Submitted:
21 April 2024
Posted:
22 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Composition in Phenolic Compounds of By-Products
| Species | Phenolic Compounds | References |
|---|---|---|
| Artichoke | Apigenin, Caffeic acid, Caffeoylquinic acid, Chlorogenic acid, Coumaric acid, Cynarin, Ferulic acid, Luteolin Naringenin, Narirutin, Quinic acid | [7,9,10,11] |
| Broccoli | Caffeic acid, Chlorogenic acid, Coumaroylquinic acid, Ferulic acid, Kaempferol, Quercetin, Sinapic acid | [13,15,19,20] |
| Cauliflower | Caffeic acid, Coumaric acid, Ferulic acid, Kaempferol, Lutein, Quercetin, Sinapic acid | [16,43,44] |
| Citrus sp. | Apigenin, Benzoic acid, Caffeic acid, Caffeine, Caffeoylquinic acid, Caffeoyltartaric acid, Catechol, Catechin, Chlorogenic acid, Cinnamic acid, Cyanidin, Delphinidin, Dihydroxyflavone, Diosmin, Ellagic acid, Eriocitrin, Eriodictyol, Ferulic acid, Gallic acid, Gentisic acid, Hesperetin, Isorhamnetin, Isosakuranetin, Kaempferol, Luteolin, Malvidin, Myricetin, Naringenin, Naringin, Narirutin, Neoeriocitrin, Neohesperidin, p-OH-benzoic acid, Pelargonidin, Peonidin, Phloretin, Propylgallate, Quercetin, Resveratrol, Rosmarinic acid, Rutin, Scopoletin, Sinapic acid, Sinensetin, Syringic acid, Vanillin, Vanillic acid, Vitexin | [21,22,23,24,31,45,46,47,48] |
| Grape | Apigenin, Catechol, Catechin, Caftaric acid, Chlorogenic acid, Chrysoeriol, Cinnamic acid, Coumaric acid, Coutaric acid, Cyanidin, Delphinidin, Ellagic acid, Epicatechin, Eriodictyol, Ferulic acid, Gallic acid, Hesperidin, Hydroxybenzoic acid, Hyperoside, Isorhammnetin, Kaempferol, Luteolin, Malvidin, Morin, Myricetin, Naringenin, Peonidin, Petunidin, Procyanidin, Protocatechuic acid, Pyrogallol, Quercetin, Resveratrol, Rosmarinic acid, Rutin, Sinapaldehyde, Synergistic acid, Syringic acid, Vanillic acid, Ɛ-viniferin | [3,25,28,49,50,51,52,53] |
| Tomato | Apigenin, Caffeic acid, Catechin, Chloretic acid, Chlorogenic acid, Chrysin, Cinnamic acid, Coumaric acid, Eugenol, Gallic acid, Isoquercetin, Isorhamnetin, Kaempferol, Luteolin, Myricetin, Naringenin, p-OH-benzoic acid, Protocatechuic acid, Quercetin, Resveratrol, Rutin, Sinapic acid, Syringic acid, Vanillic acid | [3,15,25,30,31,54,55] |
| Onion | Coumaric acid, Ferulic acid, Isorhamnetin, Kaempferol, Myricetin, p-OH-benzoic acid, Protocatechuic acid, Quercetin, Vanillic acid, Vanillinic acid | [35,37] |
| Mushrooms | Caffeic acid, Catechin, Catechin gallate, Chlorogenic acid, Cinnamic acid, Coumaric acid, Ferulic acid, Gallic acid, Luteolin, Myricetin, Naringenin, p-OH-benzoic acid, Protocateic acid, Rutin, Syringic acid, Vanillic acid | [4,56,57,58,59] |
3. Extraction Processes and Inner Stability of Compounds
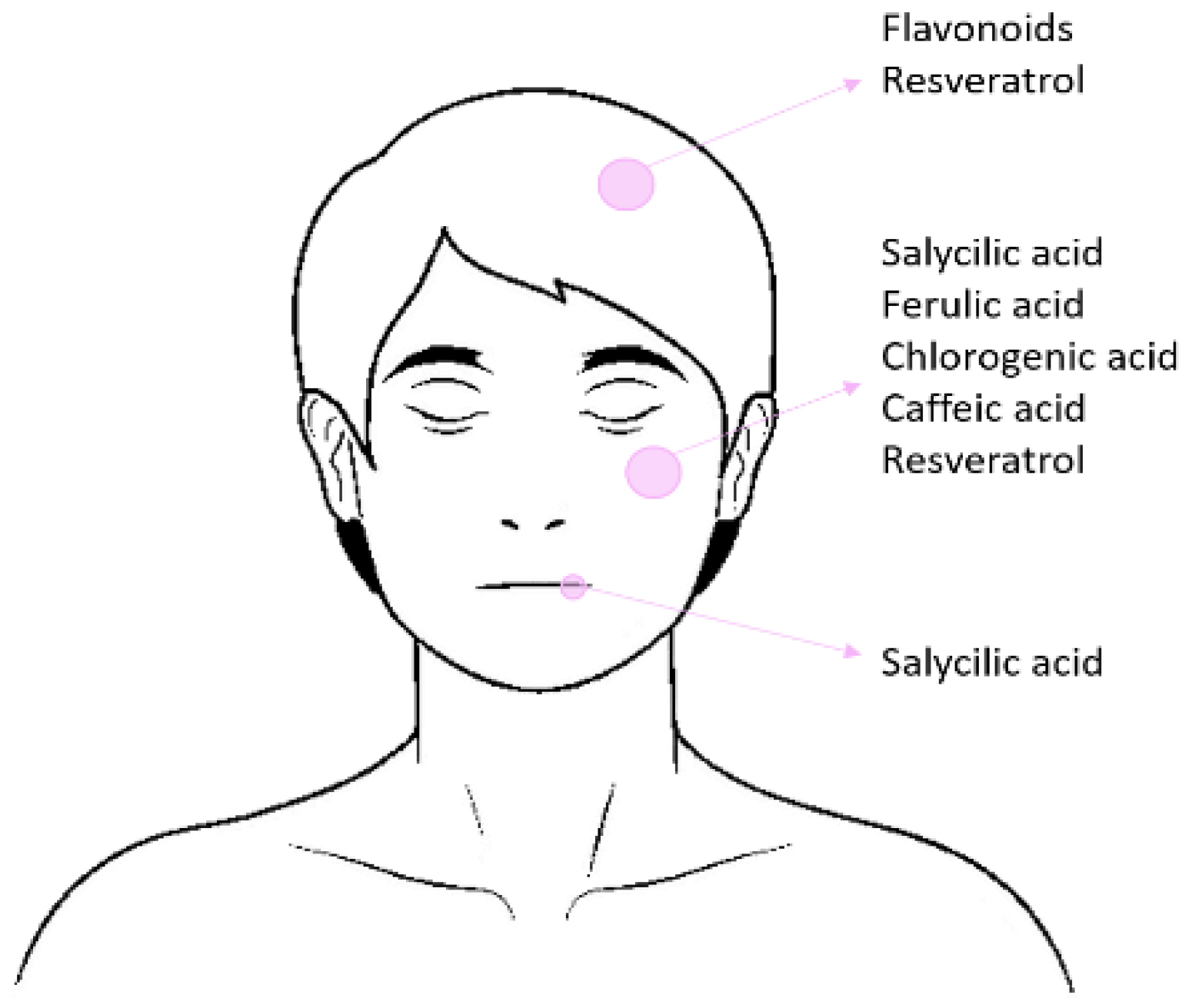
4. Cosmetic Formulation
4.1. Polar Phenolic Compounds
4.2. Non-Polar Phenolic Compounds
5. In Vitro Effects
5.1. Antioxidant Effect
5.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
5.3. Antimicrobial Effect
6. In Vivo Effects
| Plant Specie | Formulation | Cohort | In Vivo Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brassica oleracea var. Capitata f. rubra (red cabbage) | Ethosomal Carbopol 2% gel | Female human | Strong antioxidant activity with remarkable dermocosmetic benefits for skin. | [191] |
| Centella asiatica | Emulsion and hidrogel (5% extract) | Human | Moisturizing and anti-inflammatory activities. | [129] |
| Citrus x sinensis (red orange) | Aqueous/Aqueous-ethanolic solution extract | Healthy human with UVB-induced skin erythema | Antioxidant by radical scavenger activity: skin photoprotection | [186] |
| ROCTM | Human forearm | Photoprotective, anti-erythematic and antiaging activitiea | [197] | |
| Citrus unshiu (mandarin) | Ethanolic extract | Female SKH1-hairless mice. | Anti-inflammatory activity, useful as an anti-atopic agent. | [184] |
| Coffea arabica (coffee) | Alpha-tocopherol extract (5 mg/cm2). | Female hairless mice | Antioxidant and photo-protective activities | [198] |
| Cynara cardunculus var. Scolymus (artichoke) | Ethanolic extract formulated in cream (0,002%) | Female human with sagging face | Improvement of endothelial cells integrity, by enhancement of skin roughness and elasticity | [64] |
| Diospyros kaki (persimmon) | Emulgel | Human | Anti-aging activity. | [199] |
| Morus alba (mulberry) | Oil/water emulsion with 4% ethanolic extract. | Human | Whitening, antierythemic and moisturizing activities. | [166] |
| Moringa (moringa) | Cream (14% paraffin oil) formulation | Male human | Moisturizing activity. | [200] |
| Solanum lycopersicum (tomato) | Glycerinated formulation (3%) | Human | Moisturizing activity. | [171] |
| Vitis vinífera (grape) | Hydroethanolic extract (4 mg/40 μl/cm2) | SKH-1 hairless mice. | Photoprotective activity (against UV-B skin damage) | [173] |
| Oil-in-water solution (10%) | Healthy human | Photoprotective activity, synergic with sunscreen chemicals formulationAntioxidant and anti-photoaging activities. | [175] [176] |
|
| Sarmentine (1%) cream | Human | Anti-aging, moisturizing and skin whitening activities | [177] | |
| β-ciclodextrine formulated with solution (0,1%) | Human | Anti-aging activity | [178] |
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panzella, L. Natural Phenolic Compounds for Health, Food and Cosmetic Applications. Antioxidants 2020, Vol. 9, Page 427 2020, 9, 427. [CrossRef]
- Balasundram, N.; Sundram, K.; Samman, S. Phenolic Compounds in Plants and Agri-Industrial by-Products: Antioxidant Activity, Occurrence, and Potential Uses. Food Chem 2006, 99, 191–203. [CrossRef]
- Abbasi-Parizad, P.; De Nisi, P.; Scaglia, B.; Scarafoni, A.; Pilu, S.; Adani, F. Recovery of Phenolic Compounds from Agro-Industrial by-Products: Evaluating Antiradical Activities and Immunomodulatory Properties. Food and Bioproducts Processing 2021, 127, 338–348. [CrossRef]
- Antunes, F.; Marçal, S.; Taofiq, O.; Morais, A.M.M.B.; Freitas, A.C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Pintado, M. Valorization of Mushroom By-Products as a Source of Value-Added Compounds and Potential Applications. Molecules 2020, Vol. 25, Page 2672 2020, 25, 2672. [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Aparicio, I. Plant-Based by-Products. Food Waste Recovery: Processing Technologies, Industrial Techniques, and Applications 2021, 367–397. [CrossRef]
- Szabo, K.; Mitrea, L.; Călinoiu, L.F.; Teleky, B.E.; Martău, G.A.; Plamada, D.; Pascuta, M.S.; Nemeş, S.A.; Varvara, R.A.; Vodnar, D.C. Natural Polyphenol Recovery from Apple-, Cereal-, and Tomato-Processing By-Products and Related Health-Promoting Properties. Molecules 2022, Vol. 27, Page 7977 2022, 27, 7977. [CrossRef]
- Dabbou Sihema; Dabbou Samiaa; Pandino Gaetanoc; Lombardo Sarac; Mauromicale Giovanni c; Chahdoura Hassibaa; Gasco Laura d; Helal Ahmed Noureddinea In Vitro Antioxidant Activities and Phenolic Content in Crop Residues of Tunisian Globe Artichoke. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M. Recovery of High Added-Value Components from Food Wastes: Conventional, Emerging Technologies and Commercialized Applications. Trends Food Sci Technol 2012, 26, 68–87. [CrossRef]
