1. Introduction
According to the latest findings from UN Climate Change News, a staggering 30 million individuals were compelled to vacate their residences in the year 2020 as a direct consequence of climate-induced disturbances. The exacerbation of climate issues in recent times has posed a grave threat to the existence and well-being of the human species. In the year 2021, the occurrence of severe climatic conditions in isolation has led to substantial financial ramifications, with insurance claims amounting to a staggering sum exceeding USD 120 billion. The escalating prevalence of a myriad of environmental concerns has engendered a considerable amount of interest in the pursuit of remedies to effectively tackle these issues and bolster the prospects of environmental sustainability (Medrano et al., 2020; Yasir et al., 2020; Chavez et al., 2021; Begum et al., 2022). Environmental issues arise primarily as a consequence of human behaviour. In order to ameliorate the current state of the environment, it is imperative that a shift in behavioural patterns be undertaken. Engaging in environmentally conscious behaviour serves as a potent instrument in tackling environmental challenges and upholding the integrity of our natural surroundings. This practice effectively curtails the squandering of precious natural resources, mitigates the release of harmful pollutants, and mitigates the detrimental impact on our environment (Weingärtner et al., 2021; Rahmani et al., 2022). As per the scholarly works of Lee et al. (2020), Yu et al. (2022), and Bresciani et al. (2023), it is posited that pro-environmental behaviour encompasses a repertoire of deliberate actions or conduct that seeks to mitigate the adverse ramifications of one's actions on the ecological and constructed realms. It may encompass endeavours such as engaging in recycling practices, actively participating in environmental advocacy initiatives, or conscientiously employing eco-conscious products, thereby encompassing both communal and personal spheres. The adoption of pro-environmental behaviours has been shown to have a significant impact on enhancing environmental sustainability and performance, resulting in a reduction of emissions, pollution, and environmental degradation (Lange et al., 2018; Li et al., 2019; Schmitt et al., 2018; Truelove and Gillis, 2018; Lange and Dewitte, 2019). Pro-environmental behaviour, when viewed through the prism of sustainability, can be delineated as the conscious and deliberate engagement in activities that foster and enhance the overall ecological equilibrium, thereby promoting long-term environmental sustainability. In essence, this study posits that endeavours undertaken with the deliberate intention of safeguarding the environment and enhancing its capacity for long-term viability are deemed to be pro-environmental in nature (Yuan and Cao, 2022).
Smart manufacturing, a distinguished domain within the realm of manufacturing, harnesses the power of computer-integrated technologies and capabilities to enhance the efficacy of production processes, bolster the potential for recyclability, and optimize the intricate web of supply chain operations. The methodologies encompassed within this framework encompass the strategic arrangement of supply chains, the implementation of automation and industrial robotics, the application of intelligent production planning and control techniques, the utilization of intelligent procurement strategies, and the establishment of intelligent supply chains. Utilizing internet-enabled apparatus for the purpose of overseeing the production process, smart manufacturing represents a technologically advanced approach (Oluyisola et al., 2020; Özkan et al., 2020). The underlying concept of intelligent manufacturing revolves around the optimization of supply and demand requirements, both in the present and future, through the harmonization of physical and digital operations within factory settings and throughout various supply chain endeavours. As per the scholarly works of Davis et al. (2015), Phuyal et al. (2020), Musonda and Gambo (2021), Weingärtner et al. (2021), and Rahmani et al. (2022), it has been established that the concept of smart production is precisely employed to denote the realm of digital production networks. A smart manufacturing system represents a concerted endeavour to optimize its capacities through the utilization of state-of-the-art technologies that enable expeditious and extensive dissemination of digital information across diverse industrial systems. In order to optimize energy and labour utilisation and enhance manufacturing efficiency, "smart manufacturing" (Lu et al., 2016; Canas et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2023) incorporates and utilizes advanced robotics, big data processing, and artificial intelligence.
In the nation of Ghana, numerous governing bodies have endeavoured to implement policies and initiatives aimed at fostering sustainable industrialization, as outlined in Sustainable Development Goal 9. Additionally, their efforts have been directed towards promoting decent employment opportunities and fostering economic development, aligning with the objectives of Sustainable Development Goal 8. Furthermore, Ghana's commitment to sustainable consumption and production, as emphasized in Sustainable Development Goal 12, has been a focal point of their endeavours. Lastly, the pursuit of climate action has also been a prominent aspect of their agenda, recognizing the urgent need to address environmental concerns. An illustrative instance would be the manifestation of Ghana's enduring strategic vision aimed at cementing its middle-income status and fostering an economy propelled by industry, capable of generating commendable employment opportunities that are both suitable and enduring for the purpose of development. This vision finds expression in the National Entrepreneurship and Innovation Programme (NEIP). Furthermore, it is imperative to acknowledge that the fundamental objectives of NEIP encompass the provision of unwavering assistance to nascent enterprises, with the ultimate aim of fostering their transformation into prosperous ventures. Moreover, NEIP is resolute in its commitment to furnish financial resources and establish incubation centers, as substantiated by the scholarly works of Appiah et al. (2022) and the NEIP report (2022). Furthermore, in July 2021, a transitory collaboration between Results for Development and the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs was inaugurated, aiming to delve into the intricacies of Ghana's innovation ecosystem. In the interim, it has come to attention that several challenges persistently recur in previous assessments of Ghana's innovation ecosystem. Ghana harbors a substantial and burgeoning reservoir of innovations that possess the capacity to profoundly enhance developmental outcomes. Nevertheless, there exist several impediments that hinder the triumphant alignment of this abundant supply with the corresponding demand, encompassing both the individual inventors and the broader ecosystem. The UNDESA-R4D Demand-Led Innovator Support Program serves as a prime illustration of an endeavour aimed at formulating a comprehensive strategy that effectively harmonizes and equalizes the requisites of the ecosystem (demand) with the necessities of innovators (supply) (NEIP report, 2021; Appiah at al., 2023).
This paper examine the implications of smart manufacturing practices on pro-environmental behaviour using the Natural Resources-Based View (NRBV) and the Dynamic Capability Theory (DCT). It also develops a baseline moderated mediation model to explain the relationship between smart manufacturing and pro-environmental behaviour with a role of green dynamic capability, and green innovation. In order to promote responsible consumption and production, sustainable industrialization, climate action, respectable work, and economic growth, as well as the achievement of Agenda 2030, this study offers substantial and intriguing insights for policymakers, practitioners, academics, and theorists. Furthermore, an additional significant contribution pertains to the implementation of smart manufacturing practices within the manufacturing industry, which serves to promote environmentally conscious behaviour, attain environmental sustainability, and enhance environmental performance. Again, the social implication of the study includes the realisation of SDGs including no poverty, zero hungry, decent job and economic growth, responsible consumption and production as well as actions taken to combat climate change. Finally, this paper has re-examined the relationship between smart manufacturing practices and pro-environmental behaviour with a focus on a developing country where such innovative studies have not been adequately explored.
The study has been guided by the following research questions: RQ1- What are the relationships between smart manufacturing practices and pro-environment behaviour. RQ2-What is the mediating role of smart manufacturing adoption on the relationship between sustainable production intention and pro-environmental behaviour? RQ3-What is the moderating role of green dynamic capability and environmental orientation on the relationship between sustainable production intention and pro-environmental behaviour? This paper is divided into six parts. The introduction is covered in part one, the literature review and creation of hypotheses is covered in section two, the research methodology is covered in section three, the findings are covered in section four, the discussions are covered in section five, and the conclusions and implications are included in section six.
