Submitted:
11 April 2024
Posted:
11 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and DNA Isolation
2.2. Genotyping
2.3. Phenotypes Collection and Dataset Editing
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.5. Allelic Model
2.6. Genotypic Model
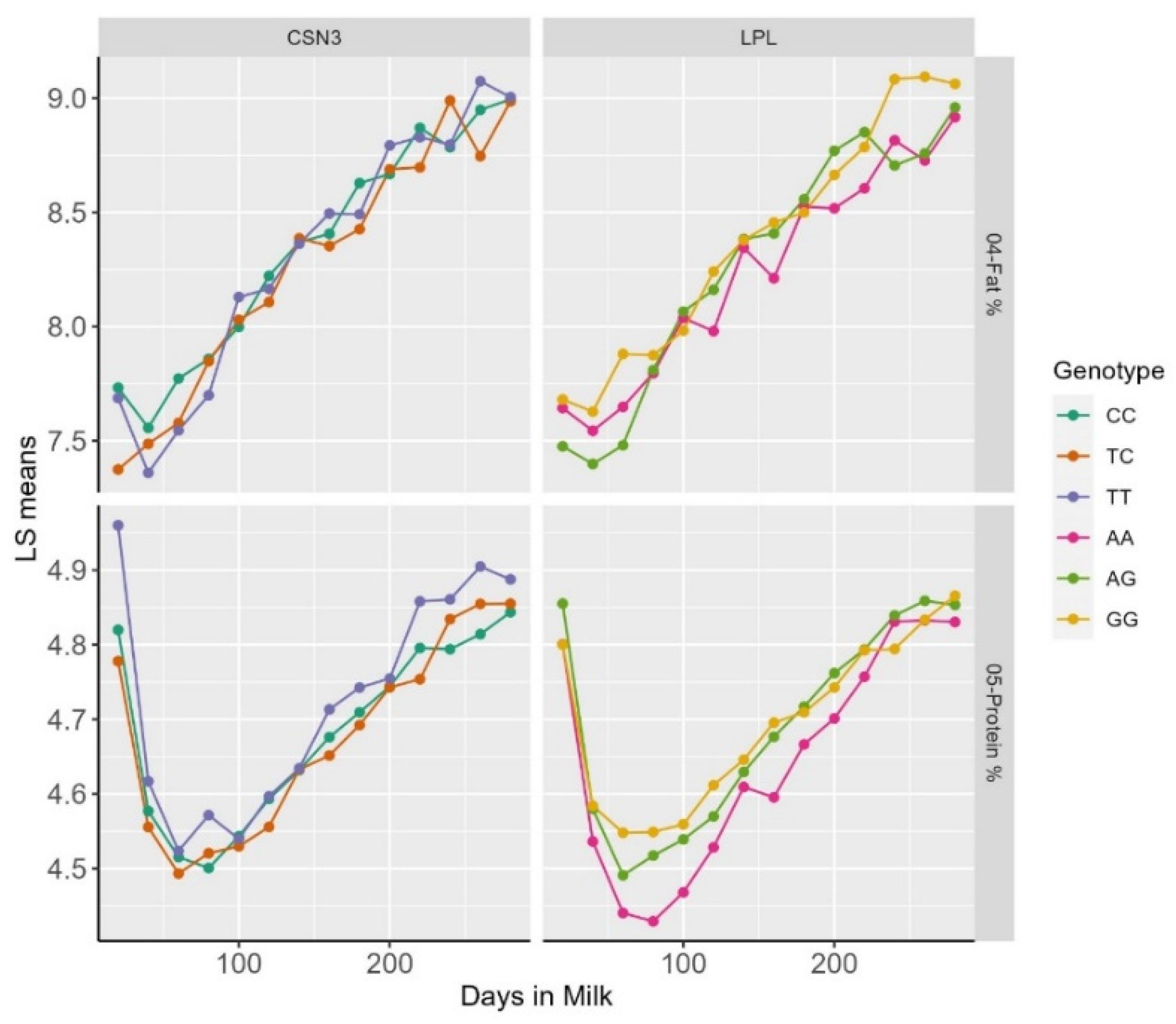
3. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Statistics of live animals. URL http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QA. 2021.
