1. Introduction
Air pollution from road traffic is
a combination of exhaust emissions (a mixture of gaseous pollutants and
particles from fuel combustion and the volatilization/degradation of lubricants
at the tailpipe) and non-exhaust emissions (mechanical abrasion of brakes,
tyres and road surfaces, resuspension). Road traffic is a major contributor to
non-exhaust emissions which are dependent on weather conditions [1–3], topographical factors of the
built environment in cities as well as road structures [4–6].
Deterioration of air quality in
cities has become a major concern together with environmental and health
impacts [7–13]: there
are more than 430,000 premature deaths every year in Europe and 7 million/year
around the world
[14,15]. Many phenomena can occur during particle exhaust emissions, such
as: atmospheric resuspension of particles, mixing – dispersion, coagulation,
evaporation, dilution and turbulence, resuspension
[16–23]. Kwak et al.
[24] indicated that particles
emitted by tyre wear, in laboratory tests, are in the range of 2–3 μm, while
road surfaces create larger ones. Measuring particle emissions from the
tyres-road wear is complex, in particular because it involves mechanical abrasion
and the resuspension of wear particles deposited on road surfaces
[25]. In fact, a non-negligible
percentage of particles may be deposited. Compared to fine and ultra-fine
particles, these are mainly of large size
[26,27]. Jeong et al.
[28] confirmed that Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd, Sn, Sb, Pb are the major
non-exhaust pollutants emitted by road transport. Indeed, the significant
components of tyres are SBR styrene rubber, butadiene rubber, natural rubber,
organic peroxides, nitro compounds, selenium zinc, and other metals
[29–31]. Kreider et al.
[32] confirmed that the elements
(Ca, Fe, K, S, Zn, Mg, Al, Si, Ti) are emitted from road materials. Zinc
compounds is a tyre marker
[33,34]. Hildemann et al.
[35] and Gustafsson et al.
[36] cited Zn among the elemental compounds. Dahl et al.
[37], Pant and Harrison et al.
[38], and Harrison et al.
[39] found that tyres contain about
1% Zn as inorganic Zn such as ZnO and ZnS, and organic compounds. Khardi et al.
[6] suggested the S
and Zn as tyre tracers. Beji et al.
[40], Khardi and Bernoud-Hubac
[27] confirmed that C, S, Cr, Cu, Ce and Zn compounds are emitted into
the air by road vehicles. They confirm that Zn is a particle tracer of tyre
emissions. Particles emissions are generally thermal in nature due to friction
with the road surface. Harrison et al.
[41] indicated that the emitted non-exhaust particles are in both the
coarse (PM2.5-10)
and fine (PM2.5)
fractions, with a larger proportion in the former.
Effects of particle emissions by
road traffic on human health and environment have been regularly reported
[42,43]. The major observed impacts
are related to the cardiovascular system (strokes and ischemic heart diseases),
lungs inflammations, asthma, chronic lungs diseases, cancers, pulmonary
fibroses, …
[10,22,23,44–53]. It would be very complex and useless to indicate all the found
references on this topic. The literature describing health impacts and
toxicological studies regarding road traffic emissions is very extensive and
reflects the severity of transport particulate emissions. Many given analyses
are based on particle sizes but very rare analyses resulted in studies of these
impacts according to the chemical composition of the emitted particles.
Chronic diseases such as asthma,
cancers, and heart diseases are well documented in the open literature; they
are associated to pollutant exposure. It is confirmed that road transport
contributes to the described impacts
[21–23,39,41,54].
Few reliable and specified
information exists on biological mechanisms and toxicology of non-exhaust
particles
[55–59],
especially those having the potential to penetrate cell membranes, and / or
penetrating the lung alveoli
[16,54,57,60–62].
Liu et al.
[54] suggested that highest
particle counts were observed in the size range of 0.25-0.5 µm, and can be
extended to the interval 0.25-10 μm. Particles can reach the alveoli, thus
causing toxic effects in the lungs
[63]. Particles less than 0.5 µm enter the bronchi and lungs. Between
0.1 µm and 1 µm fine particles can therefore penetrate deep into the
respiratory system. This highlights the link between the mechanical properties
of the particles and the risk that they are deposited in the respiratory
system.
Some of them can pass through the
lung epithelium and can be transported in the blood to other organs
[64]. The main effect on cells
would seem to be the formation of reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress.
Genotoxic damage was observed with
an increase in micronucleus formation and TNF-alpha release from lung
macrophages
[65],
which can have serious health consequences
[66,67]. Kreider at al.
[68] suggested a risk assessment calculation for humans considering
exposure duration.
The largest particles are stopped
by inertia in the nasopharyngeal segment, but the smallest particles (less 2
µm) are also stopped by Brownian diffusion. Above 10 µm particles are stopped
by the nose and do not enter the respiratory system.
This paper focuses on the
so-called non-exhaust emissions by the tyre-road friction. It presents an
original experimental work related to the particle’s emissions by the abrasion
of tyres and road in real driving conditions in urban, suburban and highway
areas. Therefore, the results on emission factors are the fruit of a new method
coupled with a fine and efficient analysis. The effective new method, based on
Multivariate data analysis (Hierarchical Classification on Principal Components
‘HCPC’), was used to investigate clusters of size distribution and pollutants
identification (chemical characterization). The method was carried out in
three-stage: Initially, a specification of the most predominant granulometric
intervals of tyre-road emissions; Secondly, an analysis of the chemical
composition of the emitted pollutants and their importance; Finally, the
provision of the emission factors of the road-tyre pollutants supported by a
solid statistical analysis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Set-Up
Experiments were carried out in
and around the city of Lyon (Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Region, France) in three
different experimental conditions (urban, suburban and highway) during the
summer period. The road traffic was very heavy in Lyon and its suburbs with
about 180,000 vehicles a day. 70% of the vehicles travel less than 3 km
[69]. As regards the highway,
85,760 vehicles travel every day, of which
were trucks and 81% light
vehicles [70].
Table 1 presents measurement features (type of road, travelled distances,
average meteorological conditions) during experiments in real-time driving
conditions. The experiments were carried out on a total distance of 1,950 km:
450 km in urban areas, 650 km in suburban boulevards and 850 km on the highway
(Figure 1).
Table 1.
Real driving conditions (wind speed less than 4 m/s).
Table 1.
Real driving conditions (wind speed less than 4 m/s).
