1. Introduction
Heavy metal ions which are transported into aquatic environment via industrial effluents affect aquatic life. They are harmful because of their hazardous bio-accumulative nature. One of the most hazardous heavy metal contaminants is Chromium Cr(VI), which has been utilized extensively and on a massive scale in a number of sectors, including metal cleaning, dyes, leather, textiles, and plating. Cr(VI) is a transition metal, steel-gray, lustrous, stiff, and having brittle appearance [1-4]. Cr(VI) has a high degree of oxidation resistance even at high temperatures. Cr(VI) is exceedingly poisonous and carcinogenic; therefore its excess presence in food, water, or the environment may seriously harm the biota. For this reason, several environmental protection agencies have established a chromium limit that is acceptable as long as no acute or long-term effects on human health have been documented. According to the World Health Organization (WHO 1958), 0.05 mg/L of chromium is the maximum level that should be present in water. The Maximum Contaminant Limit (MCL) and Maximum Contaminant Limit Goal (MCLG) for chromium in water were both set at 0.1 parts per million (ppm) by the United States Environmental and Protection Agency (US EPA) in 2012. (100ppb). The Maximum Contaminant Limit (MCL) for chromium in drinking water is 0.05 mg/L, according to a 2013 report from the California Department of Public Health. The public health objective for Cr (VI) is 0.02 ppb; however the maximum contamination level is established at 10ppb. [4-5]. The quick removal of Cr (VI) ions from contaminated water has been focused from the last few decades and numerous techniques has been utilized such as electrochemical deposition, ion exchange, adsorption, biological methods, and membrane separation. Adsorption separation is the fastest, most practical, and least expensive method for the quick removal of harmful pollutants. The adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) ions from wastewater has occasionally been accomplished using a variety of adsorbents, including zeolite, activated carbon, metal oxides, waste industrial material, and nano-composites, etc. For the quick removal of heavy Cr(VI) ions a variety of metal oxide nanostructures have been employed including cellulose based iron oxide nanoparticle composites, titanium oxides, aluminum oxides, and copper oxides [6-7].
In the present research investigations, synthesised Fe2O3/Cellulose nano-composites and CuOx-NPs are being characterised and used for the direct removal of Cr(VI) ions from an aqueous environment. Additionally, the adsorption properties of these adsorbents are being compared. The results obtained suggest that the synthesised Fe2O3/cellulose and CuOx-NPs are useful for adsorption and can potentially be used multiple times without losing their effectiveness.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The used papers served as a source of cellulose and were purchased from the local market. All of the reagents utilised in the experiment were of analytical grade. Iron(III) oxide, sodium hydroxide, copper chloride, copper nitrates, and urea were acquired from the commercial supplier Sigma-Aldrich.
2.2. Synthesis of Fe2O3/Cellulose Nanocomposite
Synthesis of Fe
2O
3/cellulose using the precipitation method involves a two-stage process. During the initial phase, previously utilised copy paper was fragmented into smaller segments, subjected to three rounds of washing with distilled water, and afterwards immersed in a solution containing 40% H
2SO
4. The mixture was subjected to filtration and afterwards washed four times with distilled water. Following this, the mixture was dried in an oven maintained at a temperature of 50 °C. In addition, a quantity of 3.3 gram of dried material was introduced into a solution containing NaOH, thiourea, and urea at a temperature of 261.15 Kelvin. The solution was then stirred for duration of 25 minutes in an environment saturated with nitrogen [
8]. During the second stage of the experiment, a solution containing 15 ml of Fe
2Cl
3.6H
2O (weighing 13.51g) and FeCl
2.4H
2O (weighing 4.97g) was prepared. This solution was then added drop by drop to the cellulose solution and vigorously stirred for duration of 180 minutes at room temperature. The composite material that was synthesised underwent a filtration process, followed by rinsing with distilled water, ethanol, and acetone. The synthesised substance were further dried in an oven at a temperature of 323.15 K and thereafter stored.
2.3. Synthesis of CuOx-NPs
Copper oxide nanoparticles (CuOx-NPs) were synthesised utilising the precipitation method, employing copper chloride (CuCl2) and copper nitrate (Cu(NO3)2.3H2O) as precursor materials. To initiate the experiment, every precursor was initially dissolved in 100 millilitres of distilled water to achieve a concentration of 0.1 M. Subsequently, a 0.1 M NaOH solution was gradually introduced into the mixture under constant stirring until the pH level reached 14, resulting in the formation of black precipitates indicative of the presence of N2 gas. The black precipitate was collected and later subjected to washing procedures until the pH was adjusted to 7.0. Distilled water was used initially, followed by a wash with 100% ethanol. The yields were thereafter subjected to a drying process at a temperature of 80 °C for duration of 16 hours, as indicated in references [9-10]. Subsequently, the synthesised materials passed through a calcination process at a temperature of 500 °C for duration of 4 hours.
2.4. Characterization and Batch Adsorption Study
The synthesised materials, which are Fe
2O
3/Cellulose and CuOx-NPs, were subjected to comprehensive characterization using essential analytical techniques. In order to determine the characteristics of the freshly synthesised nanoparticles, the morphological and elemental analyses were investigated through the JSM-IT800 Schottky Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope, JEOL Ltd. Investigation involved the utilisation of synthesised materials for the purpose of conducting an adsorption study. To establish the standard stock solution of chromium (VI) ions with a concentration of 500 parts per million (ppm), a mass of 0.5 gram of chromium was solubilized in 1000 milliliters of distilled water. The initial concentrated solution was subjected to additional dilution in order to attain the desired concentrations, employing the dilution formula denoted as C
1V
1=C
2V
2. A solution was prepared and supplemented with 0.1 g of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) and iron(III) oxide (Fe
2O
3) composite. The specimen underwent agitation for approximately 30 minutes within a water bath shaker. Subsequently, the sample was subjected to filtration in order to isolate any remaining Cr (VI) species. The quantification of Cr (VI) was accomplished using Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) through the application of
[Eq. 1].
