Submitted:
20 March 2024
Posted:
26 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
MSC: 62-04; 62D20; 62F10; 62N01; 62N03; 62N05
1. Introduction
2. Proposed Method
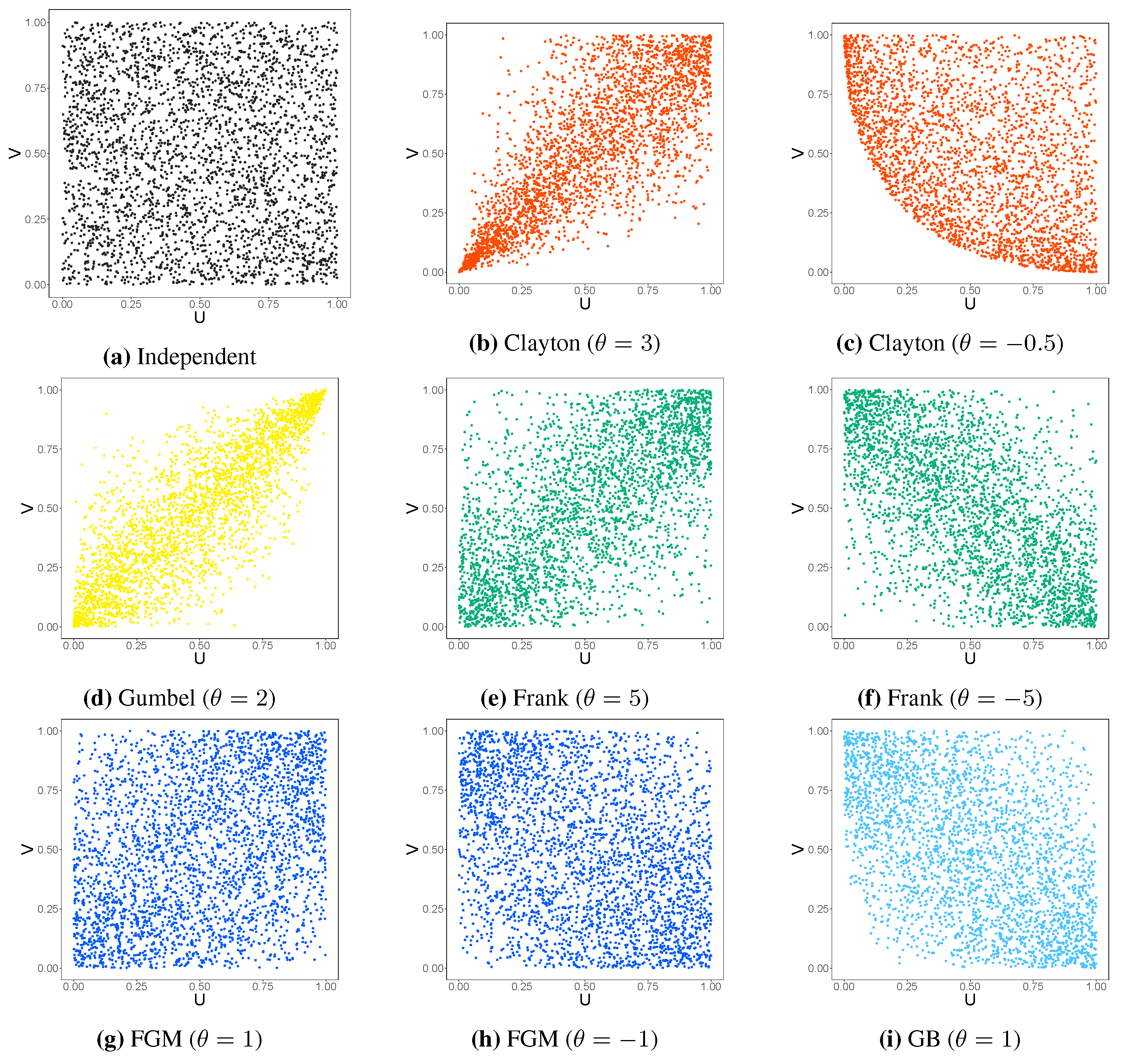
2.1. Copula Models for Dependent Survival Time
- The independence copula:
- The Clayton copula ([24]):
- The Gumbel copula ([25]):
- The Frank copula ([26]):
- The Farlie-Gumbel-Morgenstern (FGM) copula ([27]):
- The independence copula:
- The Clayton copula:
- The Gumbel copula:
- The Frank copula:
- The FGM copula:
- The GB copula:
2.2. Proposed Method for Computing p
- The Clayton copula
- The Gumbel copula
- The Frank copula
- The FGM copula
- The GB copula
2.3. Computing p with Follow-Up Time
- The Clayton copula
- The Gumbel copula
- The Frank copula
- The FGM copula
- The GB copula
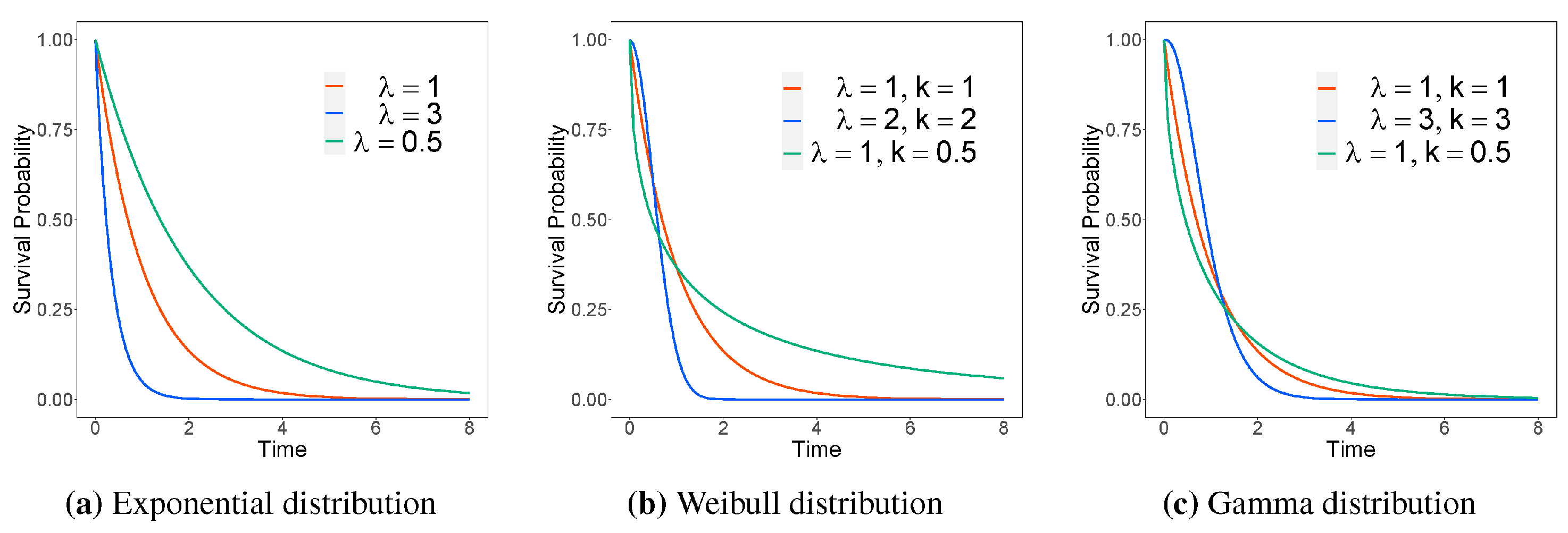
