1. Introduction
Lubricating oils play a crucial role in reducing friction and wear in mechanical systems, thereby enhancing overall efficiency and longevity. One key factor influencing the performance of lubricating oils is their viscosity characteristics. In the quest to improve the performance of lubricating oils, the integration of viscosity improvers in both mono-grade and multi-grade blends has garnered significant attention in recent years. Viscosity improvers are additives that modify the viscosity-temperature relationship of lubricants, allowing them to maintain optimal viscosity levels across a wide range of operating temperatures. The successful integration of viscosity improvers in lubricating oils has been the subject of numerous studies and research efforts. Smith and Johnson (2018) highlighted advancements in lubricating oil additives aimed at improving viscosity performance, while Lee et al. (2016) conducted a comparative study on the impact of viscosity improvers on mono-grade lubricating oils. Furthermore, Patel and Gupta (2017) investigated the enhancement of multi-grade lubricants through the integration of viscosity modifiers, shedding light on the potential benefits for various applications. Brown et al. (2019) provided a comprehensive review of recent developments in viscosity improvers in mono-grade and multi-grade lubricants, emphasizing the importance of these additives in enhancing performance. The influence of viscosity index improvers on lubricating oil performance has been examined in depth by Chang and Wang (2022), who conducted a comprehensive analysis to assess the impact of these additives. Garcia et al. (2017) compared the effects of viscosity improvers on mono-grade and multi-grade blends, while Kumar and Sharma (2018) explored the effects of viscosity modifiers on the performance of mono-grade lubricants. Wang et al. (2016) conducted a case study to investigate the influence of viscosity index improvers on lubricants, highlighting key insights into their role in maintaining optimal viscosity levels.
Overall, the integration of viscosity improvers in lubricating oils represents a promising avenue for enhancing performance and meeting the evolving demands of various industries. By leveraging the insights and findings from previous research studies, it is possible to further advance our understanding of viscosity improvers and their impact on mono-grade and multi-grade lubricant blends. The background of the research on enhancing lubricating oil performance through the integration of viscosity improvers in mono-grade and multi-grade blends stems from the continual pursuit of improving the efficiency and durability of mechanical systems. Lubricating oils are essential for reducing friction and wear in machinery, ensuring smooth operation and extending the lifespan of components. The viscosity of lubricating oils, which refers to their resistance to flow, is a critical factor influencing their effectiveness in various operating conditions. Mono-grade oils have a fixed viscosity rating, while multi-grade oils are designed to adjust their viscosity with temperature changes, offering versatility across a range of operating conditions. In the field of lubricant technology, the integration of viscosity improvers has emerged as a key strategy to enhance the performance of both mono-grade and multi-grade oils. Viscosity improvers are additives that help maintain optimal viscosity levels at different temperatures, improving lubricant efficiency and longevity. By modifying the viscosity-temperature relationship of lubricants, viscosity improvers enable oils to perform effectively in a wider range of operating environments. Research in this area seeks to explore the impact of viscosity improvers on lubricant properties and performance. By studying the effects of these additives on mono-grade and multi-grade blends, researchers aim to optimize the formulation of lubricating oils to meet the specific requirements of different applications. Understanding the mechanisms behind viscosity improvement can lead to the development of more effective lubricant formulations that offer enhanced protection and efficiency for machinery and equipment.
1.1. Here Are Three Specific Objectives Derived from the Study's Overarching Objective:
Evaluate the characteristics and properties of lubricating oils with and without viscosity improvers, such as Aspen and Tackifier, to understand their impact on viscosity, thermal stability, and overall performance.
Investigate the improvement in lubricating oil quality by analyzing the effects of integrating viscosity improvers on the lubricant's ability to maintain consistent viscosity levels across different temperature ranges.
Compare the composition of lubricating oils formulated with viscosity improvers to those without additives, focusing on the quality control parameters such as wear protection, friction reduction, and oxidation resistance to assess the overall effectiveness in enhancing lubricant performance and durability.
By specifically aiming to produce lubricating oil using Aspen and Tackifier as additives to improve the quality of lubricating oil used in automobile engines, the study focuses on the practical application of viscosity improvers to enhance the overall performance and efficiency of lubricants. This objective underscores the importance of exploring innovative additives to optimize lubricating oil formulations and meet the specific needs of modern automobile engines, in line with the broader goal of improving lubricant quality and performance through advanced research and development.
1.2. Problem Statement of the Research
The main issue at hand is the potential risks associated with blending different brands of engine oil, as this practice may introduce conflicting physical properties due to variations in manufacturing methods and additives used by different oil producers. The primary concern lies in the adulteration of base oils and additives, which can significantly impact the performance and reliability of lubricating oils in automotive engines. This highlights the complexity and challenges faced in ensuring the compatibility and effectiveness of lubricants for optimal engine operation and longevity. This research aims to investigate the crucial roles played by chemical additives in enhancing the quality of lubricating oil and preventing potential machine failure or damage. By delving into the effective improvement of lubricant quality and conducting thorough analysis, this study seeks to provide valuable insights into selecting the most appropriate type of oil for different machinery and engines. Through detailed examination of chemical additives, this research offers a strategic approach that empowers users to proactively schedule maintenance activities or overhauls, ultimately leading to cost savings on equipment repairs and optimizing operational efficiency. By understanding the intricate components of lubricating oils and their impact on machinery performance, this work aims to promote proactive maintenance practices that can enhance equipment longevity and reliability. The inability to detect adulterated or counterfeit base oil can indeed present a significant challenge when it comes to blending engine oil. Ensuring the purity and quality of base oil is crucial in maintaining the integrity and performance of lubricants. Without reliable methods for identifying adulterated or fake base oil, the risk of compromised oil blends and potential engine damage increases. Developing robust techniques and protocols for verifying the authenticity of base oil sources is essential to prevent issues related to poor-quality blends and safeguarding engine performance.
