Submitted:
18 April 2024
Posted:
22 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Field-Programmable Gate Array
- Reconfigurability: FPGAs are reconfigurable [14] and can define their digital logic circuits through programming, allowing developers to redesign the FPGA’s functions according to application requirements repeatedly.
- High parallel processing capability: FPGAs have multiple independent logic circuits and data paths that can run in parallel, enabling them to efficiently perform parallel processing for multiple tasks and hence provide high-performance computing power.
- Low latency and high-frequency operation: Due to the fact that FPGA’s logic circuits composed of gate arrays and have high optimization capabilities, it can achieve low latency and high-frequency operation. This makes it ideal for applications requiring high-speed processing.
- Customizability: FPGAs are highly flexible in customization and can be designed and optimized according to application requirements. This includes design of logic circuits, data paths, memory, and interfaces.
- Software and hardware co-design: FPGAs provide the ability to co-design software and hardware on a single chip [15]. This provides higher system integration and performance.
- Suitable for rapid development and testing: FPGAs have a rapid development cycle. Developers can quickly develop and test them within a shorter period [16].
1.2. Experimental Protocol
2. Related Works
2.1. CLDNN Model Architecture
2.2. Consecutive Facial Emotion Recognition
3. Facial Emotion Recognition Methods and Parameter Setting
3.1. CLDNN Model
| CNN + LSTM + DNN | CNN + GRU + DNN | ||
| Execution Time on FPGA | Accuracy | Execution Time on FPGA | Accuracy |
| 11.70 sec | 99.51% | 11.67 sec | 97.86% |
3.2. Experimental Environment for Model Training on PC
3.3. Consecutive Facial Emotion Recognition
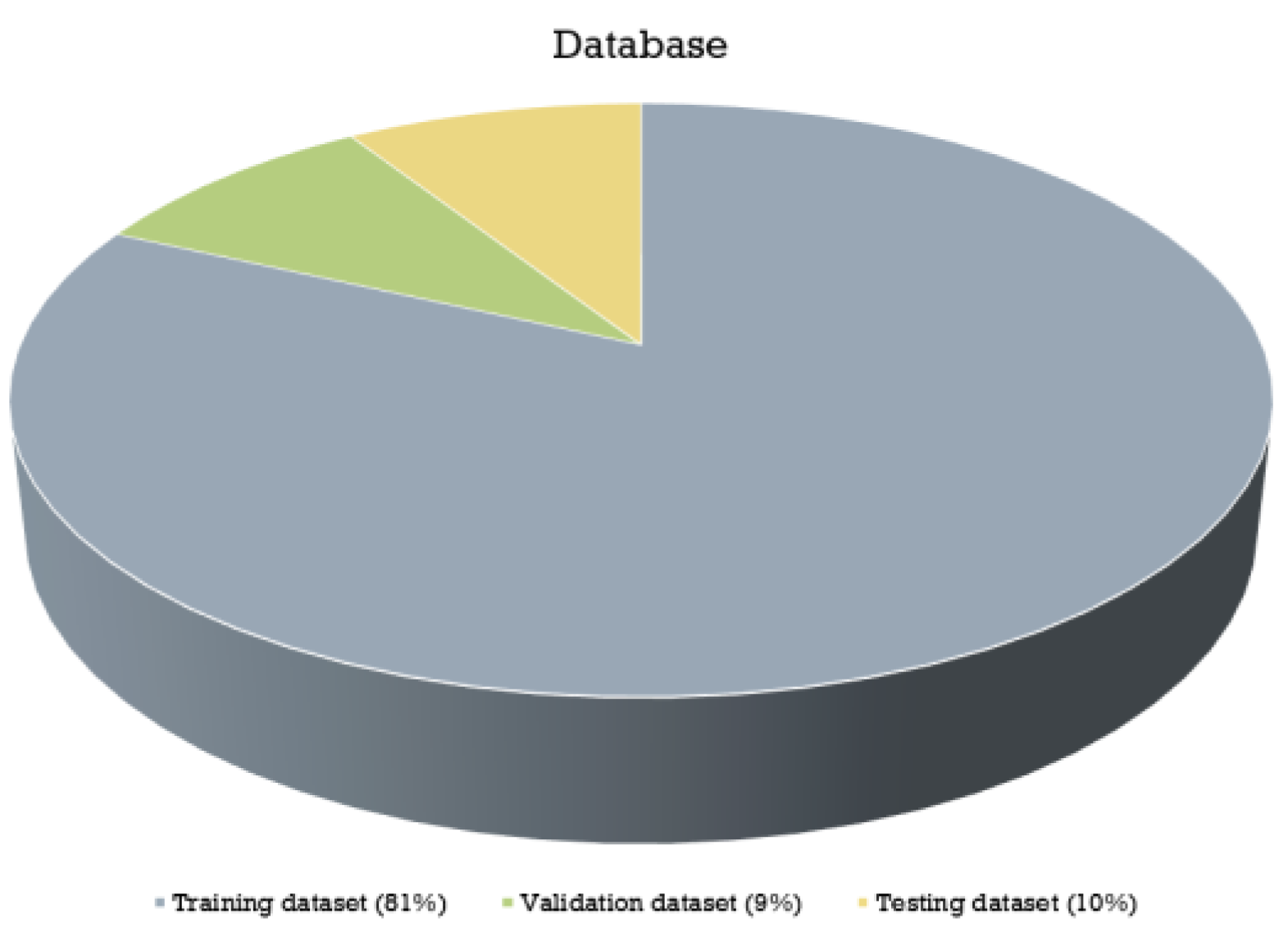
3.3.1. Databases
3.3.1.1. RAVDESS
3.3.1.2. BAUM-1s
3.3.1.3. eNTERFACE’05
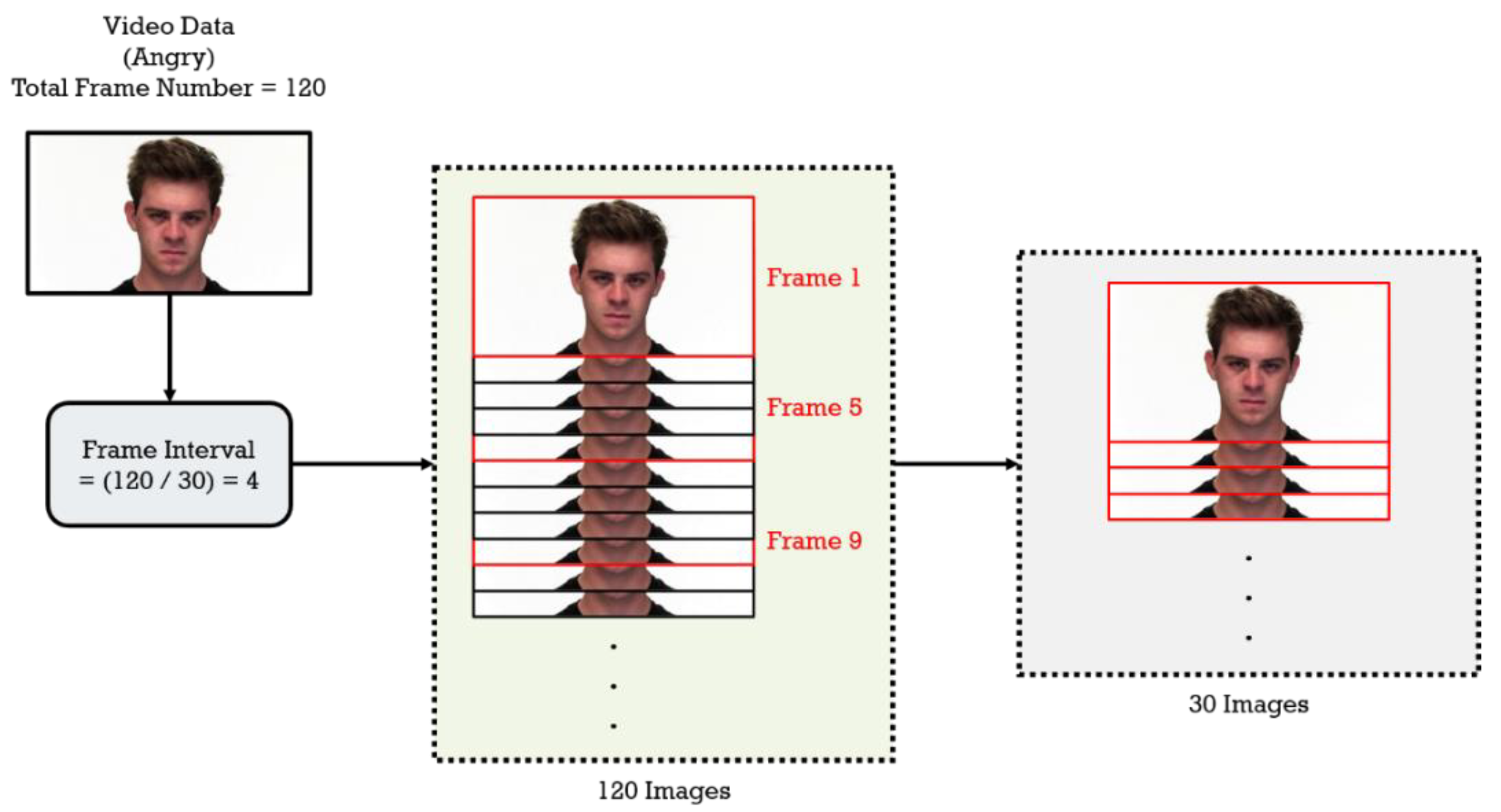
3.3.2. Pre-Processing
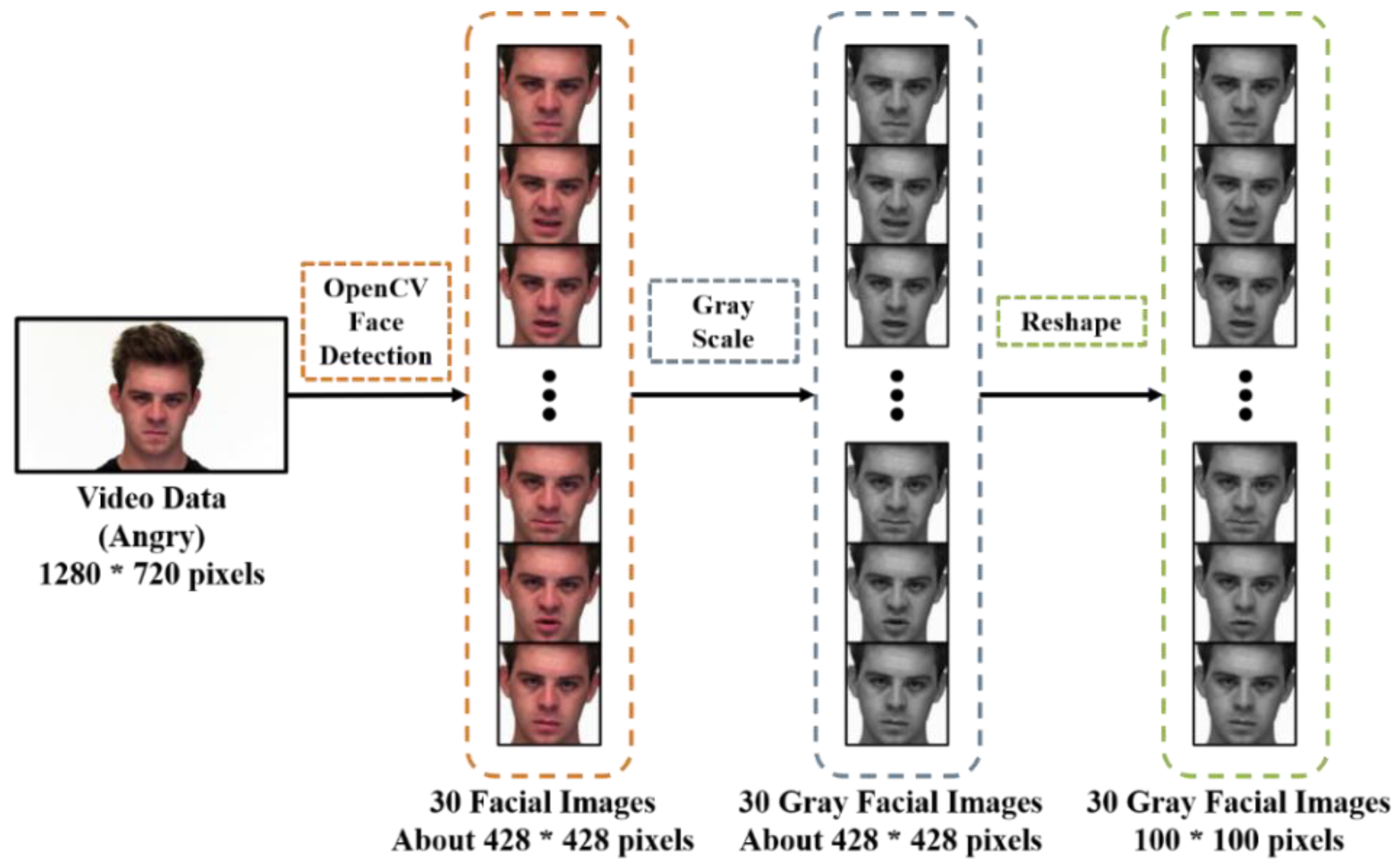
3.3.2.1. Facial Detection
3.3.2.2. Grayscale Conversion
3.3.2.3. Resize
3.3.3. Experiments
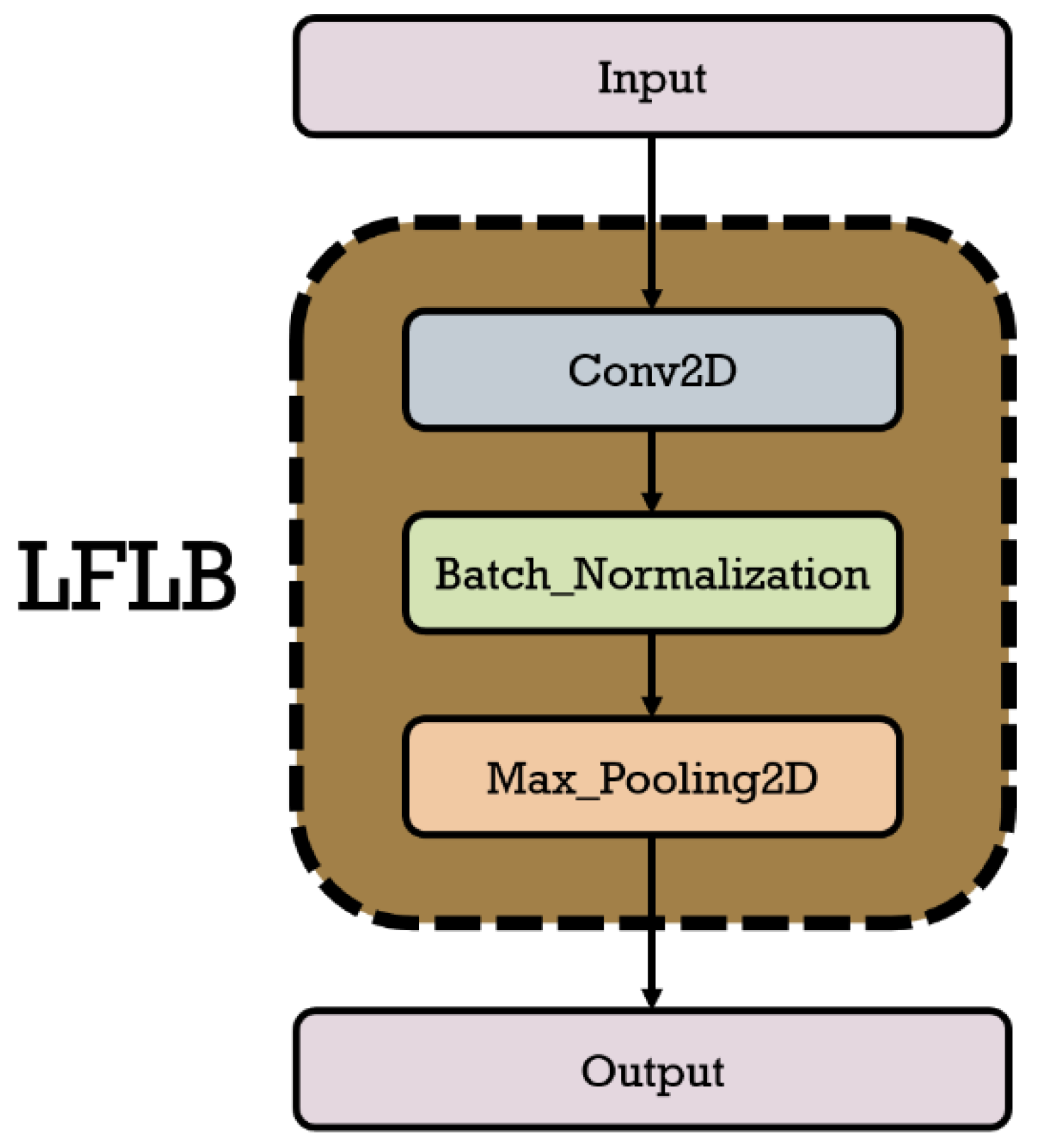
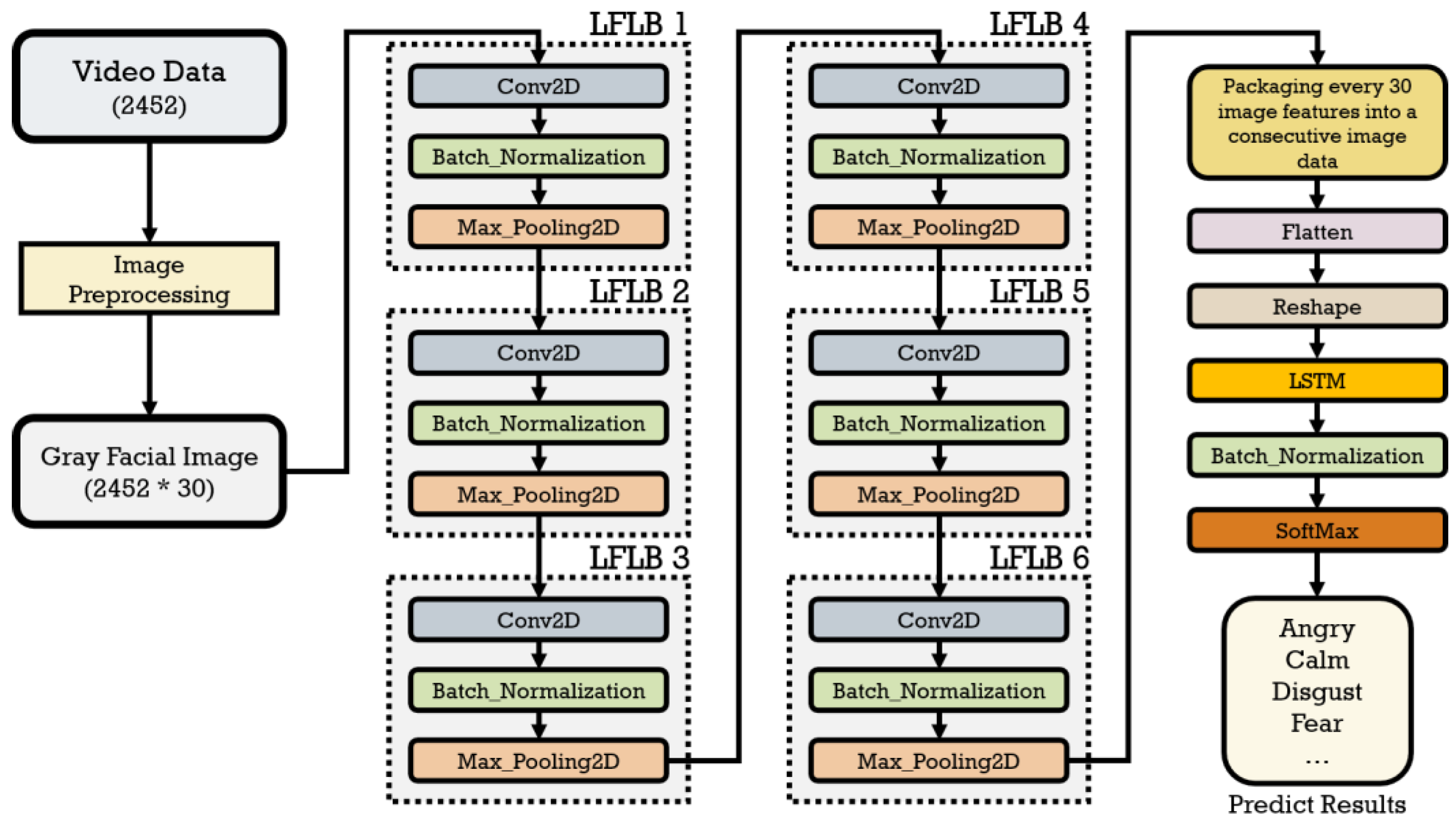
3.3.3.1. Local Feature Learning Block
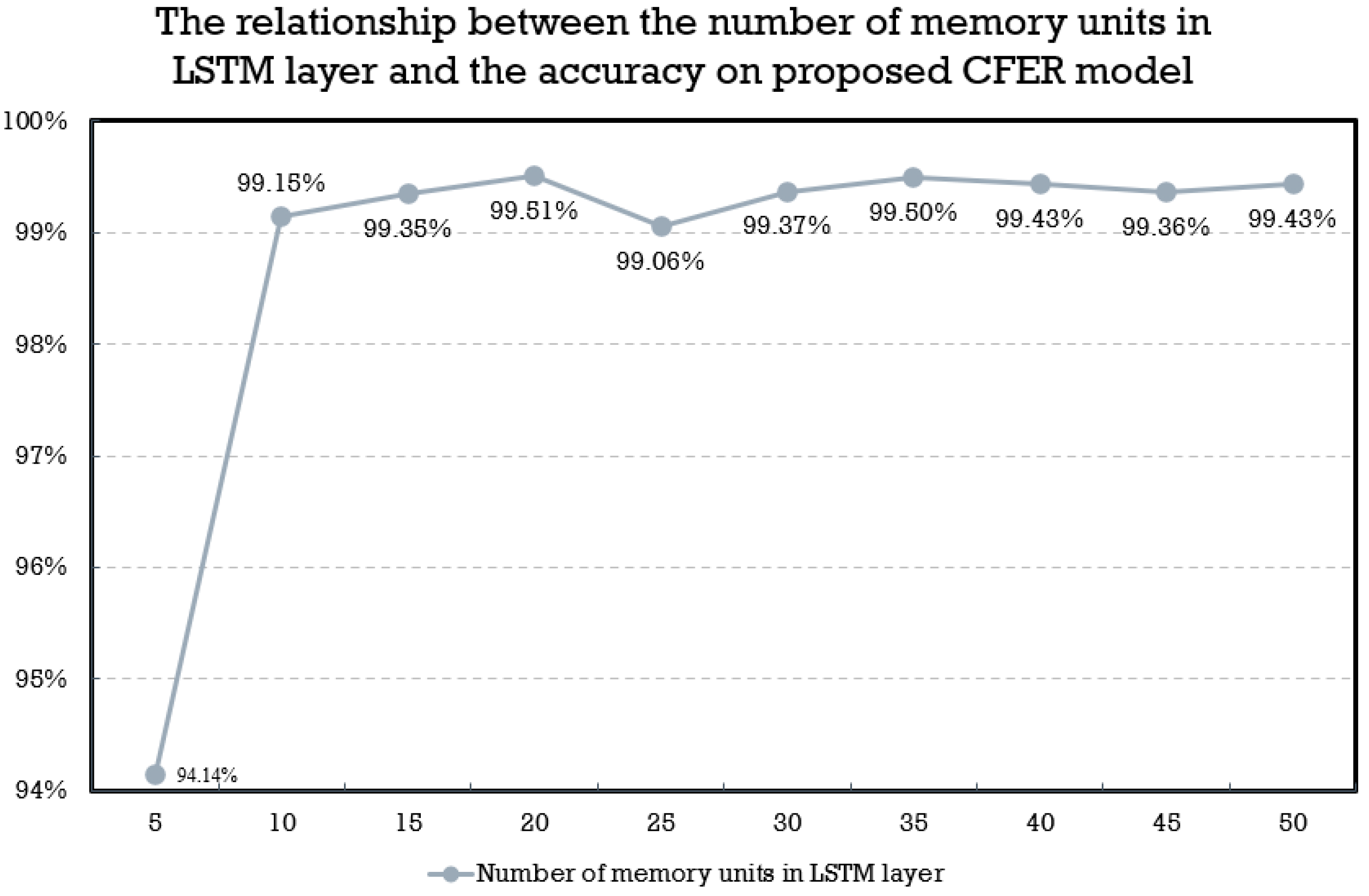
3.3.3.2. Training Process and Parameters
4. Experimental Results
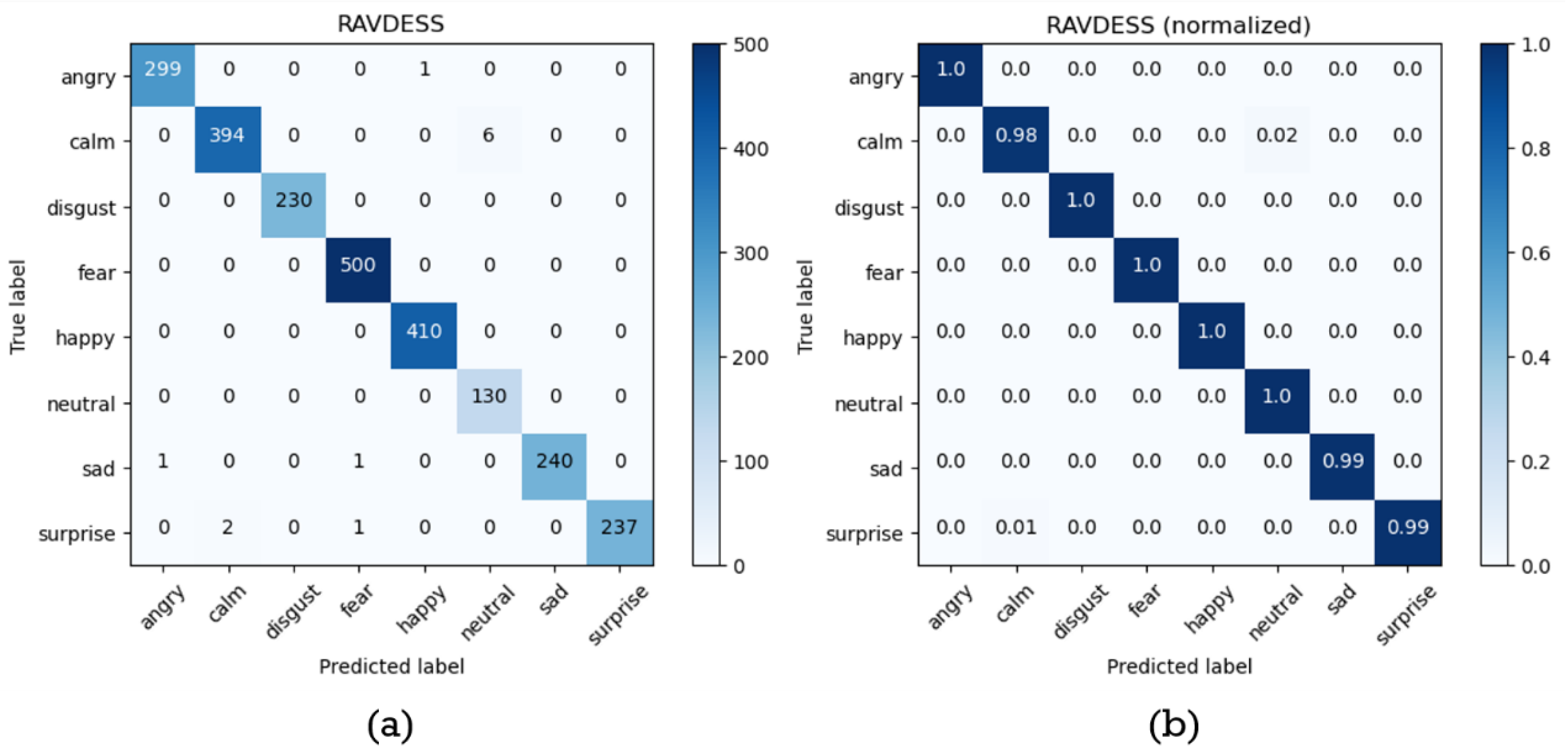
4.1. Experiments on RAVDESS Database
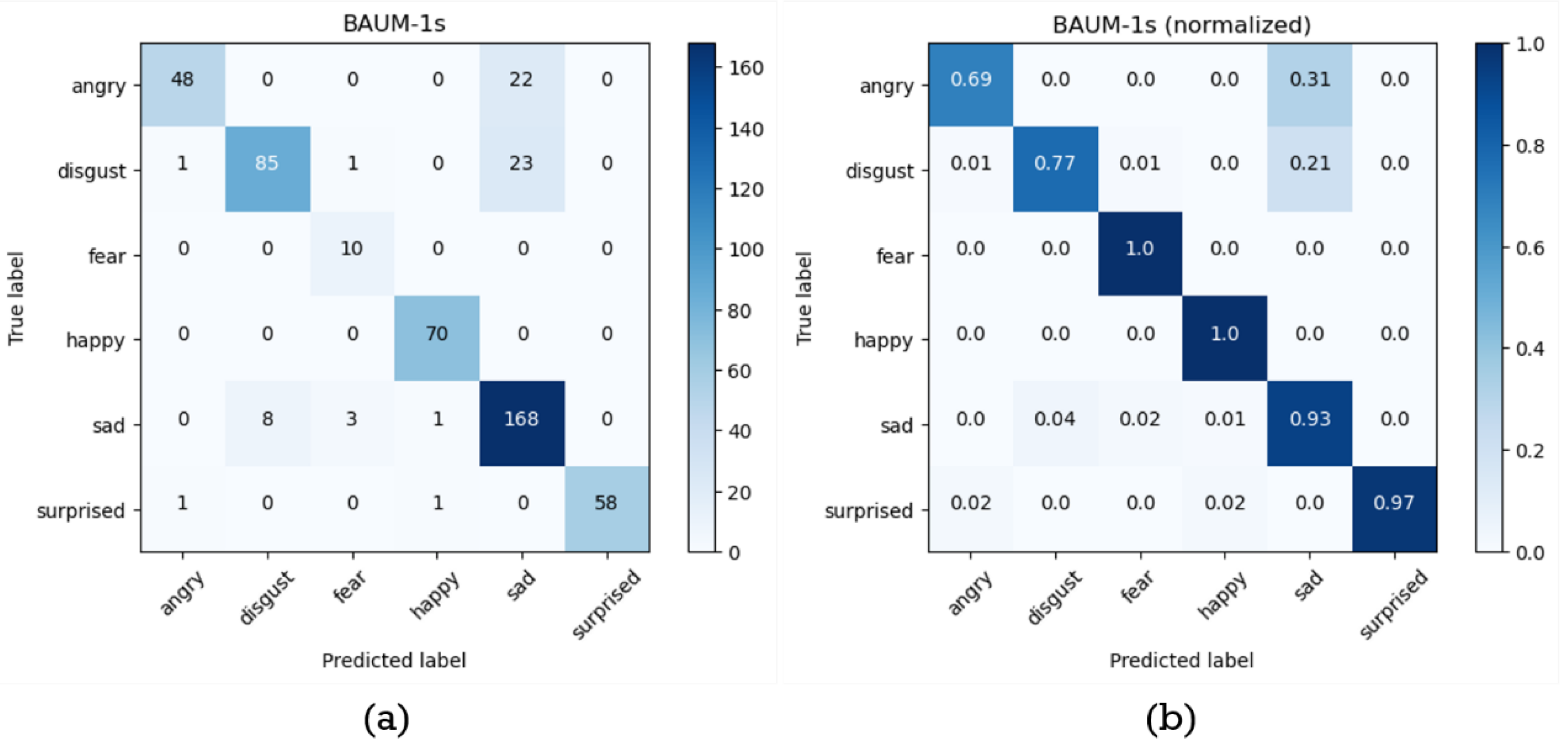