- Claus, T.; Maruyama, S.A.; Palombini, S. V.; Montanher, P.F.; Bonafé, E.G.; de Oliveira Santos Junior, O.; Matsushita, M.; Visentainer, J. V. Chemical Characterization and Use of Artichoke Parts for Protection from Oxidative Stress in Canola Oil. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2015, 61, 346–351. [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-moreno, N.; Cimminelli, M.J.; Volpe, F.; Ansó, R.; Esparza, I.; Mármol, I.; Rodríguez-yoldi, M.J.; Ancín-azpilicueta, C. Phenolic Composition of Artichoke Waste and Its Antioxidant Capacity on Differentiated Caco-2 Cells. Nutrients 2019, Vol. 11, Page 1723 2019, 11, 1723. [CrossRef]
- Mena-García, A.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, S.; Ruiz-Matute, A.I.; Sanz, M.L. Exploitation of Artichoke Byproducts to Obtain Bioactive Extracts Enriched in Inositols and Caffeoylquinic Acids by Microwave Assisted Extraction. J Chromatogr A 2020, 1613, 460703. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cano, D.; Pérez-Llamas, F.; Frutos, M.J.; Arnao, M.B.; Espinosa, C.; López-Jiménez, J.Á.; Castillo, J.; Zamora, S. Chemical and Functional Properties of the Different By-Products of Artichoke (Cynara Scolymus L.) from Industrial Canning Processing. Food Chem 2014, 160, 134–140. [CrossRef]
- Costa-Pérez, A.; Moreno, D.A.; Periago, P.M.; García-Viguera, C.; Domínguez-Perles, R. A New Food Ingredient Rich in Bioaccessible (Poly)Phenols (and Glucosinolates) Obtained from Stabilized Broccoli Stalks. Foods 2022, 11, 1734. [CrossRef]
- Nartea, A.; Fanesi, B.; Pacetti, D.; Lenti, L.; Fiorini, D.; Lucci, P.; Frega, N.G.; Falcone, P.M. Cauliflower By-Products as Functional Ingredient in Bakery Foods: Fortification of Pizza with Glucosinolates, Carotenoids and Phytosterols. Curr Res Food Sci 2023, 6, 100437. [CrossRef]
- Aires, A.; Carvalho, R.; Saavedra, M.J. Reuse Potential of Vegetable Wastes (Broccoli, Green Bean and Tomato) for the Recovery of Antioxidant Phenolic Acids and Flavonoids. Int J Food Sci Technol 2017, 52, 98–107. [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, G.B.; Raes, K.; Coelus, S.; Struijs, K.; Smagghe, G.; Van Camp, J. Ultra(High)-Pressure Liquid Chromatography–Electrospray Ionization-Time-of-Flight-Ion Mobility-High Definition Mass Spectrometry for the Rapid Identification and Structural Characterization of Flavonoid Glycosides from Cauliflower Waste. J Chromatogr A 2014, 1323, 39–48. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xia, Y.; Liu, H.-Y.; Guo, H.; He, X.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, D.-T.; Mai, Y.-H.; Li, H.-B.; Zou, L.; et al. Nutritional Values, Beneficial Effects, and Food Applications of Broccoli (Brassica Oleracea Var. Italica Plenck). Trends Food Sci Technol 2022, 119, 288–308. [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, G.B.; Raes, K.; Coelus, S.; Struijs, K.; Smagghe, G.; Van Camp, J. Ultra(High)-Pressure Liquid Chromatography–Electrospray Ionization-Time-of-Flight-Ion Mobility-High Definition Mass Spectrometry for the Rapid Identification and Structural Characterization of Flavonoid Glycosides from Cauliflower Waste. J Chromatogr A 2014, 1323, 39–48. [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Perles, R.; Martínez-Ballesta, M.C.; Carvajal, M.; García-Viguera, C.; Moreno, D.A. Broccoli-Derived By-Products—A Promising Source of Bioactive Ingredients. J Food Sci 2010, 75, C383–C392. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xia, Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Guo, H.; He, X.Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, D.T.; Mai, Y.H.; Li, H. Bin; Zou, L.; et al. Nutritional Values, Beneficial Effects, and Food Applications of Broccoli (Brassica Oleracea Var. Italica Plenck). Trends Food Sci Technol 2022, 119, 288–308. [CrossRef]
- Fathy, H.M.; Abd El-Maksoud, A.A.; Cheng, W.; Elshaghabee, F.M.F. Value-Added Utilization of Citrus Peels in Improving Functional Properties and Probiotic Viability of Acidophilus-Bifidus-Thermophilus (ABT)-Type Synbiotic Yoghurt during Cold Storage. Foods 2022, 11, 2677. [CrossRef]
- Alamoudi, S.A.; Saad, A.M.; Alsubhi, N.H.; Alrefaei, G.I.; Al-Quwaie, D.A.; Binothman, N.; Aljadani, M.; Alharbi, M.; Alanazi, H.; Babalghith, A.O.; et al. Upgrading the Physiochemical and Sensory Quality of Yogurt by Incorporating Polyphenol-Enriched Citrus Pomaces with Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Antitumor Activities. Front Nutr 2022, 9, 999581. [CrossRef]
- Argun, M.E.; Argun, M.Ş.; Arslan, F.N.; Nas, B.; Ates, H.; Tongur, S.; Cakmakcı, O. Recovery of Valuable Compounds from Orange Processing Wastes Using Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction. J Clean Prod 2022, 375, 134169. [CrossRef]
- Gavahian, M.; Yang, Y.H.; Tsai, P.J. Power Ultrasound for Valorization of Citrus Limon (Cv. Eureka) Waste: Effects of Maturity Stage and Drying Method on Bioactive Compounds, Antioxidant, and Anti-Diabetic Activity. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 2022, 79, 103052. [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Reddivari, L.; Huang, J.Y. Enhancement of Phenolic Compounds Extraction from Grape Pomace by High Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma. LWT 2020, 133, 109970. [CrossRef]
- Trikas, E.D.; Melidou, M.; Papi, R.M.; Zachariadis, G.A.; Kyriakidis, D.A. Extraction, Separation and Identification of Anthocyanins from Red Wine by-Product and Their Biological Activities. J Funct Foods 2016, 25, 548–558. [CrossRef]
- Chakka, A.K.; Babu, A.S. Bioactive Compounds of Winery By-Products: Extraction Techniques and Their Potential Health Benefits. Applied Food Research 2022, 2, 100058. [CrossRef]
- El Gengaihi, S. Antioxidant Activity of Phenolic Compounds from Different Grape Wastes. J Food Process Technol 2014, 05. [CrossRef]
- Almeida, P. V.; Rodrigues, R.P.; Gaspar, M.C.; Braga, M.E.M.; Quina, M.J. Integrated Management of Residues from Tomato Production: Recovery of Value-Added Compounds and Biogas Production in the Biorefinery Context. J Environ Manage 2021, 299, 113505. [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, N.; Chiou, A.; Pyriochou, V.; Peristeraki, A.; Karathanos, V.T. Bioactive Phytochemicals in Industrial Tomatoes and Their Processing Byproducts. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2012, 49, 213–216. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Inda, B.; Esparza, I.; Moler, J.A.; Jiménez-Moreno, N.; Ancín-Azpilicueta, C. Valorization of Agri-Food Waste through the Extraction of Bioactive Molecules. Prediction of Their Sunscreen Action. J Environ Manage 2023, 325, 116460. [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.A.; Mansour, H.E.A.; Mosalam, E.M.; El-Shiekh, R.A.; Ezzat, S.M.; Zayed, A. Valorization of By-Products Derived from Onions and Potato: Extraction Optimization, Metabolic Profile, Outstanding Bioactivities, and Industrial Applications. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 1823–1858.