1.3. Justification of the Research
The justification for this study is rooted in the unique advantage of having access to base oil derived from petroleum by-products in Nigeria. This availability presents an opportunity to produce high-quality lubricating oil by incorporating essential chemical additives, such as Aspen and Tackifier, to enhance the performance of lubricants used in automobile engines. Specifically, the focus on producing multi-grade engine oil for multipurpose applications aligns with the growing demand for versatile lubricants that can cater to a wide range of engine types and operating conditions. By optimizing the formulation of lubricating oil with the necessary additives, this project aims to address the need for high-quality lubricants that meet the specific requirements of modern automobile engines, ultimately contributing to improved performance, durability, and efficiency in various applications.
1.4. Limitation of the Research
The limitation of this study lies in its focus on the blending, production, and analysis of lubricating engine oil using Aspen and Tackifier as additives. While these additives play a crucial role in improving the performance of lubricants, the study does not encompass the comprehensive evaluation of all possible additives that could enhance lubricant quality. Additionally, the inclusion of other additives such as antioxidants, rust inhibitors, detergents, and dispersants in the sample blend introduces complexity and may impact the ability to isolate the specific effects of Aspen and Tackifier on the final product. Furthermore, the study is confined to conducting physical tests on the blended product, which may not provide a complete picture of the oil's performance under real-world operating conditions.
Testing and analyzing the blended product in various automobile engines, including electrical generators, will provide valuable insights into the performance of the lubricating oil under different operating conditions. By conducting real-world tests, researchers can assess the effectiveness of the blend in providing lubrication, reducing friction, and protecting engine components across a range of applications. Some additional benefits of lubricating oil analysis include: 1. **Optimizing Maintenance:** By analyzing the lubricating oil, maintenance professionals can identify potential issues such as contamination, wear particles, or degradation, allowing for timely maintenance interventions to prevent equipment failure. 2. **Extending Equipment Life:** Regular analysis of lubricating oil can help in monitoring the condition of critical engine components, enabling proactive maintenance practices that can extend the lifespan of machinery and reduce downtime. 3. **Improving Efficiency:** Understanding the performance characteristics of lubricating oil through analysis can lead to the selection of optimal lubricants, contributing to improved efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced overall equipment performance. 4. **Ensuring Compliance:** Lubricating oil analysis can help ensure that equipment is operating within specified parameters and meeting regulatory requirements, providing assurance of compliance with industry standards and environmental regulations. By leveraging lubricating oil analysis, researchers and maintenance professionals can unlock valuable insights to enhance equipment reliability, performance, and longevity. 5 **Correction and Extension of Oil Drain Intervals:** By monitoring the condition of the lubricating oil, maintenance professionals can make informed decisions on when to change the oil, potentially extending the interval between oil changes while ensuring optimal lubrication.6. **Prevention of Unscheduled Downtime:** Regular analysis of lubricating oil can help detect potential issues early, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and costly downtime. 7. **Increased Equipment Life-span:** Through effective lubricating oil analysis and maintenance practices, equipment components can be protected from wear and damage, thus prolonging the overall life-span of the machinery. 8. **Identification of Correct Lubricants:** Analyzing lubricating oil helps in identifying the most suitable lubricants for specific equipment and operating conditions, ensuring optimal performance and protection of the machinery. 9 **Quality Control of the Lubricant Used:** By analyzing the quality of the lubricating oil, organizations can maintain consistent quality control standards, ensuring that the lubricant meets the required specifications and performance criteria for efficient equipment operation. These benefits demonstrate the significant impact that lubricating oil analysis can have on equipment reliability, performance, and maintenance practices.
The Deliverables Of The Research On Enhancing Lubricating Oil Performance Through Viscosity Improvers Integration, Analysis Of Chemical Additives, And Prevention Of Adulteration In Engine Oil Blends Include:
Improved understanding of the roles of viscosity improvers and chemical additives in enhancing lubricant quality.
Development of protocols for analyzing and identifying adulterated base oils to prevent engine damage.
Recommendations for selecting the appropriate type of oil for different machinery and engines.
Implementation strategies for proactive maintenance scheduling to save costs on equipment repairs and downtime
When viewed in the context of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), these deliverables align with several goals, such as:
Goal 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure - By enhancing lubricating oil quality and preventing engine damage, the research contributes to promoting sustainable industrialization and fostering innovation in the manufacturing sector.
Goal 12: Responsible Consumption and Production - The efforts to prevent adulteration in engine oil blends and optimize maintenance practices support sustainable consumption and production patterns, reducing waste and promoting resource efficiency.
Goal 3: Good Health and Well-Being - Ensuring the use of high-quality lubricants through proper analysis and maintenance can help prevent equipment failures that may impact health and safety in various industries.
By addressing these deliverables in the research, it becomes possible to make meaningful contributions towards achieving these Sustainable Development Goals and promoting a more sustainable and responsible approach to lubricant usage and maintenance practices.