- Zhang, Y.; Colli, L.; Barker, J. Asian water buffalo: Domestication, history and genetics. Animal genetics 2020, 51, 177-191. [CrossRef]
- Iannuzzi, L.; King, W.; Di Berardino, D. Chromosome evolution in domestic bovids as revealed by chromosome banding and FISH-mapping techniques. Cytogenetic and Genome Research 2009, 126, 49-62. [CrossRef]
- MacGregor, R. The domestic buffalo. 1941.
- Pauciullo, A.; Versace, C.; Perucatti, A.; Gaspa, G.; Li, L.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Zheng, H.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Shang, J.-H. Oocyte aneuploidy rates in river and swamp buffalo types (Bubalus bubalis) determined by Multi-color Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (M-FISH). Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 8440. [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.; Wang, T.; Gao, N.L.; Liu, Z.; Cui, K.; Duan, Y.; Wu, S.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, C. The microbiome of the buffalo digestive tract. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 823. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Shi, W.; Jiang, J.; Li, Z.; Fu, P.; Yang, C.; Rehman, S.u.; Pauciullo, A.; Liu, Q.; Shi, D. Comparative metabolomics analysis of milk components between Italian Mediterranean buffaloes and Chinese Holstein cows based on LC-MS/MS technology. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262878. [CrossRef]
- Low, W.Y.; Tearle, R.; Bickhart, D.M.; Rosen, B.D.; Kingan, S.B.; Swale, T.; Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Murphy, T.D.; Young, R.; Lefevre, L. Chromosome-level assembly of the water buffalo genome surpasses human and goat genomes in sequence contiguity. Nature communications 2019, 10, 260. [CrossRef]
- Iamartino, D.; Nicolazzi, E.L.; Van Tassell, C.P.; Reecy, J.M.; Fritz-Waters, E.R.; Koltes, J.E.; Biffani, S.; Sonstegard, T.S.; Schroeder, S.G.; Ajmone-Marsan, P. Design and validation of a 90K SNP genotyping assay for the water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185220. [CrossRef]
- Cesarani, A.; Biffani, S.; Garcia, A.; Lourenco, D.; Bertolini, G.; Neglia, G.; Misztal, I.; Macciotta, N.P.P. Genomic investigation of milk production in Italian buffalo. Italian Journal of Animal Science 2021, 20, 539-547. [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Liang, A.; Liang, S.; Ma, X.; Lu, X.; Duan, A.; Pang, C.; Hua, G.; Liu, S.; Campanile, G. Integrative analysis of transcriptome and GWAS data to identify the hub genes associated with milk yield trait in buffalo. Frontiers in genetics 2019, 10, 36. [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Deng, T.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, T.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, S.; Shao, B.; Wei, P.; Sun, H.; Khan, F. Systematic analyses for candidate genes of milk production traits in water buffalo (Bubalus Bubalis). Animal genetics 2019, 50, 207-216. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liang, A.; Campanile, G.; Plastow, G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Salzano, A.; Gasparrini, B.; Cassandro, M.; Yang, L. Genome-wide association studies to identify quantitative trait loci affecting milk production traits in water buffalo. Journal of dairy science 2018, 101, 433-444. [CrossRef]
- Pauciullo, A.; Cosenza, G.; Steri, R.; Coletta, A.; Jemma, L.; Feligini, M.; Di Berardino, D.; Macciotta, N.P.; Ramunno, L. An association analysis between OXT genotype and milk yield and flow in Italian Mediterranean river buffalo. Journal of dairy research 2012, 79, 150-156. [CrossRef]
