Submitted:
15 April 2024
Posted:
15 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Multi-Satellite Scheduling Problem Based on Task Merging Mechanism
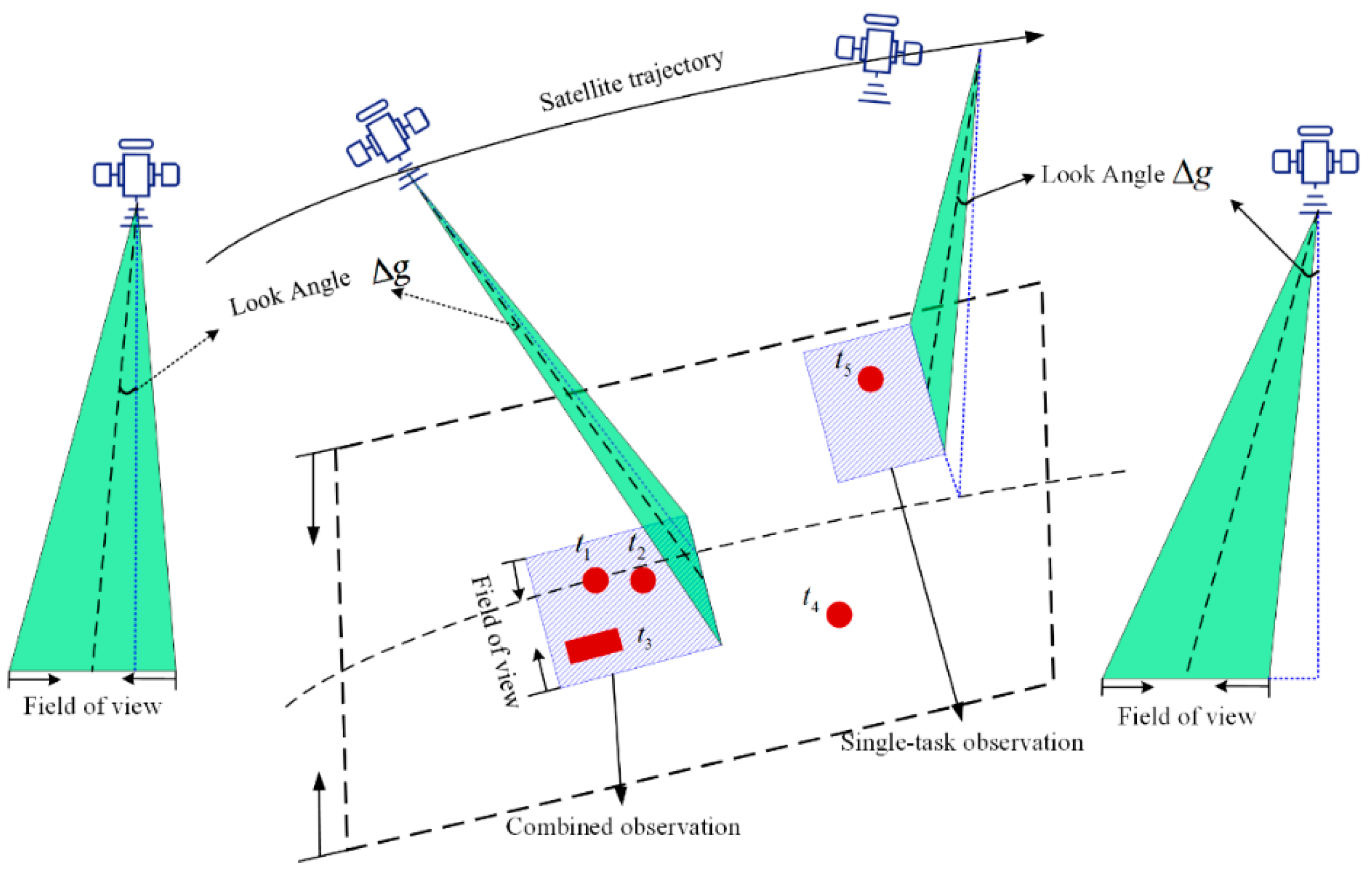
2.1. The Observation of Task Merging
2.2. Scheduling Model for Merging Task Observations
3. Task Merging Method
3.1. Task Merging Method Based MS
3.2. Subsection
4. A Two-Stage Multi-Satellite Scheduling Algorithm Based on Task Merging Mechanism
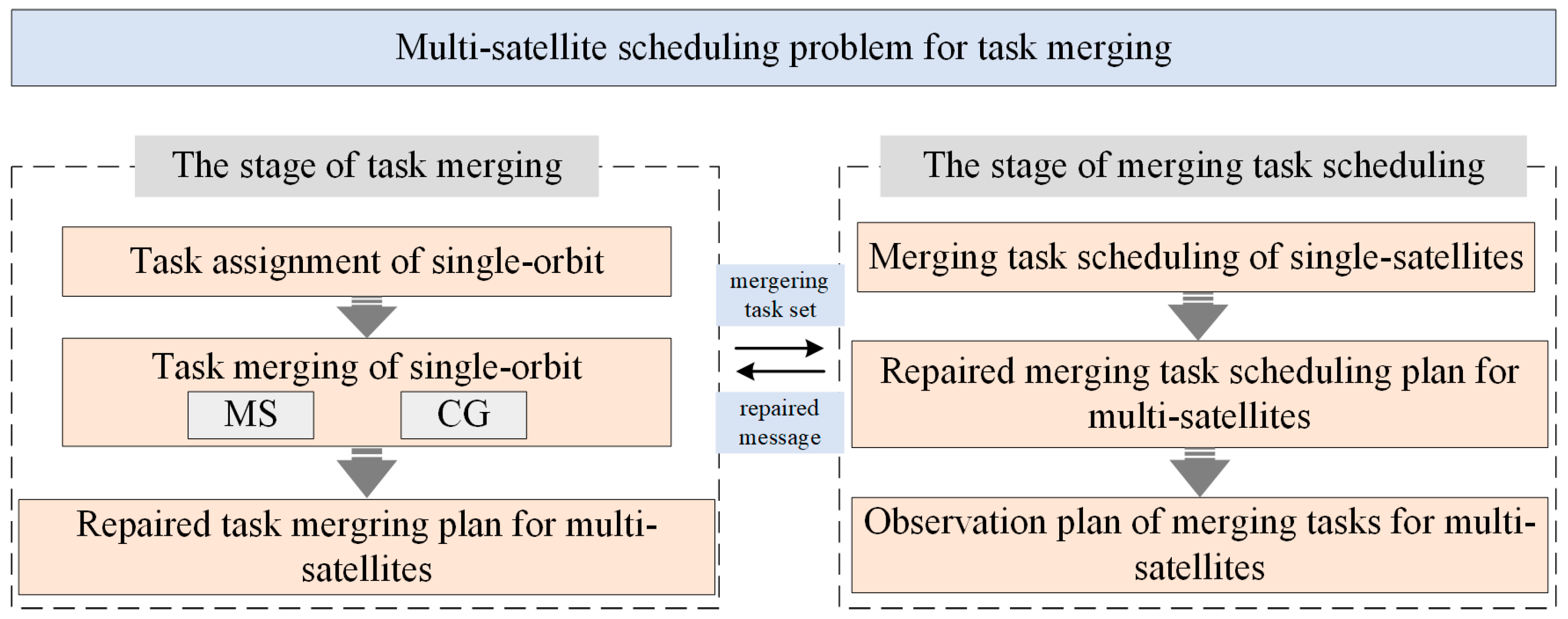
4.1. Algorithmic Architecture
- 1.
- The stage of task merging
- 2.
- The stage of merging tasks scheduling
4.2. Task Merging Algorithm
-
MS Merging algorithm
- Step 1. Preprocess the mono-tasks for task merging, and randomly select a merging task as the initial center of the cluster on a random satellite orbit.
- Step2. Compute the set of points covered within the elliptical region, the drift vector , the new center point , and update the center point .
- Step3. Calculate whether the stopping criterion is satisfied, is a small constant.
- Step 4. If the stopping criterion is not satisfied, go to Step 2 until the stopping criterion is satisfied.
- Step 5. If the stop criterion is satisfied, judge whether the task covered in is merged successfully. If the merging is successful, mark that the task covered in has been visited; if the task merging fails, the task covered in continues to try to merge in other orbits, and if there is no subsequent observation opportunity, mark that it has been visited.