| Type of route |
Distance travelled per trip |
Average temperature (°C) |
Strength of the wind (km/h) |
Relative humidity (%) |
| Urban (U) |
45 km |
17 |
7 |
45 |
| Suburban (SUB) |
65 km |
15 |
11 |
39 |
| Highway (H) |
85 km |
18 |
8 |
53 |
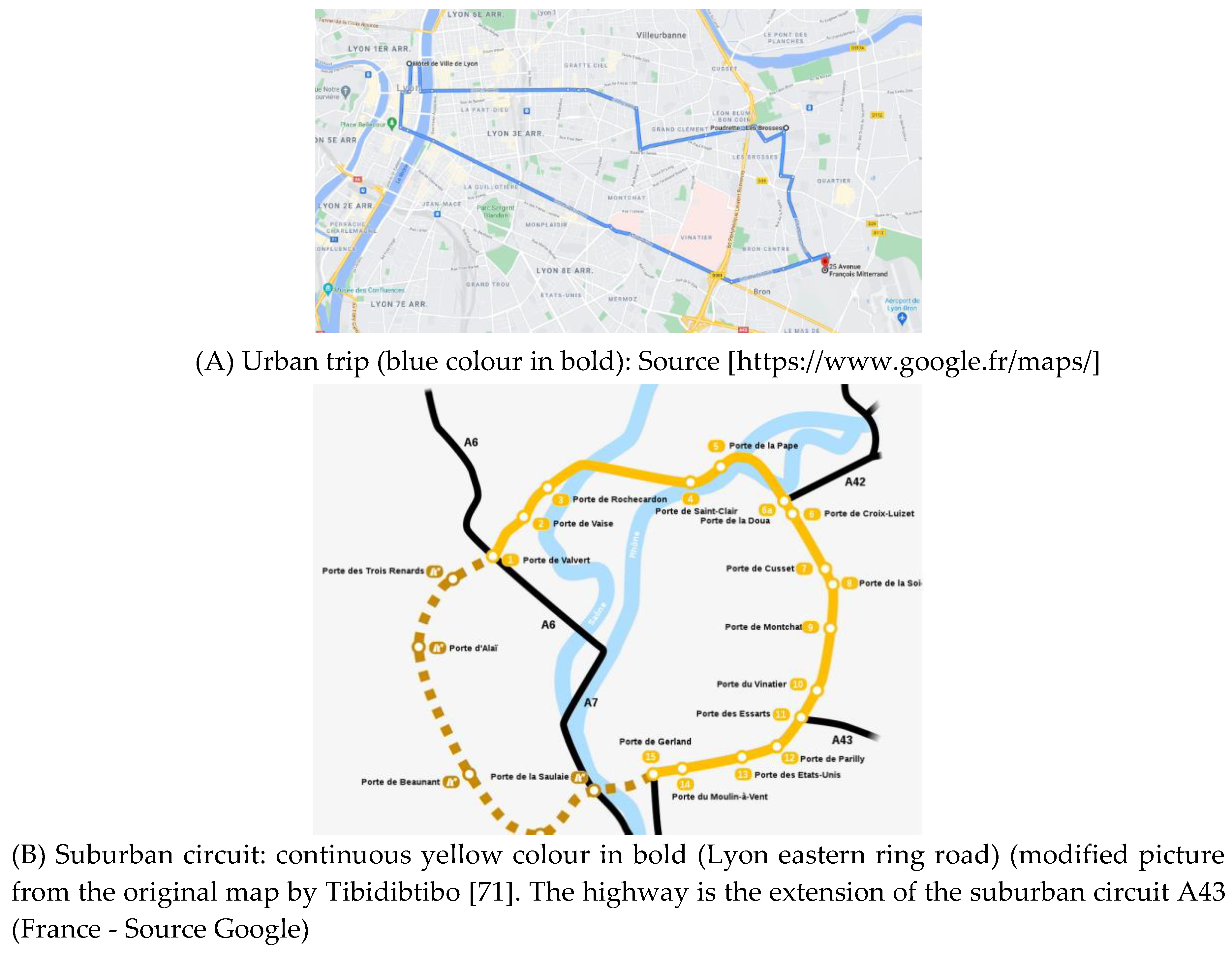
Figure 1.
Experimental areas (A, B) and altimetry (C) where data were collected in urban, suburban and highway areas in real driving conditions.
Figure 1.
Experimental areas (A, B) and altimetry (C) where data were collected in urban, suburban and highway areas in real driving conditions.
The topographical map of the city
of Lyon (surface area, 47.87 km2) and its surroundings are given in the
Figure 1. The average altitude
of the city and surrounding area is 210m, the minimum is 161m, and the maximum
is 333m (Altimetry of Lyon, 2023). The urban environment of Lyon presented an
average road gradient of 12%, with the steepest gradient at 30%. In suburban
and motorway environments, the average gradient was 3 % on 70% of the
experimental routes, and 4.2% on the remaining 30%.
The instantaneous speed of the
vehicle and position have been collected using a global positioning system
under real-world monitoring with a sampling of 1 Hz. The duration of each experiment depended on the road type and the fluidity of the
road traffic.
In this experimental work, the
simultaneous measure of sizes of particles (granulometry) together with the
collect of particles on carbon adhesive tabs (ϕ =12 and 47 mm) and on
polycarbonate Whatman® Nuclepore™ Track-Etched Membranes (ϕ = 25 mm,
pore size 0.4μm) enabled the analyses of their chemical composition and
identification. Membranes were considered free of traces of the chemical
elements Si, Sb, S, Fe, Mg, and Na. They ensured no contamination (high
chemical resistance, good thermal stability, smooth flat surface for good
visibility of particles). No distinction can be made between tyres emissions
and road abrasion emissions. All measuring instruments
were synchronized. An electronic device, having a fixed impedance, has been
used by injecting a square wave signal every 5 minutes to guarantee a
synchronization between measurement systems. An optical particle counter ‘OPC’
GRIMMTM EDM 180
[73]
was used to measure particles concentrations (diameter range [0.35µm,22.5µm])
with a flow rate of 1.2 l/min and 0.1μg/m3 resolution. This OPC is a
real-time measurement in ambient air of PM10,
PM2.5 and PM1. It is considered as an automated monitoring system using a
diagnosis software system. It has an efficient counting statistics and
reproducibility of dust concentrations with low to high levels. GRIMMTM EDM 180
has been calibrated in the Grimm Group company using a dolomite dust. In
comparison with other existing laboratory systems used in this research field,
the preference for the GRIMM system was due to its easy operability and
effectiveness (small size, light weight, high battery life, low power
consumption, large data storage capacity, 12 V power supply, …). All the used
data collection systems were synchronized thus allowing a good results
explanation of the observed data. Before every measurement campaign, zero
calibration was regulated on the GRIMM. During experimentation, a Global
Positioning System (GPS) was used to collect the vehicle trajectory parameters,
its speed and acceleration. Temperature of brake pads was also recorded in
real-driving conditions. All measured signals were synchronized.
Each measurement was followed by
blank tests lasting 15 minutes each in order to remove any impurities that may
have been present in a residual way in the GRIMM pipe. Summer tyres were used
to study particle emissions caused by the abrasive contact between the tyres
and the road surface.
