Submitted:
10 April 2024
Posted:
11 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of RKIP and pRKIP Levels in Urine Sample
3.2. Evaluation of RKIP and pRKIP Levels in Serum Samples
- - INDIRECT ELISA
- -SANDWICH ELISA
| PHASE 1 | PHASE 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | Lung cancer |
Healthy Controls | p-value | All | Lung cancer |
healthy Controls | p-value | ||
| Subjects (n) | 42 (100) | 21 (100) | 21 (100) | 41 (100) | 18 (100) | 21 (100) | |||
| Mean Age | 65.5 ± 6.3 | 67.1 ± 6.6 | 63.9 ± 5.5 | 0.089 | 68.0 ± 6.8 | 69.8 ± 6.7 | 66.1 ± 6.4 | 0.083 | |
| Sex | |||||||||
| Female | 18 (42.9) | 10 (47.6) | 8 (38.1) | 16 (39.0) | 11 (61.1) | 5 (23.8) | |||
| Male | 24 (57.1) | 11 (52.4) | 13 (61.9) | 0.76 | 24 (58.5) | 9 (50.0) | 15 (71.4) | 0.11 | |
| Smoking status | |||||||||
| Current smokers | 15 (35.7) | 7 (33.3) | 8 (38.1) | 8 (19.5) | 2 (11.1) | 6 (28.6) | |||
| Ex-smokers | 20 (47.6) | 9 (42.9) | 11 (52.4) | 25 (61.0) | 12 (66.7) | 13 (61.9) | |||
| Never-smokers | 7 (16.7) | 5 (23.8) | 2 ( 9.5) | 0.60 | 7 (17.1) | 6 (33.3) | 1 ( 4.8) | 0.081 | |
| Mean Pack-years | 51.1 ± 35.3 | 58.9 ± 35.0 | 44.6 ± 35.1 | 0.24 | 30.5 ± 29.5 | 30.0 ± 29.1 | 30.9 ± 30.6 | 0.93 | |
| Commorbidities | |||||||||
| AH1 | 17 (40.5) | 11 (52.4) | 6 (28.6) | 0.21 | 19 (46.3) | 12 (66.7) | 7 (33.3) | 0.20 | |