- Pauciullo, A.; Cosenza, G.; Steri, R.; Coletta, A.; La Battaglia, A.; Di Berardino, D.; Macciotta, N.P.; Ramunno, L. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the promoter region of river buffalo stearoyl CoA desaturase gene (SCD) is associated with milk yield. Journal of dairy research 2012, 79, 429-435. [CrossRef]
- Pauciullo, A.; Ramunno, L.; Macciotta, N.P.; Gaspa, G.; Coletta, A.; Apicella, E.; Gallo, D.; Cosenza, G. Genetic variability detected at the lactoferrin locus (LTF) in the Italian Mediterranean river buffalo. Animal Production Science 2016, 56, 102-107. [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Tingzhu, Y.; Pasandideh, M.; Liang, A.; Hua, G.; Schreurs, N.M.; Raza, S.H.A.; Salzano, A.; Campanile, G.; Gasparrini, B. Genetic Association of PPARGC1A Gene Single Nucleotide Polymorphism with Milk Production Traits in Italian Mediterranean Buffalo. BioMed Research International 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, A.; Li, Z.; Du, C.; Hua, G.; Salzano, A.; Campanile, G.; Gasparrini, B.; Yang, L. An association analysis between PRL genotype and milk production traits in Italian Mediterranean river buffalo. Journal of Dairy Research 2017, 84, 430-433. [CrossRef]
- Bonfatti, V.; Giantin, M.; Gervaso, M.; Coletta, A.; Dacasto, M.; Carnier, P. Effect of CSN1S1-CSN3 (αS1-κ-casein) composite genotype on milk production traits and milk coagulation properties in Mediterranean water buffalo. Journal of dairy science 2012, 95, 3435-3443. [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, G.; Iannaccone, M.; Auzino, B.; Macciotta, N.; Kovitvadhi, A.; Nicolae, I.; Pauciullo, A. Remarkable genetic diversity detected at river buffalo prolactin receptor (PRLR) gene and association studies with milk fatty acid composition. Animal genetics 2018, 49, 159-168. [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, G.; Pauciullo, A.; Macciotta, N.; Apicella, E.; Steri, R.; La Battaglia, A.; Jemma, L.; Coletta, A.; Di Berardino, D.; Ramunno, L. Mediterranean river buffalo CSN1S1 gene: Search for polymorphisms and association studies. Animal Production Science 2015, 55, 654-660. [CrossRef]
- Pauciullo, A.; Martorello, S.; Carku, K.; Versace, C.; Coletta, A.; Cosenza, G. A novel duplex ACRS-PCR for composite CSN1S1–CSN3 genotype discrimination in domestic buffalo. Italian Journal of Animal Science 2021, 20, 1264-1269. [CrossRef]
- Zicarelli, L.; Di Palo, R.; Napolano, R.; Tonhati, H.; De Carlo, E.; Gagliardi, R.; Di Luccia, A.; la Gatta, B. Influence of αS1-casein and κ-casein polymorphism on the curd yield of Italian Mediterranean buffalo (Bubalus bubalis L.) milk. International Dairy Journal 2020, 100, 104559. [CrossRef]
- Correddu, F.; Serdino, J.; Manca, M.G.; Cosenza, G.; Pauciullo, A.; Ramunno, L.; Macciotta, N.P. Use of multivariate factor analysis to characterize the fatty acid profile of buffalo milk. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2017, 60, 25-31. [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, G.; Gallo, D.; Auzino, B.; Gaspa, G.; Pauciullo, A. Complete CSN1S2 Characterization, Novel Allele Identification and Association With Milk Fatty Acid Composition in River Buffalo. Frontiers in Genetics 2021, 11, 622494. [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, G.; Macciotta, N.P.; Nudda, A.; Coletta, A.; Ramunno, L.; Pauciullo, A. A novel polymorphism in the oxytocin receptor encoding gene (OXTR) affects milk fatty acid composition in Italian Mediterranean river buffalo. Journal of Dairy Research 2017, 84, 170-180. [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Cosenza, G.; Gaspa, G.; Iannaccone, M.; Macciotta, N.; Chemello, G.; Di