4.2. Experiments on BAUM-1s Database
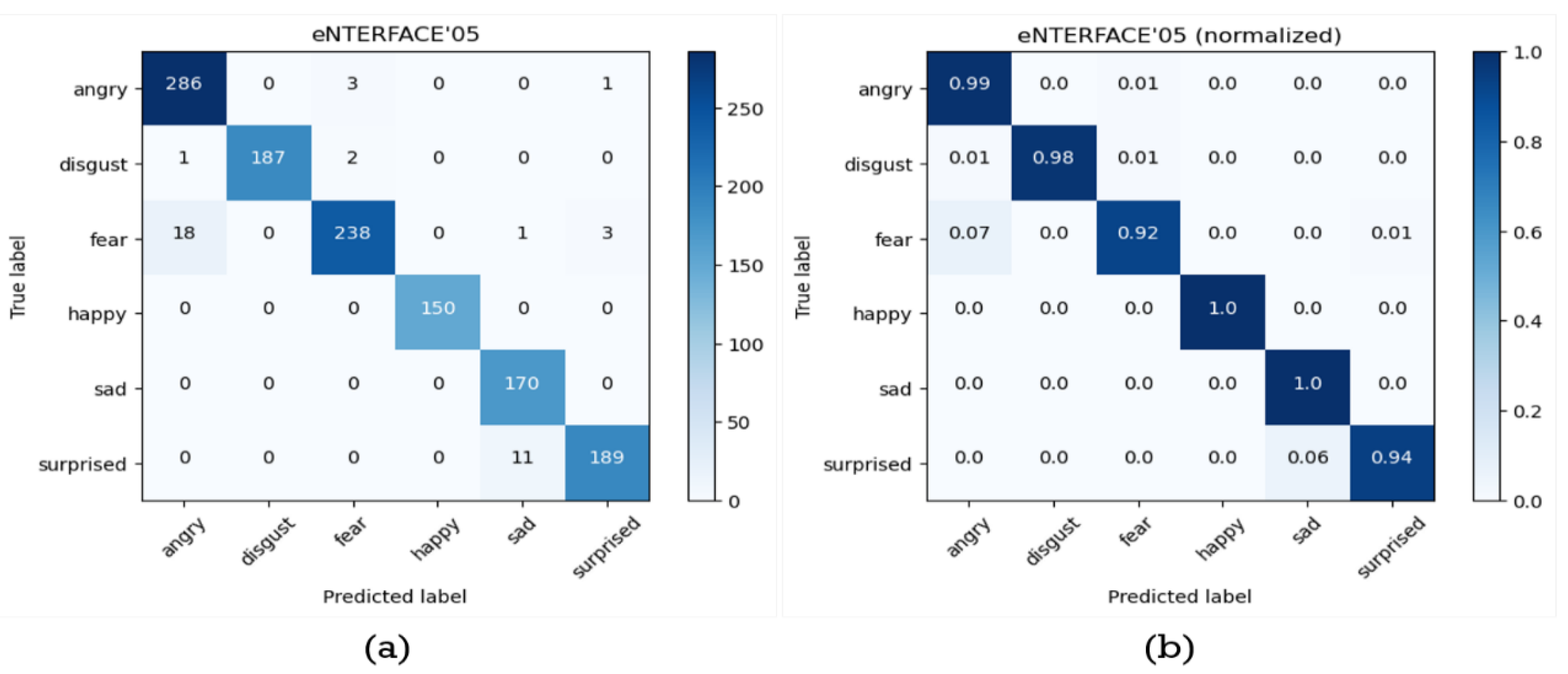
4.3. Experiments on eNTERFACE’05 Database
5. Experiments for FPGA Implementation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Izquierdo-Reyes, J.; Ramirez-Mendoza, R.A.; BustamanteBello, M.R.; Navarro-Tuch, S.; Avila-Vazquez, R. Advanced Driver Monitoring for Assistance System (ADMAS) Based on Emotions. IEEE International Journal of Interactive Design and Manufacturing 2018, 12, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, N.; Unnikrishnan, K.; Jayakrishnan, R. “Fraud Detection by Facial Expression Analysis Using Intel RealSense and Augmented Reality,” International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems, pp. 919-923, Madurai, India, Mar., 2018.
- Nijsse, B.; Spikman, J.M.; Visser-Meily, J.M.; de Kort, P.L.; van Heugten, C.M. Social Cognition Impairments in the Long-Term Post Stroke. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2019, 100, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninaus, M.; Greipl, S.; Kiili, K.; Lindstedt, A.; Huber, S.; Klein, E.; Moeller, K. Increased Emotional Engagement in Game-based Learning-A Machine Learning Approach on Facial Emotion Detection Data. Computers & Education 2019, 142, 103641. [Google Scholar]