| Cardiac disease | 4 ( 9.5) | 4 (19.0) | 0 ( 0.0) | 0.11 | 3 ( 7.3) | 0 ( 0.0) | 3 (14.3) | 0.23 | |
| Metabolic disease2 | 17 (40.5) | 8 (38.1) | 9 (42.9) | 1.00 | 12 (29.3) | 5 (27.8) | 7 (33.3) | 0.73 | |
| COPD3 | 4 ( 9.5) | 0 ( 0.0) | 4 (19.0) | 0.11 | 3 ( 7.3) | 0 ( 0.0) | 3 (14.3) | 0.23 | |
| PHASE 1 | PAHSE 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Histology | Adenocarcinoma | 17 | 13 |
| squamous-cell carcinoma | 1 | 2 | |
| Neuroendocrine | 3 | 3 | |
| Stage | IA | 5 | 3 |
| IA2 | 6 | 2 | |
| IA3 | 4 | 4 | |
| IB | 6 | 2 | |
| IIB | - | 3 | |
| IIIA | - | 4 |
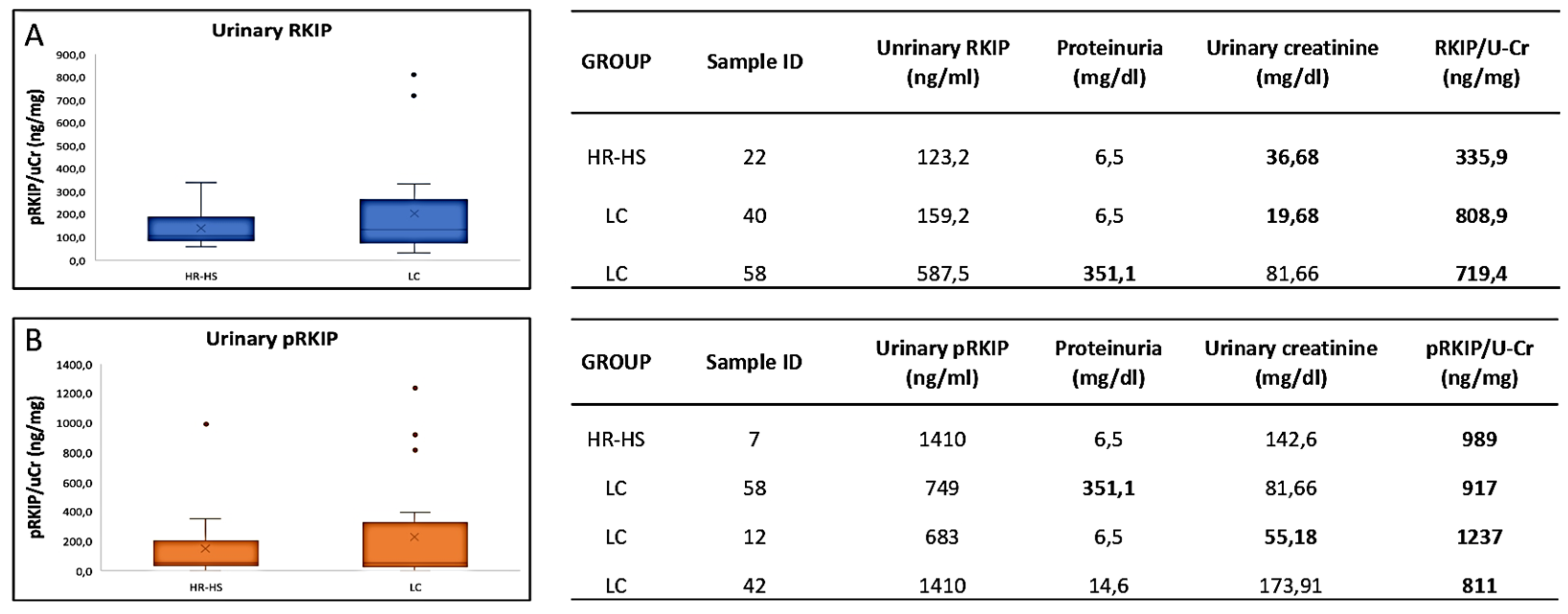
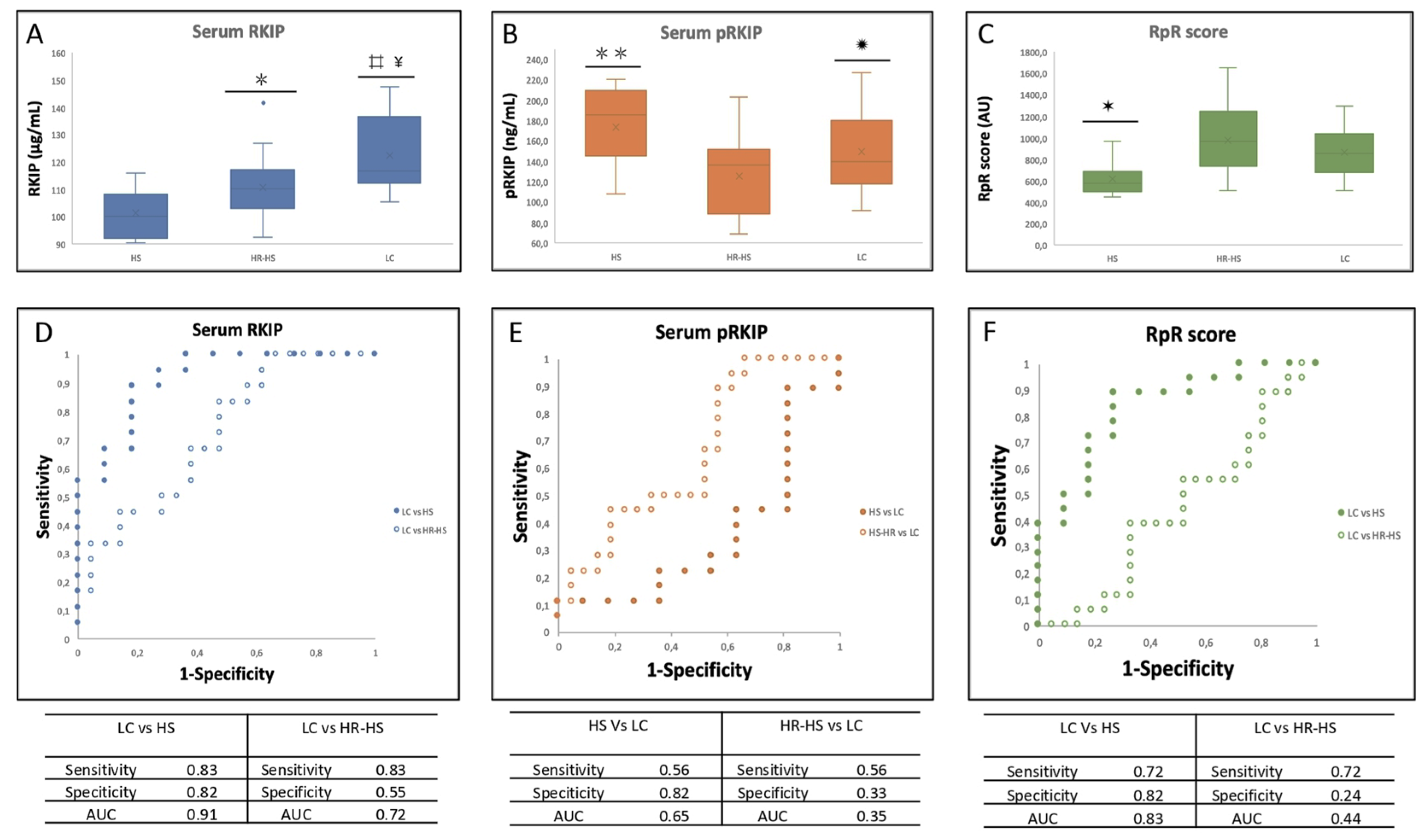
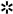 = p-value < 0.005 HS vs HR-HS; ✹ = p-value < 0.05 HR-HS vs LC;
= p-value < 0.005 HS vs HR-HS; ✹ = p-value < 0.05 HR-HS vs LC; 
 = p-value < 0.0005 HS-HR vs HS; ✶ = p-value < 0.005 HS vs HR-HS and LC . D. AUC obtained by measuring total serum RKIP in LC vs HS (solid circles) or HR-HS (empty circles); E AUC obtained by measuring serum pRKIP in Hs vs LC (solid circles) or HR-HS vs LC (empty circles); F. AUC obtained by measuring serum RKIP/pRKIP ratio in Hs vs LC (solid circles) or HR-HS vs LC (empty circles);
