1. Introduction
Recently, many smart materials are actively being studied as actuators and sensors for control applications such as automotive suspension, precision mechanism and vibration control. Among many smart materials, both electrorheological fluid (ERF) activated by an electric voltage and magnetorheological materials (MRM) stimulated by a magnetic intensity are very attractive candidates for various applications due to several inherent advantages including controllable apparent viscosity by the external stimuli, reversible phase characteristics, fast response time adaptable to most of dynamic systems and easy design of feedback controller associated with a semi-active actuating capability. In the early of 1990s, the study of ERFs is more active than MRM since the preparation of ERF itself and manufacturing of application systems is much simpler than those of MRMs. For example, the applications of ERF need only positive and negative electrode to activate the fluid without any extra electric circuit. However, it has been recognized from several works that the field-dependent force (damping force) generated from ERF due to the electrical field is too weak to apply practical dynamic systems. Therefore, the dramatic change of the research trend from ERF to MRM has been arisen in the early of 2000s. In general, the MRM has almost same material characteristics as ERF, but produces much higher the filed-dependent damping force (around 500 times) with relatively low power. Since then, numerous works on the MRM have been carried out to enhance the field-dependent properties of material itself as well as to increase control performance of application systems. As a result, some commercialized products using MRM are now available in several fields including automotive suspension damper, automotive seat damper and polishing machine for precise surface roughness. It is noted here that in this work MRMs can be classified into the magnetorheological fluid (MRF), magnetorheological elastomer (MRE) and magnetorheological plastomer (MRP).
The review articles on the ERF itself published so far have considered several factors to enhance the field-dependent characteristics [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. For examples, several different particles such as alfa silica, alumina, polyurethane, mannitol, aluminum oleate, boron, carbon, colloidal silica, nylon powder and barium titanate have been mixed with various carrier fluids including silicone oil, transformer oil, dielectric oil, olive oil, caster oil, mineral oil, kerosene, grease and carbon tetrachloride. Several additives such as liquid crystal and surface coating with the carbon nanotube have been also undertaken to increase the damping force and durability of ERF. And some fundamental theories including the dynamic behaviors of small and large motions, the mechanism of chain-like formation, constitutive equations, and operating flow modes have been studied a lot over 2 decades. Due to some benefits of ERF such as fast response time and easy controllability of apparent viscosity, it has been applied to many systems of automotive shock absorber, vibration control of flexible structures, medical devices (haptic master for surgical robot, knee rehabilitation orthotic, prosthesis), brake/clutch mechanisms, energy transportation and storage [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. On the other hand, the review articles on the MRM classified by MR fluid, MR elastomer and MR plastomer are much more than those of the ERF after some devices of vibration control have been appeared in the real market as commercial products. Similar to the ERF, many investigations to enhance MR effect were done by utilizing several particles (iron oxide, iron carbide, carbonyl iron, silicon steel, low carbon steel and nickel), carrier liquids (silicone oil, polyalphaolefin, mineral oil, paraffin oil and aromatic alcohol), additives (guar gum, antioxidant, metal oxide powders and viscosity modifier) and surface coatings (carbon nanotube, polyaniline, zirconia and polycarbonate) [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23]. As for the application systems using MRM, there are many review articles treating various systems or devices: MR dampers for automotive suspension system, MR dampers for civil engineering, large-sized MR mounts, control aspects of MRM application systems, energy harvesting MR dampers and vibration control of flexible structures [
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36]. However, most of works on the MRM done so far have been focused on the actuators or actuating mechanism instead of the sensors or sensing devices. This is because the desired force produced from ERFs and MRMs can be easily achieved by applying external fields of electric voltage or/and magnetic field intensity. However, despite of the numerous works on these smart materials, commercial products are strictly limited due to a couple of severe problems: particles sedimentation and thermal effect during working operation [
37,
38]. This directly indicates that several challenging problems need to be resolved to use as actuators or sensors of the smart materials considered in this review article.
It has been identified from the literature survey that even though some studies have been carried out on the possibility of the ERF and MRM as sensors’ fabrication, there is no review article focusing on sensors and sensing devices utilizing these smart materials. Consequently, the main technical contribution of this review article is to summarize recent works on the sensors and sensing devices which are available or devised from the ERF and MRM. The review is proceeded in a chronological manner and the sequence of the review is undertaken in the following order: ERF sensors, MRF sensors, MRE sensors and MRP sensors. In conclusion, some challenging future works are briefly described to commercially make the smart materials-based sensors which have high precision, easy calibration, high resolution and high accuracy in real environment. In addition, a couple of modern technologies such as a neural network are suggested to fabricate high performance sensors utilizing the smart materials featuring several principal parameters to be appropriately adjusted or tune.
2. ERF Sensors
As mentioned in Introduction, an ERF is a kind of suspension consisted of the fine dielectric particles and carrier viscous oils and hence it exhibits fast changing rheological properties in the presence of applied electric field. In other words, both stiffness and damping properties are functions of the applied electrical field. Therefore, several sensors could be devised for the properties of ERF. Kim et al. [
39] devised a wave transmission sensor by embedding ERF into the aluminum sandwich structures where a small-sized piezoelectric patch is used for transmitter and receiver, respectively. It was found from this work that the magnitude and frequency of the transmitted signals and sensitivity of the device can be identified in time or frequency domain. Han and Choi [
40] devised a bi-directional clutch featuring a spherical ERF joint in which a torque is measured as a function of the field intensity. In this work, many data relating the torque and field intensity need to be collected as a reference data and hence constant torque or sinusoidal torque depending on the field configuration is measured just like a fuzzy rule. Sagar et al. [
41] measured a constant force in shoe sole using the variable stiffness of ERF. In this work, the sensing range of the force was achieved by changing the concentration of the copper particles. Then, the force was compared with the result measured from the universal testing machine. Zhang et al. [
42] developed an integrated sensor using ERF and conducting polymer (CP) where ERF use as an exciting actuator and CP as a sensor. It was found that the exciting displacement was well measured up to 20 Hz, but when the vibration frequency is higher than 20 Hz the CP sensor can hardly detect the displacement. This kind of sensor mechanism has many potential applications including ERF microvalves and the microchip with the CP sensor to achieve high control accuracy. Choi et al. [
43] developed a speed sensor of a direct current (DC) motor by utilizing ERF as a brake system. From the fuzzy table between the torque and motor speed as a function of the field intensity, the speed of the motor is measured for the torque response the DC motor. In fact, this mechanism can be used as a torque sensor if the motor speed is measured by an encoder embedded in servo DC motor. Wettels et al. [
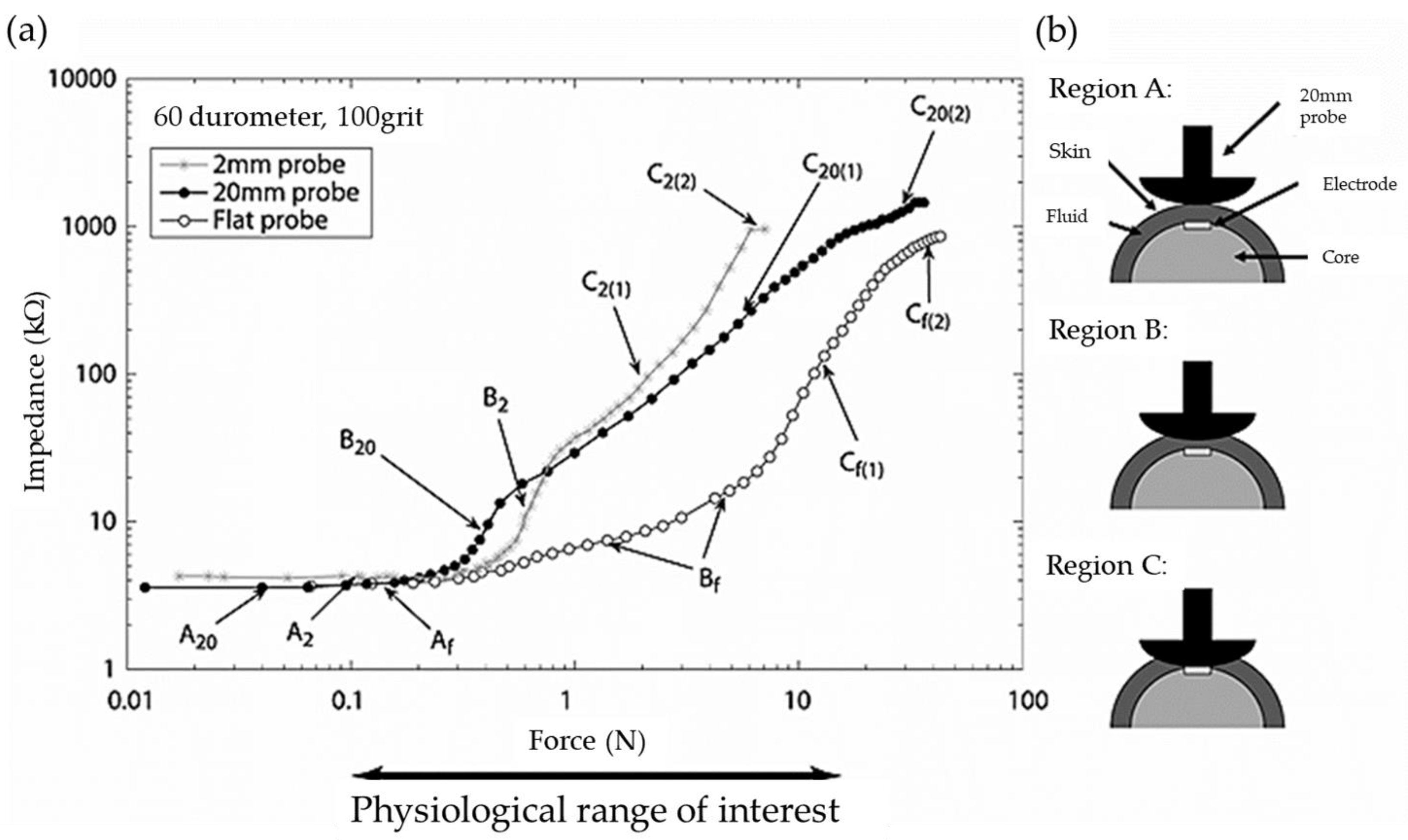
44] proposed a robust tactile sensor array which mimics the mechanical properties and also distributed touch receptors of the human fingertip using ERF filled within an elastomeric skin. It has been found that the force ranging from 0.1 to 30 N by applying the electrical filed to the muti-electrodes.
