Submitted:
25 April 2024
Posted:
26 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
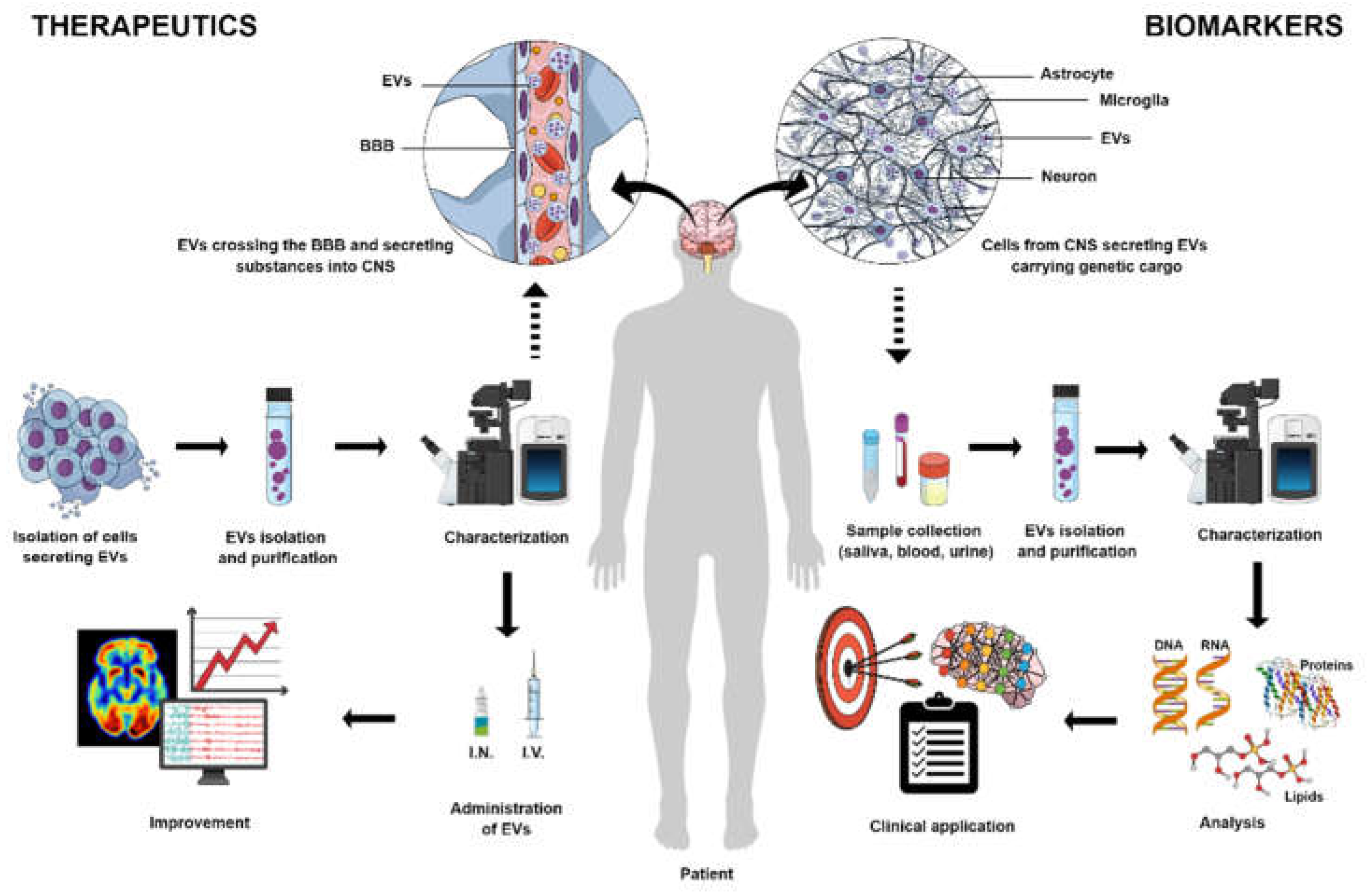
1. Background
2. Potential and Applications of EVs-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
3. Central Nervous System as a Target and Niche for EVs
4. EVs as Biomarkers for CNS Diseases
5. Alzheimer’s Disease
6. Parkinson’s Disease
7. Huntington’s Disease
8. Multiple Sclerosis
9. Epilepsy
10. Traumatic Brain Injury
11. EVs as Treatment for CNS diseases
12. Alzheimer Disease (AD)
13. Parkinson Disease (PD)
14. Huntington Disease (HD)
15. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
16. Epilepsy
17. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
18. EVs and CRISPR-Based Gene Editing Systems
19. Conclusion and future perspectives
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abels, E.R.; Breakefield, X.O. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA Cargo Selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumperman, J.; Raposo, G. The complex ultrastructure of the endolysosomal system. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014, 6, a016857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Thery, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akers, J.C.; Gonda, D.; Kim, R.; Carter, B.S.; Chen, C.C. Biogenesis of extracellular vesicles (EV): exosomes, microvesicles, retrovirus-like vesicles, and apoptotic bodies. J Neurooncol. 2013, 113, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoorvogel, W.; Strous, G.J.; Geuze, H.J.; Oorschot, V.; Schwartz, A.L. Late endosomes derive from early endosomes by maturation. Cell 1991, 65, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pols, M.S.; Klumperman, J. Trafficking and function of the tetraspanin CD63. Exp Cell Res. 2009, 315, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Moita, C.; van Niel, G.; Kowal, J.; Vigneron, J.; Benaroch, P.; et al. Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J Cell Sci. 2013, 126 Pt 24, 5553–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baietti, M.F.; Zhang, Z.; Mortier, E.; Melchior, A.; Degeest, G.; Geeraerts, A.; et al. Syndecan-syntenin-ALIX regulates the biogenesis of exosomes. Nat Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Zhan, W.; Gao, Y.; Huang, L.; Gong, R.; Wang, W.; et al. RAB31 marks and controls an ESCRT-independent exosome pathway. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, J.S. The potential theragnostic (diagnostic+therapeutic) application of exosomes in diverse biomedical fields. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018, 22, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Tang, Y.; Yang, L.; Peng, X.; Li, B.; Fan, Q.; et al. Rab GTPases: Central Coordinators of Membrane Trafficking in Cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021, 9, 648384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.; Morohashi, Y.; Yoshimura, S.; Manrique-Hoyos, N.; Jung, S.; Lauterbach, M.A.; et al. Regulation of exosome secretion by Rab35 and its GTPase-activating proteins TBC1D10A-C. J Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, R.W.; Zimmerberg, J. Dynamic Relationship of the SNARE Complex with a Membrane. Biophys J. 2019, 117, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, F.J.; Bebelman, M.P.; Jimenez, C.R.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Janssen, H.; Neefjes, J.; et al. Quantifying exosome secretion from single cells reveals a modulatory role for GPCR signaling. J Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, M.R.; Lacy, P.; Odemuyiwa, S.O.; Steward, M.; Davoine, F.; Kita, H.; et al. A critical role for vesicle-associated membrane protein-7 in exocytosis from human eosinophils and neutrophils. Allergy. 2006, 61, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, N.; Roche, P.A. Mast cells possess distinct secretory granule subsets whose exocytosis is regulated by different SNARE isoforms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008, 105, 2580–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Xue, X.; Li, L.; Xu, D.; Li, S.; Li, S.C.; et al. Ectosome biogenesis and release processes observed by using live-cell dynamic imaging in mammalian glial cells. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2021, 11, 4604–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricarico, C.; Clancy, J.; D'Souza-Schorey, C. Biology and biogenesis of shed microvesicles. Small GTPases. 2017, 8, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Souza-Schorey, C.; Clancy, J.W. Tumor-derived microvesicles: shedding light on novel microenvironment modulators and prospective cancer biomarkers. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucki, R.; Bachelot-Loza, C.; Zachowski, A.; Giraud, F.; Sulpice, J.C. Calcium induces phospholipid redistribution and microvesicle release in human erythrocyte membranes by independent pathways. Biochemistry. 1998, 37, 15383–15391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Fu, Z.; Zou, L. Mechanism and Potential of Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Infectious Diseases. Front Microbiol. 2021, 12, 761338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowen, A.; Shahjin, F.; Chand, S.; Odegaard, K.E.; Yelamanchili, S.V. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Challenges in Clinical Applications. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Wang, S.; Zhao, R.C. Exosomes from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: a new therapeutic paradigm. Biomark Res. 2019, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Guerrero, J.A.; Ripa, I.; Andreu, S.; Bello-Morales, R. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Demyelination of the Central Nervous System. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, M.D.; MacLean, A.G. Extracellular Vesicles as a Means of Viral Immune Evasion, CNS Invasion, and Glia-Induced Neurodegeneration. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 695899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Woodson, M.; Sherman, M.B.; Neelakanta, G.; Sultana, H. Exosomes mediate Zika virus transmission through SMPD3 neutral Sphingomyelinase in cortical neurons. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulliam, L.; Sun, B.; Mustapic, M.; Chawla, S.; Kapogiannis, D. Plasma neuronal exosomes serve as biomarkers of cognitive impairment in HIV infection and Alzheimer's disease. J Neurovirol. 2019, 25, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koniusz, S.; Andrzejewska, A.; Muraca, M.; Srivastava, A.K.; Janowski, M.; Lukomska, B. Extracellular Vesicles in Physiology, Pathology, and Therapy of the Immune and Central Nervous System, with Focus on Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Therapeutic Tools. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiera, G.; Di Liegro, C.M.; Di Liegro, I. Extracellular Membrane Vesicles as Vehicles for Brain Cell-to-Cell Interactions in Physiological as well as Pathological Conditions. Biomed Res Int. 2015, 2015, 152926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassama, Y.; Favereaux, A. Emerging Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in the Central Nervous System: Physiology, Pathology, and Therapeutic Perspectives. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 626043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andras, I.E.; Toborek, M. Extracellular vesicles of the blood-brain barrier. Tissue Barriers. 2016, 4, e1131804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhbeis, C.; Frohlich, D.; Kramer-Albers, E.M. Emerging roles of exosomes in neuron-glia communication. Front Physiol. 2012, 3, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpech, J.C.; Herron, S.; Botros, M.B.; Ikezu, T. Neuroimmune Crosstalk through Extracellular Vesicles in Health and Disease. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurachi, M.; Mikuni, M.; Ishizaki, Y. Extracellular Vesicles from Vascular Endothelial Cells Promote Survival, Proliferation and Motility of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells. Plos One. 2016, 11, e0159158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.F.; Li, J.; Zi, H.X.; Bu, J.W.; et al. Neurons secrete miR-132-containing exosomes to regulate brain vascular integrity. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiera, G.; Proia, P.; Alberti, C.; Mineo, M.; Savettieri, G.; Di Liegro, I. Neurons produce FGF2 and VEGF and secrete them at least in part by shedding extracellular vesicles. J Cell Mol Med. 2007, 11, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chivet, M.; Javalet, C.; Laulagnier, K.; Blot, B.; Hemming, F.J.; Sadoul, R. Exosomes secreted by cortical neurons upon glutamatergic synapse activation specifically interact with neurons. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014, 3, 24722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachenal, G.; Pernet-Gallay, K.; Chivet, M.; Hemming, F.J.; Belly, A.; Bodon, G.; et al. Release of exosomes from differentiated neurons and its regulation by synaptic glutamatergic activity. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011, 46, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, Y.; Yelick, J.; Jin, S.; Tian, Y.; Chiang, M.S.R.; Higashimori, H.; et al. Exosome reporter mice reveal the involvement of exosomes in mediating neuron to astroglia communication in the CNS. Nat Commun. 2019, 10, 4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Korner, R.; Gaitanos, L.; Klein, R. Exosomes mediate cell contact-independent ephrin-Eph signaling during axon guidance. J Cell Biol. 2016, 214, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldie, B.J.; Dun, M.D.; Lin, M.; Smith, N.D.; Verrills, N.M.; Dayas, C.V.; et al. Activity-associated miRNA are packaged in Map1b-enriched exosomes released from depolarized neurons. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 9195–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruhbeis, C.; Frohlich, D.; Kuo, W.P.; Amphornrat, J.; Thilemann, S.; Saab, A.S.; et al. Neurotransmitter-triggered transfer of exosomes mediates oligodendrocyte-neuron communication. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, J.; Lachenal, G.; Court, M.; Hirrlinger, J.; Chatellard-Causse, C.; Blot, B.; et al. Exosomes are released by cultured cortical neurones. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2006, 31, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, F.; Turola, E.; Riganti, L.; Caleo, M.; Gabrielli, M.; Perrotta, C.; et al. Microvesicles released from microglia stimulate synaptic activity via enhanced sphingolipid metabolism. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyo, U.B.; Wu, L.J. Bidirectional microglia-neuron communication in the healthy brain. Neural Plast. 2013, 2013, 456857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, L.; Regan, M.; Higashimori, H.; Ng, S.K.; Esau, C.; Vidensky, S.; et al. Neuronal exosomal miRNA-dependent translational regulation of astroglial glutamate transporter GLT1. J Biol Chem. 2013, 288, 7105–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrini, I.; Song, J.H.; Diez, D.; Hanayama, R. Neuronal exosomes facilitate synaptic pruning by up-regulating complement factors in microglia. Sci Rep. 2015, 5, 7989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, Q.; Raffo-Romero, A.; Arab, T.; Van Camp, C.; Drago, F.; Forte, S.; et al. Isolation of microglia-derived extracellular vesicles: towards miRNA signatures and neuroprotection. J Nanobiotechnology. 2019, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Broek, B.; Pintelon, I.; Hamad, I.; Kessels, S.; Haidar, M.; Hellings, N.; et al. Microglial derived extracellular vesicles activate autophagy and mediate multi-target signaling to maintain cellular homeostasis. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020, 10, e12022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolicelli, R.C.; Bergamini, G.; Rajendran, L. Cell-to-cell Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Focus on Microglia. Neuroscience. 2019, 405, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgoci, A.N.; Duhamel, M.; Raffo-Romero, A.; Mallah, K.; Aboulouard, S.; Lefebvre, C.; et al. Location of neonatal microglia drives small extracellular vesicles content and biological functions in vitro. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020, 9, 1727637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prada, I.; Gabrielli, M.; Turola, E.; Iorio, A.; D'Arrigo, G.; Parolisi, R.; et al. Glia-to-neuron transfer of miRNAs via extracellular vesicles: a new mechanism underlying inflammation-induced synaptic alterations. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuyama, K.; Sun, H.; Usuki, S.; Sakai, S.; Hanamatsu, H.; Mioka, T.; et al. A potential function for neuronal exosomes: sequestering intracerebral amyloid-beta peptide. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, C.M.; Nicaise, A.M.; Bongarzone, E.R.; Givogri, M.; Reiter, C.R.; Heintz, O.; et al. Astrocyte Support for Oligodendrocyte Differentiation can be Conveyed via Extracellular Vesicles but Diminishes with Age. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luarte, A.; Henzi, R.; Fernandez, A.; Gaete, D.; Cisternas, P.; Pizarro, M.; et al. Astrocyte-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Regulate Dendritic Complexity through miR-26a-5p Activity. Cells. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturini, A.; Passalacqua, M.; Pelassa, S.; Pastorino, F.; Tedesco, M.; Cortese, K.; et al. Exosomes From Astrocyte Processes: Signaling to Neurons. Front Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proia, P.; Schiera, G.; Mineo, M.; Ingrassia, A.M.; Santoro, G.; Savettieri, G.; et al. Astrocytes shed extracellular vesicles that contain fibroblast growth factor-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor. Int J Mol Med. 2008, 21, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stronati, E.; Conti, R.; Cacci, E.; Cardarelli, S.; Biagioni, S.; Poiana, G. Extracellular Vesicle-Induced Differentiation of Neural Stem Progenitor Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaele, S.; Lombardi, M.; Verderio, C.; Fumagalli, M. TNF Production and Release from Microglia via Extracellular Vesicles: Impact on Brain Functions. Cells. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, F.; Perrotta, C.; Novellino, L.; Francolini, M.; Riganti, L.; Menna, E.; et al. Acid sphingomyelinase activity triggers microparticle release from glial cells. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Borgmann, K.; Edara, V.V.; Stacy, S.; Ghorpade, A.; Ikezu, T. Activated human astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles modulate neuronal uptake, differentiation and firing. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020, 9, 1706801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Sheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Ding, L.; Xu, X.; Xia, X.; et al. Astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles: A double-edged sword in central nervous system disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021, 125, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Cao, X.; Gong, A.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from astrocytes facilitated neurite elongation by activating the Hippo pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2022, 411, 112937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.; Knosche, T.R. Action potential propagation and synchronisation in myelinated axons. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019, 15, e1007004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruhbeis, C.; Kuo-Elsner, W.P.; Muller, C.; Barth, K.; Peris, L.; Tenzer, S.; et al. Oligodendrocytes support axonal transport and maintenance via exosome secretion. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer-Albers, E.M. Extracellular vesicles in the oligodendrocyte microenvironment. Neurosci Lett. 2020, 725, 134915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer-Albers, E.M.; Bretz, N.; Tenzer, S.; Winterstein, C.; Mobius, W.; Berger, H.; et al. Oligodendrocytes secrete exosomes containing major myelin and stress-protective proteins: Trophic support for axons? Proteomics Clin Appl. 2007, 1, 1446–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarraga-Valderrama, L.R.; Sheridan, G.K. Extracellular vesicles and intercellular communication in the central nervous system. FEBS Lett. 2021, 595, 1391–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, S.L.N.; Breakefield, X.O.; Weaver, A.M. Extracellular Vesicles: Unique Intercellular Delivery Vehicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanez-Mo, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borras, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saint-Pol, J.; Gosselet, F.; Duban-Deweer, S.; Pottiez, G.; Karamanos, Y. Targeting and Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier with Extracellular Vesicles. Cells. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustapic, M.; Eitan, E.; Werner, J.K., Jr; Berkowitz, S.T.; Lazaropoulos, M.P.; Tran, J.; et al. Plasma Extracellular Vesicles Enriched for Neuronal Origin: A Potential Window into Brain Pathologic Processes. Front Neurosci. 2017, 11, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.D.; Gercel-Taylor, C. The origin, function, and diagnostic potential of RNA within extracellular vesicles present in human biological fluids. Front Genet. 2013, 4, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, H.; Zheng, J.C. Exosomal miRNAs in central nervous system diseases: biomarkers, pathological mediators, protective factors and therapeutic agents. Prog Neurobiol. 2019, 183, 101694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.F.; Wu, N.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Circulating microRNAs: a novel class of potential biomarkers for diagnosing and prognosing central nervous system diseases. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2013, 33, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, O. Biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Med. 2021, 27, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Shin, K.Y.; Chang, K.A. Brain-Derived Exosomal Proteins as Effective Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomolecules 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Lin, H.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Dai, Y.; Jia, W.; et al. Neurogranin as a cognitive biomarker in cerebrospinal fluid and blood exosomes for Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Transl Psychiatry. 2020, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Zhu, M.; Kong, C.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, Q.; et al. Blood neuro-exosomal synaptic proteins predict Alzheimer's disease at the asymptomatic stage. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Yang, G.; Yan, Q.Q.; Zhao, J.; Li, S. Exosome-encapsulated microRNAs as promising biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. Rev Neurosci. 2019, 31, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, G.H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.C.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.R.; Guo, H.D. Effects of exosomal miRNAs in the diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Mech Ageing Dev. 2021, 200, 111593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Giau, V.; An, S.S. Emergence of exosomal miRNAs as a diagnostic biomarker for Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Sci. 2016, 360, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, J.; Li, S. Potential Roles of Exosomal MicroRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Application in Alzheimer's Disease. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 7027380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durur, D.Y.; Tastan, B.; Ugur Tufekci, K.; Olcum, M.; Uzuner, H.; Karakulah, G.; et al. Alteration of miRNAs in Small Neuron-Derived Extracellular Vesicles of Alzheimer's Disease Patients and the Effect of Extracellular Vesicles on Microglial Immune Responses. J Mol Neurosci. 2022, 72, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.T.; Liu, C.G.; Gao, S.C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.C. The Serum Exosome Derived MicroRNA-135a, -193b, and -384 Were Potential Alzheimer's Disease Biomarkers. Biomed Environ Sci. 2018, 31, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Vogrinc, D.; Goricar, K.; Kunej, T.; Dolzan, V. Systematic Search for Novel Circulating Biomarkers Associated with Extracellular Vesicles in Alzheimer's Disease: Combining Literature Screening and Database Mining Approaches. J Pers Med. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpente, M.; Fenoglio, C.; D'Anca, M.; Arcaro, M.; Sorrentino, F.; Visconte, C.; et al. MiRNA Profiling in Plasma Neural-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Alzheimer's Disease. Cells. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Gu, H.; Guo, Q.; Liang, S.; Xue, J.; Yao, F.; et al. Profiling of Serum Exosome MiRNA Reveals the Potential of a MiRNA Panel as Diagnostic Biomarker for Alzheimer's Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 3084–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xie, X.Y.; Sui, X.F.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.B. Profile of Pathogenic Proteins and MicroRNAs in Plasma-derived Extracellular Vesicles in Alzheimer's Disease: A Pilot Study. Neuroscience. 2020, 432, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aharon, A.; Spector, P.; Ahmad, R.S.; Horrany, N.; Sabbach, A.; Brenner, B.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles of Alzheimer's Disease Patients as a Biomarker for Disease Progression. Mol Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 4156–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; et al. Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, G.; Loov, C.; Persson, E.; Lazaro, D.F.; Takeda, S.; Bergstrom, J.; et al. Secretion and Uptake of alpha-Synuclein Via Extracellular Vesicles in Cultured Cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Liu, C.; Cook, T.J.; Bullock, K.M.; Zhao, Y.; Ginghina, C.; et al. Plasma exosomal alpha-synuclein is likely CNS-derived and increased in Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuendl, A.; Kraus, T.; Chatterjee, M.; Zapke, B.; Sadowski, B.; Moebius, W.; et al. alpha-Synuclein in Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Is a Potential Biomarker of Parkinson's Disease. Mov Disord. 2021, 36, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Zhou, L.; Luo, N.; Yao, M.; et al. A longitudinal study on alpha-synuclein in plasma neuronal exosomes as a biomarker for Parkinson's disease development and progression. Eur J Neurol. 2020, 27, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Hopfner, F.; Katsikoudi, A.; Hein, R.; Catli, C.; Evetts, S.; et al. Serum neuronal exosomes predict and differentiate Parkinson's disease from atypical parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020, 91, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Tian, C.; Stewart, T.; Aro, P.; Soltys, D.; Bercow, M.; et al. Development of a Sensitive Diagnostic Assay for Parkinson Disease Quantifying alpha-Synuclein-Containing Extracellular Vesicles. Neurology. 