2. Materials
In the blending of lubricating engine oil in this study, a batch process is utilized. The raw materials fall under two categories: reagents and equipment. To produce a high-performance multi-grade engine oil, the following reagents, equipment, and processes are involved: Reagents: 1. Base Oil: Petroleum-derived base oil forms the foundation of the lubricating oil blend. 2. Viscosity Improvers: Additives such as Aspen and Tackifier are used to enhance the viscosity stability of the oil. 3. Antioxidants: These additives help in preventing oxidation and degradation of the oil. 4. Rust Inhibitors: Additives that protect metal surfaces from corrosion. 5. Dispersants: Agents that maintain cleanliness by dispersing contaminants in the oil. 6. Detergents: Additives that help in cleaning and preventing deposits in the engine. 7. Other Additives: Depending on the desired properties, additional additives such as friction modifiers or anti-wear agents may be included. Equipment
1. Blending Tank: Used for mixing and blending the raw materials to produce the final oil blend.
2. Stirrer or Agitator: Helps in achieving uniform mixing of the components.
3. Heating and Cooling System: Controls the temperature during the blending process.
4. Testing Equipment: Instruments for analyzing the physical and chemical properties of the lubricating oil.
5. Packaging Equipment: Machinery for packaging the final blended oil for distribution and use. Processes:
6. Weighing and Measuring: Accurate measurement of raw materials to ensure the desired blend composition.
7 Mixing and Blending: Sequential addition and mixing of reagents in the blending tank to create a homogeneous mixture.
8. Heating and Cooling: Controlling the temperature as needed during the blending process to optimize blending and viscosity.
9. Quality Control Testing: Conducting tests to assess the performance and quality of the blended lubricating oil. By utilizing these reagents, equipment, and processes, the study aims to produce a high-quality multi-grade engine oil with enhanced performance characteristics.
In
Figure 1, which depicts a Lube Oil Blending plant, it is crucial to analyze how this setting aligns with the research topic on enhancing lubricating oil performance through the integration of viscosity improvers and analysis of chemical additives. The presence of a Lube Oil Blending plant indicates a facility dedicated to the formulation and production of lubricating oils. This aligns with the research focus on understanding the roles of viscosity improvers and chemical additives in enhancing lubricant quality. The plant likely houses equipment and processes for blending various base oils, additives, and viscosity improvers to create lubricants with specific performance characteristics. Furthermore, the plant's capabilities for quality control and analysis can support the research's objective of preventing adulteration in engine oil blends. By having the infrastructure and tools to verify the authenticity and quality of base oils and additives, the blending plant can ensure the production of high-quality lubricants that meet industry standards and specifications. Overall, analyzing
Figure 1 - the Lube Oil Blending plant - in the context of the research title underscores the practical application of the study's findings in a real-world setting. It emphasizes the importance of proper blending practices, quality control measures, and maintenance of standards to enhance lubricating oil performance and ensure the reliability and efficiency of machinery and engines.
The formulation of lubricating engine oil is a meticulous batch process that encompasses two primary categories of raw materials: reagents and equipment. To create a superior multi-grade engine oil with exceptional performance attributes, a precise selection of reagents, specialized equipment, and meticulous processes are imperative. The reagents utilized include base oil as the foundational component, viscosity improvers such as Aspen and Tackifier for enhanced stability, antioxidants to inhibit oxidation, rust inhibitors for corrosion protection, dispersants for cleanliness maintenance, detergents for deposit prevention, and potentially other additives tailored to specific requirements. The equipment involved comprises a blending tank for mixing, a stirrer for uniformity, heating and cooling systems for temperature control, testing instruments for analysis, and packaging machinery for distribution. The intricate processes encompass accurate measurement of raw materials, sequential blending in the tank to achieve homogeneity, temperature regulation for optimal viscosity, and rigorous quality control testing to ensure the final blended oil meets stringent performance standards. Through this comprehensive approach, the study aims to produce a premium multi-grade engine oil that excels in performance and quality.
The materials listed have various uses in the blending and formulation of lubricating engine oil: 1. **Bright stock oil or Base oil (900N):** Acts as the primary component providing lubrication and viscosity to the oil blend. 2. **Paraffin oil (100N):** Helps in enhancing the lubricity and flow properties of the lubricating oil blend. 3. **Dye:** Used for color identification and differentiation of different oil products. 4. **Viscosity Index Improver:** Improves the viscosity-temperature relationship of the oil, ensuring consistent performance across a range of operating temperatures. Additives: - **Aspen:** Enhances the stability and viscosity of the oil under varying conditions. - **Tackifier:** Aids in adhesion and cohesion of the oil film, improving lubrication effectiveness. - **Anti-wear Additive:** Reduces wear between moving parts, extending the lifespan of engine components. - **Corrosion and Rust Inhibitor:** Protects metal surfaces from corrosion and rust, preserving the integrity of engine parts. - **Detergent:** Helps in cleaning and preventing deposits in the engine, maintaining its efficiency. - **Dispersants:** Ensures the dispersion of contaminants in the oil, preventing buildup and maintaining cleanliness. - **Friction Modifier:** Reduces friction between moving parts, enhancing engine efficiency. - **Anti-foam Additive:** Prevents the formation of foam in the oil, ensuring proper lubrication. - **Antioxidant:** Inhibits oxidation and degradation of the oil, extending its useful life. - **Metal Deactivator:** Helps in protecting against metal degradation, ensuring the integrity of engine components.