2.4. Marginal Survival Distributions
- The exponential distribution:where is a rate parameter.
- The Weibull distribution:where is a scale parameter and is a shape parameter.
- The gamma distribution:where is a scale parameter and is a shape parameter, and is the gamma function, and is the lower incomplete gamma function. The gamma distribution has no simple closed-form expression for the inverse survival function. Therefore, one can use approximations for the inverse survival function. In Section 3, we use the R function “qgamma” to calculate the quantile funciton of the gamma distribution.
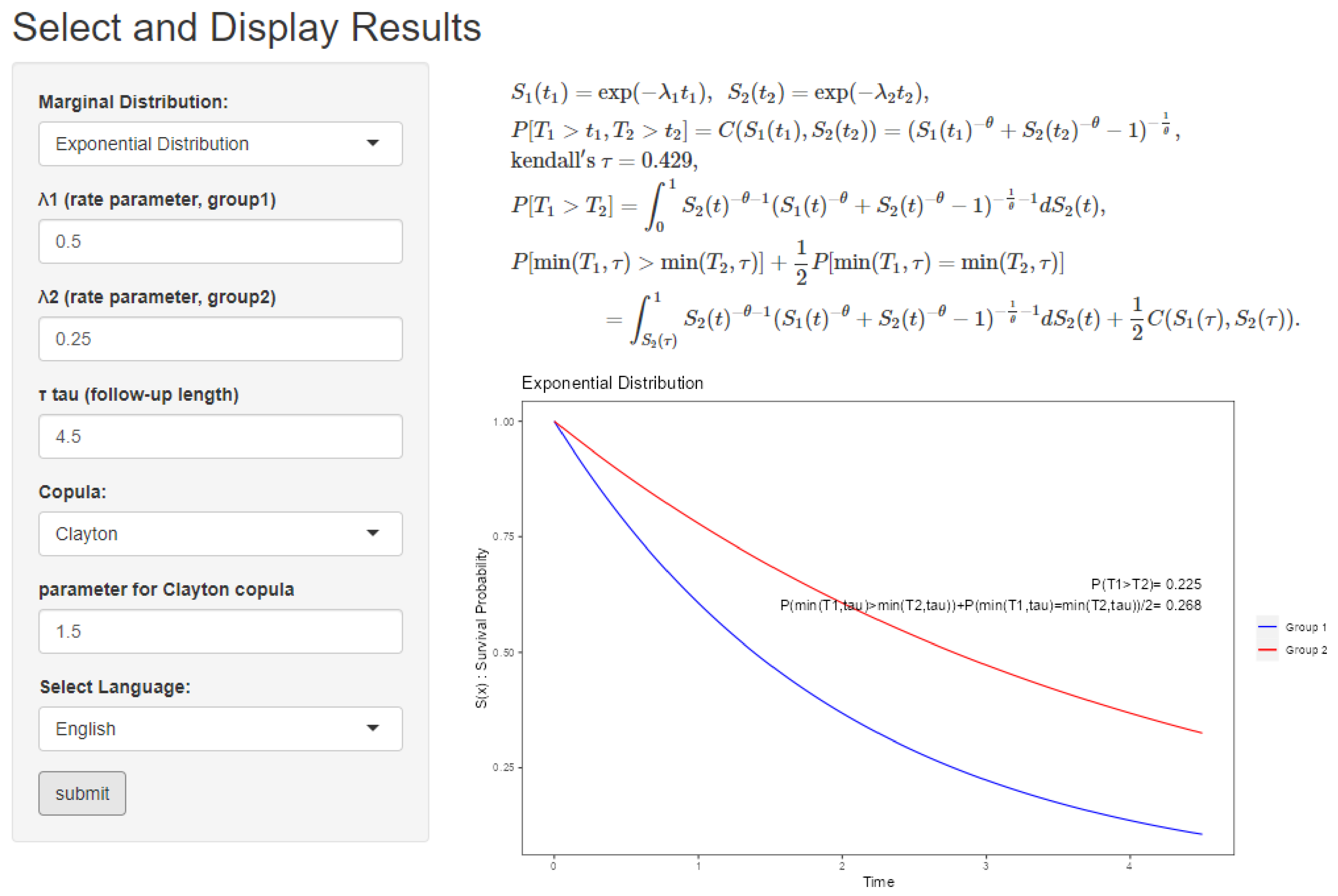
3. Software and Web App
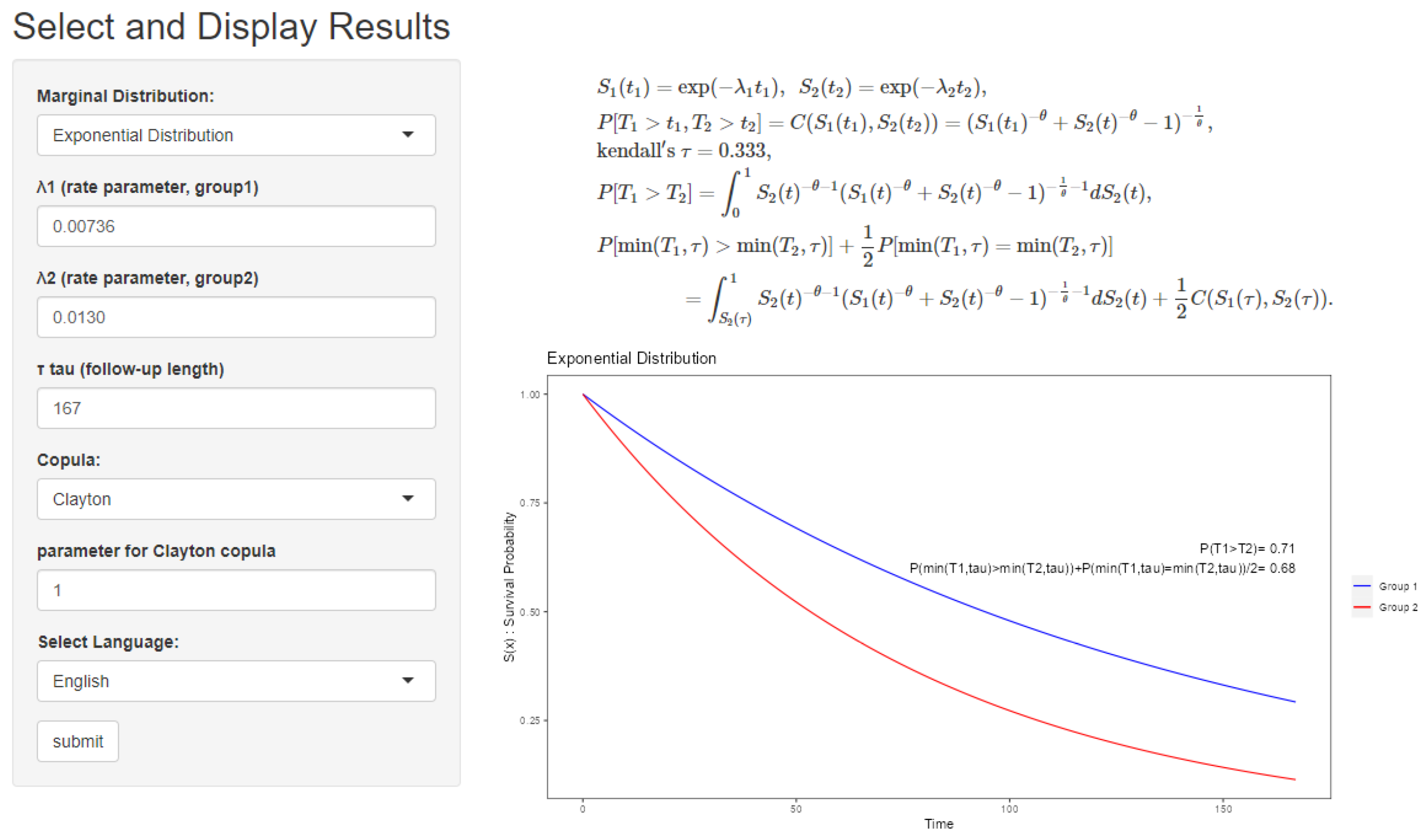
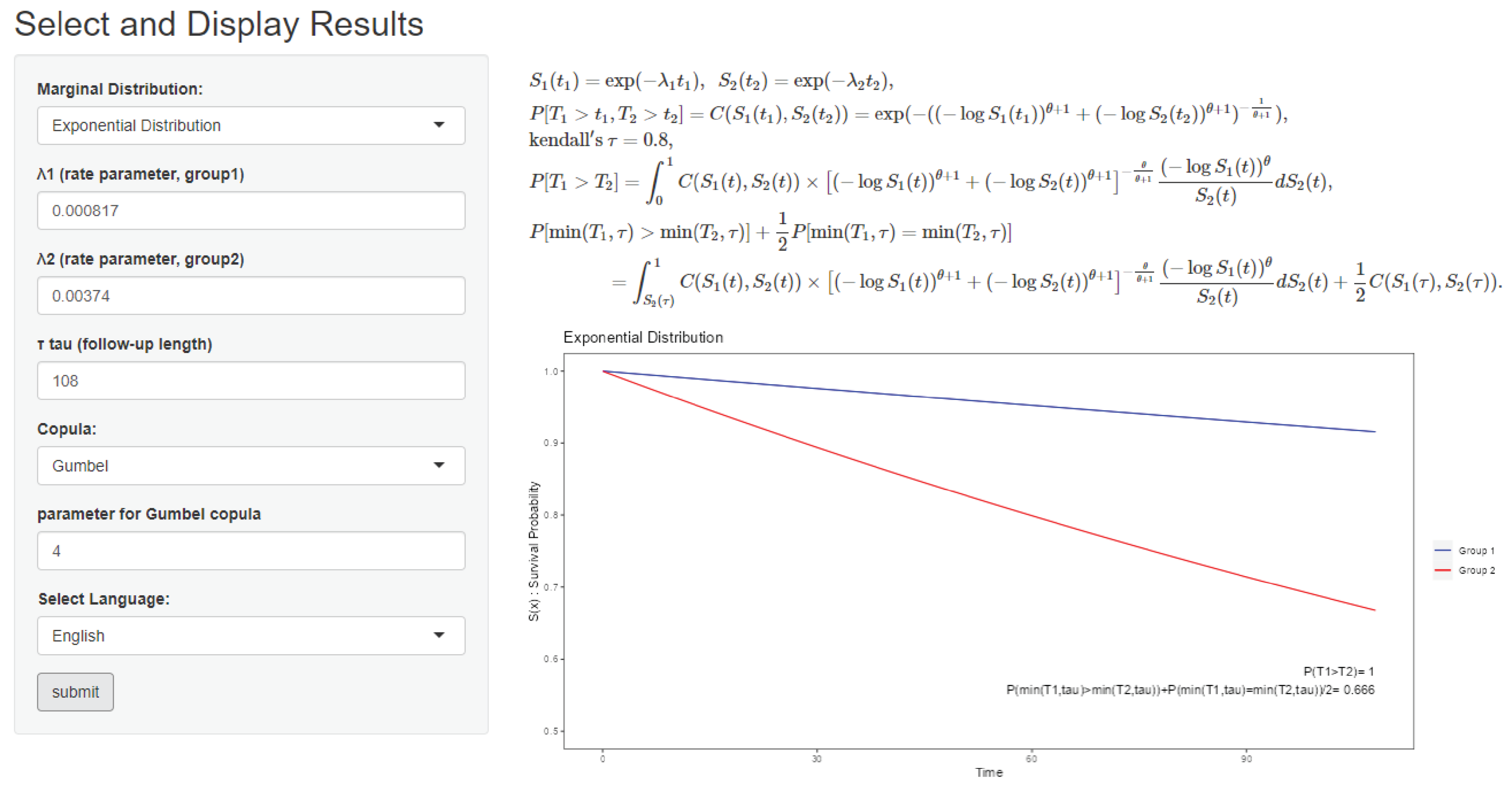
3.1. Input
3.2. Output
4. Simulation Studies
5. Numerical Examples
