Submitted:
22 April 2024
Posted:
22 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
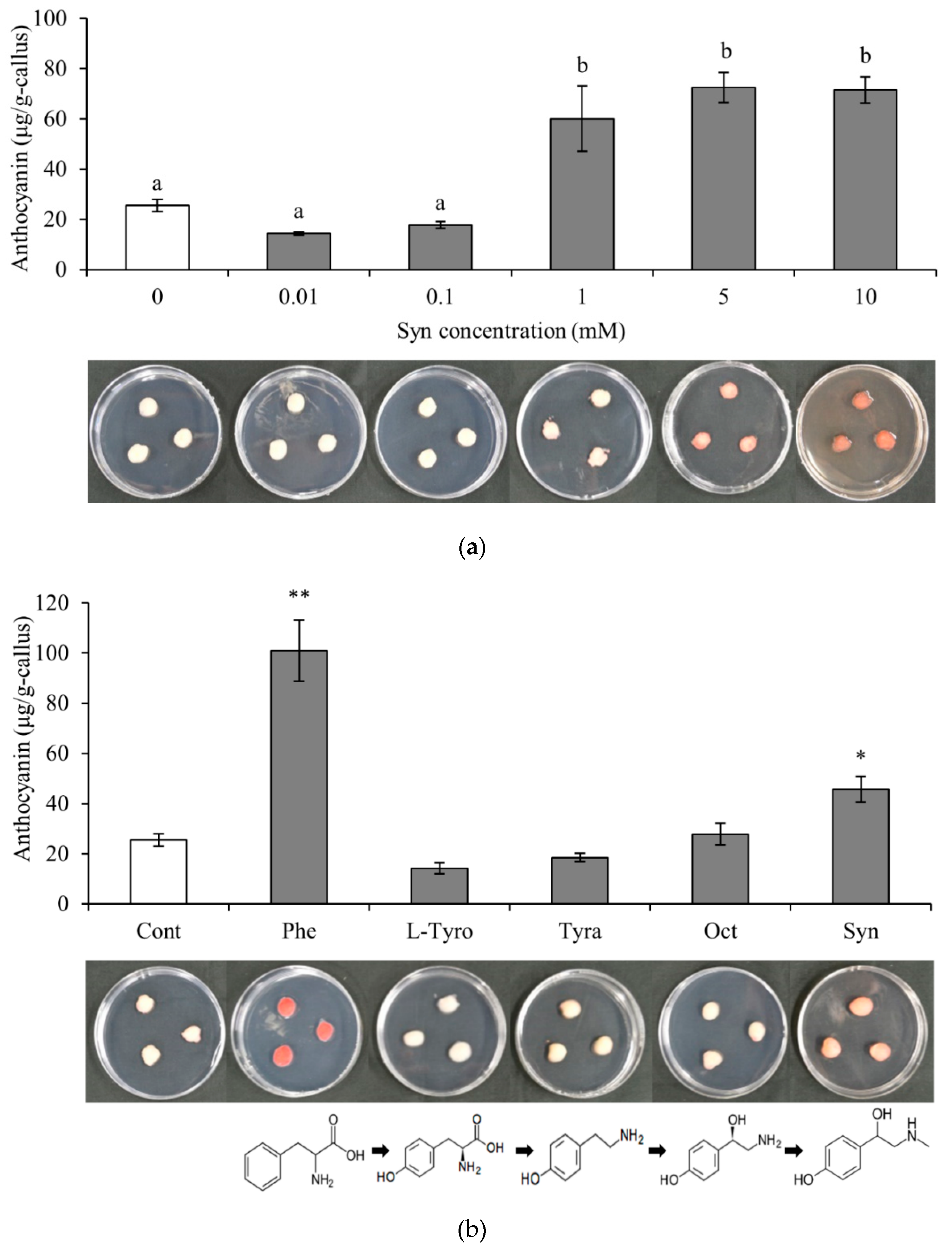
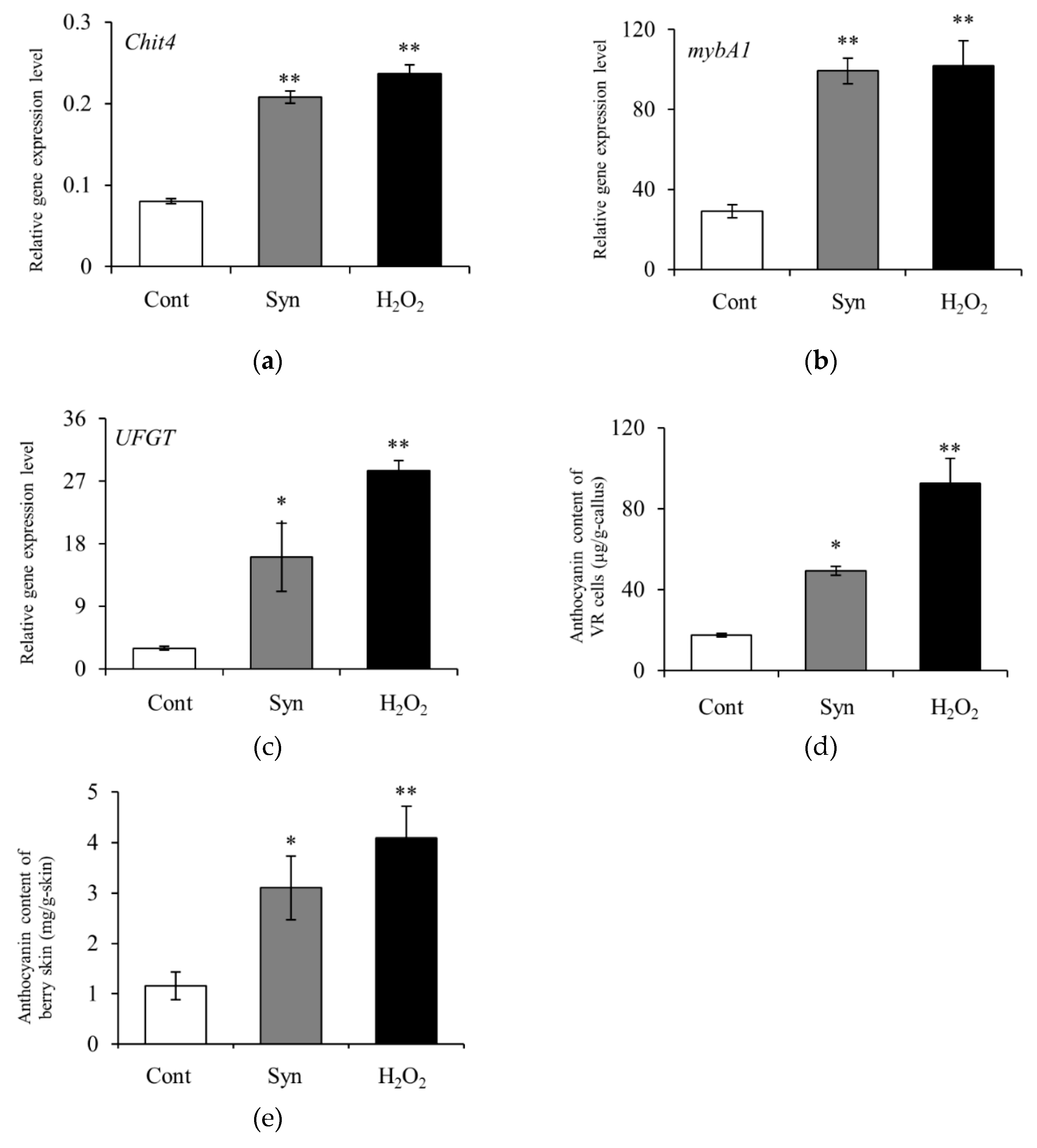
2.1. Syn induces Anthocyanin Accumulation in VR Cells
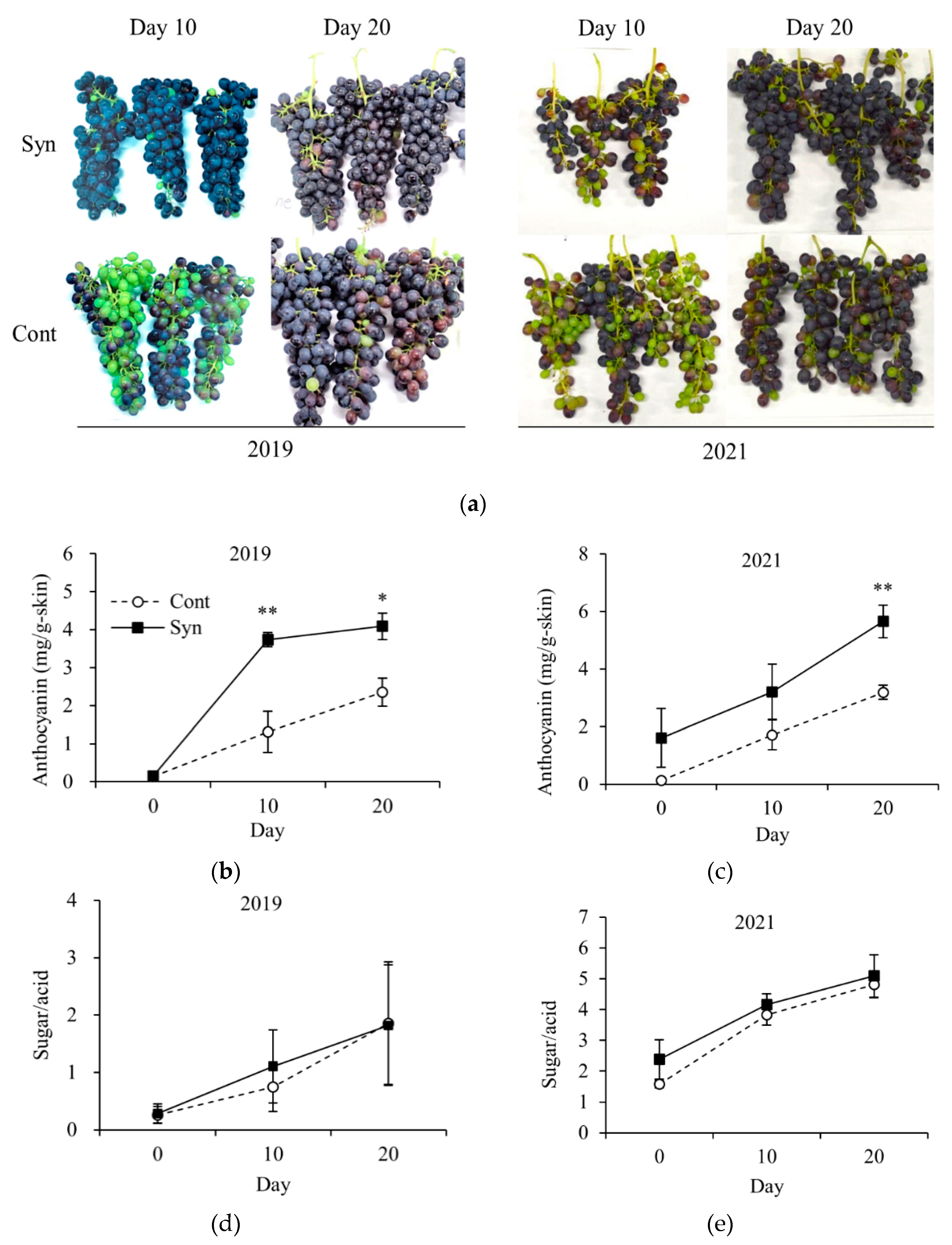
2.2. Syn Promotes Anthocyanin Accumulation in Grape Skin in Field Trials
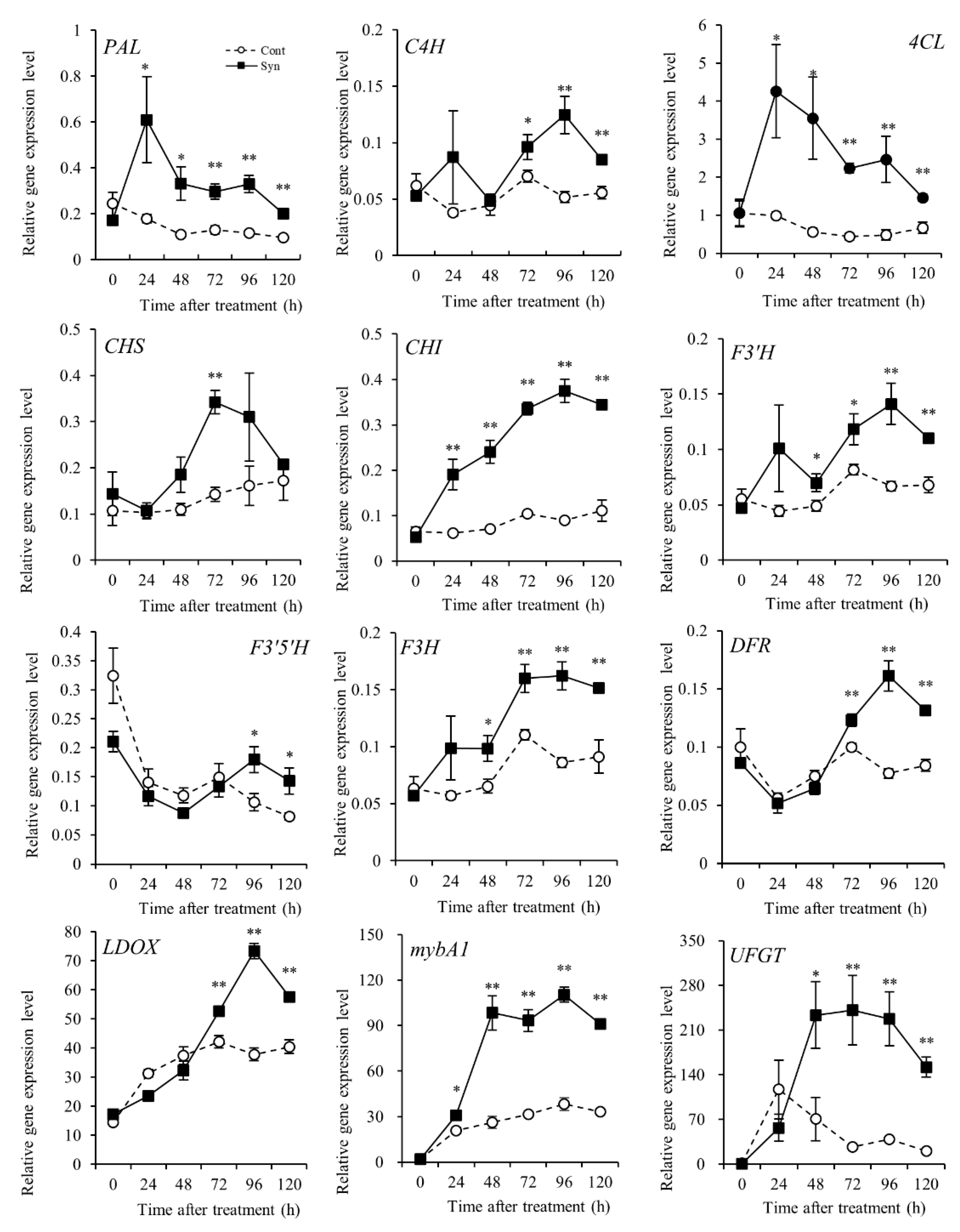
2.3. Syn Increases Expression Levels of Anthocyanin-Biosynthesis-Related Genes
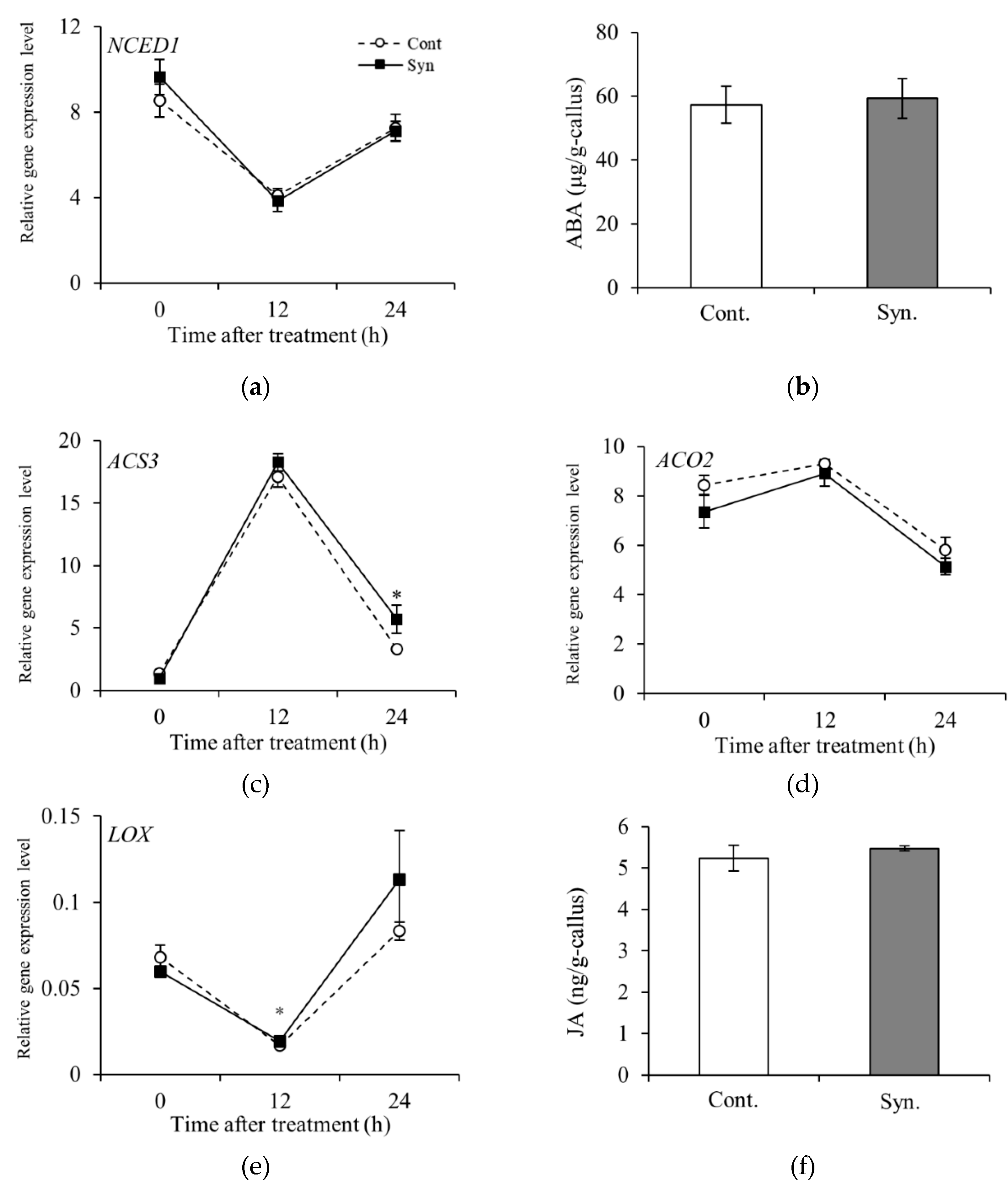
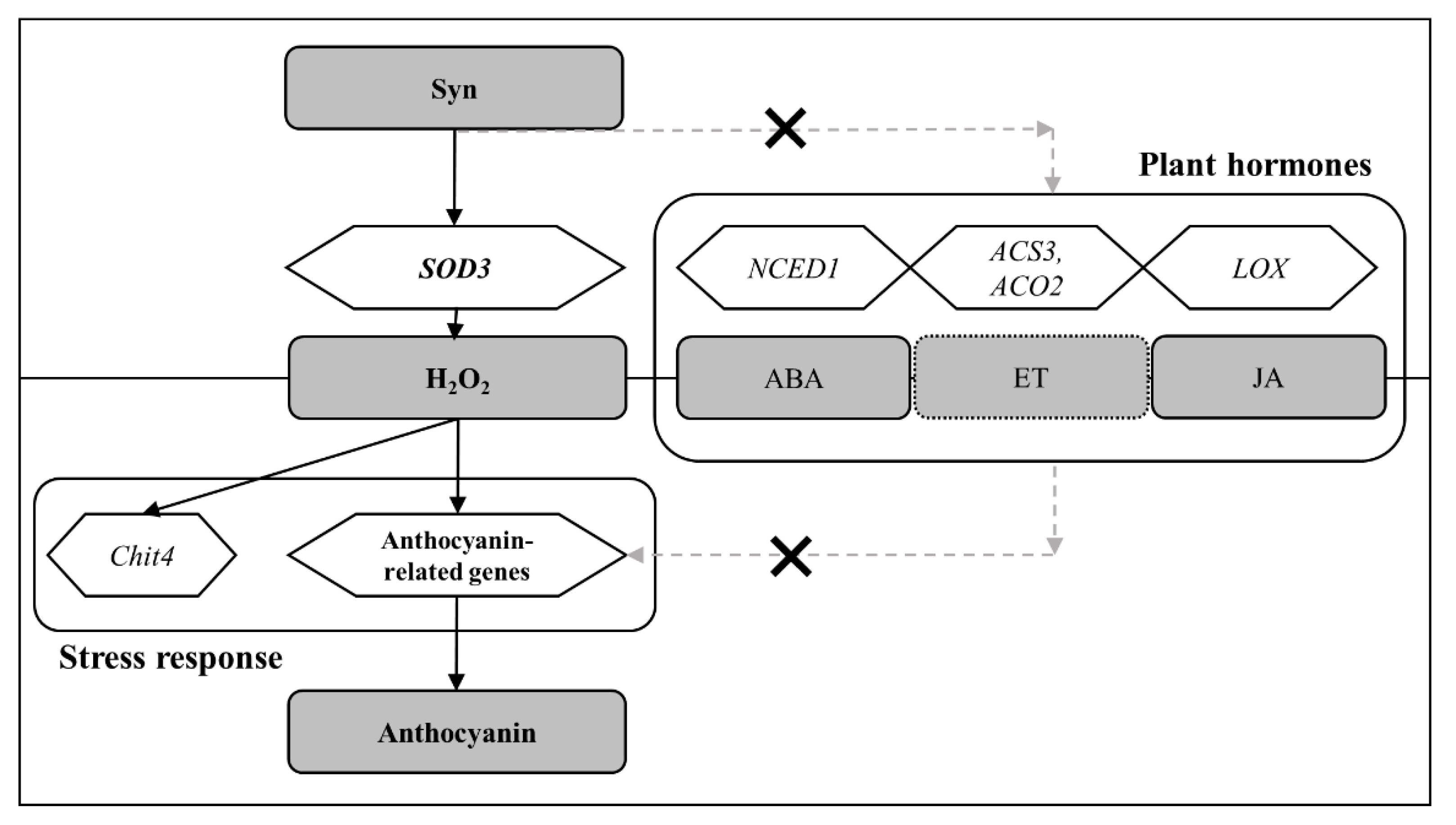
2.4. Syn Does Not Affect the Increase in the Production of Phytohormones, Which Promote Anthocyanin Accumulation
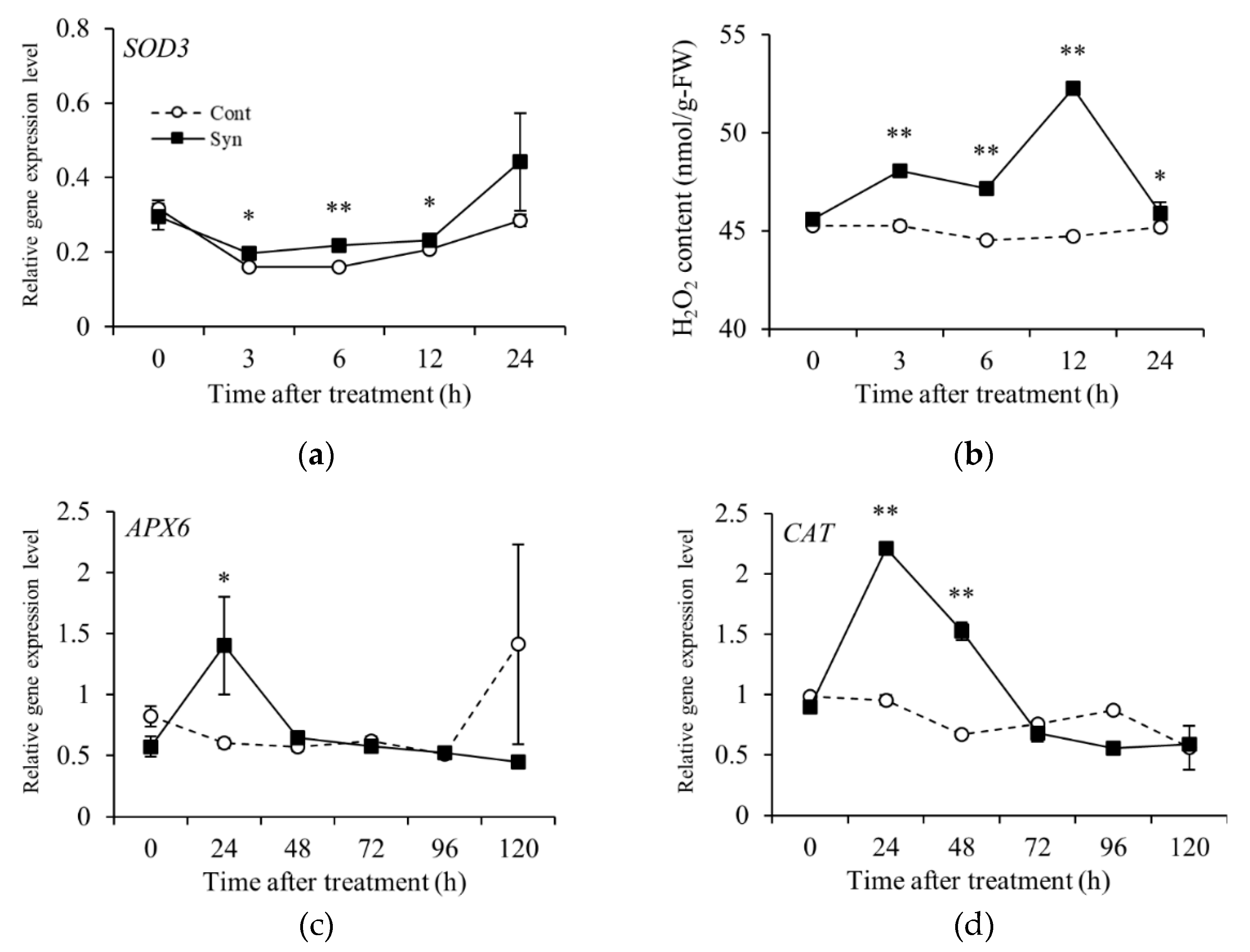
2.4. Syn Increases Anthocyanin Content via H2O2
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Vitro Trials
4.2. Field Trials
4.3. Total RNA Isolation
4.4. Real-Time RT-PCR Analysis
4.5. Total Anthocyanin Content
4.6. Sugar/Acid Ratio
4.7. Phytohormone Contents
4.8. H2O2 Content
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chorti, E.; Guidoni, S.; Ferrandino, A.; Novello, V. Effect of different cluster sunlight exposure levels on ripening and anthocyanin accumulation in Nebbiolo grapes. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2010, 61, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellarin, S. D.; Matthews, M. A.; Di Gaspero, G.; Gambetta, G. A. Water deficits accelerate ripening and induce changes in gene expression regulating flavonoid biosynthesis in grape berries. Planta 2007, 227, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Goto-Yamamoto, N.; Kitayama, M.; Hashizume, K. Effect of high temperature on anthocyanin composition and transcription of flavonoid hydroxylase genes in ‘Pinot noir’ grapes (Vitis vinifera). J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2007, 82, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoki, S.; Hattori, T.; Ishiai, S.; Tanaka, S.; Mikami, M.; Arita, K.; Nagasaka, S; Suzuki S. Vanillylacetone up-regulates anthocyanin accumulation and expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes by inducing endogenous abscisic acid in grapevine tissues. J. Plant Physiol. 