Submitted:
29 March 2024
Posted:
02 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. PLA/PCL Fiber Geometry
3.2. Thermal Characteristics of PLA/PCL Binary Fiber Composition
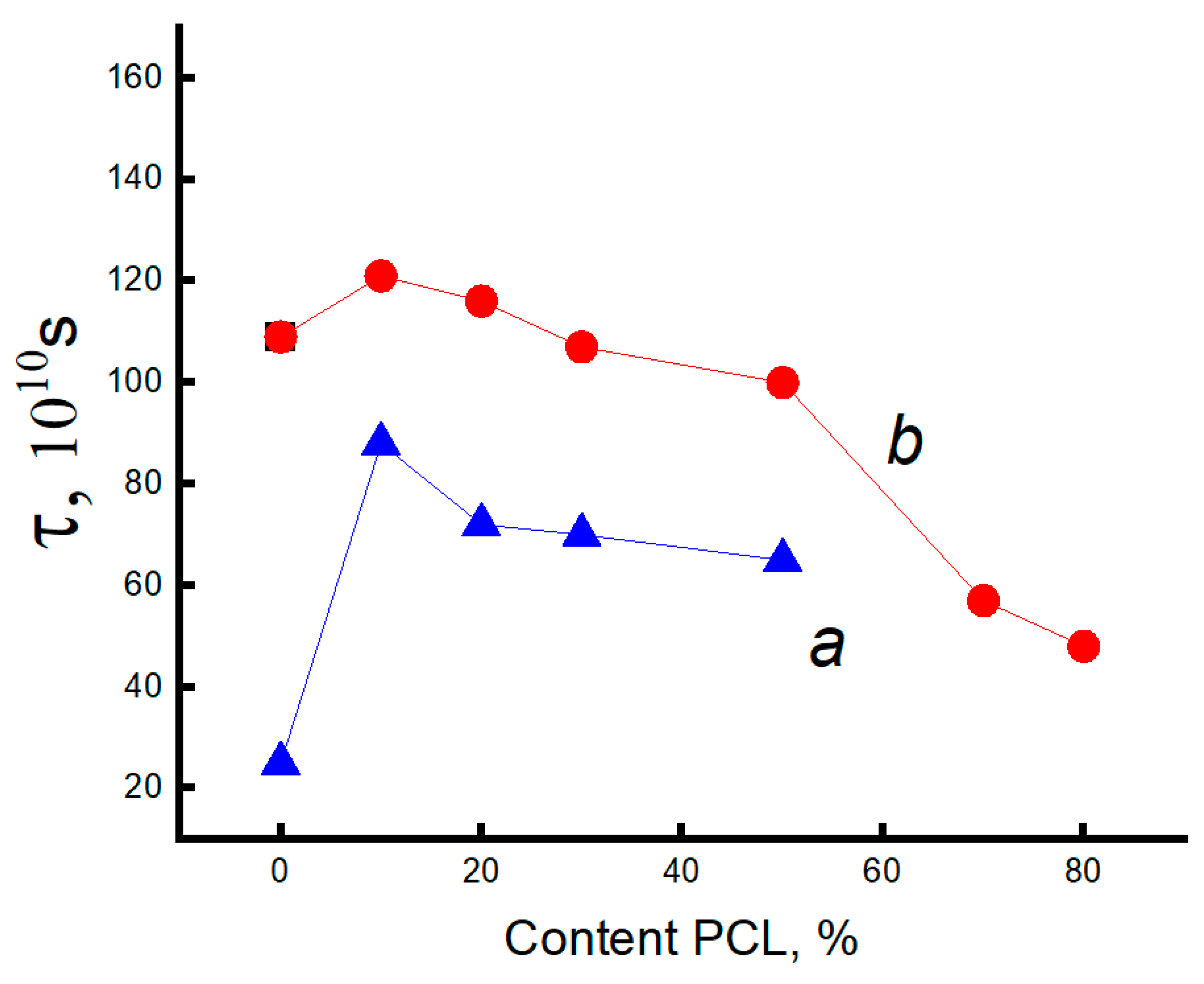
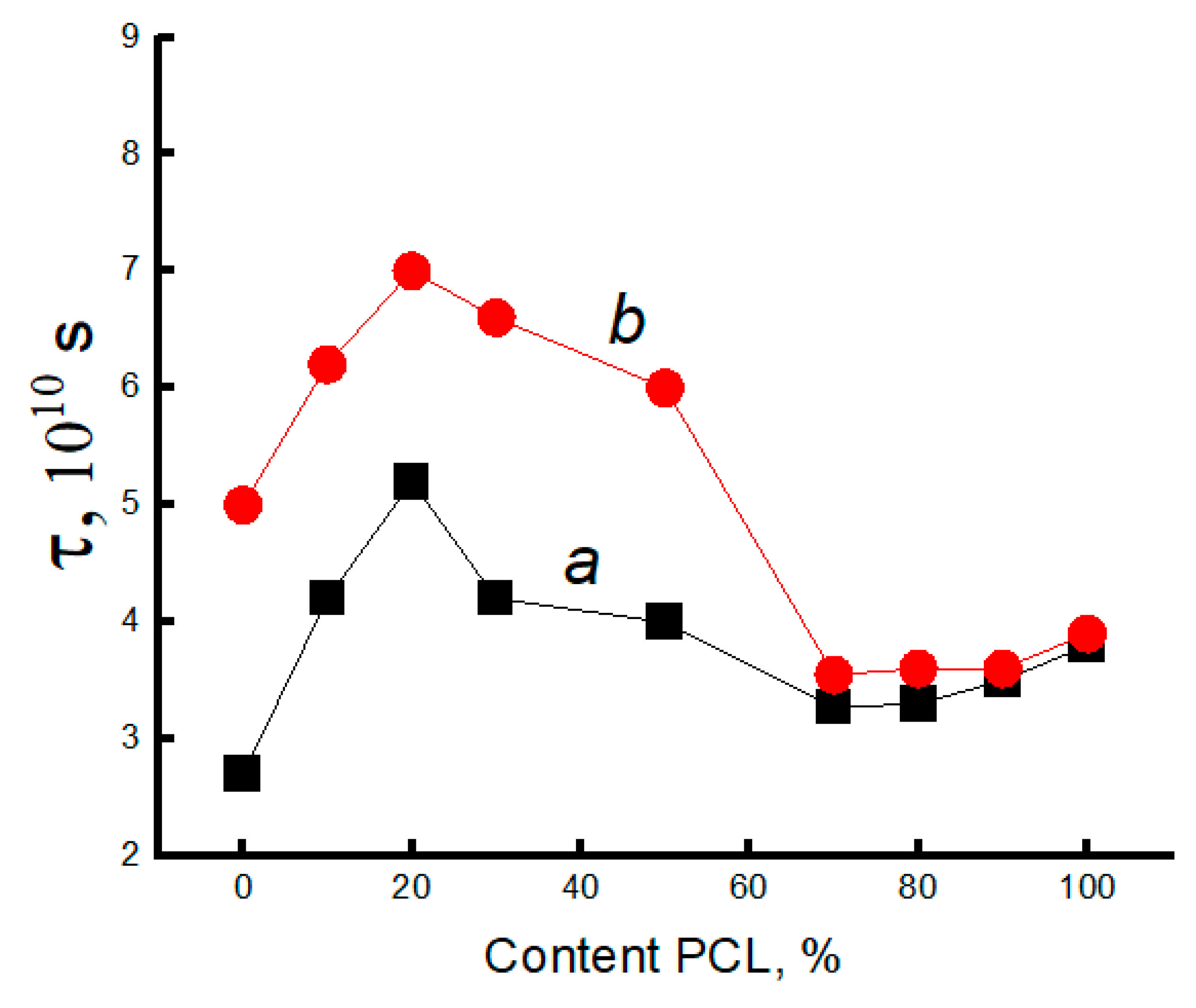
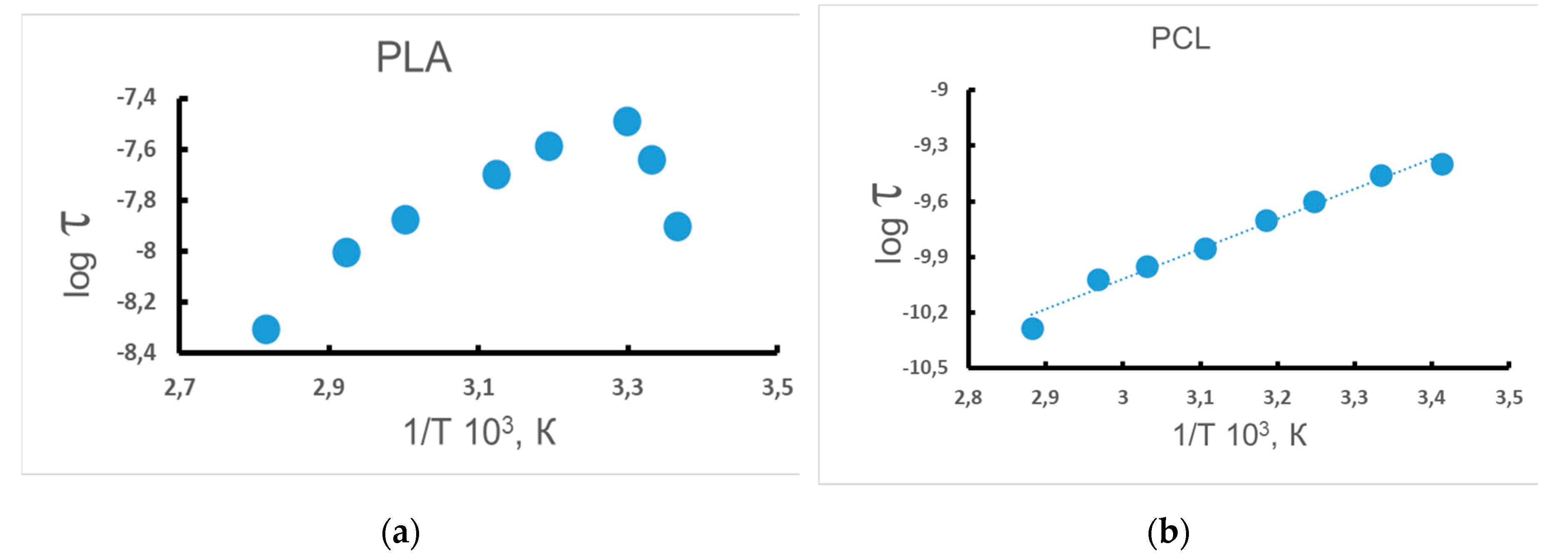
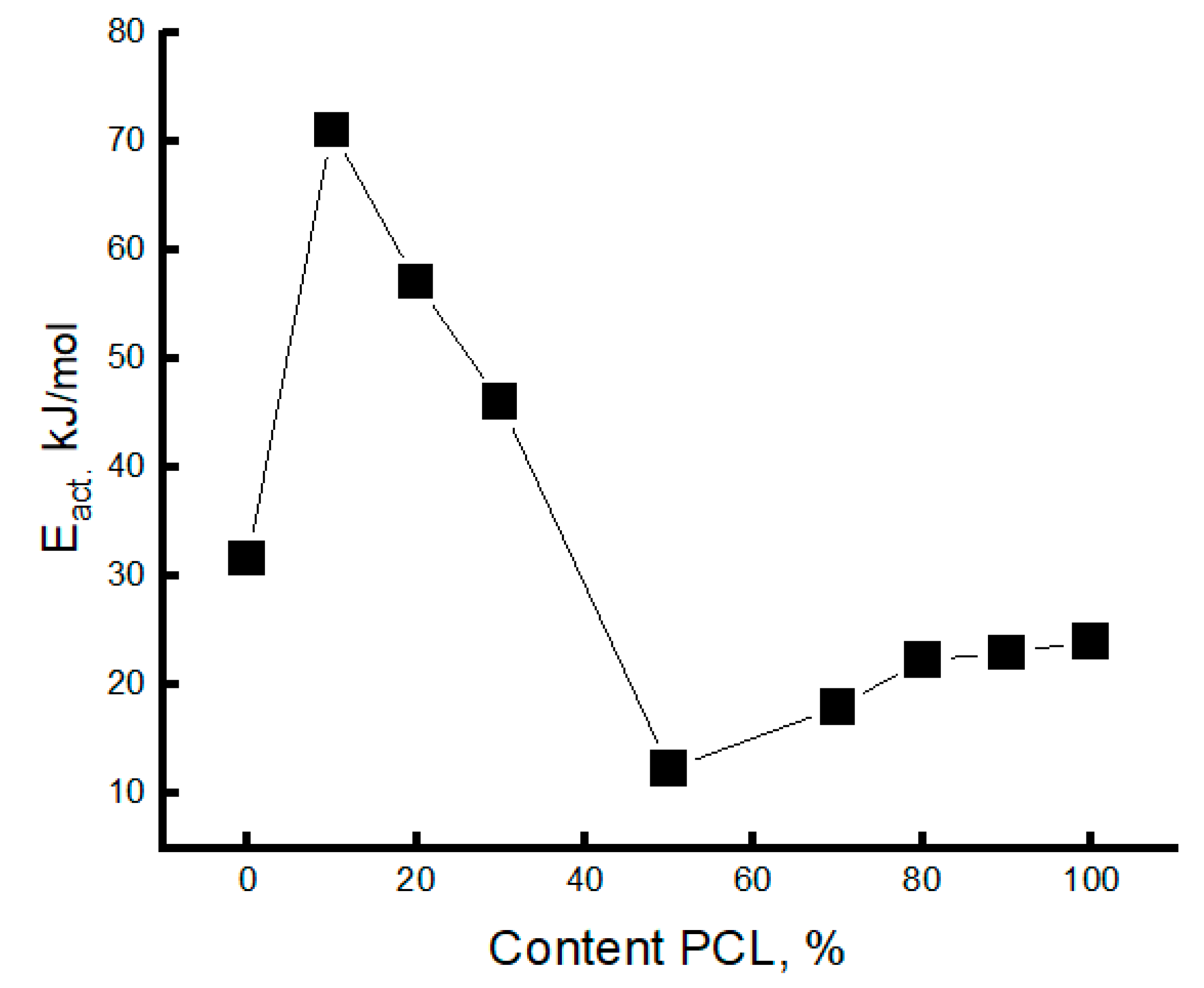
3.3. Dynamic Characteristics of the Amorphous Phase of Mixed PLA/PCL Compositions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pires, P.C.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Pedrosa, K.; Lopes, D.; Lopes, J.; Macário-Soares, A.; Peixoto, D.; Giram, P.S.; Veiga, F.; Paiva-Santos, A.C. Polymer-based biomaterials for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications: A focus on topical drug administration. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, R.; Beltrami, B.; Regondi, S.; Lunetta, C. Polymeric biomaterials for 3D printing in medicine: An overview. Ann. 3D Print. Med. 2021, 2, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Ogunseitan, O.A.; Wong, M.H.; Tang, Y. Sustainable materials alternative to petrochemical plastics pollution: A review analysis. Sustain. Horizons 2022, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zou, S.; Li, P. Aging of plastics in aquatic environments: Pathways, environmental behavior, ecological impacts, analyses and quantifications. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Auras, R.; Uysal-Unalan, I. Role of stereocomplex in advancing mass transport and thermomechanical properties of polylactide. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 3416–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. S. Ray, R. Banerjee. Introduction: sustainability, polylactide and polylactide-based composites. Sustainable Polylactide-Based Composites 2023, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aworinde, A.K.; Adeosun, S.O.; Oyawale, F.A.; Emagbetere, E.; Ishola, F.A.; Olatunji, O.; Akinlabi, S.A.; Oyedepo, S.O.; Ajayi, O.O.; Akinlabi, E.T. Comprehensive data on the mechanical properties and biodegradation profile of polylactide composites developed for hard tissue repairs. Data Brief 2020, 32, 106107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- T. Patrício, A. Glória, and P. Bártolo. Mechanical and biological behaviour of PCL and PCL/PLA scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 32, 1645–1650. [CrossRef]
- Todo, M.; Park, S.-D.; Takayama, T.; Arakawa, K. Fracture micromechanisms of bioabsorbable PLLA/PCL polymer blends. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2007, 74, 1872–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Auras, L.T. Lim, S.E.M. Selke. Optical Properties. In ‘Poly (lactic acid): synthesis, structures, properties, processing, and applications’. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2010. 113–124. [CrossRef]
- L. Fambri, and C. Migliaresi. Crystallization and thermal properties, in Poly(lactic acid): Synthesis, Structures, Properties, Processing, and Applications, 2022. Chapter 8. [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Pandey, P.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Toughening of Polylactic Acid: An Overview of Research Progress. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2015, 55, 1623–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.-C. Effect of Extrusion Temperature on the Physico-Mechanical Properties of Unidirectional Wood Fiber-Reinforced Polylactic Acid Composite (WFRPC) Components Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Polymers 2018, 10, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, J.R.; Ruckh, T.T.; Popat, K.C. Bone tissue engineering: A review in bone biomimetics and drug delivery strategies. Biotechnol. Prog. 2009, 25, 1539–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M., Vert. Degradable and bioresorbable polymers in surgery and in pharma-cology: beliefs and facts. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine. 2009, 20, 437–446. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, R.; Kumar, S.; Pandey, R.; Mahajan, A.; Nandana, D.; Katti, D.S.; Mehrotra, D. Polycaprolactone as biomaterial for bone scaffolds: Review of literature. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2020, 10, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachirahuttapong, S.; Thongpin, C.; Sombatsompop, N. Effect of PCL and Compatibility Contents on the Morphology, Crystallization and Mechanical Properties of PLA/PCL Blends. Energy Procedia 2016, 89, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, A.; Rao, R.U.; Suman, K.; Rambabu, V. Preparation and Characterization of Biodegradable PLA/PCL Polymeric Blends. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkli, A.; Tabatabay, C.; Gurny, R.; Heller, J. Biodegradable polymers for the controlled release of ocular drugs. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1998, 23, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiberg, S.; Zhu, X.X. Polymer microspheres for controlled drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 282, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelny, I.; Ujcic, A.; Fambri, L.; Slouf, M. Phase Structure, Compatibility, and Toughness of PLA/PCL Blends: A Review. Front. Mater. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rodríguez, N.; Lopez-Arraiza, A.; Meaurio, E.; Sarasua, J.R. Crystallization, morphology, and mechanical behavior of polylactide/poly(ɛ-caprolactone) blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2006, 46, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V. Mittal, T.Akhatar, G. Luckachan, and N. Matsko. PLA, TPS and PCL binary and ternary blends: structural characterization and time-dependent morp-hological changes. Colloid Polymer Science 2015, 293, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostafinska, A.; Fortelny, I.; Nevoralova, M.; Hodan, J.; Kredatusova, J.; Slouf, M. Synergistic effects in mechanical properties of PLA/PCL blends with optimized composition, processing, and morphology. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 98971–98982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquijo, J.; Guerrica-Echevarria, G.; Eguiazábal, J.I. Melt processed PLA/PCL blends: Effect of processing method on phase structure, morphology, and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Aguilar, M.; Puig, R.; Sazdovski, I.; Fullana-I-Palmer, P. Polylactic Acid/Polycaprolactone Blends: On the Path to Circular Economy, Substituting Single-Use Commodity Plastic Products. Materials 2020, 13, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matta, A.; Rao, R.U.; Suman, K.; Rambabu, V. Preparation and Characterization of Biodegradable PLA/PCL Polymeric Blends. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostafinska, A.; Fortelny, I.; Nevoralova, M.; Hodan, J.; Kredatusova, J.; Slouf, M. Synergistic effects in mechanical properties of PLA/PCL blends with optimized composition, processing, and morphology. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 98971–98982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raquez, J.; Vanderstappen, S.; Meyer, F.; Verge, P.; Alexandre, M.; Thomassin, J.; Jérôme, C.; Dubois, P. Design of Cross-Linked Semicrystalline Poly(ε-caprolactone)-Based Networks with One-Way and Two-Way Shape-Memory Properties through Diels–Alder Reactions. Chem. – A Eur. J. 2011, 17, 10135–10143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M.D. Hager, M. D.; S. Bode, C. Weber, U.S. Schubert. Shape memory polymers: Past, present and future developments. Progress in Polymer Science 2015, 49–50, 3–33. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Tobías, H.; Morales, G.; Ledezma, A.; Romeso, J.; Saldivas, R.; Langlois, V. Electrospinning and elec-trospraying techniques for designing novel antibacterial poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)/zinc oxide nanofibrous composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 8593–8612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordanskii, A.L.; Ol’khov, A.A.; Karpova, S.G.; Kucherenko, E.L.; Kosenko, R.Y.; Rogovina, S.Z.; Chalykh, A.E.; Berlin, A.A. Influence of the structure and morphology of ultrathin poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) fibers on the diffusion kinetics and transport of drugs. Polymer Science. A. 2017, 59, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, S.G.; Ol’khov, A.A.; Iordanskii, A.L.; Lomakin, S.M.; Shilkina, N.S.; Popov, A.A.; Gumargalieva, K.Z.; Berlin, A.A. Nonwoven blend composites based on poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)–chitosan ultrathin fibers prepared via electrospinning. Polymer Science. A 2016, 58, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, D.F.; Rosa, D.S.; Rezende, J.; Ponce, P.; Lugão, A.B. Biodegradation of γ Irradiated Poly 3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) Films Blended with Poly(Ethyleneglycol). J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.-C. Effect of Extrusion Temperature on the Physico-Mechanical Properties of Unidirectional Wood Fiber-Reinforced Polylactic Acid Composite (WFRPC) Components Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Polymers 2018, 10, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, J.R.; Ruckh, T.T.; Popat, K.C. Bone tissue engineering: A review in bone biomimetics and drug delivery strategies. Biotechnol. Prog. 2009, 25, 1539–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vert, M. Degradable and bioresorbable polymers in surgery and in pharmacology: beliefs and facts. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 20, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, R.; Kumar, S.; Pandey, R.; Mahajan, A.; Nandana, D.; Katti, D.S.; Mehrotra, D. Polycaprolactone as biomaterial for bone scaffolds: Review of literature. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2020, 10, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiberg, S.; Zhu, X.X. Polymer microspheres for controlled drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 282, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortelny, I.; Ujcic, A.; Fambri, L.; Slouf, M. Phase Structure, Compatibility, and Toughness of PLA/PCL Blends: A Review. Front. Mater. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rodríguez, N.; Lopez-Arraiza, A.; Meaurio, E.; Sarasua, J.R. Crystallization, morphology, and mechanical behavior of polylactide/poly(ɛ-caprolactone) blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2006, 46, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V.; Akhtar, T.; Luckachan, G.; Matsko, N. PLA, TPS and PCL binary and ternary blends: structural characterization and time-dependent morphological changes. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 293, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y.N. Filatov. Electroforming of fibrous materials (EFV-process). Moscow: Oil and Gas, 1997.