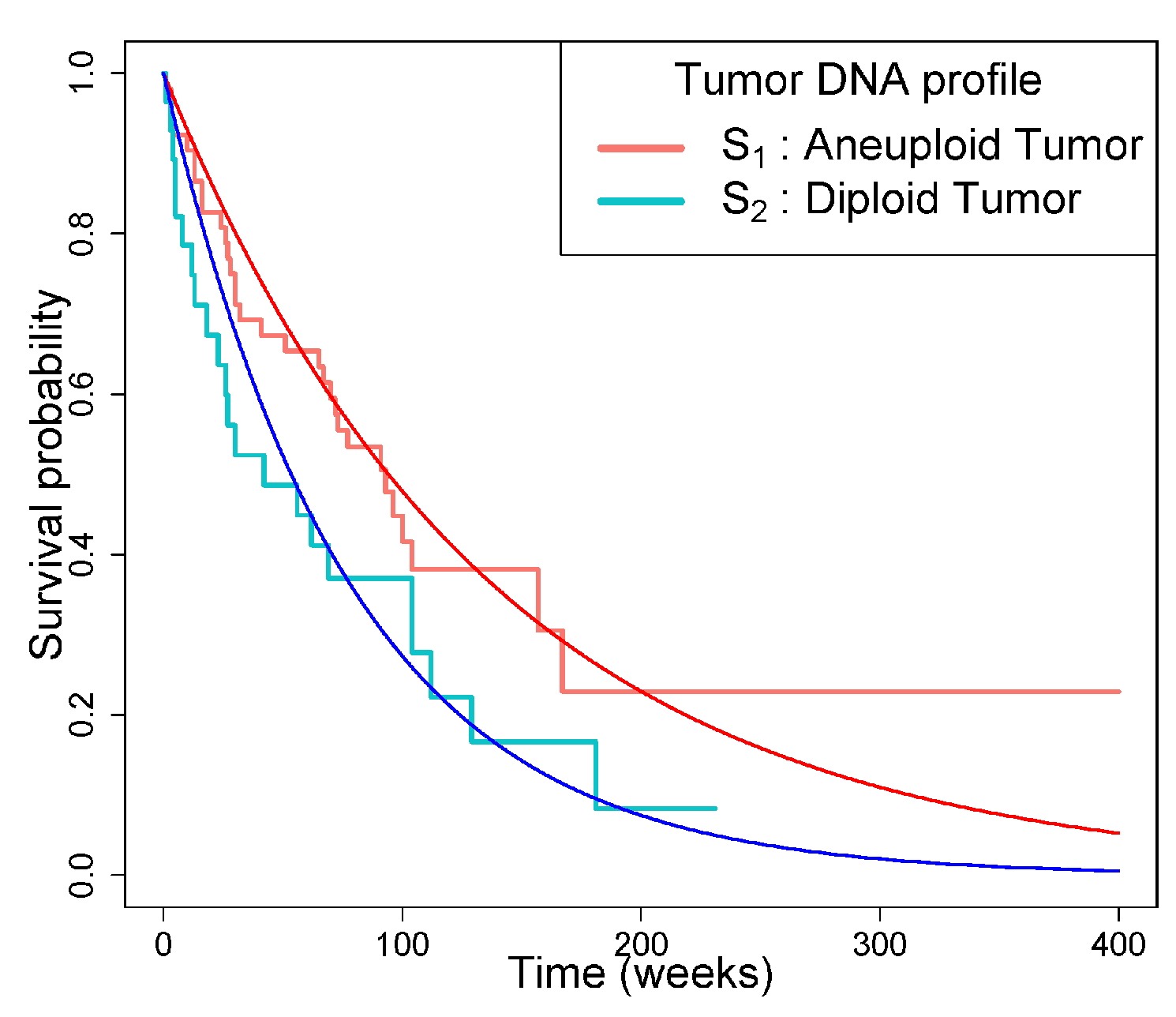
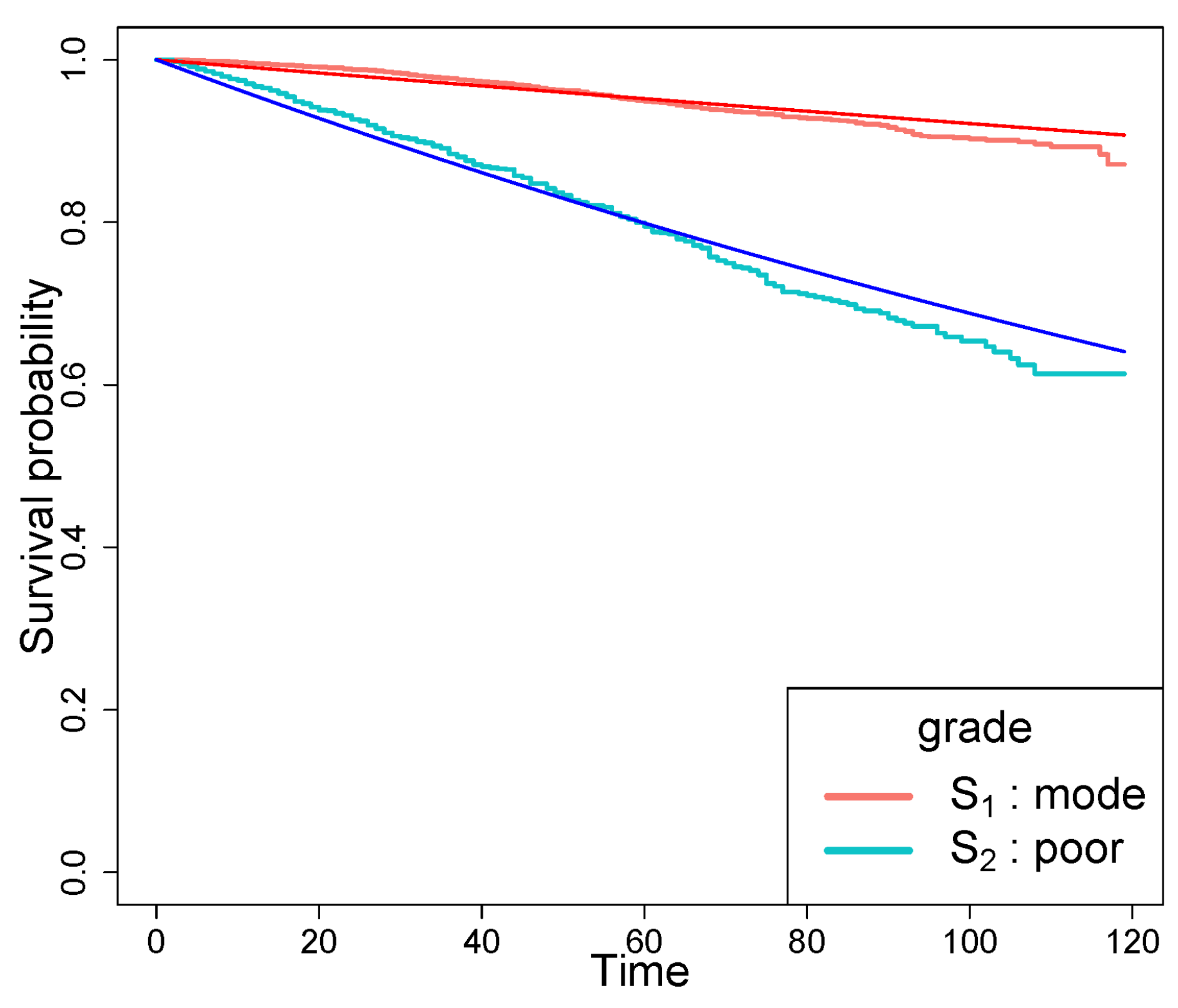
5.1. Tongue Cancer Data
5.2. Prostate Cancer Data
6. Conclusion
Funding
References
- Efron, B. The two sample problem with censored data. Proceedings of the fifth Berkeley symposium on mathematical statistics and probability, 1967, Vol. 4, pp. 831–853.
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a test of whether one of two random variables is stochastically larger than the other. Ann. Math. Statistics 1947, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocock, S.J.; Ariti, C.A.; Collier, T.J.; Wang, D. The win ratio: a new approach to the analysis of composite endpoints in clinical trials based on clinical priorities. European Heart Journal 2011, 33, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaum, Z.W. On a