Initial and equilibrium concentrations of chromium (VI) metal, denoted as Co and Ce (mg.L-1) respectively, are of interest in this context. Additionally, the quantity of chromium (VI) adsorbed at equilibrium, represented as qe (mg/g), and the volume of the solution, denoted as V (mL), are also relevant parameters. The influence of different parameters on the adsorption process was investigated, encompassing temperature, initial concentration, contact time, ionic strength, and pH. The identical methodology was also employed to explore the efficacious elimination of hexavalent chromium (Cr (VI)) from a true sample.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
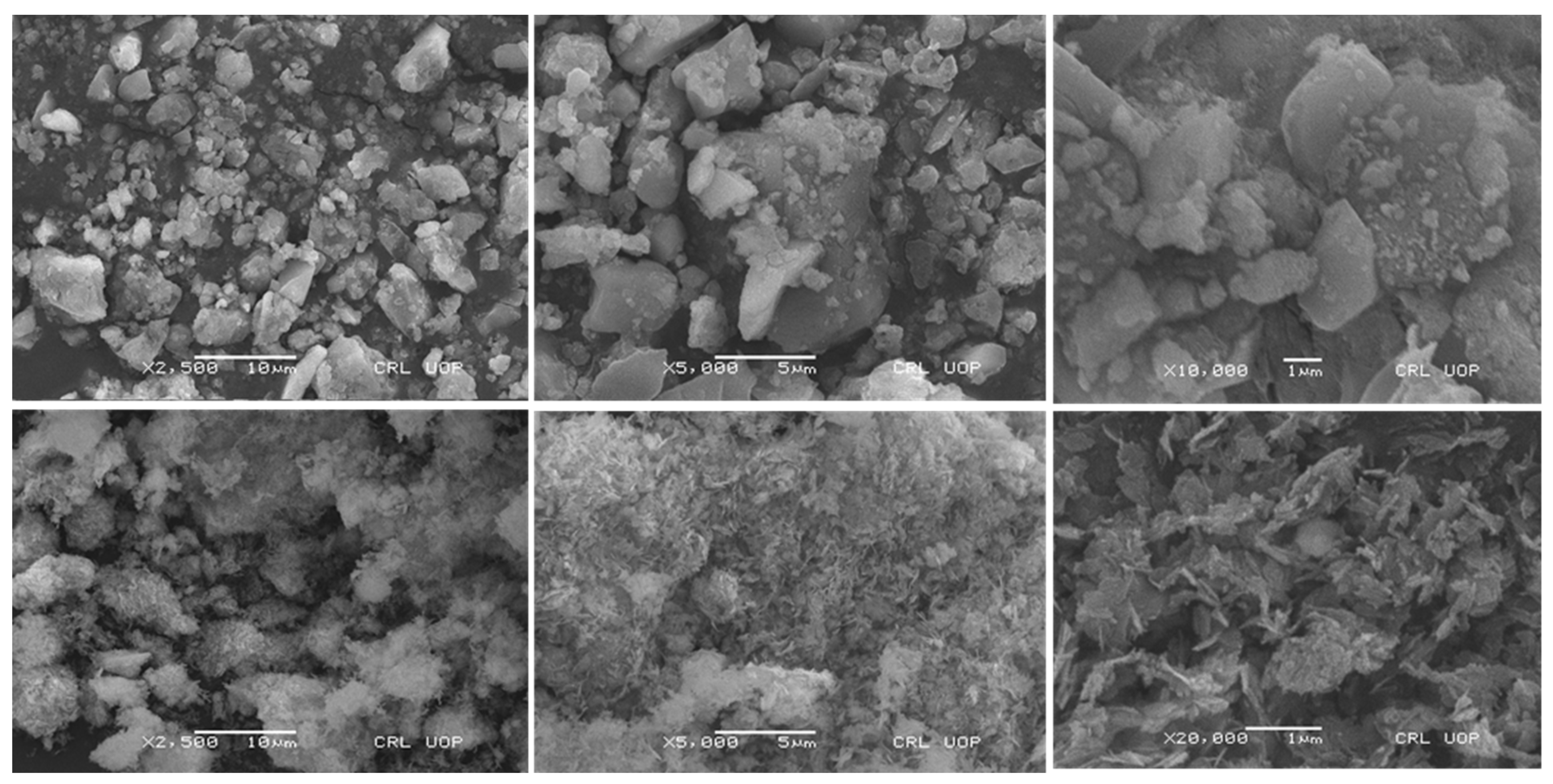
The synthesis of Fe
2O
3/Cellulose and CuO-NPs was achieved using the co-precipitation method, and the SEM analysis conclusively validates the successful synthesis of these nanomaterials, as showed in [
Figure 1]. SEM analysis reveal a densely packed surface with Cr(VI) ions attached to the adsorbent materials. This observation corresponds to the favorable electrostatic interactions and efficient metal adsorption in the acidic environment due to the presence of elevated hydronium ions (H+). Conversely, under extremely acidic conditions, SEM images show a weakened and less stable adsorbent surface due to surface oxidation processes. This phenomenon aligns with the decrease in metal adsorption observed in these conditions. This shift adversely affects the attachment of chromium oxyanions to the adsorbent surface. The SEM analysis also suggests that at higher pH levels, the presence of an increased concentration of hydroxyl groups (OH-) in the solution leads to repulsion between chromium oxyanions and OH- ions, reducing the availability of adsorption sites and competition for these sites.
