On the growth impact of different eco-innovation business strategies [165]. | |
| Institutional pressure and eco-innovation: The mediating role of green absorptive capacity and strategically environmental orientation among manufacturing SMEs in Egypt [166]. | |
| External pressures and regulations | Environmental pressures and eco-innovation in manufacturing SMEs [167]. |
| Effects of the Fit between Size and Environmental Uncertainty on Manufacturing SMEs’ Innovation Activity [168]. | |
| Adoption of green innovations by SMEs: an investigation about the influence of stakeholders [169]. | |
| Determinants of eco-innovation initiatives toward sustainability in manufacturing SMEs: Evidence from Bangladesh [170] | |
| Institutional pressure and eco-innovation [171] | |
| Sustainable business performance | Eco-Innovation Capabilities and Sustainable Business Performance during the COVID-19 Pandemic [172] |
| Corporate sustainability and firm performance in small and medium enterprises in Ghana: Mediating role of green innovation [173]. | |
| Green manufacturing practices and SMEs’ sustainable performance: a moderated mediation mechanisms of green innovation and managerial discretion [174]. | |
| Determinants of eco-innovation capabilities adapted by Malaysian SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic [175]. | |
| Innovative Green Initiatives in the Manufacturing SME Sector in Poland [176]. | |
| Sustainable competitive advantage | Drivers of multiple eco-innovation and the impact on sustainable competitive advantage [177]. |