use of the Mann-Whitney statistic. Proceedings of the Third Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, 1954–1955, vol. I. Univ. California Press, Berkeley-Los Angeles, Calif., 1956, pp. 13–17.
- Dobler, D.; Pauly, M. Bootstrap- and permutation-based inference for the Mann-Whitney effect for right-censored and tied data. TEST 2018, 27, 639–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emura, T.; Hsu, J.H. Estimation of the Mann-Whitney effect in the two-sample problem under dependent censoring. Comput. Statist. Data Anal. 2020, 150, 106990–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Mukherjee, M. On estimation of stress-strength reliability with log-Lindley distribution. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2021, 91, 128–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubarth, K.; Sattler, P.; Zimmermann, H.G.; Konietschke, F. Estimation and Testing of Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney Effects in Factorial Clustered Data Designs. Symmetry 2022, 14. https://www.mdpi.com/2073-8994/14/2/244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Goldiner, C. Fixed-accuracy confidence interval estimation of P(X<Y) under a geometric-exponential model. Jpn. J. Stat. Data Sci. 2021, 4, 1079–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cruz, R.; Salinas, H.S.; Meza, C. Reliability Estimation for Stress-Strength Model Based on Unit-Half-Normal Distribution. Symmetry 2022, 14. https://www.mdpi.com/2073-8994/14/4/837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.; Naik-Nimbalkar, U.V.; Kale, M.M. Effect of Dependency on the Estimation of P[Y>X] in Exponential Stress-strength Models. Austrian Journal of Statistics 2022, 51, 10–34, https://www.ajs.or.at/index.php/ajs/article/view/1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, C.P.; Mütze, T.; Konietschke, F. Group sequential methods for the Mann-Whitney parameter. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2022, 31, 2004–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Nayal, A.S.; Tyagi, A. Estimation of P [Y< Z] under Geometric-Lindley model. Ricerche di Matematica, 2023; 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hand, D.J. On Comparing Two Treatments. The American Statistician 1992, 46, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, W.G.; Cox, G.M. Experimental designs; John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York; Chapman & Hall, Ltd., London, 1957; pp. xiv+617. 2nd ed.