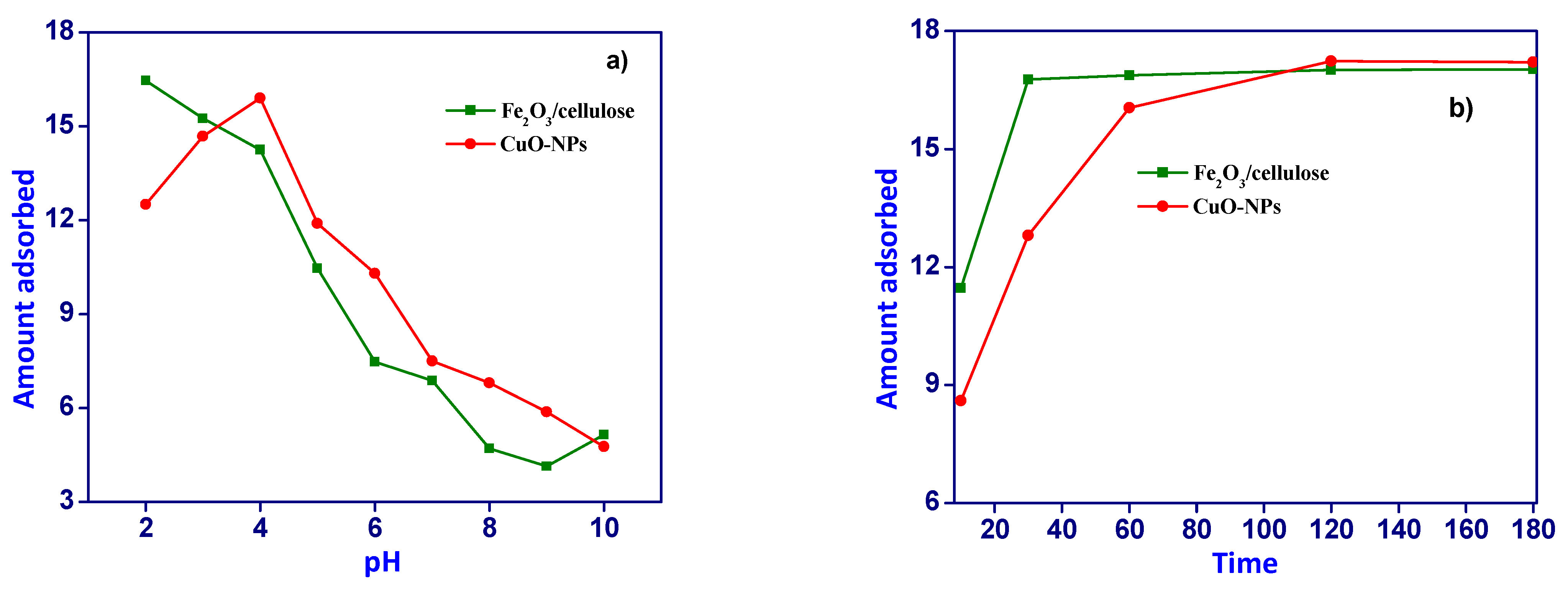
3.2. Effect of pH Adsorption and Contact Time
The adsorption behavior of Cr(VI) ions onto the surfaces of Fe
2O
3/cellulose and CuOx nanoparticles (NPs) was investigated across a pH range spanning from 2.0 to 10.0, utilizing a fixed concentration of 300 mg/L. The experimental outcomes are presented graphically in [
Figure 2a]. The adsorption of Cr(VI) ions on Fe
2O
3/cellulose and CuOx-NPs displays a significant dependency on pH. Maximum adsorption of Cr(VI) ions was observed at pH values of 2.0 and 4.0. This phenomenon can be attributed to the elevated concentrations of hydronium ions (H+) present on the adsorbent surface within an acidic environment, thereby intensifying the electrostatic interactions between the negatively charged chromium ions and the protonated sorbent.
This enhanced interaction enhances the efficiency of metal adsorption. However, it should be noted that the adsorbent surface experiences a weakening and loss of stability under extremely acidic conditions, primarily due to surface oxidation processes, which in turn diminishes the capacity for metal adsorption. These observations are consistent with the fact that CuOx nanoparticles possess a nearly neutral point of zero charge, around 6.9. Consequently, as the pH level rises from its optimal value (pH 3.5) towards the alkaline range, the degree of protonation of the CuOx nanoparticles surface gradually decreases. Beyond this point, the surface acquires a net negative charge, rendering it less favorable for the attachment of chromium oxyanions. Moreover, at higher pH levels, the concentration of hydroxyl groups (OH-) in the solution increases, leading to repulsion between chromium oxyanions and OH- ions, resulting in competition for the limited available adsorption sites. This competition reduces the removal efficiency of Cr(VI) ions from the solution [11-12].
To establish the optimal experimental conditions for the adsorption of Cr(VI) ions onto CuOx nanoparticles (CuOx-NPs) and Fe
2O
3/cellulose composites, we conducted contact time experiments. The findings demonstrated that equilibrium for Cr(VI) ion adsorption on CuOx-NPs was attained after 120 minutes, while equilibrium for adsorption on Fe
2O
3/cellulose was reached within 60 minutes, as illustrated in [
Figure 2b]. Initially, the rapid adsorption of Cr(VI) ions was facilitated by the abundance of unoccupied binding sites on the surfaces of CuOx-NPs and Fe
2O
3/cellulose composites, coupled with a substantial concentration gradient between the adsorbate and the solid phase of the synthesized materials. However, with prolonged contact time, the number of available active sites for adsorption diminished, and there was an increase in repulsive forces between the ions that had already adsorbed onto the adsorbent surface and those still in the solution. Consequently, the adsorption of Cr(VI) ions proceeded more slowly as the system approached equilibrium due to ion competition for the limited accessible binding sites [13-14].
Table 1.
Various adsorbent utilized for Cr(VI) adsorption.
Table 1.
Various adsorbent utilized for Cr(VI) adsorption.
| S. No |
Adsorbent type |
Qmax(mg/g) |
Percent, % |
Reference |
| 1 |
N77 cation exchange resins |
35.38mg/g |
95 |
[15] |
| 2 |
SKN1 cation exchange resins |
46.34 mg/g |
95 |
[15] |
| 3 |
carbon aerogel electrodes |
- |
94.69 |
[16] |
| 4 |
C1 activated carbon |
- |
98.86 |
[17] |
| 5 |
C2 activated carbon |
- |
98.6 |
[17] |
| 6 |
C3 activated carbon |