Stasio, L.; Pauciullo, A. Sequencing of lipoprotein lipase gene in the Mediterranean river buffalo identified novel variants affecting gene expression. Journal of dairy science 2020, 103, 6374-6382. [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Cosenza, G.; Iannaccone, M.; Macciotta, N.; Guo, Y.; Di Stasio, L.; Pauciullo, A. The single nucleotide polymorphism g. 133A> C in the stearoyl CoA desaturase gene (SCD) promoter affects gene expression and quali-quantitative properties of river buffalo milk. Journal of dairy science 2019, 102, 442-451. [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Cosenza, G.; Nicolae, I.; Bota, A.; Guo, Y.; Di Stasio, L.; Pauciullo, A. Transcript analysis at DGAT1 reveals different mRNA profiles in river buffaloes with extreme phenotypes for milk fat. Journal of dairy science 2017, 100, 8265-8276. [CrossRef]
- Pauciullo, A.; Cosenza, G.; D’avino, A.; Colimoro, L.; Nicodemo, D.; Coletta, A.; Feligini, M.; Marchitelli, C.; Di Berardino, D.; Ramunno, L. Sequence analysis and genetic variability of stearoyl CoA desaturase (SCD) gene in the Italian Mediterranean river buffalo. Molecular and Cellular Probes 2010, 24, 407-410. [CrossRef]
- Goossens, M.; Kan, Y.Y. [49] DNA analysis in the diagnosis of hemoglobin disorders. In Methods in enzymology; Elsevier: 1981; Volume 76, pp. 805-817. [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Shook, G. An optimum transformation for somatic cell concentration in milk. Journal of Dairy Science 1980, 63, 487-490. [CrossRef]
- Grisart, B.; Coppieters, W.; Farnir, F.; Karim, L.; Ford, C.; Berzi, P.; Cambisano, N.; Mni, M.; Reid, S.; Simon, P. Positional candidate cloning of a QTL in dairy cattle: Identification of a missense mutation in the bovine DGAT1 gene with major effect on milk yield and composition. Genome research 2002, 12, 222-231. [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Negrini, R.; De Marchi, M.; Campanile, G.; Neglia, G. Phenotypic characterization of milk yield and quality traits in a large population of water buffaloes. Animals 2020, 10, 327. [CrossRef]
- Rosati, A.; Van Vleck, L.D. Estimation of genetic parameters for milk, fat, protein and mozzarella cheese production for the Italian river buffalo Bubalus bubalis population. Livestock Production Science 2002, 74, 185-190. [CrossRef]
- AIA. Italian Breeders Association (Associazione Italiana Allevatori, AIA) Bollettino online. Statistiche ufficiali. URL http://bollettino.aia.it/Contenuti.aspx?CD_GruppoStampe=RS&CD_Specie=C4. 2022.
- Chen, Y.; Atashi, H.; Vanderick, S.; Mota, R.; Soyeurt, H.; Hammami, H.; Gengler, N. Genetic analysis of milk urea concentration and its genetic relationship with selected traits of interest in dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science 2021, 104, 12741-12755. [CrossRef]
- Samoré, A.; Romani, C.; Rossoni, A.; Frigo, E.; Pedron, O.; Bagnato, A. Genetic parameters for casein and urea contentin the Italian Brown Swiss dairy cattle. Italian Journal of Animal Science 2007, 6, 201-203. [CrossRef]
- Ariyarathne, H.B.; Correa-Luna, M.; Blair, H.T.; Garrick, D.J.; Lopez-Villalobos, N. Genetic parameters for efficiency of crude protein utilisation and its relationship with production traits across lactations in grazing dairy cows. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research 2021, 64, 62-82. [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Villalobos, N.; Correa-Luna, M.; Burke, J.; Sneddon, N.; Schutz, M.; Donaghy, D.; Kemp, P. Genetic parameters for milk urea concentration and milk traits in New Zealand grazing dairy cattle. NZJ Anim. Sci. Prod 2018, 78, 56-61.
