Submitted:
02 April 2024
Posted:
03 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Animals and Location
2.2. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
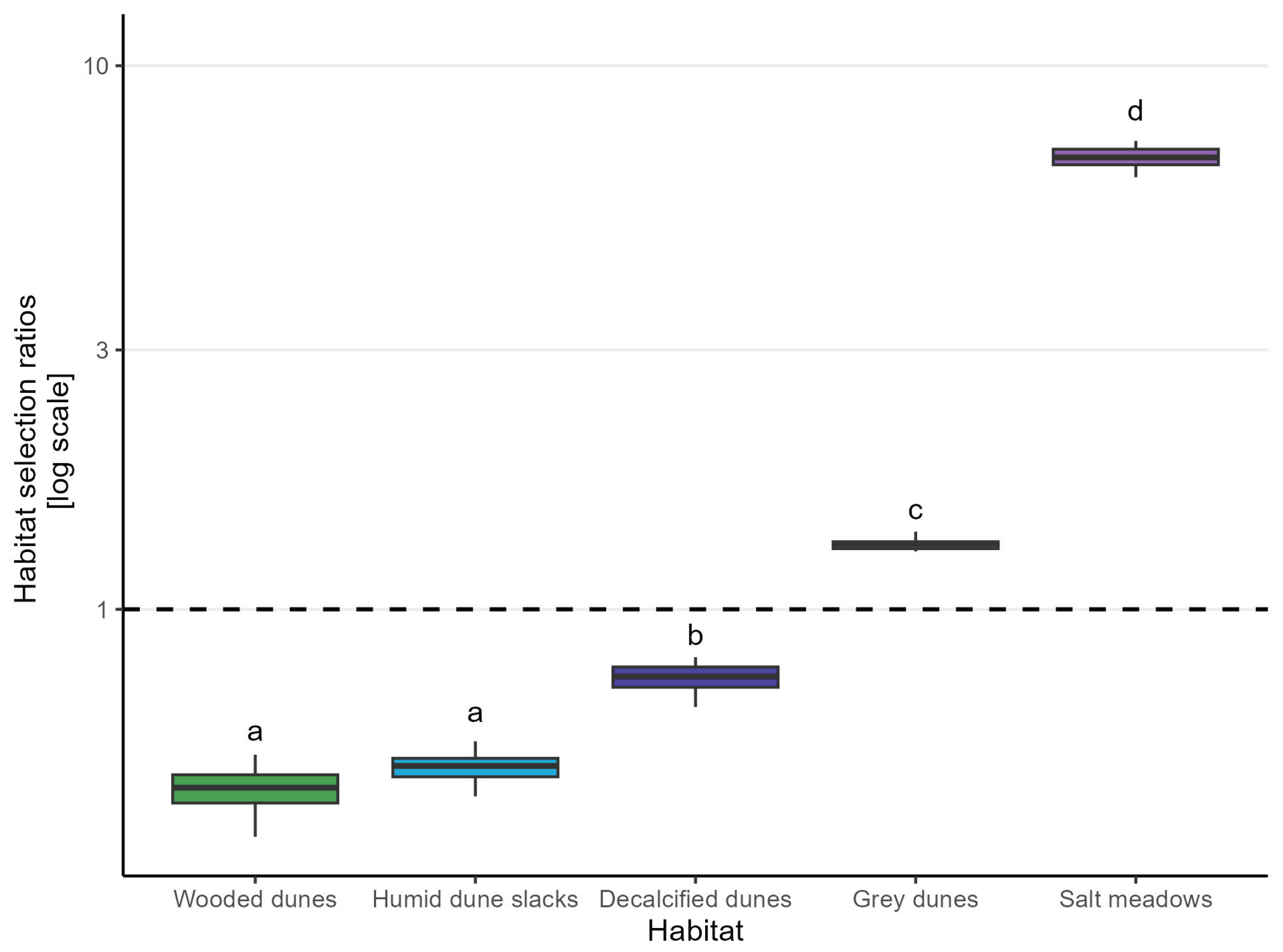
3.1. Habitat Preference
| Habitat | Median Selection Ratio | MAD |
|---|---|---|
| Salt Meadow | 6.78 | 0.36 |
| Grey dunes | 1.32 | 0.04 |
| Decalficied dunes | 0.75 | 0.05 |
| Humid dune slacks | 0.52 | 0.03 |
| Wooded dunes | 0.47 | 0.04 |
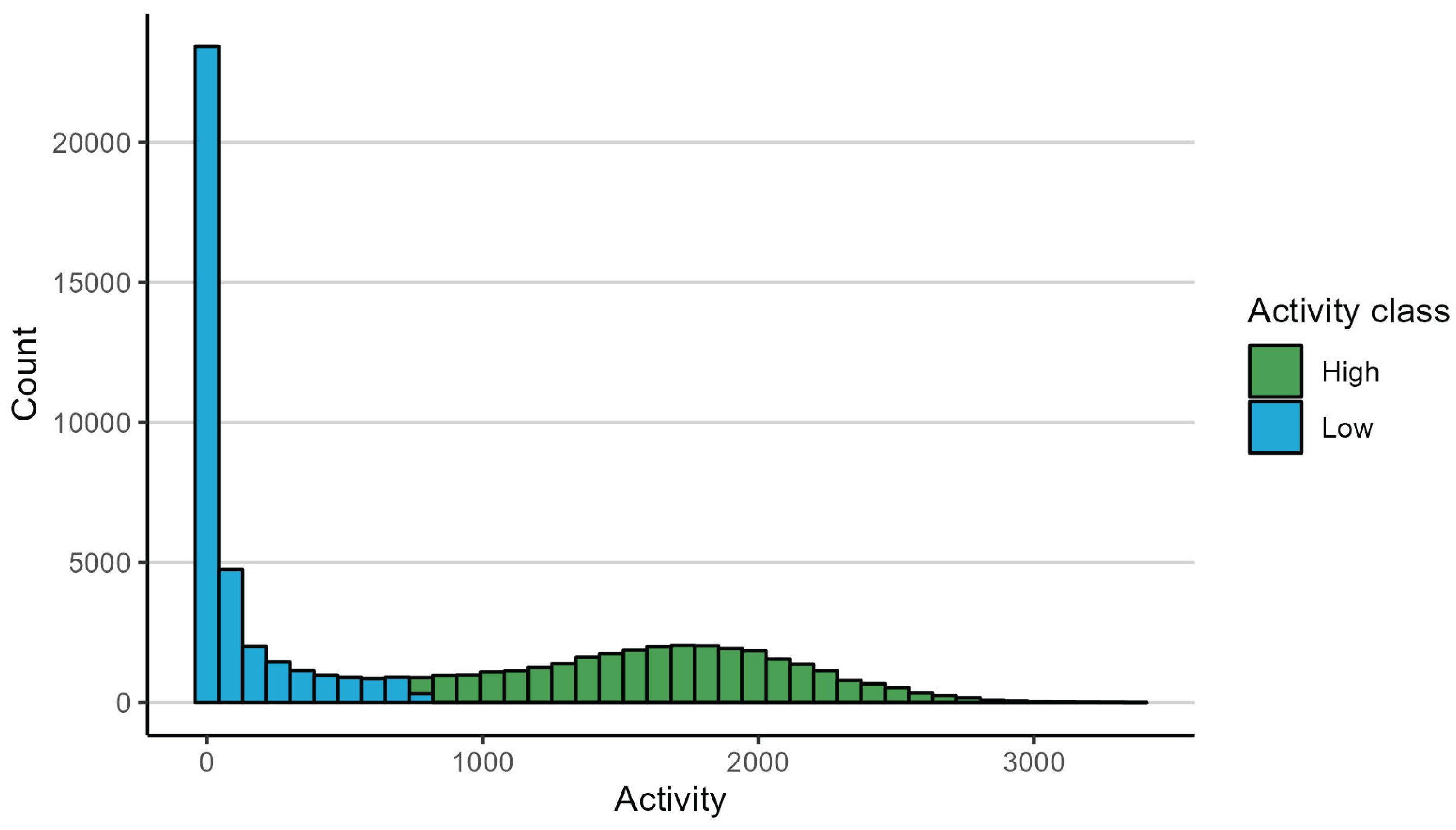
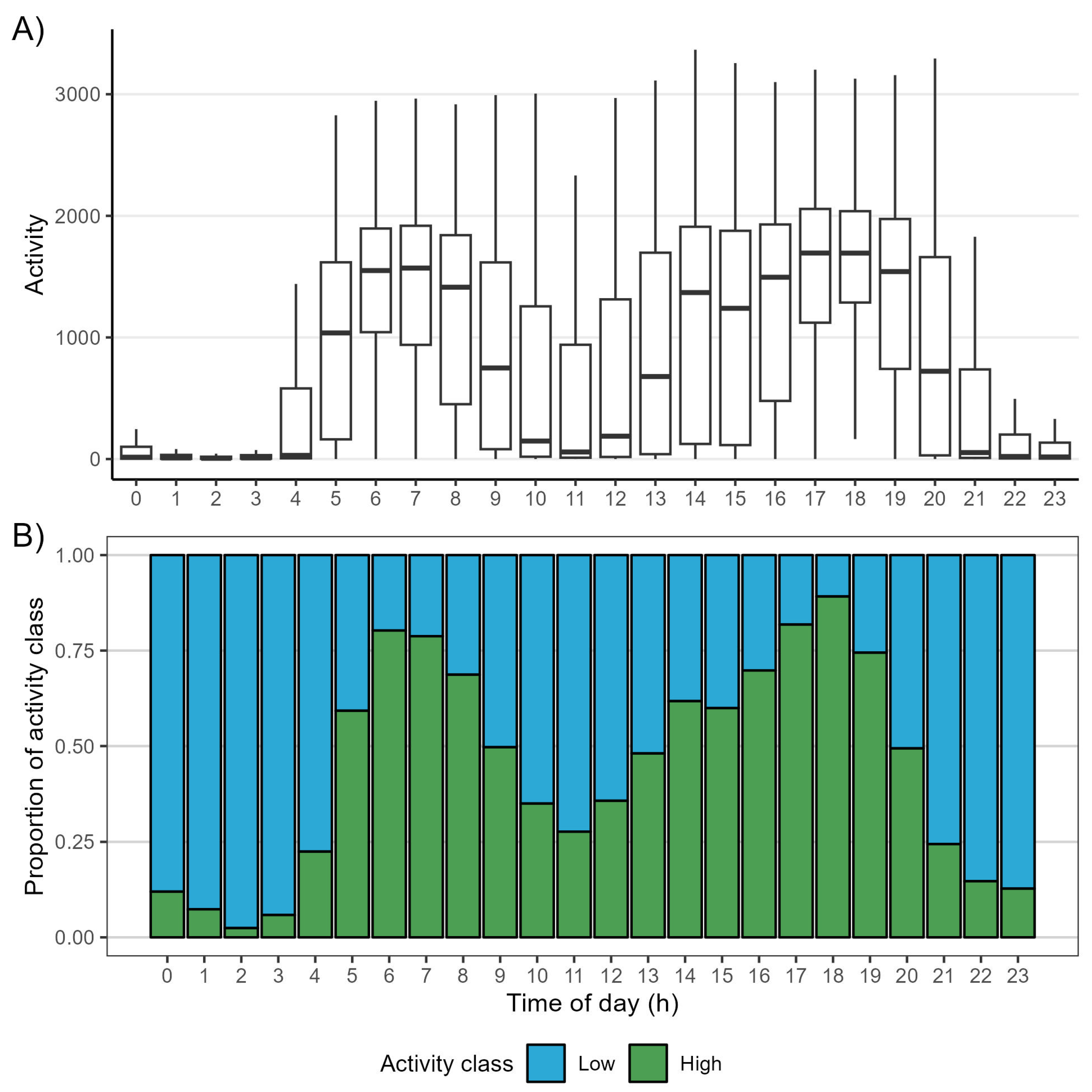
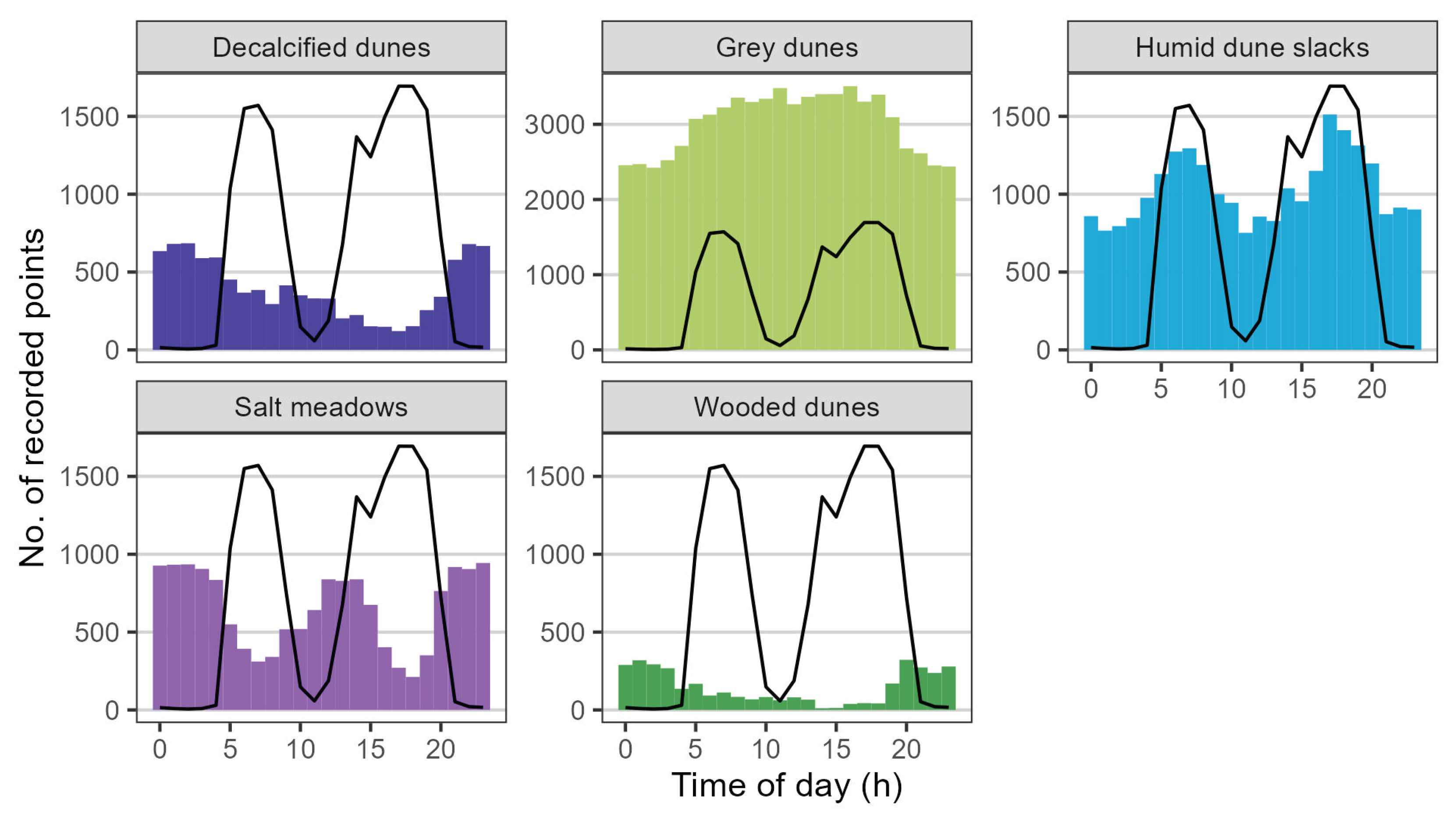
3.2. Daily Activity Patterns and Behaviour Classification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jachowski, D.S.; Slotow, R.; Millspaugh, J.J. Good virtual fences make good neighbors: opportunities for conservation. Animal Conservation 2014, 17, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlin, A.; Brunberg, E.; Hultgren, J.; Høgberg, N.; Rydberg, A.; Skarin, A. Animal