Figure 1 presents the schematic diagram for the proposed tactile sensor array in which three different regions representing different force levels are shown from the low force to the high force. Sheng and Wen [
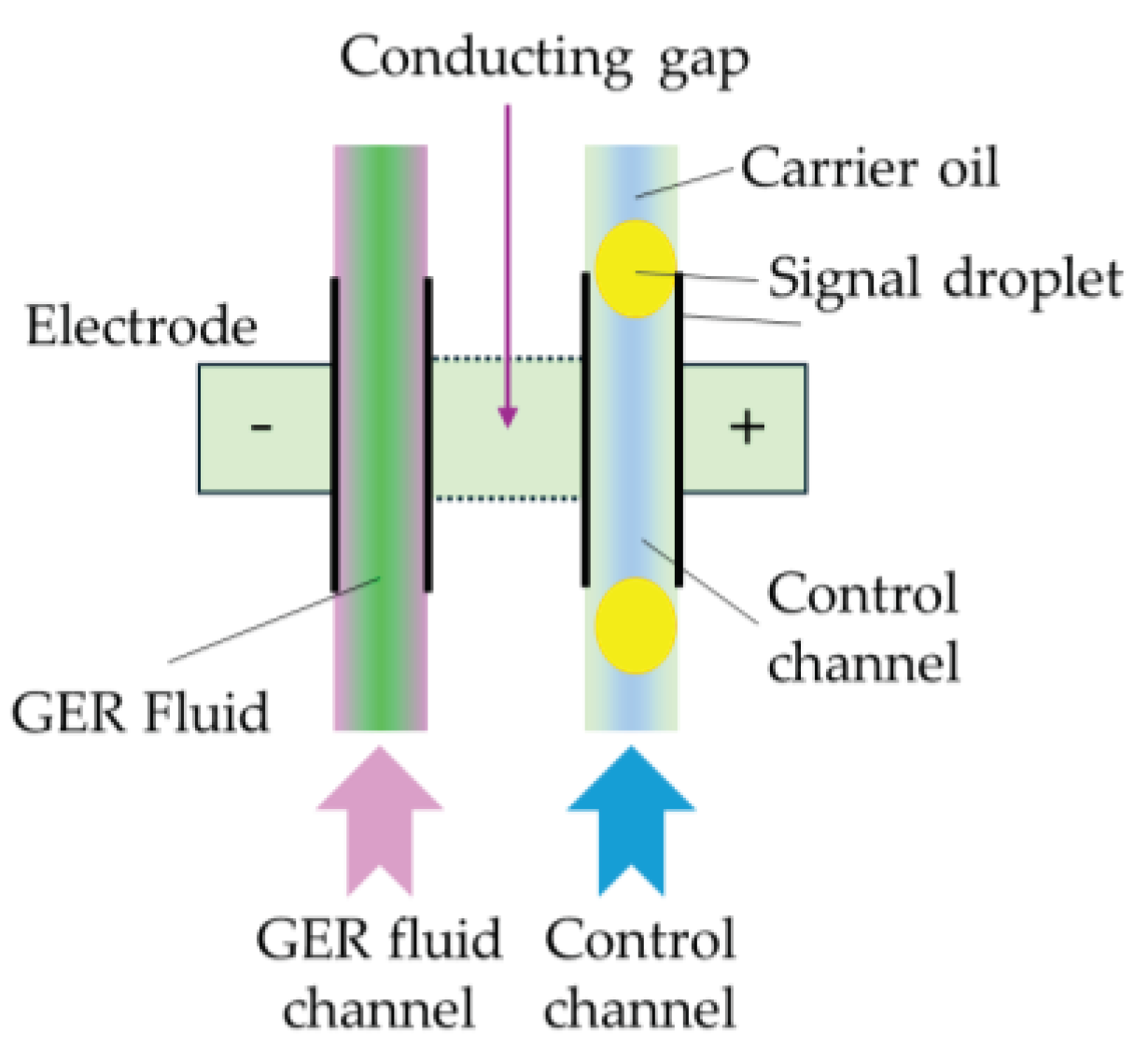
45] reviewed ERFs in terms of mechanisms, dynamics and microfluidics applications. They introduced a very interesting a logic-gate operation device which can be used as switch sensors in servo control systems.
Figure 2 presents an operational principle of the logic-gate in which two parallel channels are separated by a conducting gap to pass ERF and fluid signal. In this device, two electrodes are formed on the walls of two respective channels, while another conducting gap interconnects between the ERF channel and signal fluid channel resulting in another electrode. Therefore, the signal indicating the fluid status can be tuned by an appropriate movement of the signal droplet.
Oh et al. [
46] developed a haptic master which is applicable to the minimally invasive surgery by robotic systems in which ERF can sense the repulsive force to be occurred in the surgical point. By establishing the relationship between the generated force for 4 DOF haptic master and applied input current, the desired force is achieved from the signals from the load cell embedded at the haptic gripper, control current from the microprocessor and fuzzy logic based on the established table. Lee et al. [
47] established a repulsive force feedback control system operated by a master-slave robot which is controlled by ERF haptic master featuring a spherical joint mechanism. The force and rotational angle of the haptic master is measured by the load cell and encoder, respectively, and the robot arms are controlled by the servo motors. In order to measure the force of the skin-cancer-like tissue (palpation) during the surgical operation, a phantom tissue is made and the force which is controlled from the haptic master by the electrical field is applied to the phantom to provide the desired force. This sensing system integrating the ERF-based haptic master whose force is controllable cab be usefully applicable to the robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery (RMIS). Liu et al. [
48] proposed a tactile display to achieve a surface felt from the human touch using the force responses from ERF tactile array device. It was found from experimental test that the sensed surface could be controlled by adjusting the input voltage and the touch sensitivity of the proposed tactile array is able to applicable as a surface touch sensor if the touching force normal to the display’s surface is well applied using a feedback control algorithm. Yoon et al. [
49] have studied that ERF is able to respond by light and electric field by mixing various photosensitive molecules. Therefore, the newly formulated ERF can be treated as a new type of the photocell which can be applicable to basic element of many sensors based on electric circuits producing the out current, voltage and resistance. However, it is possible to be made when the effect of the photo additive only can be identified from the field-dependent rheological properties. Chou et al. [
50] proposed an electrorheological display (ED) to prevent a plague which transmits fast to a variety of wildlife rodents. In order to achieve this goal, they made EDs consisting of two indium tin oxide glasses with spacers to contain core-shell structured polystyrene microspheres (SMs) by emulsion polymerization to absorb the magnetic nanoparticles (FNs) to encapsulate dispersed SM@FN. Then, the transmittances of ED loading SMs@FNs can be identified as a function of the frequency at a certain voltage-on and hence the transmission of the plague may be protected. Mazursky et al. [
51] embedded a sensing mechanism using ERF in which tactile sensations at small scale are conveyed from the field-dependent resistive force of the haptic feedback system. They made a deflection sensor and verified its effectiveness where the sensor design was done on the basis of the stress-sensitive resistive film in bending to the ERF haptic actuator. Jekal et al. [
52] introduced ERFs which have different colors with specific properties and applications. They made a series of TiO2-coated synthetic mica materials colored white, yellow, red, violet, blue and green using a facile sol-gel method and those are identified by naked eyes. Therefore, the users easily select proper ERF by observing the color in which many data such as the field-dependent yield stress, sedimentation stability, particle sizes, carrier liquid, conductivity, dispersion stability are provided in a standard manner. It is noted that the colorful ERF is not a sensor but plays a role of the visual selection to achieve desired field-dependent characteristics. Mazursky et al. [
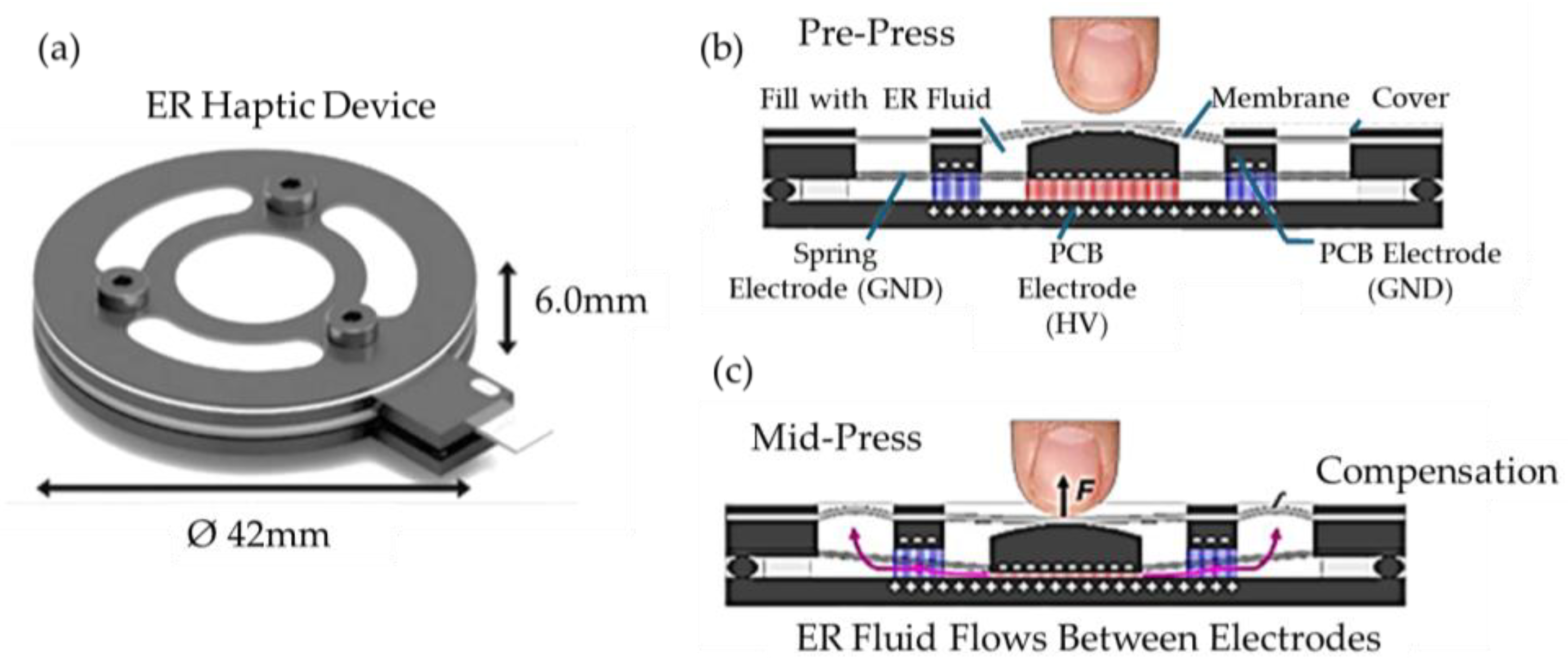
53] proposed a miniature haptic module based on ERF to convey both combined stiffness and vibrotactile sensations at a small scale.
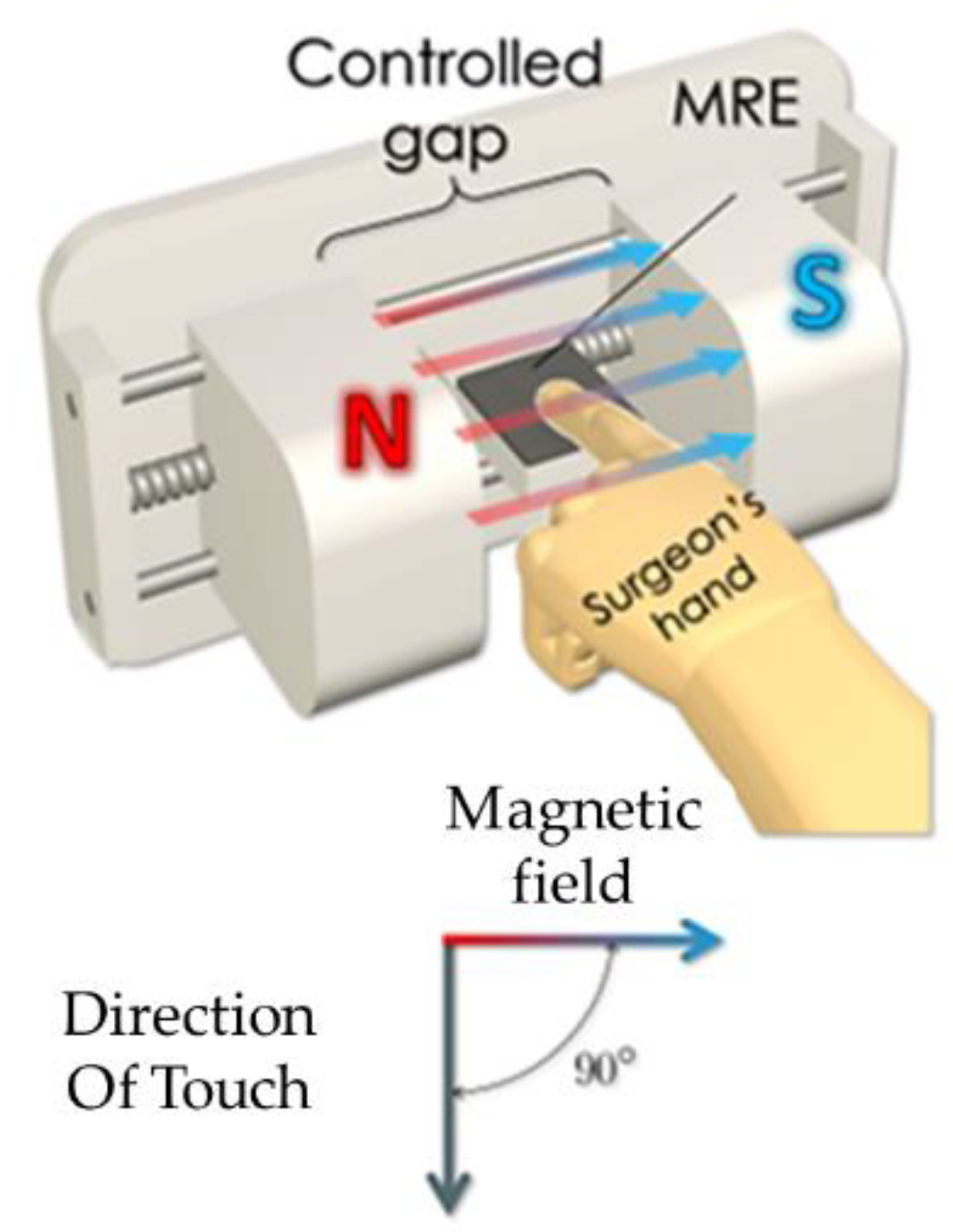
Figure 3 shows the schematic and working principle of a cylindrical ER device in which a user presses upon the membrane surface, the grounded spring electrode is displaced vertically by squeezing the ERF between the grounded spring and high voltage electrodes. The fluid flows radially through parallel electrodes by the pressure gradient from the press and hence the membranes between the slots are to be deformed elastically. Thus, by applying the voltage to the electrodes, a microstructural deformation is occurred by the force which is felt by the user’s finger. It is noted that the force is a function of the pressure and the applied voltage and hence an appropriate dynamic range of simultaneous kinesthetic and tactile sensation can be devised foe several applications including the surgical robot finger.