- Fan, Y.; Park, S.S. Sharp bounds on the distribution of treatment effects and their statistical inference. Econometric Theory 2010, 26, 931–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, M.P.; Brittain, E.H.; Shih, J.H.; Follmann, D.A.; Gabriel, E.E. Causal estimands and confidence intervals associated with Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney tests in randomized experiments. Stat. Med. 2018, 37, 2923–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emura, T.; Matsui, S.; Rondeau, V. Survival analysis with correlated endpoints; SpringerBriefs in Statistics, Springer, Singapore, 2019; pp. xvii+118. [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Hu, X.J.; Wang, R. Evaluating association between two event times with observations subject to informative censoring. J. Amer. Statist. Assoc. 2023, 118, 1282–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emura, T.; Pan, C.H. Parametric likelihood inference and goodness-of-fit for dependently left-truncated data, a copula-based approach. Statist. Papers 2020, 61, 479–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklar, M. Fonctions de répartition à n dimensions et leurs marges. Publ. Inst. Statist. Univ. Paris 1959, 8, 229–231. [Google Scholar]
- Nelsen, R.B. An introduction to copulas, second ed.; Springer Series in Statistics, Springer, New York, 2006; pp. xiv+269. [CrossRef]
- Geenens, G. (Re-)Reading Sklar (1959);A Personal View on Sklar’s Theorem. Mathematics 2024, 12. https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7390/12/3/380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, D.G. A model for association in bivariate life tables and its application in epidemiological studies of familial tendency in chronic disease incidence. Biometrika 1978, 65, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbel, E.J. Distributions des valeurs extrêmes en plusieurs dimensions. Publ. Inst. Statist. Univ. Paris 1960, 9, 171–173. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, M.J. On the simultaneous associativity of F(x,y) and x+y-F(x,y). Aequationes Math. 1979, 19, 194–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, D. Einfache Beispiele zweidimensionaler Verteilungen. Mitteilungsbl. Math. Statist. 1956, 8, 234–235. [Google Scholar]
- Chesneau, C. On the Gumbel-Barnett extended Celebioglu-Cuadras copula. Jpn. J. Stat. Data Sci. 2023, 6, 759–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toparkus, A.M.; Weißbach, R. Testing Truncation Dependence: The Gumbel-Barnett Copula. 2024; arXiv:stat.ME/2305.19675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; dos Reis, R.C.P.; Gottselig, M.M.F.; Fisch, P.; Knauth, D.R.; Vigo, A. Clayton copula for survival data with dependent censoring: an application to a tuberculosis treatment adherence data. Stat. Med. 2023, 42, 4057–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Ding, Y. Copula-based semiparametric regression method for bivariate data under general interval censoring. Biostatistics 2021, 22, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradian, H.; Larocque, D.; Bellavance, F. Survival forests for data with dependent censoring. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2019, 28, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzana, W.; Basree, M.M.; Diawara, N.; Shboul, Z.A.; Dubey, S.; Lockhart, M.M.; Hamza, M.; Palmer, J.D.; Iftekharuddin, K.M. Prediction of Rapid Early Progression and Survival Risk with Pre-Radiation MRI in WHO Grade 4 Glioma Patients. Cancers 2023, 15. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/15/18/4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escarela, G.; Carrière, J.F. Fitting competing risks with an assumed copula. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2003, 12, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H. Semiparametric marginal regression analysis for dependent competing risks under an assumed copula. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2010, 72, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.H.; Emura, T. Likelihood-based inference for bivariate latent failure time models with competing risks under the generalized FGM copula. Comput. Statist. 2018, 33, 1293–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.H.; Konno, Y.; Chang, Y.T.; Emura, T. Estimation of a common mean vector in bivariate meta-analysis under the FGM copula. Statistics 2019, 53, 673–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.H.; Konno, Y.; Chang, Y.T.; Emura, T. Copula-Based Estimation Methods for a Common Mean Vector for Bivariate Meta-Analyses. Symmetry 2022, 14. https://www.mdpi.com/2073-8994/14/2/186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobler, D.; Pauly, M. Factorial analyses of treatment effects under independent right-censoring. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2020, 29, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emura, T.; Ditzhaus, M.; Dobler, D.; Murotani, K. Factorial survival analysis for treatment effects under dependent censoring. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2024, 33, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.F. Applied survival analysis using R; Vol. 473, Springer, 2016.
- Greenland, S.; Fay, M.P.; Brittain, E.H.; Shih, J.H.; Follmann, D.A.; Gabriel, E.E.; Robins, J.M. On causal inferences for personalized medicine: how hidden causal assumptions led to erroneous causal claims about the D-value. Amer. Statist. 2020, 74, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Cai, Z.; Zhou, X.H. Using secondary outcome to sharpen bounds for treatment harm rate in characterizing heterogeneity. Biom. J. 2018, 60, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SUSAM, S.O. A multi-parameter Generalized Farlie-Gumbel-Morgenstern bivariate copula family via Bernstein polynomial. Hacettepe Journal of Mathematics and Statistics 2022, 51, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Distribution | Copula | ||||||||||||