- Benito-Román, Ó.; Blanco, B.; Sanz, M.T.; Beltrán, S. Subcritical Water Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Onion Skin Wastes (Allium Cepa Cv. Horcal): Effect of Temperature and Solvent Properties. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1233. [CrossRef]
- Nile, S.H.; Nile, A.S.; Keum, Y.S.; Sharma, K. Utilization of Quercetin and Quercetin Glycosides from Onion (Allium Cepa L.) Solid Waste as an Antioxidant, Urease and Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors. Food Chem 2017, 235, 119–126. [CrossRef]
- Benito-román, Ó.; Blanco, B.; Sanz, M.T.; Beltrán, S. Subcritical Water Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Onion Skin Wastes (Allium Cepa Cv. Horcal): Effect of Temperature and Solvent Properties. Antioxidants 2020, Vol. 9, Page 1233 2020, 9, 1233. [CrossRef]
- Nile, S.H.; Nile, A.S.; Keum, Y.S.; Sharma, K. Utilization of Quercetin and Quercetin Glycosides from Onion (Allium Cepa L.) Solid Waste as an Antioxidant, Urease and Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors. Food Chem 2017, 235, 119–126. [CrossRef]
- Burri, S.C.M.; Ekholm, A.; Håkansson, Å.; Tornberg, E.; Rumpunen, K. Antioxidant Capacity and Major Phenol Compounds of Horticultural Plant Materials Not Usually Used. J Funct Foods 2017, 38, 119–127. [CrossRef]
- Salachna, P.; Łopusiewicz; Wesołowska, A.; Meller, E.; Piechocki, R. Mushroom Waste Biomass Alters the Yield, Total Phenolic Content, Antioxidant Activity and Essential Oil Composition of Tagetes Patula L. Ind Crops Prod 2021, 171, 113961. [CrossRef]
- Gąsecka, M.; Magdziak, Z.; Siwulski, M.; Mleczek, M. Profile of Phenolic and Organic Acids, Antioxidant Properties and Ergosterol Content in Cultivated and Wild Growing Species of Agaricus. European Food Research and Technology 2018, 244, 259–268. [CrossRef]
- Rong, P.; ; Liu, H.; Gan, B.; Wu, D.; Li, H.; Gan, R.; He, X.; Rong, P.; Liu, H.; Gan, B.; et al. Co-Fermentation of Edible Mushroom By-Products with Soybeans Enhances Nutritional Values, Isoflavone Aglycones, and Antioxidant Capacity of Douchi Koji. Foods 2022, Vol. 11, Page 2943 2022, 11, 2943. [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; Burgos, N.; Barnard, A.; Evans, G.; Preece, J.; Graz, M.; Ruthes, A.C.; Jiménez-Quero, A.; Martínez-Abad, A.; Vilaplana, F.; et al. Agaricus Bisporus and Its By-Products as a Source of Valuable Extracts and Bioactive Compounds. Food Chem 2019, 292, 176–187. [CrossRef]
- Umaña, M.; Eim, V.; Garau, C.; Rosselló, C.; Simal, S. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Ergosterol and Antioxidant Components from Mushroom by-Products and the Attainment of a β-Glucan Rich Residue. Food Chem 2020, 332, 127390. [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, G.B.; Smagghe, G.; Raes, K.; Van Camp, J. Combined Alkaline Hydrolysis and Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction for the Release of Nonextractable Phenolics from Cauliflower (Brassica Oleracea Var. Botrytis) Waste. J Agric Food Chem 2014, 62, 3371–3376. [CrossRef]
- Llorach, R.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Ferreres, F.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. HPLC-DAD-MS/MS ESI Characterization of Unusual Highly Glycosylated Acylated Flavonoids from Cauliflower (Brassica Oleracea L. Var. Botrytis) Agroindustrial Byproducts. J Agric Food Chem 2003, 51, 3895–3899. [CrossRef]
- Bocco, A.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Richard, H.; Berset, C. Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Composition of Citrus Peel and Seed Extracts. J Agric Food Chem 1998, 46, 2123–2129. [CrossRef]
- Goulas, V.; Manganaris, G.A. Exploring the Phytochemical Content and the Antioxidant Potential of Citrus Fruits Grown in Cyprus. Food Chem 2012, 131, 39–47. [CrossRef]
- Scurria, A.; Sciortino, M.; Albanese, L.; Nuzzo, D.; Zabini, F.; Meneguzzo, F.; Alduina, R.; Presentato, A.; Pagliaro, M.; Avellone, G.; et al. Flavonoids in Lemon and Grapefruit IntegroPectin**. ChemistryOpen 2021, 10, 1055–1058. [CrossRef]
- Viuda-Martos, M.; Fernandez-Lopez, J.; Sayas-Barbera, E.; Sendra, E.; Perez-Alvarez, J.A. PHYSICOCHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THE ORANGE JUICE WASTE WATER OF A CITRUS BY-PRODUCT. J Food Process Preserv 2011, 35, 264–271. [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.; Abdrabba, S. Physico-Chemical Characteristics, Fatty Acid, Composition of Grape Seed Oil and Phenolic Compounds of Whole Seeds, Seeds and Leaves of Red Grape in Libya; 2015; Vol. 2;.