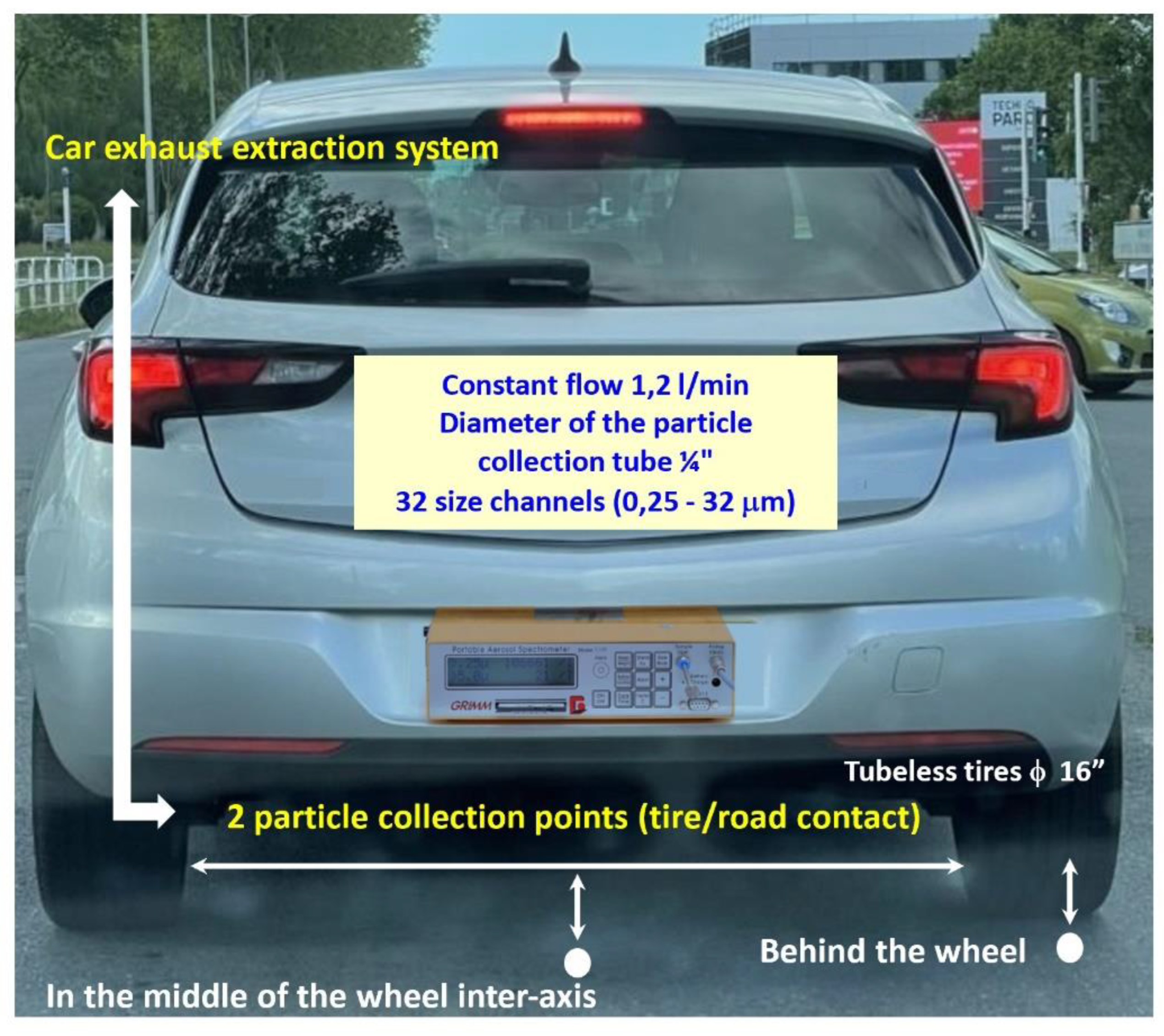
The two following sampling points
were: 1. In the middle of the wheel inter-axis, 3 cm from the road surface. 2.
Behind the wheel at 2 cm from the middle of the wheel and 3 cm from the road
surface. The inlet sampler pipe was fixed in the vertical axis of the wheel.
The particle collection tube has a diameter of ¼”.
Figure 2 shows the
experimental configuration of the light vehicle.
Figure 2.
Two measurement points: 1. Behind the wheel (2 cm from the middle of the wheel and 3 cm from the road surface). 2. In the middle of the wheel inter-axis, 3 cm from the road surface. The particle collection tube has a diameter of ¼”.
Figure 2.
Two measurement points: 1. Behind the wheel (2 cm from the middle of the wheel and 3 cm from the road surface). 2. In the middle of the wheel inter-axis, 3 cm from the road surface. The particle collection tube has a diameter of ¼”.
The exhaust pipe was located
outside of the vehicle on the left rear side. Thus, the installed car exhaust
extraction system is a 6 cm diameter tube attached to the exhaust pipe (20 cm
length, followed by a 90° elbow and a 170 cm high tube). This configuration had
the advantage of avoiding a mix data collection between exhaust and non-exhaust
emissions. Control tests were carried out to ensure that the exhaust and
non-exhaust mixture of emissions was not collected by the measurement system.
Indeed, the sampling probe was placed in the centre axis between the wheels and
at a 3 cm distance from the road surface. This ground distance confirmed the
absence of exhaust particles in the collected data. However, measurements in
this position showed that resuspension-induced particles were found. The
position of the sampling, due to the screen effect of the two wheels,
guaranteed that 98% of the collected particles were emitted by abrasion due to
contact between the tyres and the road. The tests were carried out on days when
road traffic was very low, off-peak hours, to avoid cross-contamination from
other vehicles.
Brake system temperature control
and exhaust emissions: the control of the brake temperature was an important
element to analyse the exhaust emission rate, and subsequently the potential
contamination of the collected tyre-road data. Indeed, the increase in brake
friction could have had an impact in terms of contamination of measurements at
the tyre-to-road contact point. This is one reason why the brakes temperature
was followed during the experiments because the latter gave an information on
their emission rate. A specific system to monitor these emissions was not
installed but the brakes temperature was controlled in case some data seemed
inconsistent. For this reason, tapered metal plates were installed on the back
of the four wheels to avoid this possible contamination. The measured brake
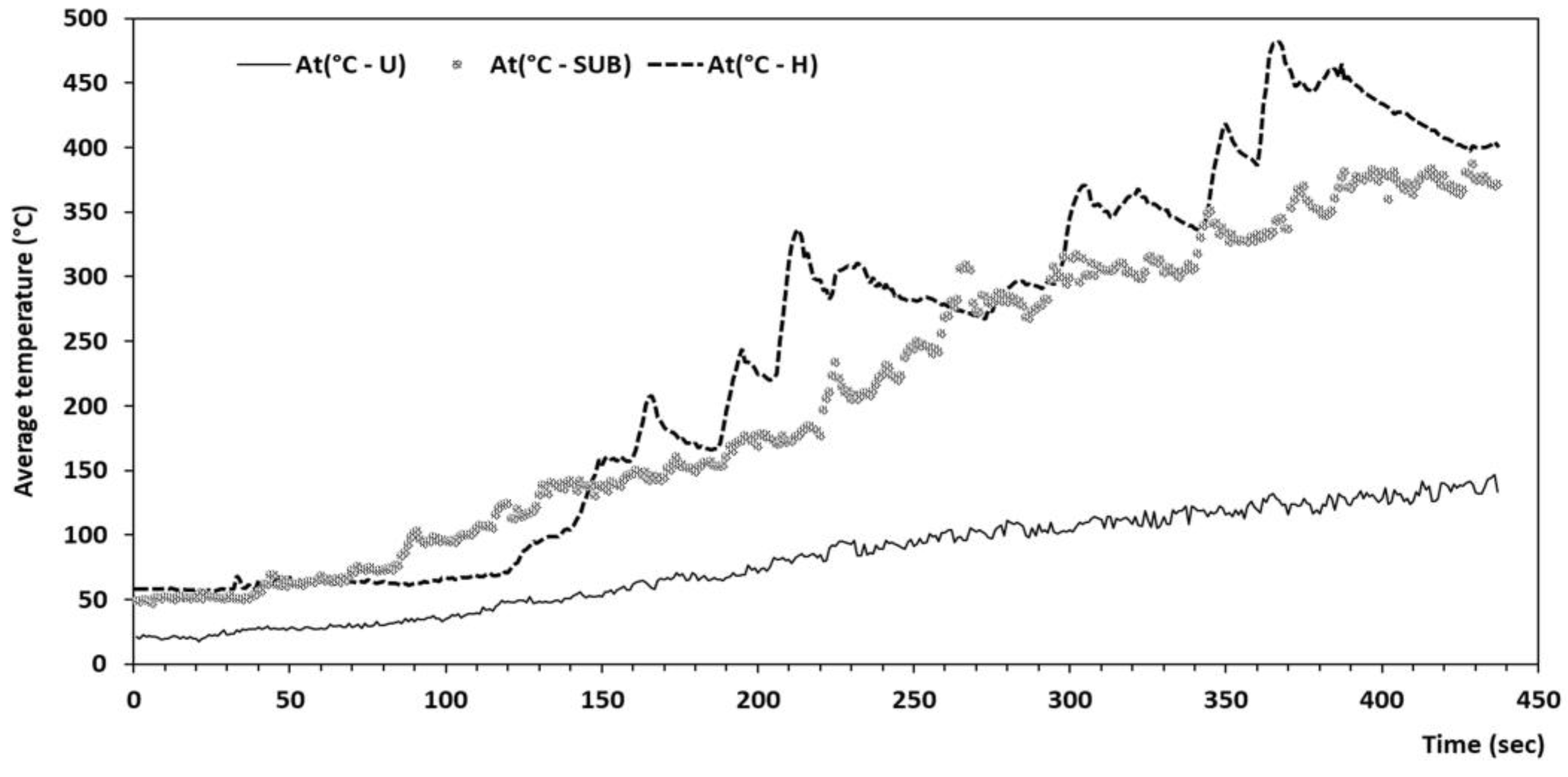
temperature is given in the following Figure 3:
Figure 3.