Salunkhe et al. [
54] presented general properties and applications of ERFs showing recent status of the science and technology. They asserted that ERF has potential applications as sensors, rollable screens and keypads sticks. The ERF sensors are active sensors which are generally used for self-monitoring and control of vibrations in several flexible structures such as building structure design. Using the same concept as the above, the ERF can be used as a detector of seismography or working performance of bridge health. Pavlikova et al. [
55] developed a new type of ERF using a nano-silica grafting approach to discuss on the drawback of conventional ERFs consisting of carbonyl iron particles which possess high electrical conductivity and hence the limitation of the field-dependent rheological characteristics. The carbonaceous particles treated by thermal carbonization in an inert atmosphere were coated by mesoporous nano-silica to obtain the semi-conducting particles. It was identified this work that the conventional ERF caused a short circuit of the measuring device at the electric field of intensity 1 kV/mm, while the proposed ERF was successfully measured up to 3kV/mm, giving less thermal conductivity, higher sedimentation stability and higher yield stress than conventional ERF. Therefore, form the enhanced performances, the coating material amount, coating thickness, dielectric property of the coating material could be identified by the fuzzy table in which the relation between the coating specifications and rheological performances are summarized as a function of the electrical field intensity. Musialek et al. [
56] estimated design parameters of a viscous clutch system using a transfer function which contains principal dynamic parameters of a hydraulic viscous clutch operated and controlled by ERF. The mathematical transfer function of the system was formulated as the first-order system with the time delay and the prototype of the system was tested. It has been found that the simulated operation with the estimated parameters is same as the measured one with high accuracy under external disturbances. Therefore, the principal design parameters such as the orifice diameter of ERF flow could be identified from the proposed approach. Spotowski et al. [
57] formulated a sensing mechanism using a strain gauge sensor and viscous brake filled with ERF to measure the impact of the rotational speed of the input shaft. In other words, this device measures constant pressing force exerted on the ERF brake connected to the shaft of the electric motor and thus different values of the pressing force can be obtained by changing the angular velocity of the motor as well as applying different voltages to the electrodes. Therefore, the final target of this work is to make a device to exert a constant pressing force (DECPF) to measure the force which is dependent on the angular velocity of ERF brake and the level of voltage applied to the electrodes. This kind of sensing mechanism is applicable to optimally control the braking force of many types of brakes and clutches. Recently, Liang et al. [
58] reviewed the ERF technology in terms of the fabrication of ERF itself, material characterization, constitutive models, coil structures, energy related issue, various applications and introduction of electrorheological elastomer (ERE) with sensor applications such as force sensor and speed of table tennis.
3. MRF Sensor
The field-dependent rheological properties of MRF such as the yield stress is much higher than those of ERF and more stable since it is magnetic-sensitive instead of high voltage. Therefore, the applications of MRF as an actuator or sensor have a wider range than ERF. Flores and Liu [
59] demonstrated a possibility of using MRF as a in vitro cancer therapy device by mechanically blocking the blood vessels to a tumor. In this work, a simple blood network consisting of four branches of blood vessels where one of branches is used as a container of the blood vessels with the cavity and either two or four vessels are subjected to the magnetic field. Then, the weight of the leaking blood downstream from the magnets is measured to judge the field intensity for the cancer therapy. Jung et al. [
60] investigated the sensing ability of electromagnetic induction (EMI) system connected to MRF dampers for vibration control. Thus, according to the Faraday’s law of the electromagnetic induction, the emf signal, produced from EMI, is proportional to the velocity of motion. Therefore, the induced emf voltage signal is converted to the velocity signal generated from mechanical shaking table. Troung and Ahn [
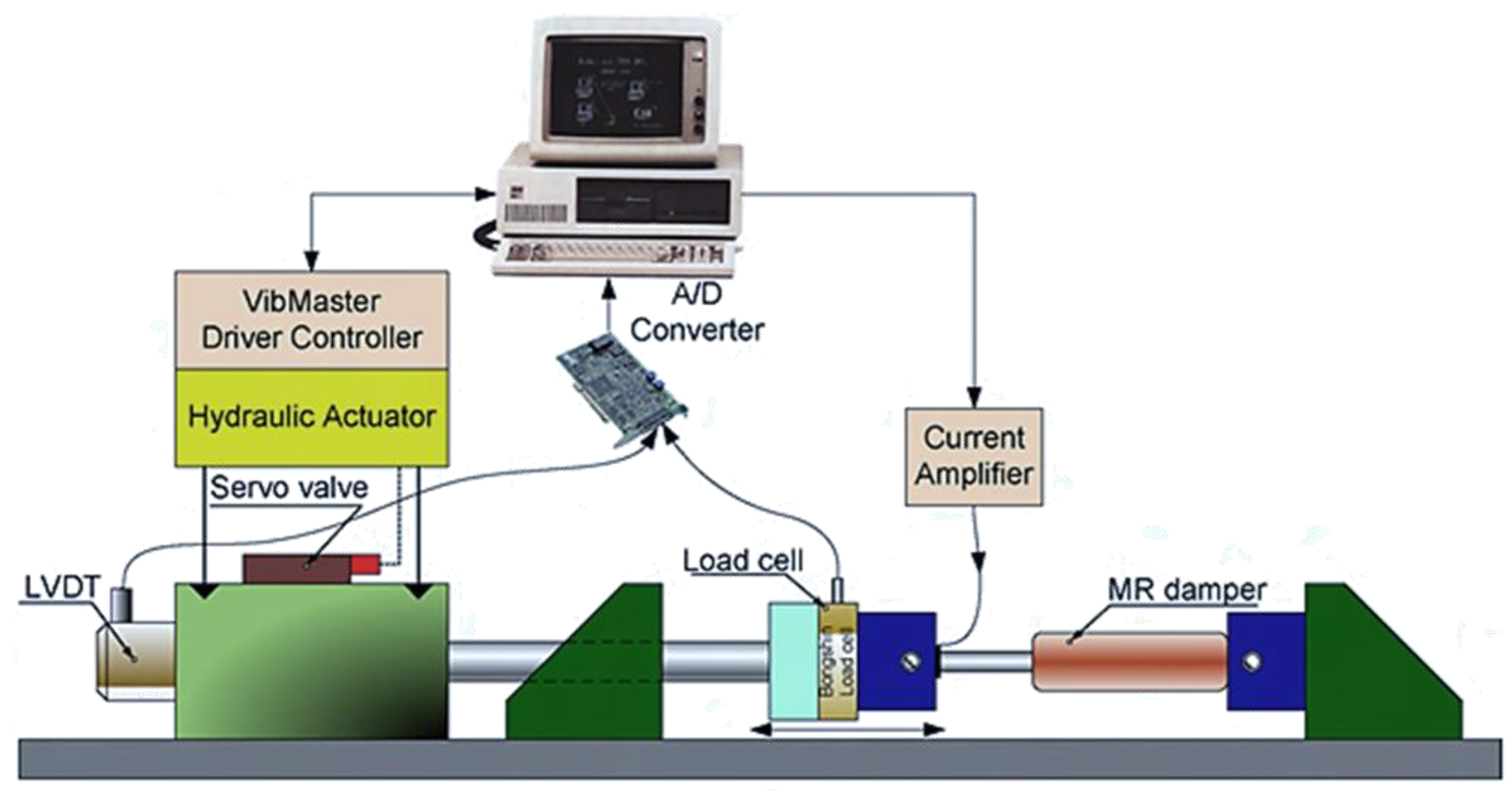
61] proposed a black-box model (BBM) for identification of MR damper featured by self-sensing behavior in which a fuzzy mapping system was used to estimate damper’s characteristics. In order to improve the accuracy of the suggested model, the back propagation learning rules based on the gradient descent method was utilized to train the fuzzy parameters to minimize the modeling error function. Then, the proposed BBM with the optimized parameters can be used as a virtual sensor to measure the damping force of a vibration control system equipped with MR damper.
Figure 4 shows the schematic configuration and working principle of the proposed sensing mechanism. It is seen from the figure that a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) is used to measure the displacement of the piston rod of MR damper, while a load cell is attached to measure the field-dependent damping force. Then, the field-dependent damping force can be measured form the back signals measured by the LVDT and load cells and processed in the data acquisition system as input and output signals. Kaluvan et al. [
62] developed a new measurement method of the field-dependent yield stress of MRF using the resonance concept of the beam. The resonance frequency of the cantilevered beam is changed due to the magnetic field intensity and hence the change of the yield stress can be measured by analyzing the shifted in resonance frequency. Kaluvan et al. [
63,
64] surveyed the sensors and sensing networks made from MRF. As a first example, the resonant sensor was introduced in which the output frequency was changed or tuned as a function of the physical parameters of MRF such as viscosity. The proposed method is accomplished by utilizing resonant behavior of the cantilever structure associated with the piezoelectric excitation and detection. Secondly, a new type of current sensor using MRF was discussed in the oscillatory shear motion. The change of in resonant frequency of the cantilever beam due to the shear mode rheological effect of MRF for the corresponding input current is measured, followed by the formulating the relationship between the resonant frequency and input current. Besides, the magnetic flux sensor could be devised using MRF.