2021, 96, e2332–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, X.; Tian, J.; Chen, Y.; Yan, Y.; Pu, J.; Zhang, B. Central Nervous System-Derived Exosomal Alpha-Synuclein in Serum May Be a Biomarker in Parkinson's Disease. Neuroscience. 2019, 413, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, G.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. alpha-Synuclein in salivary extracellular vesicles as a potential biomarker of Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett. 2019, 696, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Niu, W.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Niu, C. Differential expression and significance of miRNAs in plasma extracellular vesicles of patients with Parkinson's disease. Int J Neurosci. 2022, 132, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.Y.; Lu, J.M.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Li, M.C.; Lu, T.; An, X.S.; et al. MicroRNA biomarkers of Parkinson's disease in serum exosome-like microvesicles. Neurosci Lett. 2017, 644, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Huang, L.; Shao, C.; Nie, T.; Xia, L.; Cui, B.; et al. Several miRNAs derived from serum extracellular vesicles are potential biomarkers for early diagnosis and progression of Parkinson's disease. Transl Neurodegener. 2021, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, I.; Radeghieri, A.; Paolini, L.; Porrini, V.; Pilotto, A.; Padovani, A.; et al. MicroRNA-34a-5p expression in the plasma and in its extracellular vesicle fractions in subjects with Parkinson's disease: An exploratory study. Int J Mol Med. 2021, 47, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasi, F.; Masciandaro, S.M.; Carratore, R.D.; Dell'Anno, M.T.; Signore, G.; Falleni, A.; et al. Proteomics Profiling of Neuron-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles from Human Plasma: Enabling Single-Subject Analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Kojima, M.; Kurosawa, T.; Sasaki, R.; Ichihara, S.; Hiraku, Y.; et al. Proteomic Profiling of Exosomal Proteins for Blood-based Biomarkers in Parkinson's Disease. Neuroscience. 2018, 392, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Rong, C.; Ke, R.; Meng, S.; Yan, X.; Ke, H.; et al. Differential proteomic analysis of serum exosomes reveals alterations in progression of Parkinson disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019, 98, e17478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Kojima, K.; Mobley, J.A.; West, A.B. Proteomic analysis of urinary extracellular vesicles reveal biomarkers for neurologic disease. EBioMedicine. 2019, 45, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Chen, Z.T.; Zhou, R.L.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.Z. Increased DJ-1 and alpha-Synuclein in Plasma Neural-Derived Exosomes as Potential Markers for Parkinson's Disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.H.; Yi, S.; Seo, H.; Son, I.; Seol, W. Increased DJ-1 in urine exosome of Korean males with Parkinson's disease. Biomed Res Int. 2014, 2014, 704678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, K.B.; Rawlins, A.B.; Clark, R.G.; Alcalay, R.N.; Standaert, D.G.; Liu, N.; et al. Ser(P)-1292 LRRK2 in urinary exosomes is elevated in idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2016, 31, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.; Chung, C.C.; Chen, J.H.; Yu, R.C.; Hong, C.T. Cytokine Profile in Plasma Extracellular Vesicles of Parkinson's Disease and the Association with Cognitive Function. Cells. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McColgan, P.; Tabrizi, S.J. Huntington's disease: a clinical review. Eur J Neurol. 2018, 25, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Abels, E.R.; Redzic, J.S.; Margulis, J.; Finkbeiner, S.; Breakefield, X.O. Potential Transfer of Polyglutamine and CAG-Repeat RNA in Extracellular Vesicles in Huntington's Disease: Background and Evaluation in Cell Culture. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, H.L.; Lamontagne-Proulx, J.; St-Amour, I.; Mason, S.L.; Rowley, J.W.; Cloutier, N.; et al. Platelet abnormalities in Huntington's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019, 90, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, H.L.; Lamontagne-Proulx, J.; St-Amour, I.; Mason, S.L.; Weiss, A.; Chouinard, S.; et al. Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles in Huntington's disease. J Neurol. 2018, 265, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciregia, F.; Urbani, A.; Palmisano, G. Extracellular Vesicles in Brain Tumors and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017, 10, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, R.; Giovannoni, G. Multiple sclerosis - a review. Eur J Neurol. 2019, 26, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaroni, F.; Visconte, C.; Serpente, M.; Golia, M.T.; Gabrielli, M.; Huiskamp, M.; et al. miR-150-5p and let-7b-5p in Blood Myeloid Extracellular Vesicles Track Cognitive Symptoms in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Cells. 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, M.; Ghabaee, M.; Naser Moghadasi, A.; Izad, M. Altered Expression of miR-326 in T Cell-derived Exosomes of Patients with Relapsing-remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 18, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenz-Cuesta, M.; Alberro, A.; Munoz-Culla, M.; Osorio-Querejeta, I.; Fernandez-Mercado, M.; Lopetegui, I.; et al. The First Dose of Fingolimod Affects Circulating Extracellular Vesicles in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Int J Mol Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonda, M.; Amoruso, A.; Grasso, R.; Di Francescantonio, V.; Avolio, C. Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Affect Monocyte-Derived Microvesicle Production. Front Neurol. 2017, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoruso, A.; Blonda, M.; D'Arrigo, G.; Grasso, R.; Di Francescantonio, V.; Verderio, C.; et al. Effect of fingolimod action on the release of monocyte-derived microvesicles in multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimmunol. 2018, 323, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimkhani, S.; Beadnall, H.N.; Wang, C.; Suter, C.M.; Barnett, M.H.; Buckland, M.E.; et al. Serum Exosome MicroRNAs Predict Multiple Sclerosis Disease Activity after Fingolimod Treatment. Mol Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 1245–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo-Haymour, N.; Bergamini, G.; Russo, G.; Kulic, L.; Knuesel, I.; Martin, R.; et al. Differential Expression of Serum Extracellular Vesicle miRNAs in Multiple Sclerosis: Disease-Stage Specificity and Relevance to Pathophysiology. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmaj, I.; Cichalewska, M.; Namiecinska, M.; Galazka, G.; Horzelski, W.; Selmaj, K.W.; et al. Global exosome transcriptome profiling reveals biomarkers for multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2017, 81, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, K.; Maltby, V.E.; Scott, R.J.; Tajouri, L.; Lechner-Scott, J. Erythrocyte microRNAs show biomarker potential and implicate multiple sclerosis susceptibility genes. Clin Transl Med. 2020, 10, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimkhani, S.; Vafaee, F.; Young, P.E.; Hur, S.S.J.; Hawke, S.; Devenney, E.; et al. Exosomal microRNA signatures in multiple sclerosis reflect disease status. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 14293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, P.; Nogueras-Ortiz, C.; Kim, S.; Delgado-Peraza, F.; Calabresi, P.A.; Kapogiannis, D. Synaptic and complement markers in extracellular vesicles in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2021, 27, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyano, A.L.; Li, G.; Boullerne, A.I.; Feinstein, D.L.; Hartman, E.; Skias, D.; et al. Sulfatides in extracellular vesicles isolated from plasma of multiple sclerosis patients. J Neurosci Res. 2016, 94, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galazka, G.; Mycko, M.P.; Selmaj, I.; Raine, C.S.; Selmaj, K.W. Multiple sclerosis: Serum-derived exosomes express myelin proteins. Mult Scler. 2018, 24, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzucco, M.; Mannheim, W.; Shetty, S.V.; Linden, J.R. CNS endothelial derived extracellular vesicles are biomarkers of active disease in multiple sclerosis. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.S.; Acevedo, C.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Bogacz, A.; Cross, J.H.; Elger, C.E.; et al. ILAE official report: a practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2014, 55, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karttunen, J.; Heiskanen, M.; Lipponen, A.; Poulsen, D.; Pitkanen, A. Extracellular Vesicles as Diagnostics and Therapeutics for Structural Epilepsies. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoof, R.; Jimenez-Mateos, E.M.; Bauer, S.; Tackenberg, B.; Rosenow, F.; Lang, J.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid microRNAs are potential biomarkers of temporal lobe epilepsy and status epilepticus. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, H.; Xie, W.; Meng, F.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Altered microRNA profiles in plasma exosomes from mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis. Oncotarget. 2017, 8, 4136–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitai, D.L.G.; Dos Santos, Y.D.R.; Upadhya, R.; Kodali, M.; Madhu, L.N.; Shetty, A.K. Extracellular Vesicles in the Forebrain Display Reduced miR-346 and miR-331-3p in a Rat Model of Chronic Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Mol Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 1674–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hua, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhu, M.; et al. Circulating MicroRNAs From Plasma Small Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers in Pediatric Epilepsy and Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022, 15, 823802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.D.; Pan, H.Y.; Huang, J.B.; Liu, X.P.; Li, J.H.; Ho, C.J.; et al. Circulating MicroRNAs from Serum Exosomes May Serve as a Putative Biomarker in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Cells. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, R.; Wang, M.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Serum Exosomal Proteins F9 and TSP-1 as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Newly Diagnosed Epilepsy. Front Neurosci. 2020, 14, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blennow, K.; Brody, D.L.; Kochanek, P.M.; Levin, H.; McKee, A.; Ribbers, G.M.; et al. Traumatic brain injuries. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016, 2, 16084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, K.; Yang, Z.; Haber, M.; Flamholz, M.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Sandsmark, D.; et al. Extracellular vesicles as distinct biomarker reservoirs for mild traumatic brain injury diagnosis. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondello, S.; Guedes, V.A.; Lai, C.; Czeiter, E.; Amrein, K.; Kobeissy, F.; et al. Circulating Brain Injury Exosomal Proteins following Moderate-To-Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: Temporal Profile, Outcome Prediction and Therapy Implications. Cells. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manek, R.; Moghieb, A.; Yang, Z.; Kumar, D.; Kobessiy, F.; Sarkis, G.A.; et al. Protein Biomarkers and Neuroproteomics Characterization of Microvesicles/Exosomes from Human Cerebrospinal Fluid Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6112–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Elahi, F.M.; Mustapic, M.; Kapogiannis, D.; Pryhoda, M.; Gilmore, A.; et al. Altered levels of plasma neuron-derived exosomes and their cargo proteins characterize acute and chronic mild traumatic brain injury. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 5082–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Pereira, M.; Raukar, N.; Reagan, J.L.; Queseneberry, M.; Goldberg, L.; et al. Potential biomarkers to detect traumatic brain injury by the profiling of salivary extracellular vesicles. J Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 14377–14388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.; Mustapic, M.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Lange, R.; Gulyani, S.; Diehl, T.; et al. Higher exosomal tau, amyloid-beta 42 and IL-10 are associated with mild TBIs and chronic symptoms in military personnel. Brain Inj. 2018, 32, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottshall, J.L.; Guedes, V.A.; Pucci, J.U.; Brooks, D.; Watson, N.; Sheth, P.; et al. Poor Sleep Quality is Linked to Elevated Extracellular Vesicle-Associated Inflammatory Cytokines in Warfighters With Chronic Mild Traumatic Brain Injuries. Front Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 762077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, V.A.; Kenney, K.; Shahim, P.; Qu, B.X.; Lai, C.; Devoto, C.; et al. Exosomal neurofilament light: A prognostic biomarker for remote symptoms after mild traumatic brain injury? Neurology 2020, 94, e2412–e2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, S.; Leete, J.; Shahim, P.; Pattinson, C.; Guedes, V.A.; Lai, C.; et al. Extracellular vesicle concentrations of glial fibrillary acidic protein and neurofilament light measured 1 year after traumatic brain injury. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.; Hemphill, M.; Yang, Z.; Beard, K.; Sewell, E.; Shallcross, J.; et al. Multi-Dimensional Mapping of Brain-Derived Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA Biomarker for Traumatic Brain Injury Diagnostics. J Neurotrauma. 2020, 37, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghai, V.; Fallen, S.; Baxter, D.; Scherler, K.; Kim, T.K.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Alterations in Plasma microRNA and Protein Levels in War Veterans with Chronic Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2020, 37, 1418–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devoto, C.; Lai, C.; Qu, B.X.; Guedes, V.A.; Leete, J.; Wilde, E.; et al. Exosomal MicroRNAs in Military Personnel with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: Preliminary Results from the Chronic Effects of Neurotrauma Consortium Biomarker Discovery Project. J Neurotrauma. 2020, 37, 2482–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puffer, R.C.; Cumba Garcia, L.M.; Himes, B.T.; Jung, M.Y.; Meyer, F.B.; Okonkwo, D.O.; et al. Plasma extracellular vesicles as a source of biomarkers in traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 2020, 134, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaimardanova, A.A.; Solovyeva, V.V.; Chulpanova, D.S.; James, V.; Kitaeva, K.V.; Rizvanov, A.A. Extracellular vesicles in the diagnosis and treatment of central nervous system diseases. Neural Regen Res. 2020, 15, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gratpain, V.; Mwema, A.; Labrak, Y.; Muccioli, G.G.; van Pesch, V.; des Rieux, A. Extracellular vesicles for the treatment of central nervous system diseases. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021, 174, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mager, I.; Breakefield, X.O.; Wood, M.J.; SELA. Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 347–357. [Google Scholar]