- Badaoui, B.; Serradilla, J.; Tomas, A.; Urrutia, B.; Ares, J.; Carrizosa, J.; Sanchez, A.; Jordana, J.; Amills, M. Identification of two polymorphisms in the goat lipoprotein lipase gene and their association with milk production traits. Journal of dairy science 2007, 90, 3012-3017. [CrossRef]
- Brzáková, M.; Rychtářová, J.; Čítek, J.; Sztankóová, Z. A candidate gene association study for economically important traits in Czech dairy goat breeds. Animals 2021, 11, 1796. [CrossRef]
- Crepaldi, P.; Nicoloso, L.; Coizet, B.; Milanesi, E.; Pagnacco, G.; Fresi, P.; Dimauro, C.; Macciotta, N.P.P. Associations of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase α, stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase, and lipoprotein lipase genes with dairy traits in Alpine goats. Journal of dairy science 2013, 96, 1856-1864. [CrossRef]
- Marchitelli, C.; Contarini, G.; De Matteis, G.; Crisà, A.; Pariset, L.; Scatà, M.C.; Catillo, G.; Napolitano, F.; Moioli, B. Milk fatty acid variability: Effect of some candidate genes involved in lipid synthesis. Journal of dairy research 2013, 80, 165-173. [CrossRef]
- Legarra, A.; Garcia-Baccino, C.A.; Wientjes, Y.C.; Vitezica, Z.G. The correlation of substitution effects across populations and generations in the presence of nonadditive functional gene action. Genetics 2021, 219, iyab138. [CrossRef]
- Jollès, P.; Loucheux-Lefebvre, M.-H.; Henschen, A. Structural relatedness of κ-casein and fibrinogen γ-chain. Journal of Molecular Evolution 1978, 11, 271-277. [CrossRef]
- Luyendyk, J.P.; Schoenecker, J.G.; Flick, M.J. The multifaceted role of fibrinogen in tissue injury and inflammation. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 2019, 133, 511-520. [CrossRef]
- Córdova-Dávalos, L.E.; Jiménez, M.; Salinas, E. Glycomacropeptide bioactivity and health: A review highlighting action mechanisms and signaling pathways. Nutrients 2019, 11, 598. [CrossRef]
- Olsen, W.; Liang, N.; Dallas, D.C. Macrophage-Immunomodulatory Actions of Bovine Whey Protein Isolate, Glycomacropeptide, and Their In Vitro and In Vivo Digests. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4942. [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Park, S.H.; Dallas, D.C. The Role of Bovine Kappa-Casein Glycomacropeptide in Modulating the Microbiome and Inflammatory Responses of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3991. [CrossRef]
- Viale, E.; Tiezzi, F.; Maretto, F.; De Marchi, M.; Penasa, M.; Cassandro, M. Association of candidate gene polymorphisms with milk technological traits, yield, composition, and somatic cell score in Italian Holstein-Friesian sires. Journal of dairy science 2017, 100, 7271-7281. [CrossRef]