= p-value < 0.0005 HS-HR vs HS; ✶ = p-value < 0.005 HS vs HR-HS and LC . D. AUC obtained by measuring total serum RKIP in LC vs HS (solid circles) or HR-HS (empty circles); E AUC obtained by measuring serum pRKIP in Hs vs LC (solid circles) or HR-HS vs LC (empty circles); F. AUC obtained by measuring serum RKIP/pRKIP ratio in Hs vs LC (solid circles) or HR-HS vs LC (empty circles);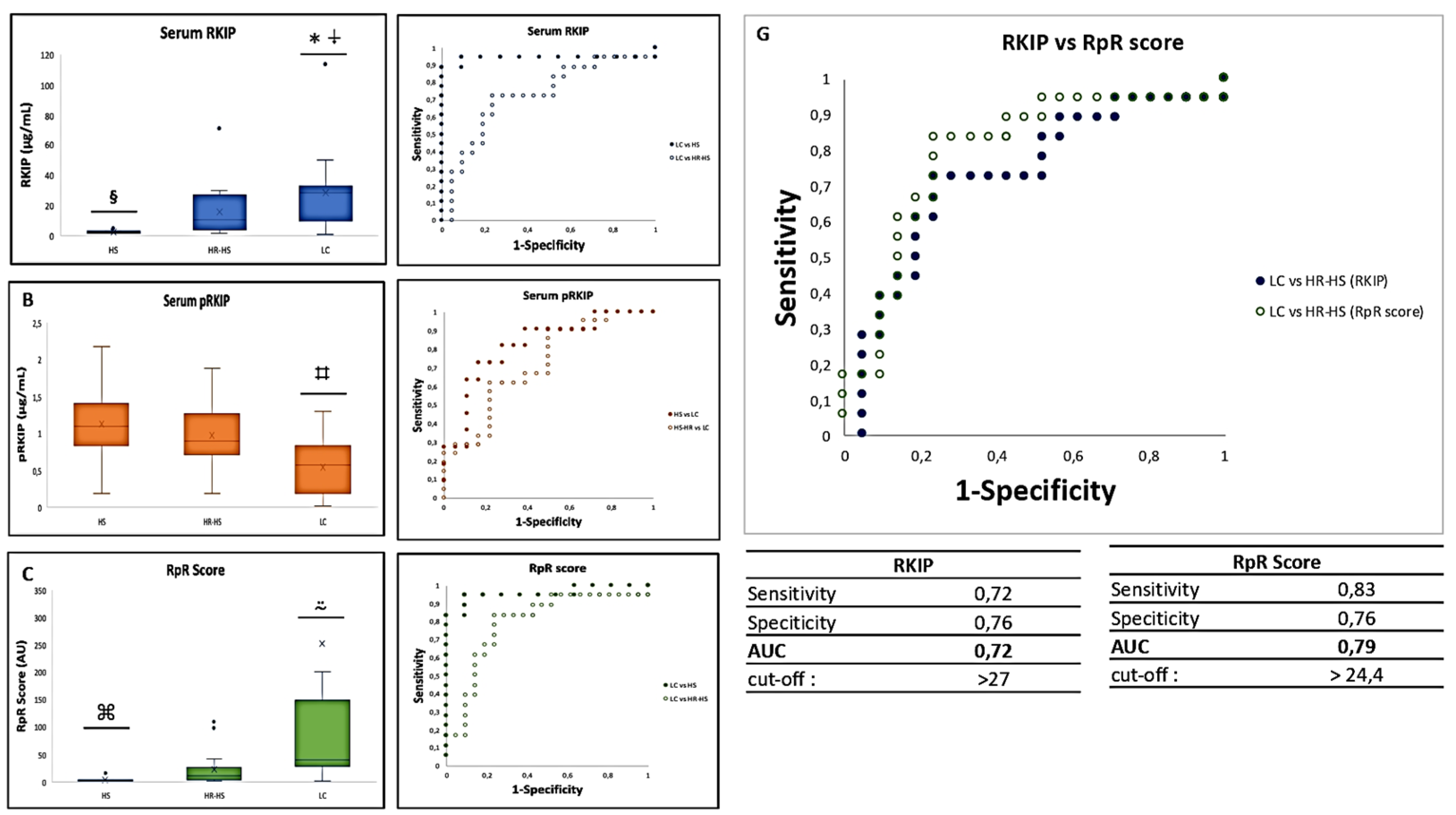
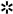 = p-value 3.3883E-07 LC vs HS; ⍖= p-value < 0.05 LC vs HR-HS; § = p-value < 0.001 HS vs HR-HS; ⌗ = p-value < 0.005 LC vs HS and HR-HS; ⍨ = p-value < 0.01 LC vs HS and HR-HS; ⌘= p-value < 0.01 HS vs HR-HS .D. AUC obtained by measuring total serum RKIP in LC vs HS (solid circles) or HR-HS (empty circles); E AUC obtained by measuring serum pRKIP in Hs vs LC (solid circles) or HR-HS vs LC (empty circles); F. AUC obtained by measuring serum RKIP/pRKIP ratio in LC vs HS ( solid circles) or LC vs HR-HS (empty circles); G. Comparison of AUC obtained by classifying LC over HR-HS patients by RKIP vs. RpR score
= p-value 3.3883E-07 LC vs HS; ⍖= p-value < 0.05 LC vs HR-HS; § = p-value < 0.001 HS vs HR-HS; ⌗ = p-value < 0.005 LC vs HS and HR-HS; ⍨ = p-value < 0.01 LC vs HS and HR-HS; ⌘= p-value < 0.01 HS vs HR-HS .D. AUC obtained by measuring total serum RKIP in LC vs HS (solid circles) or HR-HS (empty circles); E AUC obtained by measuring serum pRKIP in Hs vs LC (solid circles) or HR-HS vs LC (empty circles); F. AUC obtained by measuring serum RKIP/pRKIP ratio in LC vs HS ( solid circles) or LC vs HR-HS (empty circles); G. Comparison of AUC obtained by classifying LC over HR-HS patients by RKIP vs. RpR score4. Discussion
