1. Introduction
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a global health concern classified as the seventh-leading cause of death worldwide [
1]. In 2019, it was reported that 296 million people had chronic HBV (CHB) infections, and there were approximately 1.5 million new infections. HBV leads to 820,000 deaths annually [
2]. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and HBV share similar transmission routes and previous studies have reported rapid progression of HBV infection to cirrhosis, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) among people with HIV/HBV [
3,
4,
5,
6]. In 2021 it was estimated that the national HIV prevalence in Botswana was 20.8% among adults of 15-64 years, with 0.2% annual incidence [
7]. The prevalence HIV/HBV in Botswana has been found to range between 1.74% and 10.6% [
5,
8,
9,
10]. These statistics urgently call for a clear policy on HBV treatment in PLWH particularly as Botswana does not routinely screen for HBV among PLWH initiating antiretroviral therapy (ART).
All CHB patients with HIV co-infection are supposed to be enrolled for treatment using recommended nucleoside analogues (NAs) while HBV mono-infected individuals with treatment-qualifying HBV viral loads should be considered for disease monitoring if they tested positive for HBsAg [
11]. According to the WHO, the most effective NAs to inhibit HBV are tenofovir and entecavir (ETV) [
2]. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI), such as lamivudine (3TC), ETV, tenofovir (TFV) and their derivatives, directly block viral DNA polymerase [
12]. In 2000, Botswana endorsed WHO recommendations for hepatitis B vaccine administration within 24 hours after birth, followed by three doses at 2, 3, and 4 months to reduce perinatal and early horizontal transmission [
13]. Currently, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), 3TC, and dolutegravir (DTG), (TLD) is the first-line regimen for HIV treatment in Botswana. The regimen is also effective against HIV/HBV coinfection as both TDF and 3TC have anti-HBV activity [
14].
