Submitted:
29 April 2024
Posted:
30 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bed Bug Populations
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Topical Assays of Technical Grade Broflanilide
2.4. Efficacy of the Broflanilide-Based Aerosol Formulation (IMZOPS 60)
2.4.1. Direct Spray Assays on Adult Bed Bugs
2.4.2. Direct Spray Assays on Bed Bug Eggs
2.4.3. Residual Assays against Adult Bed Bugs
2.4.4. Residual Assays with First Instar Bed Bugs
2.4.5. Aged Residual Assays against Adult Bed Bugs
2.5. Behavioral Responses to Harborages Treated with IMZOPS 60
2.5.1. One-Choice Harborage Assays
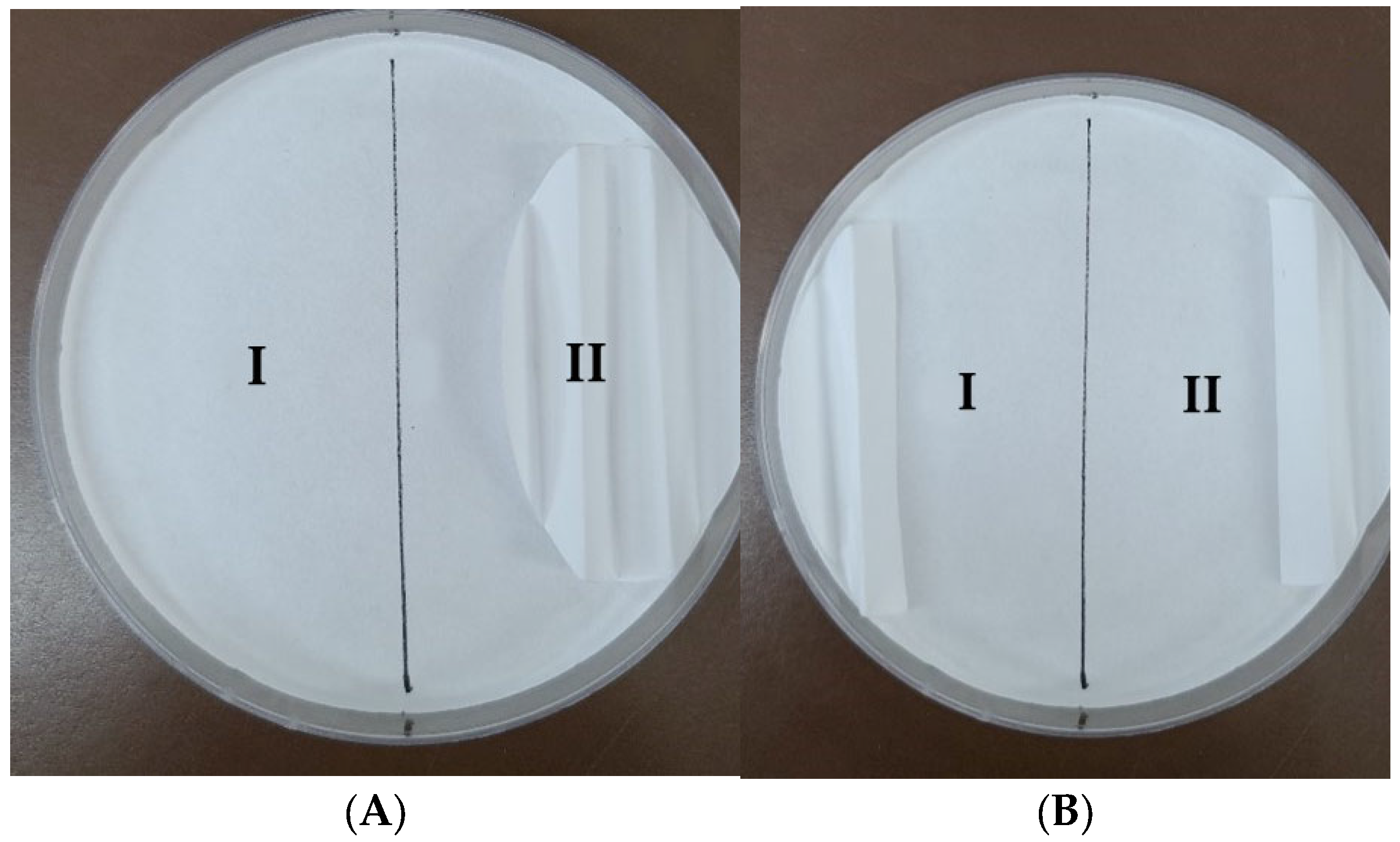