4.1. Study Limitation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. [CrossRef]
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7-34. [CrossRef]
- Alexander M, Kim SY, Cheng H. Update 2020: Management of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung. 2020;198(6):897-907. [CrossRef]
- Chu GCW, Lazare K, Sullivan F. Serum and blood based biomarkers for lung cancer screening: a systematic review. BMC Cancer. 2018;18(1):181. Published 2018 Feb 13. [CrossRef]
- Van Kimmenade RR, Januzzi JL Jr. Emerging biomarkers in heart failure. Clin Chem. 2012;58(1):127-138. [CrossRef]
- Conserva, F., Barozzino, M., Pesce, F. et al. Urinary miRNA-27b-3p and miRNA-1228-3p correlate with the progression of Kidney Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy. Sci Rep 9, 11357 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Harris AC, Ferrara JL, Braun TM, et al. Plasma biomarkers of lower gastrointestinal and liver acute GVHD. Blood. 2012;119(12):2960-2963. [CrossRef]
- Papale M, Di Paolo S, Magistroni R, et al. Urine proteome analysis may allow noninvasive differential diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(11):2409-2415. [CrossRef]
- Gasparri R, Guaglio A, Spaggiari L. Early Diagnosis of Lung Cancer: The Urgent Need of a Clinical Test. J Clin Med. 2022;11(15):4398. Published 2022 Jul 28. [CrossRef]