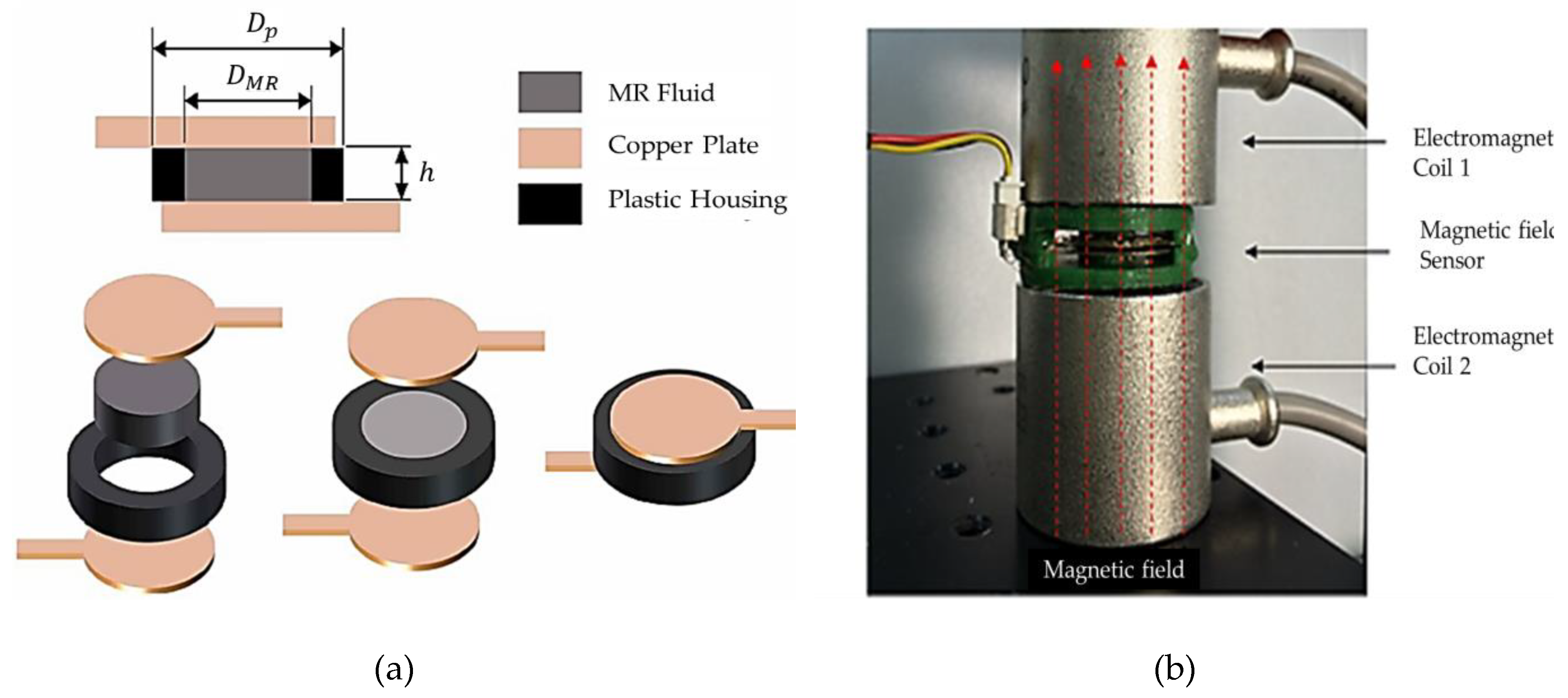
Figure 5 presents the configuration of the flux measurement sensor. As seen from
Figure 5 (a), the measurement device produces the different signals depending on the thickness of MRF which directly indicate the change of the variable register (VR) (or variable rheological properties). This mechanism of the MRF-VR is based on the interaction between ferromagnetic iron particles of the MRF which causes the electrical resistance to be field dependent. Two copper plates are attached to the top and bottom of the plastic housing fully filled with MRF. The variables of H and
are the height and diameter of the plastic housing, respectively, and DMR is the diameter of the contact area between the electrodes and MRF. In fact, it has been identified from experimental test shown in
Figure 5(b) that the initial resistance (maximum) for the two MRF-VRs is 104 and 17.58 MG (ohm), and the final values (minimum) are measured by 4.46 and 2,09 Mg. When the contact area is larger, more electrons easily pass the MRF through the higher number of iron particle bridges generated between the two electrodes. Kaluvan et al. [
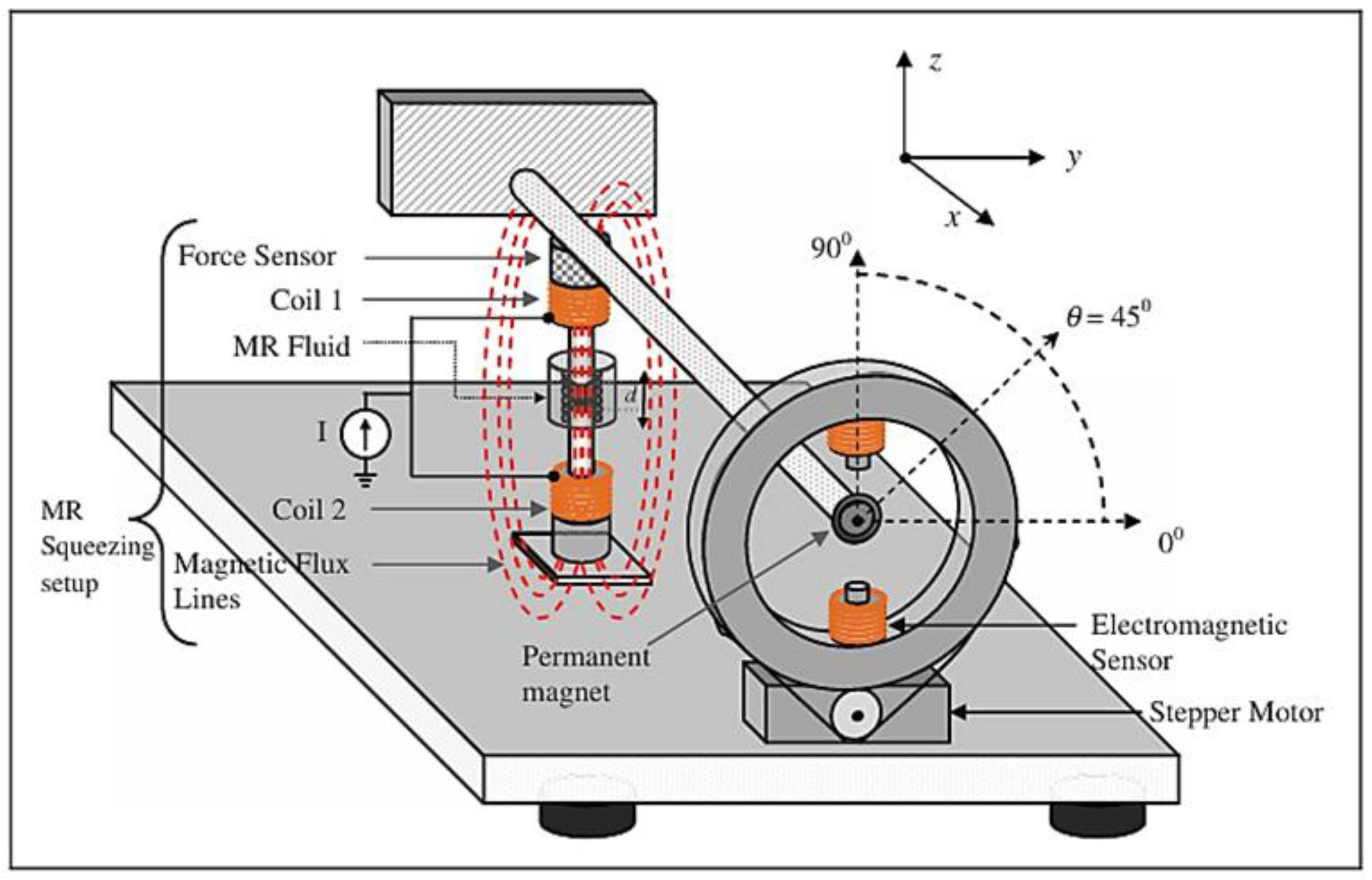
65] developed a new measurement method to achieve the dynamic signals of MRF subjected to squeeze operation mode as shown in
Figure 6. The disc-type permanent magnet is attached to the free end of the cantilever rod and an electromagnetic actuator is placed near to the permanent magnet. The MRF is placed between the gap d to form the squeeze effect, and then the horizontal direction of the vibration of the cantilever rod produces the shear mode operation in the MRF squeezing setup. Similarly, both the vertical and intermediate directions of the rod vibration produce the squeeze and coupled mode operations. Therefore, the field-dependent dynamic behavior of the MRF is measured for several directions of actuation angle. More specifically, the dynamic force and vibration amplitude reduction at different operation modes of the MRF can be measured form the measurement methodology.
Kim et al. [
66] devised a new tactile device using the MRF sponge cell to realize the viscoelastic sensation of human’s real organs such as stomach in which the surgeons can directly contact the sponge cell during the robot surgery. The effectiveness of the proposed device has been demonstrated by measuring the relation time, bending moment and repulsive forces at various input currents and comparing with the existing values corresponding to each human organ. Pepe et al. [
67] presented an electronically controlled suspension system installed MR damper on a real car which relies on a sensor network capable of acquiring a large real-time dataset collecting the car vibration and trim. The information on the car is elaborated by an electronical controller based on a new controller, variational feedback control (VFC), which drives a set of semi-active MR dampers. In the real time realization, a number of key performance indexes such as high ride comfort and limited vertical acceleration are considered to emphasize how the VFC is able to sneak into problematic regions of the performance planes because they are characterized by different and antithetic features of the suspension system. It is noted here that this article does not present MFR sensor directly. But, it shows the sensing network of the feedback control system associated with MR damper. Li et al. [
68] proposed a new displacement sensor by embedding the soft MRF film with ferromagnetic particles which can induce the scattering on the evanescent field of a planar waveguide at a proximity distance. This distance can be controlled precisely by the magnetic intensity showing a maximum sensitivity of ~2.62 dB/T. Park et al. [
69] proposed a controllable tactile device capable of realizing repulsive forces from human tissues using MRF with porous polyurethane foam (PPE). It is called MRP tactile sensor. In the fabrication process of the samples, MRF was immersed into PPE and tested under the squeeze mode.
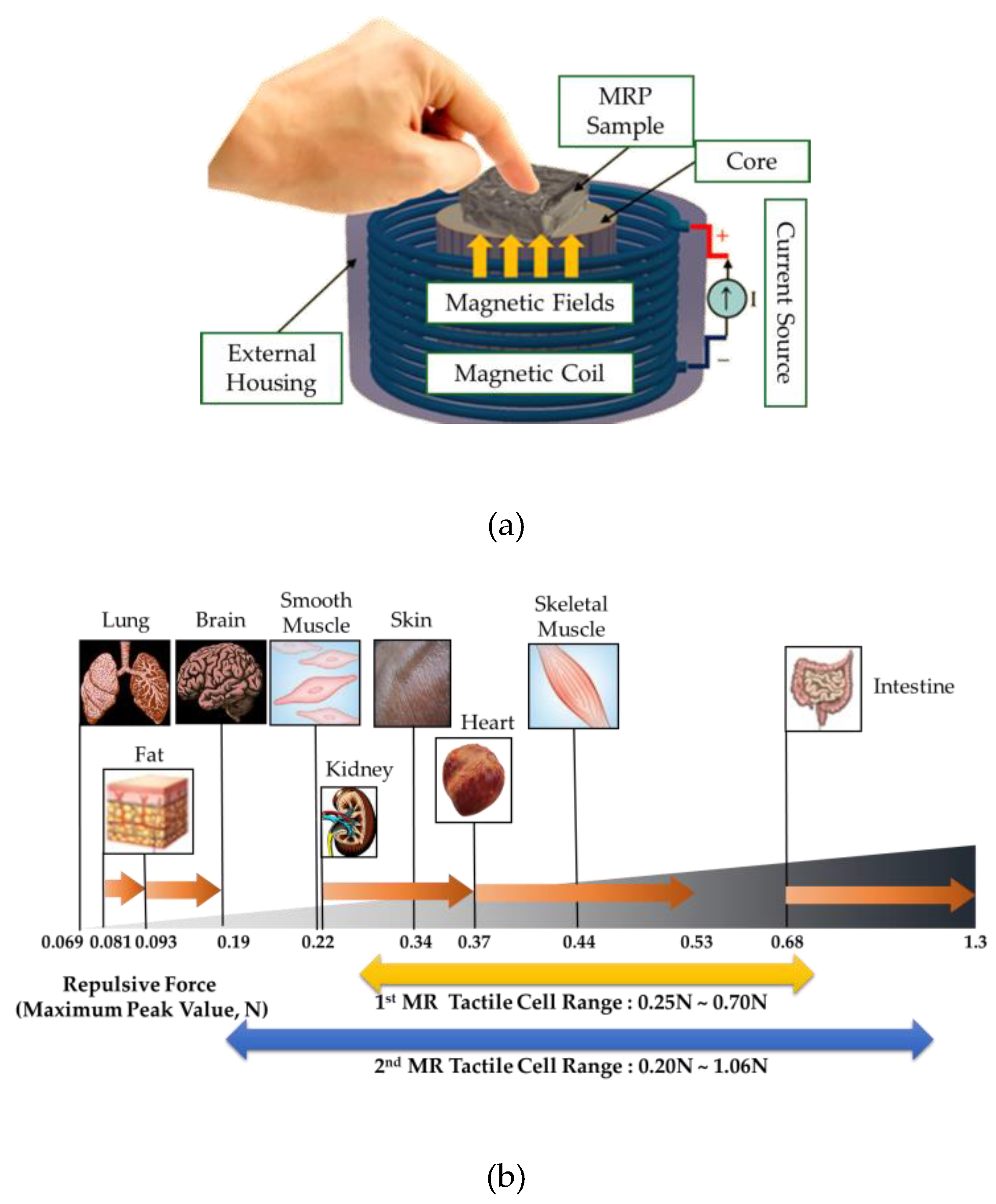
Figure 7 (a) presents a simple schematic configuration of the proposed tactile device in which the hand of the tester is located in the same axis as the direction of the magnetic field. Thus, the repulsive force measured from the tactile force can be controlled by the magnetic field intensity.