- Step6. Traverse the other track information in turn until all tasks have been accessed.
- Step7. Modify and optimize the mono-tasks belonging to different orbits to determine the optimal task merging plan.
-
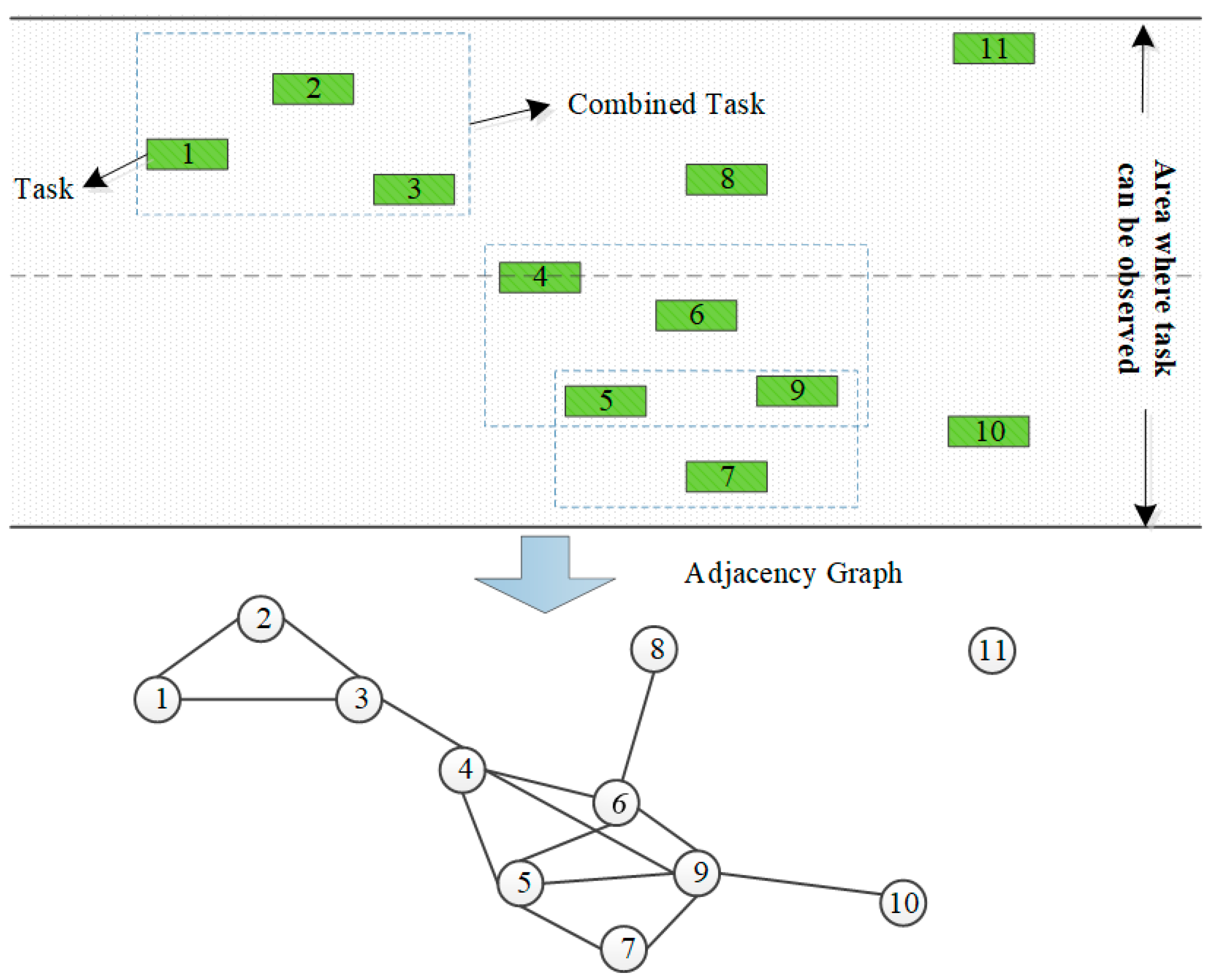
CG Merging algorithm
- Step1. Determine, one by one, whether any two points in the set V of mono-tasks satisfy the merging constraints of the tasks. If satisfied, connect an edge between the two points. Generate the neighborhood undirected graph of the observation task.