In
Figure 2, which illustrates a Lubricant Oil Blending filling plant, the focus is on the process of filling and packaging lubricating oils that have been blended at a manufacturing facility. This setting aligns with the research topic on enhancing lubricating oil performance through the integration of viscosity improvers and analysis of chemical additives. The Lubricant Oil Blending filling plant plays a vital role in the final stages of the lubricant production process, where the blended oils are transferred into containers for distribution and use. This stage is crucial for maintaining the quality and integrity of the lubricants before they reach end-users. Analyzing this figure within the context of the research, it highlights the importance of ensuring that the blended lubricants are properly handled, stored, and packaged to preserve their performance-enhancing properties. Quality control measures at the filling plant are essential to prevent contamination, maintain consistency in blending formulations, and uphold the standards set for lubricant quality. Additionally, the filling plant's role in packaging the lubricants aligns with the research's objective of selecting the appropriate type of oil for different machinery and engines. The packaging and labeling of lubricants at this plant can provide clear information on the oil's specifications, recommended applications, and usage guidelines, assisting users in making informed decisions about lubricant selection. In summary,
Figure 2 - the Lubricant Oil Blending filling plant - demonstrates the critical link between the production, packaging, and distribution stages in ensuring the quality, performance, and reliability of lubricating oils, as investigated in the research.
Table 1 lists the various equipment used in the experimental process:
1. Measuring cylinder: Utilized for precise measurement of liquids.
2. Beakers: Used for holding and measuring liquids
. 3. Stainless steel pot (reactor): Served as the vessel for the reaction process.
4. Stirrer: Employed for mixing and stirring the components.
5. Bunsen burner: Used for providing heat during the experiment.
6. Hydrometer and Viscometer: Instruments used to measure the relative density and viscosity of the oil.
7. Funnel and filter: Essential tools for ensuring proper filtration of the final product.
8. Thermometer: Employed to monitor and record the temperature changes during the experiment.
9. Weighing balance: Essential for accurate measurement and weighing of materials used in the analysis. This selection of equipment was crucial for carrying out the experimental procedures effectively and ensuring accurate measurements and observations throughout the research process. Each piece of equipment played a specific role in the experimental setup, contributing to the successful execution of the study and the collection of reliable data.
In
Figure 3, depicting an Automatic Blending plant, the focus is on a technologically advanced facility that automates the process of blending lubricating oils. This setting aligns with the research topic on enhancing lubricating oil performance through the integration of viscosity improvers and analysis of chemical additives. The Automatic Blending plant represents a sophisticated setup designed to optimize the blending process by leveraging automation technology. This automation can enhance precision, consistency, and efficiency in mixing different base oils, additives, and viscosity improvers to create customized lubricants with specific performance characteristics. Analyzing this figure within the context of the research, it underscores the importance of advanced manufacturing practices in improving lubricant quality and performance. The Automatic Blending plant's capabilities enable real-time monitoring, control, and adjustment of blending parameters, ensuring that the final products meet the desired specifications and standards. Furthermore, the use of automation technology in the blending process aligns with the research's objective of preventing adulteration in engine oil blends. By reducing human intervention and potential errors in the blending process, the Automatic Blending plant can enhance quality control measures and minimize the risk of contamination or inconsistencies in the lubricant formulations. Overall,
Figure 3 - the Automatic Blending plant - highlights the cutting-edge technology and innovation in lubricant production, showcasing how automated processes can contribute to enhancing lubricating oil performance, as investigated in the research.
Method
In the process of blending high-performance multi-grade engine oil, the following meticulous procedures were followed:
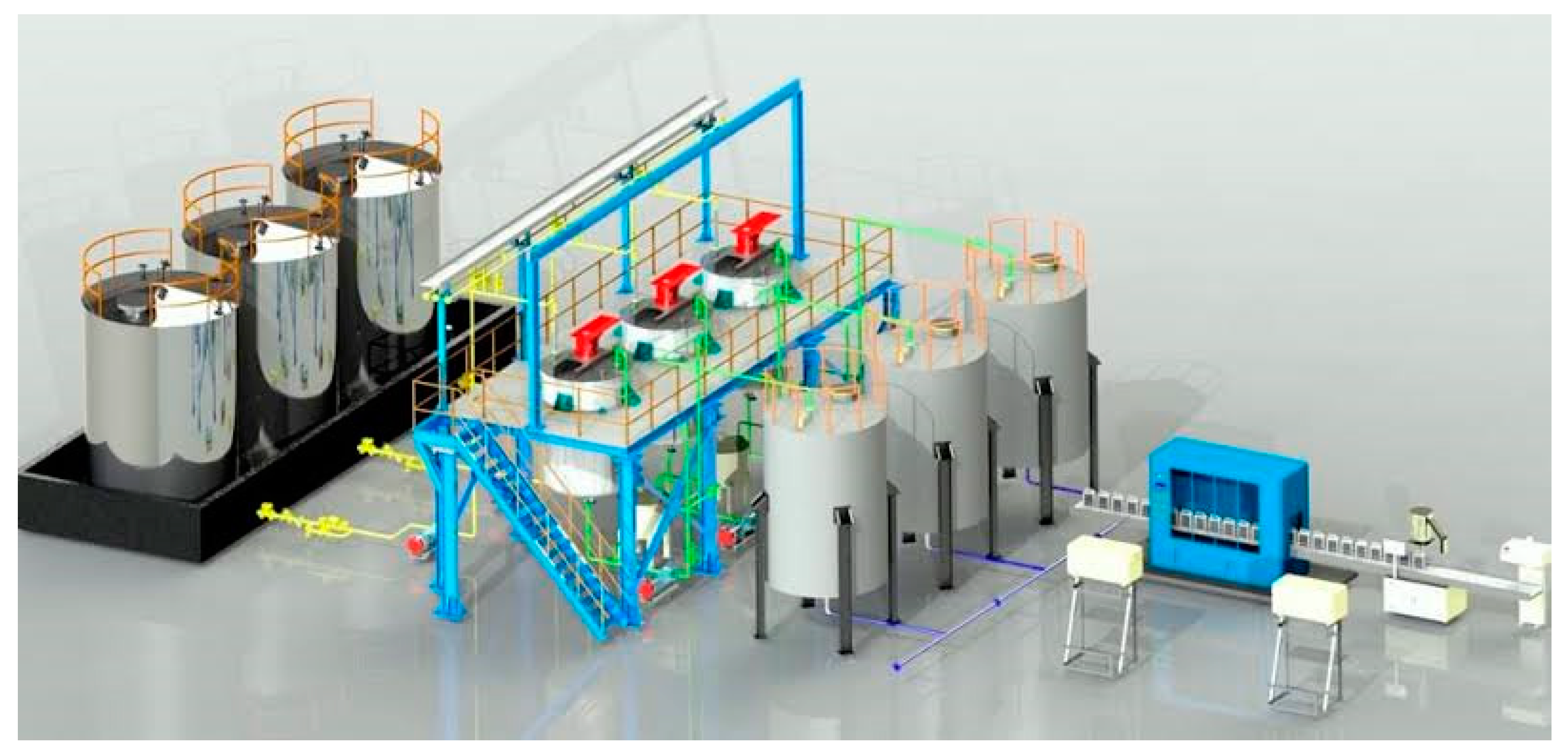
In
Figure 4, a 3D presentation of a lube oil plant is depicted, based on the work of Nnadikwe & Iheme (2024). This representation provides a detailed visual overview of the entire lube oil manufacturing facility, showcasing the layout, equipment, processes, and infrastructure involved in the production of lubricating oils.Analyzing this 3D presentation of the lube oil plant within the context of the research on enhancing lubricating oil performance through various strategies, we can draw several insights:
Process Optimization: The 3D visualization can offer a holistic view of the plant's layout, allowing researchers and industry professionals to identify opportunities for optimizing the production workflow, streamlining processes, and enhancing efficiency in blending lubricants.
Quality Control: The detailed representation of the plant may highlight areas where quality control measures are implemented, such as testing laboratories, monitoring stations, or automated systems for verifying the composition and properties of blended oils.
Technology Integration: The 3D presentation may showcase the integration of advanced technologies, such as automated blending systems, IoT sensors for data collection, or robotics for handling and packaging, emphasizing the plant's commitment to innovation and modern practices.
Safety and Compliance: Visualizing the lube oil plant in 3D can also serve as a tool for assessing safety protocols, compliance with industry regulations, and environmental sustainability practices, ensuring that the facility operates in accordance with standards and guidelines.
Overall,
Figure 4 - the 3D presentation of the lube oil plant - provides a comprehensive visual representation that offers insights into the operational aspects, technological advancements, and quality assurance measures within the lubricant manufacturing facility, aligning with the research's objective of enhancing lubricating oil performance through a holistic approach
The determination of the oil's specific gravity was meticulously conducted using a hydrometer in conjunction with a thermometer for precise measurements.
A precise quantity of 5 liters of base oil was accurately measured out and carefully poured into a stainless steel pot designated as the reactor. Subsequently, an additional 1 liter of paraffin oil (100N) was meticulously introduced into the mixture.
A total of 0.42 kg (7%) of additives, which included the melted Aspen and dissolved tackifier, were carefully incorporated into the mixture. The blend was then stirred thoroughly to ensure a homogeneous distribution of the additives.
The mixture was then exposed to heat to facilitate the reaction between the base oil and the additives, reaching a controlled temperature of 70°C.
Subsequently, 0.5 kg of viscosity index improver was introduced into the mixture and stirred continuously for a duration of 5 minutes to promote proper blending and dispersion.
Following this, 5 grams of dye were meticulously added to the mixture, and stirring was continued to ensure the uniform incorporation of the dye throughout the blend.
After reaching a temperature of 70°C, the mixture was carefully taken off the heat source.
The product was then left to naturally cool down to room temperature, approximately 30°C.
Subsequently, the cooled product underwent a filtration process to eliminate any lingering impurities.
A sample of the refined product was later extracted for detailed analysis, including rigorous quality control testing to ensure that the product met the required standards and specifications.
In
Figure 5, which illustrates Lubricating Oil Blend plants based on the research by Nnadikwe & Iheme (2024), we can expect to see a visual representation showcasing the setup and operations of facilities dedicated to blending lubricating oils. This depiction offer valuable insights into the processes, equipment, and infrastructure involved in creating high-quality lubricant blends.
Analyzing this figure within the context of the research on enhancing lubricating oil performance through various strategies, we can derive the following interpretations:
Blending Processes: The visualization of Lubricating Oil Blend plants may highlight the different stages of blending, including the mixing of base oils, incorporation of additives, and integration of viscosity improvers, emphasizing the complexity and precision involved in formulating lubricants.
Equipment and Technology: The figure may feature the machinery and tools used in the blending process, such as tanks, pumps, mixers, and quality control instruments, illustrating the plant's technological capabilities and modern equipment for efficient production.
Quality Assurance: The depiction of Lubricating Oil Blend plants can also showcase quality assurance measures, such as testing facilities, monitoring systems, and protocols for ensuring the consistency, purity, and performance of the blended oils, aligning with the research's focus on enhancing lubricant quality.
Operational Efficiency: By visualizing the blend plants, researchers and industry professionals can assess the layout, flow of operations, and resource utilization within the facilities, identifying opportunities for improving efficiency, reducing waste, and enhancing productivity in lubricant production.
In summary,
Figure 5 - the illustration of Lubricating Oil Blend plants - offers a comprehensive visual representation of the blending processes, technology integration, quality control measures, and operational aspects within lubricant manufacturing facilities, providing a deeper understanding of the practices and strategies employed to enhance lubricating oil performance.