| Eco-marketing and digital innovation | An Analysis of Eco-Innovation Capabilities among Small and Medium Enterprises in Malaysia [178]. |
| Environmental and technological factor diffusion with innovation and firm performance: Empirical evidence from manufacturing SMEs [179]. | |
| Unraveling the transformation: the three-wave time-lagged study on big data analytics, green innovation and their impact on economic and environmental performance in manufacturing SMEs [180]. | |
| Digital technology and circular economy practices [181]. | |
| Non-technological Innovation | Environmental objectives and non-technological innovation in Spanish manufacturing SMEs [182]. |
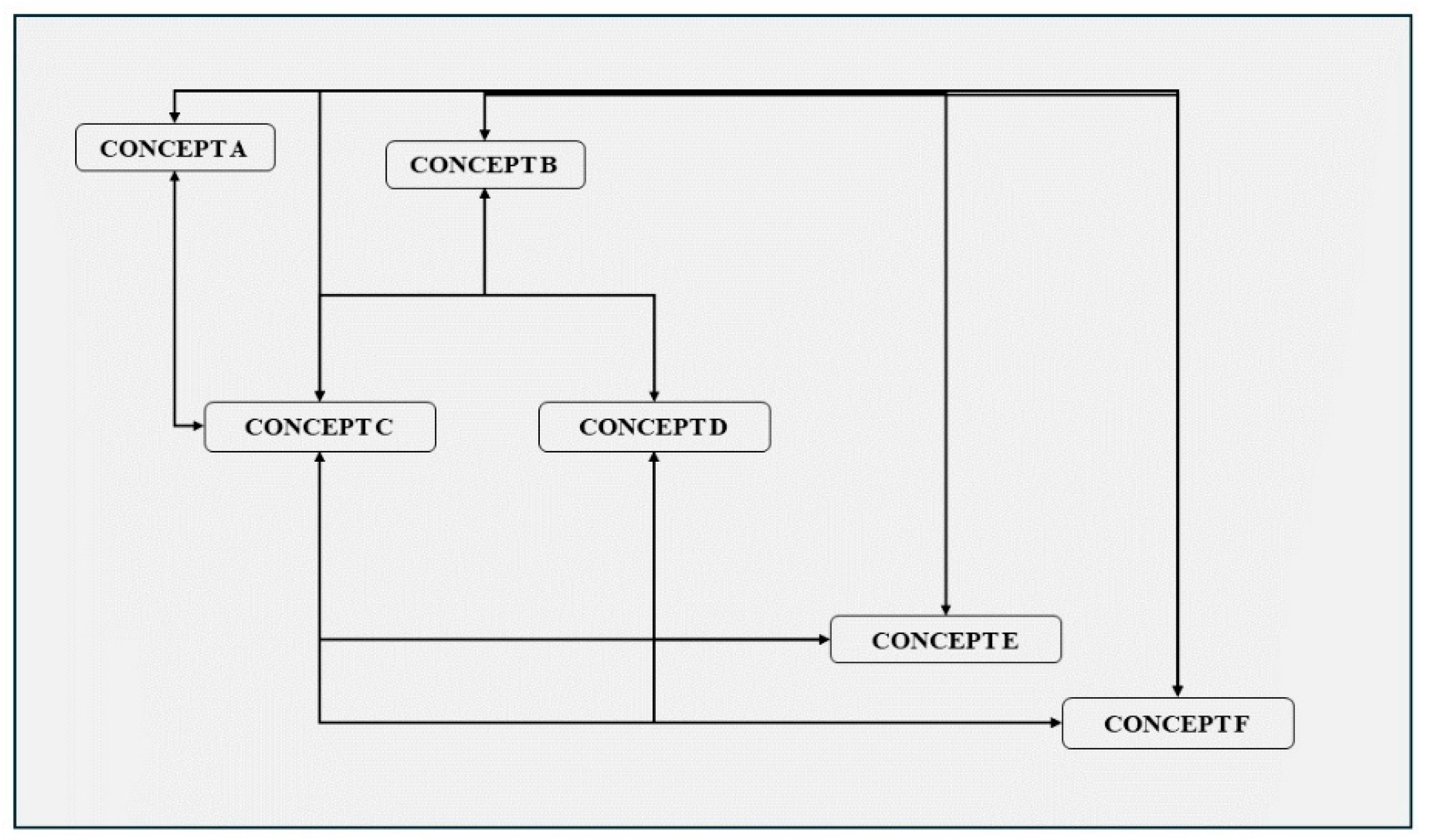
3.2. Causal Map
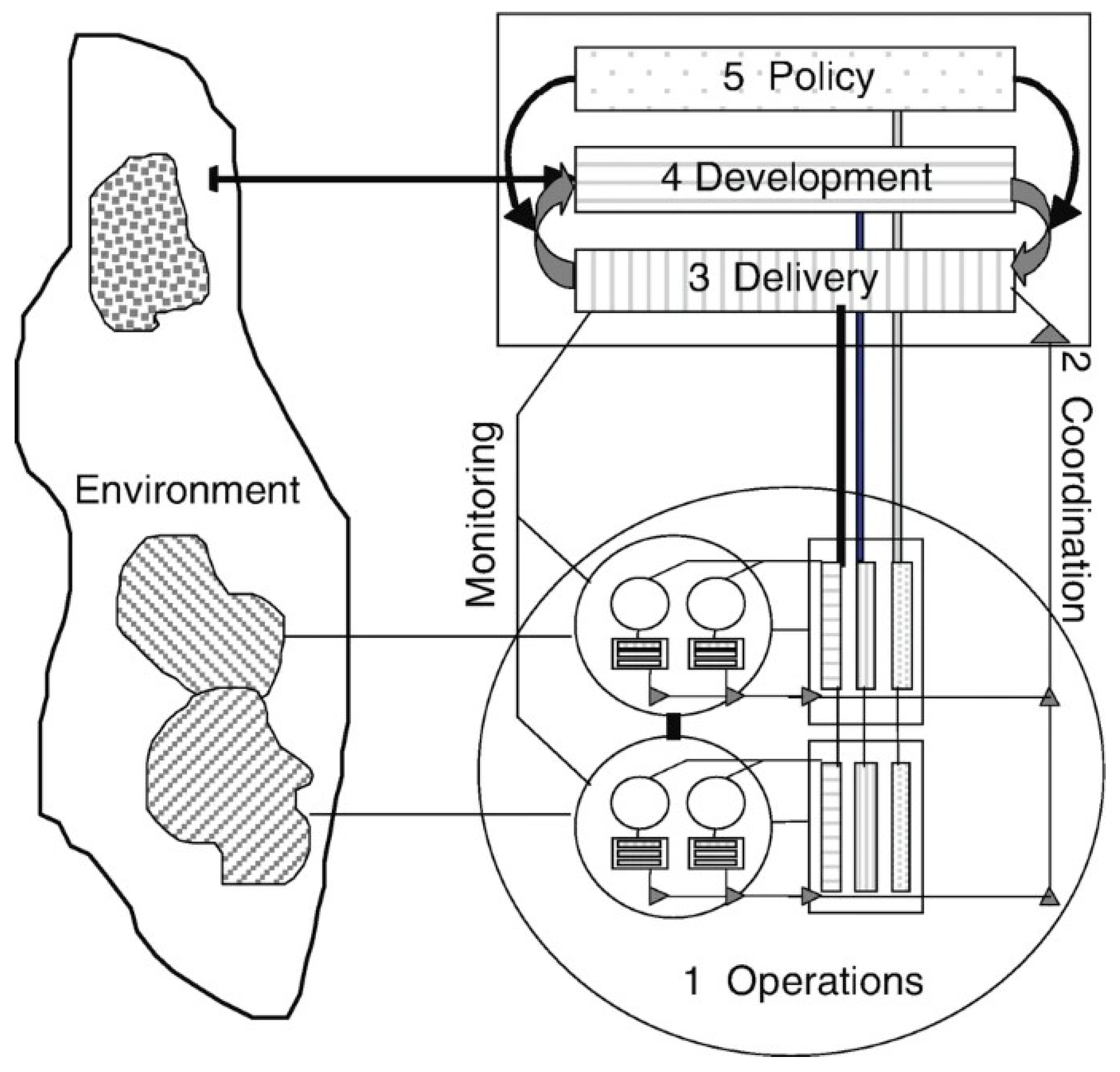
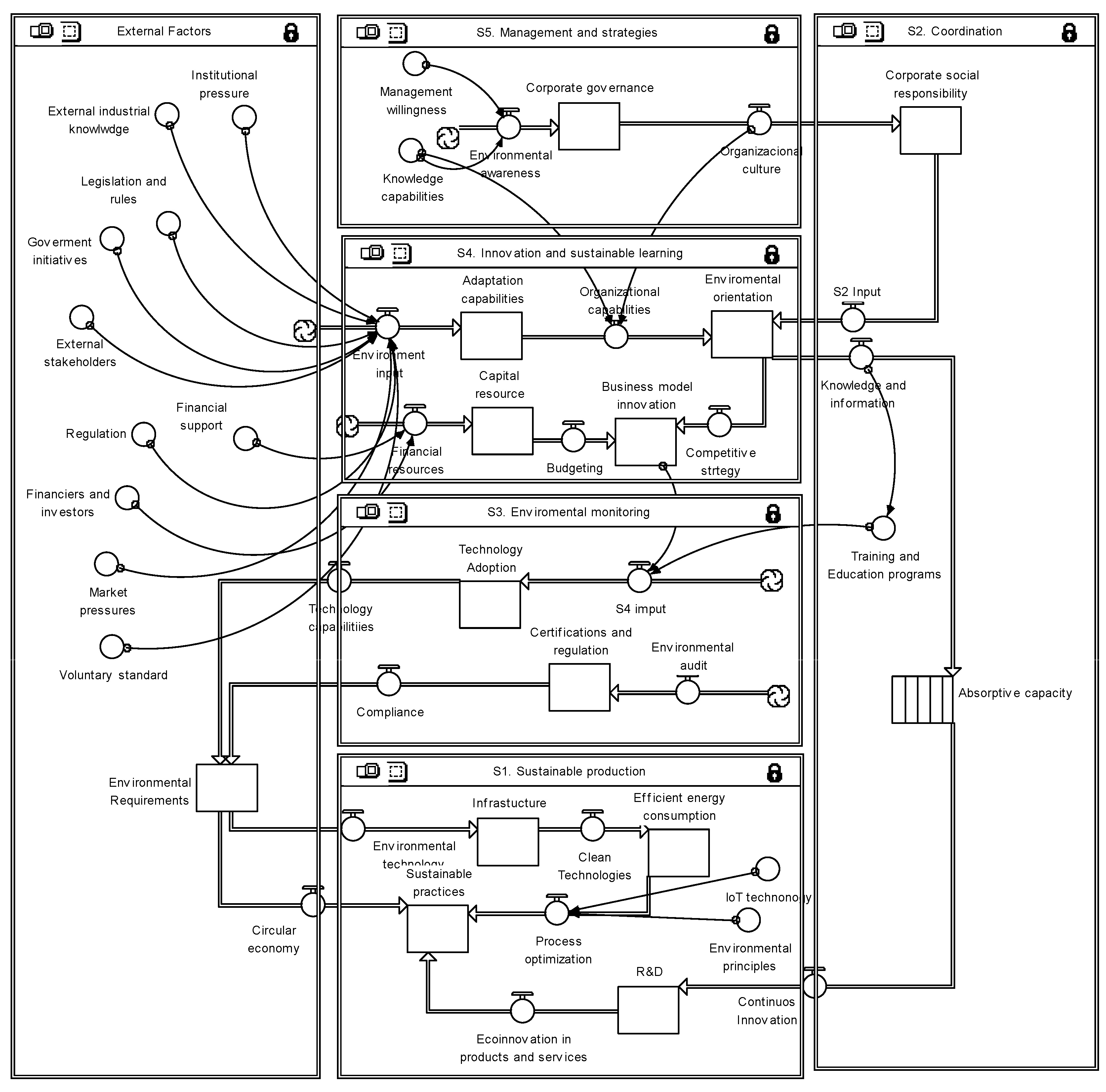
3.3. Viable System Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nikolova-Alexieva, V.; Alexieva, I.; Valeva, K.; Petrova, M. Model of the Factors Affecting the Eco-Innovation Activity of Bulgarian Industrial Enterprises. Risks 2022, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, C.P.; del Río, P.; Carrillo-Hermosilla, J. On the contribution of eco-innovation features to a circular economy: A microlevel quantitative approach. Bus. Strat. Environ. 2021, 30, 1531–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Special Report: Global Warming of 1.5 °C. 2018. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15/ (accessed on 18 August 2022).