- Leal, C.; Gouvinhas, I.; Santos, R.A.; Rosa, E.; Silva, A.M.; Saavedra, M.J.; Barros, A.I.R.N.A. Potential Application of Grape (Vitis Vinifera L.) Stem Extracts in the Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Industries: Valorization of a by-Product. Ind Crops Prod 2020, 154, 112675. [CrossRef]
- Pintać, D.; Majkić, T.; Torović, L.; Orčić, D.; Beara, I.; Simin, N.; Mimica–Dukić, N.; Lesjak, M. Solvent Selection for Efficient Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Grape Pomace. Ind Crops Prod 2018, 111, 379–390. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Gómez, R.; Zalacain, A.; Alonso, G.L.; Salinas, M.R. Vine-Shoot Waste Aqueous Extracts for Re-Use in Agriculture Obtained by Different Extraction Techniques: Phenolic, Volatile, and Mineral Compounds. J Agric Food Chem 2014, 62, 10861–10872. [CrossRef]
- Sciortino, M.; Avellone, G.; Scurria, A.; Bertoli, L.; Carnaroglio, D.; Bongiorno, D.; Pagliaro, M.; Ciriminna, R. Green and Quick Extraction of Stable Biophenol-Rich Red Extracts from Grape Processing Waste. ACS Food Science and Technology 2021, 1, 937–942. [CrossRef]
- Akao, S. Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Antioxidant Contents in Crop Residues for Potential Cascade Utilization. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 9, 1535–1542. [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Morales, M.; Espinosa-Alonso, L.G.; Espinoza-Torres, L.C.; Delgado-Vargas, F.; Medina-Godoy, S. Phenolic Content and Antioxidant and Antimutagenic Activities in Tomato Peel, Seeds, and Byproducts. J Agric Food Chem 2014, 62, 5281–5289. [CrossRef]
- Chuang, W.Y.; Liu, C.L.; Tsai, C.F.; Lin, W.C.; Chang, S.C.; Der Shih, H.; Shy, Y.M.; Lee, T.T. Evaluation of Waste Mushroom Compost as a Feed Supplement and Its Effects on the Fat Metabolism and Antioxidant Capacity of Broilers. Animals 2020, Vol. 10, Page 445 2020, 10, 445. [CrossRef]
- Ghahremani-Majd, H.; Dashti, F. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Cultivated Button Mushrooms (Agaricus Bisporus). Hortic Environ Biotechnol 2015, 56, 376–382. [CrossRef]
- Heleno, S.A.; Prieto, M.A.; Barros, L.; Rodrigues, A.; Barreiro, M.F.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Optimization of Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Ergosterol from Agaricus Bisporus L. by-Products Using Response Surface Methodology. Food and Bioproducts Processing 2016, 100, 25–35. [CrossRef]
- Reis, F.S.; Martins, A.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Antioxidant Properties and Phenolic Profile of the Most Widely Appreciated Cultivated Mushrooms: A Comparative Study between in Vivo and in Vitro Samples. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2012, 50, 1201–1207. [CrossRef]
- Sticher, O. Natural Product Isolation. Nat Prod Rep 2008, 25, 517–554. [CrossRef]
- Olejar, K.J.; Fedrizzi, B.; Kilmartin, P.A. Influence of Harvesting Technique and Maceration Process on Aroma and Phenolic Attributes of Sauvignon Blanc Wine. Food Chem 2015, 183, 181–189. [CrossRef]
- Ćujić, N.; Šavikin, K.; Janković, T.; Pljevljakušić, D.; Zdunić, G.; Ibrić, S. Optimization of Polyphenols Extraction from Dried Chokeberry Using Maceration as Traditional Technique. Food Chem 2016, 194, 135–142. [CrossRef]
- Garbetta, A.; Capotorto, I.; Cardinali, A.; D’Antuono, I.; Linsalata, V.; Pizzi, F.; Minervini, F. Antioxidant Activity Induced by Main Polyphenols Present in Edible Artichoke Heads: Influence of in Vitro Gastro-Intestinal Digestion. J Funct Foods 2014, 10, 456–464. [CrossRef]
- D’Antuono, I.; Carola, A.; Sena, L.M.; Linsalata, V.; Cardinali, A.; Logrieco, A.F.; Colucci, M.G.; Apone, F. Artichoke Polyphenols Produce Skin Anti-Age Effects by Improving Endothelial Cell Integrity and Functionality. Molecules 2018, 23. [CrossRef]
- Safdar, M.N.; Kausar, T.; Jabbar, S.; Mumtaz, A.; Ahad, K.; Saddozai, A.A. Extraction and Quantification of Polyphenols from Kinnow ( Citrus Reticulate L.) Peel Using Ultrasound and Maceration Techniques. J Food Drug Anal 2017, 25, 488–500. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Q.; Chen, J.C.; Liu, D.H.; Ye, X.Q. Simultaneous Extraction of Phenolic Compounds of Citrus Peel Extracts: Effect of Ultrasound. Ultrason Sonochem 2009, 16, 57–62. [CrossRef]
- Ghomari, O.; Sounni, F.; Massaoudi, Y.; Ghanam, J.; Drissi Kaitouni, L.B.; Merzouki, M.; Benlemlih, M. Phenolic Profile (HPLC-UV) of Olive Leaves According to Extraction Procedure and Assessment of Antibacterial Activity. Biotechnology Reports 2019, 23, e00347. [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, B.; Christen, P. Recent Extraction Techniques for Natural Products: Microwave-Assisted Extraction and Pressurised Solvent Extraction. Phytochemical Analysis 2002, 13, 105–113. [CrossRef]
- Sałata, A.; Lombardo, S.; Pandino, G.; Mauromicale, G.; Buczkowska, H.; Nurzyńska-Wierdak, R. Biomass Yield and Polyphenol Compounds Profile in Globe Artichoke as Affected by Irrigation Frequency and Drying Temperature. Ind Crops Prod 2022, 176, 114375. [CrossRef]
- Antony, A.; Farid, M. Effect of Temperatures on Polyphenols during Extraction. Applied Sciences 2022, Vol. 12, Page 2107 2022, 12, 2107. [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.Y.; Eh Suk, V.R.; Gew, L.T. Plant Polyphenols as Green Sunscreen Ingredients: A Systematic Review. J Cosmet Dermatol 2022, 21, 5409–5444. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Lin, L.G.; Ye, W.C. Techniques for Extraction and Isolation of Natural Products: A Comprehensive Review. Chinese Medicine (United Kingdom) 2018, 13, 1–26. [CrossRef]
- Mollica, A.; Stefanucci, A.; Zengin, G.; Locatelli, M.; Macedonio, G.; Orlando, G.; Ferrante, C.; Menghini, L.; Recinella, L.; Leone, S.; et al. Polyphenolic Composition, Enzyme Inhibitory Effects Ex-Vivo and in-Vivo Studies on Two Brassicaceae of North-Central Italy. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2018, 107, 129–138. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Huang, S.; Sun, J.; Song, X.; Nishanbaev, S.Z.; Benito, M.J.; Wu, Y. Effects of Polyphenols and Glucosinolates in Broccoli Extract on Human Gut Microorganisms Based on Simulation In Vitro. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 45096–45106. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, B.; Chen, X.; Huang, P.; Chen, K.; Ma, Y.; Agarry, I.E.; Kan, J. Optimization and Comparison of Nonconventional Extraction Techniques for Soluble Phenolic Compounds from Brocade Orange (Citrus Sinensis) Peels. J Food Sci 2022, 87, 4917–4929. [CrossRef]
- Cotoras, M.; Vivanco, H.; Melo, R.; Aguirre, M.; Silva, E.; Mendoza, L. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of the Antioxidant and Prooxidant Activity of Phenolic Compounds Obtained from Grape (Vitis Vinifera) Pomace. Molecules 2014, Vol. 19, Pages 21154-21167 2014, 19, 21154–21167. [CrossRef]
- Souhila, M.; Nacéra, M. Biological Activities of Phenolics in Different Parts of Local Cultivar of Globe Artichoke (Cynara Cardunculus, Var. Scolymus L.). Biology and Life Sciences Forum 2022, Vol. 16, Page 30 2022, 16, 30. [CrossRef]
- De Zordi, N.; Cortesi, A.; Kikic, I.; Moneghini, M.; Solinas, D.; Innocenti, G.; Portolan, A.; Baratto, G.; Dall’Acqua, S. The Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction of Polyphenols from Propolis: A Central Composite Design Approach. J Supercrit Fluids 2014, 95, 491–498. [CrossRef]
- Casas, L.; Mantell, C.; Rodríguez, M.; Ossa, E.J.M. de la; Roldán, A.; Ory, I. De; Caro, I.; Blandino, A. Extraction of Resveratrol from the Pomace of Palomino Fino Grapes by Supercritical Carbon Dioxide. J Food Eng 2010, 96, 304–308. [CrossRef]
- Arnáiz, E.; Bernal, J.; Martín, M.T.; Diego, J.C.; Bernal, J.L.; Recio, L.T. Optimisation of the Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Antioxidants from Broccoli Leaves. Food Anal Methods 2016, 9, 2174–2181. [CrossRef]
- Alara, O.R.; Abdurahman, N.H. Kinetics Studies on Effects of Extraction Techniques on Bioactive Compounds from Vernonia Cinerea Leaf. J Food Sci Technol 2019, 56, 580–588. [CrossRef]
- Rudić, S.; Dimitrijević-Branković, S.; Dimitrijević, S.; Milić, M. Valorization of Unexploited Artichoke Leaves Dust for Obtaining of Extracts Rich in Natural Antioxidants. Sep Purif Technol 2021, 256, 117714. [CrossRef]
- Hayat, K.; Hussain, S.; Abbas, S.; Farooq, U.; Ding, B.; Xia, S.; Jia, C.; Zhang, X.; Xia, W. Optimized Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Phenolic Acids from Citrus Mandarin Peels and Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity in Vitro. Sep Purif Technol 2009, 70, 63–70. [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.; Dahmoune, F.; Moussi, K.; Remini, H.; Dairi, S.; Aoun, O.; Khodir, M. Comparison of Microwave, Ultrasound and Accelerated-Assisted Solvent Extraction for Recovery of Polyphenols from Citrus Sinensis Peels. Food Chem 2015, 187, 507–516. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Deng, Z.; Liu, R.; Loewen, S.; Tsao, R. Bioaccessibility, in Vitro Antioxidant Activities and in Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Activities of a Purple Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum L.). Food Chem 2014, 159, 353–360. [CrossRef]
- Vinatoru, M. An Overview of the Ultrasonically Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Principles from Herbs.