2. Literature Review
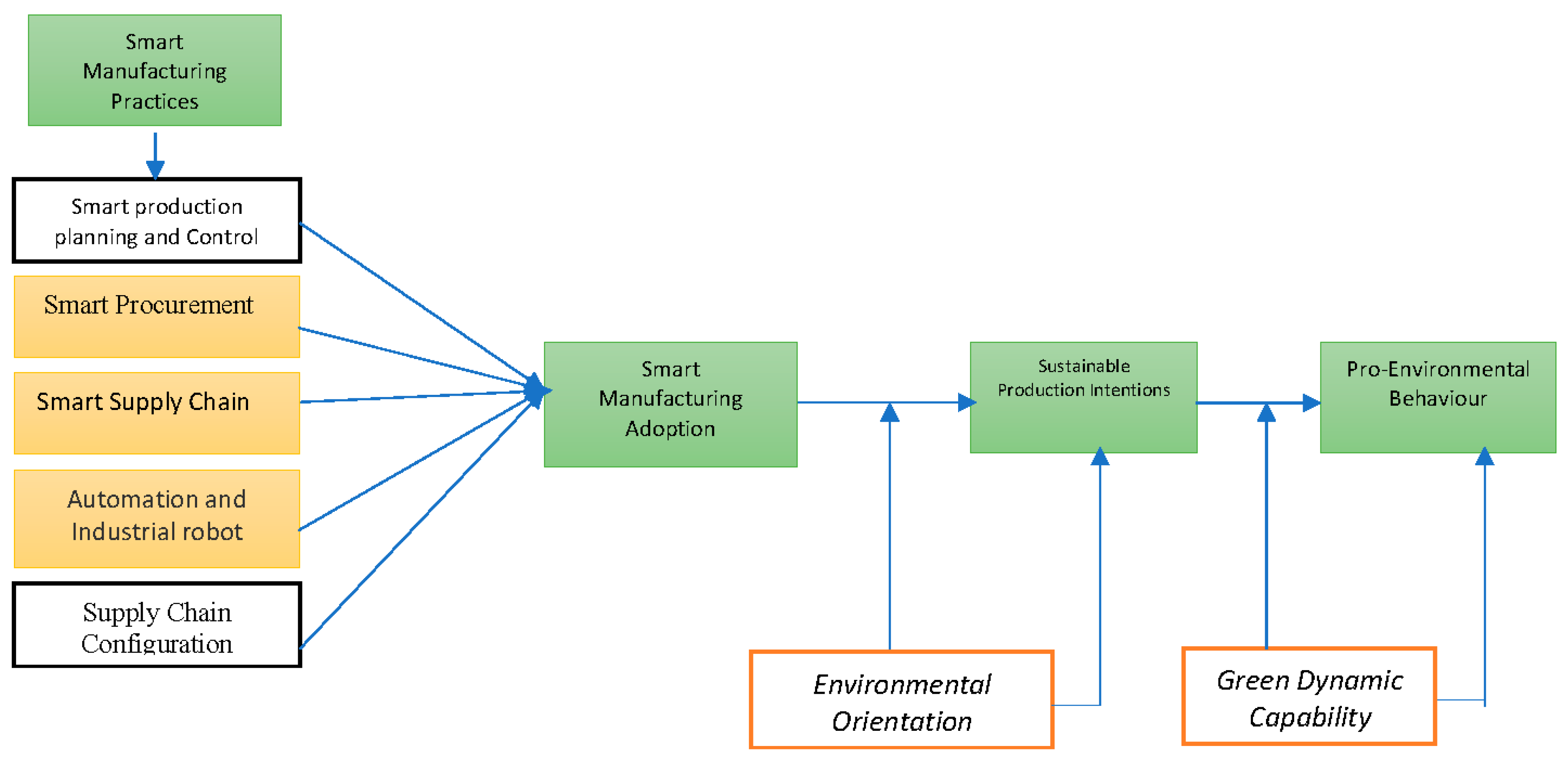
The main propositions of the paper are based on NRBV and DCT. These theories have been used in the current study to enhance the relationship between smart manufacturing and pro-environmental behaviour. According to Hart (1995), companies that embrace sustainability principles demonstrate superior performance in comparison to those who do not implement such programs. The integration of NRBV smart manufacturing practices, including smart procurement, smart supply chain management, smart production planning and control, automation and industrial robotics, and supply chain configuration, along with pro-environmental behaviour, has the potential to contribute to various positive outcomes such as pollution reduction, biodiversity preservation, promotion of product stewardship, and advancement of sustainable development (Begum et al., 2022; Yuan and Cao, 2022; Yu et al., 2022; Bresciani et al., 2023). The concept of dynamic capabilities has been previously discussed. Dynamic capabilities refer to the aptitude and assets that can be effectively aligned and realigned to accommodate changes in the business landscape. According to Teece et al. (1990, 1997), dynamic capabilities refer to the competencies and assets possessed by a firm, enabling it to proficiently integrate, expand, and adapt its internal and external resources. These qualities are crucial for organisations to successfully navigate and exert influence in the face of swiftly changing business environments. The valuation of dynamic talents in markets does not align with their true worth to a buyer who has complementary assets, particularly those that are cospecialized. This implies that an organisation with a multitude of these competencies may potentially achieve atypical profits. This has the potential to significantly enhance the company's profitability.
Sensing, seizing, and transforming are distinct characteristics shown by organizations that facilitate their ability to adapt and mutually develop in response to changes in the economic environment. The possession of such competencies is of utmost importance for ensuring sustained profitability in the long run (Teece, 2007b). This publication is one of the few scholarly works that has contributed to the development of a smart manufacturing model by incorporating the theories of NRBV and DCT. These two ideas are mutually complementary when used in conjunction. Consequently, the present research has integrated the aspects of both theories in order to establish a novel paradigm that has been used for the purpose of elucidating pro-environmental behaviour. The newly built baseline model has been shown in the
Figure 1:
2.1. Hypotheses Development
Smart Production Planning and Control and Smart Manufacturing Adoption
The scholarly literature has elucidated the relationship between Smart Production Planning and Control (PPC) and sustainable performance through the works of Farias Bueno et al. (2020), Oluyisola et al. (2020), Rahmani et al. (2022), Saad et al. (2021), and Canas et al. (2022). The focal point of Production Planning and Control (PPC) revolves around the effective administration of manufacturing operations, aiming to strategically coordinate and supervise the utilization of current industrial assets and materials, while also contemplating the integration of forthcoming production systems that possess enhanced flexibility and adaptability. Significantly, prior research conducted by Oluyisola et al. (2020) and Rahmani et al. (2022) has delved into the utilization and advantages of Smart PPC within this particular domain. A highly refined PPC system harnesses state-of-the-art technology, encompassing the IoTs big-data, and cloud or edge-based machine learning, to enhance the efficiency and efficacy of PPC processes. The facilitation of PPC activities is effectively achieved through the utilization of enterprise resource planning tools and spreadsheet solutions, as highlighted by De Man and Strandhagen (2018). Based on the extant body of evidence, it becomes apparent that PPC assumes a pivotal role in cultivating sustainable performance. The current study puts forth the following hypotheses:
H1. Smart Production Planning and Control is a significant of determinants of smart manufacturing adoption.
Smart Procurement and Smart Manufacturing Adoption
The existing literature, exemplified by Safdarian et al. (2015), Musonda and Gambo (2021), and Weingärtner et al. (2021), has elucidated the correlation between smart procurement (SP) and its influence on sustainable performance. The acronym "SP" denotes the utilization of technological advancements to optimize and streamline traditionally arduous and labor-intensive procurement procedures. Intelligent procurement tools leverage cutting-edge technologies such as machine learning, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and advanced data analytics to enhance the efficiency, precision, and seamless nature of the procurement process. The utilization of cutting-edge technologies, notably artificial intelligence, serves to alleviate procurers from the burdensome and repetitive tasks, thereby facilitating enhanced efficacy (Henneberry, 2023). Moreover, SP entails the utilization of advanced technological solutions to streamline and mechanize mundane procurement activities. Intelligent procurement has the potential to harness automation in various aspects such as contract management, vendor management, and request management, among others (Ngatia and Kenyatta, 2016; Chalmers, 2022). SP represents a pioneering procurement methodology that holds the potential to enhance operational efficiency and optimize the efficacy of the purchasing process. Once more, the utilization of SP facilitates enhanced coordination and communication among purchasers, suppliers, and additional stakeholders, thereby yielding the potential for cost reduction and the attainment of superior product quality. Furthermore, the essence lies in the fulfillment of customer requirements; in the advancement and refinement of our assortment of contemporary acquisition methodologies; in the collaboration with the industrial sector (Wang and Deng, 2018; Özkan et al., 2020). Based on the current circumstances, it is evident that intelligent procurement plays a pivotal role in fostering enduring performance. The present study posits the following hypothesis:
H2. Smart Procurement is a significant determinant of smart manufacturing adoption.
Smart Supply Chain and Smart Manufacturing Adoption
The extant literature (e.g., Chen et al., 2019; Gupta et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2023) is evident that SSC has been studied enormously. The SSC, is a sophisticated framework that harnesses cutting-edge technology and employs automated data analysis techniques to streamline the intricate process of goods and services distribution, ensuring optimal efficiency from suppliers to end consumers. SCC is further expounded upon through the interconnectedness of three fundamental attributes, namely connection, collaboration, and customization. The interconnectedness of SCC is a result of the intricate network that binds together various entities, assets, IT systems, and products. This interconnectedness is further accentuated by the remarkable extent of engagement with customers, suppliers, and IT systems, as noted by Butner (2010). The phenomenon known as SSC, or Smart Supply Chain, is distinguished by the utilization of diverse and sophisticated Information and Communication Technologies within the manufacturing domain. The primary objective is to enhance the seamless exchange of information among disparate entities, encompassing objects, IT systems, and enterprises (Scherbakov and Silkina, 2019; Shao et al., 2021). The prominence of SSC ought to be underscored not solely by the elevated degree of confidence exhibited among the constituents of the supply chain, but also by the establishment of a robust rapport between the information systems and information technologies involved (Ejdys, 2017). Based on the current circumstances, it is evident that the implementation of an intelligent supply chain system significantly influences the attainment of sustainable performance. The study proposes as follows:
H3. Smart supply chain is a significant determinant of smart manufacturing adoption.
Automation and Industrial Robots and Smart Manufacturing Adoption
Several researches have been conducted on the subject of automation and robotics (Cai et al., 2019; Tantawi et al., 2019; Aghimien et al., 2020; Enríquez et al., 2020; Lowenberg-DeBoer et al., 2020). Industrial automation refers to the use of computer software, machinery, or other technological means to execute activities that would otherwise be performed by human beings. Industrial robots are widely recognized as a fundamental element of competitive production strategies, as they strive to integrate optimal productivity, superior quality, and versatile flexibility while minimizing costs. Automation refers to the process of transforming a labor process, technique, or equipment from manual operation or control to automated operation or control (Gerovitch and Slava, 2003). The field of robotics is primarily concerned with the development and study of systems that consist of sensors and actuators. These systems are designed to function independently or with little human intervention, and they often collaborate with people in their operations (Humbert, 2007; Goldberg, 2012). Automation refers to the use of control systems and information technologies with the aim of diminishing the reliance on human labor in the manufacturing and provision of products and services. Robots have a comparable degree of flexibility to that of humans, using advanced methods of feedback vision and reasoning capabilities (Lowry, 2019; Groover, 2019). The potential outcomes and impacts of automation might vary significantly based on the socioeconomic and organizational decisions made during the process. Robotic systems present themselves as appealing options for reducing costs in labor-intensive tasks, extending beyond the automotive sector to include a wide range of industrial applications. Based on the current evidence, it is evident that the use of automation and robotics significantly contributes to the achievement of sustainable performance. The study proposes as follows:
H4. Automation and robotics significantly determinant of smart manufacturing adoption.