Figure 7 (b) represents the relationship between the maximum repulsive (or peak) values achieved from the proposed MRP and stiffness of the human tissues. It is seen that the sample of MRP2 which has 100 ppi PPE has a wider range covering more human tissues than MRP1 which has 25 ppi PPE. It is noted that a tactile device covering all human tissues could be made by adjusting the particle concentration and the magnetic field intensity. Park and Choi [
70] presented a new type of tactile transfer cell using MRF which can be effectively applied to robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery. In fact, the proposed tactile device consists of two smart materials: MRF and magnetorheological elastomer (MRE), whose viscoelastic properties are controllable by an external magnetic field. The relationship between the field-dependent repulsive force and compressive deformation depth is formulated to achieve the field-dependent Young’s modulus utilizing the finite element method. It has been confirmed that the proposed tactile transfer cell can mimic the repulsive force (hardness) of several human organs. Park et al. [
71] presented a dynamic tactile device utilizing a spherical shape of MR structure whose dynamic motions of magnitude and frequency can be controlled by the magnetic field intensity. After manufacturing a prototype, a sinusoidal magnetic field which has different exciting frequency and magnitude is applied to the sample, and then the dynamic motion of the contraction and relaxation depending on the exciting magnetic field has been observed. As one of test results, when 10% deformation was occurred, the instantaneous force was generated from 2.8N to 8.8N and the force when relaxed was measured from 1.2N to 3.5N. It has been also shown that the repulsive force within this range can be implemented using the acceptable input current. Such a special tactile sensing structure proposed in this work can be used as a sensor to measure the field-dependent viscoelastic properties of the human tissues such as stomach, liver, and body. In addition, it is usefully applied to robot surgery because it can mimic the dynamic motions of various human organs under various surgical conditions. Kang et al. [
72] proposed a measurement method of the field-dependent pressure drop with and without the cavitation in MR dampers. It has been identified that the low initial pressure causes the cavitation resulting in abnormal damping force versus displacement and damping force versus piston velocity. In addition, it has been visually observed that the phase delay of the damping force is increased as the stroke increases during extension since the internal pressure of the damper is too low. Song et al. [
73] developed a haptic interface utilizing to provide feedback passive feedback force with high force fidelity and low inertia. As for the slave robot, a catheter and a guidewire can be navigated simultaneously which allows the two degrees of action. The resistance force of the catheter navigation is then measured and reflected to the user through the master haptic interface. It has been experimentally demonstrated that the proposed feedback device provides not only the haptic feedback, but also captures the surgeon’s manipulation of the catheter by applying the magnetic field to the detection circuit. Bhat et al. [
74] wrote a review article of MRF-based reliability devices from the perspective of modeling, sensors and control strategies. Especially, several types of the rehabilitation devices including knee sleeves, prophylactic braces, functional braces, knee and angle orthoses with MRF dampers. In addition, several types of sensors associated with MRF-based rehabilitation devices are introduced and discussed sensing characteristics: flexible resistive sensor, body-oriented sensor, multi-measurement sensor and mechanical sensor. Park et al. [
75] presented a new sensor mimicking the dynamic contraction and relaxation motions of human tissues utilizing both MRF and MRE. As for the MRF, MRF-122EG produced by Lord Corporation (Parker Load, Cary, NC, USA [
76] was used and MRE was fabricated by mixing the CIPs with the silicone rubber based on the 3D printed mold and curing process for 4 hours.
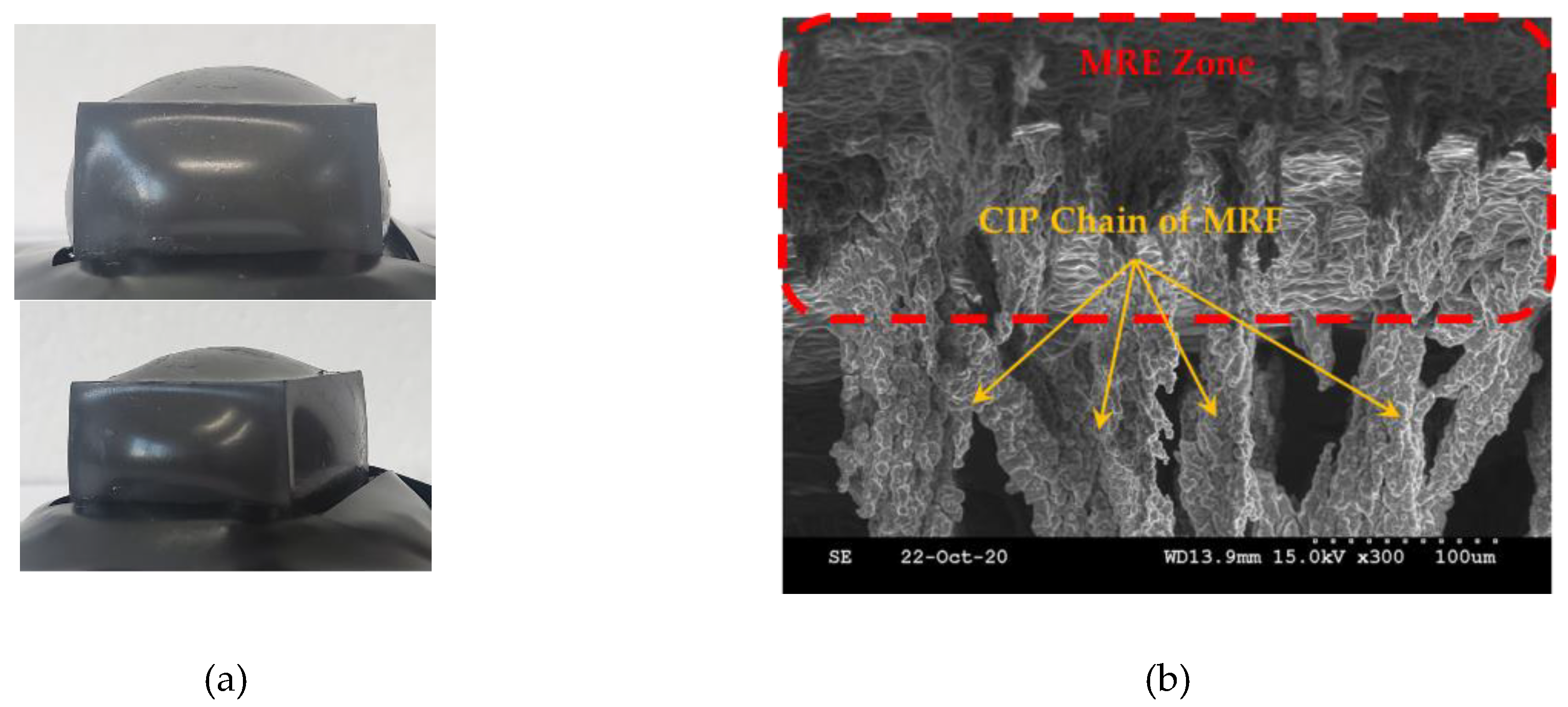
Figure 8 (a) presents a sample of the fabricated sensor and
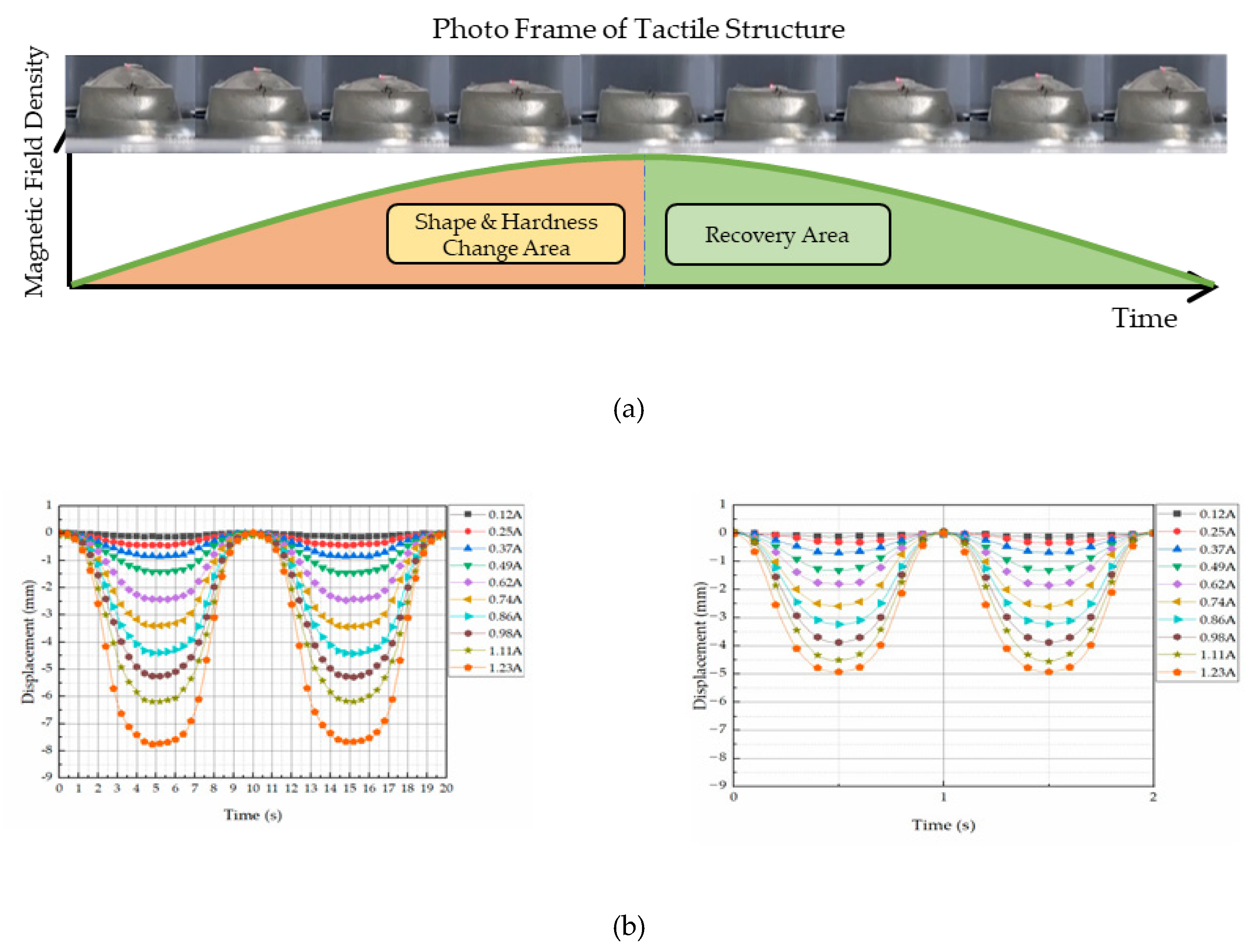
Figure 8 (b) shows the inside-microstructure inside in the presence of the magnetic field. It is expected form the figure that the CIP chains within the MRF extended from the form the surface zone of the MRE as a function of the magnetic field intensity. Therefore, the proposed sensor can change the dynamic shape by the input magnetic field. In other words, the magnitude and frequency of the sensor can be controlled by applying the corresponding input magnetic field.
Figure 9 (a) shows one of dynamic motion results under the influence of the magnetic field during a 1/2 frequency cycle. It is clearly observed from the figure that as the magnetic intensity increases, the maximum shape change (maximum contraction) is occurred due to the increment of the downward and sideways pulling force. If the strength of the magnetic field is off, the original shape is restored as it enters the recovery zone. Therefore, the time-dependent and field dependent stress can be considered as the relaxation of the viscoelastic property. This dynamic motion can be represented by the displacement change as a function of the exciting frequency as shown in
Figure 9 (b). It is observed that as the input current increases, the displacement is increased at the interval and the displacement (or deformation) of the proposed sensor is decreased as the input frequency increases. Therefore, the dynamic motions of various human organs which have different amplitude and frequency can be realized from the proposed sensing device.