- Rabelo, R.S.; MacHado, M.T.C.; Martínez, J.; Hubinger, M.D. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction and Nanofiltration of Phenolic Compounds from Artichoke Solid Wastes. J Food Eng 2016, 178, 170–180. [CrossRef]
- Reche, C.; Rosselló, C.; Umaña, M.M.; Eim, V.; Simal, S. Mathematical Modelling of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Kinetics of Bioactive Compounds from Artichoke By-Products. Foods 2021, Vol. 10, Page 931 2021, 10, 931. [CrossRef]
- Saleh, I.A.; Vinatoru, M.; Mason, T.J.; Abdel-Azim, N.S.; Aboutabl, E.A.; Hammouda, F.M. A Possible General Mechanism for Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE) Suggested from the Results of UAE of Chlorogenic Acid from Cynara Scolymus L. (Artichoke) Leaves. Ultrason Sonochem 2016, 31, 330–336. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Badr, A.; Desjardins, Y.; Gosselin, A.; Angers, P. Characterization of Industrial Broccoli Discards (Brassica Oleracea Var. Italica) for Their Glucosinolate, Polyphenol and Flavonoid Contents Using UPLC MS/MS and Spectrophotometric Methods. Food Chem 2018, 245, 1204–1211. [CrossRef]
- González-Centeno, M.R.; Comas-Serra, F.; Femenia, A.; Rosselló, C.; Simal, S. Effect of Power Ultrasound Application on Aqueous Extraction of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity from Grape Pomace (Vitis Vinifera L.): Experimental Kinetics and Modeling. Ultrason Sonochem 2015, 22, 506–514. [CrossRef]
- Gómez-García, R.; Martínez-A ´ Vila •, G.C.G.; Aguilar, C.N. Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Antioxidative Phenolics from Grape (Vitis Vinifera L.) Residues. 3 Biotech 2012 2:4 2012, 2, 297–300. [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.Y.; Howard, L.R. Effects of Solvent and Temperature on Pressurized Liquid Extraction of Anthocyanins and Total Phenolics from Dried Red Grape Skin. J Agric Food Chem 2003, 51, 5207–5213. [CrossRef]
- Alara, O.R.; Abdurahman, N.H.; Ukaegbu, C.I. Extraction of Phenolic Compounds: A Review. Curr Res Food Sci 2021, 4, 200–214. [CrossRef]
- de Lima Cherubim, D.J.; Buzanello Martins, C.V.; Oliveira Fariña, L.; da Silva de Lucca, R.A. Polyphenols as Natural Antioxidants in Cosmetics Applications. J Cosmet Dermatol 2020, 19, 33–37. [CrossRef]
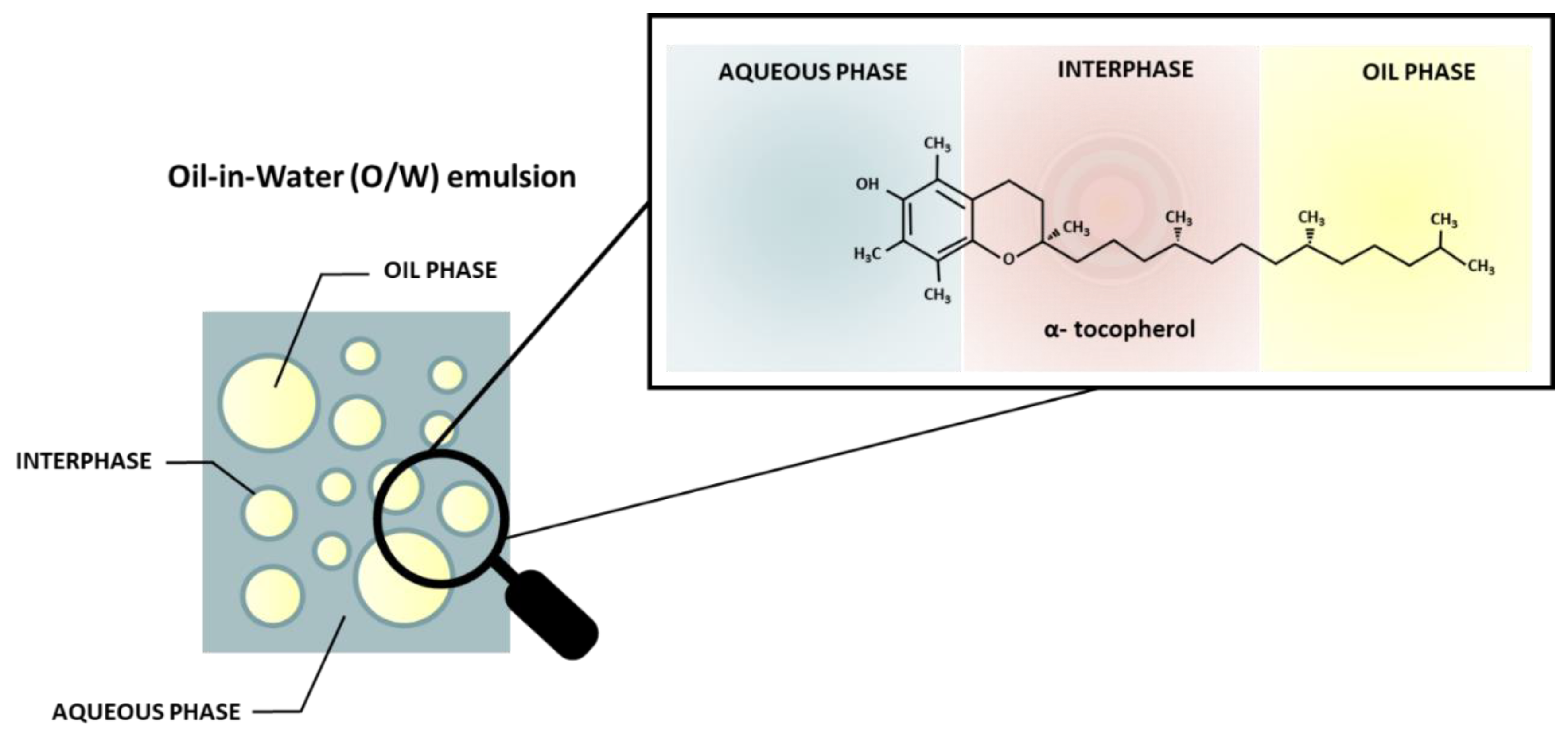
- Cholakova, D.; Vinarov, Z.; Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D. Self-Emulsification in Chemical and Pharmaceutical Technologies. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 2022, 59, 101576. [CrossRef]
- Berton-Carabin, C.C.; Ropers, M.H.; Genot, C. Lipid Oxidation in Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Involvement of the Interfacial Layer. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 2014, 13, 945–977. [CrossRef]
- Bock, A.; Steinhäuser, U.; Drusch, S. Partitioning Behavior and Interfacial Activity of Phenolic Acid Derivatives and Their Impact on β-Lactoglobulin at the Oil-Water Interface. Food Biophys 2021, 16, 191–202. [CrossRef]
- Romsted, L.S.; Bravo-Díaz, C. Modeling Chemical Reactivity in Emulsions. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 2013, 18, 3–14. [CrossRef]
- Di Mattia, C.D.; Sacchetti, G.; Mastrocola, D.; Sarker, D.K.; Pittia, P. Surface Properties of Phenolic Compounds and Their Influence on the Dispersion Degree and Oxidative Stability of Olive Oil O/W Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll 2010, 24, 652–658. [CrossRef]
- Almajano, M.P.; Delgado, M.E.; Gordon, M.H. Albumin Causes a Synergistic Increase in the Antioxidant Activity of Green Tea Catechins in Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Food Chem 2007, 102, 1375–1382. [CrossRef]
- Leopoldini, M.; Chiodo, S.G.; Russo, N.; Toscano, M. Detailed Investigation of the OH Radical Quenching by Natural Antioxidant Caffeic Acid Studied by Quantum Mechanical Models. J Chem Theory Comput 2011, 7, 4218–4233. [CrossRef]
- Yesiltas, B.; Sørensen, A.D.M.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Anankanbil, S.; Guo, Z.; Jacobsen, C. Modified Phosphatidylcholine with Different Alkyl Chain Length and Covalently Attached Caffeic Acid Affects the Physical and Oxidative Stability of Omega-3 Delivery 70% Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Food Chem 2019, 289, 490–499. [CrossRef]
- Magnani, C.; Isaac, V.L.B.; Correa, M.A.; Salgado, H.R.N. Caffeic Acid: A Review of Its Potential Use in Medications and Cosmetics. Analytical Methods 2014, 6, 3203–3210. [CrossRef]
- Milenković, D.; Đorović, J.; Petrović, V.; Avdović, E.; Marković, Z. Hydrogen Atom Transfer versus Proton Coupled Electron Transfer Mechanism of Gallic Acid with Different Peroxy Radicals. Reaction Kinetics, Mechanisms and Catalysis 2018, 123, 215–230. [CrossRef]
- Di Mattia, C.D.; Sacchetti, G.; Mastrocola, D.; Pittia, P. Effect of Phenolic Antioxidants on the Dispersion State and Chemical Stability of Olive Oil O/W Emulsions. Food Research International 2009, 42, 1163–1170. [CrossRef]
- Terpinc, P.; Abramovič, H. A Kinetic Approach for Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity of Selected Phenolic Acids. Food Chem 2010, 121, 366–371. [CrossRef]
- Kittipongpittaya, K.; Panya, A.; Phonsatta, N.; Decker, E.A. Effects of Environmental PH on Antioxidant Interactions between Rosmarinic Acid and α-Tocopherol in Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions. J Agric Food Chem 2016, 64, 6575–6583. [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.B.; Wang, B.; Zisu, B.; Adhikari, B. Complexation between Flaxseed Protein Isolate and Phenolic Compounds: Effects on Interfacial, Emulsifying and Antioxidant Properties of Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll 2019, 94, 20–29. [CrossRef]
- Gulcin, İ. Antioxidants and Antioxidant Methods: An Updated Overview. Archives of Toxicology 2020 94:3 2020, 94, 651–715. [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.R.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.H. Oxidative Stability of Oil-in-Water Emulsions with α-Tocopherol, Charged Emulsifier, and Different Oxidative Stress. Food Sci Biotechnol 2018, 27, 1571–1578. [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Astete, C.E.; Sabliov, C.M. Entrapment and Delivery of α-Tocopherol by a Self-Assembled, Alginate-Conjugated Prodrug Nanostructure. Food Hydrocoll 2017, 72, 62–72. [CrossRef]
- Gim, S.Y.; Jung, J.; Kwon, Y.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, G.H.; Lee, J.H. Effects of Chitosan and Collagen Containing α-Tocopherol on the Oxidative Stability in Bulk Oil and Oil-in-Water Emulsion. Food Sci Biotechnol 2018, 27, 947–956. [CrossRef]
- Marefati, A.; Bertrand, M.; Sjöö, M.; Dejmek, P.; Rayner, M. Storage and Digestion Stability of Encapsulated Curcumin in Emulsions Based on Starch Granule Pickering Stabilization. Food Hydrocoll 2017, 63, 309–320. [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.R.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, B. Bioaccessibility and Antioxidant Activity of Curcumin after Encapsulated by Nano and Pickering Emulsion Based on Chitosan-Tripolyphosphate Nanoparticles. Food Research International 2016, 89, 399–407. [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, X.Y.; Lee, J.H. Effects of Flavonoids on Physical and Oxidative Stability of Soybean Oil O/W Emulsions. Food Sci Biotechnol 2015, 24, 851–858. [CrossRef]