- Wiklander, O.P.B.; Brennan, M.A.; Lotvall, J.; Breakefield, X.O.; El Andaloussi, S. Advances in therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles. Sci Transl Med. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, K.; Klyubin, I.; Kim, Y.; Jung, J.H.; Mably, A.J.; O'Dowd, S.T.; et al. Exosomes neutralize synaptic-plasticity-disrupting activity of Abeta assemblies in vivo. Mol Brain. 2013, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuyama, K.; Sun, H.; Sakai, S.; Mitsutake, S.; Okada, M.; Tahara, H.; et al. Decreased amyloid-beta pathologies by intracerebral loading of glycosphingolipid-enriched exosomes in Alzheimer model mice. J Biol Chem. 2014, 289, 24488–24498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuda, T.; Tsuchiya, R.; Kosaka, N.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takagaki, K.; Oki, K.; et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells secrete functional neprilysin-bound exosomes. Sci Rep. 2013, 3, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attaluri, S.; Jaimes Gonzalez, J.; Kirmani, M.; Vogel, A.D.; Upadhya, R.; Kodali, M.; et al. Intranasally administered extracellular vesicles from human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural stem cells quickly incorporate into neurons and microglia in 5xFAD mice. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1200445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananbeh, H.; Vodicka, P.; Kupcova Skalnikova, H. Emerging Roles of Exosomes in Huntington's Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didiot, M.C.; Hall, L.M.; Coles, A.H.; Haraszti, R.A.; Godinho, B.M.; Chase, K.; et al. Exosome-mediated Delivery of Hydrophobically Modified siRNA for Huntingtin mRNA Silencing. Mol Ther. 2016, 24, 1836–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Im, W.; Mook-Jung, I.; Kim, M. MicroRNA-124 slows down the progression of Huntington's disease by promoting neurogenesis in the striatum. Neural Regen Res. 2015, 10, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.M.; Wiklander, P.B.; Nordin, J.Z.; Al-Shawi, R.; Wood, M.J.; Vithlani, M.; et al. Systemic exosomal siRNA delivery reduced alpha-synuclein aggregates in brains of transgenic mice. Mov Disord. 2014, 29, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.T.; Im, W.; Ban, J.J.; Lee, M.; Jung, K.H.; Lee, S.K.; et al. Exosome-Based Delivery of miR-124 in a Huntington's Disease Model. J Mov Disord. 2017, 10, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhya, R.; Shetty, A.K. Extracellular Vesicles for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson's Disease. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 1438–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, R.; Bojar, D.; Rizzi, G.; Hamri, G.C.; El-Baba, M.D.; Saxena, P.; et al. Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson's disease treatment. Nat Commun. 2018, 9, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Lin, Q.; Huang, L.; Fu, Y.; Wang, L.; He, S.; et al. Dopamine-loaded blood exosomes targeted to brain for better treatment of Parkinson's disease. J Control Release. 2018, 287, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusic, A.D.; Pusic, K.M.; Clayton, B.L.; Kraig, R.P. IFNgamma-stimulated dendritic cell exosomes as a potential therapeutic for remyelination. J Neuroimmunol. 2014, 266, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggio, L.; Paterno, G.; Vivarelli, S.; L'Episcopo, F.; Tirolo, C.; Raciti, G.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles as Nanotherapeutics for Parkinson's Disease. Biomolecules. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Q.; Upadhya, D.; Hattiangady, B.; Kim, D.K.; An, S.Y.; Shuai, B.; et al. Intranasal MSC-derived A1-exosomes ease inflammation, and prevent abnormal neurogenesis and memory dysfunction after status epilepticus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017, 114, E3536–E3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chopp, M.; Meng, Y.; Katakowski, M.; Xin, H.; Mahmood, A.; et al. Effect of exosomes derived from multipluripotent mesenchymal stromal cells on functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity in rats after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 2015, 122, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drommelschmidt, K.; Serdar, M.; Bendix, I.; Herz, J.; Bertling, F.; Prager, S.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate inflammation-induced preterm brain injury. Brain Behav Immun. 2017, 60, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodali, M.; Madhu, L.N.; Reger, R.L.; Milutinovic, B.; Upadhya, R.; Gonzalez, J.J.; et al. Intranasally administered human MSC-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit NLRP3-p38/MAPK signaling after TBI and prevent chronic brain dysfunction. Brain Behav Immun. 2023, 108, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodali, M.; Madhu, L.N.; Reger, R.L.; Milutinovic, B.; Upadhya, R.; Attaluri, S.; et al. A single intranasal dose of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles after traumatic brain injury eases neurogenesis decline, synapse loss, and BDNF-ERK-CREB signaling. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1185883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.A.; Moss, L.D.; Lee, J.Y.; Tajiri, N.; Acosta, S.; Hudson, C.; et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 in exosomes drives regenerative function and modulates inflammation-linked networks following traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2018, 15, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Benson, M.; et al. ClinVar: public archive of interpretations of clinically relevant variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D862–D868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villiger, L.; Joung, J.; Koblan, L.; Weissman, J.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Gootenberg, J.S. CRISPR technologies for genome, epigenome and transcriptome editing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.J.; Liu, D.R. Prime editing for precise and highly versatile genome manipulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2023, 24, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.C.; Zhang, T.; Gao, J.Q. The in vivo fate and targeting engineering of crossover vesicle-based gene delivery system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022, 187, 114324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, N.; et al. Delivery of CRISPR/Cas systems for cancer gene therapy and immunotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021, 168, 158–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostyushev, D.; Kostyusheva, A.; Brezgin, S.; et al. Gene Editing by Extracellular Vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21, 7362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, E.A.; Lee, J.; Hotta, A. Delivery of CRISPR-Cas tools for in vivo genome editing therapy: Trends and challenges. J Control Release. 2022, 342, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Hu, S.; Chen, X. Non-viral delivery systems for CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing: Challenges and opportunities. Biomaterials. 2018, 171, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, V.; Zhang, F.; Dahlman, J.E. Drug delivery systems for CRISPR-based genome editors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 875–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Yang, Y.; Oh, S.J.; Hong, Y.; Seo, M.; Jang, M. Cancer-derived exosomes as a delivery platform of CRISPR/Cas9 confer cancer cell tropism-dependent targeting. J Control Release. 