2.5.2. Two-Choice Harborage Assays
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Topical Assays of Technical Grade Broflanilide
3.2. Efficacy of the Broflanilide-Based Aerosol Formulation (IMZOPS 60)
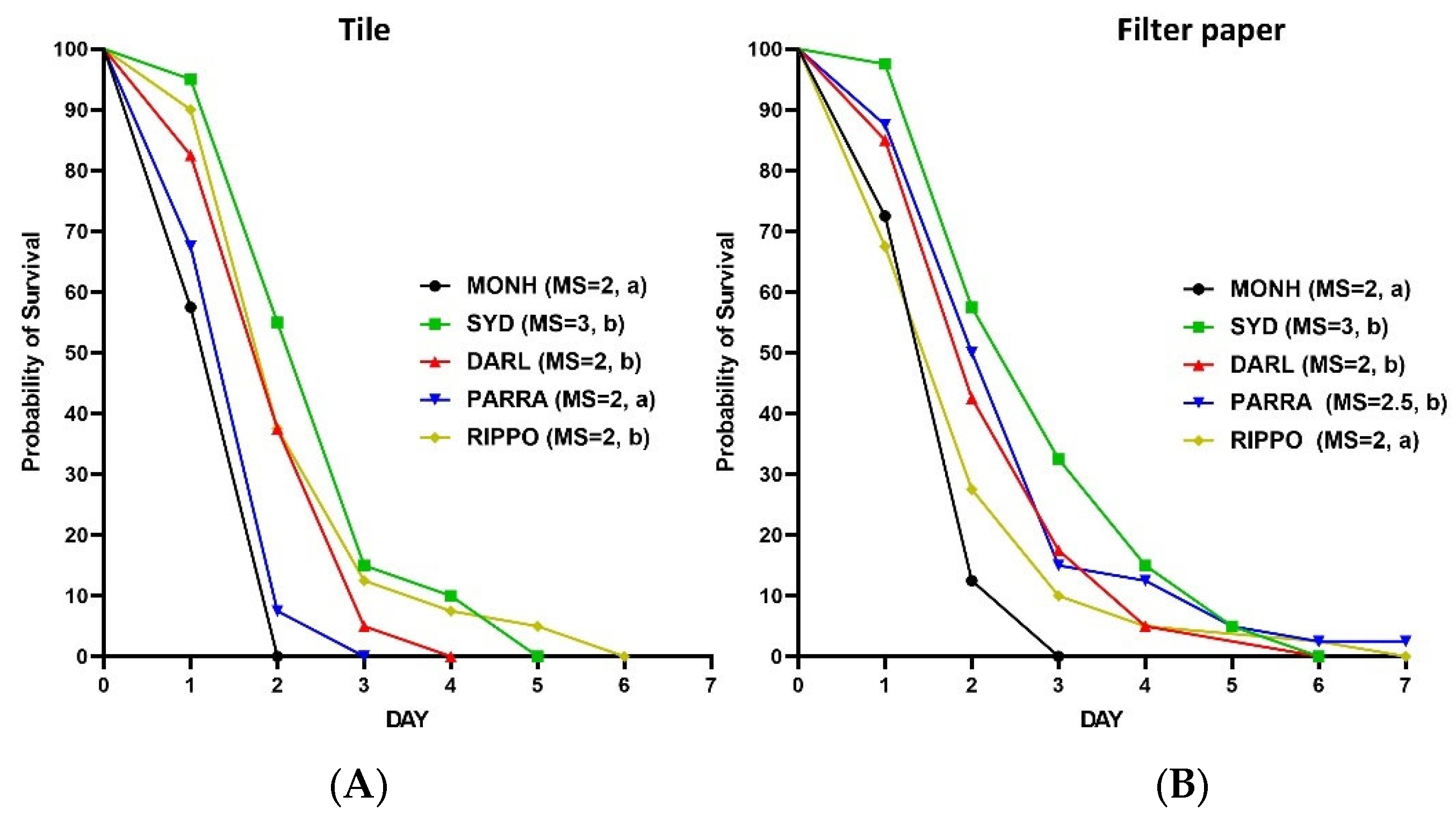
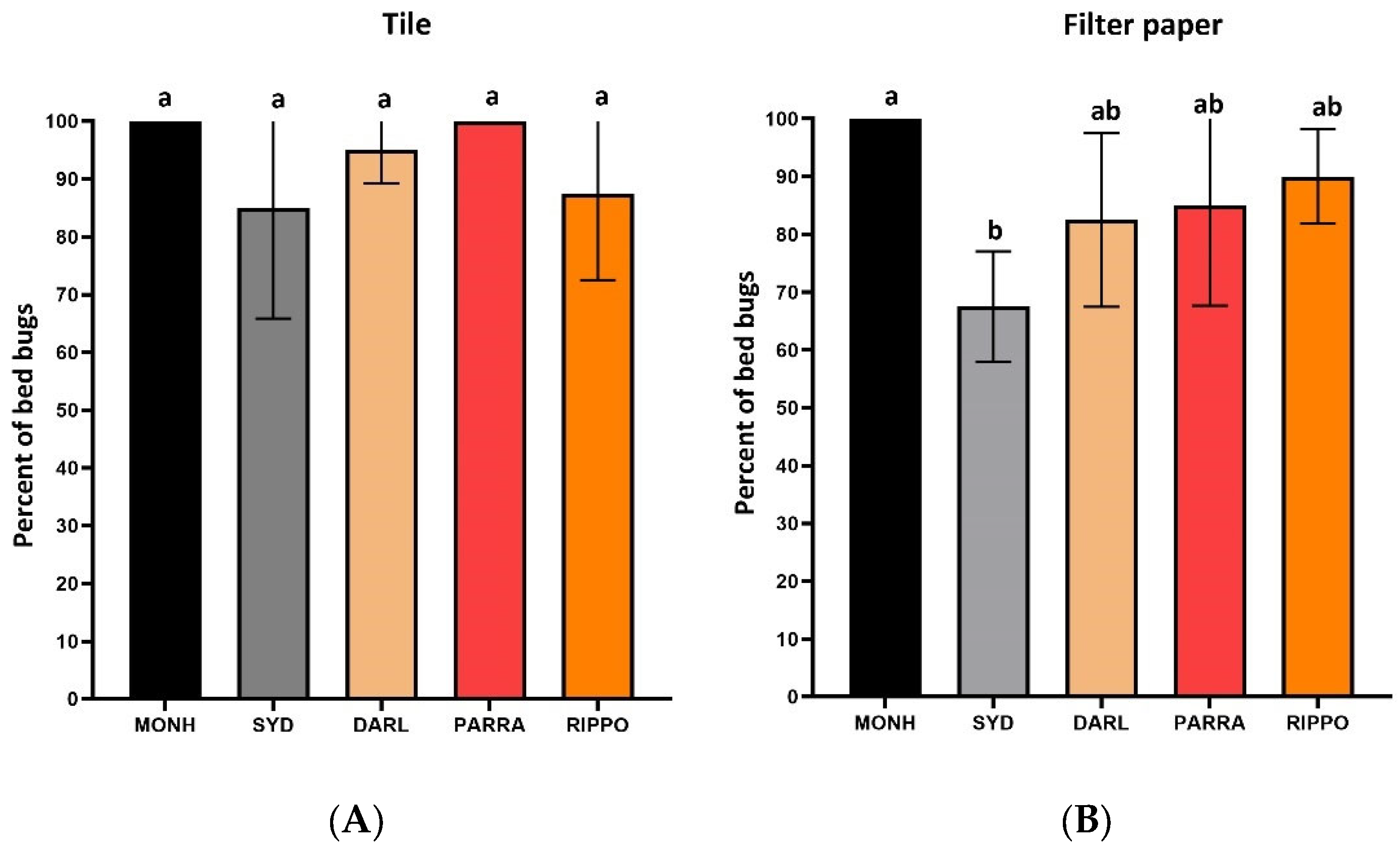
3.2.1. Direct Spray on Adult Bed Bugs
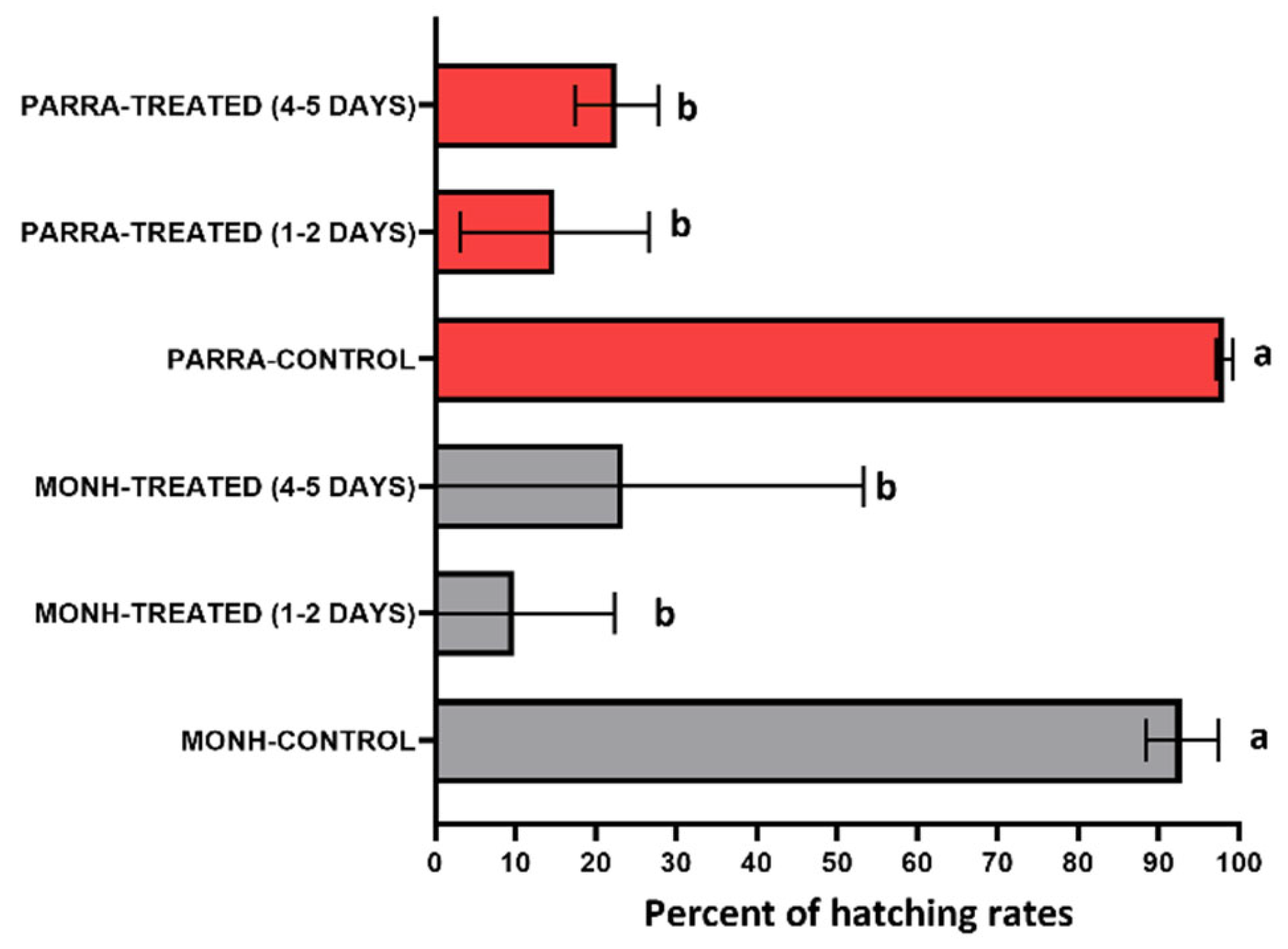
3.2.2. Direct Spray on Bed Bug Eggs
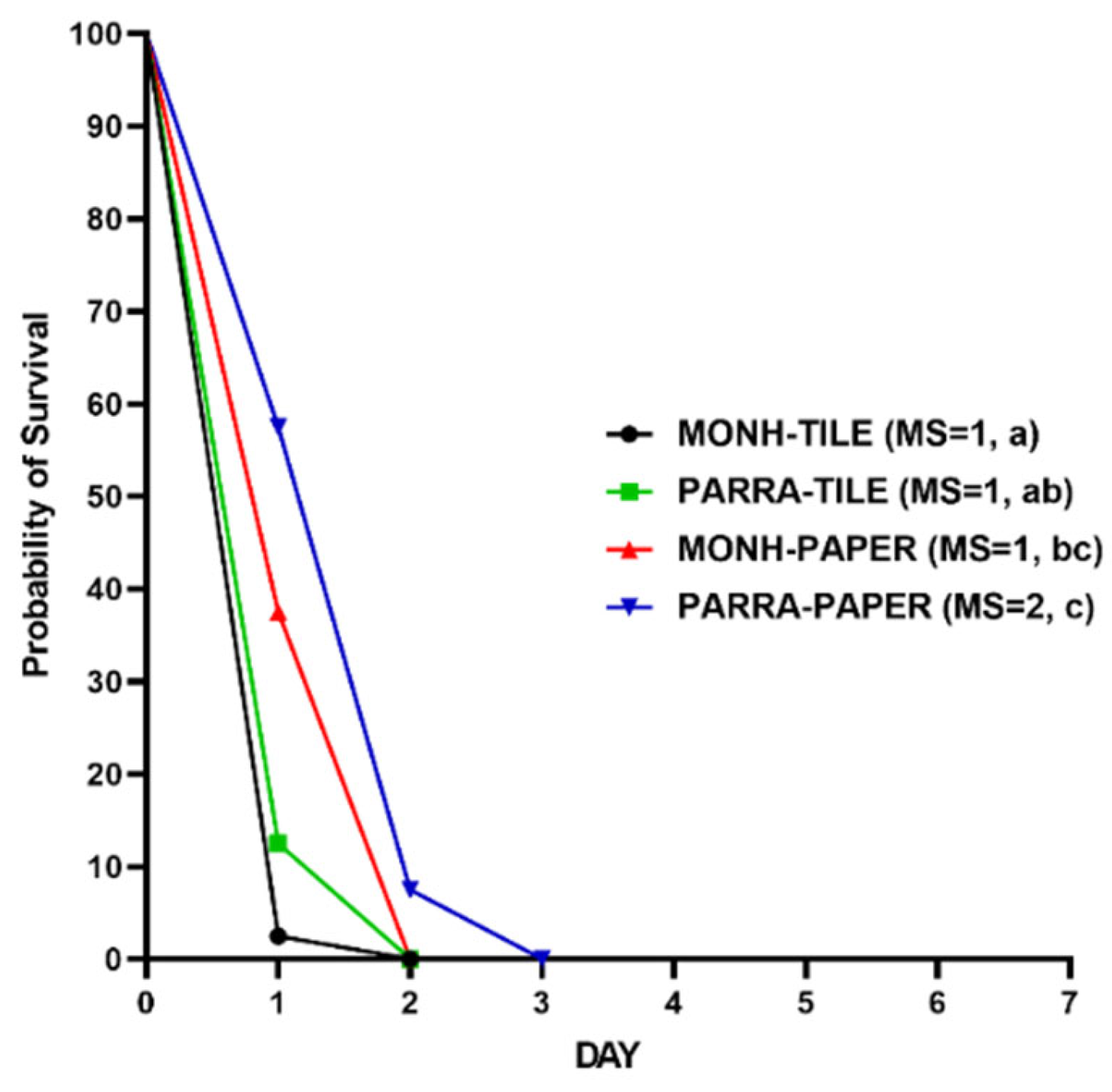
3.2.3. Residues against Adult Bed Bugs
3.2.4. Residues against First Instar Bed Bugs
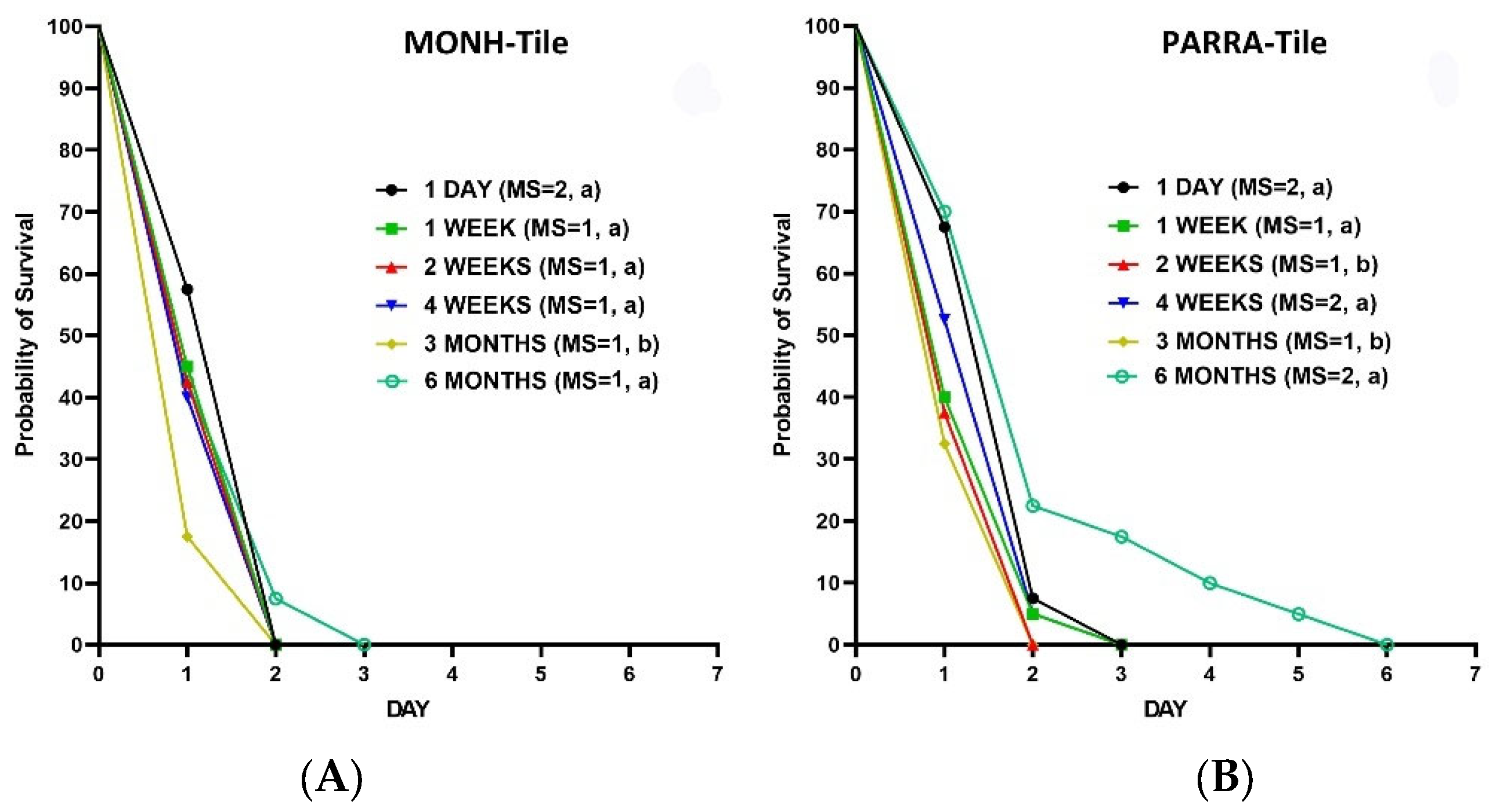
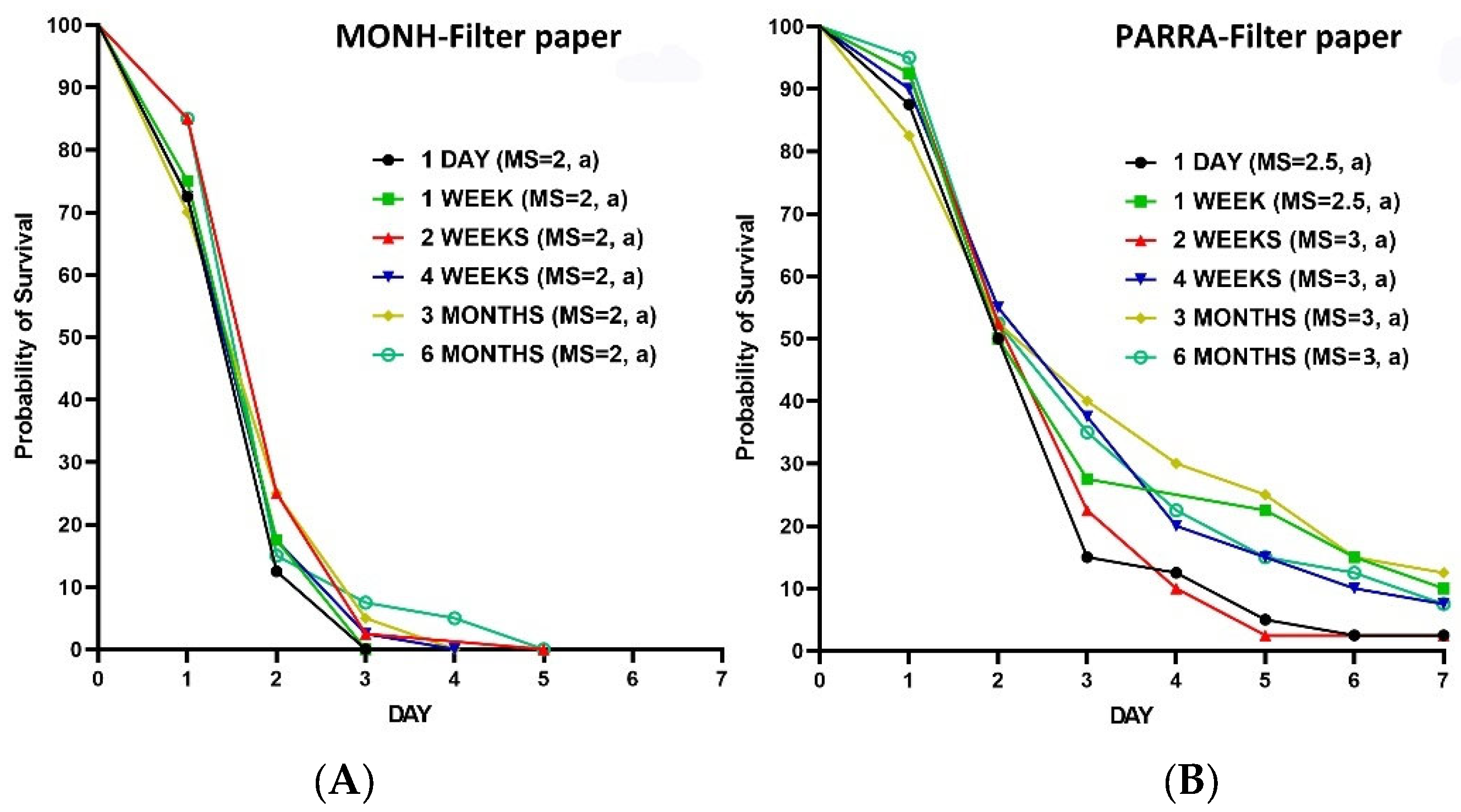
3.2.5. Aged Residues against Adult Bed Bugs