- Pepe MS, Etzioni R, Feng Z, et al. Phases of biomarker development for early detection of cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93(14):1054-1061. [CrossRef]
- Gasparri R, Sabalic A, Spaggiari L. The Early Diagnosis of Lung Cancer: Critical Gaps in the Discovery of Biomarkers. J Clin Med. 2023;12(23):7244. Published 2023 Nov 23. [CrossRef]
- Deleonardis A, Papale M. Methods to Study Posttranslational Modification Patterns in Cytotoxic T-Cells and Cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2325:137-153. PMID: 34053056. [CrossRef]
- Kim, G. E., Kim, N. I., Lee, J. S., Park, M. H., & Yoon, J. H. (2017). Reduced RKIP Expression is Associated With Breast Neoplastic Progression and is Correlated With Poor Outcomes and Aberrant Methylation in Breast Carcinoma. Applied immunohistochemistry & molecular morphology : AIMM, 25(7), 467–474; [CrossRef]
- Luo D., Zhang Z., Zhang Z., et al. Aberrant expression of miR-362 promotes lung cancer metastasis through downregulation of sema3A. J Immunol Res. 2018, 2018:1687097.
- Gong Z., Chen X., Zhang Y.C., Liu C., Wang Z., Xu X., Zhu J., Xue T. LncRNA GATA6-AS1 Inhibits the Progression of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Repressing microRNA-543 to Up-Regulating RKIP. Cancer Manag Res. 2020, 12, 9327–9338.