4. MRE and MRP Sensors
As well known, the conventional magnetorheological elastomer (MRE) is composed of micro-sized magnetizable particles, matrix and additives considering high saturation magnetization, high permeability and low remnant magnetization of the particles such as CIP. Since the resistance of the ERP is controllable by the magnitude of the magnetic intensity, it can be applicable to several types of sensors such as pressure sensor. Li et al. [
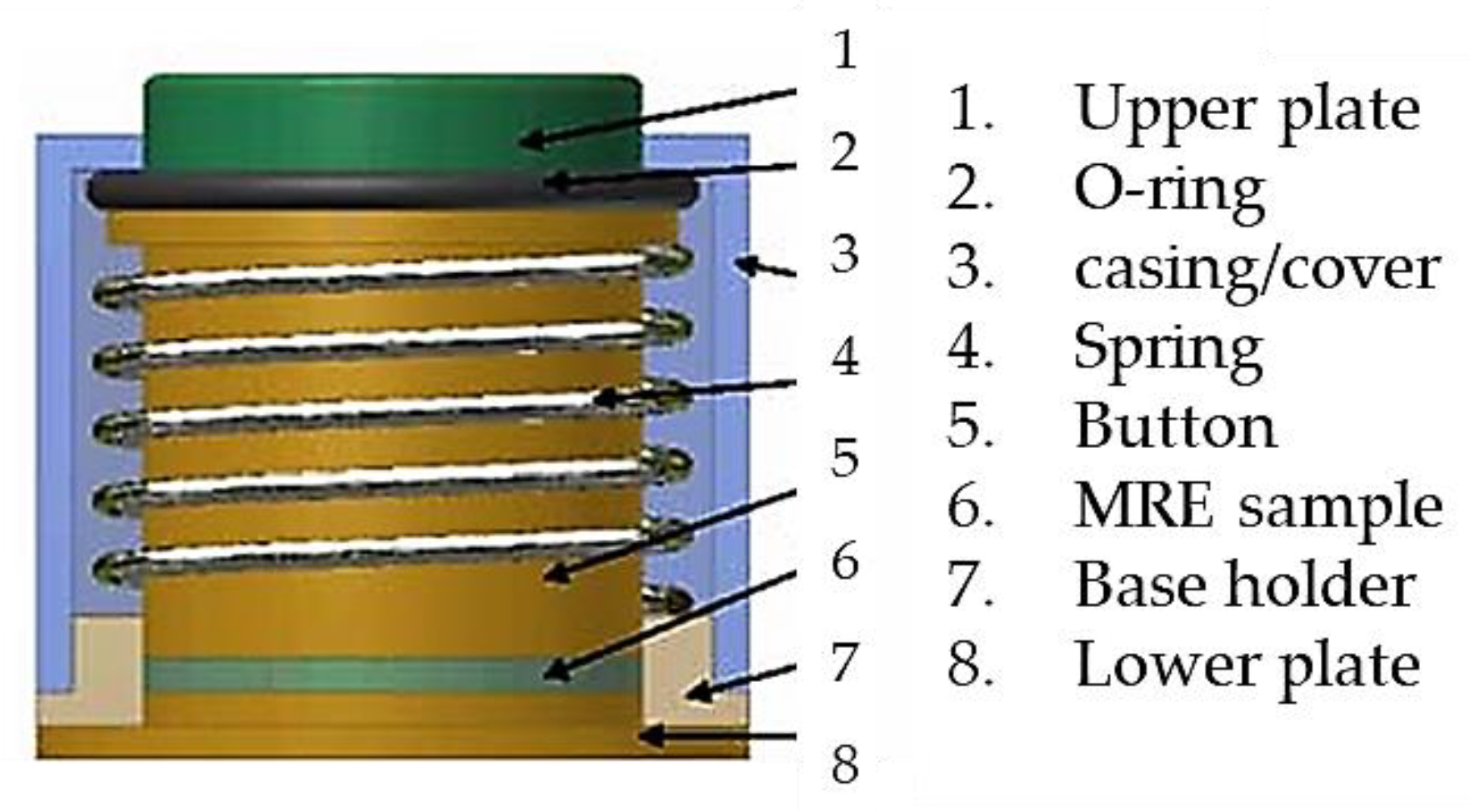
77] proposed a new force sensor using MRE which has three components: mechanical unit, electrical circuit and LED display unit.
Figure 10 presents the schematic configuration and working principle of the MRE force sensor. It is seen that mechanical design consists of 8 components. The base holder is used to connect all parts together and separate the electrodes, while the lower plate is fixed on the base holder with strong adhesive. The MRE sample is fixed between the lower plate and the button. When the upper plate is screwed, the rubber O-ring can provide the button a preload which is adjustable by screwing or unscrewing. Therefore, the preload can be applied on the MRE sample for a primary deformation and the metal spring is pressed to get a primary deformation yielding that the spring provides a recovery force to the sensor. This sensing concept has been proved by formulating the relationship between the voltage and external loading (force). Faidley et al. [
78] investigated a possibility of MRE as sensing mechanism by making 5 mm thick MRE sample consisting of silicone rubber and CIPs of 9 um diameter. As for the testing samples, both the initial bulk magnetization and the length aligned MREs are used to distinguish the different behavior. It is noted that the magnetization of each particle is driven closer to the direction of the applied field so that they become more closely aligned with each other which results in the decrement of the dipole-dipole interaction between neighboring particles. Thus, as the sample is stretched and its cross-sectional area inside the pick-up coil decreases the magnetic flux in the coil changes. Now, this change in flux induces a voltage in the pick-up coil. In other words, a strong correlation between the output induced voltage and the input strain-rate making the materials very promising for large strain, non-contact strain-rate sensors and force sensors in the proportional alignment region. Du and Chen [
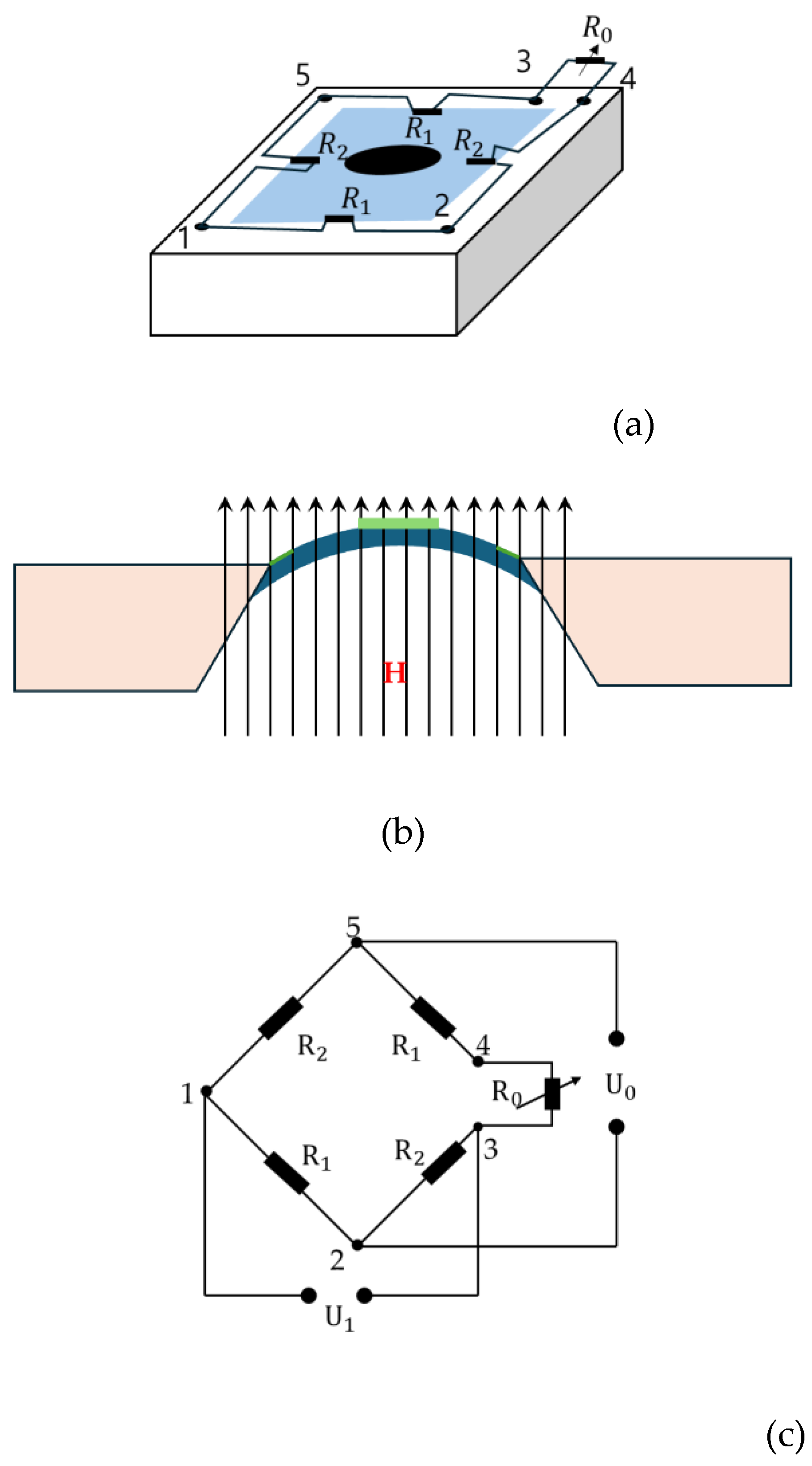
79] developed a low-cost magnetometer based on the magneto-strictive effect of MRE. The micromechanical sensor consists of a silicon sensitivity diaphragm embedded with a piezoresistive Wheatstone bridge and a MRE layer attached to the diaphragm.
Figure 11 presents the schematic configuration and working principle of the magnetometer based on MRE layer. It is seen from
Figure 11(a) that the magnetic field sensor consists of a silicon cup structure and disklike MRE layer attached to the sensitivity diaphragm (SD). The silicon cup has four piezoresistors placed along the periphery of the SD and connected with a Wheatstone bridge configuration. The sensors’ cross-section with the magnetic field is shown in
Figure 11(b) where the SD will move to a displacement due the magnetic field.
Figure 11(c) shows a simple circuit diagram of the Wheatstone bride where R2 and R1 are the piezo-resistors perpendicular and parallel to the SD edge. It is noted that the number of
Figure 11(a) and (c) denote the node marks. It has been found from this work that the proposed sensor has a good linearity in the magnetic field range of 0-120 kA/m, but the saturation is occurred at the above of 150 kA/m. In addition, it was also observed that the remnant magnetostriction of the MRE decreases and the repeatability becomes better. Some future works on the optimal shape, optimal concentration of the magnetic particles, optimal size are to be further explored to be applicable as a practical sensing device. Ghafoorianfar and Gordaninejad [
80] proposed a wireless MRE sensor which is capable of sensing compression and shear. The MRE sensor system consists of a disk-shape MRE sample with two thin steel electrodes attached to both sides and two wires connected to electrodes to obtain the change of the electrical resistance from the piezo-resistance behavior of MRE when various axial and shear stresses are applied. It has been found from experimental results that two orders of the magnitude change in resistance under 8% compressive strain is achieved and the MRE sample with 35% vol.% of the iron particles exhibits more than 30 times increase in resistance with applying up to 100% shear strain. Behrooz et al. [
81] presented an adaptive bridge bearing which can sense structural loads and tune its properties to mitigate unwanted vibrations using MRE layers in which the stiffness, structural wind and traffic load are dependent on the magnetic field. After fabricating a protype of MRE sample combined with the shear, compression and electrical resistance, MRE compression tests were undertaken. It has been shown that the force-displacement loops increase as the magnetic field increases and the strain of the MRE increases from 10% to 50% and the stiffness increases from 215 lb/in to 244 lb/in with the increasing frequency. Therefore, a robust bearing design can be achieved by controlling the magnetic-field dependent the stiffness of MRE layers that ensures the desired performances. Qi et al. [
82] et al. designed a self-powered magnetic-field sensor using MRE and triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) which can be used for both time-varying and uniform magnetic field sensing. This sensor relies on the contact electrification and electrostatic induction of TENG to generate an electrical signal responding to the magnetic-induced deformation of MRE without nay external power or stimuli. It has been shown that the proposed sensor exhibits a fast response time of 20 ms and maximum sensitivity of 16 mV/mT with 60 wt% MRE. It is noted that the sensitivity and detecting range can be adjusted by changing several parameters of the sensing device. LI et al. [
83] fabricated a new self-sensing bearing based on anisotropic MRE consisting of multi-walled carbon nanotube, CIPs with polydimethylsiloxane matrix and the self-sensing characteristics of the MRE such as multi-field coupling of the load and magnetic fields were tested. Then, it has been applied to vibration system to reduce vibration up to 30%. Therefore, the results presented in this work indicate that the modified MRE bearing could be simultaneously used as an actuator and a sensor. Hooshiar et al. [
84] proposed a stiffness display using MRE which can be applicable to manual surgery or robotic minimally invasive surgery.
Figure 12 shows a schematic configuration and working principle of the proposed display device. In this work, the rubber-based bi-layer composite MRE was used to alleviate nonlinear contact problem of the soft material and a pair of the permanent magnetic was employed to generate the magnetic field. A slim sheet of the composite MRE was placed at the mid-span of two permanent magnets and two DC servo motors were used for controlling the magnetic field through the changing the gap distance between the magnets. In addition, a force sensor was placed to measure the touch force in a proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller implementation through the closed-loop manner. It has been shown from experimental test that the range of the tactile forces and stiffness are within the favorable range from 8% to 16 % reported in the previous works. Wang et al. [
85] proposed a wireless inductive sensing device using MRE to measure body deformation of soft pneumatic actuators (SPAs).