welfare implications of digital tools for monitoring and management of cattle and sheep on pasture. Animals (Basel) 2021, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goliński, P.; Sobolewska, P.; Stefańska, B.; Golińska, B. Virtual Fencing Technology for Cattle Management in the Pasture Feeding System–A Review. Agriculture (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umstatter, C. The evolution of virtual fences: A review. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2011, 75, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretas, I.L.; Dubeux, J.C.B.; Cruz, P.J.R.; Queiroz, L.M.D.; Ruiz-Moreno, M.; Knight, C.; Flynn, S.; Ingram, S.; Pereira Neto, J.D.; Oduor, K.T.; et al. Monitoring the Effect of Weed Encroachment on Cattle Behavior in Grazing Systems Using GPS Tracking Collars. Animals (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, E.D.; Henkin, Z.; Gutman, M.; Dolev, A.; Genizi, A.; Ganskopp, D. Inference of Animal Activity From GPS Collar Data on Free-Ranging Cattle. Rangeland Ecology & Management 2005, 58, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovarelli, D.; Bacenetti, J.; Guarino, M. A review on dairy cattle farming: Is precision livestock farming the compromise for an environmental, economic and social sustainable production? Journal of Cleaner Production 2020, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaintrub, M.O.; Levit, H.; Chincarini, M.; Fusaro, I.; Giammarco, M.; Vignola, G. Review: Precision livestock farming, automats and new technologies: possible applications in extensive dairy sheep farming. Animal (Cambridge, England) 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanidakis, C.; Tzamaloukas, O.; Simitzis, P.; Panagakis, P. Precision Livestock Farming Applications (PLF) for Grazing