- Huerta-Yepez S., Yoon N.K., Hernandez-Cueto A., Mah V., Rivera-Pazos C.M., Chatterjee D., Vega M.I., Maresh E.L., Horvath S., Chia D., et al. Expression of phosphorylated raf kinase inhibitor protein (pRKIP) is a predictor of lung cancer survival. BMC Cancer. 2011, 11:259. [CrossRef]
- Al-Mulla, F.; Bitar, M.S.; Thiery, J.P.; Zea, T.T.; Chatterjee, D.; Bennett, L.; Park, S.; Edwards, J.; Yeung, K.C. Clinical implications for loss or diminution of expression of Raf-1 kinase inhibitory protein and its phosphorylated form in ductal breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 3, 446–464.
- Papale M, Netti GS, Stallone G, Ranieri E. Understanding Mechanisms of RKIP Regulation to Improve the Development of New Diagnostic Tools. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(20):5070. Published 2022 Oct 17. [CrossRef]
- Klysik J. et al. Signaling crossroads: The function of Raf kinase inhibitory protein in cancer, the central nervous system and reproduction. Cell. Signal. 2008, 20, 1-9., Yesilkanal AE Rosner MR. Targeting Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein Regulation and Function Cancers (Basel), 2018, 9 (10), 306.
- Wang A. Duan G., Zhao C., Gao Y., Liu X., Wang Z., Li W., Wang K., Wang W. Reduced RKIP expression levels are associated with frequent non-small cell lung cancer metastasis and STAT3 phosphorylation and activation, Oncol Lett. 2017, 5 (13), 3039-3045.
- Wang Q., Wu X., Wu T., Li G., Shi Y. Clinical Significance of RKIP MRNA Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Tumor Biol. 2014;35:4377–4380. [CrossRef]
- Xiong Y, Zhang X, Lin Z, et al. SFTA1P, LINC00968, GATA6-AS1, TBX5-AS1, and FEZF1-AS1 are crucial long non-coding RNAs associated with the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(4):3985-3993. [CrossRef]
- Bedri SK, Nilsson OB, Fink K, et al. Plasma protein profiling reveals candidate biomarkers for multiple sclerosis treatment. PLoS One. 2019;14(5):e0217208. Published 2019 May 29. [CrossRef]
- Black RC, Khurshid H. NSCLC: An Update of Driver Mutations, Their Role in Pathogenesis and Clinical Significance. R I Med J (2013). 2015;98(10):25-28. Published 2015 Oct 1.
- Gasparri R, Capuano R, Guaglio A, et al. Volatolomic urinary profile analysis for diagnosis of the early stage of lung cancer. J Breath Res. 2022;16(4):10.1088/1752-7163/ac88ec. Published 2022 Sep 2. [CrossRef]
- Papale M, Vocino G, Lucarelli G, et al. Urinary RKIP/p-RKIP is a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(25):40412-40424. [CrossRef]
- Zebisch A, Caraffini V, Sill H. RAF Kinase Inhibitor Protein in Myeloid Leukemogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22):5756. Published 2019 Nov 16. [CrossRef]
- Elinav E, Nowarski R, Thaiss CA, Hu B, Jin C, Flavell RA. Inflammation-induced cancer: crosstalk between tumours, immune cells and microorganisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(11):759-771. [CrossRef]
- Balkwill F, Charles KA, Mantovani A. Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell. 2005;7(3):211-217. [CrossRef]
- Frankenberger C, Rabe D, Bainer R, et al. Metastasis Suppressors Regulate the Tumor Microenvironment by Blocking Recruitment of Prometastatic Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cancer Res. 2015;75(19):4063-4073. [CrossRef]
- Datar I, Qiu X, Ma HZ, et al. RKIP regulates CCL5 expression to inhibit breast cancer invasion and metastasis by controlling macrophage infiltration [published correction appears in Oncotarget. 2016 May 3;7(18):26925]. Oncotarget. 2015;6(36):39050-39061. [CrossRef]
- Gabriela-Freitas M, Pinheiro J, Raquel-Cunha A, Cardoso-Carneiro D, Martinho O. RKIP as an Inflammatory and Immune System Modulator: Implications in Cancer. Biomolecules. 2019;9(12):769. Published 2019 Nov 22. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