Control of average brake temperatures during road travels.
Figure 3.
Control of average brake temperatures during road travels.
Temperature of brakes has the
advance to be able to give to the research in tribology or dynamics of the
contact some knowledge elements on the behaviour of the braking systems. The
measured average temperatures in urban, suburban and motorway experiments are
respectively 17°C, 47°C and 56°C. The maximum temperatures reached are
respectively 147°c, 387°C and 482°C. The increase of the brake’s temperature
occurs largely during the suburban and highway experiments (braking due to
speed). With the dynamics of the vehicle in real driving conditions, no
contamination of the experimental data was observed. Moreover, the results of
the presented chemical analyses confirmed this. This precaution, to which was
added the installation of a casing fixed on the exhaust pipeline extended up to
one meter above the roof of the vehicle, enabled the avoidance of this double
contamination through brake and exhaust emissions.
The aim of this paper is to
calculate emission factors for pollutants emitted by tyre and road abrasion,
the experiments followed the established and known procedure from the
literature. Indeed, an emission factor is applied for each vehicle category in the
fleet. In the case of the experiments, it was expressed as the number of
pollutants per kilometer (#/km), designating the number of pollutants emitted
by the vehicle over one-kilometer journey. It depended mainly on: the vehicle
type, its engine and technical features (carburation: petrol, diesel, LNG,
hybrid... and cubic capacity: small, medium, etc.), its date of entry into
service (which determines its age and therefore its wear), average vehicle
speed, track gradient, average traffic speed, and the proportion of the journey
made with a cold engine.
The vehicle used was an ASTRA CDTI
(year 2020) and had the following technical specifications: - Fuel type
(Diesel) - Engine displacement (1496 cm3 Inline 3) - Horsepower (120
HP) - Maximum torque (221 lb-ft) - Top Speed (210 km/h).
The proportion of the experimental
journey carried out with a cold engine was 2%. 84% of Lyon’s streets are
limited to 30 km/h, i.e., 610 kilometres out of 727. The rest of the streets
are limited to 50 km/h. Average speeds during the urban, suburban and motorway
tests were 40 km/h, 80 km/h and 125 km/h respectively. Data relating to the
city of Lyon (topography, slopes, and percentage of road slopes ...) are
described above and have been represented in
Figure 1.
2.2. Analysis of the Tyre-Road Surface Particles by SEM-EDX - Statistical Analysis
Analysis of the collected
particles from dust sampling in real driving condition on the carbon membranes
was carried out with the Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) associated with
Energy Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX)
[74] for identifying the elemental composition of pollutants. SEM uses
an electron beam able to scan a focused stream of electrons over a given
surface to produce an image with a resolution less than 1 nm. Indeed, the
electrons interact with the atoms of the sample to analyse giving signals of
chemical composition of the collected pollutants. The combination of these two
techniques provided an identification of the pollutants elemental composition.
The data generated consisted of spectra showing the chemical elements
collected. Thus, energy of individual photons was measured to establish spectra
representing the energy-dependent distribution of X-rays. The X-photons were
captured by a solid-state detector, a lithium-doped silicon semiconductor,
cooled with liquid nitrogen. X-photons cause ionization in the semiconductor.
Free electron-hole pairs migrate under the effect of the polarization electric
field and cause current pulses whose height is proportional to the energy of
the photon. One can separate the impulses according to their height, and thus
count the photons incidents according to their energy. This method has a good
sensitivity in particular for photons with an energy between 0.2 and 20 keV.
The number of photons is assessed and the count rate is expressed in count per
second (cps). The main known limitation of this chemical analysis system is the
width of each peak of the spectrum. Indeed, the enlargement of a peak could
reflect the superposition of two or more chemical elements whose energy is close.
The greater the enlargement of the peak, the more difficult the possibility of
identifying a chemical element. For morphological analysis and the
microanalysis of the collected dust, the use of the JSM-6510LV (JEOL Ltd.) was
privileged as it is a high-performance SEM for a fast characterization of
chemical elements. The JSM-6510LV low vacuum scanning electron microscope
(SEM), with its high resolution of 3.0 nm at 30 kV, is a high-performance SEM
for the reliable identification of pollutants.
The JSM was coupled to an EDX
spectrometer (Oxford Aztec-DDI X MAXN 50, JEOL
[75]. SEM analyses were performed
at different magnifications and provided specific information on the
composition of the particles. The analyses of the particles gave a comparison
of their EDX spectra: retro-scattered electrons; intensity varying between 20
kV and 30kV (high resolution of 3.0 nm at 30 kV); working distance equal to
12mm (accelerating voltage from 500V to 30 kV); variation of pressure between
10 and 270 Pa; magnification x5 to 300,000 (printed as a 128mm x 96mm
micrograph); objective lens apertures: three position, controllable in X⁄Y
directions); maximum specimen size: 125 mm
∅ full
coverage; specimen stage: eucentric goniometer (X = 80 mm, Y = 40 mm, Z = 5-48
mm, R = 360° (endless), tilt -10⁄+90°), computer controlled 2, 3 or 5 axis
motor drive. The resolution is much higher compared to optical microscopes,
with a greater focal depth.
The fully automated INCA software
(ETAS Company) was used to analyse the collected particles. The surfaces
analysed for the pollutants chemical identification were all equivalent, and
were of the order of 24 mm2. INCA offered a wide variety of efficient and fast
functions to analyse data (flash programming, measurement data analysis,
calibration data management, and automated parameters optimization) [76]. The combined system used a
motorized turntable that enabled automatic analysis of 1,000 particles for each
sample. In addition to the INCA software, the application of the HCPC method
for the collected data provided structure of data in terms of a partition on
each granulometry interval, an identification of chemical elements, and
consequently gave a hierarchy structure of the sets of different identified
particles. This method was favoured over other simple classical methods that
exist in literature, such as Student’s t test, …. It is based on numerical data
classification methods [77,84] with a simplified application framework. Indeed, it is complete,
efficient and provides excellent quality results. This method allowed the
following analysis process:
- -
Original data - Extraction of particle size ranges
- -
Identification of intervals in order of importance
- -
Assignment of intervals to identified sets of different identified particles groups
- -
Homogenization of the sets according to their predominance. This step assumed, a priori, that the sets of the same identified particles were homogeneous
- -
Start of the calculations and then construction of the sets of particles
- -
Result with a hierarchy tree by granulometric intervals and by chemical element sets, having no consequences on relative loss of inertia of the used calculation algorithm
- -
The last processing step checks error propagation and providing means, Min, gravity centres, …
Data were processed with the R
software [78] which is
a free and open software environment for statistical computing. It compiles and
runs on a wide variety of platforms. It is a language of programming.