| Exponential | Clayton | 1 | 0.33 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 0.645 | 0.643 | 0.737 | 0.738 | 0.744 | 0.746 |
| 5 | 0.71 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 0.704 | 0.706 | 0.872 | 0.872 | 0.881 | 0.883 | ||
| 10 | 0.83 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 0.746 | 0.745 | 0.920 | 0.921 | 0.930 | 0.930 | ||
| Gumbel | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 0.629 | 0.631 | 0.666 | 0.666 | 0.666 | 0.665 | |
| 4 | 0.80 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 0.798 | 0.799 | 0.961 | 0.961 | 0.970 | 0.969 | ||
| Frank | -5 | -0.46 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 0.615 | 0.615 | 0.622 | 0.622 | 0.622 | 0.622 | |
| 1 | 0.11 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 0.636 | 0.636 | 0.684 | 0.684 | 0.685 | 0.685 | ||
| 5 | 0.46 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 0.674 | 0.674 | 0.771 | 0.768 | 0.773 | 0.772 | ||
| FGM | -1 | -0.22 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 0.617 | 0.617 | 0.633 | 0.634 | 0.633 | 0.631 | |
| 0 | 0.00 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 0.629 | 0.629 | 0.666 | 0.666 | 0.666 | 0.666 | ||
| 1 | 0.22 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 0.642 | 0.641 | 0.699 | 0.697 | 0.700 | 0.702 | ||
| GB | 0.5 | -0.21 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 0.623 | 0.624 | 0.642 | 0.643 | 0.642 | 0.641 | |
| 1 | -0.36 | 1 | - | 2 | - | 0.617 | 0.616 | 0.629 | 0.628 | 0.629 | 0.632 | ||
| Weibull | Clayton | 1 | 0.33 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.497 | 0.496 | 0.594 | 0.589 | 0.603 | 0.602 |
| 5 | 0.71 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.482 | 0.480 | 0.644 | 0.645 | 0.653 | 0.654 | ||
| 10 | 0.83 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.472 | 0.472 | 0.645 | 0.645 | 0.654 | 0.653 | ||
| Gumbel | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.511 | 0.509 | 0.560 | 0.562 | 0.562 | 0.562 | |
| 4 | 0.80 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.425 | 0.424 | 0.584 | 0.585 | 0.593 | 0.594 | ||
| Frank | -5 | -0.46 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.528 | 0.530 | 0.542 | 0.541 | 0.542 | 0.543 | |
| 1 | 0.11 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.505 | 0.504 | 0.566 | 0.565 | 0.569 | 0.572 | ||
| 5 | 0.46 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.486 | 0.486 | 0.592 | 0.595 | 0.597 | 0.597 | ||
| FGM | -1 | -0.22 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.521 | 0.523 | 0.548 | 0.549 | 0.549 | 0.551 | |
| 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.511 | 0.509 | 0.560 | 0.563 | 0.562 | 0.562 | ||
| 1 | 0.22 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.501 | 0.503 | 0.572 | 0.574 | 0.575 | 0.577 | ||
| GB | 0.5 | -0.21 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.519 | 0.520 | 0.549 | 0.546 | 0.549 | 0.548 | |
| 1 | -0.36 | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.526 | 0.526 | 0.545 | 0.545 | 0.545 | 0.545 | ||
| Gamma | Clayton | 1 | 0.33 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.529 | 0.529 | 0.651 | 0.649 | 0.679 | 0.678 |
| 5 | 0.71 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.530 | 0.528 | 0.763 | 0.763 | 0.809 | 0.810 | ||
| 10 | 0.83 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.534 | 0.533 | 0.817 | 0.816 | 0.862 | 0.863 | ||
| Gumbel | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.530 | 0.530 | 0.611 | 0.612 | 0.615 | 0.614 | |
| 4 | 0.80 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.545 | 0.546 | 0.813 | 0.813 | 0.853 | 0.853 | ||
| Frank | -5 | -0.46 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.532 | 0.530 | 0.584 | 0.584 | 0.584 | 0.583 | |
| 1 | 0.11 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.530 | 0.529 | 0.622 | 0.622 | 0.628 | 0.628 | ||
| 5 | 0.46 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.530 | 0.530 | 0.679 | 0.679 | 0.694 | 0.692 | ||
| FGM | -1 | -0.22 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.531 | 0.533 | 0.591 | 0.591 | 0.592 | 0.591 | |
| 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.530 | 0.529 | 0.611 | 0.610 | 0.615 | 0.614 | ||
| 1 | 0.22 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.529 | 0.529 | 0.631 | 0.631 | 0.639 | 0.640 | ||
| GB | 0.5 | -0.21 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.531 | 0.532 | 0.597 | 0.598 | 0.598 | 0.598 | |
| 1 | -0.36 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 0.532 | 0.532 | 0.589 | 0.592 | 0.590 | 0.588 | ||
| Copula | marginal distribution | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent | KM estimator | - | - | 0.632 |
| Independent | exponential | - | 0.638 | 0.633 |
| Clayton | exponential | 1 | 0.709 | 0.676 |
| 5 | 0.856 | 0.799 | ||
| Gumbel | exponential | 4 | 0.906 | 0.862 |
| Frank | exponential | -5 | 0.600 | 0.600 |
| 5 | 0.733 | 0.714 | ||
| FGM | exponential | -1 | 0.609 | 0.609 |
| 1 | 0.666 | 0.658 | ||
| GB | exponential | 0.5 | 0.617 | 0.617 |
| 1 | 0.606 | 0.606 |
| Copula | marginal distribution | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent | KM estimator | - | - | 0.679 |
| Independent | exponential | - | 0.821 | 0.625 |
| Clayton | exponential | 1 | 0.889 | 0.626 |
| 5 | 0.958 | 0.635 | ||
| Gumbel | exponential | 4 | 0.997 | 0.665 |
| Frank | exponential | -5 | 0.753 | 0.624 |
| 5 | 0.924 | 0.632 | ||
| FGM | exponential | -1 | 0.777 | 0.623 |
| 1 | 0.865 | 0.626 | ||
| GB | exponential | 0.5 | 0.786 | 0.624 |
| 1 | 0.764 | 0.623 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