- Čítek, J.; Brzáková, M.; Hanusová, L.; Hanuš, O.; Večerek, L.; Samková, E.; Jozová, E.; Hoštičková, I.; Trávníček, J.; Klojda, M. Somatic cell score: Gene polymorphisms and other effects in Holstein and Simmental cows. Animal Bioscience 2022, 35, 13. [CrossRef]
- Prinzenberg, E.-M.; Brandt, H.; Bennewitz, J.; Kalm, E.; Erhardt, G. Allele frequencies for SNPs in the αS1-casein gene (CSN1S1) 5′ flanking region in European cattle and association with economic traits in German Holstein. Livestock Production Science 2005, 98, 155-160. [CrossRef]
| Genotype | Records | Buffaloes(%) | Lactations | NLbuffalo±sd | TDbuffalo±sd | TDlact±sd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| αs1-CN | ||||||
| CC | 6527 | 280 (41.2) | 1043 | 3.8±1.7 | 23.3±15.2 | 6.1±1.6 |
| CT | 6638 | 291 (42.8) | 1054 | 3.6±1.7 | 22.8±14.4 | 6.1±1.5 |
| TT | 2257 | 109 (16.0) | 399 | 3.3±1.7 | 23.6±12.9 | 6.4±1.8 |
| κ-CN | ||||||
| CC | 7229 | 314 (46.2) | 1171 | 3.7±1.7 | 23.0±14.7 | 6.0±1.5 |
| CT | 6294 | 282 (41.5) | 991 | 3.7±1.7 | 22.2±14.5 | 6.3±1.6 |
| TT | 2219 | 84 (12.3) | 334 | 3.4±1.7 | 26.4±12.3 | 6.7±1.7 |
| SCD | ||||||
| AA | 9920 | 425 (62.5) | 1570 | 3.7±1.7 | 23.3±14.6 | 6.2±1.6 |
| AC | 4781 | 211 (31.0) | 765 | 3.6±1.7 | 22.7±13.8 | 6.1±1.6 |
| CC | 1041 | 44 (6.50) | 161 | 3.7±1.7 | 23.7±16.0 | 6.1±1.6 |
| LPL | ||||||
| AA | 1943 | 94 (13.9) | 303 | 3.1±1.7 | 20.7±12.9 | 6.3±1.7 |
| AG | 7450 | 319 (46.9) | 1190 | 3.5±1.7 | 23.4±14.3 | 6.1±1.5 |
| GG | 6349 | 267 (39.2) | 1003 | 3.9±1.7 | 23.8±15.1 | 6.2±1.6 |
| Total | 15742 | 680 (100) | 2496 | 3.6±1.7 | 23.2±14.5 | 6.1±1.2 |
| Gene | Product | SNP | Position (nucleotide) |
Alleles | Genotypes | MAF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSN1S1 | αs1-casein | AJ005430:c.578C>T | Exon 17 (89) |
C/T | A/B | 0.37 |
| CSN3 | κ-casein | HQ677596:c.536C>T | Exon 4 (377) |
C/T | A/B | 0.33 |
| SCD | Stearoyl CoA Desaturase | FM876222:g.133A>C | Promoter (-461) |
A/C | A/B | 0.21 |
| LPL | Lipoprotein Lipase | AWWX01438720.1:g14229A>G | Exon 1 (107) |
A/G | A/B | 0.37 |
| Descriptive | Pearson correlation | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | Records (TD±sd)1 | N buffaloes1 | Mean ± sd | min | max | dFY | dPY | dFP | dPP | SCS | Urea | |
| dMY (kg/d) | 14,219 (22.5±14.0) | 645 | 8.81 ± 4.15 | 0.20 | 26.8 | 0.90 | 0.97 | -0.21 | -0.24 | -0.18 | 0.08 | |
| dFY (kg/d) | 14,222 (22.1±13.5) | 645 | 0.74 ± 0.35 | 0.02 | 3.27 | * | 0.90 | 0.18 | -0.12 | -0.16 | 0.06 | |
| dPY (kg/d) | 14,303 (22.2±13.6) | 645 | 0.40 ± 0.19 | 0.01 | 1.27 | * | -0.16 | -0.06 | -0.17 | 0.09 | ||
| dFP (g/100g) | 14,222 (22.1±13.5) | 645 | 8.52 ± 1.68 | 3.52 | 15.42 | * | 0.31 | 0.04 | -0.05 | |||