3.3. Behavioral Responses to Harborages Treated with IMZOPS 60
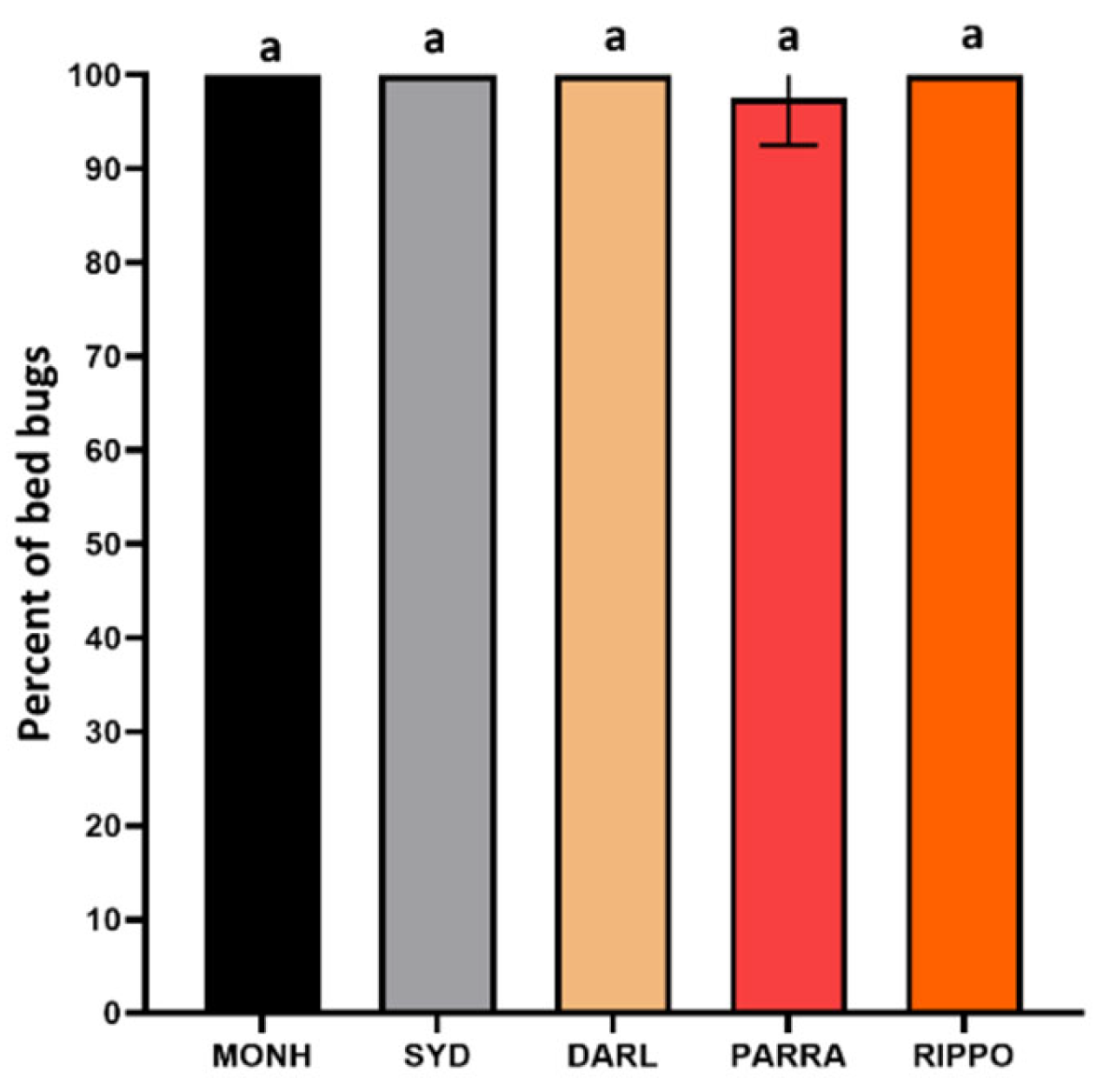
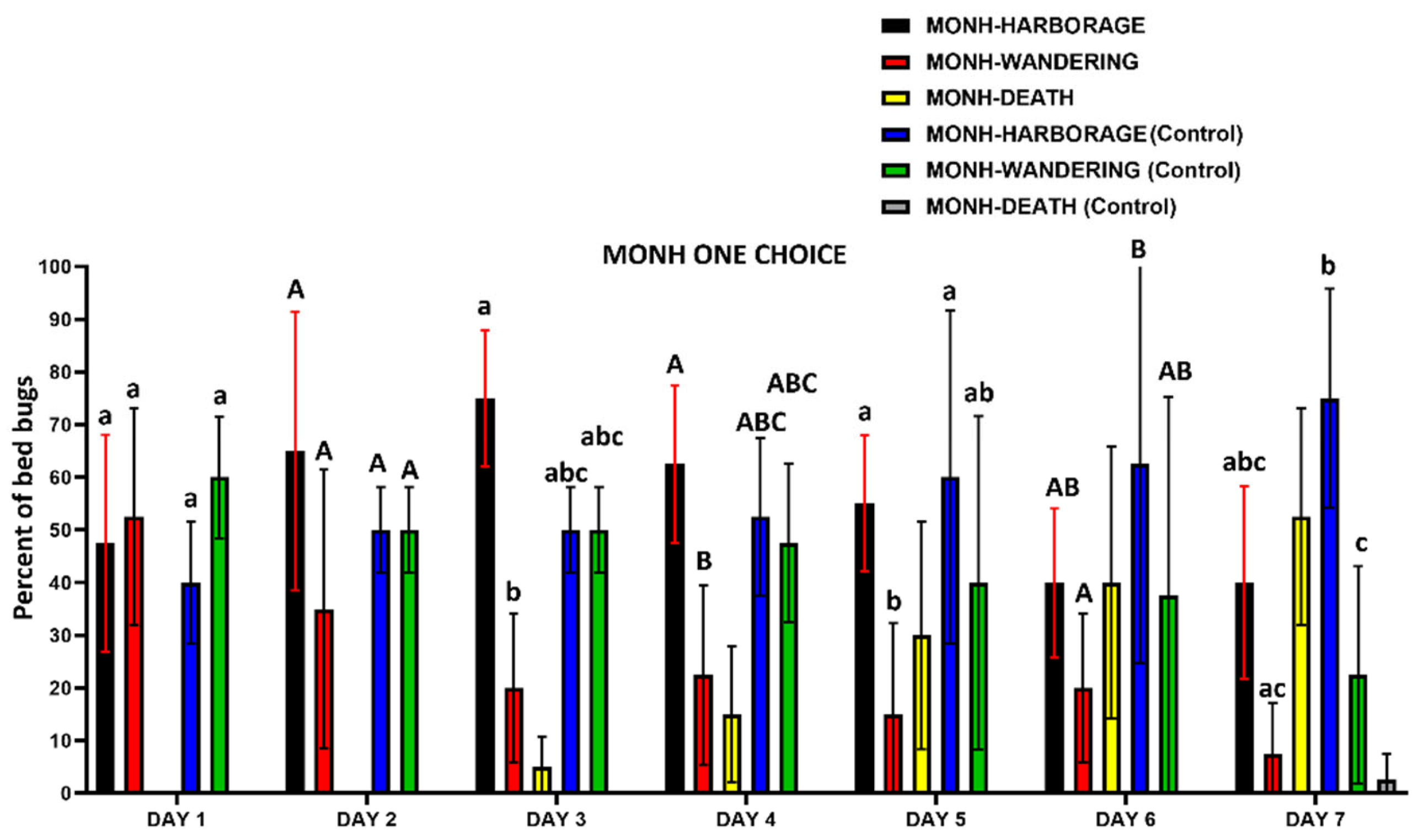
3.3.1. One-Choice Harborage Assays
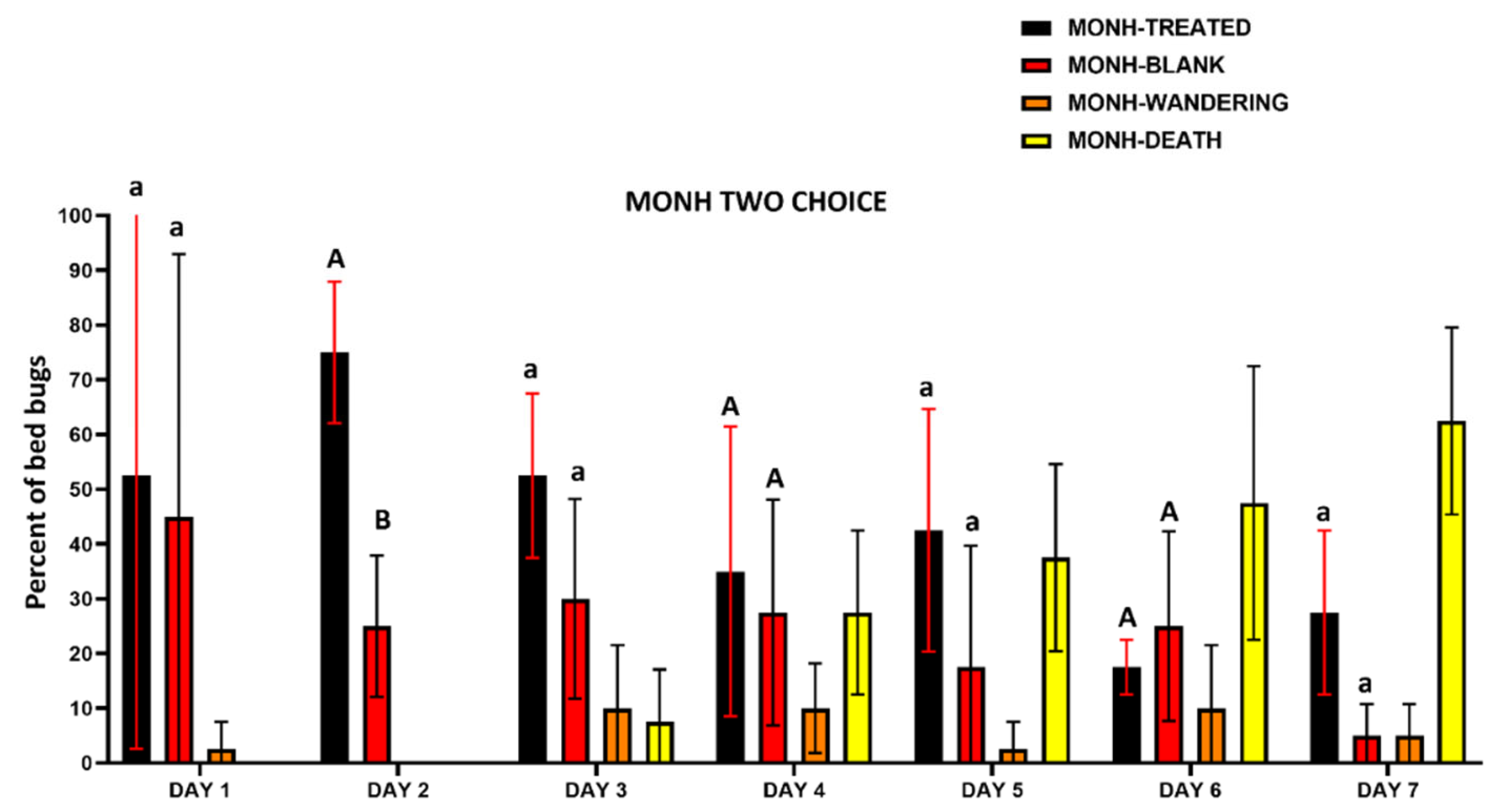
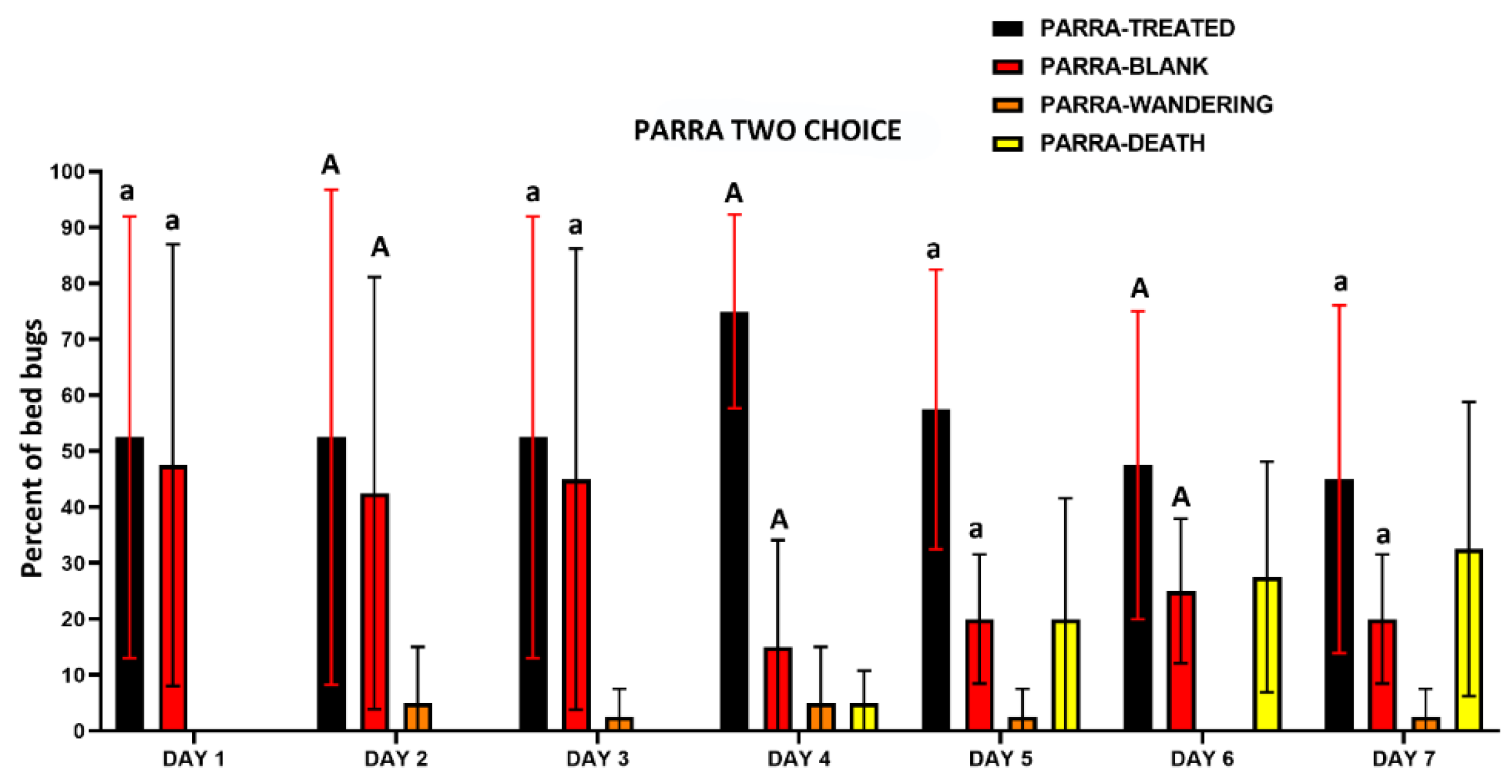
3.3.2. Two-Choice Harborage Assays
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dang, K.; Doggett, S.L.; Singham, G.V.; Lee, C.Y. Insecticide resistance and resistance mechanisms in bed bugs, Cimex spp. (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- oggett, S. L., D. M. Miller, and C. Y. Lee. 2018. Advances in the Biology and Management of Modern Bed Bugs; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, United