The diagnosis and clinical monitoring of HBV infection is based on the use of serological tests for the detection of viral antigens such as HBsAg and HBeAg as well as molecular assays for quantification of HBV viral load (VL) [
15]. Clinically HBeAg is a significant non-particulate protein that indicates HBV replication, infectivity and disease severity because of its immunomodulatory properties and association with high HBV VL [
16]. A positive HBeAg test indicates elevated or high levels of the virus as a result of active viral replication while a negative HBeAg result indicates low or no virus in the blood [
17,
18,
19]. Quantification of HBV VL requires expensive equipment which is scarce in rural communities of middle-income countries like Botswana. Thus, there is a need for an alternative assay that is affordable and easy to use where nucleic acid tests (NAT) are not readily available. This study therefore aimed to evaluate the use of HBeAg as a proxy for HBV VL to determine treatment eligibility for the first time in Botswana.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
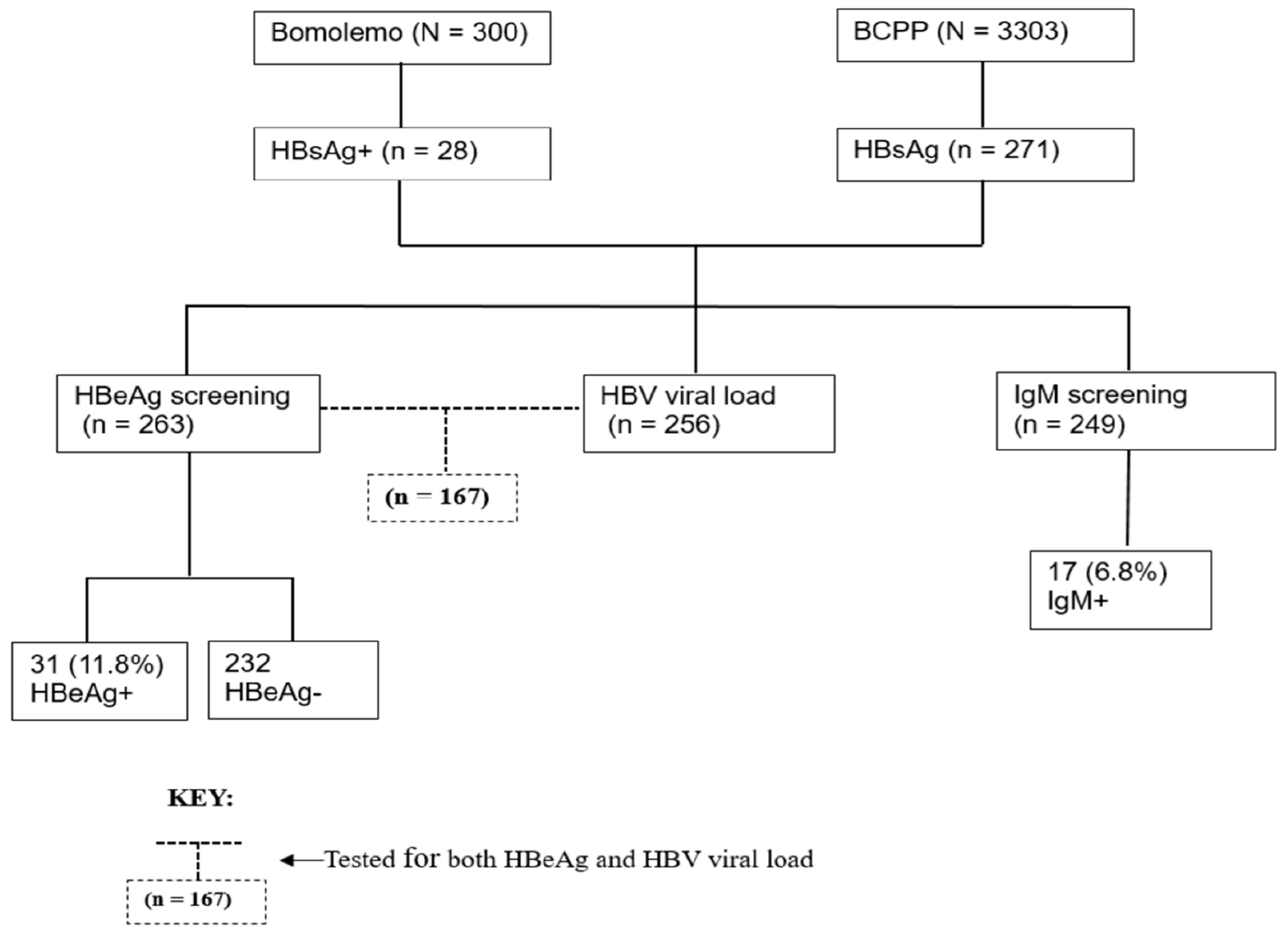
This was a retrospective and cross-sectional study which utilized plasma samples (n=299) of confirmed HBsAg positive participants from two parent studies, Bomolemo study and Botswana Combination Prevention Project (BCPP) [
5,
20]. Bomolemo (2008-2009) assessed the effectiveness and tolerability of Truvada as the NRTI backbone used in first-line highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) for adults in Botswana. The study enrolled 309 PLWH who were treatment-naïve, 18 years or older and had CD4+ T-cell counts less than or equal to 250 cells/mm
3, or had an acquired immune deficiency syndrome defining illness [
21]. The BCPP study (2013-2018) determined the certainty that, implementation of an improved combination prevention package, will substantially reduce population-level, cumulative HIV incidence in a specified geographical region over the course of three years. The BCPP study enrolled 12610 participants aged 16-64 in 30 rural and peri-urban communities in Botswana, regardless of CD4+ T-cell counts or degree of HIV disease [
22].