- Budil, D.E.; Lee, S.; Saxena, S.; Freed, J.H. Nonlinear-Least-Squares Analysis of Slow-Motion EPR Spectra in One and Two Dimensions Using a Modified Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm. J. Magn. Reson. Ser. A 1996, 120, 155–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V.P. Timofeev, A.Yu. Misharin, Y.V. Tkachev. Biophys. 2011, 56, 420.
- A.L. Buchachenko, A.M. A.L. Buchachenko, A.M. Wasserman. Stable radicals. Moscow: Chemistry, 1973.
- Možar, K.B.; Miloloža, M.; Martinjak, V.; Cvetnić, M.; Kušić, H.; Bolanča, T.; Grgić, D.K. ; Potential of Advanced Oxidation as Pretreatment for Microplastics Biodegradation. Separations 2023, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkhov, A.A.; Karpova, S.G.; Tyubaeva, P.M.; Zhulkina, A.L.; Zernova, Y.N.; Iordanskii, A.L. Effect of Ozone and Ultraviolet Radiation on Structure of Fibrous Materials Based on Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and Polylactide. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2020, 11, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kučera, F.; Petruš, J.; Jančář, J. The structure-hydrolysis relationship of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). Polym. Test. 2019, 80, 106095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonos, P.; Terzopoulou, Z.; Koutsoumpis, S.; Zidropoulos, S.; Kripotou, S.