Animals. Agriculture (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.L.M.; Lea, J.M.; Keshavarzi, H.; Lee, C. Virtual Fencing Is Comparable to Electric Tape Fencing for Cattle Behavior and Welfare. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, M.J.; Grau-Campanario, P.; Mullan, S.; Held, S.D.E.; Stokes, J.E.; Lee, M.R.F.; Cardenas, L.M. Factors Affecting Site Use Preference of Grazing Cattle Studied from 2000 to 2020 through GPS Tracking: A Review. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, J.; Bork, E.W.; Blenis, P.V.; Alexander, M.J. Cattle habitat selection and associated habitat characteristics under free-range grazing within heterogeneous Montane rangelands of Alberta. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 2013, 146, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengeya, F.M.; Murwira, A.; De Garine-Wichatitsky, M. Seasonal habitat selection and space use by a semi-free range herbivore in a heterogeneous savanna landscape: Habitat selection and space use. Austral Ecology 2014, 39, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roever, C.; DelCurto, T.; Rowland, M.; Vavra, M.; Wisdom, M. Cattle grazing in semiarid forestlands: Habitat selection during periods of drought. Journal of Animal Science 2015, 93, 3212–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofastrud, M.; Devineau, O.; Zimmermann, B. Habitat selection of free-ranging cattle in productive coniferous forests of south-eastern Norway. Forest Ecology and Management 2019, 437, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, M.; Vallin, H.; Roberts, B. Animal board invited review: Grassland-based livestock farming and biodiversity. Animal (Cambridge, England) 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L. Biomasseproduktion på danske naturarealer. Technical report, Natur og Landbrug, 2012.