2017, 266, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAndrews, K.M.; Xiao, F.; Chronopoulos, A.; LeBleu, V.S.; Kugeratski, F.G.; Kalluri, R. Exosome-mediated delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 for targeting of oncogenic KrasG12D in pancreatic cancer. Life Sci Alliance. 2021, 4, e202000875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Shi, Q.; Yang, T.; et al. In Vivo Visualized Tracking of Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Using CRISPR-Cas9 System. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022, 21, 15330338221085370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, S.; Foot, N.; Ang, C.S.; et al. Arrestin-Domain Containing Protein 1 (Arrdc1) Regulates the Protein Cargo and Release of Extracellular Vesicles. Proteomics. 2018, 18, e1800266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, L.; Freed, E.O. ARRDC1 as a mediator of microvesicle budding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012, 109, 4025–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, J.; Kadungure, T.; Beyene, J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Q. ARMMs as a versatile platform for intracellular delivery of macromolecules. Nat Commun. 2018, 9, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Yang, X.; Li, Q.; et al. Myristoylation of Src kinase mediates Src-induced and high-fat diet-accelerated prostate tumor progression in mice. J Biol Chem. 2017, 292, 18422–18433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, K.; McConnell, R.E.; Xu, K.; et al. A versatile platform for generating engineered extracellular vesicles with defined therapeutic properties. Mol Ther. 2021, 29, 1729–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitley, J.A.; Kim, S.; Lou, L.; et al. Encapsulating Cas9 into extracellular vesicles by protein myristoylation. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022, 11, e12196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Goemans, N.; Takeda, S.; Mercuri, E.; Aartsma-Rus, A. Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeau, N.; Fortin-Archambault, A.; Gérard, C.; Rousseau, J.; Yaméogo, P.; Tremblay, J.P. Serum extracellular vesicles for delivery of CRISPR-CAS9 ribonucleoproteins to modify the dystrophin gene. Mol Ther. 2022, 30, 2429–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Lyu, P.; Yoo, K.; et al. Engineered extracellular vesicles as versatile ribonucleoprotein delivery vehicles for efficient and safe CRISPR genome editing. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021, 10, e12076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, P.; Lung, M.S.Y.; Okuzaki, Y.; et al. Extracellular nanovesicles for packaging of CRISPR-Cas9 protein and sgRNA to induce therapeutic exon skipping. Nat Commun. 2020, 11, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Disease | Author | Year | Sample type | EVs type reported | Main findings - Biomarkers | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s disease | Kim, K. Y.; et al | 2021 | Plasma/Serum | Brain-derived exosomes | Protein | ↑ | Aβ-42 |
| t-tau | |||||||
| p-T181-tau | |||||||
| p-S396-tau | |||||||
| Liu, W.; et al | 2020 | Plasma | Neuronally derived exosomes | Protein | ↓ | Ng | |
| Jia, L.; et al | 2021 | Plasma | Neuronal-derived exosomes | Protein | ↓ | Ng | |
| GAP43 | |||||||
| SNAP25 | |||||||
| SYT1 | |||||||
| Li, F.; et al | 2020 | Serum | Extracellular vesicles | Protein | ↑ | Aβ1-42 | |
| total-tau | |||||||
| P-T181-tau | |||||||
| P-S396-tau | |||||||
| miRNA | ↑ | hsa- miR-424-5p | |||||
| hsa-miR-3065-5p | |||||||
| hsa-miR-93-5p | |||||||
| ↓ | hsa-miR-1306-5p | ||||||
| Durur, D. Y.; et al | 2022 | Plasma | Small neuron-derived extracellular vesicles (sNDEVs) | miRNA | ↑ | Let-7e | |
| Yang, T. T.; et al | 2018 | Serum | Exosomes | miRNA | ↑ | miR-135a | |
| miR-384 | |||||||
| ↓ | miR-193b | ||||||
| Aharon, A.; et al | 2020 | Plasma (platelet-poor plasma) | Extracellular vesicles | miRNA | ↓ | has-let-7g-5p | |
| has-miR126-3p | |||||||
| has-miR142-3p | |||||||
| has-miR146a-5p | |||||||
| has-mir26b-5p | |||||||
| has-mir223-3p | |||||||
| Cell marker | ↑ | CD171/L1CAM - axonal | |||||
| MOG - glial | |||||||
| CD31+ CD41-%, %CD144 - endothelial | |||||||
| Cytokine | ↑ | IFN-γ | |||||
| RANTES | |||||||
| GRO | |||||||
| IL-2 | |||||||
| IL-8 | |||||||
| AgRP | |||||||
| Growth Factor Content | ↑ | PDGF-BB | |||||
| TPO | |||||||
| ↓ | UPAR | ||||||
| VEGF-D | |||||||
| Receptors VEGFR-2 and 3 | |||||||
| FGF-4 | |||||||
| EGF | |||||||
| ANG-1 | |||||||
| Parkinson’s Disease | Shi, M.; et al | 2014 | Plasma | Exosomes | Protein | ↑ | α-syn |
| Stuendl, A.; et al | 2021 | Plasma | Extracellular vesicles | Protein | ↑ | α-syn | |
| Niu, M.; et al | 2020 | Plasma | Neuronal-derived exosomes | Protein | ↑ | α-syn | |
| Jiang, G.; et al | 2020 | Serum | Neuron-derived exosomes | Protein | ↑ | α-syn | |
| Chung, C-C.; et al | 2021 | Plasma | Extracellular vesicles | Protein | ↓ | α-syn | |
| Si, X.; et al | 2019 | Serum | CNS-derived exosomes | Protein | ↓ | α-syn | |
| Cao, Z.; et al | 2019 | Saliva | Exosomes | Protein | ↑ | α-synOlig | |
| α-synOlig/α-syn total ratio | |||||||
| Ho, D. H.; et al | 2014 | Urine | Exosomes | Protein | ↑ | Protein deglycase DJ-1 | |
| Zhao, Z-H.; et al | 2019 | Plasma | Neural-derived exosomes | Protein | ↑ | Protein deglycase DJ-1 | |
| Exosomes/total Protein deglycase DJ-1 ratio | |||||||
| α-syn | |||||||
| Fraser, K. B.; et al | 2016 | Urine | Exosomes | Protein | ↑ | Ser(P)-1292 LRRK2 | |
| Yao, Y-F.; et al | 2018 | Plasma | Exosomes | miRNA | ↑ | miR-331-5p | |
| ↓ | miR-505 | ||||||
| Xie, S.; et al | 2020 | Plasma | Extracellular vesicles | miRNA | ↑ | hsa-miR-30c-2-3p | |
| ↓ | hsa-miR-15b-5p | ||||||
| hsa-miR-138-5p | |||||||
| hsa-miR-338-3p | |||||||
| hsa-miR-106b-3p | |||||||
| hsa-miR-431-5p | |||||||
| Cao, X-Y.; et al | 2017 | Serum | Exosomes | miRNA | ↑ | miR-195 | |
| miR-24 | |||||||
| ↓ | miR-19b | ||||||
| He, S.; et al | 2021 | Serum | Extracellular vesicles | miRNA | ≠ | hsa-miR-374a-5p | |
| hsa-miR-374b-5p | |||||||
| hsa-miR-199a-3p | |||||||
| hsa-miR-28-5p | |||||||
| hsa-miR-22-5p | |||||||
| hsa-miR-151a-5p | |||||||
| Grossi, I.; et al | 2021 | Plasma | Pure small extracellular vesicles | miRNA | ↑ | miR-34a-5p | |
| Chan, L.; et al | 2021 | Plasma | Extracellular vesicles | Cytokine | ↑ | pro-IL-1β (pro-interleukin) | |
| TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor) | |||||||
| Multiple sclerosis | Scaroni, F.; et al | 2022 | Plasma | Myeloid Evs | miRNA | ↑ | miR-150-5p |
| ↓ | let-7b-5p | ||||||
| Azimi, M.; et al | 2019 | Whole blood | T Cell-derived Exosomes | miRNA | ↑ | miR-326 | |
| Selmaj, I.; et al | 2017 | Serum | Exosomes | miRNA | ↓ | hsa-miR-122-5p | |
| hsa-miR-196b-5p | |||||||
| hsa-miR-301a-3p | |||||||
| hsa-miR-532-5p | |||||||
| Groen, K.; et al | 2020 | Whole blood | Erythrocyte-derived EVs | miRNA | ↑ | hsa-miR-148-5p | |
| Ebrahimkhani, S.; et al | 2017 | Serum | Exosomes | miRNA | ↑ | miR-15b-5p | |
| miR-451a | |||||||
| miR-30b-5p | |||||||
| miR-342-3p | |||||||
| miR-127-3p | |||||||
| miR-370-3p | |||||||
| miR-409-3p | |||||||
| miR-432-5p | |||||||
| Moyano, A.; et al | 2016 | Plasma | Small Evs | Glycolipid | ↑ | C16:0 sulfatide | |
| Galazka, G.; et al | 2018 | Serum | Exosomes | Protein | ↑ | MOG | |
| Bhargava, P.; et al | 2020 | Plasma | Neuronal-enriched EVs | Protein | ↓ | Synaptopodin | |
| Synaptophysin | |||||||
| Astrocytic-enriched EVs | Complement cascade component | ↑ | C1q | ||||
| C3 | |||||||
| C3b/iC3b | |||||||
| C5 | |||||||
| C5a | |||||||
| Factor H | |||||||
| Blandford, S.; et al | 2022 | Plasma | Extracellular vesicles | EV concentration (cell-specific) | ↑ | CD3+ (T cells) | |