Smart Manufacturing Adaption and Sustainable Production Intention
Prior empirical investigations (e.g., Davis et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020) have discovered that smart manufacturing (SM) is an emerging technology-driven methodology that monitors and controls the manufacturing process via internet-connected devices. By means of data analytics, the principal objective of SM is to streamline mechanized business processes and boost industrial output. Smart manufacturing aims to optimize current and future demand and supply dynamics throughout the supply chain and manufacturing facilities through the seamless integration of physical and digital operations. Kagermann et al. (2013) asserted that the term "smart manufacturing" is frequently employed to refer to a network of digitalized production. Davis et al. (2015) encompasses that "smart manufacturing" is a collection of production methods that employ ICTs and interconnected data to manage processes precisely. The primary objective of a highly smart manufacturing system is to optimise output by leveraging state-of-the-art technologies that enable smooth and uninterrupted data exchange across all phases of the production process. In order to optimize the allocation of resources, materials, and labour in an efficient manner, smart manufacturing systems prioritise the integration of information and communication technologies (ICT). It is also noteworthy to mention that these systems have been deliberately designed to adapt effectively to fluctuations in the market and changes in customer demand (Lu et al., 2016; Phuyal et al., 2020). Smart manufacturing is distinguished by numerous attributes, including interoperability, real-time monitoring and control, adaptable production, rapid response to market fluctuations, advanced sensor technology, and sizable data analytics. This approach aims to optimize productivity in the manufacturing sector as outlined in Wang et al (2018) and Tao and Qi (2019). Given the prevailing conditions, it is clear that the integration of smart manufacturing methods is essential to promote sustainable performance. This study raises the following hypotheses:
H5. Smart manufacturing adoption significantly relates to sustainable production intention
H6. Smart manufacturing practice significantly mediates the relationship between smart manufacturing adoption and sustainable production intention
Sustainable Production Intention and Pro-Environmental Behaviour
Among others, Tseng (2013), Samuel et al. (2013), Blok et al. (2015), Alayón et al. (2017), and Begum et al. (2022) have established that environmentally responsible manufacturing and behaviour are correlated. The concept of "sustainable production" pertains to the manufacturing procedure wherein limited resources are utilized in an efficient manner while ensuring environmental hygiene. Sustainable production involves the process of creating goods and services in a manner that minimizes the adverse effects on the environment while optimizing the utilization of scarce resources such as energy and materials. Furthermore, the economic viability of manufacturing processes is considered, which is an essential component of sustainability. Furthermore, we shall strive diligently to maintain a corporate environment that places the well-being and security of our consumers, employees, and the general public first. Furthermore, it is crucial to note that an inherent aim of sustainable production is to improve the social and spiritual welfare of every employee (Lowell Centre for Sustainable Production, 1998). Sustainable production entails the extent to which industry can support society's desire to produce wealth in a way that promotes sustainable economic growth (O'Brien, 1999). Ensuring that manufactured goods meet the current needs and preferences of society constitutes the essence of sustainable manufacturing, an expansive and intricate domain within industrial production. Concurrently, provisions must be made for the desires and requirements of future generations. According to Ron (1998), evaluating the product's advancement at every stage of its life cycle is crucial. Environmental, social, and economic factors all have an impact on sustainable production, which is a crucial component of sustainable development (Roome & Anastasiou, 2021).
According to the research work of Rosen and Kishawy (2012), the concept of sustainable manufacturing includes the production of goods using production process methods that prioritize mitigating adverse environmental impacts, conserving energy and natural resources, ensuring the well-being of workers, communities, and consumers, and promoting economic sustainability. Given the current circumstances, it is clear that the trend towards sustainable production is having a significant impact on environmentally friendly behaviour. The study proposes as follows:
H7. Sustainable production intention significantly relates to pro-environmental behaviour
H8. Sustainable production intention significantly mediates the relationship between smart manufacturing adoption and pro-environment behaviour.
Environmental Orientation
Research in academia (Horisch et al., 2017; Keszey, 2019; Chavez et al., 2021) has demonstrated a correlation between environmental orientation and endeavours to develop products and services that are favorable to the environment (sustainable production). To what extent do corporations incorporate environmental considerations into the process of formulating strategic decisions? The aforementioned involves "environmental orientation," as established by Hirunyawipada and Xiong (2018) in their study. The concept of environmental orientation means that a company recognizes its harmful impact on the environment and works ceaselessly to eliminate that impact. Like the concept of corporate social responsibility, it serves as a concrete embodiment of an organization's core principles. In addition, it is important that employees demonstrate characteristics of organizational citizenship, such as respect, sincere concern for the environment, and adherence to responsibilities to external stakeholders (Yasir et al., 2020). It includes ethical standards. This is achieved through the development of environmentally conscious individuals and a strong commitment to environmental protection (Medrano et al., 2020; Yasir et al., 2020). The adoption of an environmental orientation has the potential to have beneficial effects on both cost and productivity across a firm's whole value chain. This is achieved by implementing innovative practices that target the reduction of pollution and waste. The concept of Environmental Orientation may be seen as a corporate value that has resemblance to the notion of corporate social responsibility. It encompasses the principles of showing reverence and concern for the environment, as well as addressing the demands of external stakeholders (Banerjee, 2002; Yu and Huo, 2018). Based on the current evidence, it is evident that an environmental focus significantly influences the achievement of sustainable outcomes. The study proposes as follows:
H9. Environmental orientation significantly moderate the relationship smart manufacturing adoption and sustainable production intention.
Green Dynamic Capabilities and Sustainable Production Intention
The available research (Lin and Chen, 2017; Xing et al., 2020; Yuan and Cao, 2022; Yu et al., 2022; Bresciani et al., 2023) provides evidence supporting the association between Green Dynamic Capabilities (GDCs) and sustainable performance. GDC refer to the capacity of firms to effectively use their current resources and expertise in order to develop and enhance environmentally sustainable organizational capabilities. GDC is responsible for converting sustainable organizational skills into environmental performance indicators, namely via the implementation of eco-designing and eco-efficiency efforts throughout the process of developing new products. According to Eisenhardt and Martin (2000), dynamic capabilities refer to a distinct and recognizable business process. GDCs refer to predictable patterns of communication that organizations use to effectively allocate resources in order to accomplish their goals (Nelson and Nelson, 2002). The GDC places significant emphasis on the integration, creation, and reallocation of both internal and external resources pertaining to the field of environmental protection. According to Qiu et al. (2020), GDCs are responsible for generating novel goods and processes that have the potential to transform the business landscape and uncover lucrative commercial prospects. The use of existing knowledge and resources by enterprises facilitates the development and cultivation of green organizational skills (Lin & Chen, 2017; Teece, 2017). GDC) play a pivotal role in enhancing the endeavors of corporations to innovate in the realm of sustainability, particularly when accompanied by a robust knowledge base. GDCs refer to the overarching capacity of companies to effectively attain sustainable and environmentally friendly growth within the dynamic market landscape. According to Amui et al. (2017), the implementation of GDCs has been shown to positively impact enterprises' endeavors in green innovation. This is achieved via the enhancement of green management practices, the pursuit of green strategic goals, and the facilitation of green research and development. Based on the current evidence, it is evident that GDCs have a significant impact on promoting environmentally friendly behaviour. The study proposes as follows:
H10. GDC significantly moderates the relationship between sustainable production intention and pro-environmental behaviour
3. Research Methodology
The primary focus of this study pertains to the private sector within the nation of Ghana. The study, with a specific focus, delves into the realm of private business investors within the confines of two prominent urban centers in t Ghana. Specifically, the two cities in question are Accra and Kumasi. As per the findings of the Ghana Enterprise Agency (GEA), it has been determined that a total of 2,825 business entities have been duly formalized and registered under the auspices of the agency. Furthermore, it is noteworthy that the GEA has established a network of 190 operational district offices to effectively administer its functions and provide support to these registered enterprises. The research primarily concentrated on enterprises situated within the metropolitan regions of Kumasi and Accra. The rationale behind this decision is predicated upon the findings of the GEA report, which posit that the metropolitan regions of Kumasi and Accra persist in their preeminence within the small and medium enterprises sector, both in terms of sheer quantity and the breadth of commercial pursuits. Moreover, owing to Accra's status as the esteemed administrative capital of Ghana, a multitude of enterprises are inclined towards establishing a formidable presence within the city's boundaries, primarily driven by the desire to harness the abundant opportunities presented by the readily accessible market. The participants selected for the study comprise a cohort of SMEs owners and managers, chosen through a random sampling method. Of the designated sample size of 450, a total of 422 questionnaires were successfully collected. After conducting a more thorough examination, it was discovered that a total of 18 questionnaires had to be excluded from the analysis due to inconsistencies and the presence of multiple responses. Additionally, an additional 22 questionnaires were deemed unfit for inclusion as they were completed by individuals who were neither owners nor managers of the organization under study. Consequently, the final number of questionnaires deemed suitable for analysis amounted to 382, which represents an impressive response rate of 84.89%. The latest research endeavors (Appiah et al., 2022a; Appiah, 2022) conducted in a congruous setting have yielded comparable and valuable insights. Furthermore, it is imperative to note that the present study has employed a confirmatory research design alongside a quantitative research approach. The utilization of a quantitative research approach in this study is justified by its reliance on statistical models and adherence to the notion of objectivity in comprehending social reality. The present study employed a survey methodology, utilizing items that were quantitatively assessed using numerical ratings.