- IPCC, “Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability.” Accessed: Jan. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.ipcc.
- Riaz, A.; Ali, F.; Ashfaq, K.; Bhatti, A.; Rehman, S.U. Eco-innovation of food processing and manufacturing SMEs. Br. Food J. 2023, 125, 2988–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, D.; Bersano, G.; Birolini, V.; Uhl, R. European testing of the efficiency of TRIZ in eco-innovation projects for manufacturing SMEs. Procedia Eng. 2011, 9, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L. Božić and V. Botrić, “Eco-innovations in Croatia: Exploring entrepreneurs’ motivation,” Journal of East European Management Studies, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 484–510, Dec. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Kwak, K.; Kim, D.; Heo, C. Sustainable innovation in a low- and medium-tech sector: Evidence from an SME in the footwear industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo-Tarragona, P.; Scarpellini, S.; Moneva, J.M.; Valero-Gil, J.; Aranda-Usón, A. Classification and Measurement of the Firms’ Resources and Capabilities Applied to Eco-Innovation Projects from a Resource-Based View Perspective. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Yadav, M. “Environmental capabilities, proactive environmental strategy and competitive advantage: A natural-resource-based view of firms operating in India”. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 291, 125249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hockerts, K.; Wüstenhagen, R. Greening Goliaths versus emerging Davids — Theorizing about the role of incumbents and new entrants in sustainable entrepreneurship. J. Bus. Ventur. 2009, 25, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, D.; Lai, K.-H.; Zhu, Q. Eco-innovation and its role for performance improvement among Chinese small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 231, 107869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, O.E.; S⊘Nderga˚rd, B.; Meredith, S. Environmental Innovations in Small and Medium Sized Enterprises. Technol. Anal. Strat. Manag. 2002, 14, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.; O’dowd, P.; Dimache, A. Manufacturing SMEs doing it for themselves: developing, testing and piloting an online sustainability and eco-innovation toolkit for SMEs. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2019, 13, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ociepa-Kubicka, A.; Pachura, P. Eco-innovations in the functioning of companies. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, S.Y.P.; Guzmán, G.M. The Relationship between Eco-Innovation and Business Performance in Mexican SMEs. J. Bus. Econ. Policy 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. del R. Reyes-Santiago and P. Sánchez-Medina, “Eco-Innovación en Empresas Hoteleras de Oaxaca, México,” 2016.
- P. J. R. Sánchez, M. H. P. J. R. Sánchez, M. H. González, and J. C. B. Arias, “Eco-Innovation And Sustainable Production In Developing Countries. Cases Colombia And Mexico,” Economy & Business Journal, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 228–238, 2018, Accessed: Feb. 01, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://ideas.repec.org/a/isp/journl/v12y2018i1p228-238.
- Pinzón-Castro, S.Y.; Maldonado-Guzmán, G.; Toro, R.J.-D. Eco-innovation Types Adoption in Mexican Small and Medium Firms. J. Manag. Sustain. 2023, 13, p127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Juárez, L.E.; Castillo-Vergara, M. Technological Capabilities, Open Innovation, and Eco-Innovation: Dynamic Capabilities to Increase Corporate Performance of SMEs. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hoof, B.; Lyon, T.P. Cleaner production in small firms taking part in Mexico's Sustainable Supplier Program. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 41, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Medina, P.S.; Corbett, J.; Toledo-López, A. Environmental Innovation and Sustainability in Small Handicraft Businesses in Mexico. Sustainability 2011, 3, 984–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván-Vela, E.; Ruíz-Corrales, M.; Ahumada-Tello, E.; Ravina-Ripoll, R. Eco-Innovation as a Positive and Happy Industry Externality: Evidence from Mexico. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N. Khan, M. N. Khan, M. Nafees, T. Saeed, A. Khan, and A. Bashir, “INDUSTRIAL SYMBIOSIS AND INDUSTRIAL WASTE MANAGEMENT INWOOD-BASED INDUSTRIES,” Journal of industrial pollution control, 2018.
- W. B. Stiles, “Qualitative Research: Evaluating the Process and the Product,” Handbook of Clinical Health Psychology, pp. 477–499, Jan. 2005. [CrossRef]
- Xuehong, Q. Qualitative Research. Chin. Educ. Soc. 2002, 35, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtman, M. Qualitative Research for the Social Sciences; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, United States, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kosciejew, M. Book Review: Documentary Research in the Social Sciences by Malcolm Tight. J. Appl. Soc. Sci. 2020, 15, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhe, “Interviews: A Key Data Source in International Business Research,” Handbook of Qualitative Research Methods for International Business, pp. xviii–xviii, Jan. 2004. [CrossRef]
- Sachan, A. Singh, and N. Sachan, “Interview Method in Research,” SEAJCRR July, vol. 1, no. 1, p. 2012, 2012.
- Chadwick, C.; Super, J.F.; Kwon, K. Resource orchestration in practice: CEO emphasis on SHRM, commitment-based HR systems, and firm performance. Strat. Manag. J. 2014, 36, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.L.; Dowell, G. Invited Editorial: A Natural-Resource-Based View of the Firm. J. Manag. 2010, 37, 1464–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbertson, R.W.; Furseth, P.I. Digital services and competitive advantage: Strengthening the links between RBV, KBV, and innovation. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 152, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, K.; Battour, M.; Aboelmaged, M.; Abdelkareem, R.S. Linking internal environmental capabilities to sustainable competitive advantage in manufacturing SMEs: The mediating role of eco-innovation. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. I. Dirisu and O. S. Ibidunni, “PRODUCT DIFFERENTIATION: A TOOL OF COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE AND OPTIMAL ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE (A STUDY OF UNILEVER NIGERIA PLC),” vol. 9, no. 34, pp. 1857–7881, 2013.