- Matsugu, M.; Mori, K.; Mitari, Y.; Kaneda, Y. Subject Independent Facial Expression Recognition with Robust Face Detection using a Convolutional Neural Network. Neural Networks 2003, 16, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramerdorfer, C.; Kampel, M. Facial Expression Recognition using Convolutional Neural Networks: State of the Art. arXiv preprint arXiv:1612.02903, Dec., 2016.
- Ayadi, M.E.; Kamel, M.S.; Karray, F. Survey on Speech Emotion Recognition: Features, Classification Schemes, and Databases. Pattern Recognition 2011, 44, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, R.A.; Jones, E.; Babar, M.I.; Jan, T.; Zafar, M.H.; Alhussain, T. Speech Emotion Recognition Using Deep Learning Techniques: A Review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 117327–117345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devika, K.N.; Bhakthavatchalu, R. Design of Reconfigurable LFSR for VLSI IC Testing in ASIC and FPGA. International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing, Chennai, India, Feb., 2017.
- Deschamps, J.P.; Bioul, G.J.A. Synthesis of Arithmetic Circuits: FPGA, ASIC and Embedded Systems. New York, USA: Wiley-Interscience, ISBN: 9780471687832, Feb., 2006.
- Fetcher, B.H. FPGA Embedded Processors: Revealing True System Performance. Embedded Systems Conference, pp. 1-18, San Francisco, USA, 2005.
- Bazil Raj, A.A. FPGA-based Embedded System Developer’s Guide. Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press, ISBN: 9781315156200, Oct., 2018.
- Rupani, A.; Sujediya, G. A Review of FPGA Implementation of Internet of Things. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering 2016, 4, 16203–16207. [Google Scholar]
- Hauck, S.; DeHon, A. Reconfigurable Computing: The Theory and Practice of FPGA-Based Computation. San Francisco, CA, USA: Morgan Kaufmann, ISBN: 9780080556017, Nov., 2007.
- Pellerin, D.; Thibault, S. Practical FPGA Programming in C. Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: Prentice Hall Press, ISBN: 9780131543188, Apr., 2005.
- Kilts, S. Advanced FPGA Design: Architecture, Implementation, and Optimization. New York, USA: Wiley-IEEE Press, ISBN: 9780470054376, Jun., 2007.
- Sainath, T.N.; Vinyals, O.; Senior, A.; Sak, H. Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Fully Connected Deep Neural Networks. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech Signal Processing, South Brisbane, QLD, Australia, Apr., 2015.
- Ryumina, E.; Karpov, A. Facial Expression Recognition using Distance Importance Scores Between Facial Landmarks.” International Conference on Computer Graphics and Machine Vision, pp. 1-10, Dec., 2020.
- Sagonas, C.; Tzimiropoulos, G.; Zafeiriou, S.; Pantic, M. 300 Faces in-the-Wild Challenge: The first facial landmark localization Challenge. IEEE Workshops International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 397-403, Sydney, NSW, Australia, Dec., 2013.
- Ma, F.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, S.L.; Zhang, L. Learning Better Representations for Audio-Visual Emotion Recognition with Common Information. Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. Joint Face Detection and Alignment using Multitask Cascaded Convolutional Networks. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 2016, 23, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaratrotkamjorn, A.; Choksuriwong, A. Bimodal Emotion Recognition using Deep Belief Network. International Computer Science and Engineering Conference, pp. 103-109, Phuket, Thailand, Nov., 2019.
- Chen, Z.Q.; Pan, S.T. Integration of Speech and Consecutive Facial Image for Emotion Recognition Based on Deep Learning. Master’s Thesis, National University of Kaohsiung, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 2021.