Kingdom, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Doggett, S.L.; Dwyer, D.E.; Penas, P.F.; Russell, R.C. Bed bugs: clinical relevance and control options. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 164–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, A.; Potter, M.F.; Potter, D.A.; Haynes, K.F. Insecticide resistance in the bed bug: a factor in the pest's sudden resurgence? J. Med. Entomol. 2007, 44, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Potter, M.F. 2011. The history of bed bug management – with lessons from the past. Am. Entomol. 2011, 57, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C. Y., D. M. Miller, and S. L. Doggett. 2018. Chapter 30: Chemical control. In Advances in the Biology and Management of Modern Bed Bugs; Doggett, S.L., Miller, D.M., Lee, C.Y., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, United Kingdom, 2018; pp. 311–321. [Google Scholar]
- Doggett, S.L.; Lee, C.Y. Historical and contemporary control options against bed bugs, Cimex spp. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2023, 68, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, M.F.; Haynes, K.F.; Fredericks, J. Bed bugs across America: the 2015 bed bugs without borders survey. PestWorld 2015, November/December, 4–14. [Google Scholar]
- Katsuta, H.; Nomura, M.; Wakita, T.; Daido, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kawahara, A.; Banba, S. Discovery of broflanilide, a novel insecticide. J. Pestic. Sci. 2019, 44, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC). Available online: https://irac-online.org (access on 28 March 2024).
- Govoetchan, R.; Fongnikin, A.; Syme, T.; Small, G.; Gbegbo, M.; Todjinou, D.; Rowland, M.; Nimmo, D.; Padonou, G.G.; Ngufor, C. VECTRONTM T500, a new broflanilide insecticide for indoor residual spraying, provides prolonged control of pyrethroid-resistant malaria vectors. Malar. J. 2022, 21, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Herk, W.G.; Warren, R.L.; Bailey, T. Wireworm (Coleoptera: Elateridae) intoxication symptoms indicate the postharvest presence of broflanilide residues in soil collected from potato fields. J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 116, 1998–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Hu, F.; Wang, P.; Fu, W.; Liu, X. Broflanilide effectively controls Helicoverpa armigera and Spodoptera exigua exhibiting diverse susceptibilities to chlorantraniliprole and emamectin benzoate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 1262–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority (APVMA). Available online: https://apvma.gov.au (access on 28 March 2024).