- Toiu, A.; Vlase, L.; Oniga, I.; Benedec, D.; Tămaş, M. HPLC ANALYSIS OF SALICYLIC DERIVATIVES FROM NATURAL PRODUCTS; 2011; Vol. 59;.
- Brackett W. The Chemistry of Salicylic Acid. Cosmet Derm. 1997, 10, 5–6.
- Arif, T. Salicylic Acid as a Peeling Agent: A Comprehensive Review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2015, 8, 455–461. [CrossRef]
- Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. Phenolic Acids Used in the Cosmetics Industry as Natural Antioxidants. 2019.
- Carlotti, M.E.; Battaglia, L.; Ugazio, E.; Gallarate, M.; Debernardi, F. Study on the Release Properties and Stability of o/w Emulsions Containing Salicylic Acid and Zinc Oxide. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 2004, 14, 119–126. [CrossRef]
- Imayama, S.; Ueda, S.; Isoda, M. Histologic Changes in the Skin of Hairless Mice Following Peeling With Salicylic Acid. Arch Dermatol 2000, 136, 1390–1395. [CrossRef]
- Combrinck, J.; Otto, A.; Du Plessis, J. Whey Protein/Polysaccharide-Stabilized Emulsions: Effect of Polymer Type and PH on Release and Topical Delivery of Salicylic Acid. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 588–600. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Pruthi, V. Potential Applications of Ferulic Acid from Natural Sources. Biotechnology Reports 2014, 4, 86–93. [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.J.; Hartley, R.D. Phenolic Constituents of the Cell Walls of Monocotyledons. Biochem Syst Ecol 1980, 8, 153–160. [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, A.; Cristiano, M.C.; Pandolfo, R.; Greco, M.; Fresta, M.; Paolino, D. Improvement of Ferulic Acid Antioxidant Activity by Multiple Emulsions: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Nanomaterials 2021, Vol. 11, Page 425 2021, 11, 425. [CrossRef]
- Pernin, A.; Bosc, V.; Soto, P.; Le Roux, E.; Maillard, M.N. Lipid Oxidation in Oil-in-Water Emulsions Rich in Omega-3: Effect of Aqueous Phase Viscosity, Emulsifiers, and Antioxidants. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology 2019, 121, 1800462. [CrossRef]
- Pernin, A.; Bosc, V.; Maillard, M.N.; Dubois-Brissonnet, F. Ferulic Acid and Eugenol Have Different Abilities to Maintain Their Inhibitory Activity against Listeria Monocytogenes in Emulsified Systems. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 433333. [CrossRef]
- Ratz-Łyko, A.; Arct, J. Resveratrol as an Active Ingredient for Cosmetic and Dermatological Applications: A Review. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy 2019, 21, 84–90.
- Kotha, R.R.; Tareq, F.S.; Yildiz, E.; Luthria, D.L. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants—A Critical Review on In Vitro Antioxidant Assays. Antioxidants 2022, Vol. 11, Page 2388 2022, 11, 2388. [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, I.G.; Apetrei, C. Analytical Methods Used in Determining Antioxidant Activity: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, Vol. 22, Page 3380 2021, 22, 3380. [CrossRef]
- Lattanzio, V.; Kroon, P.A.; Linsalata, V.; Cardinali, A. Globe Artichoke: A Functional Food and Source of Nutraceutical Ingredients. J Funct Foods 2009, 1, 131–144. [CrossRef]
- Pistón, M.; Machado, I.; Branco, C.S.; Cesio, V.; Heinzen, H.; Ribeiro, D.; Fernandes, E.; Chisté, R.C.; Freitas, M. Infusion, Decoction and Hydroalcoholic Extracts of Leaves from Artichoke (Cynara Cardunculus L. Subsp. Cardunculus) Are Effective Scavengers of Physiologically Relevant ROS and RNS. Food Research International 2014, 64, 150–156. [CrossRef]
- Marques, P.; Marto, J.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Pacheco, R.; Fitas, M.; Pinto, P.; Serralheiro, M.L.M.; Ribeiro, H. Cynara Scolymus L.: A Promising Mediterranean Extract for Topical Anti-Aging Prevention. Ind Crops Prod 2017, 109, 699–706. [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zhao, S.; Ning, Z.; Zeng, H.; Shu, Y.; Tao, O.; Xiao, C.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Citrus Fruits as a Treasure Trove of Active Natural Metabolites That Potentially Provide Benefits for Human Health. Chemistry Central Journal 2015 9:1 2015, 9, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, B.; Malfa, G.A.; Acquaviva, R.; La Mantia, A.; Di Giacomo, C. Phytocomplex of a Standardized Extract from Red Orange (Citrus Sinensis L. Osbeck) against Photoaging. Cells 2022, 11, 1447. [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xu, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H. Protective Effect of Lemon Peel Polyphenols on Oxidative Stress-Induced Damage to Human Keratinocyte HaCaT Cells Through Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Front Nutr 2021, 7, 606776. [CrossRef]
- Gudiño, I.; Martín, A.; Casquete, R.; Prieto, M.H.; Ayuso, M.C.; Córdoba, M.G. Evaluation of Broccoli (Brassica Oleracea Var. Italica) Crop by-Products as Sources of Bioactive Compounds. Sci Hortic 2022, 304, 111284. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, D.W.; Lim, S.R.; Sung, J.; Kim, T.H.; Min, I.S.; Choi, C.H.; Lee, S.J. Kaempferol Blocks the Skin Fibroblastic Interleukin 1β Expression and Cytotoxicity Induced by 12-o-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-Acetate by Suppressing c-Jun n-Terminal Kinase. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3079. [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.M.; Hossain, M.L.; Mitra, K.; Hossain, B.; Bithi, U.H.; Uddin, M.N. Phytochemicals and In-Vitro Antioxidant Activity Analysis of Aloe Vera by-Products (Skin) in Different Solvent Extract. J Agric Food Res 2022, 10, 100460. [CrossRef]
- Benincasa, C.; La Torre, C.; Plastina, P.; Fazio, A.; Perri, E.; Caroleo, M.C.; Gallelli, L.; Cannataro, R.; Cione, E. Hydroxytyrosyl Oleate: Improved Extraction Procedure from Olive Oil and By-Products, and In Vitro Antioxidant and Skin Regenerative Properties. Antioxidants 2019, Vol. 8, Page 233 2019, 8, 233. [CrossRef]
- Maluf, D.F.; Gonçalves, M.M.; D’Angelo, R.W.O.; Girassol, A.B.; Tulio, A.P.; Pupo, Y.M.; Farago, P. V. Cytoprotection of Antioxidant Biocompounds from Grape Pomace: Further Exfoliant Phytoactive Ingredients for Cosmetic Products. Cosmetics 2018, Vol. 5, Page 46 2018, 5, 46. [CrossRef]
- Hoss, I.; Rajha, H.N.; El Khoury, R.; Youssef, S.; Manca, M.L.; Manconi, M.; Louka, N.; Maroun, R.G. Valorization of Wine-Making By-Products’ Extracts in Cosmetics. Cosmetics 2021, Vol. 8, Page 109 2021, 8, 109. [CrossRef]
- Limsuwan, T.; Amnuikit, T. Effect of Grape Seed Extract in Sunscreen Lotion on Sun Protection Factor (SPF) Determined by in Vitro Method. ACM International Conference Proceeding Series 2017, Part F130950, 109–112. [CrossRef]
- Ziemlewska, A.; Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Nizioł-Łukaszewska, Z. Assessment of Cytotoxicity and Antioxidant Properties of Berry Leaves as By-Products with Potential Application in Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Products. Scientific Reports 2021 11:1 2021, 11, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.; Palmeira-de-Oliveira, A.; Das Neves, J.; Sarmento, B.; Amaral, M.H.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Coffee Silverskin: A Possible Valuable Cosmetic Ingredient. Pharm Biol 2015, 53, 386–394. [CrossRef]