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Kyritsis, A.; Pissis, P. Rigid amorphous fraction and segmental dynamics in nanocomposites based on poly(l–lactic acid) and nano-inclusions of 1–3D geometry studied by thermal and dielectric techniques. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 82, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaev, P.; Aliev, I.; Iordanskii, A.; Wasserman, A. Molecular dynamics of the spin probes in dry and wet poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) films with different morphology. Polymer 2001, 42, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, O.S.S.; Iordanskii, A.; Olkhov, A.; Khvatov, A.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Kildeeva, N.; Artsis, M.; Zaikov, G. Comparative Dynamic Characteristics of Electrospun Ultrathin Fibers and Films Based on Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). Chemistry & Chemistry Technology. 2016, 10, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
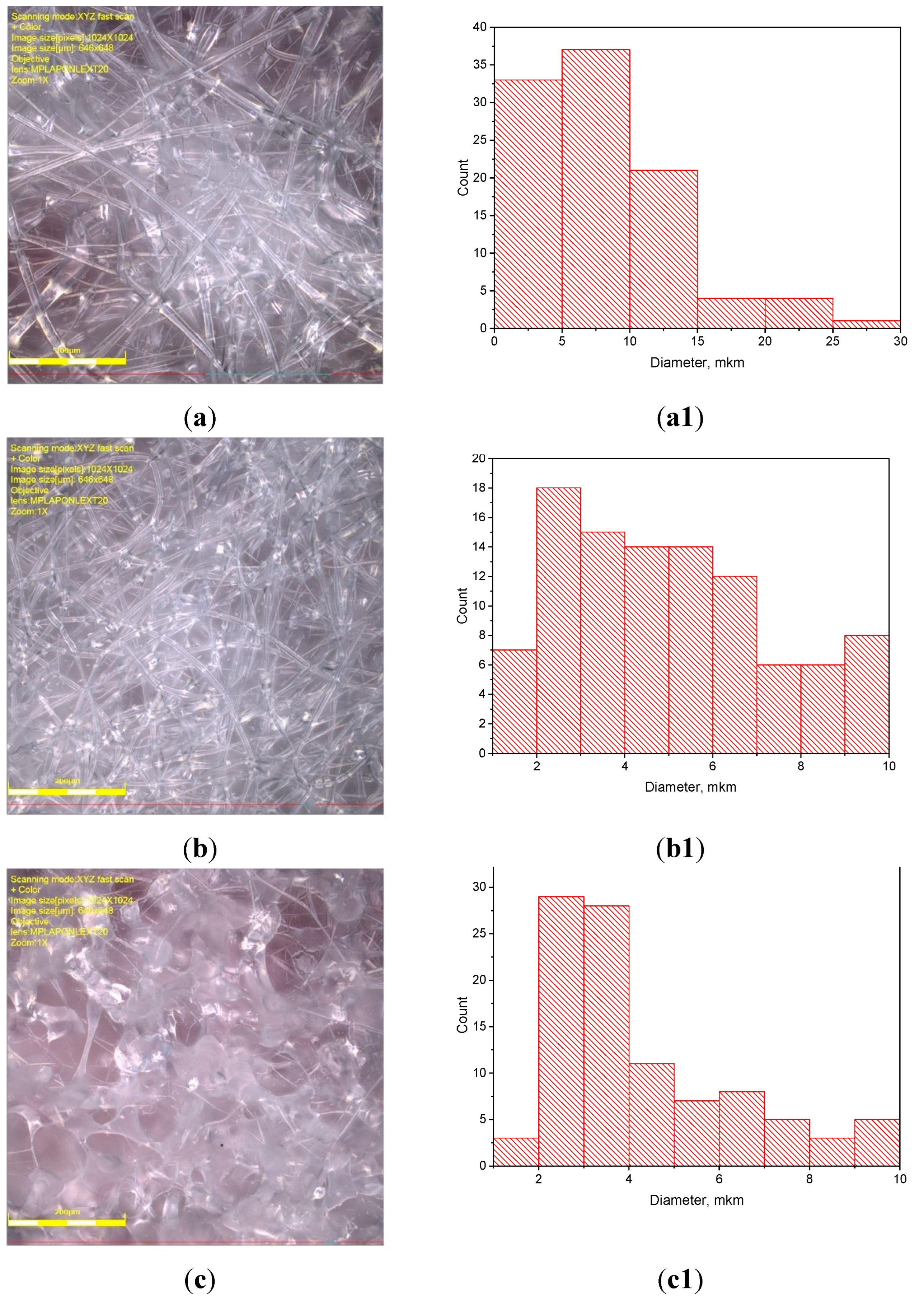
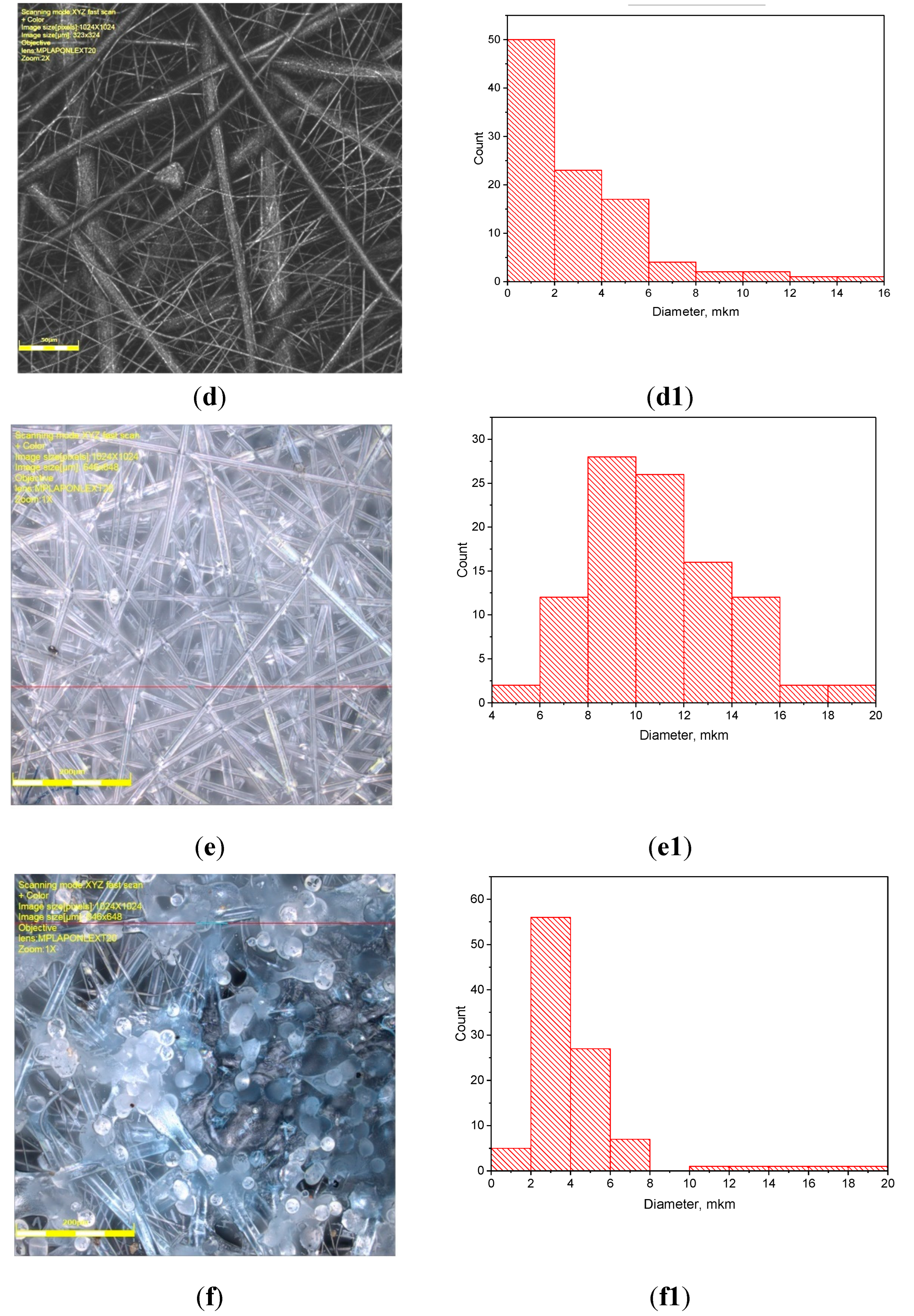
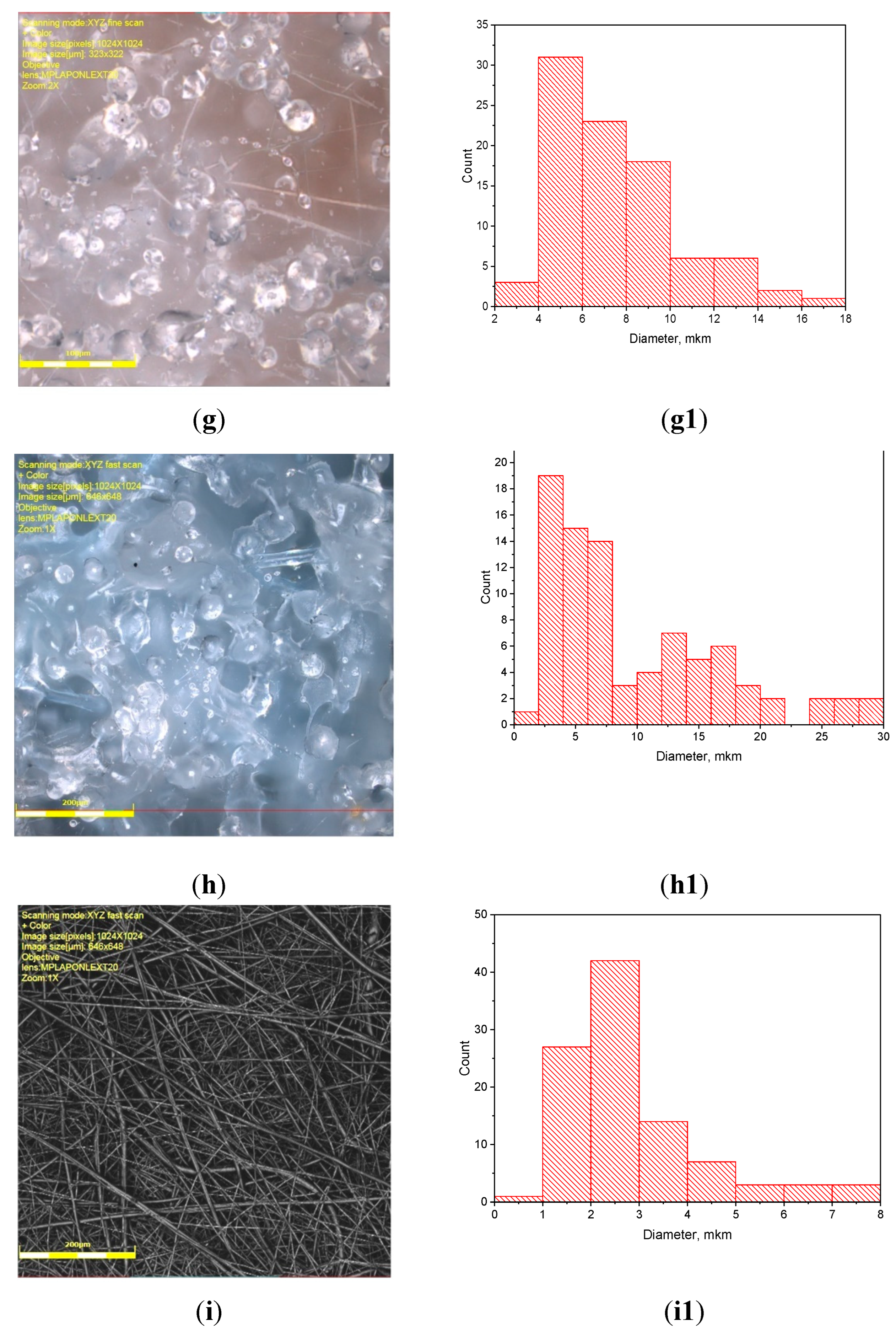
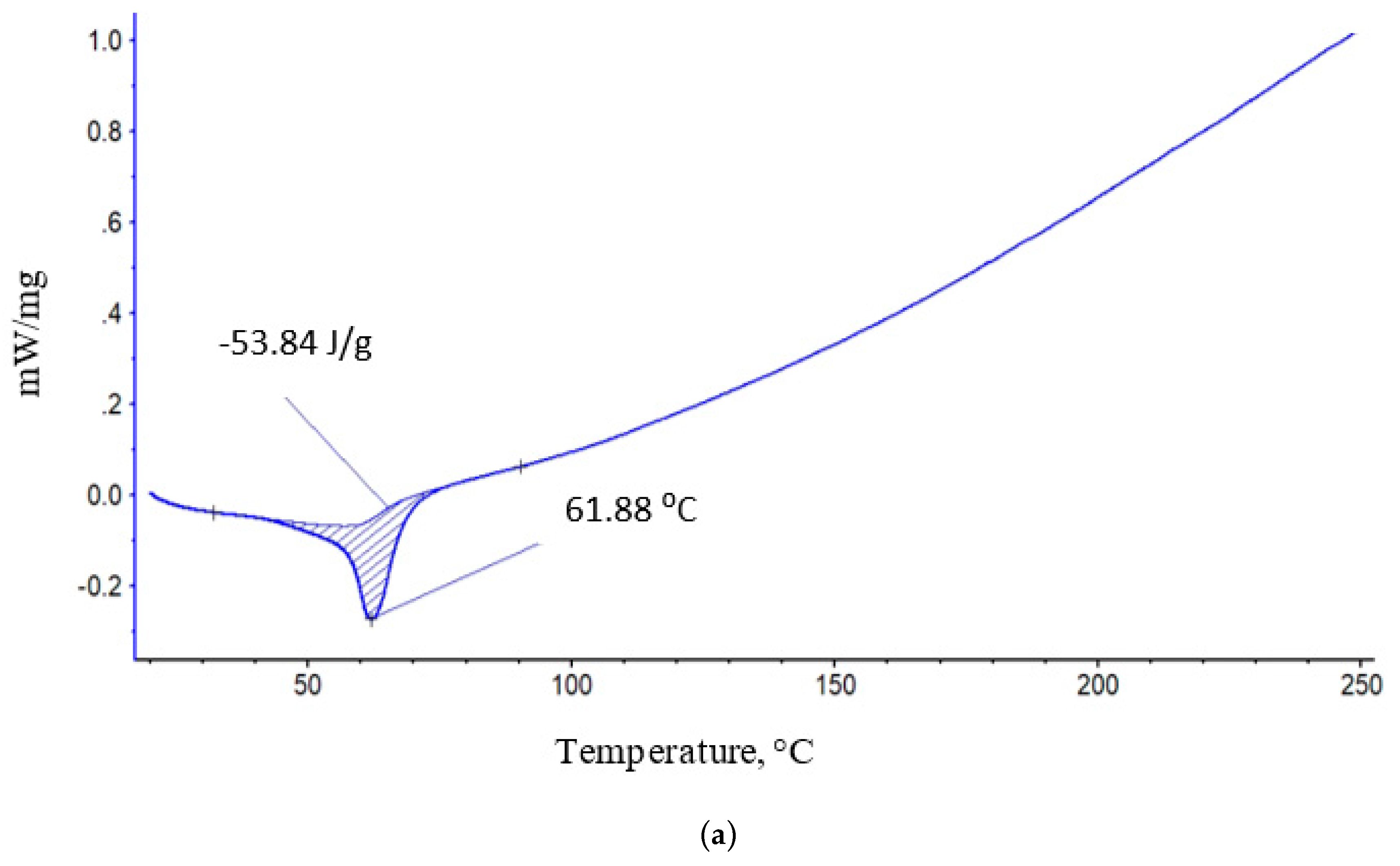
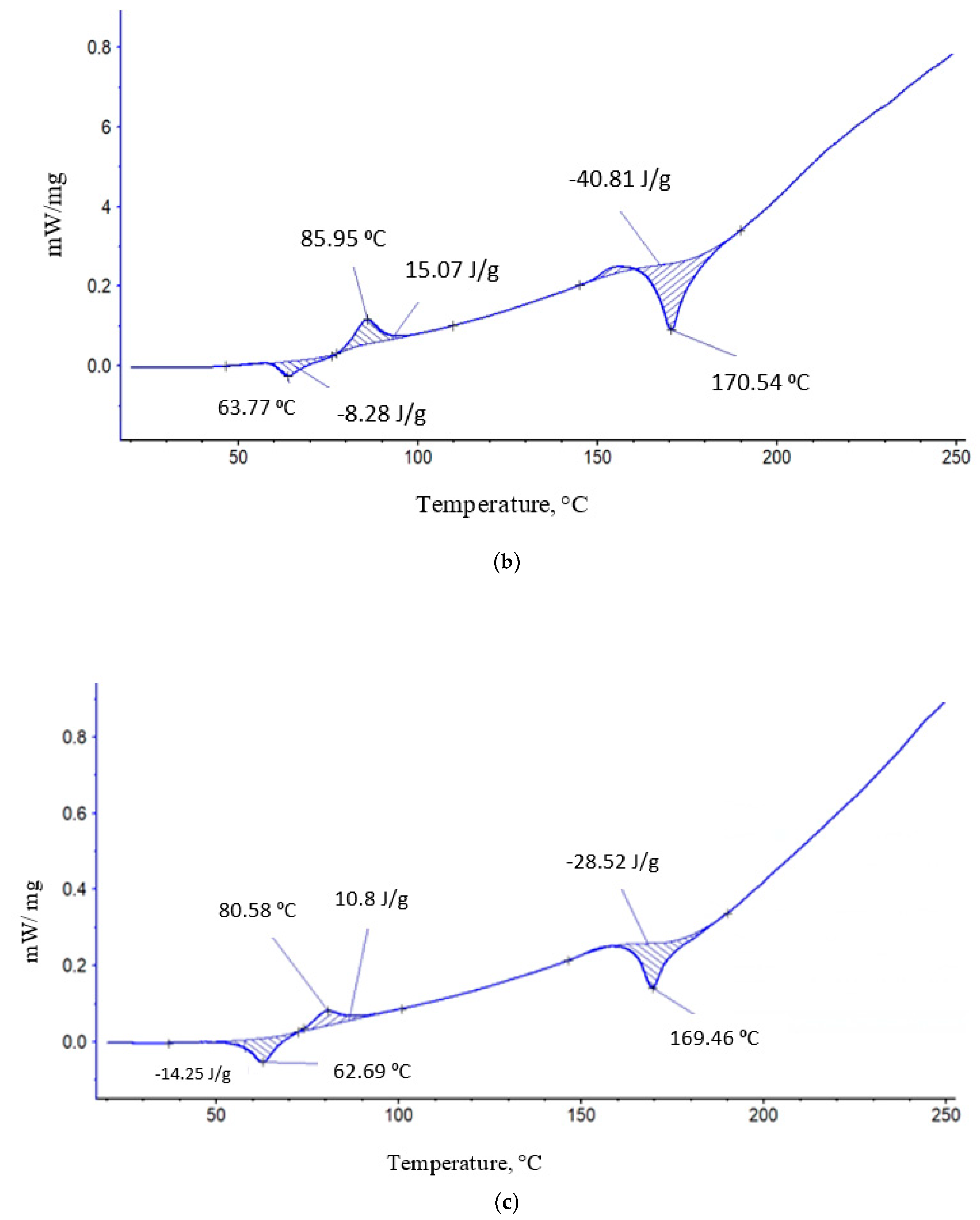