The study centers its attention on SMEs that are engaged in various sectors such as Transportation, Oil and Gas, Hospitality, Construction, Recreation, and Tourism, among other industries. The criteria for inclusion were as follows: i) SMEs that are owned by individuals of Ghanaian nationality. ii) SMEs that are duly registered in accordance with the legal framework; iii) SMEs that have demonstrated a commendable longevity of over three years. The measurement instruments underwent adaptation based on prior studies that were closely aligned with the underlying theoretical assumptions. Table I provides additional information regarding the measurement of constructs, including the quantity of measurement items utilized and the underlying theoretical foundations. The process of data collection was carried out through the utilization of structured questionnaires and the implementation of a 5-Point Likert's Typed Scale of measurement. In this particular context, we assign the numerical values of 5, 4, 3, 2, and 1 to represent the levels of agreement or disagreement. More specifically, a rating of 5 signifies a strong inclination towards agreement, while a rating of 4 indicates agreement, a rating of 3 denotes neutrality, a rating of 2 signifies disagreement, and a rating of 1 represents a strong inclination towards disagreement.
Table I.
Measurement Instruments; Sources; number of Items and underlying Theory.
Table I.
Measurement Instruments; Sources; number of Items and underlying Theory.
Construct
(Type of construct) |
No. of Items |
Underlying Theory |
- ✓
Sustainable Production Intention |
4 |
NRBV |
- ✓
Pro-environmental Behaviour |
4 |
NRBV |
- ✓
Smart Production Planning and Control |
4 |
DCT |
- ✓
Smart Procurement |
3 |
DCT |
- ✓
Smart Supply Chain |
4 |
DCT |
- ✓
Automation and Industrial Robot |
3 |
DCT |
- ✓
Supply Chain Configuration |
3 |
DCT |
- ✓
Smart Manufacturing Adoption |
4 |
DCT |
- ✓
Environmental Orientation |
4 |
NRBV |
- ✓
Green Dynamic Capability |
4 |
NRBV |
Ethical Considerations
This paper involves human participants as a result all due ethical considerations have been observed; including respect of human right, anonymity, confidentiality, protection from harm and informed consent. Ethical approval of the ethical review committee of the Kumasi Technical University in Kumasi, Ghana has been sorted to conduct this study.
In order to enhance comprehension and discern intricate connections and patterns among latent variables, scholars employ the structural equation modelling framework offered by partial least squares (PLS-SEM). By adhering to the structural plan illustrated in Figure 1, this enquiry employs a reflective framework and concentrates on a solitary variable (an indicator). In the context of PLS-SEM, the external model and the internal model are two distinct categories of model fit requirements that must be identified and carefully considered. The external model evaluates the reliability and validity of the connection between variables. In order to assess the fit of the external model, measurement models are employed, while regression analyses serve as the foundation for evaluating the structural model of the internal model (Hair et al., 2017; Hair et al., 2019). A thorough examination was conducted on path coefficients and T-values to derive an approximation of the structural model. The statistical measures mentioned above were employed to assess the validity of the hypothesis. The measurement model was evaluated for construct validity, specifically focusing on the assessment of convergence and variability of the measures. To establish the construct validity of a test, it is crucial to demonstrate both strong convergent and discriminant validity. Strong correlation between test results and results of other assessments measuring the same premise is crucial, indicating significant convergent validity. The test results should demonstrate a lack of correlation with assessments designed to measure different constructs, indicating a high level of discriminant validity (Hair et al., 2019). This study employed composite reliability (CR), Cronbach's alpha, and factor loading as analysis techniques to evaluate the adequacy of convergent validity. Furthermore, discriminant validity was evaluated using Average Variance Extracted and Cross Loading techniques.
4. Results
Descriptive Statistics and Variance Inflation Factor (VIF)
The results of the summary data and VIF can be seen in Table II. The study gives the distribution measures, skewness and kurtosis scores, as well as the means and standard deviations. The average scores were found to be between 3.620 and 3.904. The subjects had standard deviations that ranged from 0.926 to 1.204, which shows that there was a lot of variation (SD > 1). To check for multicollinearity, numbers of the variance inflation factor (VIF) were used. The study's results show that the VIF values were between 1.183 and 0.425, which is less than the accepted level of 5 set by Hair et al. (2014). As shown by the variance inflation factor (VIF) being less than 5, the results show that multilinearity is not a big problem. To check if the distribution was regular, the skewness and kurtosis numbers were looked at. The values for skewness were between -1.041 and -0.350, and the values for kurtosis were between -0.569 and 0.846. In this case, the numbers were between -1.041 and -0.350 and between -0.569 and 0.846. Based on these results, it looks like the distribution fits the normality assumption.
Table II.
Descriptive Statistics and Variance Inflation Factor (VIF).
Table II.
Descriptive Statistics and Variance Inflation Factor (VIF).
| Constructs |
Items |
Mean |
STD, Dev. |
Skewness |
Kurtosis |
VIF |
| Automation and Industrial Robot |
AIR1 |
3.732 |
1.201 |
-.827 |
-.123 |
2.521 |
| AIR2 |
3.687 |
1.010 |
-.350 |
-.876 |
1.183 |
| AIR3 |
3.834 |
1.063 |
-.804 |
.139 |
2.571 |
| Green Dynamic Capability |
GDC1 |
3.620 |
1.180 |
-.611 |
-.569 |
3.265 |
| GDC2 |
3.773 |
1.149 |
-.768 |
-.171 |
2.481 |
| GDC3 |
3.636 |
1.175 |
-.661 |
-.381 |
3.070 |
| GDC4 |
3.751 |
1.200 |
-.837 |
-.121 |
2.332 |
| Green Environmental orientation |
GE01 |
3.808 |
1.002 |
-.774 |
.399 |
2.131 |
| GEO2 |
3.703 |
1.204 |
-.716 |
-.330 |
2.203 |
| GEO3 |
3.665 |
1.164 |
-.702 |
-.297 |
2.300 |
| GEO4 |
3.684 |
1.163 |
-.756 |
-.237 |
1.908 |
| Pro- Environmental Behavior |
PRO-EN1 |
3.895 |
.988 |
-.806 |
.428 |
1.970 |
| PRO-EN2 |
3.760 |
1.065 |
-.753 |
.004 |
3.849 |
| PRO-EN3 |
3.757 |
1.066 |
-.855 |
.277 |
3.255 |
| PRO-EN4 |
3.815 |
1.053 |
-1.041 |
.846 |
2.596 |
| Smart manufacturing Adoption |
SMA1 |
3.716 |
1.090 |
-.711 |
-.164 |
3.341 |
| SMA2 |
3.863 |
1.080 |
-1.008 |
.617 |
4.239 |
| SMA3 |
3.904 |
.994 |
-.807 |
.394 |
4.266 |
| SMA4 |
3.764 |
1.067 |
-.753 |
-.006 |
3.772 |
| Smart Procurement |
SP1 |
3.831 |
1.064 |
-1.035 |
.786 |
2.647 |
| SP2 |
3.856 |
1.064 |
-.909 |
.404 |
2.513 |
| SP3 |
3.760 |
1.089 |
-.796 |
.024 |
3.083 |
| Sustainable Production Initiative |
SPI1 |
3.757 |
1.066 |
-.855 |
.277 |
3.222 |
| SPI2 |
3.744 |
1.084 |
-.779 |
.019 |
6.425 |
| SPI3 |
3.802 |
1.054 |
-.896 |
.461 |
3.394 |
| SPI4 |
3.786 |
.926 |
-.385 |
-.567 |
1.475 |
| Smart Production Planning and Control |
SPPC1 |
3.799 |
1.055 |
-.886 |
.439 |
4.744 |
| SPPC2 |
3.760 |
1.016 |
-.663 |
-.002 |
2.733 |
| SPPC3 |
3.808 |
1.002 |
-.774 |
.399 |
6.206 |
| |
SSC2 |
3.853 |
1.065 |
-.898 |
.381 |
2.507 |
| SSC3 |
3.732 |
1.084 |
-.828 |
.102 |
3.757 |
Measurement Model - Construct Validity
Table III displays the outcomes of the model measurement, which is also referred to as structure validation. This evaluation comprises two components: convergent and discriminant validity. Convergent validity of the model was assessed using CR, CA, and factor loadings. According to the findings, the CR values ranged from 0.859 to 0.952, which is higher than the minimal criterion of 0.7 that is considered acceptable. The results of
Table 5 indicate that the factor loadings are higher than the minimum allowable level of 0.7. The results indicate that the model exhibits strong convergent validity. The AVE values range from 0.677 to 0.868, all of which exceed the minimum threshold of 0.5. Table III displays the quadratic AVE values along the diagonal. The correlation coefficients of the structures were smaller than the quadratic values, indicating acceptable discriminant validity (Hair et al., 2019). Table IV displays the HTMT ratios, which were analyzed to assess the robustness of the hetero-identification-to-mono-identification. The values fell within the range of 0.043 to 0.789, all of which were below the minimum recommended threshold of 0.85 (Henseler et al., 2015). The results have provided sufficient justification for accepting the validity of the construct (measurement model).
Table III.
Discriminant Validity and convergent validity, Fornell-Larcker Criterion.
Table III.
Discriminant Validity and convergent validity, Fornell-Larcker Criterion.
| |
CA |
CR |
AVE |
AIR |
GDC |
GEO |
Pro-EB |
SM A |
SP |
SPPC |
SSC |
SPI |
| AIR |
.753 |
.859 |
.677 |
.883 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| GDC |
.907 |
.935 |
.782 |
.796 |
.884 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| GEO |
.858 |
.904 |
.701 |
.706 |
.762 |
.837 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Pro-EB |
.901 |
.931 |
.772 |
.714 |
.797 |
.771 |
.879 |
|
|
|
|
|
| SMA |
.906 |
.934 |
.781 |
.714 |
.781 |
.786 |
.763 |
.884 |
|
|
|
|
| SP |
.895 |
.934 |
.826 |
.722 |
.791 |
.801 |
.660 |
.746 |
.909 |
|
|
|
| SPPC |
.924 |
.952 |
.868 |
.739 |
.779 |
.795 |
.732 |
.786 |
.607 |
.932 |
|
|
| SSC |
.906 |
.934 |
.779 |
.754 |
.804 |
.669 |
.705 |
.753 |
.748 |
.766 |
.883 |
|
| SPI |
.865 |
.909 |
.719 |
.746 |
.795 |
.815 |
.759 |
.699 |
.726 |
.920 |
.716 |
.848 |
Table IV.