- Livingstone, S.R.; Russo, F.A. The Ryerson Audio-Visual Database of Emotional Speech and Song (RAVDESS): a Dynamic, Multimodal Set of Facial and Vocal Expressions in North American English. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0196391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeshina, S.O.; Ibrahim, H.; Teoh, S.S.; Hoo, S.C. Custom Face Classification Model for Classroom using Haar-like and LBP Features with Their Performance Comparisons. Electronics 2021, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cao, Y.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Face Recognition based on Haar Like and Euclidean Distance. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2021, 1813, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutter, S.; Hung, J.; Liu, C.; Wechsler, H. Comparative Performance Evaluation of Gray-Scale and Color Information for Face Recognition Tasks. Heidelberg, Berlin, Germany: Springer, ISBN: 9783540453444, Aug., 2001.
- Bhattacharya, S.; Kyal, C.; Routray, A. Simplified Face Quality Assessment (SFQA). Pattern Recognition Letters 2021, 147, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, A.; Ramya, R.S.; Ayushi, S.; Bhumika, R.; Adhoksh, P.; Jhawar, K.; Shah, A.; Venugopal, K.R. Tropical Cyclone Tracking and Forecasting Using BiGRU [TCTFB]. Research Square preprint 2022, PPR553621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Hirota, K.; Jia, Z.; Zhao, L.; Jin, X.; Dai, Y. Multimodal Emotion Recognition Based on Feature Selection and Extreme Learning Machine in Video Clips. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing 2023, 14, 1903–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Rathod, H.; Thakkar, S.; Darji, A. Multimodal Emotion Recognition Using SDA-LDA Algorithm in Video Clips. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing 2021, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Experimental environment | |
| CPU | Intel® Core™ i7-10700 CPU 2.90GHz Manufacturer: Intel Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 32GB Manufacturer: NVIDIA Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA |
| IDE | Jupyter notebook (Python 3.7.6) |
| Deep learning frameworks | TensorFlow 2.9.1, Keras 2.9.0 |
| Label | Number of Data | Proportion |
| Angry | 376 | 15.33% |
| Calm | 376 | 15.33% |
| Disgust | 192 | 7.83% |
| Fear | 376 | 15.33% |
| Happy | 376 | 15.33% |
| Neutral | 188 | 7.39% |
| Sad | 376 | 15.33% |
| Surprised | 192 | 7.83% |
| Total | 2,452 | 100% |
| Label | Number of Data | Proportion |
| Angry | 59 | 10.85% |
| Disgust | 86 | 15.81% |
| Fear | 38 | 6.99% |
| Happy | 179 | 32.90% |
| Sad | 139 | 25.55% |
| Surprised | 43 | 7.90% |
| Total | 544 | 100% |
| Label | Number of Data | Proportion |
| Angry | 211 | 16.71% |
| Disgust | 211 | 16.71% |
| Fear | 211 | 16.71% |
| Happy | 208 | 16.47% |
| Sad | 211 | 16.71% |
| Surprised | 211 | 16.71% |
| Total | 1,263 | 100% |
| Number of LFLBs | Number of Local Features | Accuracy |
| 3 | 2704 | 28.89% |
| 4 | 784 | 52.96% |
| 5 | 256 | 88.58% |
| 6 | 64 | 99.51% |
| 7 | 16 | 32.68% |
| Model Architecture | Information | |
| LFLB 1 | Conv2d (Input) Batch_normalization Max_pooling2d |
Filters = 16, Kernel_size = 5, Strides =1 Pool_size = 5, Strides = 2 |
| LFLB 2 | Conv2d Batch_normalization Max_pooling2d |
Filters = 16, Kernel_size = 5, Strides =1 Pool_size = 5, Strides = 2 |
| LFLB 3 | Conv2d Batch_normalization Max_pooling2d |
Filters = 16, Kernel_size = 5, Strides =1 Pool_size = 5, Strides = 2 |
| LFLB 4 | Conv2d Batch_normalization Max_pooling2d |
Filters = 16, Kernel_size = 5, Strides =1 Pool_size = 5, Strides = 2 |
| LFLB 5 | Conv2d Batch_normalization Max_pooling2d |
Filters = 16, Kernel_size = 3, Strides =1 Pool_size = 3, Strides = 2 |
| LFLB 6 | Conv2d Batch_normalization Max_pooling2d |
Filters = 16, Kernel_size = 3, Strides =1 Pool_size = 3, Strides = 2 |
| Concatenation | Packages every 30 image features into a consecutive facial image feature sequence | |
| Flatten | ||
| Reshape | ||
| LSTM | Unit = 20 | |
| Batch_normalization | ||
| Dense (Output) | Unit = 8, Activation = “softmax” | |
| Training | Validation | Testing | ||||
| Loss | Acc | Loss | Acc | Loss | Acc | |
| Fold 1 | 0.0308 | 1.0000 | 0.0749 | 1.0000 | 0.4998 | 0.9919 |
| Fold 2 | 0.0366 | 1.0000 | 0.0745 | 1.0000 | 0.4517 | 1.0000 |
| Fold 3 | 0. 0192 | 1.0000 | 0.0415 | 1.0000 | 0.1363 | 1.0000 |
| Fold 4 | 0.0206 | 1.0000 | 0.0428 | 1.0000 | 0.2667 | 0.9959 |
| Fold 5 | 0.0369 | 1.0000 | 0.0593 | 1.0000 | 0.2978 | 0.9919 |
| Fold 6 | 0.0310 | 1.0000 | 0.0703 | 1.0000 | 0.4527 | 0.9959 |
| Fold 7 | 0.0179 | 1.0000 | 0.0382 | 1.0000 | 0.1913 | 0.9959 |
| Fold 8 | 0.0118 | 1.0000 | 0.0206 | 1.0000 | 0.0459 | 0.9959 |
| Fold 9 | 0.0225 | 1.0000 | 0.0378 | 1.0000 | 0.1757 | 0.9919 |
| Fold 10 | 0.0348 | 1.0000 | 0.0769 | 1.0000 | 0.2238 | 0.9919 |