2.2. Laboratory Investigations
All laboratory tests were performed according to manufacturer’s instructions at the Botswana Harvard HIV reference laboratory (BHHRL) using de-identified data from the two previous studies. Initially, 3603 plasma samples of which 300 were from Bomolemo study and 3303 were from the BCPP study were screened and selected based on their HBsAg status as determined by the Murex kit (Murex Version 2, Diasorbin, Dartford, UK). From the 3603 samples [
5,
20], 299 plasma samples tested HBsAg positive (HBsAg+) and were enrolled in the current study. The HBsAg+ samples were further tested for HBeAg using the Monolisa™ HBeAg-Ab PLUS kit (Bio-Rad, Hercules CA, USA) and anti-HBc immunoglobulin-M (IgM) using the Monolisa™ anti-HBc Plus 1 Plaque (Bio-Rad, Marnes-la-Coquette, France) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. HBV viral load was quantified on HBsAg+ samples using the COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan HBV Test version 2.0 (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) which has a broad linear range of 20 IU/mL - 1.7x10
8 IU/mL,
Figure 1.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
HBV VL cut-off of ≥ 20,000 IU/mL was used to determine treatment eligibility for CHB patients while a cut-off of ≥ 200,000 IU/mL was used for qualification for HBV PMTCT using WHO guidelines. A lower HBV viral load cut-off of 2,000 IU/mL was also investigated. Ordinal logistic regression was used to determine the association between HBV viral load categories and HBeAg status. All statistical analyses were done in the STATA version 18.0 (StataCorp LLC, College Station, Texas, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Description of Study Participants
A total of 299 HBsAg+ participants were selected from the database of the two studies, of whom most were female (63.9%) with a median age of 41 (IQR: 31-50). Most participants 216/298 (72.5%) had undetectable HIV viral load and were on ART 235/299 (78.6%). The majority of those on ART were on TDF-containing regimen 93/167 (55.7%) and 67/167(40.1%) were on 3TC-containing regimen (
Table 1). Only 31/263 (11.8%) of the selected participants had positive HBeAg status, while 39/176 (22.2%) had HBV viral load equal or greater than 2000 IU/mL,
Table 1.
3.2. Association of HBeAg and HBV Viral Load
Out of the 299 participants, only 167 consisting of 105 females and 62 males had both HBeAg and HBV VL results. Out of the 167 participants tested for both HBeAg and viral load, 23/167 (13.8%) had positive HBeAg serology while 144/167 (86.2%) had negative HBeAg serology. There was a strong positive association between HBV VL categories and HBeAg status when using both guidelines for treatment of CHB patients and for PMTCT qualification. Approximately 70.8% of participants with a viral load of equal or greater than 20,000 IU/mL also tested positive for HbeAg, [OR 55.5 (95% CI: 16.7 – 184.30], p-value<0.001. However, 29.2% of participants with a viral load equal or greater than 20,000 IU/mL tested negative for HbeAg. When using the PMTCT qualification guidelines viral load cut-offs, 87.5% of participants who have a viral load ≥200,000 IU/mL tested positive for HBeAg, therefore leaving 12.5% of participants testing negative for HBeAg,
Table 2.
4. Discussion
In this report, we investigated the validity of using HBeAg as a proxy for high viral loads for recommending HBV PMTCT prophylaxis and also for initiating HBV ART. As expected, we found an association between HBV VL and HBeAg detection. Our study showed a positive HBV VL and HBeAg association as majority, 70.8% and 87.5% of participants with positive HBeAg serology also had viral loads that qualified them for treatment for CHB and HBV PMTCT prophylaxis respectively suggesting active viral replication. Our results are consistent with what was found by Chen and colleagues who showed that HBeAg levels of signal-to-cutoff ratio 768 S/CO could adequately cover majority (94%) of their HBV carrier patients with HBV DNA >2 × 107 copies/mL [
18]. Based on the results obtained we are 95% confident that the odds of patients with HBV VL qualifying them for CHB treatment (≥20,000IU/mL) are 55.5 times higher in participants having a positive HBeAg serology. This finding is statistically significant as it indicates an association between the HBeAg status and the viral loads of participants qualifying for CHB treatment. Similarly, there is 110.4 times higher odds for participants with viral loads qualifying for PMTCT HBV treatment (≥200,000IU/mL), to have a positive HBeAg serology.
The sole use of HBeAg would however miss out other participants who would test negative for HBeAg while having high viral loads. Despite the notion that positive HBeAg serology is associated with high HBV viral loads, there were some discrepancies noted in our study as 12.5% and 29.2% of participants with negative HBeAg serology had HBV VL qualifying for HBV PMTCT and CHB treatment respectively. These participants would therefore be rendered ineligible for HBV treatment if the HBeAg assay is used instead of NAT. Also, the proportion of such participants is similar to what was found by Funk and colleagues, who reported that about 15–20% of HBeAg negative patients in Asia, the Middle East, Mediterranean basin and southern Europe had high viral DNA (>104 copies/ml) [
23]. This discrepancy can be due to the fact that CHB patients with negative HBeAg serology have naturally occurring core promoter mutations that might increase the replication efficacy of HBV which can led to faster progression to liver cirrhosis than in HBeAg-positive participants [
24].