Heterotrait-Monotrait Ratio (HTMT).
Table IV.
Heterotrait-Monotrait Ratio (HTMT).
| |
AIR |
GDC |
GEO |
Pro-EB |
SMA |
SP |
SPPC |
SSC |
SPI |
| AIR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| GDC |
.789 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| GEO |
.046 |
.704 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Pro-EB |
.693 |
.682 |
.590 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SMA |
.047 |
.760 |
.781 |
.470 |
|
|
|
|
|
| SP |
.679 |
.677 |
.444 |
.073 |
.746 |
|
|
|
|
| SPPC |
.772 |
.748 |
.688 |
.018 |
.659 |
.599 |
|
|
|
| SSC |
.055 |
.684 |
.583 |
.057 |
.045 |
.045 |
.763 |
|
|
| SPI |
.645 |
.785 |
.663 |
.052 |
.985 |
.022 |
.601 |
.506 |
|
Structural Model
The purpose of the structural model is to assess the model's predictive capacity, analyze the path coefficients, and conduct hypothesis testing using T values. The model's predictive power, as indicated by Table V and
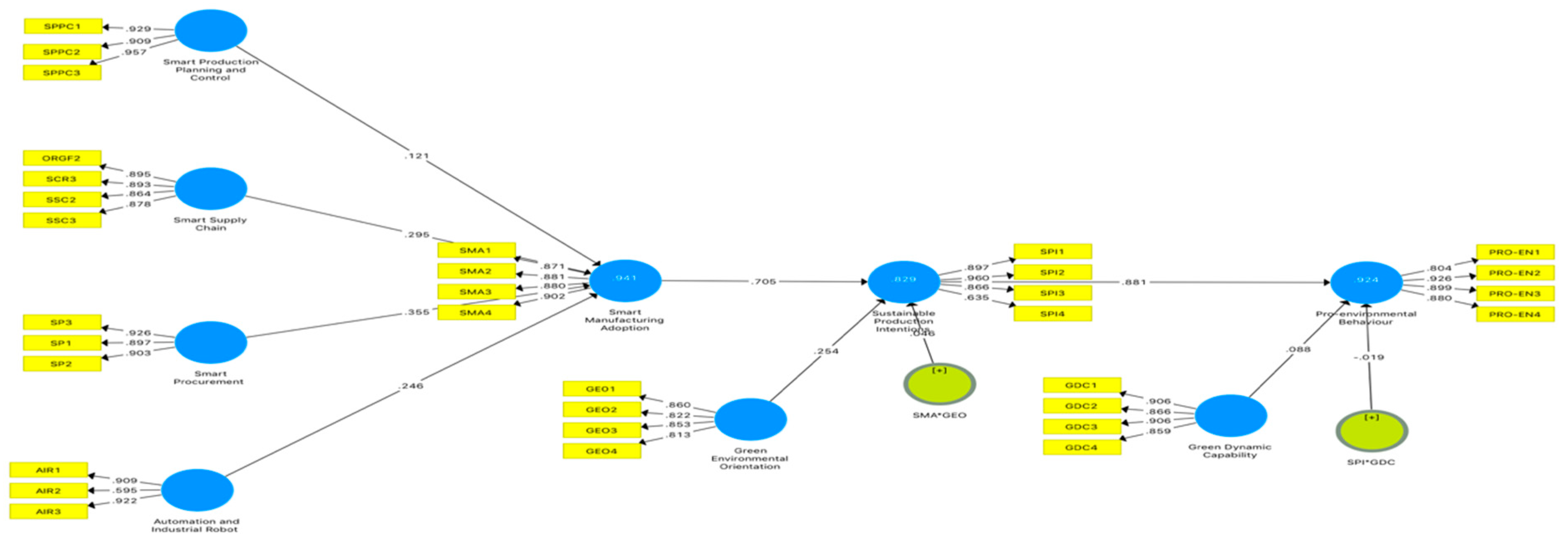
Figure 2, ranges from 0.829 to 0.941. This suggests that intelligent production planning and control, intelligent supply chain, intelligent purchasing, and automation collectively account for 94.1% of the variance in the adoption of smart manufacturing. Smart manufacturing adoption accounts for 82.9% of the variability in sustainable production intentions. The intention to engage in sustainable production accounts for 92.4% of the variability observed in pro-environmental behavior. To evaluate the predictive validity of the model in Table V, a design redundancy analysis was performed using cross-validation. The Q2 values, ranging from 0.581 to 0.728, indicate that the model possesses significant predictive relevance as they are greater than zero.
Figure 3 displays the path coefficients and corresponding hypotheses.
Table V.
Construct Crossvalidated Redundancy.
Table V.
Construct Crossvalidated Redundancy.
| |
SSO |
SSE |
Q² (=1-SSE/SSO) |
R-square (R2) |
| Automation and Robotics |
939.000 |
939.000 |
|
|
| Green Dynamic Capability |
1252.000 |
1252.000 |
|
|
| Green Environ. Orientation |
1252.000 |
1252.000 |
|
|
| Pro-environmental Behaviour |
1252.000 |
375.404 |
.700 |
.942 |
| SMA*GEO |
5008.000 |
5008.000 |
|
|
| SPI*GDC |
313.000 |
313.000 |
|
|
| Smart Manufacturing Adopt. |
1252.000 |
340.669 |
.728 |
.941 |
| Smart Procurement |
939.000 |
939.000 |
|
|
| Smart Prod. Plan and Control. |
939.000 |
939.000 |
|
|
| Smart Supply Chain |
1252.000 |
1252.000 |
|
|
| Sustainable Prod. Intentions |
1252.000 |
524.389 |
.581 |
.820 |
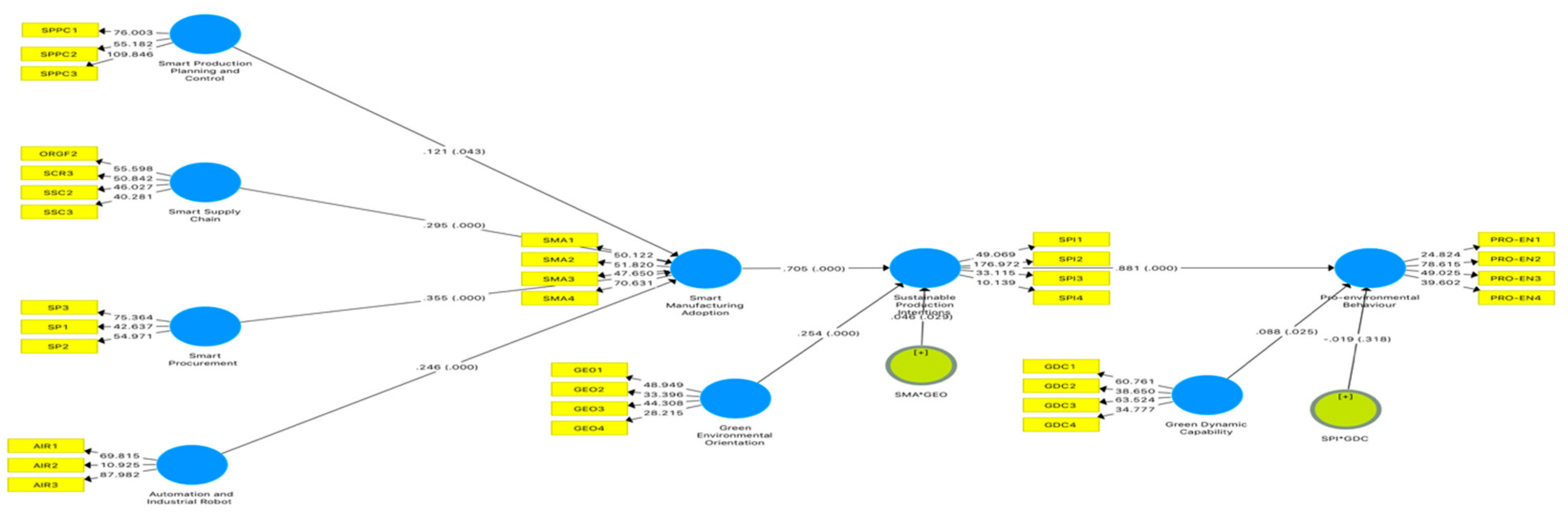
Path Coefficients and Hypothesis Testing
As showed in Table VI, AIR (B = 0.246, T-value = 7.2.460) significantly affect SMA, GDC (B = 0.088, T-value = 2.246) significantly affect Pro-EB, GEO (B = 0.254, T-value = 3.891) significantly affect SPI, SMA and GEO (B = 0.046, T-value = 2.196) significantly affect SPI, SPI and GDC (B = -0.019, T-value = 0.999) insignificantly Pro-EB, SMA (B = 0.705, T-value = 11.085) significantly SPI, SP (B = 0.355, T-value = 2.027) significantly affect SMA, SPPC (B = 0.121, T-value =2.027) significantly affect SMA, SSC (B = 0.295, T-value = 4.840) significantly SMA, SPI (B = 0.881, T-value=24.493) significantly affect Pro-EB, SPI (B = 0.041, T-value=2.149) significantly mediates SMA*GEO and Pro-EB, SMA and SPI(B = 0.221, T-value=4.569) significantly mediates SPM and Pro-EB, SMA and SPI (B = 0.153, T-values = 6.217) significantly mediates AIR and Pro-EB, SMA (B = 0.173, T-value = 6.500) significantly affect AIR and SPI. SPI (B = 0.621, T-value = 10.244) significantly mediates SMA and Pro-EB, SMA and SPI (B=0.075, T-value=1.838) significantly mediates SPPC and Pro-EB, SMA (B=0.250, T-value=4.569) significantly mediates SP and SPI, SMA and SPI (B = 0.183, T-value = 4.389) significantly mediates SSC and Pro-EB, SPI (B = 0.224, T-value = 4.814) significantly affect GEO and Pro-EB, SMA (B = 0.208, T-value = 4.377) significantly affect SPI, SMA (B = 0.085, T-value = 1.845)
Table VI.