- Kuncoro, W.; Suriani, W.O. Achieving sustainable competitive advantage through product innovation and market driving. Asia Pac. Manag. Rev. 2018, 23, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.K.; Kang, S.; Jeong, H.Y. The Effect of Market Orientation on Performance of Sharing Economy Business: Focusing on Marketing Innovation and Sustainable Competitive Advantage. Sustainability 2019, 11, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenazi, S.A.; Alanazi, T.M. The Mediating Role of Sustainable Dynamic Capabilities in the Effect of Social Customer Relationship Management on Sustainable Competitive Advantage: A Study on SMEs in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesidou, E.; Demirel, P. On the drivers of eco-innovations: Empirical evidence from the UK. Res. Policy 2012, 41, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinko, C. Green Manufacturing: An Evaluation of Environmentally Sustainable Manufacturing Practices and Their Impact on Competitive Outcomes. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2007, 54, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. E. Porter, “America’ Green Strategy,” Business and the environment: A reader, pp. 33–35, 1996.
- Galbreath, J.; Chang, C.; Tisch, D. The impact of a proactive environmental strategy on environmentally sustainable practices in service firms: The moderating effect of information use value. Bus. Strat. Environ. 2023, 32, 5420–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, U.N.; Van, M.H.; Mahmud, I.; Thuy, L.V.T. Innovation and the Sustainable Competitive Advantage of Young Firms: A Strategy Implementation Approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Otero-Neira, M. T. C. Otero-Neira, M. T. Lindman, and M. J. Fernández, “Innovation and performance in SME furniture industries: An international comparative case study,” Marketing Intelligence and Planning, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 216–232, Mar. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severo, E.A.; Sbardelotto, B.; de Guimarães, J.C.F.; de Vasconcelos, C.R.M. Project management and innovation practices: backgrounds of the sustainable competitive advantage in Southern Brazil enterprises. Prod. Plan. Control. 2019, 31, 1276–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, K.; Halim, M.A.S.A.; Omar, K. Drivers of multiple eco-innovation and the impact on sustainable competitive advantage: evidence from manufacturing SMEs in Egypt. Int. J. Innov. Sci. 2021, 14, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabadán, A.; Álvarez-Ortí, M.; Tello, J.; Pardo, J.E. Tradition vs. Eco-Innovation: The Constraining Effect of Protected Designations of Origin (PDO) on the Implementation of Sustainability Measures in the Olive Oil Sector. Agronomy 2021, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabadán, A.; González-Moreno, Á.; Sáez-Martínez, F.J. Improving Firms’ Performance and Sustainability: The Case of Eco-Innovation in the Agri-Food Industry. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsman, H. Environmental Innovations as a Source of Competitive Advantage or Vice Versa? Bus. Strat. Environ. 2013, 22, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidute-Kavaliauskiene, I.; Çiğdem. ; Vasiliauskas, A.V.; Yıldız, B. Green Innovation in Environmental Complexity: The Implication of Open Innovation. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2021, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skordoulis, M.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Ntanos, S.; Galatsidas, S.; Arabatzis, G.; Chalikias, M.; Kalantonis, P. The Mediating Role of Firm Strategy in the Relationship between Green Entrepreneurship, Green Innovation, and Competitive Advantage: The Case of Medium and Large-Sized Firms in Greece. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ar, I.M. The Impact of Green Product Innovation on Firm Performance and Competitive Capability: The Moderating Role of Managerial Environmental Concern. Procedia - Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 62, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Cantor, D.E.; Montabon, F.L. How Environmental Management Competitive Pressure Affects a Focal Firm's Environmental Innovation Activities: A Green Supply Chain Perspective. J. Bus. Logist. 2015, 36, 242–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Fussler and P. James, “Eco-Innovacion. Integrando el Medio Ambiente en la Empresa ‘Del Futuro’ - Claude Fussler - comprar libro 9788471147905 - Cervantes.” Accessed: Sep. 26, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.cervantes. 9788.
- Eco-innovation,” Encyclopedia of Creativity, Invention, Innovation and Entrepreneurship, pp. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Rusu, “Eco-innovation and its Contribution to Sustainable Development and Competitiveness,” Network Intelligence Studies, 2013.
- European Environment Agency, “The Eco-innovation Action Plan (Eco-AP) COM (2011) 899 final.” Accessed: Jun. 04, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.eea.europa.
- Ahmed, R.R.; Streimikiene, D.; Zheng, X. The Impact of Proactive Environmental Strategy on Competitive and Sustainable Development of Organizations. J. Competitiveness 2021, 13, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissdoerfer, M.; Vladimirova, D.; Evans, S. Sustainable business model innovation: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl, A.; Blazejewski, S.; Dittmer, F. The More, the Merrier: Why and How Employee-Driven Eco-Innovation Enhances Environmental and Competitive Advantage. Sustainability 2016, 8, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumelero, C.; Sbragia, R.; Evans, S. Cooperation in R & D and eco-innovations: The role in companies' socioeconomic performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 207, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsman, H. Environmental Innovations as a Source of Competitive Advantage or Vice Versa? Bus. Strat. Environ. 2013, 22, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Cantor, D.E.; Montabon, F.L. How Environmental Management Competitive Pressure Affects a Focal Firm's Environmental Innovation Activities: A Green Supply Chain Perspective. J. Bus. Logist. 2015, 36, 242–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N. K. Gandotra, “Innovation culture for sustainable competitive advantage,” Asia Pacific Journal of Research in Business Management, 2010.
- C. J. H. Mann, “Systems Thinking – Creative Holism for Managers,” Kybernetes, vol. 33, no. 8, Sep. 2004. [CrossRef]
- Pigosso, D.C.A.; Schmiegelow, A.; Andersen, M.M. Measuring the Readiness of SMEs for Eco-Innovation and Industrial Symbiosis: Development of a Screening Tool. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, I.P.; Tsinopoulos, C.; Allen, P.; Rose-Anderssen, C. New Product Development as a Complex Adaptive System of Decisions. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2006, 23, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E. Mitleton-Kelly, “Organisation as co-evolving complex adaptive systems,” 1997, Accessed: Nov. 20, 2023. [Online]. Available: http://www.bam.ac.