2017, 219, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, R.; Roberto, S. R.; De Souza, R. T.; Borges, W. F.; Anderson, M.; Waterhouse, A. L.; Cantu, D; Fidelibus, M. W; Balanco-Ulate, B. Exogenous abscisic acid promotes anthocyanin biosynthesis and increased expression of flavonoid synthesis genes in Vitis vinifera × Vitis labrusca table grapes in a subtropical region. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, A.; Nojiri, M.; Watanabe, G.; Eoki, S.; Suzuki, S. Exogenous allantoin improves anthocyanin accumulation in grape berry skin at early stage of ripening. J. Plant Physiol. 2020, 253, 153253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, M.; Ishida, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Aoki, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Enoki, S. Ethylene Induced by Sound Stimulation Enhances Anthocyanin Accumulation in Grape Berry Skin through Direct Upregulation of UDP-Glucose: Flavonoid 3-O-Glucosyltransferase. Cells 2021, 10, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concha, C. M.; Figueroa, N. E.; Poblete, L. A.; Oñate, F. A.; Schwab, W.; Figueroa, C. R. Methyl jasmonate treatment induces changes in fruit ripening by modifying the expression of several ripening genes in Fragaria chiloensis fruit. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 70, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilati, S.; Bagagli, G.; Sonego, P.; Moretto, M.; Brazzale, D.; Castorina, G.; Simoni, L.; Tonelli, C.; Guella, G.; Engelen, K.; et al. Abscisic acid is a major regulator of grape berry ripening onset: New insights into ABA signaling network. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, T.; Jeong, S. T.; Goto-Yamamoto, N.; Koshita, Y.; Kobayashi, S. Effects of temperature on anthocyanin biosynthesis in grape berry skins. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2006, 57, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes de Oliveira, A.; Mercenaro, L.; Del Caro, A.; Pretti, L.; Nieddu, G. Distinctive anthocyanin accumulation responses to temperature and natural UV radiation of two field-grown Vitis vinifera L. cultivars. Molecules 2015, 20, 2061–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G. V.; White, M. A.; Cooper, O. R.; Storchmann, K. Climate change and global wine quality. Clim. Change 2005, 73, 319–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshita, Y.; Yamane, T.; Yakushiji, H.; Azuma, A.; Mitani, N. Regulation of skin color in ‘Aki Queen’grapes: Interactive effects of temperature, girdling, and leaf shading treatments on coloration and total soluble solids. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardaguila, J.; de Toda, F. M.; Poni, S.; Diago, M. P. Impact of early leaf removal on yield and fruit and wine composition of Vitis vinifera L. Graciano and Carignan. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2010, 61, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, S.; Tanzawa, F.; Kobayashi, H.; Suzuki, S.; Takata, R.; Saito, H. Leaf removal accelerated accumulation of delphinidin-based anthocyanins in ‘Muscat Bailey A’ [Vitis× labruscana (Bailey) and Vitis vinifera (Muscat Hamburg)] grape skin. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2013, CH-062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidoni, S.; Allara, P.; Schubert, A. Effect of cluster thinning on berry skin anthocyanin composition of Vitis vinifera cv. Nebbiolo. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2002, 53, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Saito, H.; Goto-Yamamoto, N.; Kitayama, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Sugaya, S.; Gemma, H; Hashizume, K. Effects of abscisic acid treatment and night temperatures on anthocyanin composition in Pinot noir grapes. Vitis 2005, 44, 161. [Google Scholar]