|
93 |
[17] |
| 7 |
Al electrodes |
- |
97.76 |
[18] |
| 8 |
Chemical Precipitation Method |
99.74 |
[18] |
| 9 |
Eucalyptus bark (EB) |
- |
99 |
[19] |
| 10 |
Cation exchange resins 1200H |
84.04 mg/g |
- |
[20] |
| 11 |
Cation exchange resins 1500H |
188.67 mg/g |
- |
[20] |
| 12 |
Cation exchange resins IRN97H |
58.14 mg/g |
- |
[20] |
| 13 |
Dried green alga U. Lactuca |
8.91 mg/g |
52.54 |
[21] |
| 14 |
Activated carbon |
93.92 mg/g |
99.52 |
[21] |
| 15 |
Activated carbon |
28.019 mg/g |
- |
[22] |
| 16 |
Electrochemical method |
- |
86.45 |
[23] |
| 17 |
Amidoxime adsorb |
31.68 mg/g |
- |
[24] |
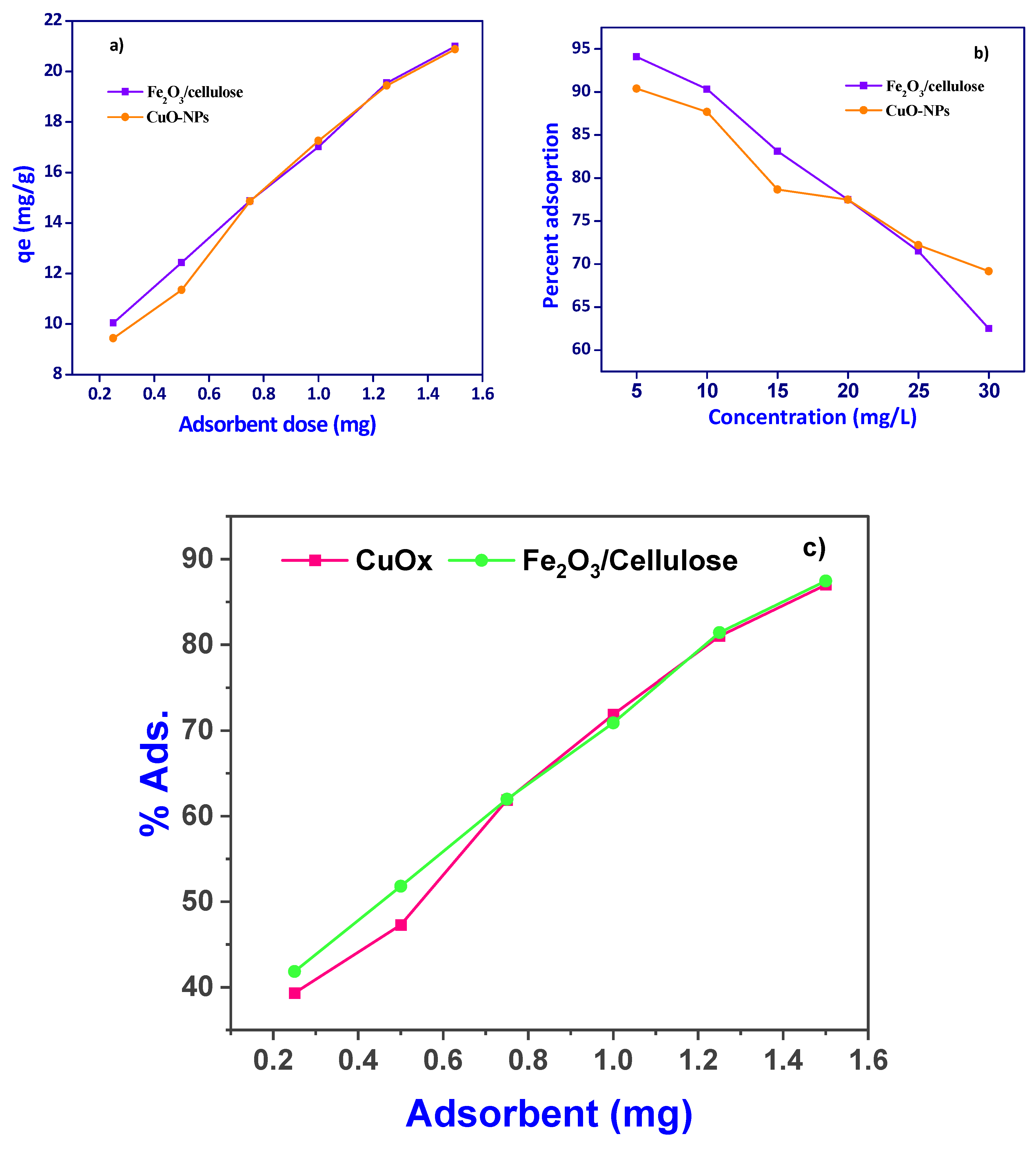
3.2. Effect of Adsorbent dosage and Adsorbate Concentration
We conducted an investigation into the effect of adsorbent dosage, with the results presented in [
Figure 3a,c]. Upon increasing the adsorbent dose, the removal of Cr(VI) ions exhibited a sharp rise, increasing from 50% to 74.08% for Fe
2O
3/cellulose and from 41% to 78% for CuOx-NPs when initial Cr(VI) ion concentrations were in the range of 1.25 mg/L. Further increases in adsorbent dose led to a gradual enhancement in removal efficiency, reaching 86.97% and 87.44% for Fe
2O
3/cellulose and CuOx-NPs, respectively [
Figure 3c]. Conversely, when examining the adsorption capacity of Fe
2O
3/cellulose and CuOx-NPs for an initial Cr(VI) ion concentration of 24 mg/L, it was observed that the adsorption capacity gradually decreased from 80 mg/g to 78 mg/g as the adsorbent dose increased. This phenomenon can be explained by the fact that the ratio of available binding sites to the amount of metal ions in the system affects the adsorbent's capacity for adsorption. At higher doses of Cr(VI) ions, the saturation of binding sites on the surface of CuOx-NPs and Fe
2O
3/cellulose composites was not achieved, resulting in a reduced adsorption capacity per unit mass of CuOx nanoparticles. Furthermore, the increased availability of surface area and open adsorption sites with higher adsorbent dosages contributed to the elevated removal of Cr(VI) ions. However, it should be noted that as equilibrium was approached, additional increases in adsorbent dosage resulted in only marginal improvements in Cr(VI) ion removal. Consequently, a dose of 1.25 g/L was selected for subsequent studies, as it balanced the desirable values of high removal efficiency and adsorption capacity per unit mass of Fe
2O
3/cellulose and CuOx-NPs adsorbent [25-26]. In comparison
Table 1., various adsorbent utilized for Cr(VI) adsorption, we examined the impact of varying Cr(VI) ion concentrations on the adsorption behavior of Fe
2O
3/cellulose and CuOx nanoparticles (CuOx-NPs), with the results showed in [
Figure 3b]. It was observed that the highest removal efficiencies, reaching 90.04% and 94.08%, were achieved at a relatively low initial metal ion concentration of 5 mg/L. As the initial concentration of Cr(VI) ions was progressively increased from 5 to 50 mg/L, the removal efficiency exhibited a consistent decline, dropping to 69.16% and 62.5%. This phenomenon can be attributed to the availability of a greater number of active surface areas and binding sites on Fe
2O
3/Cellulose and CuOx-NPs when exposed to lower Cr(VI) ion concentrations, resulting in optimal adsorption performance. Conversely, at higher initial concentrations of Cr(VI) ions, fewer sites were available for the acceptance of Cr(VI) ions on the synthesized materials, thereby leading to a decrease in the adsorption efficiency [
27].