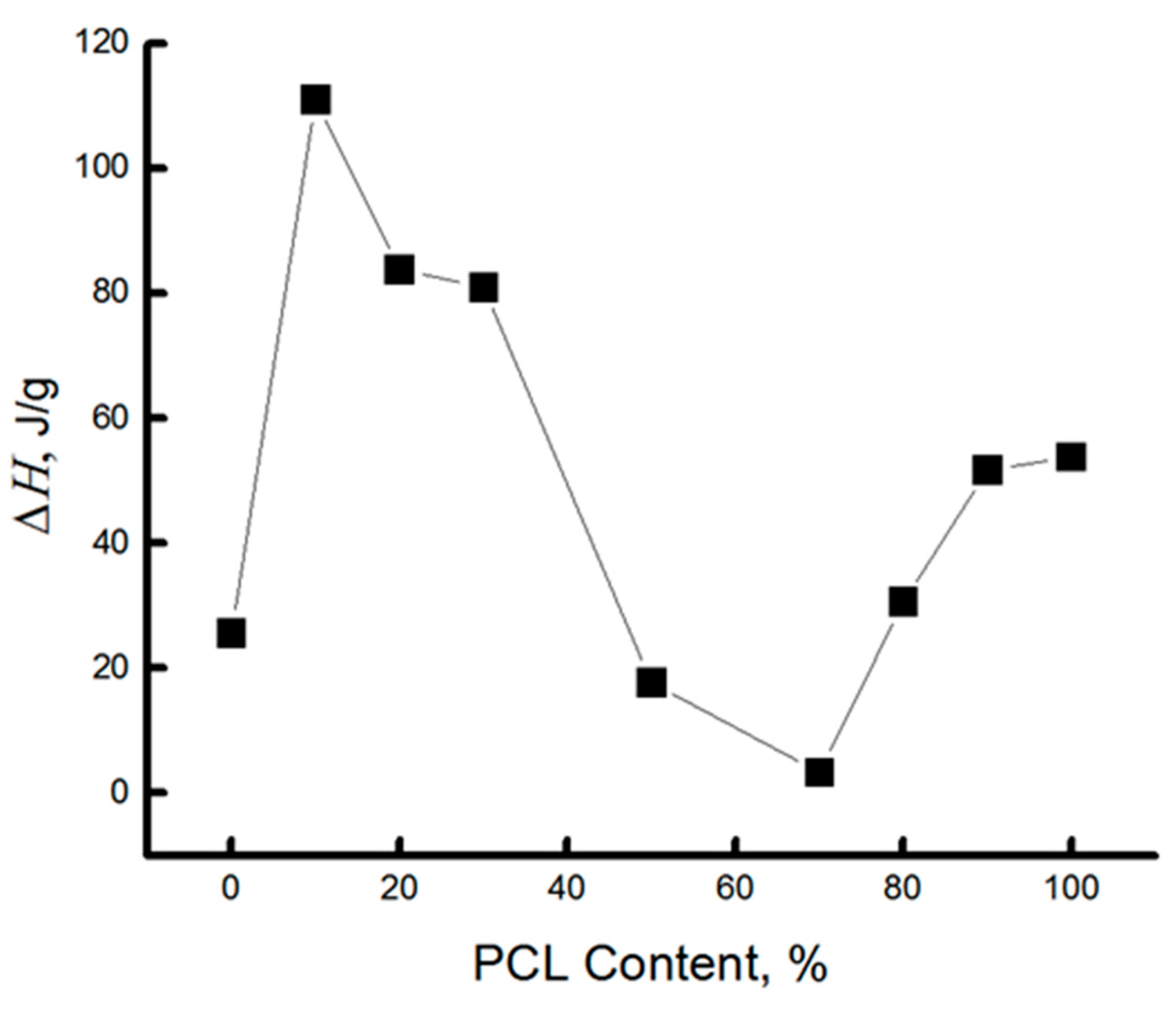
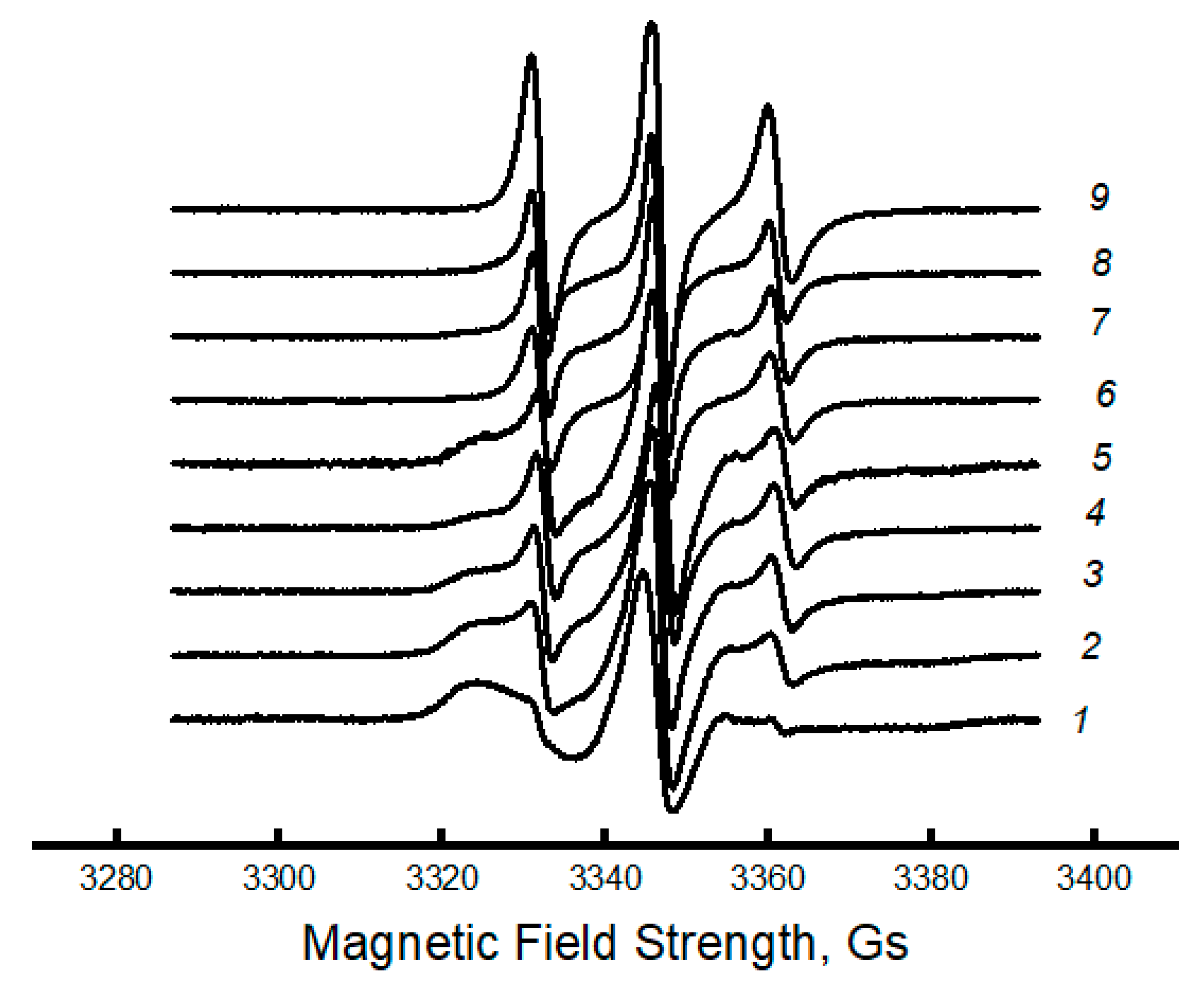
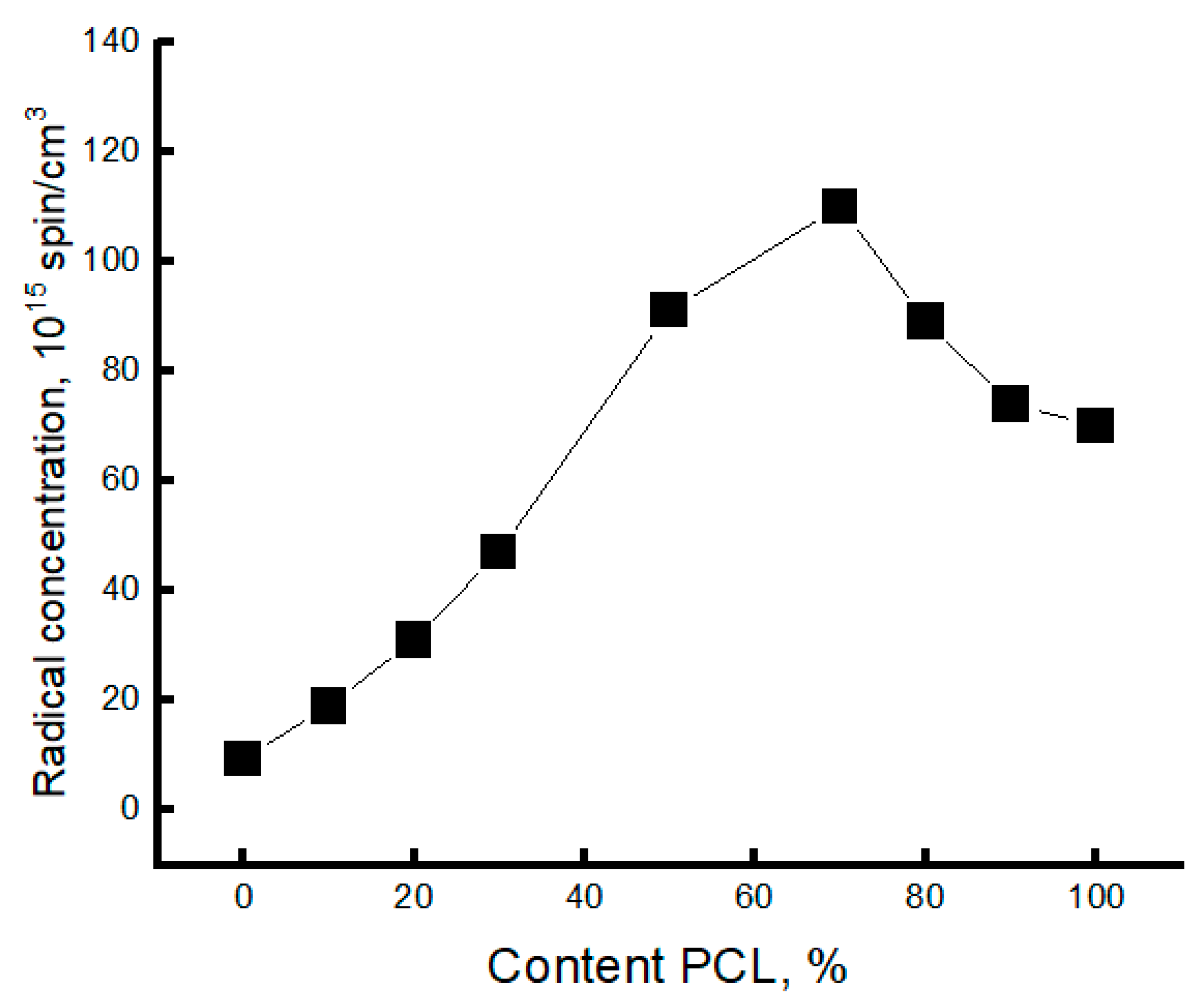
| PCL content in the mixture, % | ΔHcr., J/g | Тmelt, °С | Тgt, °С | ΔHcc, J/g | Тmelt, °С |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 25,7 | 170,54 | 63,77 | -15,07 | 86 |
| 10 | 111 | 170,1 | 63,3 | -10,7 | 82,3 |
| 20 | 83,8 | 170,1 | 63 | -8,1 | 80,8 |
| 30 | 82 | 170 | 63 | -5 | 80,1 |
| 50 | 17,7 | 169,5 | 62,7 | -3,5 | 78 |
| 70 | 3,36 | 167,9 | 62 | ||
| 80 | 30,6 | 167,5 | 61,6 | ||
| 90 | 51,7 | 165,1 | 61,4 | ||
| 100 | 53,84 | 61,8 | 61 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