- Iñigo, E.A.; Albareda, L. Understanding sustainable innovation as a complex adaptive system: a systemic approach to the firm. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 126, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Castorena, O.; Aguilera-Enríquez, L.; Pinzón-Castro, S.Y. El impacto de las estrategias, colaboración y acuerdos con los proveedores: elementos claves para el rendimiento de la Pyme manufacturera en Aguascalientes, México. Rev. CEA 2015, 1, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Magdaleno, J. El impacto de la innovación y las finanzas en la competitividad de las PYMEs manufactureras. Small Bus. Int. Rev. 2018, 2, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecere, G.; Corrocher, N.; Mancusi, M.L. Financial constraints and public funding of eco-innovation: empirical evidence from European SMEs. Small Bus. Econ. 2018, 54, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klewitz, J.; Zeyen, A.; Hansen, E.G. Intermediaries driving eco-innovation in SMEs: a qualitative investigation. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2012, 15, 442–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triguero, A.; Moreno-Mondéjar, L.; Davia, M.A. Drivers of different types of eco-innovation in European SMEs. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 92, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. del Río, J. P. del Río, J. Carrillo-Hermosilla, T. Könnölä, and M. Bleda, “Business Strategies and Capacities for Eco-Innovation,” SSRN Electronic Journal, Mar. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo-Orbegozo, U.; Vicente-Molina, M.-A.; Villarreal-Larrinaga, O. Eco-innovation strategic model. A multiple-case study from a highly eco-innovative European region. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 1347–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.; Ab Rahman, M.N.; Wahab, D.A. A systematic literature review of internal capabilities for enhancing eco-innovation performance of manufacturing firms. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1445–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arranz, N.; Arguello, N.L.; de Arroyabe, J.C.F. How do internal, market and institutional factors affect the development of eco-innovation in firms? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, D.; Mazzanti, M. Techno-organisational strategies, environmental innovations and economic performances. Micro-evidence from an SME-based industrial district. J. Innov. Econ. Manag. 3. [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Juárez, L.E.; Castillo-Vergara, M. Technological Capabilities, Open Innovation, and Eco-Innovation: Dynamic Capabilities to Increase Corporate Performance of SMEs. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triguero, A.; Moreno-Mondéjar, L.; Davia, M.A. Drivers of different types of eco-innovation in European SMEs. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 92, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, R.; Jayasundara, J.; Gamage, S.K.N.; Ekanayake, E.; Rajapakshe, P.; Abeyrathne, G. Sustainability of SMEs in the Competition: A Systemic Review on Technological Challenges and SME Performance. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2019, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossle, M.B.; de Barcellos, M.D.; Vieira, L.M.; Sauvée, L. The drivers for adoption of eco-innovation. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttol, P.; Buonamici, R.; Naldesi, L.; Rinaldi, C.; Zamagni, A.; Masoni, P. Integrating services and tools in an ICT platform to support eco-innovation in SMEs. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2011, 14, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucheli-Calvache, J.M.; Zuñiga-Collazos, A.; Osorio-Tinoco, F.; Cervantes-Rosas, M.d.L. . Proposal for an Eco-Innovation Concept for Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs). Sustainability 2023, 15, 10292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecere, G.; Corrocher, N.; Mancusi, M.L. Financial constraints and public funding of eco-innovation: empirical evidence from European SMEs. Small Bus. Econ. 2018, 54, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triguero, A.; Moreno-Mondéjar, L.; Davia, M.A. Drivers of different types of eco-innovation in European SMEs. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 92, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M.-H. Weng and C.-Y. Lin, “Determinants of green innovation adoption for small and medium-size enterprises (SMES),” African Journal of Business Management, 2011.
- Koszarek-Cyra, A. READINESS OF SMEs TO IMPLEMENT ECO-INNOVATION. 46, 48. [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, R.; Jayasundara, J.; Gamage, S.K.N.; Ekanayake, E.; Rajapakshe, P.; Abeyrathne, G. Sustainability of SMEs in the Competition: A Systemic Review on Technological Challenges and SME Performance. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2019, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, J.; Qiao, Y.; Shi, L. Effects of eco-innovation typology on its performance: Empirical evidence from Chinese enterprises. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2014, 34, 78–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossle, M.B.; de Barcellos, M.D.; Vieira, L.M.; Sauvée, L. The drivers for adoption of eco-innovation. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hanakta, R.; Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences; Illés, C. B.; Dunay, A. Intermediaries motivating eco-innovation in Jordanian small and medium enterprises. Econ. Ann. 2021, 191, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryanto, V.D.W.; Kondo, K.; Wismantoro, Y.; Andono, P.N. Entrepreneurship Orientation, Eco-innovation, Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Learning Adoption Capability: A case Study of Food SME’s in Central Java, Indonesia. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 226, 00046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamburg, I.; Vlăduţ, G.; O’brien, E. Fostering eco-innovation in SMEs through bridging research, education and industry for building a business oriented model. Proc. Int. Conf. Bus. Excel. 2017, 11, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hanakta, R.; Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences; Illés, C. B.; Dunay, A. Intermediaries motivating eco-innovation in Jordanian small and medium enterprises. Econ. Ann. 2021, 191, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasiq, M.; Kamal, M.; Ali, N. Factors Influencing Green Innovation Adoption and Its Impact on the Sustainability Performance of Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, W.; Ali, W.; Bhutto, M.Y.; Hussain, H.; Khan, N.A. Examining the determinants of green innovation adoption in SMEs: a PLS-SEM approach. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2019, 24, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D. What Should SMEs Consider to Introduce Environmentally Innovative Products to Market? Sustainability 2019, 11, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klewitz, J.; Hansen, E.G. Sustainability-oriented innovation of SMEs: A systematic review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuerva, M.C.; Triguero-Cano, Á.; Córcoles, D. Drivers of green and non-green innovation: empirical evidence in Low-Tech SMEs. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 68, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doe, J.K.; Van de Wetering, R.; Honyenuga, B.; Versendaal, J. Extended contextual validation of stakeholder approach to firm technology adoption: moderating and mediating relationships in an innovation eco-system. Soc. Bus. Rev. 2022, 17, 506–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, D.; Lai, K.-H.; Zhu, Q. Eco-innovation and its role for performance improvement among Chinese small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 231, 107869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Scandurra, G.; Carfora, A. Adoption of green innovations by SMEs: an investigation about the influence of stakeholders. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2021, 25, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. C. Hsu, K. C. C. C. Hsu, K. C. Tan, and S. H. Mohamad Zailani, “Strategic orientations, sustainable supply chain initiatives, and reverse logistics: Empirical evidence from an emerging market,” International Journal of Operations and Production Management, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 86–110, Jan. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.; Cuthbertson, R. Fitness map: a classification of internal strategic fit in service organisations. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2011, 31, 991–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-H.; Chang, K.-H.; Chen, H.-W. Strategic Orientation, Environmental Management Systems, and Eco-Innovation: Investigating the Moderating Effects of Absorptive Capacity. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christmann, P. Effects of “best practices” of environmental management on cost advantage: The role of complementary assets. Acad. Manag. J. 2000, 43, 663–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.; Kwon, H.; Roh, J.J. Implementation of strategic green orientation in supply chain. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2009, 12, 512–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, Y.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Wah, W.-X. Pursuing green growth in technology firms through the connections between environmental innovation and sustainable business performance: Does service capability matter? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arranz, N.; Arguello, N.L.; de Arroyabe, J.C.F. How do internal, market and institutional factors affect the development of eco-innovation in firms? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Quevedo, J.; Martinez-Ros, E.; Tchorzewska, K. End-of-pipe and cleaner production technologies. Do policy instruments and organizational capabilities matter? Evidence from Spanish firms. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero-Gil, J.; Surroca, J.A.; Tribo, J.A.; Gutierrez, L.; Montiel, I. Innovation vs. standardization: The conjoint effects of eco-innovation and environmental management systems on environmental performance. Res. Policy 2023, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-W. Enhancing Green Absorptive Capacity, Green Dynamic Capacities and Green Service Innovation to Improve Firm Performance: An Analysis of Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). Sustainability 2015, 7, 15674–15692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albort-Morant, G.; Henseler, J.; Cepeda-Carrión, G.; Leal-Rodríguez, A.L. Potential and Realized Absorptive Capacity as Complementary Drivers of Green Product and Process Innovation Performance. Sustainability 2018, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, L.M.; Alves, M.F.R.; Liboni, L.B. Green absorptive capacity: A mediation-moderation model of knowledge for innovation. Bus. Strat. Environ. 2018, 27, 1502–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, H. Green Innovation Sustainability: How Green Market Orientation and Absorptive Capacity Matter? Sustainability 2022, 14, 8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhman, A. Qualitative methodology for rehabilitation research1. J. Rehabilitation Med. 2005, 37, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Demuth and G. Mey, “Qualitative methodology in developmental psychology,” International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences: Second Edition, pp. 668–675, Mar. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Fossey, E.; Harvey, C.; Mcdermott, F.; Davidson, L. Understanding and Evaluating Qualitative Research. Aust. New Zealand J. Psychiatry 2002, 36, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camfield, L.; Crivello, G.; Woodhead, M. Wellbeing Research in Developing Countries: Reviewing the Role of Qualitative Methods. Soc. Indic. Res. 2008, 90, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njie, B.; Asimiran, S. Case Study as a Choice in Qualitative Methodology. IOSR J. Res. Method Educ. (IOSRJRME) 2014, 4, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Bradley, “Methodological Issues and Practices in Qualitative Research,” https://doi.org/10.1086/602620, vol. 63, no. 4, pp. 431–449, 1993. [CrossRef]
- V. Schwaighofer, “The qualitative interviews,” Tourist Destination Images and Local Culture, pp. 75–79, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Barrett, D.; Twycross, A. Data collection in qualitative research. Évid. Based Nurs. 2018, 21, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Curtis, E.; Comiskey, C.; Dempsey, O. Importance and use of correlational research. Nurse Res. 2016, 23, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Cao, Y. “The Context and Evolution of Business Environment Research: Based on the Review of Foreign Literature,” Apr. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Young, S. What do researchers know about the global business environment? Int. Mark. Rev. 2001, 18, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, L. Conducting Field Research Effectively. Am. Behav. Sci. 2019, 64, 198–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B. Sachan, A. B. Sachan, A. Singh, and N. Sachan, “Interview Method in Research,” The Southeast Asian Journal of Case Report and Review, 2012.
- S. Mikėnė, I. S. Mikėnė, I. Gaižauskaitė, and N. Valaviciene, “Qualitative Interviewing: Field-Work Realities,” Soc Work, 2013.
- K. Roulston, “Interviews in Qualitative Research,” The Encyclopedia of Applied Linguistics, pp. 1–10, Dec. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Brereton, P.; Kitchenham, B.A.; Budgen, D.; Turner, M.; Khalil, M. Lessons from applying the systematic literature review process within the software engineering domain. J. Syst. Softw. 2006, 80, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. Denyer and D. Tranfield, “Producing a systematic review.,” 2009, Accessed: Mar. 24, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://psycnet.apa. 2010.
- Adeoye-Olatunde, O.A.; Olenik, N.L. Research and scholarly methods: Semi-structured interviews. Int. Int. J. Avian Wildl. Biol. 2021, 4, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malterud, K.; Siersma, V.D.; Guassora, A.D. Sample Size in Qualitative Interview Studies. Qual. Heal. Res. 2016, 26, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, W.C. Conducting Semi-Structured Interviews. In Handbook of Practical Program Evaluation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 492–505. [Google Scholar]
- C. E. Wilson, “Semi-Structured Interviews,” Interview Techniques for UX Practitioners, pp. 2014; 41. [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Thematic analysis. In APA Handbook of Research Methods in Psychology, Vol. 2. Research Designs: Quantitative, Qualitative, Neuropsychological, and Biological; Cooper, H., Camic, P.M., Long, D.L., Panter, A.T., Rindskopf, D., Sher, K.J., Eds.; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N. Steils, “Non-participant observation online: using screen recording and trace analysis for collecting and analyzing individual behaviors online,” 2019.
- Abernethy, M.A.; Horne, M.; Lillis, A.M.; Malina, M.A.; Selto, F.H. A multi-method approach to building causal performance maps from expert knowledge. Manag. Account. Res. 2005, 16, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. E. Hopkins, “Lessons learned through reflecting on a classroom observation,” 2017. [CrossRef]
- Handley, M.; Bunn, F.; Lynch, J.; Goodman, C. Using non-participant observation to uncover mechanisms: Insights from a realist evaluation. Evaluation 2019, 26, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrko, S. Howick, and C. Eden, “Risk systemicity and city resilience.” Jun. 21, 2017. Accessed: Mar. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://pureportal.strath.ac.
- Eden, C. Analyzing cognitive maps to help structure issues or problems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 159, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.; Nelson, H.; Armstrong, D. “Revealed causal mapping as an evocative method for information systems research,” Proceedings of the Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, vol. 2000-January, 2000. [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, Y.S.; Guba, E.G.; Pilotta, J.J. Naturalistic Inquiry; SAGE: Beverly Hills, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Shmatkov, D. THE USE OF CAUSAL MAPS AS INTERDISCIPLINARY DIDACTIC REDUCTION METHOD. Adv. Educ. 2016, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. Hoverstadt, “The Viable System Model,” Systems Approaches to Managing Change: A Practical Guide, pp. 2010. [CrossRef]
- Fedotova, I. THE MODEL OF VIABLE SYSTEM OF AN ENTERPRISE INNOVATION ACTIVITY MANAGEMENT. Econ. Transp. Complex 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford. Beer, “Diagnosing the system for organizations,” p. 152, 1985, Accessed: Apr. 03, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://search.worldcat. 1146.