| Average | 0.0262 | 1.0000 | 0.0536 | 1.0000 | 0.2741 | 0.9951 |
| Label | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-score |
| Angry | 0.9992 | 0.9967 | 0.9967 | 0.9967 |
| Calm | 0.9967 | 0.9949 | 0.9850 | 0.9899 |
| Disgust | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| Fear | 0.9992 | 0.9960 | 1.0000 | 0.9980 |
| Happy | 0.9996 | 0.9976 | 1.0000 | 0.9988 |
| Neutral | 0.9976 | 0.9559 | 1.0000 | 0.9774 |
| Sad | 0.9992 | 1.0000 | 0.9917 | 0.9959 |
| Surprised | 0.9988 | 1.0000 | 0.9875 | 0.9937 |
| Average | 0.9988 | 0.9926 | 0.9951 | 0.9938 |
| Method | Classes | Accuracy |
| E. Ryumina, et al. [18] | 8 | 98.90% |
| F. Ma, et al. [20] | 6 | 95.49% |
| A. Jaratrotkamjorn, et al. [22] | 8 | 96.53% |
| Z. Q. Chen, et al. [23] | 7 | 94% |
| Proposed model | 8 | 99.51% |
| Training | Validation | Testing | ||||
| Loss | Acc | Loss | Acc | Loss | Acc | |
| Fold 1 | 0.0505 | 0.9137 | 0.9556 | 0.9327 | 0.5868 | 0.8600 |
| Fold 2 | 0.0623 | 0.9951 | 0.2346 | 0.9405 | 0.8079 | 0.8600 |
| Fold 3 | 0. 0852 | 0.9764 | 0.5582 | 0.9428 | 0.6573 | 0.8800 |
| Fold 4 | 0.0705 | 0.9553 | 0.4763 | 0.9053 | 0.4489 | 0.8600 |
| Fold 5 | 0.0792 | 0.9202 | 0.8127 | 0.9492 | 0.5791 | 0.8400 |
| Fold 6 | 0.0801 | 0.9015 | 0.6274 | 0.9266 | 0.4527 | 0.8600 |
| Fold 7 | 0.0928 | 0.9589 | 0.3468 | 0.9134 | 0.4802 | 0.9200 |
| Fold 8 | 0.0893 | 0.9668 | 0.7501 | 0.9431 | 0.6054 | 0.9000 |
| Fold 9 | 0.0934 | 0.9015 | 0.4307 | 0.9519 | 0.4205 | 0.9400 |
| Fold 10 | 0.0683 | 0.9907 | 0.6919 | 0.9203 | 0.6596 | 0.8600 |
| Average | 0.0772 | 0.9480 | 0.5884 | 0.9326 | 0.5698 | 0.8780 |
| Label | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-score |
| Angry | 0.9520 | 0.9600 | 0.6857 | 0.8000 |
| Disgust | 0.9340 | 0.9140 | 0.7727 | 0.8374 |
| Fear | 0.9920 | 0.7143 | 1.0000 | 0.8333 |
| Happy | 0.9960 | 0.9722 | 1.0000 | 0.9859 |
| Sad | 0.8860 | 0.7887 | 0.9333 | 0.8550 |
| Surprised | 0.9960 | 1.0000 | 0.9667 | 0.9831 |
| Average | 0.9593 | 0.8915 | 0.8931 | 0.8825 |
| Paper | Classes | Accuracy |
| F. Ma, et al. [20] | 6 | 64.05% |
| B. Pan, et al. [30] | 6 | 55.38% |
| P. Tiwari [31] | 8 | 77.95% |
| Proposed model | 6 | 87.80% |
| Training | Validation | Testing | ||||
| Loss | Acc | Loss | Acc | Loss | Acc | |
| Fold 1 | 0.0437 | 0.9752 | 0.2978 | 0.9563 | 0.4727 | 0.9603 |
| Fold 2 | 0.0389 | 0.9747 | 0.1925 | 0.9632 | 0.2063 | 0.9683 |
| Fold 3 | 0.0471 | 0.9968 | 0.3194 | 0.9491 | 0.2167 | 0.9762 |
| Fold 4 | 0.0423 | 0.9604 | 0.3751 | 0.9578 | 0.4335 | 0.9603 |
| Fold 5 | 0.0312 | 0.9823 | 0.3530 | 0.9684 | 0.5808 | 0.9603 |
| Fold 6 | 0.0430 | 0.9521 | 0.2496 | 0.9467 | 0.3345 | 0.9524 |
| Fold 7 | 0.0488 | 0.9816 | 0.1693 | 0.9546 | 0.4768 | 0.9683 |
| Fold 8 | 0.0495 | 0.9873 | 0.3847 | 0.9619 | 0.3880 | 0.9762 |
| Fold 9 | 0.0456 | 0.9768 | 0.2319 | 0.9443 | 0.2920 | 0.9841 |
| Fold 10 | 0.0345 | 0.9765 | 0.3890 | 0.9691 | 0.4589 | 0.9762 |
| Average | 0.0424 | 0.9763 | 0.2962 | 0.9571 | 0.3860 | 0.9682 |
| Label | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-score |
| Angry | 0.9817 | 0.9377 | 0.9862 | 0.9613 |
| Disgust | 0.9976 | 1.0000 | 0.9842 | 0.9920 |
| Fear | 0.9786 | 0.9794 | 0.9154 | 0.9463 |
| Happy | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| Sad | 0.9905 | 0.9341 | 1.0000 | 0.9659 |
| Surprised | 0.9881 | 0.9793 | 0.9450 | 0.9618 |
| Average | 0.9894 | 0.9718 | 0.9718 | 0.9712 |
| Paper | Classes | Accuracy |
| F. Ma, et al. [20] | 6 | 80.52% |
| B. Pan, et al. [30] | 6 | 86.65% |
| P. Tiwari [31] | 7 | 61.58% |
| Proposed model | 6 | 96.82% |
| Accuracy (%) | Execution time (sec) | |
| Fold 1 | 99.19 | 11.19 |
| Fold 2 | 100.00 | 12.04 |
| Fold 3 | 100.00 | 12.15 |
| Fold 4 | 99.59 | 11.24 |
| Fold 5 | 99.19 | 11.20 |
| Fold 6 | 99.59 | 12.17 |
| Fold 7 | 99.59 | 12.06 |
| Fold 8 | 99.59 | 11.45 |
| Fold 9 | 99.19 | 11.92 |
| Fold 10 | 99.19 | 11.59 |
| Average | 99.51 | 11.70 |
| Layer | Execution time (sec) | Proportion (%) |
| Conv2D_1 | 1.3649 | 11.66 |
| Batch_Normalization_1 | 0.0008 | Less than 0.01 |
| Max_Pooling2D_1 | 0.8733 | 7.46 |
| Conv2D_2 | 6.9281 | 59.21 |
| Batch_Normalization_2 | 0.0010 | Less than 0.01 |
| Max_Pooling2D _2 | 0.2260 | 1.93 |
| Conv2D_3 | 1.5648 | 13.37 |
| Batch_Normalization_3 | 0.0009 | Less than 0.01 |
| Max_Pooling2D _3 | 0.0755 | 0.64 |
| Conv2D_4 | 0.4721 | 4.03 |
| Batch_Normalization_4 | 0.0006 | Less than 0.01 |
| Max_Pooling2D _4 | 0.0386 | 0.32 |
| Conv2D_5 | 0.0468 | 0.40 |
| Batch_Normalization_5 | 0.0006 | Less than 0.01 |
| Max_Pooling2D _5 | 0.0248 | 0.21 |
| Conv2D_6 | 0.0322 | 0.27 |
| Batch_Normalization_6 | 0.0005 | Less than 0.01 |
| Max_Pooling2D _6 | 0.0221 | 0.18 |
| LSTM | 0.0071 | 0.06 |
| Batch_Normalization_7 | 0.0000 | Less than 0.01 |
| Dense (Softmax) | 0.0002 | Less than 0.01 |
| Total | 11.70 | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