| dPP (g/100g) | 14,306 (22.2±13.6) | 645 | 4.70 ± 0.42 | 3.02 | 6.85 | * | 0.06 | 0.03 | ||||
| SCS (log) | 13,738 (22.1±13.5) | 645 | 3.18 ± 1.90 | -3.64 | 10.86 | * | 0.04 | |||||
| Urea (mg/dl) | 12,212 (19.8±12.3) | 616 | 37.16 ± 13.46 | 0.12 | 145.2 | * | ||||||
| DIM | 14,519 (22.5±14.0) | 645 | 152.69 ± 92.67 | 5.00 | 679 | |||||||
| Additive | Dominance. | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | Gene1 | α | s.e. | P | d | s.e. | P | |||
| dMY (kg/d) | CSN1S1 | 0.237 | 0.104 | 0.022 | * | 0.224 | 0.148 | 0.131 | ||
| CSN3 | 0.078 | 0.106 | 0.463 | -0.002 | 0.149 | 0.988 | ||||
| SCD | -0.106 | 0.120 | 0.374 | 0.087 | 0.159 | 0.585 | ||||
| LPL | -0.238 | 0.108 | 0.028 | * | 0.177 | 0.147 | 0.229 | |||
| dFY (kg/d) | CSN1S1 | 0.018 | 0.008 | 0.029 | * | 0.015 | 0.012 | 0.210 | ||
| CSN3 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.595 | -0.004 | 0.012 | 0.718 | ||||
| SCD | -0.012 | 0.010 | 0.213 | 0.008 | 0.013 | 0.512 | ||||
| LPL | -0.012 | 0.009 | 0.183 | 0.010 | 0.012 | 0.399 | ||||
| dPY (kg/d) | CSN1S1 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.014 | * | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.255 | ||
| CSN3 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.300 | -0.002 | 0.007 | 0.785 | ||||
| SCD | -0.005 | 0.005 | 0.317 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.503 | ||||
| LPL | -0.008 | 0.005 | 0.098 | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.208 | ||||
| dFP (g/100g) | CSN1S1 | 0.003 | 0.033 | 0.937 | -0.035 | 0.047 | 0.461 | |||
| CSN3 | -0.031 | 0.034 | 0.354 | -0.074 | 0.047 | 0.115 | ||||
| SCD | -0.052 | 0.038 | 0.164 | -0.003 | 0.050 | 0.953 | ||||
| LPL | 0.076 | 0.035 | 0.027 | * | -0.047 | 0.046 | 0.312 | |||
| dPP (g/100g) | CSN1S1 | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.260 | -0.018 | 0.014 | 0.182 | |||
| CSN3 | 0.012 | 0.010 | 0.212 | -0.019 | 0.014 | 0.173 | ||||
| SCD | -0.005 | 0.011 | 0.639 | 0.007 | 0.015 | 0.648 | ||||
| LPL | 0.020 | 0.010 | 0.050 | * | 0.007 | 0.014 | 0.631 | |||
| SCS (log(SCC/100)+3) | CSN1S1 | 0.087 | 0.041 | 0.032 | * | 0.119 | 0.057 | 0.038 | * | |
| CSN3 | 0.117 | 0.041 | 0.005 | ** | 0.067 | 0.058 | 0.247 | |||
| SCD | -0.081 | 0.046 | 0.080 | -0.076 | 0.061 | 0.216 | ||||
| LPL | 0.008 | 0.042 | 0.845 | -0.017 | 0.057 | 0.770 | ||||
| UREA (mg/dl) | CSN1S1 | -0.172 | 0.262 | 0.511 | 0.317 | 0.367 | 0.388 | |||
| CSN3 | 0.177 | 0.266 | 0.507 | 0.909 | 0.365 | 0.013 | * | |||
| SCD | 0.208 | 0.293 | 0.477 | 0.362 | 0.390 | 0.353 | ||||
| LPL | -0.029 | 0.271 | 0.915 | -0.191 | 0.361 | 0.596 | ||||
| Genotype2 | % Variance explained by random effect | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | Gene | A/B | Allelic1 | A/A | A/B | B/B | P3 | r2SNP | r2bcow | r2htd | |