- Easterbrook, J.A. Cybernetics and Management. Nature 1960, 187, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, W.L.; Beer, S. Brain of the Firm: The Managerial Cybernetics of Organization. Technol. Cult. 1974, 15, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. Gomez, “Die kybernetische Gestaltung des Operations Managements,” 1978, Accessed: Apr. 03, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.alexandria.unisg. 1103.
- Voltelen, B.; Konradsen, H.; Østergaard, B. Ethical considerations when conducting joint interviews with close relatives or family: an integrative review. Scand. J. Caring Sci. 2017, 32, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, C. Ethical issues in the selection interview. J. Bus. Ethic- 1992, 11, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allmark, P.; Boote, J.; Chambers, E.; Clarke, A.; McDonnell, A.; Thompson, A.; Tod, A.M. Ethical Issues in the Use of In-Depth Interviews: Literature Review and Discussion. Res. Ethic- 2009, 5, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, S.K.; Lee, C.H.; Amran, A. Assessing the influence of social capital and innovations on environmental performance of manufacturing SMEs. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2023, 30, 3242–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulej-Dudek, E. Ecolabnet service packages as a response to the needs of manufacturing enterprises in the SME sector of the Baltic Sea Region. Prod. Eng. Arch. 2021, 27, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.; O’dowd, P.; Dimache, A. Manufacturing SMEs doing it for themselves: developing, testing and piloting an online sustainability and eco-innovation toolkit for SMEs. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2019, 13, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-F.; Lin, H.-C.; Lee, H.-M. Innovation in manufacturing SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic: How does environmental dynamism reinforce employee proactive behavior? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 187, 122247–122247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.; O’dowd, P.; Dimache, A. Manufacturing SMEs doing it for themselves: developing, testing and piloting an online sustainability and eco-innovation toolkit for SMEs. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2019, 13, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, K.; Battour, M.; Aboelmaged, M.; Abdelkareem, R.S. Linking internal environmental capabilities to sustainable competitive advantage in manufacturing SMEs: The mediating role of eco-innovation. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, S.K.; Ooi, C.A.; Memon, K.R. The role of CSR oriented organisational culture in eco-innovation practices. World Rev. Entrep. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 16, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravella, S.; Crespi, F. On the growth impact of different eco-innovation business strategies. Econ. Politi- 2022, 39, 657–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, K.; Halim, M.A.S.A.; Omar, K.; Abdelkareem, R.S.; Battour, M.; Wu, Y.-C.J. Institutional pressure and eco-innovation: The mediating role of green absorptive capacity and strategically environmental orientation among manufacturing SMEs in Egypt. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, K.; Halim, M.A.S.A.; Omar, K.; Battour, M.; Abdelkareem, R.S. Environmental pressures and eco-innovation in manufacturing SMEs: the mediating effect of environmental capabilities. Int. J. Innov. Sci. 2023, 16, 501–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Sawng, Y.-W.; Park, T.-K. Effects of the Fit between Size and Environmental Uncertainty on Manufacturing SMEs’ Innovation Activity. Entrep. Res. J. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Scandurra, G.; Carfora, A. Adoption of green innovations by SMEs: an investigation about the influence of stakeholders. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2021, 25, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, J.; Rahman, M.S. Determinants of eco-innovation initiatives toward sustainability in manufacturing SMEs: Evidence from Bangladesh. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, K.; Halim, M.A.S.A.; Omar, K.; Abdelkareem, R.S.; Battour, M.; Wu, Y.-C.J. Institutional pressure and eco-innovation: The mediating role of green absorptive capacity and strategically environmental orientation among manufacturing SMEs in Egypt. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkiffli, S.N.A.; Zaidi, N.F.Z.; Padlee, S.F.; Sukri, N.K.A. Eco-Innovation Capabilities and Sustainable Business Performance during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu-Yeboah, S.S.; Jiang, Y.; Frempong, M.F.; Hossin, A.; Amoako, R. Corporate sustainability and firm performance in small and medium enterprises in Ghana: Mediating role of green innovation. J. Psychol. Afr. 2022, 32, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.; Al-Shari, A.; Shah, S.H.A.; Bayram, G.E.; Rahman, E.Z.; Valeri, M. Green manufacturing practices and SMEs' sustainable performance: a moderated mediation mechanisms of green innovation and managerial discretion. Eur. Bus. Rev. [CrossRef]
- Determinants of eco-innovation capabilities adapted by Malaysian SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic. Kasetsart J. Soc. Sci. 2023, 45. [CrossRef]
- Wysocki, J. Innovative Green Initiatives in the Manufacturing SME Sector in Poland. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, K.; Halim, M.A.S.A.; Omar, K. Drivers of multiple eco-innovation and the impact on sustainable competitive advantage: evidence from manufacturing SMEs in Egypt. Int. J. Innov. Sci. 2021, 14, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukri, N.K.A.; Zulkiffli, S.N. .; Mat, N.H.N.; Omar, K.; Mawardi, M.K.; Zaidi, N.F.Z. An Analysis of Eco-Innovation Capabilities among Small and Medium Enterprises in Malaysia. Adm. Sci. 2023, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, A.; Hussain, A.; Shahzad, A.; Mohelska, H.; Hassan, R. Environmental and technological factor diffusion with innovation and firm performance: Empirical evidence from manufacturing SMEs. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Jabeen, F. ; Rashid; Alshibani, S.M., Lanteri, A., Eds.; Santoro, G. Unraveling the transformation: the three-wave time-lagged study on big data analytics, green innovation and their impact on economic and environmental performance in manufacturing SMEs. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.R.; Piprani, A.Z.; Yu, Z. Digital technology and circular economy practices: future of supply chains. Oper. Manag. Res. 2022, 15, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo-Cañamares, M.; Medrano, N.; Olarte-Pascual, C. Environmental objectives and non-technological innovation in Spanish manufacturing SMEs. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, K.J.; Mills, J.; Francis, K. Sifting, sorting and saturating data in a grounded theory study of information use by practice nurses: A worked example. Int. J. Nurs. Pr. 2012, 18, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S. C. Brown, R. S. C. Brown, R. Stevens, P. Troiano, and M. Schneider, “Exploring Complex Phenomena: Grounded Theory in Student Affairs Research,” J Coll Stud Dev, 2002.