Processing of numerical data with R [79] followed the well-numerical known steps [80–82]:
- -
Import dataset in a new data matrix data
- -
Build this matrix of the scaled data and apply the Ward’s minimum variance method hierarchical clustering algorithm
- -
Identify and assess percentages of elements inside the same set. This step required the separation of experimental data on separate homogeneous sets of particles having equal variance that could minimize inertia in each set of data. This allowed the division of each set of data into three data sets (urban, suburban and highway), with the advantage of giving centroids of sets that measured how coherence was inside each set of identified particles
- -
Choose the number of sets of identified particles that seemed relevant based on data measurements
- -
Build the tree and interpret the obtained sets using the principal component analysis of FactoMineR package
- -
Interpret the partition of each set versus the obtained percentages of each chemical element
- -
Based on the previous steps, data analysis of results was grouped by type of route (urban – suburban – highway trips), granulometry interval and percentage of chemical elements which were identified.
Experiments in real-driving
conditions were carried out by the same driver and in the same atmospheric
conditions, allowing complete synthetic results without statistical bias,
confirming and appreciating the quality of homogenization step previously
announced. These analysis data exclude braking emissions: experiments were
carried out in such a way that the particles emitted by the brakes were not
recorded and did not impact whatsoever. In addition, metal wrenching and brakes
abrasion were not considered. Whenever braking occurred, the corresponding data
was systematically deleted. Particles were then classified in a family
according to their chemical composition and the result is given in the form of
a spectrum. As previously described, energy of individual photons is measured
to establish spectra representing the energy-dependent distribution of X-rays.
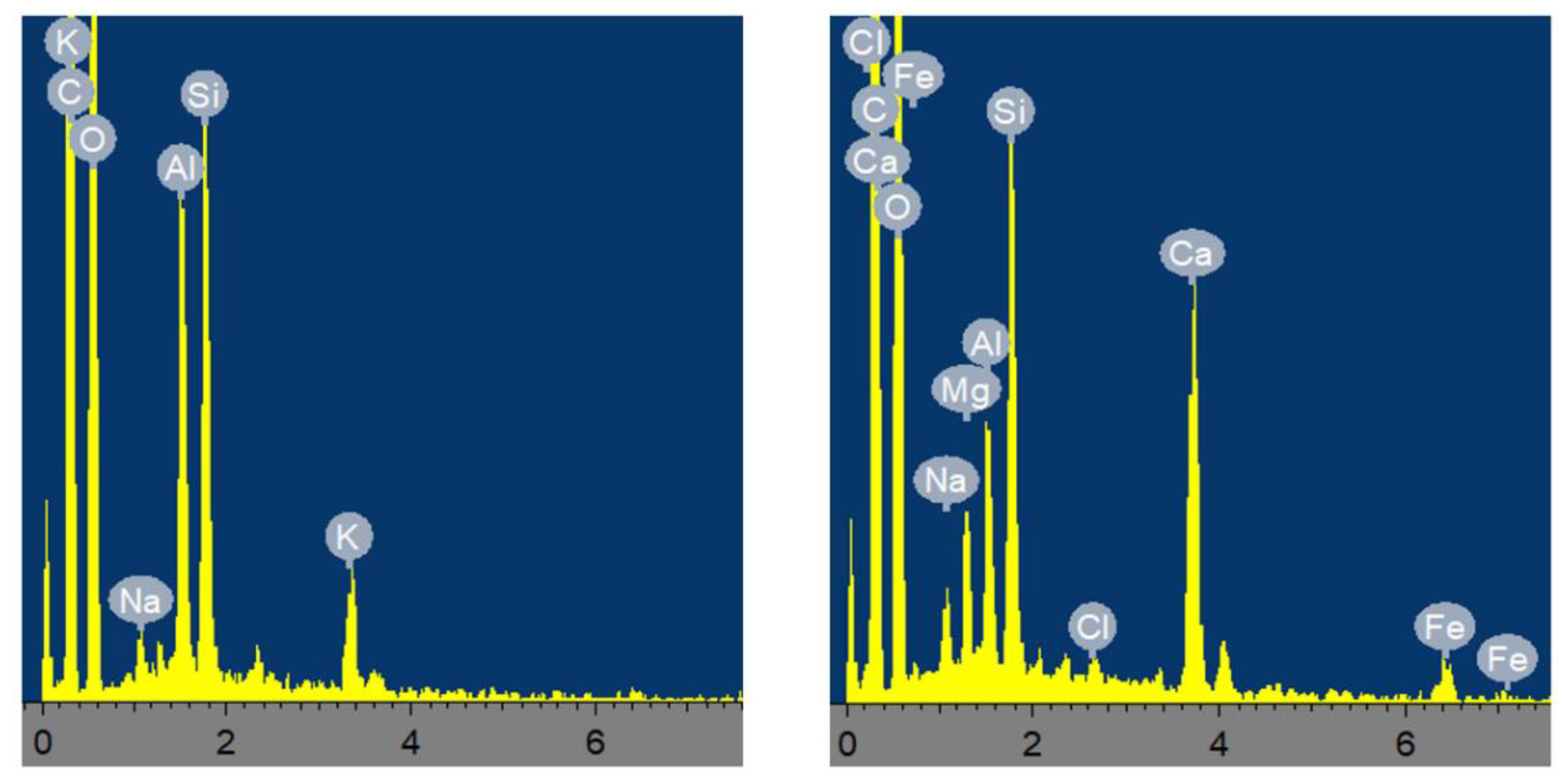
Two concrete examples of spectra
are given below (Figure 4). An elemental composition analysis was carried out using the SEM
EDX to obtain an X-ray emission spectrum for the particles. They show a
multitude of chemical elements identified with a net predominance of Si, Al,
Ca, Mg, Fe and their components.
Figure 4.
Example of two SEM-EDX spectra of particles (in Arbitrary Unit – Full scale 2054 cps).
Figure 4.
Example of two SEM-EDX spectra of particles (in Arbitrary Unit – Full scale 2054 cps).
In the spectra of the particles,
different peaks corresponding to C, O, Al, Si, Na, Al, Si, K, Fe, Ca, Mg, Na
and Cl and traces are present. This analysis was conducted spectrum by spectrum
to identify all the particles present on about a hundred sample membranes. The
different set of particles obtained during this analysis were: aluminosilicate,
iron and silicon compounds, iron and calcium oxides, calcium compounds,
silicate without aluminum, calcium phosphate, titanium and copper compounds,
chromium, sulphur and barium compounds, aluminum oxide, zirconium compound and
aluminum compounds, tungsten, …, and chemical traces. Multi-elemental particles
could be found in each set of compounds, with the identification of more than
33% of the total mass in the chemical element. If several elements had a mass
more than 3% in the same set of particles, the heaviest element was considered
and a new set of elements was created. Finally, statistical analysis of the
obtained and identified particle was carried out with the statistical software
R, in particular its FactoMineR package dedicated to multivariate data analysis [84].