- Yepes-molina, L.; Hernández, J.A.; Carvajal, M. Nanoencapsulation of Pomegranate Extract to Increase Stability and Potential Dermatological Protection. Pharmaceutics 2021, Vol. 13, Page 271 2021, 13, 271. [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.; Oliveira, H.; Fernandes, I.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Perez-Gregorio, R. Recent Advances in Extracting Phenolic Compounds from Food and Their Use in Disease Prevention and as Cosmetics. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2021, 61, 1130–1151. [CrossRef]
- Maurya, A.K.; Mohanty, S.; Pal, A.; Chanotiya, C.S.; Bawankule, D.U. The Essential Oil from Citrus Limetta Risso Peels Alleviates Skin Inflammation: In-Vitro and in-Vivo Study. J Ethnopharmacol 2018, 212, 86–94. [CrossRef]
- Carpentieri, S.; Augimeri, G.; Ceramella, J.; Vivacqua, A.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Pataro, G.; Bonofiglio, D.; Ferrari, G. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Extracts from Pulsed Electric Field-Treated Artichoke By-Products in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Human THP-1 Macrophages. Foods 2022, 11, 2250. [CrossRef]
- Punzo, A.; Porru, E.; Silla, A.; Simoni, P.; Galletti, P.; Roda, A.; Tagliavini, E.; Samorì, C.; Caliceti, C. Grape Pomace for Topical Application: Green Nades Sustainable Extraction, Skin Permeation Studies, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities Characterization in 3d Human Keratinocytes. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1181. [CrossRef]
- Richard, N.; Arnold, S.; Hoeller, U.; Kilpert, C.; Wertz, K.; Schwager, J. Hydroxytyrosol Is the Major Anti-Inflammatory Compound in Aqueous Olive Extracts and Impairs Cytokine and Chemokine Production in Macrophages. Planta Med 2011, 77, 1890–1897. [CrossRef]
- Yepes-Molina, L.; Pérez-Jiménez, M.I.; Martínez-Esparza, M.; Teruel, J.A.; Ruiz-Alcaraz, A.J.; García-Peñarrubia, P.; Carvajal, M. Membrane Vesicles for Nanoencapsulated SulforaphaneIncreased Their Anti-Inflammatory Role on an In Vitro Human Macrophage Model. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 1940. [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, M.; Morohashi, M. Pathogenesis of Acne. Medical Electron Microscopy 2001, 34, 29–40. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Summanen, P.H.; Downes, J.; Corbett, K.; Komoriya, T.; Henning, S.M.; Kim, J.; Finegold, S.M. Antimicrobial Activity of Pomegranate and Green Tea Extract on Propionibacterium Acnes, Propionibacterium Granulosum, Staphylococcus Aureus and Staphylococcus Epidermidis. J Drugs Dermatol 2015, 14, 574–578.
- Nabavi, S.F.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Izadi, M.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Daglia, M.; Nabavi, S.M. Antibacterial Effects of Cinnamon: From Farm to Food, Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Industries. Nutrients 2015, Vol. 7, Pages 7729-7748 2015, 7, 7729–7748. [CrossRef]
- Ravindran P N; Nirmal-Babu, K.; Shylaja, M.R. Cinnamon and Cassia. . CRC Press 2003.
- Foss, S.R.; Nakamura, C. V.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Cortez, D.A.G.; Endo, E.H.; Dias Filho, B.P. Antifungal Activity of Pomegranate Peel Extract and Isolated Compound Punicalagin against Dermatophytes. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 2014, 13, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Karray, A.; Krayem, N.; Saad, H. Ben; Sayari, A. Spirulina Platensis, Punica Granatum Peel, and Moringa Leaves Extracts in Cosmetic Formulations: An Integrated Approach of in Vitro Biological Activities and Acceptability Studies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2021, 28, 8802–8811. [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.C.; Chan, W.C. Nanotoxicity: The Growing Need for in Vivo Study. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2007, 18, 565–571.
- Fonseca-Santos, B.; Antonio Corrêa, M.; Chorilli, M. Sustainability, Natural and Organic Cosmetics: Consumer, Products, Efficacy, Toxicological and Regulatory Considerations. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2015, 51, 17–26. [CrossRef]
- Pistollato, F.; Madia, F.; Corvi, R.; Munn, S.; Grignard, E.; Paini, A.; Worth, A.; Bal-Price, A.; Prieto, P.; Casati, S.; et al. Current EU Regulatory Requirements for the Assessment of Chemicals and Cosmetic Products: Challenges and Opportunities for Introducing New Approach Methodologies. Arch Toxicol 2021, 95, 1867–1897.
- Knight, J.; Rovida, C.; Kreiling, R.; Zhu, C.; Knudsen, M.; Hartung, T. Continuing Animal Tests on Cosmetic Ingredients for REACH in the EU. ALTEX 2021, 38, 653–668. [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-T.; Shin, B.-S.; Kim, B.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Jo, B.-K. Inhibitory Effects of Ramulus Mori Extracts on Melanogenesis. J Cosmet Sci 2003, 54, 133–142.
- Sánchez-Salcedo, E.M.; Mena, P.; García-Viguera, C.; Hernández, F.; Martínez, J.J. (Poly)Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of White (Morus Alba) and Black (Morus Nigra) Mulberry Leaves: Their Potential for New Products Rich in Phytochemicals. J Funct Foods 2015, 18, 1039–1046. [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Hisham, J.; Shoaib Khan, H.M.; Ali Khan, B.; Saeed, T. Whitening and Antierythemic Effect of a Cream Containing Morus Alba Extract. Hygeia.J.D.Med 2012, 4, 97–103.
- Diamantino, M.E. dos S.; Chaves, A.C.T.A.; Silva, D. de M.; Lemos, G. da S.; Queiroz, R.F. Formulation of an Antioxidant Cosmetic Cream Containing Coffea Arabica Fractions. International Journal of Advanced Engineering Research and Science 2019, 6, 731–737. [CrossRef]
- Kiattisin, K.; Poomanee, W.; Leelapornpisid, P.; Viernstein, H.; Nitthikan, N.; Mueller, M.; Mai Sci, C.J. Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant Activities and Safety of Coffea Arabica Leaf Extract for Alternative Cosmetic Ingredient Antibody Formulation View Project Encapsulation of Sesbania Grandiflora Extract in Polymeric Micelles to Enhance Its Solubility, Stability, and Antibacterial Activity View Project Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant Activities and Safety of Coffea Arabica Leaf Extract for Alternative Cosmetic Ingredient; 2018; Vol. 46;.
- Santos, É.M. dos; Macedo, L.M. de; Tundisi, L.L.; Ataide, J.A.; Camargo, G.A.; Alves, R.C.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Mazzola, P.G. Coffee By-Products in Topical Formulations: A Review. Trends Food Sci Technol 2021, 111, 280–291.
- Barbulova, A.; Colucci, G.; Apone, F. New Trends in Cosmetics: By-Products of Plant Origin and Their Potential Use as Cosmetic Active Ingredients. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 82–92.
- Villacís Vargas, C.E.; Borja, D. Elaboración y Comprobación de La Eficacia in Vivo de Crema Humectante Con Extracto de Tomate (Lycopersicum Esculentum, Solanáceae) y Arazá (Eugenia Stipitata, Myrtáceae). Maestría en Ciencias y Tecnologías Cosméticas, Universidad Politécnica Salesiana: Quito, 2014.