- Step2. Find the set of complete subgraphs in the adjacency undirected graph.
- Step 2.1 For each vertex in the adjacency undirected graph, first determine whether there is an adjacency edge between node and other nodes. If there is no neighboring edge, then task constitutes a merging task alone, and record is visited; if there is a neighboring edge between and other nodes, go to Step 2.2.
- Step2.2 Record the set of nodes that have a neighbor relationship with node as , for a node in, find the set of nodes that have neighbor edges with both and . go to Step2.3.
- Step2.3 If the set is empty, the task and are combined into a merging task, record , is visited; if is non-empty, select nodein, and continue to search for the set of nodes that have neighboring edges at the same time as the nodes , , andgo to Step2.4.
- Step2.4 If is empty, then at this point nodes , , andconstitute a merging task, and the record , , and is accessed; otherwise, continue to expand the size of the current merging task by selecting nodes in the set until the set is empty. Turn to Step2.5.
- Step2.5 Until all nodes are accessed, the task synthesis process is completed.
- Step3 Determine the task merging scheme based on the set of all complete subgraphs in Step 2.
4.3. Enhanced Fireworks Algorithm
- 1.
- Explosion Operator
- 2.
- Mutation Operator
- 3.
- Mapping Rules
- 4.
- Population Renewal Strategy
- 5.
- Local optimization strategy
| Insert operator |
| Input: M elitist solutions |
| Output: Best Solution |
| 1: Select M elite solutions from the current iteration and insert each solution to search for optimization in turn. |