This paper uses the identified
chemical elements by the SEM-EDX. Particles emitted from the exhaust,
resuspension and other contaminations, etc., were known, and systematically
eliminated. In fact, this work draws on much of the open literature that has already
provided information on the wide variety of pollutants considered to be
contaminants in this particular case. Larger particles are deposited on a
variety of substrates (buildings, infrastructures, roads, ...). Finer particles
can be deposited by Brownian agitation. When there is any topography of the
area in which particles are emitted, such as a street or neighbourhood, those
with a mass greater than the gas molecules do not follow the air flow which is
responsible for transport or dispersion phenomena. They continue moving in
their original direction in which they were originally emitted. The inertia of
particles allowed them to collide or stick to obstacles in the flow. The higher
the flow velocity, the greater the mass of the particles. In particular, this
phenomenon concerns particles with a diameter greater than 1 µm. For example,
this inertia is commonly used to separate particles according to their size in
cascade impactors or cyclones [2,6,8]. Inertia of chemical species has been used to analyse the
homogeneity of the flow. Chemical species ‘i’ were assessed in all the measured
samples. Calculating the v_test meant applying the following formula [84] for species ‘i’ (i ∈ groups) to verify the
homogeneity degree of flow of particles. These sets consist of chemical
elements with the same properties or the same chemical identification obtained
by a count:
where:
- i: chemical specie (pollutant)
: frequency of the ‘i’ specie in
the set I
: frequency of the ‘i’ specie in
the all sets of data
: the relative number of ‘i’
specie in the set I versus the size
: the relative number of ‘i’
specie in all the sets of data I versus the total size of the sets
I is the set of identical chemical
species, identified by SEM-EDX, analysed for a given surface of the sampling
membrane. This surface may correspond to the total surface of the membrane if
the analysis is performed on a single membrane. In this particular case, the
MEB analysis surface was defined for all the particle collection membranes
v_test is well-known to be
sensitive to the identification sensitivity analysis. It is used in this paper
to categorial variables “i” in terms of chemical identification. This is a
necessary and sufficient condition when sets of species are different.
3. Results
Individual particle analyses
SEM-EDX and global analysis (granulometry - particle size) were performed, as
well as the calculation of the overall values for the data obtained at the
SEM-EDX, this in order to make comparisons. Thus,
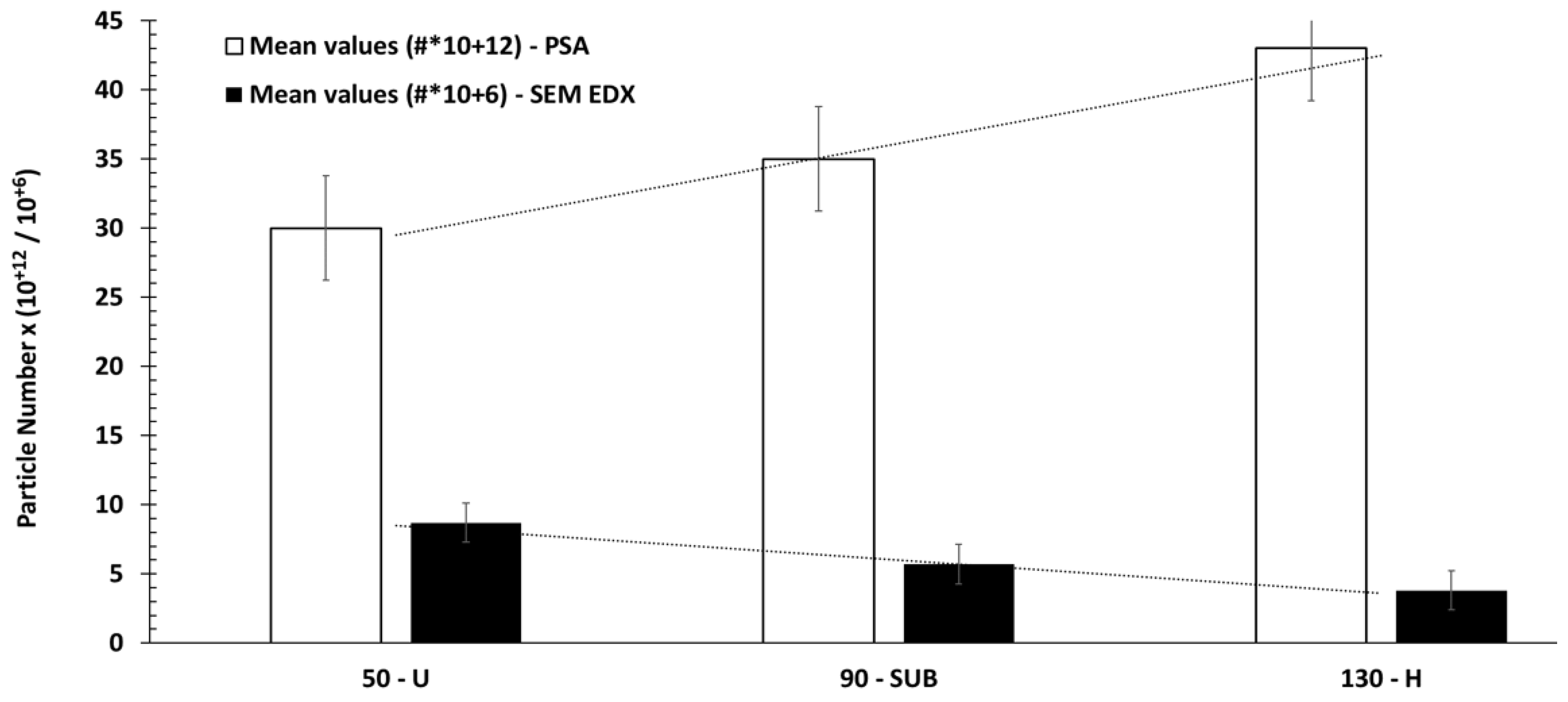
Figure 5 presents the
variations of the mean values of the particle number according to the analysis
by the SEM-EDX of the collected particles on the membranes, and by the particle
size analyser (PSA) vs. the vehicle speed. This analysis was conducted for the
three types of trips: 6 urban trips, 2 sub-urban trips and 3 highway trips. The
respective speed values for the three routes in France (45 km/h, 90 km/h and
130 km/h) represent the maximum values to be performed per site.
Figure 5.
Number of particles depending on the type of analysis (PSA and SEM-EDX) and road (urban, suburban and motorway respectively with speed limit of 45 km/h, 90 km/h, 130 km/h).
Figure 5.
Number of particles depending on the type of analysis (PSA and SEM-EDX) and road (urban, suburban and motorway respectively with speed limit of 45 km/h, 90 km/h, 130 km/h).
First of all, we can see that
there is an effect of the vehicle speed. The number of particles emitted
increases with the speed when measurements are made with a particle size
analyser. A slight inverse effect occurred when analysis was performed with the
SEM-EDX. This behaviour in the number evolution is normal and is due to the
fact that a chosen surface was targeted for EDX SEM analysis. The measured
average particle number values are:
- -
Particle size analyser: (30, 35, 43) 10+12 particles.
- -
SEM-EDX: (8.7, 5.7, 3.8) 10+6 particles.
The ratios (particle size count/
SEM-EDX count) are respectively of 6.4 10+6, 6.2 10+6 and
11.3 10+6 for urban, suburban and highway trips.
The following analysis will make
it possible to extrapolate this number of particles for the surrounding
particles collected throughout the membrane.
Several observations can be noted:
A high factor of more that 10+6 is found between the particle size values and the assessment of the total number of particles from the SEM-EDX results. This seems natural because the collection on the membranes is purely qualitative and serves more for chemical identification.
Despite uncertainties in both particle size count, there is an inversion of the curves between particle size and chemical particle counting as a function of velocity. On the one hand, considering SEM-EDX counting, more particles were collected in the urban area than on highways because of the vehicle speed. This is certainly due to the dynamics of emissions as a function. On the other hand, the inversion of this curve, obtained by the particles collected by granulometry method, seems in favour of the speed. The faster we drive, the more we collect. This Figure confirms that the physico-chemistry is preserved with this double collection independently of the variations that can be observed. Therefore, precaution must be taken when counting particles from the collection on membranes for chemical analyses. In this case, the emission dynamics, which is a function of the speed of the vehicle, could not be confirmed.