- Usinger, R.L. Monograph of Cimicidae (Hemiptera - Heteroptera); Entomological Society of America: College Park, Maryland, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, K.; Toi, C.S.; Lilly, D.G.; Bu, W.; Doggett, S. L. Detection of knockdown resistance (kdr) mutations in the common bed bug, Cimex lectularius (Hemiptera: Cimicidae) in Australia. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.S.; Ambrose, P.; Williams, J.; Morgan, J.; Praulins, G.; Ingham, V.A.; Williams, C.T.; Logan, R.A.E.; Ismail, H.M.; Malone, D. Tenebenal: a meta-diamide with potential for use as a novel mode of action insecticide for public health. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 398. [Google Scholar]
- Majid, A.H.A.; Zulaikha, Z. Laboratory bioassay on efficacy of dual mode of action insecticides (beta-cyfluthrin and imidacloprid) towards tropical bed bugs, Cimex hemipterus (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2015, 3, 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, A.; Potter, M.F.; Haynes, K.F. Evaluation of chlorfenapyr for control of the bed bug, Cimex lectularius L. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finney, D.J. Probit Analysis, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: London, United Kingdom, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, J.A.; Preisler, H.K.; Russell, R.M. Polo Plus: Probit and Logit Analysis, User’s Guide; LeOra Software: Petaluma, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Payton, M.E.; Greenstone, M.H.; Schenker, N. Overlapping confidence intervals or standard error intervals: what do they mean in terms of statistical significance? J. Insect Sci. 2003, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, M.W.; Park, R.M.; Barler, A.J. Comparing median lethal concentration values using confidence interval overlap or ratio tests. Environ. Toxicol. Chemist. 2006, 25, 1441–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Multiple comparisons of survival curves. Available online: https://www.graphpad.com/guides/prism/latest/statistics/stat_multiple_comparisons_of_surviv.htm (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Lilly, D.G.; Latham, S.L.; Webb, C.E.; Doggett, S.L. Cuticle thickening in a pyrethroid-resistant strain of the common bed bug, Cimex lectularius L. (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). PLoS One 2016, 11, e0153302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilly, D.G.; Dang, K.; Webb, C.E.; Doggett, S.L. Evidence for metabolic pyrethroid resistance in the common bed bug (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilly, D.G.; Zalucki, M.P.; Orton, C.J.; Russell, R.C.; Webb, C.E.; Doggett, S.L. Confirmation of insecticide resistance in Cimex lectularius (Hemiptera: Cimicidae) in Australia. Austral Entomol. 2015, 54, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefka, J.; Votýpka, J.; Lukeš, J.; Balvín, O. Cimex lectularius and Cimex hemipterus (bed bugs). Trends Parasitol. 2022, 38, 919–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balvìn, O.; Sasinkova, M.; Martinu, J.; Nazarizadeh, M.; Bubova, T.; Booth, W.; Vargo, E.L.; Štefka, J. Early evidence of establishment of the tropical bed bug (Cimex hemipterus) in Central Europe. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2021, 35, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chebbah, D.; Elissa, N.; Sereno, D.; Hamarsheh, O.; Marteau, A.; Jan, J.; Izri, A.; Akhoundi, M. Bed bugs (Hemiptera: Cimicidae) population diversity and first record of Cimex hemipterus in Paris. Insects 2021, 12, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Shin, E.H.; Ju, H.C.; Jeong, E.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H. The first recent case of Cimex hemipterus (Hemiptera: Cimicidae) with super-kdr mutations in the Republic of Korea. J. Med. Entomol. 2023, 60, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gapon, D. First records of the tropical bed bug Cimex hemipterus (Heteroptera: Cimicidae) from Russia. Zoosystematica Ross. 2016, 25, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, V.B.; Aksenenkoa, E.V.; Sobolevaa, V.A.; Kornevb, I.I. New data on the distribution of the tropical bed bug Cimex hemipterus and the western conifer seed bug Leptoglossus occidentalis (Heteroptera: Cimicidae, Coreidae) in the European Part of Russia. Russ. J. Biol. Invasions 2020, 11, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, I. Bugs of the past—or are they on the up? Professional Pest Controller 2003, 32, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, K.; Doggett, S.L.; Leong, X.Y.; Veera Singham, G.; Lee, C.Y. Multiple mechanisms conferring broad-spectrum insecticide resistance in the tropical bed bug (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 2473–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, K.; Doggett, S.L.; Lee, C.Y. Performance of pyrethroid-neonicotinoid mixture formulations against field-collected strains of the tropical bed bug (Hemiptera: Cimicidae) on different substrates. J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 113, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilly, D.G.; Dang, K.; Webb, C.E.; Doggett, S.L. Are Australian field-collected strains of Cimex lectularius and Cimex hemipterus (Hemiptera: Cimicidae) resistant to deltamethrin and imidacloprid as revealed by topical assay? Austral Entomol. 2018, 57, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doggett, S.L.; Cooper, R. Back with a bite: bed bugs 25 years on! FAOPMA Magazine 2024, January, 16–53. Available online: https://rb.gy/j7mnbn (access on 28 March 2024).
- Leong, X.Y.; Veera Singham, G.; Chong Shu-Chien, A.; Doggett, S.L.; Lee, C.Y. Influences of exposure time and mortality assessment interval on bioassay results of insecticide-resistant tropical bed bugs (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). Insects 2020, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinson, K.R.; Benson, E.P.; Zungoli, P.A.; Bridges Jr., W.C.; Ellis, B.R. Egg hatch rate and nymphal survival of the bed bug (Hemiptera: Cimicidae) after exposure to insecticide sprays. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 2495–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.E.; Miller, D. M. Insecticide resistance in eggs and first instars of the bed bug, Cimex lectularius (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). Insects 2015, 6, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, X.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Dang, K.; Singham, G.V.; Doggett, S.L.; Lee, C.Y. Performance of commercial insecticide formulations against different developmental stages of insecticide-resistant tropical bed bugs (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, P.R. Surfaces and other factors modifying the effectiveness of pyrethroids against insects in public health. Pestic. Sci. 1985, 6, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, M. K. 1995. Factors affecting control with residual insecticide deposits. In Understanding and controlling the German cockroach; Rust, M.K., Owens, J.M., Reierson, D.A., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York City, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 149–169. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, K.; Singham, G.V.; Doggett, S.L.; Lilly, D.G.; Lee, C.Y. Effects of different surfaces and insecticide carriers on residual insecticide bioassays against bed bugs, Cimex spp. (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 558–566. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Singh, N.; Zha, C.; Cooper, R. Efficacy of selected insecticide sprays and aerosols against the common bed bug. Cimex lectularius (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). Insects 2016, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, M.G.; Axtell, R.C. Susceptibility of the bedbug, Cimex lectularius, to selected insecticides and various treated surfaces. Med. Vet. Entomol. 1993, 7, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Locations | Strain code | Year | Maximum generation | Susceptibility |
kdr Haplotypeb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monheim, Germany, 40789 | MONH | 1960s | NA | Susceptible | A |
| Sydney, NSW Australia, 2000 | SYD | 2004 | >200 | Resistant | A/B |
| Darlinghurst, NSW Australia, 2010 | DARL | 2011 | 140 | Resistant | B/C |
| Parramatta, NSW Australia, 2150 | PARRAa | 2012 | 128 | Resistant | B |
| Ripponlea, VIC Australia, 3185 | RIPPO | 2013 | 117 | Resistant | B |
| Strains | Replicatesa | Nb | LD50 ng (95%, CI)c | LD95 ng (95%, CI) | χ2 (df) | Slop ± SE | RR50 d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MONH | 8 | 640 | 1.00 (0.38 – 1.76) A | 12.49 (5.29 – 166.16) | 25.72 (5) | 1.50 ± 0.14 | 1 |
| SYD | 4 | 360 | 1.22 (0.46 – 2.17) AB | 91.69 (39.95 – 439.89) | 2.96 (4) | 0.88 ± 0.15 | 1.22 |
| DARL | 5 | 450 | 1.03 (0.11 – 2.38) AB | 40.89 (14.79 – 972.74) | 7.42 (4) | 1.03 ± 0.16 | 1.03 |
| PARRA | 8 | 720 | 3.65 (1.83 – 7.20) B | 137.58 (43.43 – 1648.30) | 26.45 (6) | 1.04 ± 0.08 | 3.65 |
| RIPPO | 5 | 450 | 2.77 (1.52 – 4.35) AB | 283.06 (113.72 – 1346.70) | 3.34 (4) | 1.50 ± 0.19 | 2.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