- Li, H.; Deng, Z.; Liu, R.; Loewen, S.; Tsao, R. Bioaccessibility, in Vitro Antioxidant Activities and in Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Activities of a Purple Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum L.). Food Chem 2014, 159, 353–360. [CrossRef]
- Filip, A.; Clichici, S.; Doina, D.; Catoi, C. Chemopreventive Effects of Calluna Vulgaris and Vitis Vinifera Extracts on UVB-Induced Skin Damage in SKH-1 Hairless Mice Veterinary Cancer Guidelines and Protocols (VCGP) View Project Phytochemical Screening and Therapeutic Properties Evaluation of the Fluid Extract of Artemisia Annua L. View Project; 2011;
- Goufo, P.; Singh, R.K.; Cortez, I. A Reference List of Phenolic Compounds (Including Stilbenes) in Grapevine (Vitis Vinifera l.) Roots, Woods, Canes, Stems, and Leaves. Antioxidants 2020, 9. [CrossRef]
- Hübner, A.A.; Sarruf, F.D.; Oliveira, C.A.; Neto, A. V.; Fischer, D.C.H.; Kato, E.T.M.; Lourenço, F.R.; Baby, A.R.; Bacchi, E.M. Safety and Photoprotective Efficacy of a Sunscreen System Based on Grape Pomace (Vitis Vinifera l.) Phenolics from Winemaking. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Cornacchione, S.; Sadick, N.S.; Neveu, M.; Talbourdet, S.; Lazou, K.; Viron, C.; Renimel, I.; de Quéral, D.; Kurfurst, R.; Schnebert, S.; et al. In Vivo Skin Antioxidant Effect of a New Combination Based on a Specific Vitis Vinifera Shoot Extract and a Biotechnological Extract. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology 2007, 6, 8–13.
- Sharif, A.; Akhtar, N.; Khan, M.S.; Menaa, A.; Menaa, B.; Khan, B.A.; Menaa, F. Formulation and Evaluation on Human Skin of a Water-in-Oil Emulsion Containing Muscat Hamburg Black Grape Seed Extract. Int J Cosmet Sci 2015, 37, 253–258. [CrossRef]
- Moyano-Mendez, J.R.; Fabbrocini, G.; De Stefano, D.; Mazzella, C.; Mayol, L.; Scognamiglio, I.; Carnuccio, R.; Ayala, F.; La Rotonda, M.I.; De Rosa, G. Enhanced Antioxidant Effect of Trans-Resveratrol: Potential of Binary Systems with Polyethylene Glycol and Cyclodextrin. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 2014, 40, 1300–1307. [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J.P.; Kaur, A.; Singh, N. Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant Potential and Health Benefits of Citrus Peel. Food Research International 2020, 132.
- Klimek-szczykutowicz, M.; Szopa, A.; Ekiert, H. Citrus Limon (Lemon) Phenomenon—a Review of the Chemistry, Pharmacological Properties, Applications in the Modern Pharmaceutical, Food, and Cosmetics Industries, and Biotechnological Studies. Plants 2020, 9.
- Amorim, J.L.; Simas, D.L.R.; Pinheiro, M.M.G.; Moreno, D.S.A.; Alviano, C.S.; Da Silva, A.J.R.; Fernandes, P.D. Anti-Inflammatory Properties and Chemical Characterization of the Essential Oils of Four Citrus Species. PLoS One 2016, 11. [CrossRef]
- Cunha, C.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Rodrigues, M.; Araujo, A.R.T.S. Essential Oils Used in Dermocosmetics: Review about Its Biological Activities. J Cosmet Dermatol 2022, 21, 513–529.
- Nobile, V.; Burioli, A.; Yu, S.; Zhifeng, S.; Cestone, E.; Insolia, V.; Zaccaria, V.; Malfa, G.A. Photoprotective and Antiaging Effects of a Standardized Red Orange (Citrus Sinensis (L.) Osbeck) Extract in Asian and Caucasian Subjects: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Study. Nutrients 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.J.; Han, S.C.; Yi, E.J.; Kang, H.K.; Yoo, E.S. The Inhibitory Effect of Premature Citrus Unshiu Extract on Atopic Dermatitis in Vitro and in Vivo. Toxicol Res 2011, 27, 173–180.
- Saija, A.; Tomaino, A.; Trombetta, D.; Giacchi, M.; De Pasquale, A.; Bonina, F. Influence of Different Penetration Enhancers on in Vitro Skin Permeation and in Vivo Photoprotective Effect of Flavonoids; 1998; Vol. 175;.
- Bonina, F.; Saija, A.; Tomaino, A.; Locascio, R.; Rapisarda, P.; Dederen, J.C. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity and in Vivo Photoprotective Effect of a Red Orange Extract. Int J Cosmet Sci 1998, 20, 331–342. [CrossRef]
- Cartea, M.E.; Francisco, M.; Soengas, P.; Velasco, P. Phenolic Compounds in Brassica Vegetables. Molecules 2011, 16, 251–280.
- Ramesh, A.; Nandi, A.; Devanathan, S.; Jayaraman, L.; Sivaji, S. Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Oxidative, and Anti-Microbial Activities of the Phytochemicals Isolated from Various Parts of Broccoli Wastes. Journal of Advanced Biotechnology and Experimental Therapeutics 2023, 6, 67–83. [CrossRef]
- Talalay, P.; Fahey, J.W.; Healy, Z.R.; Wehage, S.L.; Benedict, A.L.; Min, C.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. Sulforaphane Mobilizes Cellular Defenses That Protect Skin against Damage by UV Radiation; 2007;
- Köksal, E.; Gülçi̇n, I. Antioxidant Activity of Cauliflower (Brassica Oleracea L.) Antioxidant Activity of Cauliflower (Brassica Oleracea L.). Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry 2008, 32.
- Khan, P.; Akhtar, N.; Khan, H.M.S.; Tasneem, R.; Zaka, H.S.; Akhtar, N.; Sharif, A. Assessment of Brassica Oleraceae L. (Brassicaceae) Extract Loaded Ethosomal Gel as a Versatile Vesicular Carrier System for Dermocosmetic Application: A Noninvasive Split-Faced Study. J Cosmet Dermatol 2022, 21, 7153–7162. [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.B.; Hossain, M.S.; Haque, M.E.; Haque, E. ANTIOXIDANT AND ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITIES OF THE LEAF EXTRACT OF BRASSICA NIGRA. IJPSR 2011, 2.
- Bozin, B.; Mimica-Dukic, N.; Samojlik, I.; Goran, A.; Igic, R. Phenolics as Antioxidants in Garlic (Allium Sativum L., Alliaceae). Food Chem 2008, 111, 925–929. [CrossRef]
- Taofiq, O.; Rodrigues, F.; Barros, L.; Barreiro, M.F.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Mushroom Ethanolic Extracts as Cosmeceuticals Ingredients: Safety and Ex Vivo Skin Permeation Studies. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2019, 127, 228–236. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Choi, M.H.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Shin, H.J. Mushroom Cosmetics: The Present and Future. Cosmetics 2016, 3.
- Tătărîngă, G.; Hăncianu, M.; Aprotosoaie, C.; Poiată, A.; Vasilescu, M.; Gafiţanu, E. Phytochemical and Microbiological Characterization of Two Allium Cepa L. Extracts in Order to Include in Dermo-Cosmetics. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi 2005, 109, 676–679.
- Nobile, V.; Michelotti, A.; Cestone, E.; Caturla, N.; Castillo, J.; Benavente-García, O.; Pérez-Sánchez, A.; Micol, V. Skin Photoprotective and Antiageing Effects of a Combination of Rosemary (Rosmarinus Officinalis) and Grapefruit (Citrus Paradisi) Polyphenols. Food Nutr Res 2016, 60. [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Torres, M.; Thiele, J.J.; Shindo, Y.; Han, D.; Packer, L. Topical Application Of-Tocopherol Modulates the Antioxidant Network and Diminishes Ultraviolet-Induced Oxidative Damage in Murine Skin; 1998; Vol. 138;.
- Kashif, M.; Naveed, A.; Pharm Sci, P.J.; Akhtar, N. Dermocosmetic Emulgels for Anti-Aging Effects: Evidence from Chromatographic and Non-Invasive Biophysical Techniques HPLC-UV Detection Method for Quantification of Loxoprofen in Human Plasma with Liquid-Liquid Extraction Technique: Application in Pharmacokinetic Study View Project Clinical Studies View Project Dermocosmetic Emulgels for Anti-Aging Effects: Evidence from Chromatographic and Non-Invasive Biophysical Techniques; 2019; Vol. 32;.
- Ali, A.; Akhtar, N.; Shoaib Khan, M.; Rasool, F.; Iqbal, F.M.; Khan, M.T.; Din, M.U.; Elahi, E. Moisturizing Effect of Cream Containing Moringa Oleifera (Sohajana) Leaf Extract by Biophysical Techniques: In Vivo Evaluation. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research 2013, 7, 386–391. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