Path coefficients and hypothesis testing.
Table VI.
Path coefficients and hypothesis testing.
| Hypothesized |
Path |
Orig. Sample |
Mean |
Std Dev |
T Statistics |
P Values |
Direction |
| Direct effects |
| H1 |
AIR -> SMA |
.246 |
.244 |
.033 |
7.460 |
.000 |
Supported |
| H2 |
SPPC -> SMA |
.121 |
.119 |
.060 |
2.027 |
.043 |
Supported |
| H3 |
SSC -> SMA |
.295 |
.291 |
.061 |
4.840 |
.000 |
Supported |
| H4 |
SP -> SMA |
.355 |
.361 |
.082 |
4.335 |
.000 |
Supported |
| H5 |
GDC-> Pro-EB |
.088 |
.092 |
.039 |
2.246 |
.025 |
Supported |
| H6 |
SMA -> SPI |
.705 |
.705 |
.064 |
11.085 |
.000 |
Supported |
| H7 |
GEO -> SPI |
.254 |
.254 |
.065 |
3.891 |
.000 |
Supported |
| H8 |
SPI-> Pro-EB |
.881 |
.878 |
.036 |
24.493 |
.000 |
Supported |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Indirect (Mediating) Effects |
| H9a |
AIR->SMA->SPI |
.173 |
.172 |
.027 |
6.500 |
.000 |
Supported |
| H9b |
SP ->SMA->SPI |
.250 |
.253 |
.055 |
4.569 |
.000 |
Supported |
| H9c |
SSC->SMA->SPI |
.208 |
.205 |
.048 |
4.377 |
.000 |
Supported |
| H10a |
SPPC->SMA->SPI |
.085 |
.086 |
.046 |
1.845 |
.066 |
Supported |
| H10b |
GEO->SPI->Pro-EB |
.224 |
.223 |
.059 |
3.814 |
.000 |
Supported |
| H10c |
SMA->SPI->Pro-EB |
.621 |
.618 |
.061 |
10.244 |
.000 |
Supported |
| |
Indirect (Moderating) Effects |
| H11 |
SMA*GEO -> SPI |
.046 |
.043 |
.021 |
2.196 |
.029 |
Supported |
| H12 |
SPI*GDC -> Pro-EB |
-.019 |
-.019 |
.019 |
.999 |
.318 |
Unsupported |
| |
Indirect (Serial Mediating) Effects |
| H13a |
SSC->SMA->SPI->Pro-EB |
.183 |
.180 |
.042 |
4.389 |
.000 |
Supported |
| H13b |
SPM ->SMA->SPI ->Pro-EB |
.221 |
.222 |
.048 |
4.569 |
.000 |
Supported |
| H13c |
AIR ->SMA->SPI->Pro-EB |
.153 |
.151 |
.025 |
6.217 |
.000 |
supported |
| H13d |
SPPC->SMA->SPI->Pro-EB |
.075 |
.075 |
.041 |
1.838 |
.067 |
Supported |
5. Discussions
A broad subdivision of the manufacturing sector, smart manufacturing entails the application of technology and computer-integrated functionalities to enhance product recycling, supply chain effectiveness, and production efficiency. It is imperative to reassess the correlation between environmentally conscious behaviour and "smart" manufacturing practices (including smart procurement, smart supply chain, smart production planning and control, automation and industrial robots, and supply chain configuration), particularly in the context of a developing nation, due to the insufficient number of innovative studies in this area. More specifically, the subsequent goals have been accomplished.
Answering RO1- To ascertain the implication of SMP on PEB among manufacturing companies. The study has found that smart manufacturing practices specifically smart procurement, smart supply chain, smart production planning and control, automation and industrial robot, supply chain configuration significantly affect pro-environmental behaviour. this is consistent with prior related studies. Smart manufacturing, a distinguished domain within the realm of manufacturing, harnesses the power of computer-integrated technologies and capabilities to enhance the efficacy of production processes, bolster the potential for recyclability, and optimize the intricate web of supply chain operations. The methodologies encompassed within this framework encompass the strategic arrangement of supply chains, the implementation of automation and industrial robotics, the application of intelligent production planning and control techniques, the utilization of intelligent procurement strategies, and the establishment of intelligent supply chains. Utilizing internet-enabled apparatus for the purpose of overseeing the production process, smart manufacturing represents a technologically advanced approach (Özkan et al., 2020). The underlying concept of intelligent manufacturing revolves around the optimization of supply and demand requirements, both in the present and future, through the harmonization of physical and digital operations within factory settings and throughout various supply chain endeavours. As per the scholarly works of Davis et al. (2015), Phuyal et al. (2020), Musonda and Gambo (2021), Weingärtner et al. (2021), and Rahmani et al. (2022), it has been established that the concept of "smart production" is precisely employed to denote the realm of digital production networks.
RO2 - To determine the mediating role of smart manufacturing adoption and sustainable production intention between SMP and PED. The study has found that smart manufacturing adoption and sustainable production intention significantly mediates the relation between Smart Manufacturing Practices and Pro-Environmental Behaviour. Engaging in environmentally conscious behaviour serves as a potent instrument in tackling environmental challenges and upholding the integrity of our natural surroundings. This practice effectively curtails the squandering of precious natural resources, mitigates the release of harmful pollutants, and mitigates the detrimental impact on our environment (Weingärtner et al., 2021; Rahmani et al., 2022). As per the scholarly works of Lee et al. (2020), Yu et al. (2022), and Bresciani et al. (2023), it is posited that pro-environmental behaviour encompasses a repertoire of deliberate actions or conduct that seeks to mitigate the adverse ramifications of one's actions on the ecological and constructed realms. It may encompass endeavours such as engaging in recycling practices, actively participating in environmental advocacy initiatives, or conscientiously employing eco-conscious products, thereby encompassing both communal and personal spheres.
RO3- To determine the moderating role of environmental orientation and green dynamic capability on the relationship between SMP and Environmental orientation. The study has found that the relationship between smart manufacturing and pro-environmental behavior is influenced by green dynamic capacity and environmental orientation. The adoption of pro-environmental behaviours has been shown to have a significant impact on enhancing environmental sustainability and performance, resulting in a reduction of emissions, pollution, and environmental degradation (Lange et al., 2018; Li et al., 2019; Schmitt et al., 2018; Truelove and Gillis, 2018; Lange and Dewitte, 2019). Pro-environmental behaviour, when viewed through the prism of sustainability, can be delineated as the conscious and deliberate engagement in activities that foster and enhance the overall ecological equilibrium, thereby promoting long-term environmental sustainability. In essence, this study posits that endeavours undertaken with the deliberate intention of safeguarding the environment and enhancing its capacity for long-term viability are deemed to be pro-environmental in nature (Yuan and Cao, 2022).
6. Conclusions and Implications
Conclusions
This paper has examined the implications of smart manufacturing practices (Smart Procurement, Smart Supply Chain, Smart Production Planning and Control, Automation and Industrial Robot, and Supply Chain Configuration) on pro-environmental behaviour and develop a baseline moderated mediation model to explain the relationship between smart manufacturing and pro-environmental behaviour as well as the indirect effects of environmental awareness and green dynamic capability. It was demonstrated that smart manufacturing practices correlate significantly and positively with pro-environmental behavior. In addition, green dynamic capability and environmental attitude establish the connection between smart manufacturing and pro-environmental conduct. The study concludes that a baseline model has been built to guide policymakers, practitioners, and academicians to explain the relationship between smart manufacturing and pro-environmental emerging countries including Ghana, Gambia, Nigeria, and Kenya. Again, the findings from this study could be used to prospect the realisation of decent job and economic growth, responsible consumption and production as well as actions taken to combat climate change. The practical and policy implications of these results have been elaborated in the next section.
Implications – Theoretical and Practical
The theoretical implication of the study includes the creation of a fundamental model that can assist policy makers, practitioners, and academics in understanding the connection between smart manufacturing and pro-environmental behaviour in low developed economic context. Again, the social implication of the study includes the realisation of decent job and economic growth, responsible consumption and production as well as actions taken to combat climate change. Moreover, the study has established that smart manufacturing practices significantly and positively relate to pro-environmental behaviour. Moreover, green dynamic capability and environmental orientation moderate the relationship between smart manufacturing and pro-environmental behaviour. Moreover, another important contribution is to achieve environmental sustainability and improve environmental performance, there is the need to adopt smart manufacturing practices in the manufacturing industries to promote pro-environmental behavior. Again, the social implication of the study includes the realisation of SDGs including no poverty, zero hungry, decent job and economic growth, responsible consumption and production as well as actions taken to combat climate change. The Government of Ghana is required to intensive and re-enforce environmental laws, policies and frameworks in order to sustain the environment. Other stakeholders and environmental actors should continuously encourage best environmental practices. Finally, this paper has re-examined the relationship between smart manufacturing practices and pro-environmental behaviour with a focus on a developing country where such innovative studies have not been adequately explored. The paper has its own limitations which is predominantly the scope and time horizon. The paper focused on manufacturing companies using a cross- sectional survey design. It is suggested that future studies should consider multiple industries and longitudinal studies.