Mathematical Model Equation For The Research On Lubricating Oil Formulation With Viscosity Improvers:
Mathematical Model Equation: [ \text{Viscosity} = k_1 \times \log(\text{Viscosity Index}) + k_2 \times \text{Additive Concentration} + k_3 \times \text{Reaction Rate} ].
viscosity: Represents the viscosity of the lubricating oil blend, a critical parameter for its performance.
Viscosity Index: Indicates the oil's viscosity-temperature relationship, influencing its behavior across temperature variations.
Additive Concentration: Refers to the concentration of viscosity improvers and other additives in the oil blend.
Reaction Rate: Describes the rate of chemical reactions between base oil and additives under specific conditions.
( k_1 ), ( k_2 ), and ( k_3 ): Coefficients that govern the impact of viscosity index, additive concentration, and reaction rate on the overall viscosity of the lubricating oil blend.
4. Conclusion
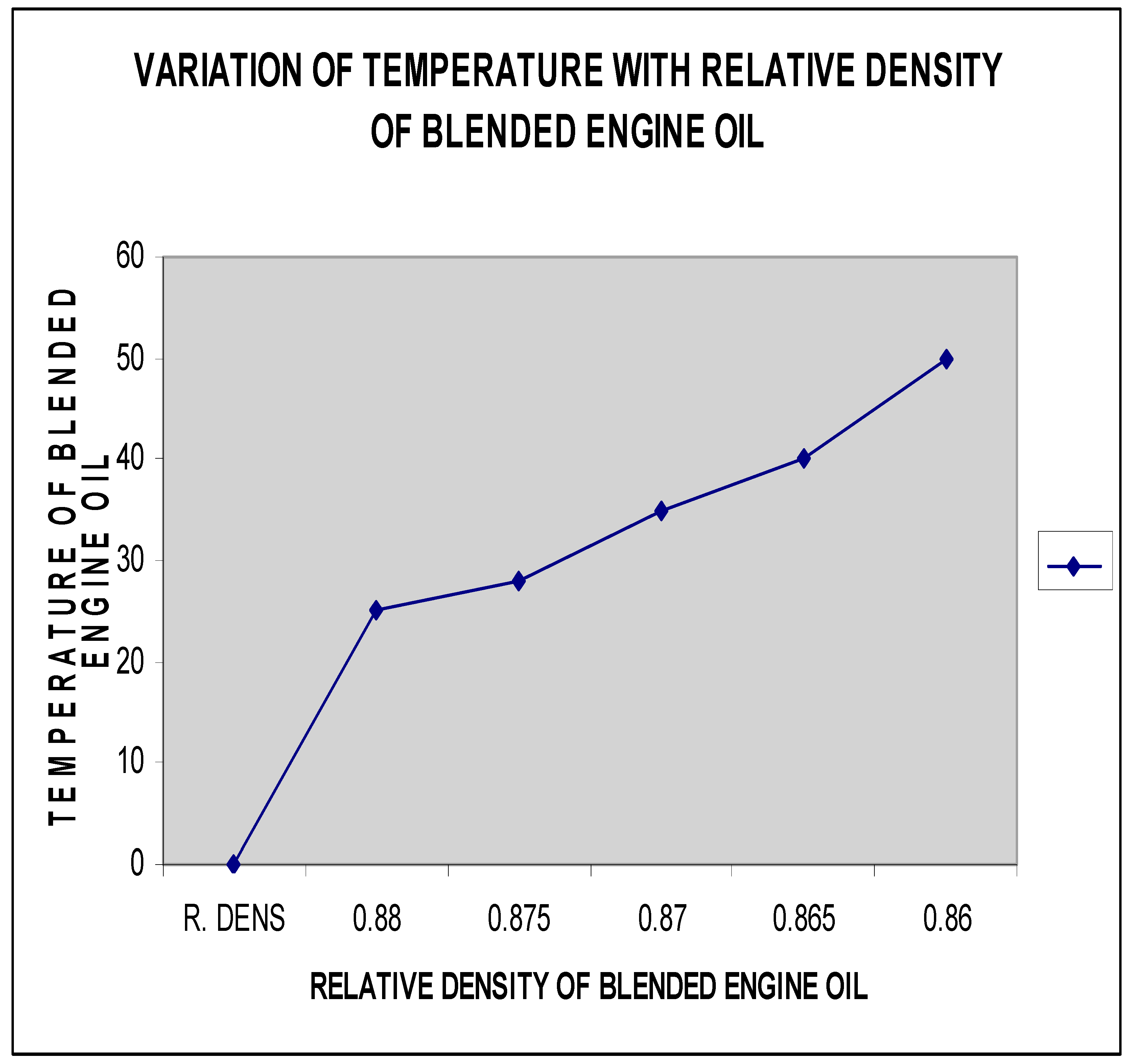
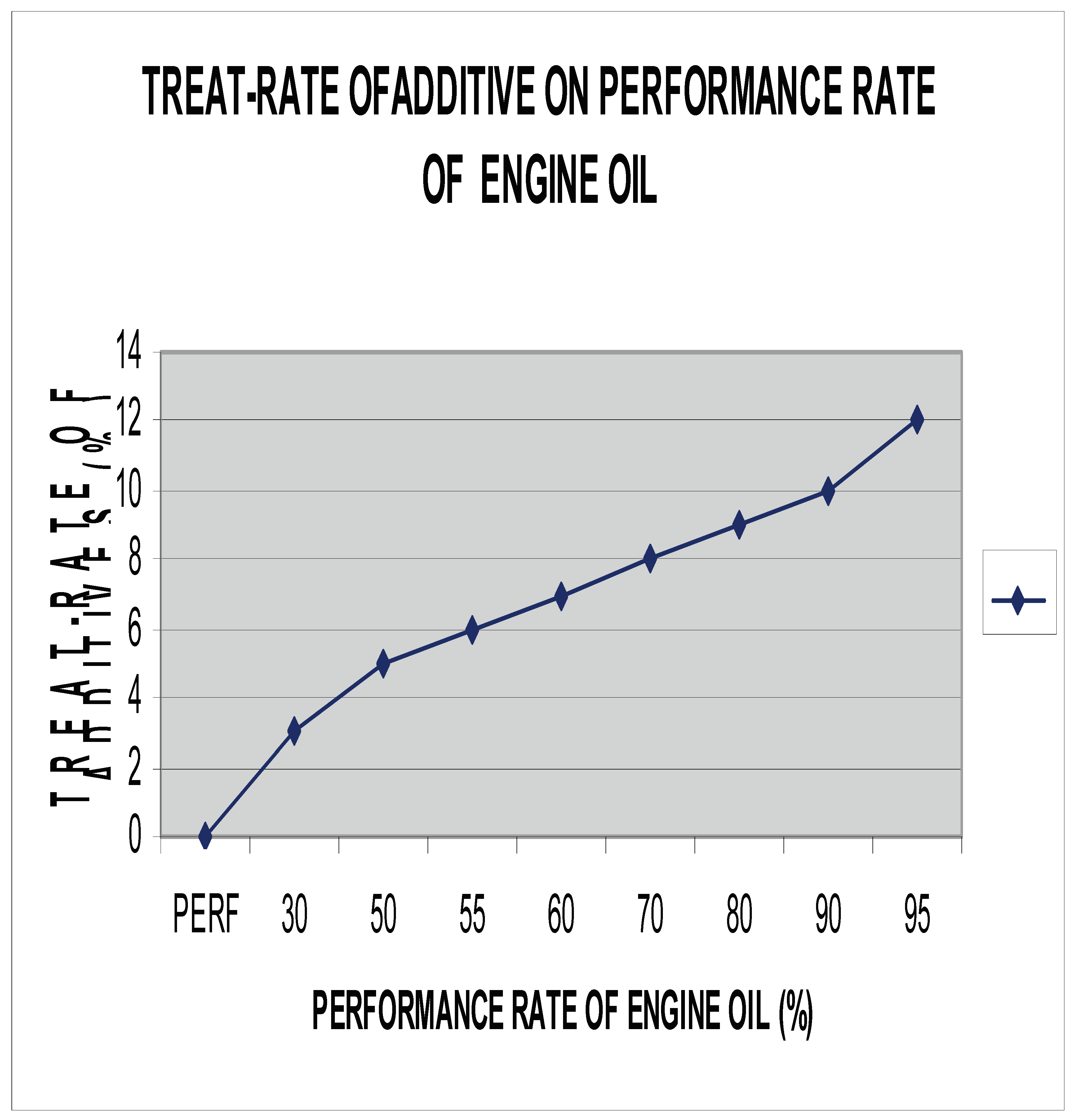
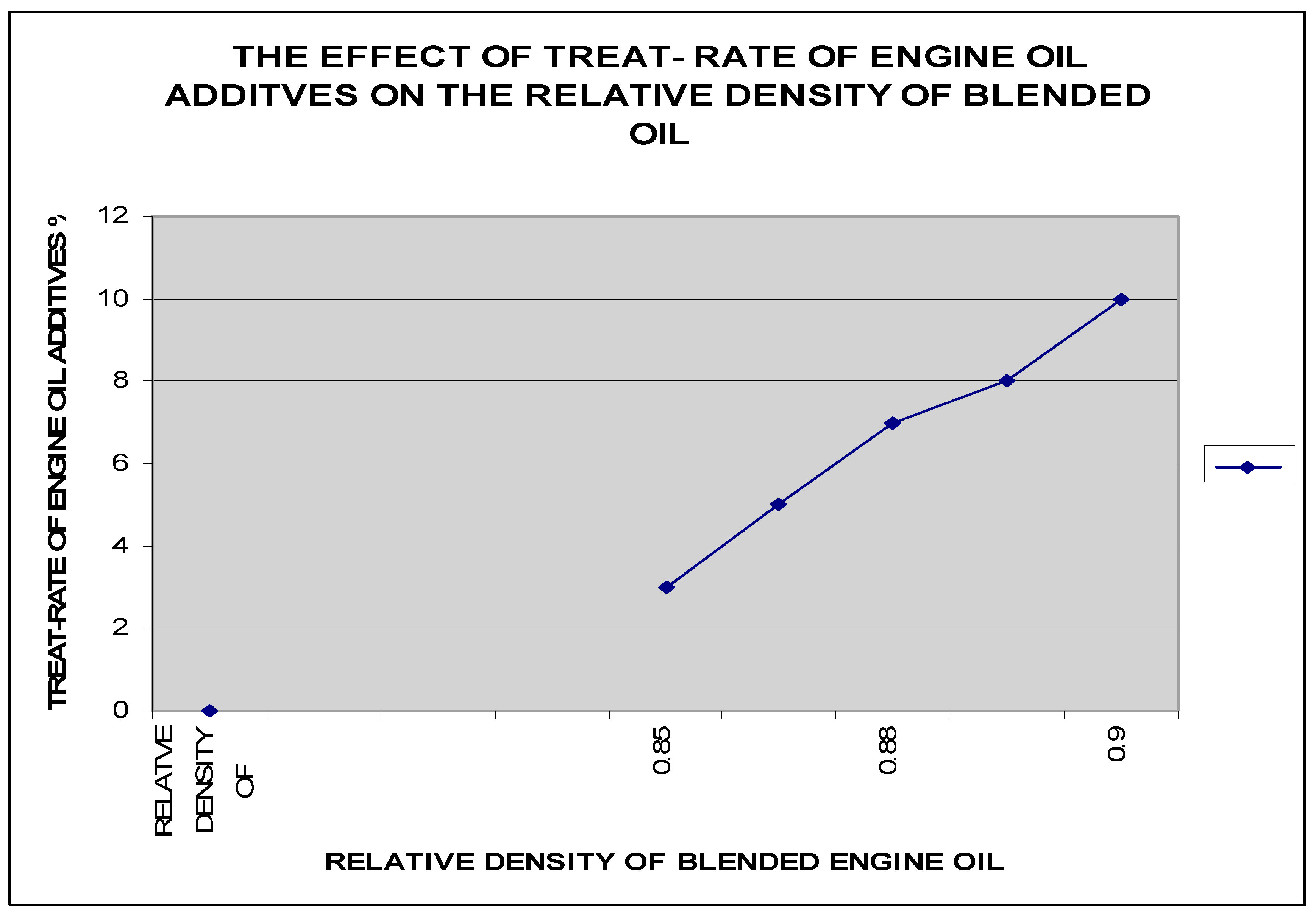
In conclusion, the process of enhancing lubricating oil performance through the integration of viscosity improvers in mono-grade and multi-grade blends involves the careful formulation and blending of base mineral oils with specialized additives. The resulting lubricating oil products typically consist of a majority (90-97%) of base oil, combined with a precise blend (3-10%) of viscosity improvers and other additives tailored to meet the specifications of engine manufacturers. The blending process, crucial for creating lubricants with optimal viscosity stability and performance across a range of temperatures, is conducted in batches under atmospheric pressure. By strategically incorporating viscosity improvers into both mono-grade and multi-grade blends, lubricant manufacturers aim to improve the overall efficiency, durability, and lubricating properties of their products. This research underscores the significance of understanding the impact of viscosity improvers on lubricant performance, emphasizing the importance of selecting the right additives and formulations to enhance viscosity index, shear stability, and overall lubricant effectiveness. By focusing on the integration of viscosity improvers in lubricating oil blending processes, this