| 2: Take the first position of the elite solution and use it to reconstruct a different solution sequence based on EWFA. |
| 3: Construct Tabu list to avoid duplicate solutions. |
5. Experiment
5.1. Experiment Settings
| Num. of tasks | Problem Size (CG/MS) | Num. of seeds (CG/MS) | Spark coefficient | Spark range |
| 100 | 97/121 | 10/10 | 50 | [2,40] |
| 200 | 191/270 | 10/12 | 50 | [2,40] |
| 300 | 275/442 | 10/15 | 50 | [2,40] |
| 400 | 360/676 | 12/20 | 50 | [2,40] |
| 500 | 453/940 | 15/22 | 50 | [2,40] |
| 600 | 519/1170 | 17/25 | 50 | [2,40] |
| 700 | 613/1404 | 20/27 | 50 | [2,40] |
5.2. Result Analysis
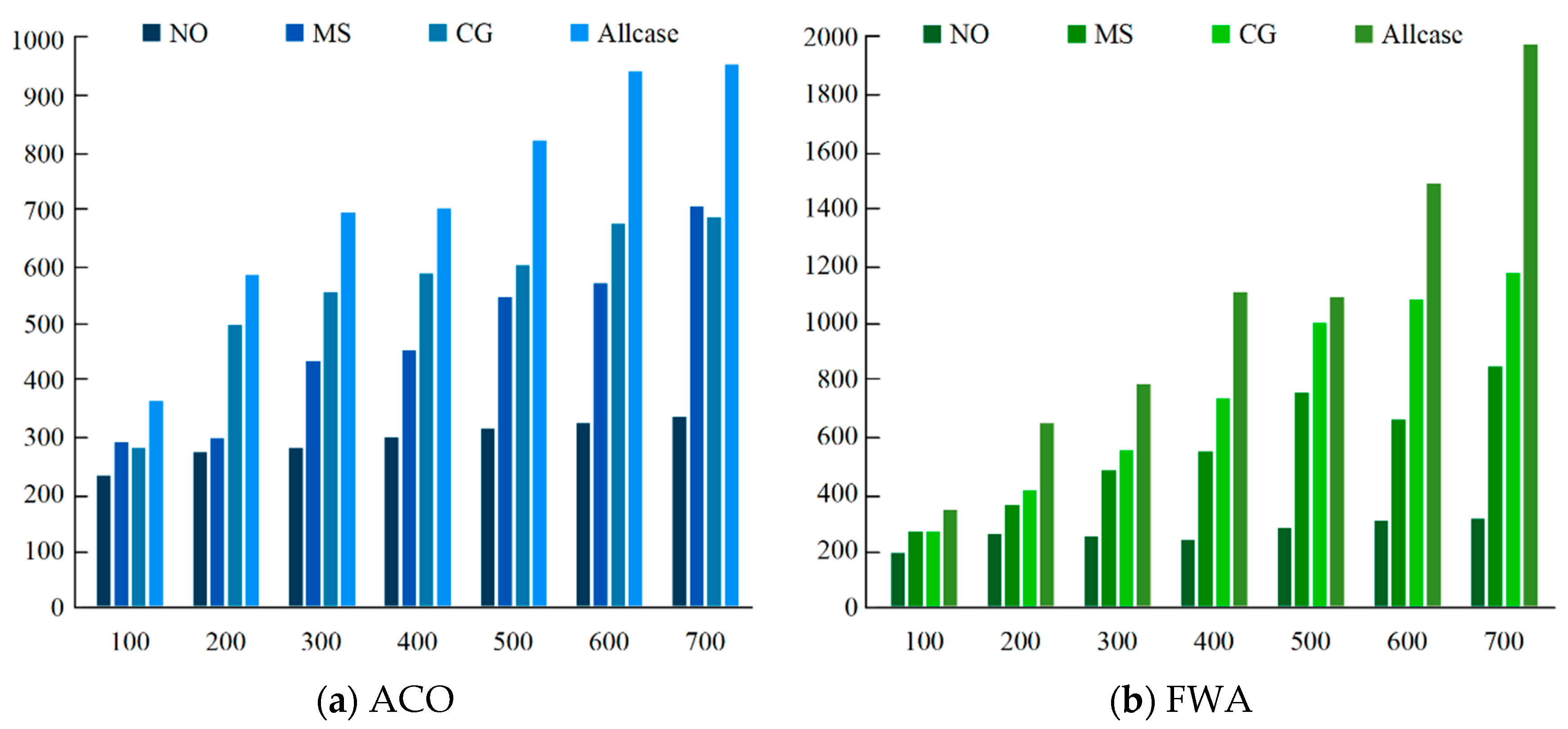
5.2.1. The Effection of Task Merging
| Num. of tasks | ACO | FWA | ||||||
| NO | MS | CG | Allcase | NO | MS | CG | Allcase | |
| 100 | 36 | 48 | 39 | 56 | 31 | 39 | 42 | 54 |
| 200 | 46 | 61 | 68 | 82 | 43 | 57 | 62 | 93 |
| 300 | 44 | 76 | 72 | 92 | 44 | 79 | 85 | 117 |
| 400 | 48 | 71 | 81 | 103 | 43 | 93 | 119 | 176 |
| 500 | 51 | 86 | 78 | 111 | 46 | 121 | 149 | 154 |
| 600 | 49 | 95 | 99 | 122 | 53 | 106 | 166 | 217 |
| 700 | 48 | 103 | 96 | 129 | 52 | 130 | 174 | 280 |
| Algorithm | MS | CG | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Num. of tasks | EACO | EFWA | EACO | EFWA | |
| 100 | 18.76 | 9.31 | 18.76 | 9.31 | |
| 200 | 65.54 | 26.12 | 65.54 | 26.12 | |
| 300 | 96.67 | 62.01 | 96.67 | 62.01 | |
| 400 | 106.41 | 98.21 | 106.41 | 98.21 | |
| 500 | 163.24 | 144.13 | 163.24 | 144.13 | |
| 600 | 218.05 | 220.21 | 218.05 | 220.21 | |
| 700 | 281.02 | 303.11 | 281.02 | 313.11 | |
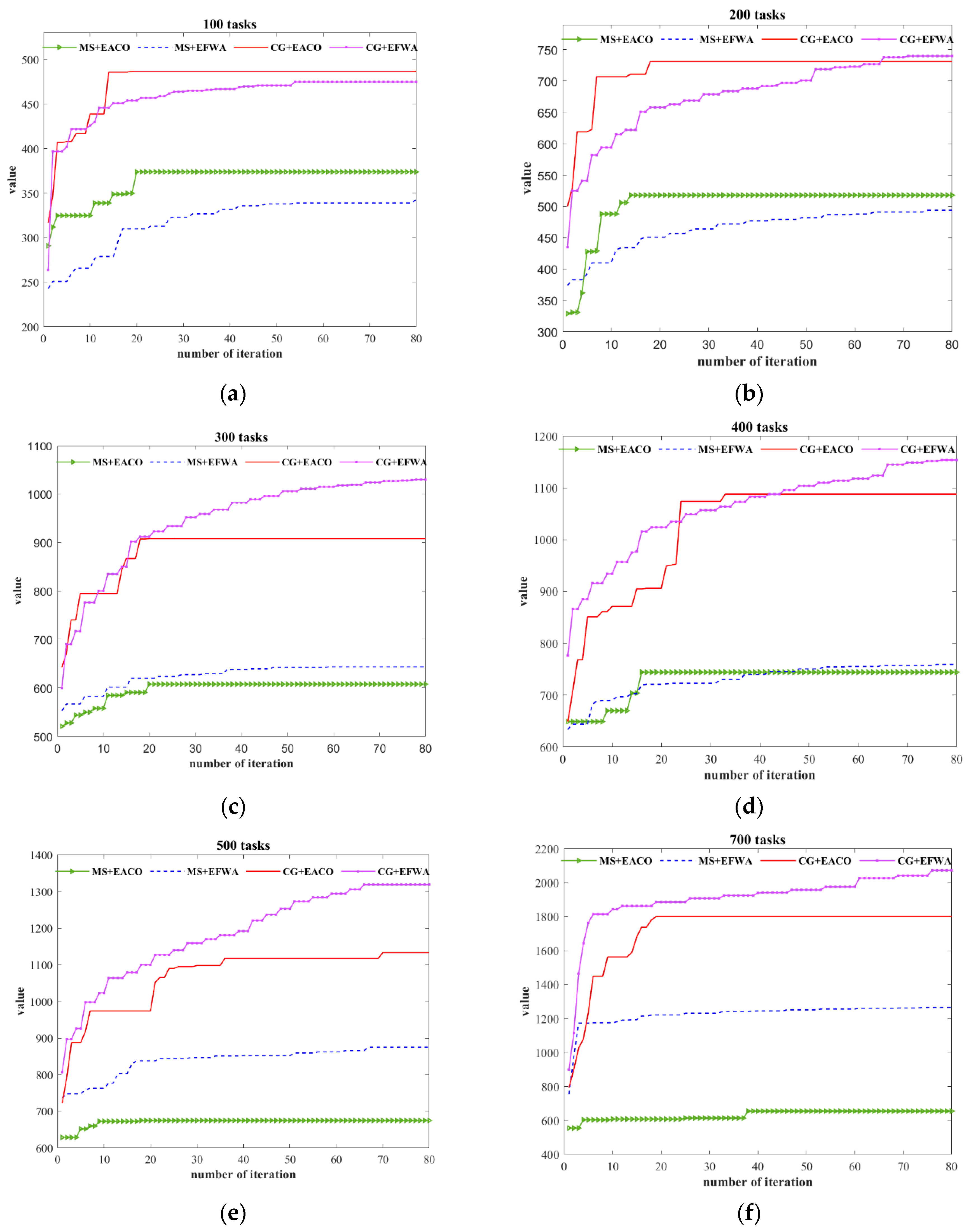