- Kaufmann, J.; Bork, E.W.; Alexander, M.J.; Blenis, P.V. Habitat selection by cattle in Foothill landscapes following variable harvest of aspen forest. Forest Ecology and Management 2013, 306, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versluijs, E.; Niccolai, L.J.; Spedener, M.; Zimmermann, B.; Hessle, A.; Tofastrud, M.; Devineau, O.; Evans, A.L. Classification of behaviors of free-ranging cattle using accelerometry signatures collected by virtual fence collars. Frontiers in Animal Science 2023, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes Marsiglio Sarout, B.; Waterhouse, A.; Duthie, C.A.; Candal Poli, C.H.E.; Haskell, M.J.; Berger, A.; Umstatter, C. Assessment of circadian rhythm of activity combined with random regression model as a novel approach to monitoring sheep in an extensive system. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 2018, 207, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.N.; Bernardes, P.A.; Romanzini, E.P.; Teobaldo, R.W.; Reis, R.A.; Munari, D.P.; Braga, L.G.; Brito, T.R. Strategy to predict high and low frequency behaviors using triaxial accelerometers in grazing of beef cattle. Animals (Basel) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogoy, K.M.C.; Chon, S.I.; Park, J.H.; Sivamani, S.; Lee, D.H.; Choi, S.H. High Precision Classification of Resting and Eating Behaviors of Cattle by Using a Collar-Fitted Triaxial Accelerometer Sensor. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiopoulos, J.; Fieberg, J.R.; Aarts, G. Species-Habitat Associations: Spatial data, predictive models, and ecological insights, 2nd Edition; University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Aaser, M.F.; Staahltoft, S.K.; Korsgaard, A.H.; Trige-Esbensen, A.; Alstrup, A.K.O.; Sonne, C.; Pertoldi, C.; Bruhn, D.; Frikke, J.; Linder, A.C. Is Virtual Fencing an Effective Way of Enclosing Cattle? Personality, Herd Behaviour and Welfare. Animals (Basel) 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, G. Comparison of the time budgets and circadian patterns of maintenance activities in sheep, cattle and horses grouped together. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 1984, 13, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenbaum, I.; Kigel, J.; Ungar, E.D.; Dolev, A.; Henkin, Z. Spatial and temporal activity of cattle grazing in Mediterranean oak woodland. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 2017, 187, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofastrud, M.; Hegnes, H.; Devineau, O.; Zimmermann, B. Activity patterns of free-ranging beef cattle in Norway. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica. Section A, Animal Science 2018, 68, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manly, B.; Mcdonald, L.; Thomas, D.; Mcdonald, T.; Erickson, W. Resource Selection by Animals: Statistical Design and Analysis for Field Studies; Vol. 63, 2002. [CrossRef]
- Northrup, J.M.; Vander Wal, E.; Bonar, M.; Fieberg, J.; Laforge, M.P.; Leclerc, M.; Prokopenko, C.M.; Gerber, B.D. Conceptual and methodological advances in habitat-selection modeling: guidelines for ecology and evolution. Ecological Applications 2022, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G.C.; Garrott, R.A. Analysis of wildlife radio-tracking data; Acedemic Press Limited: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calenge, C.; Dufour, A.B. Eigenanalysis of selection ratios from animal radio-tracking data. Ecology (Durham) 2006, 87, 2349–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QGIS. QGIS desktop 3.26, 2023. http://www.qgis.org/.
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023.