Additional discrepancies were noted in our study from the 6/143 (4.2%) and 19/151 (6.0%) participants with low HBV VL despite having positive HBeAg serology thus qualifying them for CHB treatment and HBV PMTCT respectively. This discrepancy could be attributed to the fact that HBeAg levels could vary up to 1000-fold among people with positive HBeAg serology as a result of their varying genotypes developing different mutations in the regions of the HBV genome that code for HBeAg17. We did not include sequencing results in our study however chances are, the majority of the individuals with low HBV VL were genotype A, as lower HBV DNA levels in both the HBeAg-positive and HBeAg-negative phases are among the distinctive clinical characteristics of subgenotype A1 carriers 15. Additionally, genotype A (80%) has the highest prevalence in Botswana followed by D (18.6 %) and E (1.4 %) [
25].
The presence of participants with positive HBeAg serology having low or undetectable HBV viral load could be attributed to the ART they were receiving [
26]. Approximately 56% of participants in our study were on the TDF containing regimen which inhibits DNA polymerase functionality thus preventing HBV replication by vying for DNA synthesis during virus transcription with deoxyadenosine 5′-triphosphate. The presence of this anti-viral therapy results in low viral loads and hepatitis e antibody positive seroconversion [
27]. We did not quantify HBeAg in our study, therefore these participants may have had low HBeAg levels.
5. Limitations
There were a few limitations in this study. Genotyping was not done for all participants and as a result, genotypic results were not included in the study; nonetheless, majority of participants with known HBV genotypes (90%) were subgenotype A1, which would result in biased analysis due to the limited number of alternative genotypes if genotypic results were incorporated in this study. However, understanding genotypes is crucial because various genotypes develop distinct mutations in the areas of the HBV genome that code for HBeAg and having sufficient data of the varying genotypes is critical for carrying out an effective analysis. From the 167 participants that were tested for both HBeAg and HBV DNA, only a small portion of them (23/167) had a positive HBeAg serology thus limiting the credibility of the analysis of the HBeAg marker. All the participants in this study were living with HIV and we are therefore unable to determine if the HIV infection had any impact on the results. Future studies should explore the same questions in HBV monoinfected individuals. Additionally, majority of the participants tested for both HBeAg and HBV DNA were on ART that included TDF and/or 3TC which could have affected the credibility of the HBeAg marker as a predictor of HBV DNA because the anti-HBV activity.
6. Conclusions
In conclusion the study provides significant data that highlights the positives and limitations of use of HBeAg as a proxy for HBV viral load to determine CHB treatment eligibility and for qualification of HBV PMTCT. The limitations should be taken into account whenever using HBeAg as a proxy for HBV viral loads. Furthermore, these discordances call for additional research including complete HBV genome genotyping, HBeAg quantitative assay and a cohort of participants with variables that do not affect the functionality of the HBeAg marker to determine causes of discordance between HBV viral load and HBeAg.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.G., M.A, and B.B.P.; methodology, O.L., B.B.P., K.W., G.M.; validation, K.B., T.R., W.T.C., L.B.; formal analysis, O.L. K.W., B.B.P., investigation, O.L., K.W., B.B.P., G.M., B.P., and D.D; resources, S.M., M.A., M.J., and S.G.; data curation, O.L., ; writing—original draft preparation, O.L. and K.W., X.X.; writing—review and editing, O.L., B.B.P., K.W., G.M., W.T.C., L.B., B.P., D.D., T.R., K.B., M.J., K.L., S.M., M.A., and S.G.; visualization, O.L.; supervision, M.A., M.J., K.L., and S.G; project administration, O.L., K.W., and B.B.P.; funding acquisition, M.A., M.J., and S.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Wellcome Trust (grant number 218770/Z/19/Z). W. T. C., S. M., and S. G. are partly supported through the Sub-Saharan African Network for TB/HIV Research Excellence (SANTHE 2.0) from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (INV-033558). B. B. P. and S. G. are supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Common Fund, award number U41HG006941 (H3ABioNet). H3ABioNet is an initiative of the Human Health and Heredity in Africa Consortium (H3Africa) program of the African Academy of Science. B. B. P., R. M., and S. M. are also supported by Trials of Excellence in Southern Africa (TESAIII), which is part of the EDCTP2 program supported by the European Union (grant number CSA2020NoE-3104 TESAIII). B. B. P, M. A, and S. G. are supported by the Fogarty International Center at the US National Institutes of Health (D43 TW009610). S.G and W.T.C are supported partly by NIH (award number 1G11TW012503-01).