References
- Abdel-Basset, M., Manogaran, G. and Mohamed, M. (2018). Internet of Things (IoT) and its impact on supply chain: A framework for building smart, secure and efficient systems. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2018. vol. 86, pp. 614-628. [CrossRef]
- Aghimien, D.O., Aigbavboa, C.O., Oke, A.E. and Thwala, W.D. (2020), "Mapping out research focus for robotics and automation research in construction-related studies: A bibliometric approach". Journal of Engineering, Design and Technology, Vol. 18 No. 5, pp. 1063-1079. [CrossRef]
- Alayón, C., Säfsten, K., and Johansson, G. (2017). Conceptual sustainable production principles in practice: Do they reflect what companies do? Journal of Cleaner Production, 141, 693–701. [CrossRef]
- Amui, L. B. L., Jabbour, C. C. J., de Sousa Jabbour, A. B. L., & Kannan, D. (2017). Sustainability as a dynamic organizational capability: A systematic review and a future agenda toward a sustainable transition. Journal of Cleaner Production, 142, 308–322. [CrossRef]
- Appiah, K. M. A. S. Odei, G. Kumi-Amoah, and A. S. Yeboah, (2022). “Modeling the Impact of Green Supply Chain Practices Environmental Performance: The Mediating Role of Ecocentricity.” African Journal of Economic and Management Studies, 13(4): 551–567. [CrossRef]
- Appiah, K. M. D. Sedegah, K. A. Ayisi-Addo, and K. E. Gyening. (2022). “Modeling the Influence of Industry Forces on Intention to Invest in Renewable Energy Resources with the Moderating Effect of Sustainable Competitive Strategy.” Cogent Engineering, 9(1). [CrossRef]
- Appiah, K. M. Ameko, E. Asiamah, A. T. and Duker, Q. R. (2023): Blue economy investment and sustainability of Ghana’s territorial waters: an application of structural equation modelling. International Journal of Sustainable Engineering. [CrossRef]
- Appiah, K. M., A. R. Akolaa, and K. A. Ayisi-Addo. (2022). “Modelling the Impact of Macro-environmental Forces on Investment in Renewable Energy Technologies in Ghana: The Moderating Role of Entrepreneurship Orientation Dimensions.” Cogent Economics & Finance, 10 (1). [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.B.(2002). Corporate environmentalism: The construct and its measurement. J. Bus. Res., 55 (2002), pp. 177-191. [CrossRef]
- Begum, H., Abbas, K., Alam, A.S.A.F., Song, H., Chowdhury, M.T. and Abdul Ghani, A.B. (2022)."Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the environment and socioeconomic viability: a sustainable production chain alternative", Foresight, Vol. 24 No. 3/4, pp. 456-475. [CrossRef]
- Blok, V., Long, T. B., Gaziulusoy, A. I., Ciliz, N., Lozano, R., Huisingh, D., and Boks, C. (2015). From best practices to bridges for a more sustainable future: advances and challenges in the transition to global sustainable production and consumption. Journal of Cleaner Production, 108, 19–30. [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, S., Rehman, S.U., Alam, G.M., Ashfaq, K. and Usman, M. (2023), "Environmental MCS package, perceived environmental uncertainty and green performance: in green dynamic capabilities and investment in environmental management perspectives", Review of International Business and Strategy, 33 (1) 105-126. [CrossRef]
- Bueno, A. F., Godinho Filho, M. and Frank, A. G. (2020). Smart Production Planning And Control In The Industry 4.0 Context: A Systematic Literature Review. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 106774.
- Butner, K. (2010). The Smarter Supply Chain of the Future. Strategy & Leadership. 2010. vol. 38, iss. 1, pp. 22-31.
- Cai, S., Ma, Z., Skibniewski, M. J., and Bao, S. (2019). Construction automation and robotics for high-rise buildings over the past decades: A comprehensive review. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 42, 100989. [CrossRef]
- Cañas, H., Mula, J., Campuzano-Bolarín, F., and Poler, R. (2022). A conceptual framework for smart production planning and control in Industry 4.0. Computers & Industrial Engineering. 173. [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, B.(2022). Smart procurement: What it is and where to start. What is smart procurement? https://rfp360.com/smart-procurement/.
- Chavez, R., Malik, M., Ghaderi, H., and Yu, W. (2021). Environmental orientation, external environmental information exchange and environmental performance: Examining mediation and moderation effects. International Journal of Production Economics, 240, 108222. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z., Ming, X., Zhou, T., and Chang, Y. (2019). Sustainable supplier selection for smart supply chain considering internal and external uncertainty: An integrated rough-fuzzy approach. Applied Soft Computing, 106004. [CrossRef]
- Davis J, Edgar T, and Graybill R.(2015). Smart manufacturing. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng, 2015; 6, 141–160.
- Davis, J., Edgar, T., Porter, J., Bernaden, J., and Sarli, M. (2012). Smart manufacturing, manufacturing intelligence and demand-dynamic performance. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 47, 145–156. [CrossRef]
- Davydov, R.(2022). A guide to making your supply chain smart. https://www.itransition.com/blog/smart-supply-chain.
- De Man, J. C., and Strandhagen, J. O. (2018). Spreadsheet application still dominates enterprise resource planning and advanced planning systems. Ifac-Papersonline, 51, 1224–1229.
- Eisenhardt K.M., and Martin J.A.(2000). Dynamic capabilities: What are they? Strateg. Manag. J. 2000; 21, 1105–1121. [CrossRef]
- Enríquez, J.G., Jiménez-Ramírez, A., Domínguez-Mayo, F.J., and García-García, J.A.(2020). "Robotic Process Automation: A Scientific and Industrial Systematic Mapping Study," in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 39113-39129, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Ettl, M., Feigin, G.E., Lin, G. Y., and Yao, D. D., A supply network model with base-stock control and service requirements. Operations Research, 48.
- Farias Bueno, A., Godinho Filho, M., and Germán Frank, A. (2020). Smart Production Planning and Control in the Industry 4.0 context: A systematic literature review. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 106774. [CrossRef]
- Gaur, J., Amini, M., and Rao, A.K. (2020) The impact of supply chain disruption on the closed-loop supply chain configuration profit: a study of sourcing policies. International Journal of Production Research, 58, 17. [CrossRef]
- Gerovitch and Slava (2003). Automation. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262281771_Automation/citation/download.
- Goldberg, K. (2012). What Is Automation? IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 9(1), 1–2. [CrossRef]
- Groover, P. M. (2019). Fundamentals of modern manufacturing materials, processes, and systems.
- Gupta, S., Drave, V.A., and Bag, S.(2019). Leveraging Smart Supply Chain and Information System Agility for Supply Chain Flexibility. Inf Syst Front, 21, 547–564 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Hult, G.T.M., Ringle, C.M. and Sarstedt, M. (2017). A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). 2nd Edition, Sage Publications Inc., Thousand Oaks, CA.
- Hair, J.F., Risher, J.J., Sarstedt, M. and Ringle, C.M. (2019). When to Use and How to Report the Results of PLS-SEM. European Business Review, 31, 2-24. [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.L. (1995) A Natural-Resource-Based View of the Firm. Academy of Management Review, 1014.
- Henneberry, B.(2023). What is Smart Procurement? Definition, Applications, and How to Implement. https://www.thomasnet.com/articles/procurement/smart-procurement/.
- Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2015). A New Criterion for Assessing Discriminant Validity in Variance-Based Structural Equation Modeling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43, 115-135. [CrossRef]
- Hirunyawipada T., and Xiong G.(2018). Corporate environmental commitment and financial performance: Moderating effects of marketing and operations capabilities. J. Bus. Res. 2018; 86, 22–31. [CrossRef]
- Hörisch, J., Kollat, J. and Brieger, S.A.(2017). What influences environmental entrepreneurship? A multilevel analysis of the determinants of entrepreneurs’ environmental orientation. Small Bus Econ 48, 47–69 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M. (2007). Technology and workforce: Comparison between the information revolution and the industrial revolution. Berkley: University of California, Berkley. Retrieved June 22, 2010 from http://infoscience.epfl.ch/record/146804/files/InformationSchool.pdf?version=1.
- Kagermann, H., Wahlster, W., and Helbig, J. (2013). Recommendations for implementing the strategic initiative Industrie 4.0: Final report of the Industrie 4.0 Working Group. Forschungsunion: Berlin, Germany.
- Keszey, T. (2019). Environmental orientation, sustainable behaviour at the firm-market interface and performance. Journal of Cleaner Production, 118524. [CrossRef]
- L, D., Zhao, L., Ma, S., Shao, S., & Zhang, L. (2019). What influences an individual’s pro-environmental behavior? A literature review. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 146, 28–34. [CrossRef]
- Lange, F., and Dewitte, S. (2019). Measuring pro-environmental behavior: Review and recommendations. Journal of Environmental Psychology. [CrossRef]
- Lange, F., Steinke, A., & Dewitte, S. (2018). The Pro-Environmental Behavior Task: A laboratory measure of actual pro-environmental behavior. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 56, 46–54. [CrossRef]
- Lee, P. S., Sung, Y. H., Wu, C. C., Ho, L. C., and Chiou, W. B. (2020). Using episodic future thinking to pre-experience climate change increases pro-environmental behavior. Environ. Behav. 52, 60–81. [CrossRef]
- Li, J. J., Zhang, J., Zhang, D. Y., and Ji, Q. (2019). Does gender inequality affect household green consumption behaviour in China? Energy Policy 135, 111071. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y. H., & Chen, Y. S. (2017). Determinants of green competitive advantage: The roles of green knowledge sharing, green dynamic capabilities, and green service innovation. Quality & Quantity, 51(4),1663–1685. [CrossRef]
- Lin, YH., and Chen, YS.(2017). Determinants of green competitive advantage: the roles of green knowledge sharing, green dynamic capabilities, and green service innovation. Qual Quant 51, 1663–1685 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Lowell Center for Sustainable Production. (1998). Sustainable Production: A Working Definition, Informal Meeting of the Committee Members.