Figure 13 presents a working principle of the inductive sensor for SPAs with the flat coils. As seen from the figure, the stretchable MRE skin of the soft actuator plays a role of the nonconductive ferromagnetic material which can be magnetized and demagnetized at very low magnetic field which can increases the total inductance of the coil-MRE system. When MRE skin is deformed, the average distance between MRE skin and coil changes and hence the inductance is varied. Therefore, the deformation of the MRE skin can be monitored wirelessly by measuring the inductance of the coil. It has been demonstrated that the deformation is proportional to the pressure and the inductance of the bending angle of the SPA sample is decreased during an inflation and deflation cycles.
Shabdin et al. [
86] proposed a graphite (Gr)-based MRE (Gr-MRE) to evaluate the effect of the Gr to the resistivity under applied forces and magnetic fields. It has been found from this evaluation that two relationship curves resistance (
R) under different applied force (
F) and different magnetic field (
B) are obtained. Then, it has been identified from the relationship curves that the presence of Gr fraction arrangement contributes to the conductivity of the Gr-MRE and the field-dependent modulus can be improved, particularly at low strain amplitudes, compared with conventional MRE without the additive of Gr. In addition, Form the relationships between force and field-dependent resistivity, the Gr-MRE can be one of potential force sensors. Gast and Zimmermann [
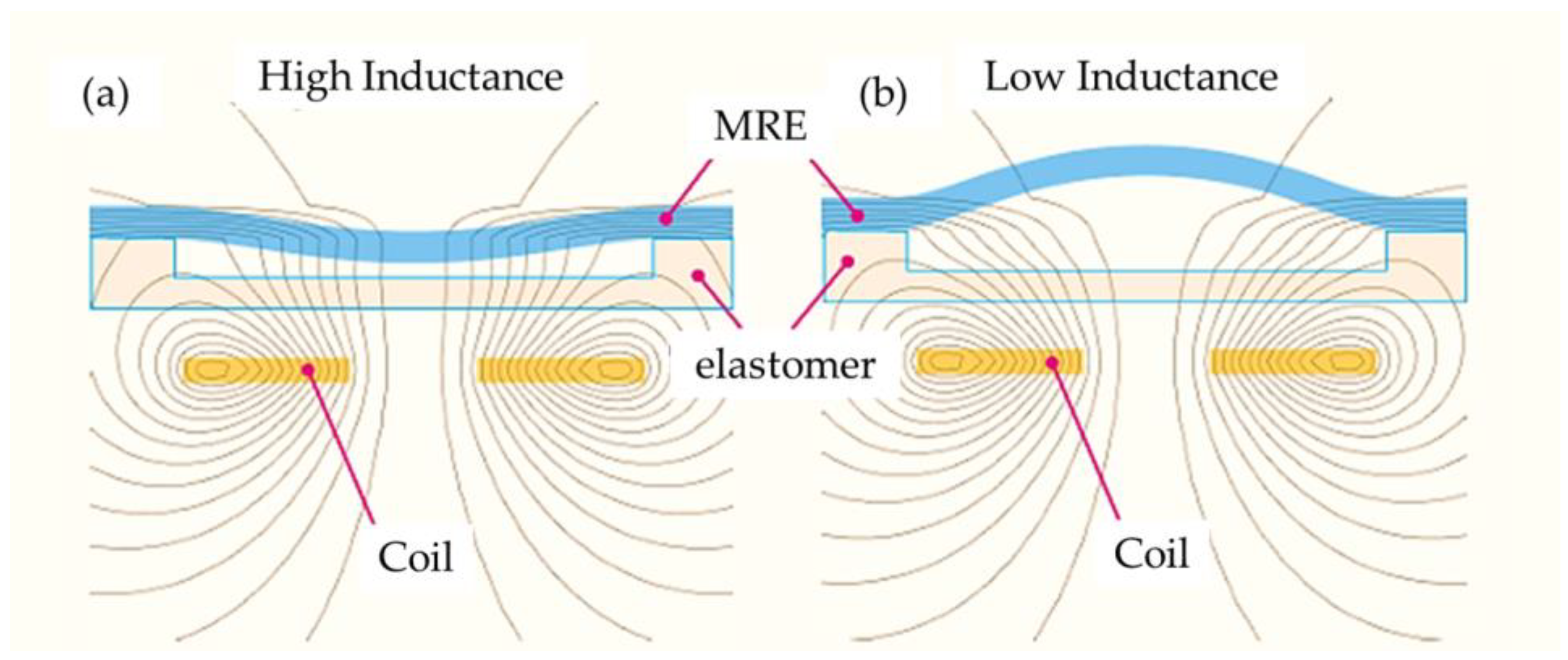
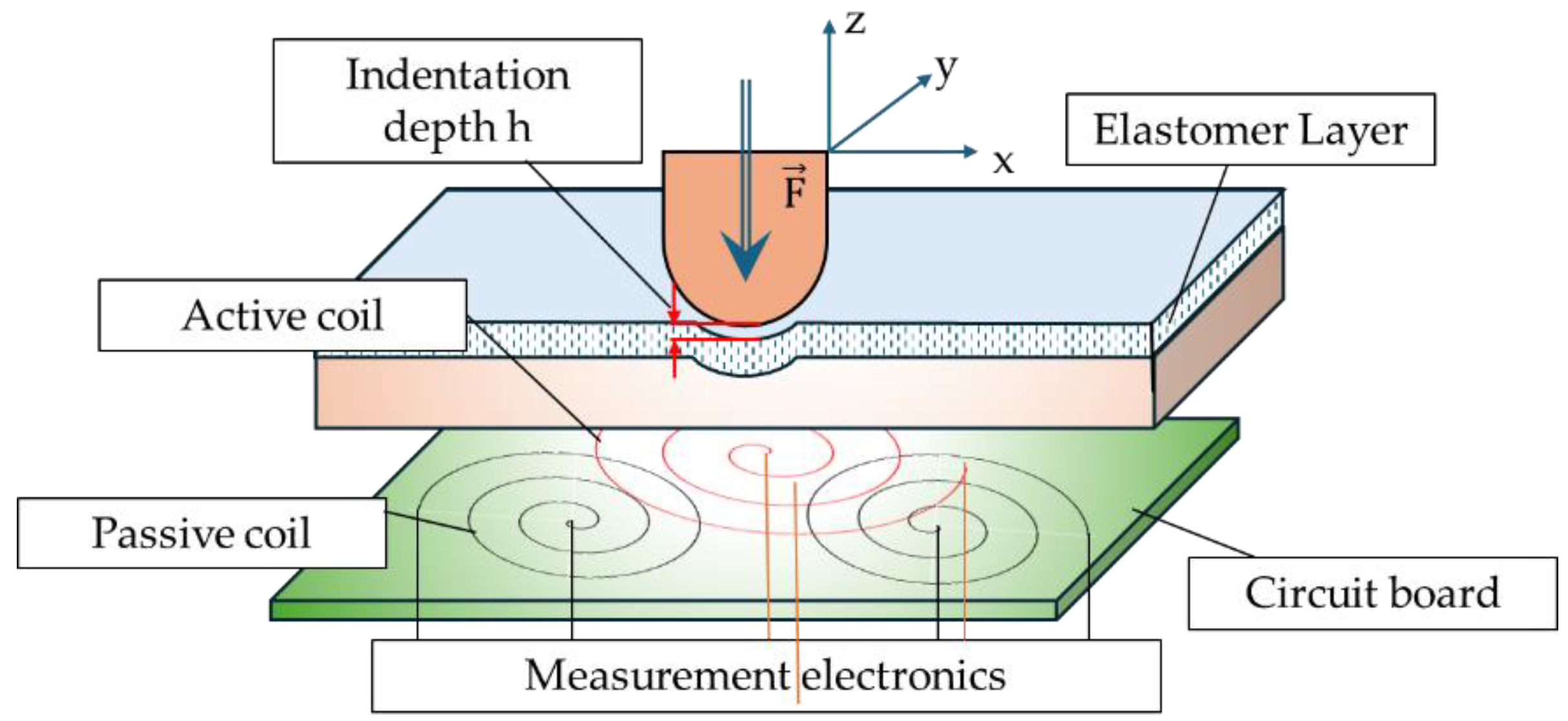
87] investigated the capability of a tactile sensor using the MRE, especially to determine the position of indentation by measuring the inductance of multiple planar coils and a soft magneto-sensitive layer.
Figure 14 shows the working principle of the proposed tactile sensor with the magnetic circuit coil board. In the figure, the indentation of depth
h is the negative z direction and hence the indentation is in a certain interval of the
x and
y position. The inductance of the magnetic coil is increased by increasing the magnetic flux intensity, and the variables of
h,
x and
y are changed or controlled. Therefore, the inductance change curve of a planar-shifted indentation with constant depth of
h can be determined by identifying the peak value (or resonance) of the induction change from the measurement electronics which is the inductance-to-digital converter operating in single channel mode which ensures an adjustment of the frequency to maintain resonance in the sense of the inductance change. Khalid et al. [
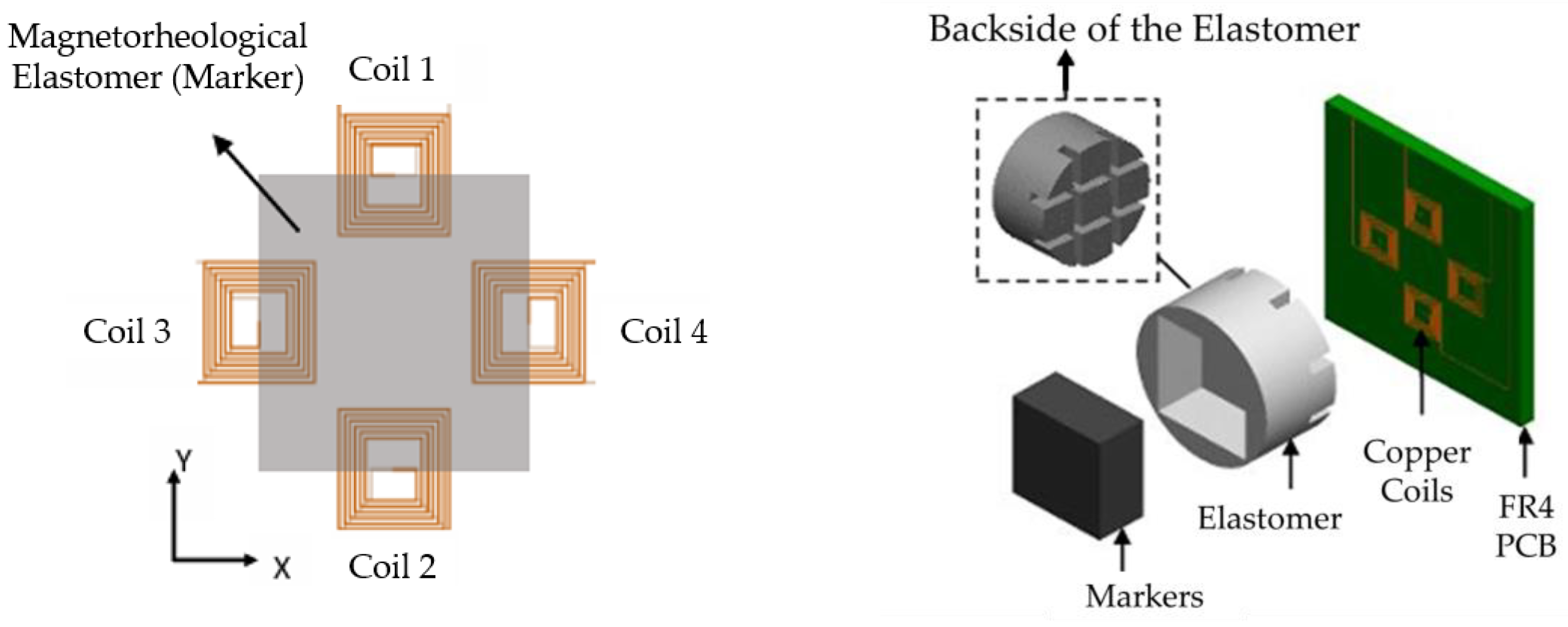
88] proposed a three-axis inductive tactile sensor using MRE which is applicable to the surgical robotic systems.