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The current study was approved by the University of Botswana Institute Review Board and Human Research Development Committee at the Botswana Ministry of Health. Reference NO: HPRD: 6/14/1.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from participants in the Bomolemo and BCPP studies.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon request from authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Botswana Prevention Combination Project study participants, Bomolemo study participants, Dikgosi and other community leaders, the clinic staff, District Health Management Teams, and Community Health Facilities at study sites; the Ya Tsie Study Team at the Botswana Harvard Health Partnership, the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Botswana, CDC Atlanta, and the Botswana Ministry of Health. The authors also thank those who served on the Ya Tsie Community Advisory Board, Laboratory Staff, and Management of Botswana Harvard HIV Reference Laboratory.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Stanaway, J.D.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Fitzmaurice, C.; Vos, T.; Abubakar, I.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Assadi, R.; Bhala, N.; Cowie, B.; et al. The global burden of viral hepatitis from 1990 to 2013: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2016, 388, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization Global Hepatitis, P. Prevention of mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus : guidelines on antiviral prophylaxis in pregnancy; World Health Organization: Geneva, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, L.Y.; Wong, D.K.; Cheung, K.S.; Seto, W.K.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Review article: hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg): an emerging marker for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2018, 47, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, R.; Davari, A.; Izadi, M.; Jonaidi, N.; Alavian, S.M. HIV/HBV Co-Infections: Epidemiology, Natural History, and Treatment: A Review Article. Iran Red Crescent Med J 2011, 13, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.; Gaseitsiwe, S.; Moyo, S.; Thami, K.P.; Mohammed, T.; Setlhare, D.; Sebunya, T.K.; Powell, E.A.; Makhema, J.; Blackard, J.T.; et al. Slow CD4+ T cell Recovery in Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Hepatitis B Virus-Coinfected Patients Initiating Truvada-Based Combination Antiretroviral Therapy in Botswana. Open Forum Infect Dis 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Lin, P.; Cheng, N. HBV/HIV Coinfection: Impact on the Development and Clinical Treatment of Liver Diseases. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021, 8, 713981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mine, M.; Stafford, K.; Laws, R.L.; Marima, M.; Lekone, P.; Ramaabya, D.; Makhaola, K.; Mapondera, P.; Wray-Gordon, F.; Akbakwuru, C.; et al. Botswana achieved the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) 95-95-95 targets: results from the Fifth Botswana HIV/AIDS Impact Survey (BAIS V), 2021. Proceedings of The 24th International AIDS Conference, Montreal, Canada & Virtual, 29th July–2nd August 2022; p. 231. [Google Scholar]
- Choga, W.T.; Anderson, M.; Zumbika, E.; Moyo, S.; Mbangiwa, T.; Phinius, B.B.; Melamu, P.; Kayembe, M.K.; Kasvosve, I.; Sebunya, T.K.; et al. Molecular characterization of hepatitis B virus in blood donors in Botswana. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, P.C.; Beloukas, A.; Malik, A.; Carlson, J.M.; Jooste, P.; Ogwu, A.; Shapiro, R.; Riddell, L.; Chen, F.; Luzzi, G.; et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Coinfection among HIV-Positive Women in South Africa and Botswana. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0134037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baruti, K.; Lentz, K.; Anderson, M.; Ajibola, G.; Phinius, B.B.; Choga, W.T.; Mbangiwa, T.; Powis, K.M.; Sebunya, T.; Blackard, J.T.; et al. Hepatitis B virus prevalence and vaccine antibody titers in children HIV exposed but uninfected in Botswana. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0237252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harlfinger, J.; Nussbaumer-Streit, B.; Gartlehner, G. Prevention of Mother-To-Child Transmission of Hepatitis B Virus: Guidelines on Antiviral Prophylaxis in Pregnancy. Gesundheitswesen 2023, 85, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, K.; Zang, N.; Wang, M.; Liang, T.; Wei, W. Synthesis and evaluation of 3-phenylisoxazoline derivatives as non-nucleoside hepatitis B virus inhibitors. Tetrahedron 2023, 130, 133177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Davis, S.; Tolle, M.; Mabikwa, V.; Anabwani, G. Prevalence of hepatitis B and hepatitis C coinfections in an adult HIV centre population in Gaborone, Botswana. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2011, 85, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health, M.o. Handbook of the Botswana 2016 Integrated HIV Clincial Care Guidelines. Care, D.o.H.A.P.a., Ed. Ministry of Health: Gaborone, Botswana, 2016.