In conclusion, counting from the
SEM-EDX is a qualitative count in favour of the chemical identification of
emitted particles. On the other hand, particle size counting is quantitative.
Based on the collection of particle size data, the analysis of the most
emissive particle size intervals is shown in the following Table 2 in order of importance
in terms of emission:
Table 2.
Predominance order of the collected particle sizes (U, SUB, H).
Table 2.
Predominance order of the collected particle sizes (U, SUB, H).
Predominance order
of particle sizes |
U |
SUB |
H |
| 1st class |
<1µm |
<1µm |
<1µm |
| 2nd class |
1-2µm |
1-2µm |
1-2µm |
| 3rd class |
- |
2-3µm |
2-3µm |
| 4th class |
- |
- |
3-4µm |
We can observe in this table that
the grain size range widens from the urban to the motorway emissions. The
particles less than 1 µm are the most present in the three road routes;
followed by interval [1 µm, 2 µm], and finally [2 µm, 3 µm] for the sub and [3
µm, 4 µm] for highway. The synthesis thus provides a general predominance of
particles emitted in the particle size range respectively [<1 µm, 2 µm],
[<1 µm, 3 µm] and [<1 µm, 4 µm] for urban, suburban and highway
experiments.
The percentages of the predominant
particle size classes are 72.7% for the first two combined classes, 21% for the
third and 6.3% for the fourth. The effect of the speed of the vehicle, and
therefore the potential for collecting particles online, is certainly obvious.
These percentages are therefore consistent with what was observed in the
literature [6,17,27,85–87]. The first two particle size classes are known to have the highest
degree of toxicity [88] because they easily penetrate the lungs and cross biological
barriers to be located in vital organs, may cause significant health
consequences.
Number concentrations are
therefore dominated by particles <1μm, while most of the mass was in
particles >1μm. This result agrees with the work of Alves et al. [89]. These authors had found
rather 0.5μm instead of 1μm, which is not really in contradiction with this
result if it is refined further, thus it would not be necessary because it does
not improve the results.
Particle larger sizes were not
collected because they were deposited on the road surface. This finding
completes the obtained results by Iijima et al. [90] in terms of size distribution
(1–10μm and 2–3μm). The results indicated in this article confirm the analysis
made by Liu et al. 54] who identified the variations in particle size range, in particular
in 0,25-4μm interval. In addition, Harrison et al. [41] confirmed in their analysis of
the non-exhaust emissions, i.e., from the brakes abrasion, tyres and wear of
the road surface, as well as from resuspension of road dusts, that the emitted
particles have to be in both the coarse (PM2.5-10) and fine (PM2.5) fractions, with a larger proportion in
the former. The results of the experiments agree with those obtained in the
open literature, in particular with Beji et al. [12], Harrison et al. [41], Liu et al. [54], Piscitello et al. [86] and Zhang et al. [87,91].
Concerning the chemical analysis,
data processing shows a wide variety of chemical elements emitted in real
driving situations. During chemical analysis, the systematic presence of carbon
and oxygen was noticed in all analysed tabs (membranes). This is found in
almost all SEM-EDX analyses reported in the open literature [6,27,40].
In order to identify the
tyres-road surface particles, carbon and oxygen C and O were excluded from the
statistical analysis. In this paper, neither the production modes of particles
nor their shapes were analysed because this would require a very complex
additional experimental work. Individual analysis is very expensive in terms of
computational time. These modes and shapes that could be subject to further
works are: 1. Nucleation mode (particles having a spherical shape with ϕ <
30 nm). 2. Accumulation (particles having an angular morphology with 100 nm
< ϕ < 200 nm). 3. Coarse mode (particles aggregated with 1 µm < ϕ).
Analysing the particle number
collected by analyser allowed to calculate the emission factor for four
different situations: 1. on an urban site where the traffic speed is between 30
and 50 km/h; 2. on a suburban site where the speed limit is 90 km/h; 3. on a
highway where the speed limit is 130 km/h; 4. in a traffic zone on an urban
site in the city of Lyon (France). Granulometric data was collected with ATMO
AURA fixed systems. Among the data collected, the following selection was made:
6 urban routes (U1 to U6), 2 suburbans (SUB1 and SUB2) and three highways (H1
to H3). For comparison, the collection then analyses focus on a series of data
recorded during 4 different days corresponding to a static urban traffic site
(S1 toS4). The data were collected during days when the weather conditions were
identical to the whole other experiments (U, SUB, H).
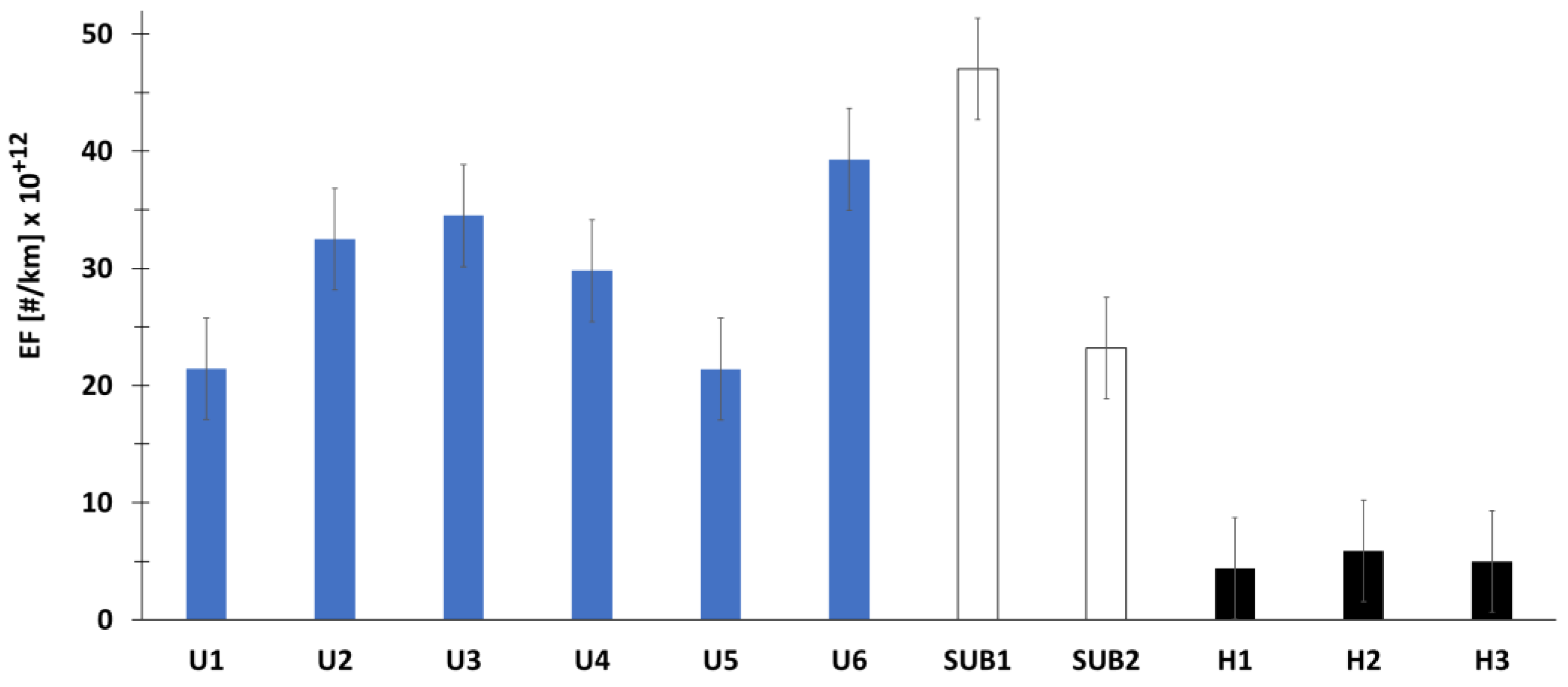
Figure 6 below shows emission factors EF in number of particles per km
travelled (#/km).