- Sickel, H.; Ihse, M.; Norderhaug, A.; Sickel, M.A. How to monitor semi-natural key habitats in relation to grazing preferences of cattle in mountain summer farming areas: An aerial photo and GPS method study. Landscape and Urban Planning 2004, 67, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessle, A.; Rutter, M.; Wallin, K. Effect of breed, season and pasture moisture gradient on foraging behaviour in cattle on semi-natural grasslands. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 2008, 111, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putfarken, D.; Dengler, J.; Lehmann, S.; Härdtle, W. Site use of grazing cattle and sheep in a large-scale pasture landscape: A GPS/GIS assessment. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 2008, 111, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Tsunekawa, A.; Tsubo, M.; Peng, F.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Lian, J. Seasonal dynamics of cattle grazing behaviors on contrasting landforms of a fenced ranch in northern China. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauler, C.M.; Isselstein, J.; Suter, M.; Berard, J.; Braunbeck, T.; Schneider, M.K.; Stevens, C. Choosy grazers: Influence of plant traits on forage selection by three cattle breeds. Functional Ecology 2020, 34, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, B.; Homburger, H.; Edwards, P.J.; Schneider, M.K. Phosphorus redistribution by dairy cattle on a heterogeneous subalpine pasture, quantified using GPS tracking. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2018, 257, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, B.; Ejrnæs, R.; Fredshavn, J. Kortlægning af habitatnaturtyper 2019. Videnskabelig rapport nr. 419, NOVANA. Aarhus Universitet, DCE - Nationalt Center for Miljø og Energi, 2021.
- Buttenschøn, R. Græsning og høslæt i naturplejen. Technical report, Center for Skov, Landskab og Planlægning/Københavns Universitet, 2007.