| CD4+ T cells and monocytes | |||||||
| CD8+ T cells | |||||||
| CD14+ (Monocytes) | |||||||
| CD19+ (B cells) | |||||||
| Mazzucco, M.; et al | 2022 | Plasma | CNS endothelial derived Evs | EV concentration | ↑ | CD3/CD4- pETX/MAL+ CD31+ | |
| CD3/CD4- pETX/MAL+ CD105+ | |||||||
| CD3/CD4- pETX/MAL+ CD144+ | |||||||
| Epilepsy | Yan, S.; et al | 2017 | Plasma | Exosomes | miRNA | ↓ | miR-4668-5p |
| miR-4322 | |||||||
| miR-8071 | |||||||
| miR-6781-5p | |||||||
| miR-197-5p | |||||||
| ↑ | miR3613-5p | ||||||
| Wang, Y.; et al | 2022 | Plasma | Small EVs | miRNA | ↑ | hsa-miR-584a-5p | |
| hsa-miR-342a-5p | |||||||
| hsa-miR-150-3p | |||||||
| hsa-miR-125b-5p | |||||||
| Chen, S-D.; et al | 2020 | Serum | Exosomes | miRNA | ↑ | miR-194-2 | |
| miR-15a | |||||||
| miR-132 | |||||||
| Lin, Z.; et al | 2020 | Serum | Exosomes | Protein | ↑ | F9 | |
| ↓ | TSP-1 | ||||||
| Traumatic brain injury | Kryshawna, B.; et al | 2021 | Plasma | Extracellular vesicles | Protein | ↑ | GFAP |
| IL6 | |||||||
| Flynn, S.; et al | 2021 | Serum | Extracellular vesicles | Protein | ↑ | GFAP | |
| Goetzl, E. J.; et al | 2019 | Plasma | Neuron-derived exosomes | Protein | ↓ | CD81 (Acute) | |
| RAB10 (Acute) | |||||||
| ↑ | Annexin VII (Acute) | ||||||
| UCH-L1 (Acute) | |||||||
| All spectrin fragments (Acute) | |||||||
| Claudin-5 (Acute) | |||||||
| Occludion (Acute) | |||||||
| NKCC-1 (Acute) | |||||||
| Aquaporin 4 (Acute/Chronic) | |||||||
| Synaptogyrin-3 (Acute/Chronic) | |||||||
| Aβ42 (Acute/Chronic) | |||||||
| P-T181-tau (Acute/Chronic) | |||||||
| P-S396 (Chronic) | |||||||
| total tau (Acute/Chronic) | |||||||
| PRPc (Acute/Chronic) | |||||||
| Cytokine | ↑ | IL-6 (Acute/Chronic) | |||||
| Gill, J.; et al | 2018 | Plasma | Neuronal-derived exosomes | Protein | ↑ | tau | |
| Aβ42 | |||||||
| Cytokine | ↑ | IL-10 | |||||
| Gottshall, J.; et al | 2022 | Plasma | Extracellular vesicles | Cytokine | ↑ | IL-6 | |
| Cheng, Y.; et al | 2019 | Saliva | Extracellular vesicles | Gene | ↑ | CDC2 | |
| CSNK1A1 | |||||||
| CTSD | |||||||
| Ko, J.; et al | 2020 | Plasma | Brain-derived Evs | miRNA | ≠ | miR-203b-5p | |
| miR-203a-3p | |||||||
| miR-206 | |||||||
| miR-185-5p | |||||||
| Ghai, V.; et al | 2020 | Plasma | Extracellular vesicles | miRNA | ↓ | miR-139-5p | |
| miR-143-3p | |||||||
| miR-146a-5p | |||||||
| miR-192-5p | |||||||
| miR-203a-3p | |||||||
| miR-21-5p | |||||||
| miR-423-5p | |||||||
| miR-483-5p | |||||||
| Disease | Author | Year | Material | Model | Via | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s disease | Katsuda, T.; et al | 2013 | MSC-EVs derived from human adipose tissue containing neprilysin | in vitro | NA | Suggests the lyse of beta amyloid peptide |
| Yuyama, K.; et al | 2014 | Neuroblastoma-derived exosomes | Heterozygotic transgenic mice that express the human APP | Stereotaxic injection | Increased clearance of beta amyloid peptite by trapping it inside the EVs and deliviering it to microglica, where it can be degraded | |
| Parkinson’s Disease | Jarmalavicuite, A.; et al | 2015 | EVs from stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth | in vitro | NA | Neuroprotective potential and preventention of apoptosis in 80% of dopaminergic neurons when maintained in 3D culture |
| Narbute, K.; et al | 2019 | EVs from stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth | Rat model | IN | Improvement of the rat gait parameters and increased tyrosine hydroxylase expression in substantia nigra | |
| Qu, M.; et al | 2018 | Blood EVs loaded with dopamine | Murine model | IV | Improvement of functional recovery without toxicity in hippocampus, liver, spleen or lungs | |
| Cooper, J. M.; et al | 2014 | Exosomes expressing RVG loaded with α-Syn siRNA | Transgenic mice expressing the human phosphorylation-mimic α-Syn | IV | Down-regulation of alpha synuclein | |
| Kojima, R.; et al | 2018 | HEK-293 T cells with a modified plasmid coding for catalase | Mice | IN | Reduction of brain inflammation, when compared to free Catalase administration | |
| Huntington’s Disease | Didiot, M-C.; et al | 2016 | Hydrophobic siRNA targeting Huntintinton mRNA in Glioblastoma EVs | Mice | Stereotactic injection in mouse striatum | Decrease of protein level in vitro and in vivo with no clinical improvement |
| Liu, T.; et al | 2015 | EVs loaded with miR-124 | R6/2 HD transgenic mice | Stereotactic injection in mouse striatum | Slowed down progression of HD, promotesd neuronal differentiation and survival | |
| Lee, S-T.; et al | 2017 | miR-124 expressing HEK293 cell line | R6/2 transgenic HD mice | Stereotactic injection in mouse striatum | Reduction of REST protein expression, no behavior improvement | |
| Wu, T.; et al | 2018 | Exosomes expressing the neuron-specific RVG peptide, loaded with siRNA targeting human huntingtin exon 1 | BACHD and N171-82Q transgenic mice | IV | Reduced HTT expression up to 46% and 54% | |
| Multiple sclerosis | Laso-Garcia, F.; et al | 2018 | MSC-EVs from human adipose tissue | Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus induced demyelinating disease | IV | Improvement in motor deficits, reducion of brain atrophy, increasion in cell proliferation in the subventricular zone and decreasion of inflammatory infiltrates in the spinal cord |
| Pusic, A. D.; et al | 2013 | IFNy-stimulated dendritic cells | Ex vivo (mature hippocampal slice cultures) / In vivo | NA / IN | Increase of myelin levels | |
| Riazifar, M.; et al | 2019 | human MSCs EVs | Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mouse model | IV | Stimulation by IFNγ reduced the mean clinical score of EAE mice compared control, reduced demyelination, decreased neuroinflammation, and upregulated the number of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) within the spinal cords of EAE mice. Co-culture of IFNγ-Exo with activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells cells in vitro reduced levels of pro-inflammatory Th1 and Th17 cytokines | |
| Epilepsy | Long, Q.; et al | 2017 | MSC-EVs from human bone marrow | Mouse model of induced status epilepticus | IN | Reduction of proinflammatory cytokines, better cognitive and memory functions. Neuroprotection, reducing neural loss, preserving GABAergic intraneurons |
| Traumatic brain injury | Doeppner, T. R.; et al | 2015 | Human bone marrow-derived MSC | Mice after focal cerebral ischemia | IV | Angiogenesis, improvement of neurological impairment, long-term neuroprotection |
| Zhang, Y.; et al | 2015 | Murine bone marrow derived MSC-EVs | Traumatic brain injured rats and mice | IV | Improvement of spatial learning, reduction of neurological deficits, better angiogenesis and neurogenesis, reduction of inflammation | |
| Kim, D-K.; et al | 2016 | Human MSCs EVs | Traumatic brain injuried mice | IV | Improvement of spatial learning and pattern separation ability, decrease of neuroinflammation | |
| Drommelschmidt. K.; et al | 2017 | Human bone marrow-derived MSC | Rodent model of inflammation-induced brain injury | IP | Improvement of long-lasting cognitive functions, amelioration of inflammation, restoration of short-term myelination deficits | |
| Gao, W.; et al | 2018 | ECFCs EVs | Traumatic Brain Injured mice | Stereotactic injection after trauma | Inhibition of PTEN expression and increasion of AKT expression, changes accompanied by reductions in Evans blue dye extravasation, brain edema and tight junction degradation | |
| Patel, N. A.; et al | 2018 | Adipose-derived stem cell EVs containing MALAT1 | Mild controlled cortical impact -induced traumatic brain injury in rat | IV | Recovery of function on motor behavior and reduction in cortical brain injury |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