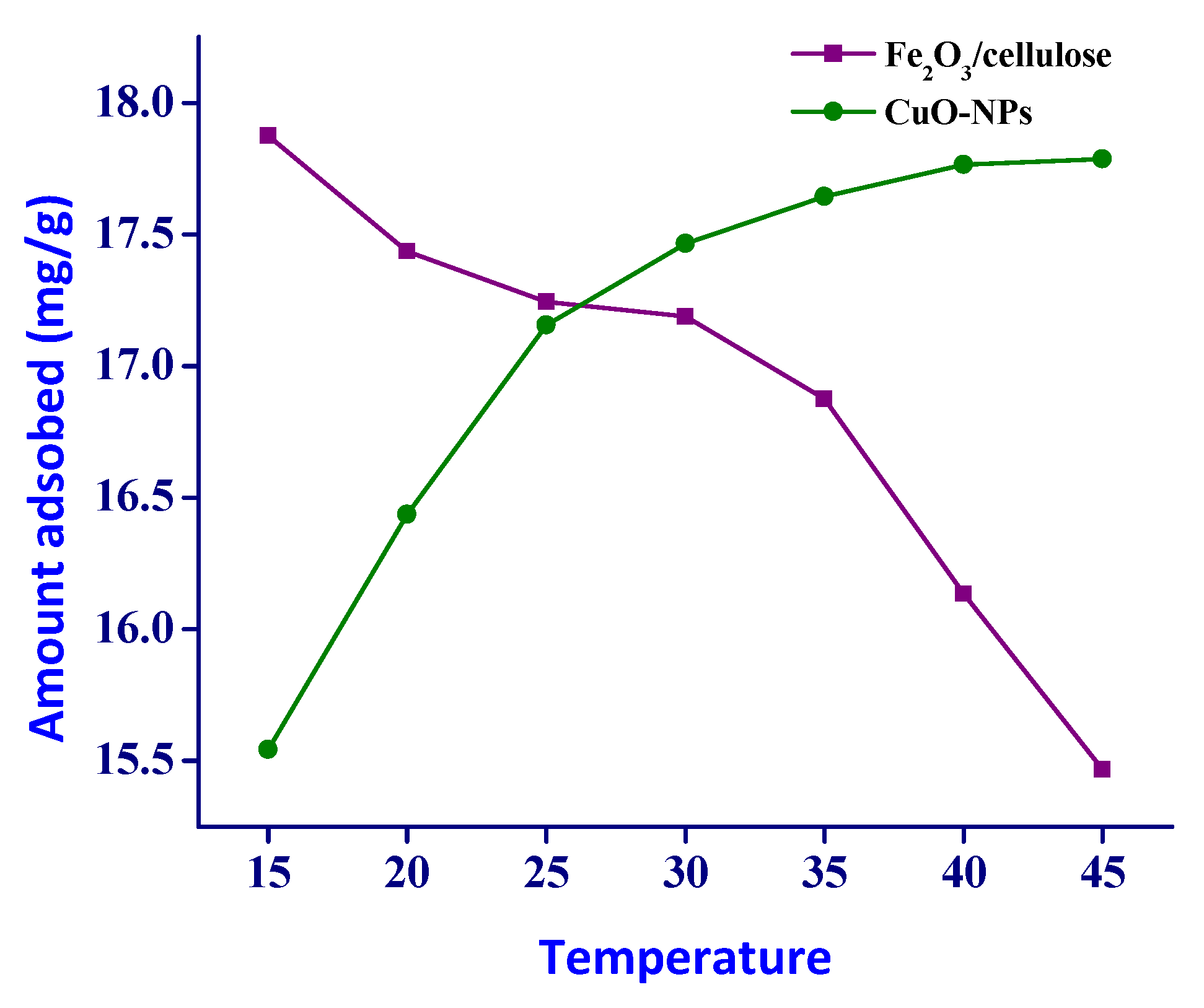
3.3. Influence of Temperature on Adsorption
A comprehensive investigation into the influence of temperature, spanning from 15°C to 45°C, on the adsorption behavior of Cr(VI) onto the surfaces of Fe
2O
3/Cellulose and CuOx nanoparticles (CuOx-NPs), and the resultant data are visually showed in [
Figure 4]. The findings unveiled a distinct temperature-dependent impact on the adsorption process. Specifically, an elevation in temperature within this specified range elicited divergent responses: a notable augmentation in the adsorption of Cr(VI) ions onto CuOx-NPs, in stark contrast to a conspicuous reduction in adsorption observed for Fe
2O
3/cellulose composites. This intriguing phenomenon can be ascribed to the noteworthy reduction in solution viscosity with increasing temperature, a well-recognized phenomenon in the realm of chemical kinetics. Elevated temperatures serve as a catalyst, enhancing the diffusion rate of adsorbate molecules. This accelerated diffusion occurs both within the exterior boundary layer and, crucially, within the intricate network of pores intrinsic to the adsorbent particles. Consequently, the heightened thermal energy facilitates more efficient interaction between the Cr(VI) ions and the CuOx-NPs, leading to an augmented adsorption capacity. In stark contrast, the adsorption performance of Cr(VI) onto Fe
2O
3/cellulose composites exhibits a counterintuitive decline with rising temperature. This paradoxical behavior can be attributed to complex interplays between temperature-induced changes in the physicochemical properties of the adsorbent and the nature of adsorbate interactions. These interactions influence the availability of active adsorption sites and, consequently, the overall adsorption efficiency [28-29].
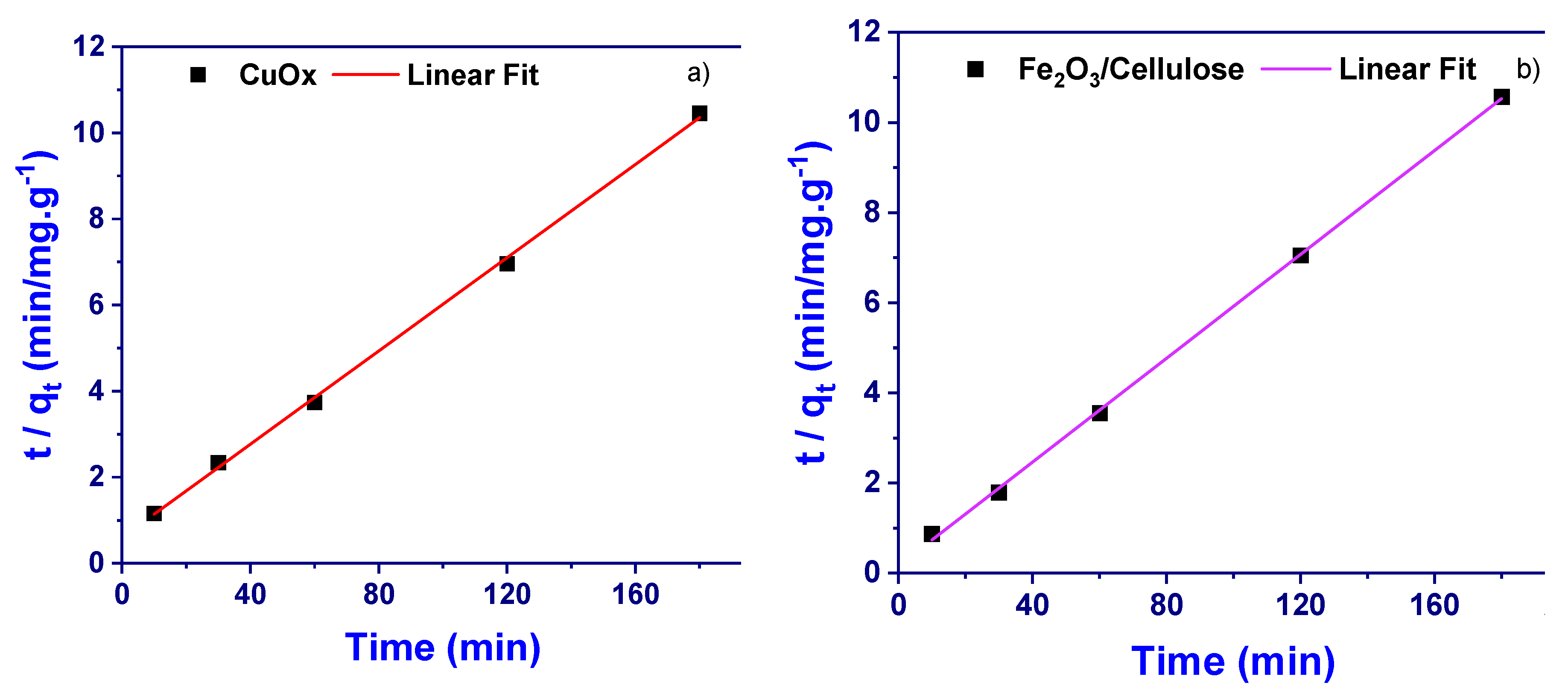
3.4. Kinetic Study
Theoretical studies were conducted to study the nature of adsorption and establish potential adsorption mechanisms. To achieve this, well-known adsorption equations and models were utilized to analyze the acquired data. In the kinetic studies, common kinetic models/equations were applied to analyze the adsorption kinetics of the newly developed adsorbent.