| dMY (kg/d) | CSN1S1 | C/T | * | 8.00b(.12) | 8.32ab(.14) | 8.47a(.20) | 0.04 | * | 0.4 | 8.6 | 37.1 |
| CSN3 | C/T | 8.15 (.13) | 8.20 (.14) | 8.39 (.22) | 0.60 | ns | 0.0 | 8.7 | 37.3 | ||
| SCD | A/C | 8.21 (.12) | 8.22 (.15) | 7.90 (.30) | 0.57 | ns | 0.0 | 8.7 | 37.3 | ||
| LPL | A/G | * | 8.46 (.21) | 8.29 (.13) | 8.01 (.14) | 0.08 | † | 0.3 | 8.7 | 37.1 | |
| dFY (kg/d) | CSN1S1 | C/T | * | 0.66 (.01) | 0.68 (.01) | 0.70 (.02) | 0.08 | † | 0.3 | 9.6 | 26.2 |
| CSN3 | C/T | 0.67 (.01) | 0.67 (.01) | 0.69 (.02) | 0.59 | ns | 0.0 | 9.6 | 26.2 | ||
| SCD | A/C | 0.68 (.01) | 0.68 (.01) | 0.64 (.02) | 0.22 | ns | 0.0 | 9.6 | 26.2 | ||
| LPL | A/G | 0.69 (.02) | 0.68 (.01) | 0.67 (.01) | 0.46 | ns | 0.0 | 9.6 | 26.2 | ||
| dPY (kg/d) | CSN1S1 | C/T | * | 0.37b (.01) | 0.38ab (.01) | 0.40a(.01) | 0.03 | * | 0.4 | 10.0 | 33.8 |
| CSN3 | C/T | 0.38 (.01) | 0.38 (.01) | 0.39 (.01) | 0.32 | ns | 0.0 | 10.1 | 34.0 | ||
| SCD | A/C | 0.38 (.01) | 0.38 (.01) | 0.36 (.01) | 0.39 | ns | 0.0 | 10.1 | 34.0 | ||
| LPL | A/G | 0.39 (.01) | 0.39 (.01) | 0.37 (.01) | 0.21 | ns | 0.1 | 10.1 | 34.0 | ||
| dFP (g/100g) | CSN1S1 | C/T | 8.33 (.06) | 8.28 (.06) | 8.34 (.08) | 0.59 | ns | 0.0 | 13.6 | 8.8 | |
| CSN3 | C/T | 8.34 (.06) | 8.26 (.06) | 8.32 (.08) | 0.29 | ns | 0.0 | 13.6 | 8.8 | ||
| SCD | A/C | 8.33 (.06) | 8.31 (.07) | 8.15 (.10) | 0.19 | ns | 0.0 | 13.6 | 8.8 | ||
| LPL | A/G | * | 8.24ab(.08) | 8.27b(.06) | 8.38a(.06) | 0.05 | * | 0.1 | 13.6 | 8.8 | |
| dPP (g/100g) | CSN1S1 | C/T | 4.68(.02) | 4.67(.02) | 4.72(.02) | 0.09 | † | 0.1 | 14.3 | 14.5 | |
| CSN3 | C/T | 4.68(.02) | 4.68(.02) | 4.73(.02) | 0.06 | † | 0.2 | 14.3 | 14.5 | ||
| SCD | A/C | 4.69(.01) | 4.69(.02) | 4.65(.03) | 0.43 | ns | 0.0 | 14.3 | 14.6 | ||
| LPL | A/G | * | 4.64(.02) | 4.69(.02) | 4.70(.02) | 0.06 | † | 0.2 | 14.3 | 14.5 | |
| SCS (log(SCC/100)+3) | CSN1S1 | C/T | * | 3.12b(.08) | 3.28a(.08) | 3.25ab(.10) | 0.04 | * | 0.2 | 25.6 | 11.7 |
| CSN3 | C/T | * | 3.13b(.02) | 3.26ab(.08) | 3.35a(.02) | 0.03 | * | 0.3 | 25.5 | 11.7 | |
| SCD | A/C | 3.24 (.07) | 3.16 (.08) | 3.07 (.13) | 0.22 | ns | 0.1 | 25.7 | 11.7 | ||
| LPL | A/G | 3.20 (.10) | 3.19 (.07) | 3.22 (.08) | 0.91 | ns | 0.0 | 25.7 | 11.7 | ||
| UREA (mg/dl) | CSN1S1 | C/T | 37.59(.62) | 37.68(.62) | 36.77(.73) | 0.23 | ns | 0.0 | 57.1 | 7.6 | |
| CSN3 | C/T | 37.24b(.62) | 38.04a(.62) | 36.80b(.76) | 0.04 | * | 0.1 | 57.1 | 7.5 | ||
| SCD | A/C | 37.45(.60) | 37.72(.65) | 37.35(.89) | 0.77 | ns | 0.0 | 57.1 | 7.6 | ||
| LPL | A/G | 38.00(.75) | 37.38(.61) | 37.60(.63) | 0.54 | ns | 0.0 | 57.1 | 7.6 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