- Peppi, M. C.; Walker, M. A.; Fidelibus, M. W. Application of abscisic acid rapidly upregulated UFGT gene expression and improved color of grape berries. Vitis 2008, 47, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu, A. K.; Gray, D. J.; Lu, J.; Gu, L. Effects of exogenous abscisic acid on antioxidant capacities, anthocyanins, and flavonol contents of muscadine grape (Vitis rotundifolia) skins. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, I. Effect of abscisic acid and defoliation on anthocyanin accumulation in' Kyoho'grapes (Vitis vinifera L.× V. labruscana Bailey). Vitis 1982, 21, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Mikami, N.; Konya, M.; Enoki, S.; Suzuki, S. Geraniol as a Potential Stimulant for Improving Anthocyanin Accumulation in Grape Berry Skin through ABA Membrane Transport. Plants 2022, 11, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, T.; Chen, Y.; Enoki, S.; Igarashi, D.; Suzuki, S. Exogenous isoleucine and phenylalanine interact with abscisic acid-mediated anthocyanin accumulation in grape. Folia Hortic. 2019, 31, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellati, F.; Benvenuti, S. Fast high-performance liquid chromatography analysis of phenethylamine alkaloids in Citrus natural products on a pentafluorophenylpropyl stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A. 2007, 1165, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragull, K.; Breksa III, A. P.; Cain, B. Synephrine content of juice from Satsuma mandarins (Citrus unshiu Marcovitch). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8874–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colker, C. M.; Kaiman, D. S.; Torina, G. C.; Perlis, T.; Street, C. Effects of Citrus aurantium extract, caffeine, and St. John's wort on body fat loss, lipid levels, and mood states in overweight healthy adults. Curr Ther Res. 1999, 60, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Hellín, J.; Del Coso, J. Acute p-synephrine ingestion increases fat oxidation rate during exercise. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 82, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, G.; Pizzolato, G.; Gucciardi, A.; Stocchero, M.; Giordano, G.; Baraldi, E.; Leon, A. Different circulating trace amine profiles in de novo and treated Parkinson’s disease patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, C. M.; Boss, P. K.; Høj, P. B. Cloning and characterization of Vitis vinifera UDP-Glucose: Flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase, a homologue of the enzyme encoded by the maize bronze-1Locus that may primarily serve to glucosylate anthocyanidins in vivo. JBC. 1998, 273, 9224–9233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Goto-Yamamoto, N.; Hirochika, H. Association of VvmybA1 gene expression with anthocyanin production in grape (Vitis vinifera) skin-color mutants. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2005, 74, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G. W.; Breen, P. J. Activity of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) and concentrations of anthocyanins and phenolics in developing strawberry fruit. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1991, 116, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Mahmood, K.; Rothstein, S. J. ROS induces anthocyanin production via late biosynthetic genes and anthocyanin deficiency confers the hypersensitivity to ROS-generating stresses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 1364–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Liu, G.; Wei, Y.; Chan, Z. The zinc-finger transcription factor ZAT6 is essential for hydrogen peroxide induction of anthocyanin synthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 97, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhu, Y.; Qi, R.; Tian, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K. Reactive oxygen species acts as an important inducer in low-temperature-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in Begonia semperflorens. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2018, 143, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, T.; Pinontoan, R.; Uozumi, N.; Miyake, C.; Asada, K.; Kolattukudy, P. E.; Muto, S. Aromatic monoamine-induced immediate oxidative burst leading to an increase in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in tobacco suspension culture. Plant Cell Physiol. 2000, 41, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinontoan, R.; Krystofova, S.; Kawano, T.; Mori, I. C.; Tsuji, F. I.; Iida, H.; Muto, S. Phenylethylamine induces an increase in cytosolic Ca2+ in yeast. BBB. 2002, 66, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, C. G.; Casalongué, C. A.; Simontacchi, M.; Marquez-Garcia, B.; Foyer, C. H. Interactions between hormone and redox signaling pathways in the control of growth and cross tolerance to stress. ENVIRON EXP BOT. 2013, 94, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M. A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Armin, S. M.; Qian, P.; Xin, W.; Li, H. Y.; Burritt, D. J.; Fujita, M.; Tran, L. S. P. Hydrogen peroxide priming modulates abiotic oxidative stress tolerance: Insights from ROS detoxification and scavenging. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, I.; Srikanth, S.; Chen, Z. Cross talk between H2O2 and interacting signal molecules under plant stress response. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozden, M.; Demirel, U.; Kahraman, A. Effects of proline on antioxidant system in leaves of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) exposed to oxidative stress by H2O2. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 119, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabayashi, R.; Yonekura-Sakakibara, K.; Urano, K.; Suzuki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nishizawa, T.; Matsuda, F.; Kojima, M.; Sakakibara, H.; Shinozaki, K.; et al. Enhancement of oxidative and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis by overaccumulation of antioxidant flavonoids. Plant J. 2014, 77, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Su, N.