3.4.1. Pseudo Second Order Kinetic Model
The model/equation is expressed as:
The linear form of this model/equation is given as:
Where qe is the amount of sample adsorbed (mg/g) at equilibrium, qt is the amount of sample adsorbed (mg/g) at any given time (t) (min) and K
2 is the pseudo-second-order reaction rate constant for adsorption (g/mg.min). The constant K
2 = to calculate the initial adsorption rate (h) (mg/g.min), at t → 0 as follows;
Where K
2 is the pseudo-second-order reaction rate constant for adsorption (g/mg.min) and qe is the amount of sample adsorbed (mg/g) at equilibrium. From the equilibrium time adsorption data, the time (t) (min) plotted with t/qt [
Figure 5a,b] with correlation co-efficient (R
2) of 0.9958 (slope = 1/qe 0.05418, CuOx), plus R
2 = 0.9958 (1/q
e= 0.05762, for Fe
2O
3/cellulose) and the pseudo-second-order-kinetic equation/model were constructed.
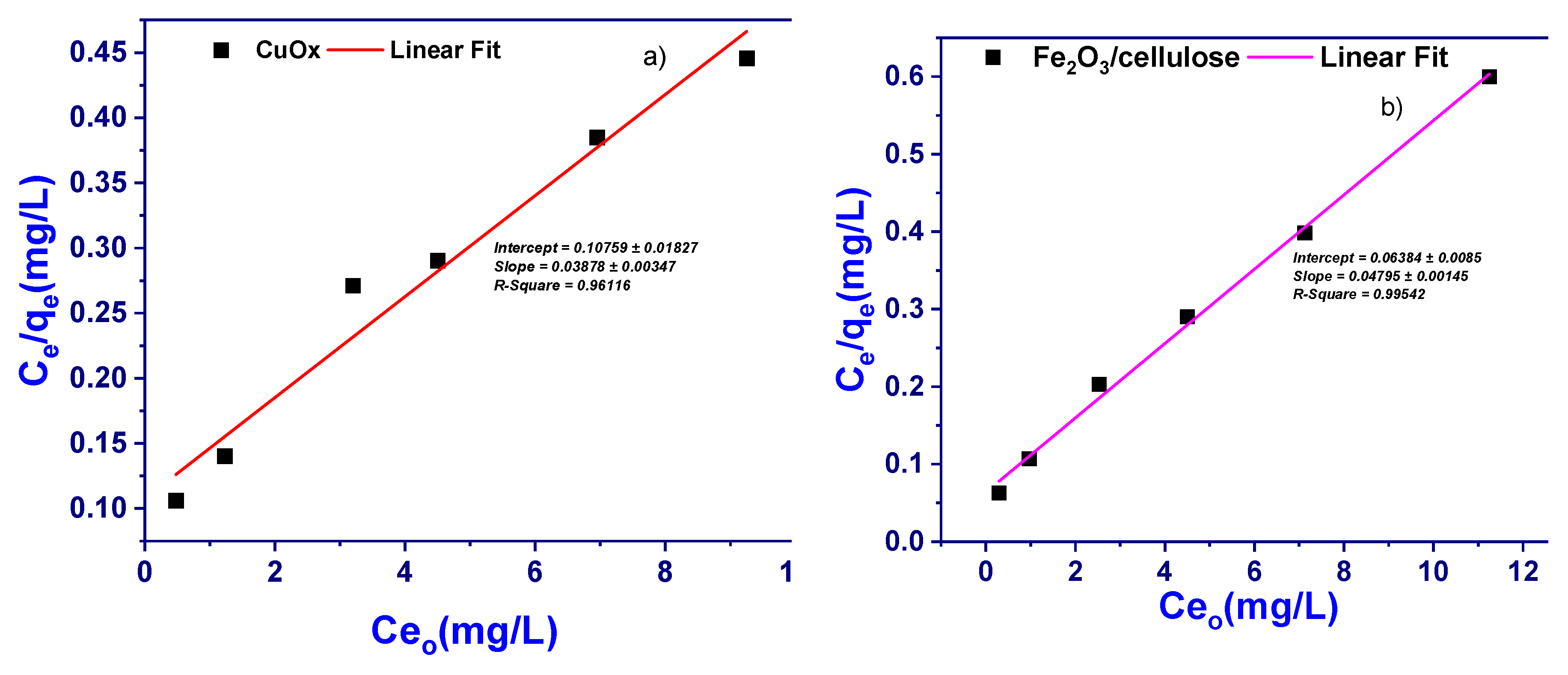
3.4.2. Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm Model
It is important to establish the most appropriate correlation for the equilibrium curves. An adsorption isotherm/model describes the relationship between the amount of adsorbate that is adsorbed on the adsorbent and the concentration of dissolved adsorbate in the liquid at equilibrium. Isotherm models such as have been used to describe the equilibrium nature of adsorption., the Langmuir adsorption isotherm/model is the most frequently used model for the adsorption of an adsorbate from a liquid solution onto the adsorbent. This model is obtained under the ideal assumption of adsorption surface. It is assumed that adsorbate occupied a site, and no further adsorption occurred a saturated value is reached and no further adsorption can take place. The Langmuir adsorption isotherm/model is used and is expressed by the following equation;
In a linear form of this equation is given as;
Where C
e is the equilibrium concentration of sample (BPB) in the solution (mg/L), q
e is the amount of sample adsorbed (mg/g), K
L and a
L are the Langmuir adsorption isotherm/model constants and are related to the maximum adsorption capacity (L/g) and bonding strength (L/mg), respectively. The theoretical monolayer adsorption capacity (Q
o, mg/g) is numerically equal to K
L/a
L.