- Sawalhah, M.N.; Cibils, A.F.; Maladi, A.; Cao, H.; Vanleeuwen, D.M.; Holechek, J.L.; Black Rubio, C.M.; Wesley, R.L.; Endecott, R.L.; Mulliniks, T.J.; et al. Forage and Weather Influence Day versus Nighttime Cow Behavior and Calf Weaning Weights on Rangeland. Rangeland Ecology & Management 2016, 69, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Anna, A.C.; da Costa, M.J.R.P.; Páscoa, A.G.; Silva, L.C.M.; Jung, J. Assessing land use by cattle in heterogeneous environments. Ciência Rural 2015, 45, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgour, R.J. In pursuit of "normal": A review of the behaviour of cattle at pasture. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 2012, 138, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.; Udal, M.; Larson, B.T.; Shearer, S. Monitoring cattle behavior and pasture use with GPS and GIS. Canadian Journal of Animal Science 2000, 80, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homburger, H.; Lüscher, A.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M.; Schneider, M.K. Patterns of livestock activity on heterogeneous subalpine pastures reveal distinct responses to spatial autocorrelation, environment and management. Movement Ecology 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganskopp, D. Manipulating cattle distribution with salt and water in large arid-land pastures: a GPS/GIS assessment. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 2001, 73, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
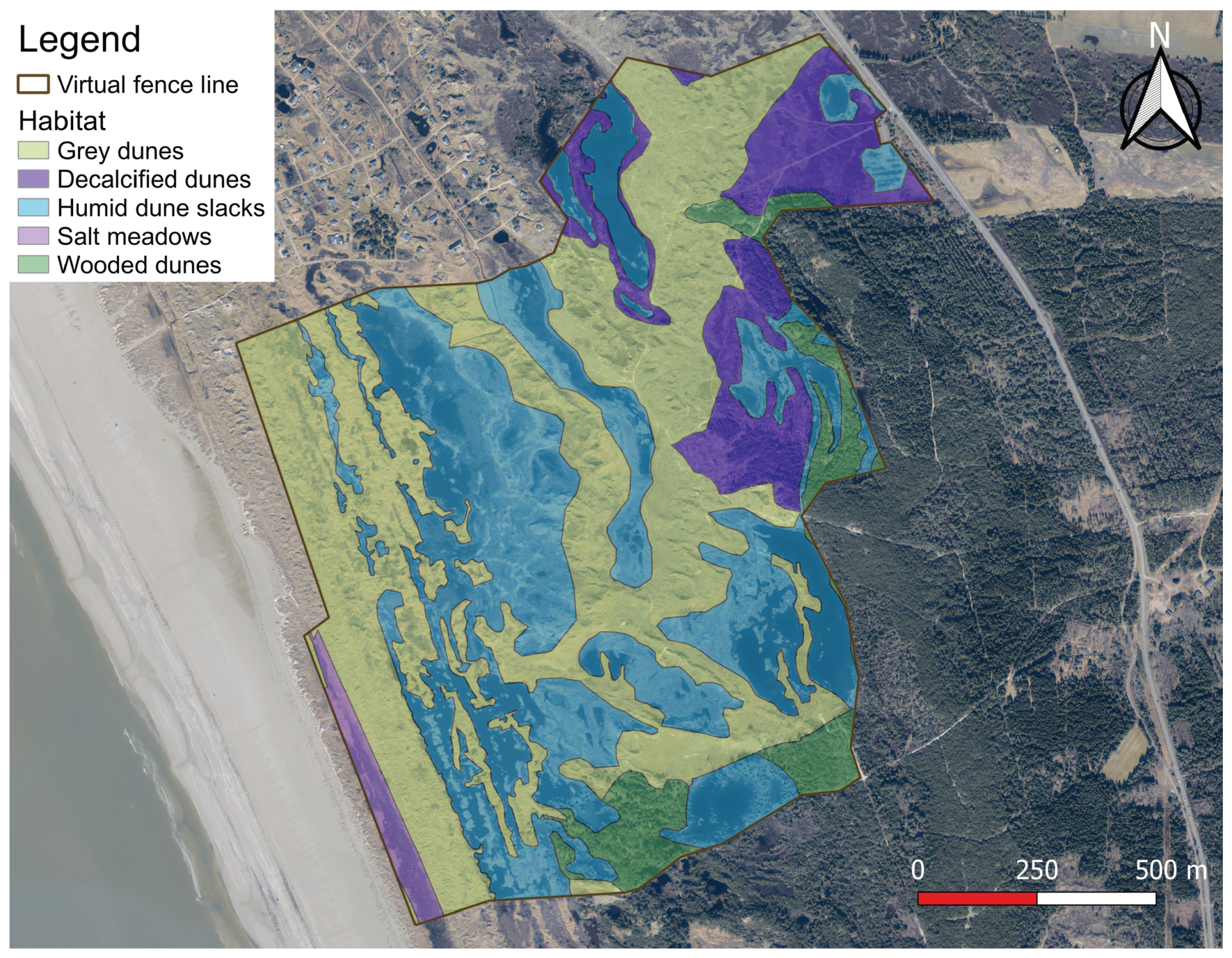
| Habitat | Characteristic species | Area (ha) | % of total area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salt meadow | Phragmites australis, Carex extensa, Carex distans, Plantago maritima, Triglochin maritima, Agrostis stolonifera | 2.9 | 1.8% |
| Wooded dunes | Pinus mugo, Pinus sylvestris, Pinus contorta, Picea sitchensis, Carex arenaria, Calluna vulgaris | 9.7 | 5.9% |
| Decalcified dunes | Calluna vulgaris, Empetrum nigrum, Carex arenaria, Avenella flexuosa, Polypodium vulgare | 16.6 | 10.2% |
| Humid dune slacks | Salix repens var. argentea, Equisetum fluviatile, Eriophorum angustifolium, Drosera intermedia, Gentiana pneumonanthe | 62.8 | 38.4% |
| Grey dunes | Ammophila arenaria, Corynephorus canescens, Carex arenaria, Calluna vulgaris, Festuca ovina, Jasione montana, Potentilla erecta, Cladina sp. | 71.5 | 43.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