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Cui, J.; Liang, Y. Hydrogen peroxide, nitric oxide and UV RESISTANCE LOCUS8 interact to mediate UV-B-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in radish sprouts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.L.; Wang, Z.G.; Li, Q.; Gu, S.C.; Zhang, G.H.; Yu, Y.H. Hydrogen peroxide treatment promotes early ripening of Kyoho grape. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2019, 25, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouvelot, S.; Varnier, A. L.; Allegre, M.; Mercier, L.; Baillieul, F.; Arnould, C.; Gianinazzi-Pearson, V.; Klarzynski, O.; Joubert, J. M.; Pugin, A.; Daire, X. A β-1, 3 glucan sulfate induces resistance in grapevine against Plasmopara viticola through priming of defense responses, including HR-like cell death. MPMI. 2008, 21, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, H.; Wahab, M. A.; Chong, J.; Bertsch, C.; Mliki, A.; Soustre-Gacougnolle, I. Thiamine induced resistance to Plasmopara viticola in grapevine and elicited host–defense responses, including HR like-cell death. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 57, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, H.; Wahab, M. A.; Chong, J.; Gertz, C.; Gandoura, S.; Mliki, A.; Bertsch, C.; Soustre-Gacougnolle, I. Methionine elicits H2O2 generation and defense gene expression in grapevine and reduces Plasmopara viticola infection. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 170, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stohs, S. J. Safety, efficacy, and mechanistic studies regarding Citrus aurantium (bitter orange) extract and p-synephrine. Phytother Res. 2017, 31, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Moreno, C.; Del Coso, J.; Giráldez-Costas, V.; González-García, J.; Gutiérrez-Hellín, J. Effects of p-synephrine during exercise: A brief narrative review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, T.; Kato, S.; Ishida, K.; Kodama, T.; Minoda, Y. Production of anthocyanins by Vitis cells in suspension culture. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1983, 47, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K. E.; Olsson, N.; Schlosser, J.; Peng, F.; Lund, S. T. An optimized grapevine RNA isolation procedure and statistical determination of reference genes for real-time RT-PCR during berry development. BMC Plant Biol. 2006, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.; Monteiro, F.; Sebastiana, M. First clues on a jasmonic acid role in grapevine resistance against the biotrophic fungus Plasmopara viticola. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2015, 142, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambino, G.; Boccacci, P.; Margaria, P.; Palmano, S.; Gribaudo, I. Hydrogen peroxide accumulation and transcriptional changes in grapevines recovered from flavescence dorée disease. Phytopathol. 2013, 103, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, H.; Chen, S.; Ji, M.; Perl, A.; Kovacs, L.; Chen, S. Stress response proteins’ differential expression in embryogenic and non-embryogenic callus of Vitis vinifera L. cv. Cabernet Sauvignon—A proteomic approach. Plant Sci. 2009, 177, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokotsuka, K.; Nagao, A.; Nakazawa, K.; Sato, M. Changes in anthocyanins in berry skins of Merlot and Cabernet Sauvignon grapes grown in two soils modified with limestone or oyster shell versus a native soil over two years. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1999, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, J.; Preston, N. W.; Timberlake, C. F. The determination of anthocyanins in aging red wines: Comparison of HPLC and spectral methods. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1986, 37, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