The C
e (mg/L) was then plotted with C
e/q
e [
Figure 6a,b] with correlation co-efficient (R
2) of 0.9907 and the Langmuir adsorption isotherm/model were constructed. In the present study, it is highlighted that the adsorbent is favorable for the adsorption onto the newly developed adsorbent under the studied conditions.
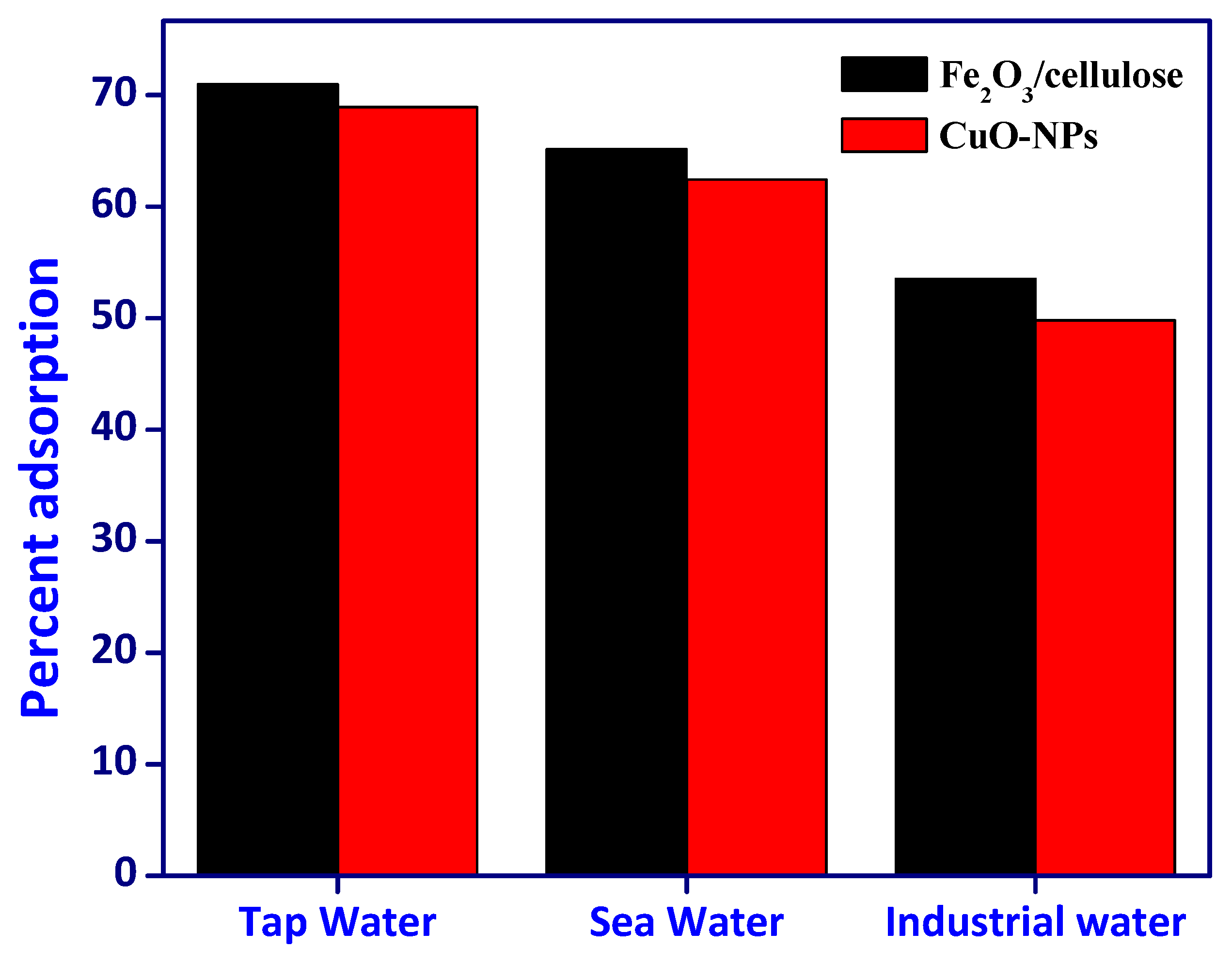
3.5. Effectiveness of Samples
In the pursuit of evaluating the effectiveness of removing Cr(VI) from authentic and synthetic wastewater samples, we employed Fe
2O
3/cellulose and CuOx nanoparticles (CuOx-NPs) under carefully optimized adsorption parameters, as illustrated in [
Figure 7]. This comprehensive assessment encompassed the utilization of three distinct true water samples (comprising tap water, well water, and river water), an industrial effluent sample, and a synthetic wastewater sample. To commence the evaluation process, each of these samples underwent individual spiking with a Cr(VI) concentration of 25 mg/L. Following the completion of the adsorption procedure, we meticulously quantified the amount of adsorbed Cr. The results unveiled a noteworthy accomplishment in the removal of Cr(VI) ions, with removal percentages ranging from 53.52% to 70.97% for authentic water samples and 49.78% to 68.93% for wastewater samples, all facilitated by the utilization of the synthesized composites. These outcomes affirm the practical applicability of the synthesized materials in the purification of authentic water samples, wastewater, and industrial effluents. Remarkably, it is worth noting that Fe
2O
3/cellulose outperformed CuOx-NPs significantly in these diverse applications, underscoring its superior performance [29-30].