- Guvenir, M.; Arikan, A. Hepatitis B Virus: From Diagnosis to Treatment. Pol J Microbiol 2020, 69, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramvis, A. Molecular characteristics and clinical relevance of African genotypes and subgenotypes of hepatitis B virus. S Afr Med J 2018, 108, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.; Aref, N.; El-Hazmi, M.; Al-Hamoudi, W.; Alswat, K.; Helmy, A.; Sanai, F.M.; Abdo, A.A. Correlation between hepatitis B surface antigen titers and HBV DNA levels. Saudi J Gastroenterol 2013, 19, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Xie, Q.; Lu, X.; Yu, C.; Xu, K.; Ruan, B.; Cao, H.; Gao, H.; Li, L. Serum HBeAg and HBV DNA levels are not always proportional and only high levels of HBeAg most likely correlate with high levels of HBV DNA: A community-based study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017, 96, e7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Hu, K.Q. Rethinking the pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. J Med Virol 2015, 87, 1989–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinius, B.B.; Anderson, M.; Gobe, I.; Mokomane, M.; Choga, W.T.; Mutenga, S.R.; Mpebe, G.; Pretorius-Holme, M.; Musonda, R.; Gaolathe, T.; et al. High Prevalence of Hepatitis B Virus Infection Among People With HIV in Rural and Periurban Communities in Botswana. Open Forum Infect Dis 2023, 10, ofac707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mupfumi, L.; Moyo, S.; Molebatsi, K.; Thami, P.K.; Anderson, M.; Mogashoa, T.; Iketleng, T.; Makhema, J.; Marlink, R.; Kasvosve, I.; et al. Immunological non-response and low hemoglobin levels are predictors of incident tuberculosis among HIV-infected individuals on Truvada-based therapy in Botswana. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0192030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaolathe, T.; Wirth, K.E.; Holme, M.P.; Makhema, J.; Moyo, S.; Chakalisa, U.; Yankinda, E.K.; Lei, Q.; Mmalane, M.; Novitsky, V.; et al. Botswana’s progress toward achieving the 2020 UNAIDS 90-90-90 antiretroviral therapy and virological suppression goals: a population-based survey. Lancet HIV 2016, 3, e221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, M.L.; Rosenberg, D.M.; Lok, A.S. World-wide epidemiology of HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B and associated precore and core promoter variants. J Viral Hepat 2002, 9, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, N.; Talukdar, R.; Mazumder, S.; Khanna, S.; Tandon, R. Management of patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Postgrad Med J 2007, 83, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.; Gaseitsiwe, S.; Moyo, S.; Wessels, M.J.; Mohammed, T.; Sebunya, T.K.; Powell, E.A.; Makhema, J.; Blackard, J.T.; Marlink, R.; et al. Molecular characterisation of hepatitis B virus in HIV-1 subtype C infected patients in Botswana. BMC Infect Dis 2015, 15, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcellin, P.; Chang, T.T.; Lim, S.G.; Tong, M.J.; Sievert, W.; Shiffman, M.L.; Jeffers, L.; Goodman, Z.; Wulfsohn, M.S.; Xiong, S.; et al. Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2003, 348, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackaert, O.; McDougall, D.; Pérez-Ruixo, C.; Pérez-Ruixo, J.J.; Jezorwski, J.; Crauwels, H.M. Population Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Darunavir and Tenofovir Alafenamide in HIV-1-Infected Patients on the Darunavir/Cobicistat/Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Alafenamide Single-Tablet Regimen (AMBER and EMERALD Studies). AAPS J 2021, 23, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).