- Lowenberg-DeBoer, J., Huang, I.Y., and Grigoriadis, V. (2020). Economics of robots and automation in field crop production. Precision Agric 21, 278–299 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Lowry, R. Michael 2019. Automation. [eBook]. P.122-126. Available at http://web.mit.edu/slava/homepage/articles/Gerovitch-Automation.pdf.
- Lu Y, Morris K and Frechette S (2016). Current Standards Landscape for Smart Manufacturing Systems vol 8107 (National Institute of Standards and Technology) ISBN 1069600690287.
- Lu, Y., Morris, K.C., and Frechette, S.(2016).Current standards landscape for smart manufacturing systems. National Institute of Standards and Technology, NISTIR, 8107 (2016), p.
- Medrano, N., Cornejo-Cañamares, M. and Olarte-Pascual, C. (2020), "The impact of marketing innovation on companies’ environmental orientation", Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, Vol. 35 No. 1, pp. 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Musonda, I. and Gambo, N. (2021)."Mediation effect of partnership on procurement strategy factors influencing sustainable smart housing development, Nigeria", Built Environment Project and Asset Management.11 (3) 454-467. [CrossRef]
- National Entrepreneurship and Innovation Programme (NEIP) (2022). A government of Ghana Initiative Report.
- Nelson R.R., and Nelson K.(2002). Technology, institutions, and innovation systems. Res. Policy. 2002; 31, 265–272. [CrossRef]
- Ngatia, Maku and Jomo Kenyatta. (2016). “Role of Public Procurement Oversight Authority on Procurement Regulations in Kenyan State Corporations. A Case of Kenya Electricity Generating Company (KenGen). International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting Finance and Management Sciences.
- Nie, D., Li, H., Qu, T., Liu, Y., and Li, C. (2020). Optimizing supply chain configuration with low carbon emission. Journal of Cleaner Production, 122539. [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, C.(1999). Sustainable production – a new paradigm for a new millennium. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 61.
- Oluyisola OE, Sgarbossa F, and Strandhagen JO. (2030). Smart Production Planning and Control: Concept, Use-Cases and Sustainability Implications. Sustainability. 2020; 12(9):3791. [CrossRef]
- Oluyisola, O. E., Sgarbossa, F., and Strandhagen, J. O. (2020). Smart Production Planning and Control: Concept, Use-Cases and Sustainability Implications. Sustainability, 12(9), 3791. [CrossRef]
- Özkan E, Azizi N, and Haass O.(2021). Leveraging Smart Contract in Project Procurement through DLT to Gain Sustainable Competitive Advantages. Sustainability. 2021; 13(23):13380. [CrossRef]
- Phuyal, S., Bista, D., and Bista, R. (2020). Challenges, Opportunities and Future Directions of Smart Manufacturing: A State of Art Review. Sustainable Futures, 2, 100023. [CrossRef]
- Qiu L., Jie X., Wang Y., and Zhao M.(2020). Green product innovation, green dynamic capability, and competitive advantage: Evidence from Chinese manufacturing enterprises. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020;27:146–165. [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M., Romsdal, A., Sgarbossa, F., Strandhagen, J.O., and Holm, M.(2022). Towards smart production planning and control; a conceptual framework linking planning environment characteristics with the need for smart production planning and control. Annual Reviews in Control, 53,370-381,1367-5788. [CrossRef]
- Ron, A.J.(1998). Sustainable production: the ultimate result of a continuous improvement. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 56–57, 99–110.
- Roome, N., and Anastasiou, I.(2021). Sustainable Production : Challenges and objectives for EU Research Policy.https://www.cairn.info/revue-reflets-et-perspectives-de-la-vie-economique-2002-1-page-35.htm.
- Rosen, M. A., and Kishawy, H. A. (2012). Sustainable Manufacturing and Design: Concepts, Practices and Needs. Sustainability, 4(2), 154–174. [CrossRef]
- Saad, S. M., Bahadori, R., Jafarnejad, H., and Putra, M. F. (2021). Smart Production Planning and Control: Technology Readiness Assessment. Procedia Computer Science, 180, 618–627. [CrossRef]
- Sabri, Y., Micheli, G. J. L., and Cagno, E. (2022) Supplier selection and supply chain configuration in the projects environment. Production Planning & Control, 33, 12. [CrossRef]
- afdarian, A., Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M., Lehtonen, M., and Aminifar, F.(2015). "Optimal Electricity Procurement in Smart Grids With Autonomous Distributed Energy Resources," in IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, vol. 6, no. 6, pp. 2975-2984, Nov. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Samuel, V. B., Agamuthu, P., and Hashim, M. A. (2013). Indicators for assessment of sustainable production: A case study of the petrochemical industry in Malaysia. Ecological Indicators, 24, 392–402. [CrossRef]
- Scherbakov, V., and Silkina, G.(2019). Logistics of smart supply chains. Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Technologies in Logistics and Infrastructure (ICDTLI 2019). Atlantis Press. 66(71). [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M. T., Aknin, L. B., Axsen, J., and Shwom, R. L. (2018). Unpacking the Relationships Between Pro-environmental Behavior, Life Satisfaction, and Perceived Ecological Threat. Ecological Economics, 143, 130–140. [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.-F., Liu, W., Li, Y., Chaudhry, H. R., and Yue, X.-G. (2021). Multistage implementation framework for smart supply chain management under industry 4.0. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 162, 120354. [CrossRef]
- Strandhagen, W. J. Alfnes, E. Strandhagen, J. O. and Vallandingham, L. (2017). The fit of industry 4.0 applications in manufacturing logistics: A multiple case study. Advances in Manufacturing, 5(8).
- Tantawi, K.H., Sokolov, A., and Tantawi, O.(2019). "Advances in Industrial Robotics: From Industry 3.0 Automation to Industry 4.0 Collaboration," 2019 4th Technology Innovation Management and Engineering Science International Conference (TIMES-iCON), Bangkok, Thailand, 2019, pp. 1-4. [CrossRef]
- Tao, F., and Qi, Q. (2019)."New IT Driven Service-Oriented Smart Manufacturing: Framework and Characteristics," in IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 81-91, Jan. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Teece, D. J. (2017). Business model and dynamic capabilities. Long Range Planning, 51, 40–49.
- Teece, D.J. (2007). Explicating Dynamic Capabilities: The Nature and Micro Foundations of (Sustainable) Enterprise Performance. Strategic Management Journal, 28, 1319-1350. [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J., Pisano, G. and Shuen, A. (1990). Firm Capabilities, Resources and the Concept of Strategy. Economic Analysis and Policy Working Paper EAP, 38, University of California, Oakland, CA.
- Teece, D.J., Pisano, G. and Shuen, A. (1997) Dynamic Capabilities and Strategic Management. Strategic Management Journal, 18, 509-533.doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0266(199708) 18, 7.
- Truelove, H. B., and Gillis, A. J. (2018). Perception of pro-environmental behavior. Global Environmental Change, 49, 175–185. [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.-L. (2013). Modeling sustainable production indicators with linguistic preferences. Journal of Cleaner Production, 40, 46–56. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B., Tao, F., Fang, X., Liu, C., Liu, Y., and Freiheit, T. (2020). Smart Manufacturing and Intelligent Manufacturing: A Comparative Review. Engineering. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Ma, Y., Zhang, L., Gao, R. X., and Wu, D. (2018). Deep learning for smart manufacturing: Methods and applications. Journal of Manufacturing Systems. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T., and Deng, S. (2018). Multi-Period Energy Procurement Policies for Smart-grid Communities with Deferrable Demand and Supplementary Uncertain Power Supplies. Omega. [CrossRef]
- Weingärtner T, Batista D, Köchli S, and Voutat G.(2021). Prototyping a Smart Contract Based Public Procurement to Fight Corruption. Computers. 2021; 10(7):85. [CrossRef]
- Wiendahl, H.-H.; Von Cieminski, G.; and Wiendahl, H.-P.(2005). Stumbling blocks of PPC: Towards the holistic configuration of PPC systems. Prod. Plan. Control, 16.
- Wu, L., Yue, X., Jin, A. and Yen, D. C.(2016). Smart supply chain management: a review and implications for future research. The International Journal of Logistics Management, 2016. vol. 27, iss. 2, pp.395-417.
- Xing X, Liu T, Shen L, and Wang J.(2020). Linking Environmental Regulation and Financial Performance: The Mediating Role of Green Dynamic Capability and Sustainable Innovation. Sustainability. 2020; 12(3):1007. [CrossRef]
- ang, H., Kumara, S., Bukkapatnam, S.T.S., and Tsung, F. (2019).The internet of things for smart manufacturing: A review, IISE Transactions. 51(11) 1190-121. [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M., Majid, A., Yasir, M., & Qudratullah, H. (2020). Promoting environmental performance in manufacturing industry of developing countries through environmental orientation and green business strategies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 123003. [CrossRef]
- Yu D, Tao S, Hanan A, Ong TS, Latif B, and Ali M. (2022).Fostering Green Innovation Adoption through Green Dynamic Capability: The Moderating Role of Environmental Dynamism and Big Data Analytic Capability. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(16):10336. [CrossRef]
- Yu, y., and Huo, B.(2018).The impact of environmental orientation on supplier green management and financial performance: The moderating role of relational capital. J. Clean. Prod, 2018.
- Yuan, B., and Cao, X.(2022).Do corporate social responsibility practices contribute to green innovation? The mediating role of green dynamic capability. Technology in Society. 68. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G., Yang, Y. and Yang, G. (2023). Smart supply chain management in Industry 4.0: the review, research agenda and strategies in North America. Ann Oper Res 322, 1075–1117 (2023). [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).