4. Conclusions
In this study, cellulose-based ferric oxide (Fe2O3/cellulose) and copper oxide nanoparticles (CuOx-NPs) were successfully synthesized using the co-precipitation approach. These newly synthesized nanoparticles were extensively characterized the synthesized materials demonstrated promise for the removal of hazardous hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) ions from aqueous solutions. The investigation into the effect of pH on Cr(VI) adsorption revealed that the optimal pH for maximum adsorption was 2.0 and 4.0. The impact of adsorbent dosage indicated that an increase in dosage led to enhanced Cr(VI) ion removal, with saturation observed at higher doses. Furthermore, the influence of adsorbate concentration on adsorption performance demonstrated that lower initial Cr(VI) ion concentrations resulted in higher removal efficiencies. Thermal influence on adsorption investigated, with CuOx-NPs exhibiting increased adsorption at higher temperatures, attributed to enhanced diffusion rates. Conversely, Fe2O3/cellulose composites showed decreased adsorption at elevated temperatures, likely due to altered surface properties. The practical applicability of Fe2O3/cellulose and CuOx-NPs were confirmed through successful Cr(VI) ion removal from real water samples, including tap water, well water, river water, and industrial effluent. These findings highlight the potential of these nanomaterials for efficient and sustainable heavy metal ion removal from aqueous environments, addressing environmental contamination concerns.
Funding
Project funding organized by authors, not sponsored by any funder agency or institution.
Acknowledgments
The authors thanked Amir Hassan of the Faculty of Natural Sciences, Novosibirsk State University, 630090, Novosibirsk, Russia, for writing editing and handling of the manuscript, and Ali Khan for project implementation and literature. Sana Ullah Khan credit for experimental section. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gautam, R.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Mahiya, S.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. Contamination of heavy metals in aquatic media: transport, toxicity and technologies for remediation, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, A.; Mishra, V.K. Hexavalent Cr, Its Toxicity and Removal Strategy: Revealing PGPB Potential in Its Remediation. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T. Ding, Y., Xu, F., Zhang, C., Zhou, M., Tang, Y., ... & Wang, S. Effects of Acute and Chronic Heavy Metal Chromium Stress on Heat Shock Protein Gene and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities of Orthetrum Albistylum Larvae. Available at SSRN 4508988.
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Adam, M.R.; Liang, X.; Goh, H.; Anouzla, A.; Sillanpää, M.; Mohyuddin, A.; Chew, K.W. Chromium Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Natural Clinoptilolite. Water 2023, 15, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.-J.; Liu, Y.; Weerasooriya, R.; Chen, X. Electrochemical Determination of Chromium(VI) with Au/UiO-66 Modified Glassy Carbon and Screen-Printed Electrodes by Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV). Anal. Lett. 2023, 57, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Ban, S.; Devkota, S.; Sharma, S.; Joshi, R.; Tiwari, A.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Joshi, M.K. Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaabani, A.; Nosrati, H.; Seyyedhamzeh, M. Cellulose@Fe2O3 nanoparticle composites: magnetically recyclable nanocatalyst for the synthesis of 3-aminoimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2013, 41, 3719–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, I. Z. & Bangladesh Atomic Energy Commission. (2015). Preparation and characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized via chemical precipitation method. Open Access Library Journal, 2(03), 1.
- Nogueira, A.E.; Giroto, A.S.; Neto, A.B.; Ribeiro, C. CuO synthesized by solvothermal method as a high capacity adsorbent for hexavalent chromium. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 498, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, A.U.; Saeed, M.; Usman, M.; Yameen, M.; Muneer, M.; Tubbsum, S. A comparative sorption study of Cr3+ and Cr6+ using mango peels: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, X.H.; Nguyen, L.H.; Van, H.T.; Nguyen, D.V.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Ha, L.T. Adsorption of Chromium(VI) onto Freshwater Snail Shell-Derived Biosorbent from Aqueous Solutions: Equilibrium, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamjidi, S.; Esmaeili, H. Chemically Modified CaO/Fe3O4 Nanocomposite by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate for Cr(III) Removal from Water. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, R.; He, D.; Saleem, A. Facile preparation of polyethyleneimine modified activated sludge-based adsorbent for hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengaraj, S.; Yeon, K.-H.; Moon, S.-H. Removal of chromium from water and wastewater by ion exchange resins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 87, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, P.; Mohan, N.; Rajagopal, C. Electrochemical removal of chromium from wastewater by using carbon aerogel electrodes. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2811–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, N.; Barsoum, B.; Eid, A.; Khalil, M. Removal of chromium(III) from tannery wastewater using activated carbon from sugar industrial waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mella, B.; Glanert, A.C.; Gutterres, M. Removal of chromium from tanning wastewater and its reuse. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 95, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, V.; Pant, K. Removal of chromium from industrial waste by using eucalyptus bark. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengaraj, S.; Joo, C.K.; Kim, Y.; Yi, J. Kinetics of removal of chromium from water and electronic process wastewater by ion exchange resins: 1200H, 1500H and IRN97H. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 102, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sikaily, A.; El Nemr, A.; Khaled, A.; Abdelwehab, O. Removal of toxic chromium from wastewater using green alga Ulva lactuca and its activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, J.; Sahu, J.; Sahoo, B.; Mohanty, C.; Meikap, B. Removal of chromium(VI) from wastewater by activated carbon developed from Tamarind wood activated with zinc chloride. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Leng, Y.; Guo, J. Electrochemical Removal of Chromium (VI) from Wastewater. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N.; Chen, J.; Seko, N. Nitrogen-Containing Fabric Adsorbents Prepared by Radiation Grafting for Removal of Chromium from Wastewater. Polymers 2018, 10, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kera, N.H.; Bhaumik, M.; Pillay, K.; Ray, S.S.; Maity, A. Selective removal of toxic Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by adsorption combined with reduction at a magnetic nanocomposite surface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 503, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Y. Chen, H. Xu, S. Wang, L. Kang, Removal of Cr(VI) from water using polypyrrole/attapulgite core-shell nanocomposites: equilibrium, thermodynamics and kinetics, RSC Advances, 4,17805-17811(2014).
- Atieh, M.A.; Bakather, O.Y.; Tawabini, B.S.; Bukhari, A.A.; Khaled, M.; AlHarthi, M.; Fettouhi, M.; Abuilaiwi, F.A. Removal of Chromium (III) from Water by Using Modified and Nonmodified Carbon Nanotubes. J. Nanomater. 2010, 2010, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, F.; Esmaeili, H. Chemically modified bentonite/Fe3O4 nanocomposite for Pb(II), Cd(II), and Ni(II) removal from synthetic wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 110, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egodawatte, S.; Datt, A.; Burns, E.A.; Larsen, S.C. Chemical Insight into the Adsorption of Chromium(III) on Iron Oxide/Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposites. Langmuir 2015, 31, 7553–7562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingamdinne, L.P.; Kim, I.-S.; Ha, J.-H.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Koduru, J.R.; Yang, J.-K. Enhanced Adsorption Removal of Pb(II) and Cr(III) by Using Nickel Ferrite-Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite. Metals 2017, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).