5.2.3. Algorithm Running Time Based on Different Task Merging
5.2.4. Algorithm Stability
| Algrithm | Merging Method | Task | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | ||||||||||
| EACO | MS | 292 | 299 | 434 | 453 | 547 | 571 | 655 | ||
| 10.12 | 13.32 | 21.43 | 20.48 | 25.55 | 26.32 | 27.42 | ||||
| 8.93 | 10.72 | 8.74 | 13.08 | 15.24 | 22.35 | 25.56 | ||||
| 0.80 | 1.43 | 2.51 | 3.76 | 3.48 | 7.24 | 8.73 | ||||
| CG | 282 | 498 | 556 | 589 | 603 | 676 | 688 | |||
| 15.32 | 17.27 | 25.21 | 28.18 | 27.50 | 28.32 | 29.35 | ||||
| 14.86 | 15.83 | 28.79 | 26.25 | 28.18 | 27.38 | 30.12 | ||||
| 0.52 | 2.34 | 3.56 | 4.76 | 9.03 | 9.75 | 9.92 | ||||
| EFWA | MS | 263 | 357 | 480 | 546 | 751 | 658 | 843 | ||
| 9.25 | 10.12 | 12.34 | 20.48 | 26.38 | 20.31 | 28.61 | ||||
| 14.67 | 15.23 | 16.25 | 16.80 | 18.31 | 17.46 | 19.86 | ||||
| 0.33 | 0.21 | 1.93 | 0.41 | 0.63 | 0.39 | 1.16 | ||||
| CG | 263 | 411 | 550 | 733 | 996 | 1079 | 1172 | |||
| 8.21 | 8.45 | 9.21 | 10.12 | 9.67 | 10.32 | 11.31 | ||||
| 13.07 | 14.81 | 15.85 | 16.32 | 17.32 | 16.87 | 18.82 | ||||
| 0.26 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.29 | 0.42 | ||||
6. Conclusion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bianchessi, N.,Cordeau, J. F.,Desrosiers, J.and et al. A heuristic for the multi-satellite, multi-orbit and multi-user management of Earth observation satellites [J]. European Journal of Operational Research,2007,Vol.177(2): 750-762. [CrossRef]
- Pei Wang, Yuejin Tan.Joint Scheduling of Heterogeneous Earth Observing Satellites for Different Stakeholders [A].SpaceOps 2008 Conference [C],2008.