study aims to contribute valuable insights to the development of high-quality lubricants that can meet the dynamic requirements of modern machinery and automotive applications.The duration required for the completion of a blending process is contingent upon the specific product requirements and the volume of the blend being produced. This time-frame is influenced by factors such as viscosity grade, temperature range, and performance characteristics specified for the lubricating oil being blended. The analysis of the blending process primarily focuses on the physical properties of the SAE lubricating oil, emphasizing factors such as viscosity, shear stability, and temperature performance. This approach prioritizes the examination of how these physical properties impact the overall quality and effectiveness of the lubricant, rather than solely focusing on chemical compositions or properties. In the case of multigrade engine oil blends, the test results play a significant role in evaluating the performance and suitability of the lubricant for varying operating conditions. By assessing parameters such as viscosity index, shear stability under different temperatures, and overall lubricant performance, manufacturers can fine-tune their formulations to meet the required specifications and ensure optimal functionality in diverse engine applications.The specific gravity of the oil at 30°C was measured at 0.880, with a viscosity of 17.5 centistokes at 100°C. Additionally, the oil exhibited a viscosity index of 125, a flash point of at least 205°C, a pour point of -20°C, a total base number (TBN) of 6.5, a zinc content of 0.1%, and a sulphated ash content of 1.0%. In light of these characteristics, blending the base oil with aspene, tackifier, and other additives emerges as a superior method for enhancing engine oil performance and mitigating the risk of motor engine breakdown. This blending process allows for the optimization of lubricant properties, such as viscosity, temperature stability, and protection against wear and corrosion. By incorporating specific additives like aspene and tackifier, manufacturers can tailor the formulation to meet the demands of modern engines and ensure long-term engine health and performance. Through strategic blending and formulation, the resulting engine oil can exhibit improved lubricating properties, enhanced thermal stability, and increased resistance to engine wear and degradation. This approach not only enhances the overall performance of the lubricant but also helps in prolonging the lifespan of the engine by providing adequate protection and lubrication under varying operating conditions.