- Mohajan, D.; Mohajan, H.K. Exploration of Coding in Qualitative Data Analysis: Grounded Theory Perspective. Res. Adv. Educ. 2022, 1, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.; Read, S.; Priest, H. A researcher’s experience of focused coding in grounded theory: What makes the final cut? Qmip Bull. 2013, 1, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, O.E.; S⊘Nderga˚rd, B.; Meredith, S. Environmental Innovations in Small and Medium Sized Enterprises. Technol. Anal. Strat. Manag. 2002, 14, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzón-Castro, S.Y.; Maldonado-Guzmán, G.; Toro, R.J.-D. Eco-innovation Types Adoption in Mexican Small and Medium Firms. J. Manag. Sustain. 2023, 13, p127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oncioiu, “Eco - Innovation in European SMEs: between Limitation and Possibilities,” 2015.
- Temri, L. Innovations technologiques environnementales dans les petites entreprises : proposition d'un modèle d'analyse. Innovations, 34. [CrossRef]
- Sukri, N.K.A.; Zulkiffli, S.N. .; Mat, N.H.N.; Omar, K.; Mawardi, M.K.; Zaidi, N.F.Z. An Analysis of Eco-Innovation Capabilities among Small and Medium Enterprises in Malaysia. Adm. Sci. 2023, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L. Temri, “Environmental Technology Innovations in SMEs: An Analytical Model,” Innovations, 2011.
- L. Fei-hong, “Study of SME’s Technology Innovation Based on the Perspective of Ecology,” Technoeconomics & Management Research, 2010.
- Sukri, N.K.A.; Zulkiffli, S.N. .; Mat, N.H.N.; Omar, K.; Mawardi, M.K.; Zaidi, N.F.Z. An Analysis of Eco-Innovation Capabilities among Small and Medium Enterprises in Malaysia. Adm. Sci. 2023, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecere, G.; Corrocher, N.; Mancusi, M.L. Financial constraints and public funding of eco-innovation: empirical evidence from European SMEs. Small Bus. Econ. 2018, 54, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Bao, C. Government Subsidy, Tax Incentives and Innovation of Small andMedium-sized Enterprises in China. ICEME 2023: 2023 the 14th International Conference on E-business, Management and Economics. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, ChinaDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- S. Parris and P. Demirel, “Innovators and Access to Finance in the UK’s Environmental Sector,” Environment for Innovation eJournal, 2012.
- Cao, X.; Bao, C. Government Subsidy, Tax Incentives and Innovation of Small andMedium-sized Enterprises in China. ICEME 2023: 2023 the 14th International Conference on E-business, Management and Economics. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, ChinaDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Guo, T.; Shi, Z. Systematic Analysis on the Environment of Innovative Small and Medium Enterprises. Phys. Procedia 2012, 24, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsawan, I.W.E.; Koval, V.; Duginets, G.; Kalinin, O.; Korostova, I. The impact of green innovation on environmental performance of SMEs in an emerging economy. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 255, 01012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadhilah, M. ; Andriyansah Strategic Implementation of Environmentally Friendly Innovation of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Indonesia. Eur. Res. Stud. J. 2017, XX, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.; Ab Rahman, M.N.; Wahab, D.A. A systematic literature review of internal capabilities for enhancing eco-innovation performance of manufacturing firms. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1445–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Juárez, L.E.; Castillo-Vergara, M. Technological Capabilities, Open Innovation, and Eco-Innovation: Dynamic Capabilities to Increase Corporate Performance of SMEs. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppmann, J. The Role of Interfirm Knowledge Spillovers for Innovation in Mass-Produced Environmental Technologies: Evidence from the Solar Photovoltaic Industry. Organ. Environ. 2016, 31, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothe, C.; Nguyen-Thi, U.T.; Triguero. Innovative products and services with environmental benefits: design of search strategies for external knowledge and absorptive capacity. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2017, 61, 1934–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczewska, M. KNOWLEDGE AS A KEY RESOURCE CONTRIBUTING TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF ECO-INNOVATIONS BY COMPANIES-SUPPLIERS OF ENVIRONMENTALLY SOUND TECHNOLOGIES. CBU Int. Conf. Proc. 2016, 4, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albort-Morant, G.; Leal-Rodríguez, A.L.; De Marchi, V. Absorptive capacity and relationship learning mechanisms as complementary drivers of green innovation performance. J. Knowl. Manag. 2018, 22, 432–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study focus | Key Findings | Author and year |
|---|---|---|
| Eco-innovation types adoption | Poduct, process, and management eco-innovation are key types adopted by SMEs in the automotive industry. | Sandra Yesenia Pinzón-Castro, Gonzalo Maldonado-Guzmán, R. J. Toro, 2023 [19]. |
| Technological capabilities and Eco-Innovation | Technological capability significantly influences eco-innovation and improves corporate performance. | L. Valdez-Juárez, M. Castillo-Vergara, 2020 [20]. |
| Cleaner production | Waste recycling and prevention projects yield higher economic and environmental value than other projects. | B. Hoof, Thomas P. Lyon, 2013 [21]. |
| Eco-innovation as industry Externality | Eco-innovation motivated by market pressures leads to competitive advantages and sustainable development. | Galván-Vela, E., Ruíz-Corrales, M., Ahumada-Tello, E., & Ravina-Ripoll, R, 2023 [19]. |
| Industrial symbiosis | Industrial symbiosis strategies in industrial areas reveal opportunities for systemic eco-innovation. | M. Puente, E. R. Arozamena, S. Evans, 2015 [24]. |
| Environmental innovation in handicraft businesses | Environmental innovation in handicraft businesses improves sustainability across economic, social, and environmental dimensions. | P. Sánchez-Medina, J. Corbett, Arcelia Toledo-López, 2011 [22]. |
| Step. 1 | Conceptual limits for document search in WOS and SCOPUS: 1. Search equation: (eco-innovation OR ecological innovation OR environmental innovation) AND (manufacturing OR manufacture) AND (smes OR small Business). 2. Search period: the last five years from the date of the most recent publication (2019-2024), the search date was May 23, 2024. A total of 37 documents were obtained. |
| Step 2 | Definition of criteria for document search in WOS and SCOPUS: 3. Selected fields: Article title, Abstract, Keywords. 4. Documents: articles |
| Step 3 | Definition of exclusion criteria for the documents found: 5. Review articles. 6. Exclusion for duplicity. 7. For not being research in EI. 8. For not presenting causal relationships. 9. A total of 24 documents were reviewed. |
| Expert | Experience and knowledge | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Corporate Social Responsibility, corporate environmental management and sustainability. | January 24, 2024. |
| 2 | Sustainable development with experience in organizational implementation of ESG (environmental, social and governance) issues in Mexico and Latin America. | February 7, 2024. |
| 3 | Clean industry, industrial engineering, craft processes, general organizational consultancy. | May 4, 2024. |
| 4 | Biology, circular economy and ecotechnologies. | May 4, 2024. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