- Hu H Y,Zhang X Q,Liu J.Multiple imaging satellites scheduling method based on AMPL modeling language [J]. Systems Engineering and Electrorncs, 2012,3:517-522.
- Qiu D S,Guo H, He C, and et al. Intensive Task Scheduling Method for Multi-agilelmaging Satellites [J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2013, 34(4):882-889.
- He R J, Gao P, Bai B C et at al. Models, algorithms and applications to the mission planning system of imaging satellites [J]. Systems nngineering-Theory&Practice, 2011(3):411-422.
- Bai B C, He R J, Li J F and et al. Satellite orbit task merging problem and its dynamic programming algorithm [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(7):1738-1742.
- Bai B C, He R J, Li J F and et al. Imaging Satellite Observation Scheduling with Task Merging [J]. ACT A AERONAUTICA ET AST RONAUTICA SINICA, 2009(11):169-175.
- Xu Y L, Xu P D, Wang H L and et al. Clustering of Imaging Reconnaissance Tasks Based on Clique Partition [J]. OPERATIONS RESEARCH AND MANAGEMENT SCIENCE, 2010, 19(4):143-149.
- Wang J, Li J, Chen H Z. A Multi-Objective Imaging Scheduling Approach of Earth Observation Satellite for Emergent Conditions [J]. ACTA ELECTRONICA SINICA, 2008, 36(9):1715-1722.
- Liu X L, Bai B C, et al. Multi satellites scheduling algorithm based on task merging mechanism [J]. Applied Mathematics & Computation, 2014, 230: 687 -700. [CrossRef]
- Zhang M, Wang J D, Wei B. Satellite scheduling method for intensive tasks based on improved fireworks algorithm [J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2018(9):2712-2719. DOI: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2018030547.
- Yu J, Yang W Y, Liu X L, Xing L N. Intensive task merging method and scheduling algorithm for imaging satellites [J]. J.Huazhong Univ. of Sci.&Tech. (Natural Science Edition), 2021, Vol(49): 73-78.
- Mo H, Zeng M. A Lite Fireworks Algorithm for Optimization [J].2023. [CrossRef]
- Song Y J, Xing L N, Chen Y W. Two-stage hybrid planning method for multi-satellite joint observation planning problem considering task splitting [J].COMPUTERS & INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING,2022,Vol.174: 108795. [CrossRef]
| Algorithm1: Enhanced Fireworks Algorithm |
|---|
| Input: Merging Task Set |
| Output: Scheme for Allocating Time Windows to Satellites in Merging Task |
| 1: for i=1:Iter |
| 2: sonsnum_array; |
| 3: for j=1: seednum (sons_generate) |
| 4: for k=1: sonsnum_array(j) |
| 5: search for sparks; |
| 6: end |
| 7: end |
| 8: GaussMutation; |
| 9: Local Optimization Operator for Seed Fireworks; |
| 10: Population intervention operator; |
| 11: Record and choose the best solution |
| 12: end |
| 13: Output best solution |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