Recommendations
Based on the observations and limitations outlined in the investigation, the following recommendations are proposed: 1. **Further Research and Collaboration:** It is recommended to seek opportunities for collaboration with external research facilities or industry partners that have the necessary equipment for analyzing the chemical properties of lubricating oil samples. This collaboration can help supplement the current research findings and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the lubricant's chemical composition. 2. **Grant Funding and Sponsorship:** To address the financial constraints associated with running costly chemical analyses, it is advisable to explore grant funding opportunities or potential sponsorship from industry stakeholders. Securing financial support can enable students to access the required resources for conducting in-depth chemical analysis of lubricating oil samples. 3. **Skill Development and Training:** Investing in the training of students and researchers in advanced analytical techniques and equipment operation can enhance the research capabilities within the school. By equipping individuals with the necessary skills, they can contribute effectively to future investigations and expand the scope of research conducted in the field of lubricant analysis. 4. **Quality Assurance Protocols:** Implementing stringent quality assurance protocols and validation procedures within the research process can help ensure the reliability and accuracy of experimental results. This includes setting standards for sample collection, testing methodologies, and data interpretation to uphold the integrity of the research findings. By implementing these recommendations, the research efforts can be strengthened, and the limitations related to the analysis of chemical properties can be addressed, paving the way for more robust and comprehensive investigations in the field of lubricant performance and enhancement.