Figure 15 presents the schematic configuration of the sensor and working principle. The sensor consists of copper coils on a printed circuit board and patterned elastomer layer between the marker and coils where the marker is the mixture of a material with high magnetic permeability and elastomer. The markers and coils are separated by a layer of the elastomer such that there is an initial gap between the coils and markers. When a force is applied on the sensor’s surface, the marker displaces from the initial position changing either the overlap area between the marker and the coils or the distance between them. This change in the position of the marker causes a change in the resonance frequency of the LC circuit through which the inductance is calculated. Therefore, the applied force can be estimated by measuring the change of the inductance values. It is noted that the direction of the applied force can be also identified by configuring the positions of the coils. Tasin et al. [
89] made a new type of MRE to enhance both storage modulus, magnetostriction magnitude and reaction (normal) force to investigate a potential application of the proposed MRE as sensors or sensing devices. The proposed MRE samples consist of the polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) silicone rubber and high CIPs which have average diameter of 5
um with a spherical shape to have specific characterizations including high saturation magnetization, high permeability, high normal force and low remanent magnetization. It has been shown that the target specifications are achieved from experimental measurement and noted that force sensors and pressure sensors could be devised based on the results presented in this work since moderate stiffness (or midrange modulus) could ensure high durability of the sensors while maintaining sufficient magnetostriction magnitude. Costi et al. [
90] presented the first case of a 3D printable self-sensing MRE and cyclic mechanical compression and tensile mode analysis at high deformation up to 20%. The fabricated MRE samples containing the styrene-based thermoplastic elastomer (TPS) and carbon black (CB) fillers and hence have two properties of MR effect and piezoresistive effect providing a self-sensing capability. It has been shown that several properties including the magneto-resistive, magneto-strictive and hall effects could be achievable by selecting optimal ratios between the CIP concentrations and amount of the fillers as a function of the magnetic field. Therefore, various types of the self-sensing devices which have diverse shapes can be simply made from the 3D printing technology.
Recently, a magneto-sensitive viscoelastic polymer consisting of low cross-link polyurethane (PU) and magnetic particles, called magnetorheological plastomer (MRP) is actively studied in the sense of the development of enhanced MRP itself and various applications, especially sensor application. Xu et al. [
91] experimentally investigated the flow motions operated under the squeeze flow mode of MRP including elastic deformation region, stress relaxation region and plastic flow region. It was found from this work that the field-dependent compressive and tensile yield stress yield stress are sensitive to the magnetic field which provides a possibility of the sensor fabrication of the proposed MRP consisted of the CIP and plastic polyurethane matrix. Xuan et al. [
92] surveyed the state-of-art on the science and technology level of the MRPs. Several different types of MRPs were introduced and their field-dependent characteristics were discussed in the sense of the application as sensors. The types of MRPs are classified by the mixing materials (matrix): silica gel, polymer gel, hydrogel, cross-linked polyurethane, triblock copolymer polystyrene, and petroleum jelly. In addition, several properties of MRPs such as deformable shape, field-dependent conductivity and MR effect depending on the magnetic field were discussed for various applications as actuators or sensors. Xu et al. [
93] proposed a new MRP whose resistance can be controllable and hence can be used as strain sensor. As a first step, carbon filler-doped MRP samples with the carbon micro-fibers, carbon nanotubes and their mixtures were made to observe both the ME effect and magnetic field dependent electrical property. It has been shown that the vibration range of the resistance is increased by increasing the oscillation amplitude and the period of the resistance is the half of the period of the strain showing possible application to multifunctional properties including sensors. Qi et al. [
94] developed a versatile MRP based on polycaprolactone (PCL) and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) which can have 3D printability, switchable mechanics, shape memory and self-healing properties. After characterization of the proposed MRP, several features which achievable features the proposed MRP such as static and dynamic viscoelasticity, shape memory property and self-healing property were presented and discussed. Hapipi et al. [
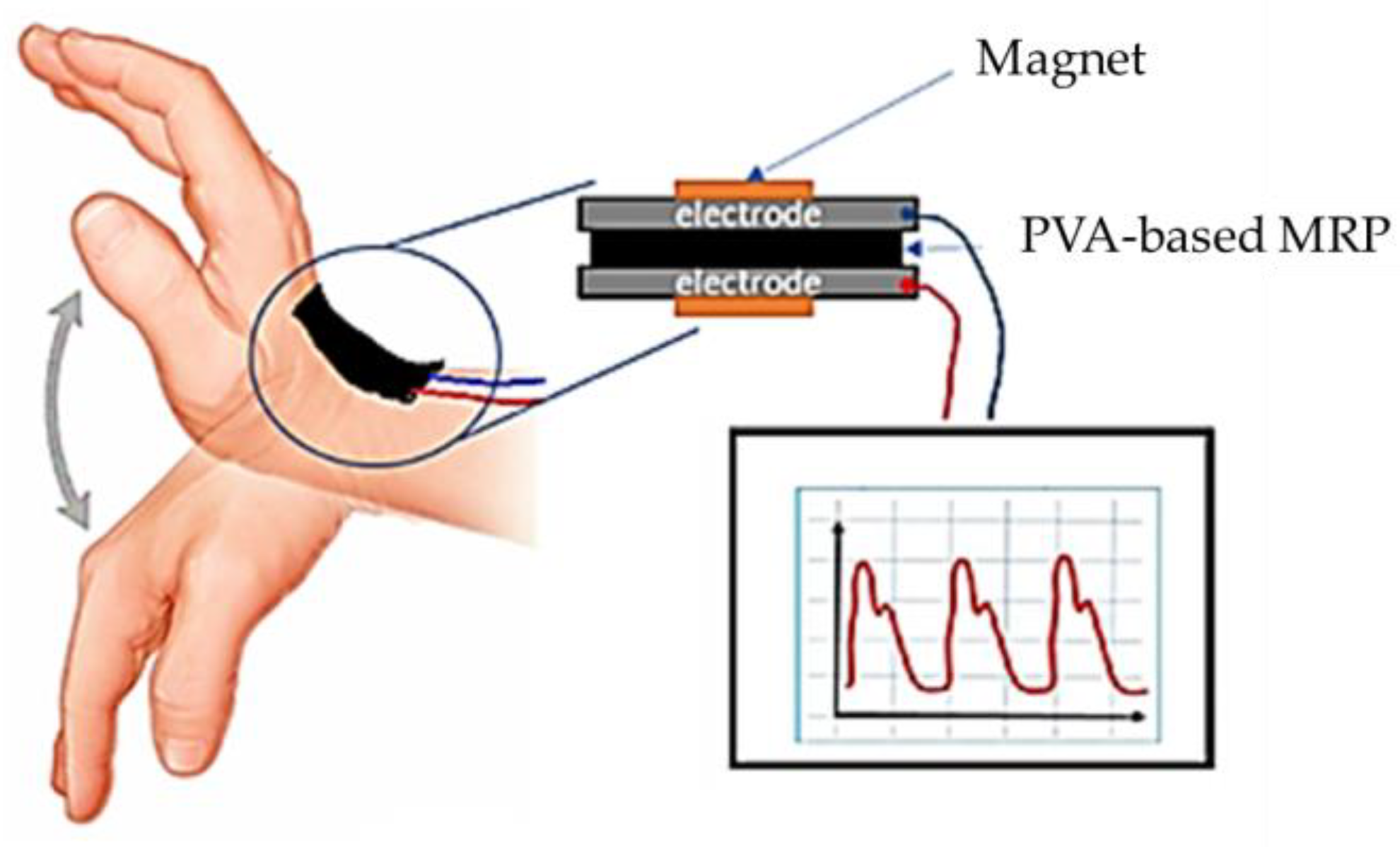
95] proposed a new type of MRP based on the polyvinyl alcohol (PVA-based MRP) which possesses the excellent MR effect which is a potential candidate of actuator. In addition, the proposed MRP produces a shear stiffening (ST) effect which is very beneficial in fabrication pressure strain sensor. The PVA-based MRP exhibits ST behavior, which is a common phenomenon in which the viscosity increases when the materials are exposed to external stress beyond their critical shear rate. Both excellent flexibility and conductivity are good properties to fabricate pressure strain sensors.
Figure 16 shows the schematic of the pressure or strain sensor to detect human wrist motions of bending and stretching utilizing the PVA-based MRP. Since MRP is flexible, it can be applicable to several soft systems where the pressure strain needs to be sensed as an output or a feedback signal in the closed loop control systems. Xu et al. [
96] proposed a flexible self-powered magnetism/pressure dual-mode sensor consisting of MR plastomer (MRP) in which the proposed pressure sensor is sensitive to a slight pressure (1.3 kPa) as well as responsive to a small magnetic field (12 mT). The working mechanism of this sensor is based on the displacement reaction of Fe and CuSO4, and the micro-scale carbonyl iron (CIP) in the MRP electrode aggregated into the chain-like structures resulting in the enhancement of the electrochemical activity of ions in the electrolyte of the electrode materials. Zaini [
97] used a graphite to fabricate MRP which has sensing capability owing to its flexibility, soft nature, responsiveness to external magnetic field and conductive electricity. The main goal of this work is to investigate the electrical properties of MRP such as conductivity required absolutely to use as a potential sensor. It has been found from experiment that the conductivity of 10 wt.% graphite is increases up to 178.06% which is the highest at the magnetic flux density of 400 mT. The wide change of the conductivity and the sensitivity of the proposed MRP depending upon the magnetic field intensity can contribute to the potential applications sensing detection devices. Hapipi et al. [
98] fabricated the polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) based MRP to enhance MR effect as well as shear stiffening (ST) effect by the magnetic field. After fabrication several samples by varying the solvent ratios of binary solvent mixture (dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to water, the field-dependent properties were tested. It has been identified that the MR and ST effects are dependent on the solvent ratios and hence appropriate actuators and sensors could be devised by adjusting both the field intensity and solvent ratios. Amlee et al. [
99] proposed a hydrogel based MRP (HMRP) with a certain amount of the graphite to use as a force sensor. In this work, HMRP with 0 wt.% up to 15 wt.% were prepared and tested under applied force ranging from 0 N to 5 N. It has been shown that the force can be measured from the resistance change of the HMRP with and without the magnetic field for practical feasibility in the medical area for physiology or therapy. Pang et al. [
100] fabricated a new type of MRPs using a series of hollow powder (HGP) to enhance impact resistance of the material and dynamic compressive properties under high strain rate. It has been shown that the magnetic-induced yield stress is increased from 7.3 MPa to 17. 1 MPa by adding 9 vol.% CIP. However, it was also found that this benefit could not be achieved when the mass ratio of HGP was larger than 0.67. This directly indicates that the volume fraction of the CIP and HGP is equivalently significant to obtain advanced properties of the proposed MRP so that it can be applicable to sensors and actuators.
5. Conclusion
In this review article, sensors or sensing devices using electrorheological fluids (ERFs) and magnetorheological materials (MRMs) classified into magnetorheological fluid (MRF), magnetorheological elastomer (MRE) and magnetorheological palstomer (MRP) have been surveyed and their measurement characteristics have been discussed in the sense of working principle and measurand as well as physical parameters. One of most popular sensors using the proposed smart materials is a force sensor which can be easily fabricated from a relationship between the input field (electrical voltage or magnetic field) and a simple electrical circuit representing the output resistive signals which can produce the force form the field-dependent stiffness and damping. Besides, strain sensor, displacement sensor and magnetic measurement device were also proposed by several researchers. In fact, there are several excellent properties of the proposed materials to make several different types of sensors which are physical parameters including stress, modulus, viscosity, stiffness and damping, are controlled as a function of the input field. This unique property can produce a great potential to devise many different sensors including accelerometer. However, so far there is no commercially available sensors or sensing devices made from these smart materials even though there are several actuators which are commercially available in the real market.
In order to bring the smart materials-based sensors to the real marketplace, more studies on the rating the sensors’ specifications should be carried out in future. The detailed specifications to satisfy sensors’ requirement include high accuracy, high precision, small resolution, long repeatability, high sensitivity, easy calibration, temperature compensation and optimized electrical circuits. An optimal fabrication of material itself which possesses a high adaptability to sensing devices instead of actuating mechanism is also crucial to achieve high performances of the sensors and sensing devices. It is suggested that one way to accomplish such sensors’ specifications, advanced materials adaptable to sensors should be developed using modern technologies, a neural network integrating artificial intelligence and a fuzzy algorithm associated with deep learning, to determine the principal ingredients of the smart materials such as volume of the particles, viscosity of the carrier liquids, proper additives and sensitive electrical circuits. Furthermore, the big data analysis may be required to achieve several relationships among important parameters for sensing devices of the input fields, output signals, signal convertors and calibration factors can be effectively utilized.