Figure 6.
Emission factors for three different driving situations. Maximum authorized speed [Urban ‘U’ (50 km/h) – Suburban ‘SUB’ (90 km/h) – Highway ‘H’ (130 km/h)].
Figure 6.
Emission factors for three different driving situations. Maximum authorized speed [Urban ‘U’ (50 km/h) – Suburban ‘SUB’ (90 km/h) – Highway ‘H’ (130 km/h)].
The emission factors are of the
order of 30 10+12 #/km and 35 10+12 #/km for urban and
sub-urban respectively. We observe that there is a difference between urban and
peri-urban of 5 10+12 #/km. However, on highway, the emission
factor, on average in the order of 5 10+12 #/km, is much lower than
the two previous situations. Emission factor obtained on the highway trip is of
the same order of the magnitude as the difference between urban routes and
suburban driving situations. The number of particles was calculated for a
duration equal to the duration of urban experiments U1 to U6. Finally, for the
urban traffic situation site, we have on average a number equal to 43 10+12
#/cm3 (S). This value (number of particles per unit volume) cannot
be related to an emission factor obtained in real driving conditions. However,
this higher value, in static urban site, can be considered quite high. This is
due to the accumulation of pollutants in a fixed urban site, corresponding to
the ambient air pollution in this urban point location.
The obtained EF for the three
types of experiments are above the value of the euro 6 standard (fixed at 6 10+11
#/km) for both diesel and petrol vehicles. It can also be noted that these EFs
are below of the values corresponding to diesel vehicles not equipped with
particle filter (6 10+13 #/km) where ratios are of 2 (U), 1.7 (SUB),
12 (H) and 1.4 (S). As a reminder, the New European Driving Cycle gave a limit
value of 6 10+11 #/km (Euro 6b) for PN (number of particles per km)
for spark-ignition engines (gasoline, LPG, etc.), including hybrids, and a
limit value of 6 10+12 #/km for diesel engines only, including
hybrids. In the future, we shall be seeing stricter regulations on the limit
values that must not be exceeded.
It can be noted that the number of
particles is quite similar in the city static situation compared to experiments
performed in real driving conditions. This is due both to the dispersion of
pollutants but also to the effect of accumulation in a localized static point.
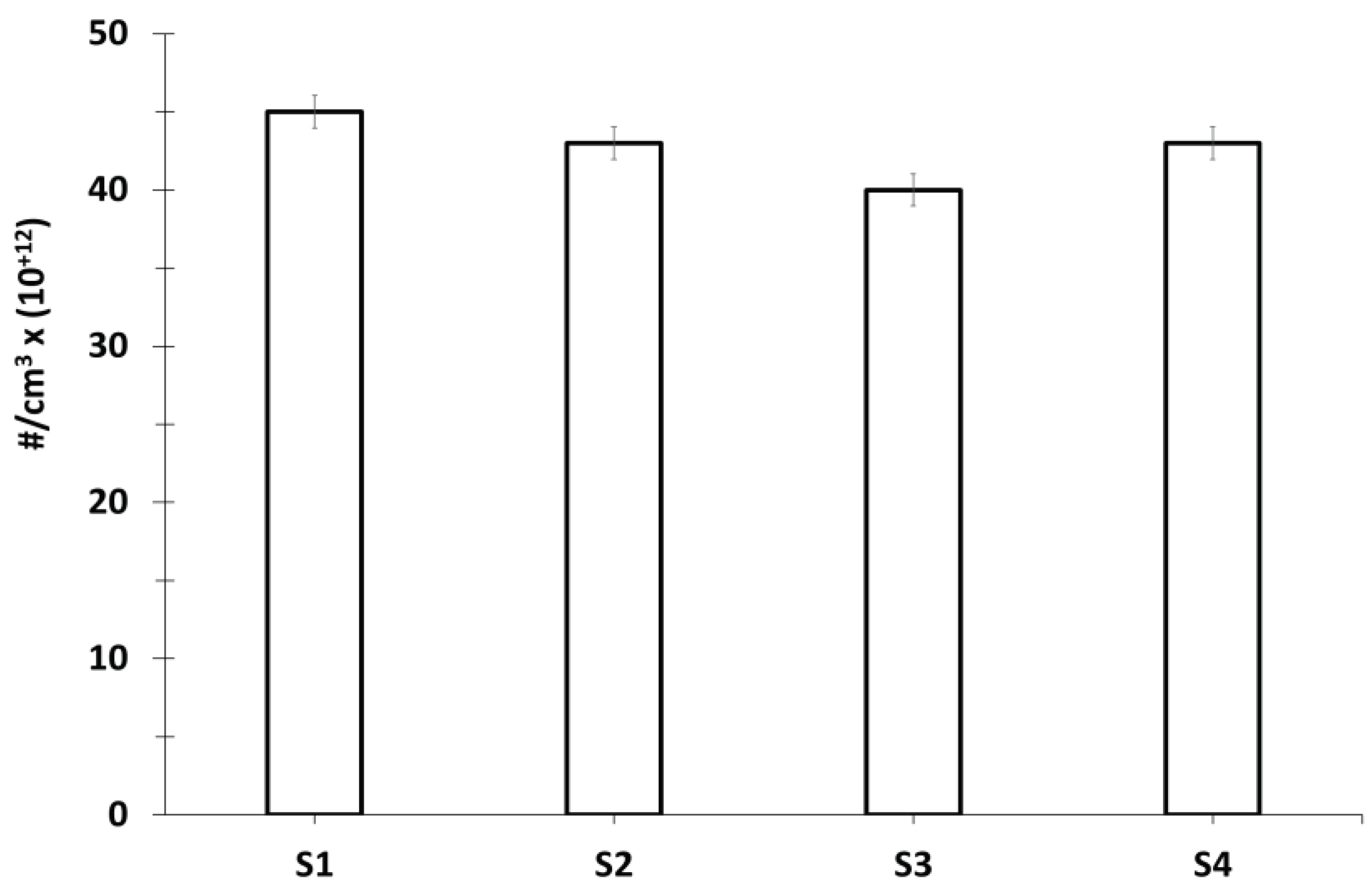
Figure 7 shows the number of
particles per cm3 at this static point in the urban area of Lyon.
For all the performed experimental measurements, with uncertainties, the number
of particles per cm3 is greater in static situation in city (≈ 42.8
10+12 #/cm3) than in real driving situation
(approximately 30 10+12 #/cm3 in urban and 35,1 10+12
#/cm3 in suburban). This is due both to the dispersion of pollutants
but also to the effect of accumulation in a localized unpoint.
Figure 7.
Evaluation of the average number of particles per cm3 in the traffic site, at a fixed location in an urban environment (S1 – S2 – S3 – S4).
Figure 7.
Evaluation of the average number of particles per cm3 in the traffic site, at a fixed location in an urban environment (S1 – S2 – S3 – S4).
These results allowed to evaluate
the average corrective factor ACF between analysis of emission factors obtained
by particle size analysis and those obtained by identification using the MED
EDX. These average factors are respectively 3,4 10+6 (urban), 6,1 10+6
(suburban) and 11,3 10+6 (highway).
Thus, the number of particles used
in the chemical identification of pollutants, obtained by the SEM-EDX analysis,
is multiplied by this corrective factor to obtain the number of particles that
would be analysed online in real driving situation. This analysis enabled to
establish the emission factors by chemical element, as presented in the
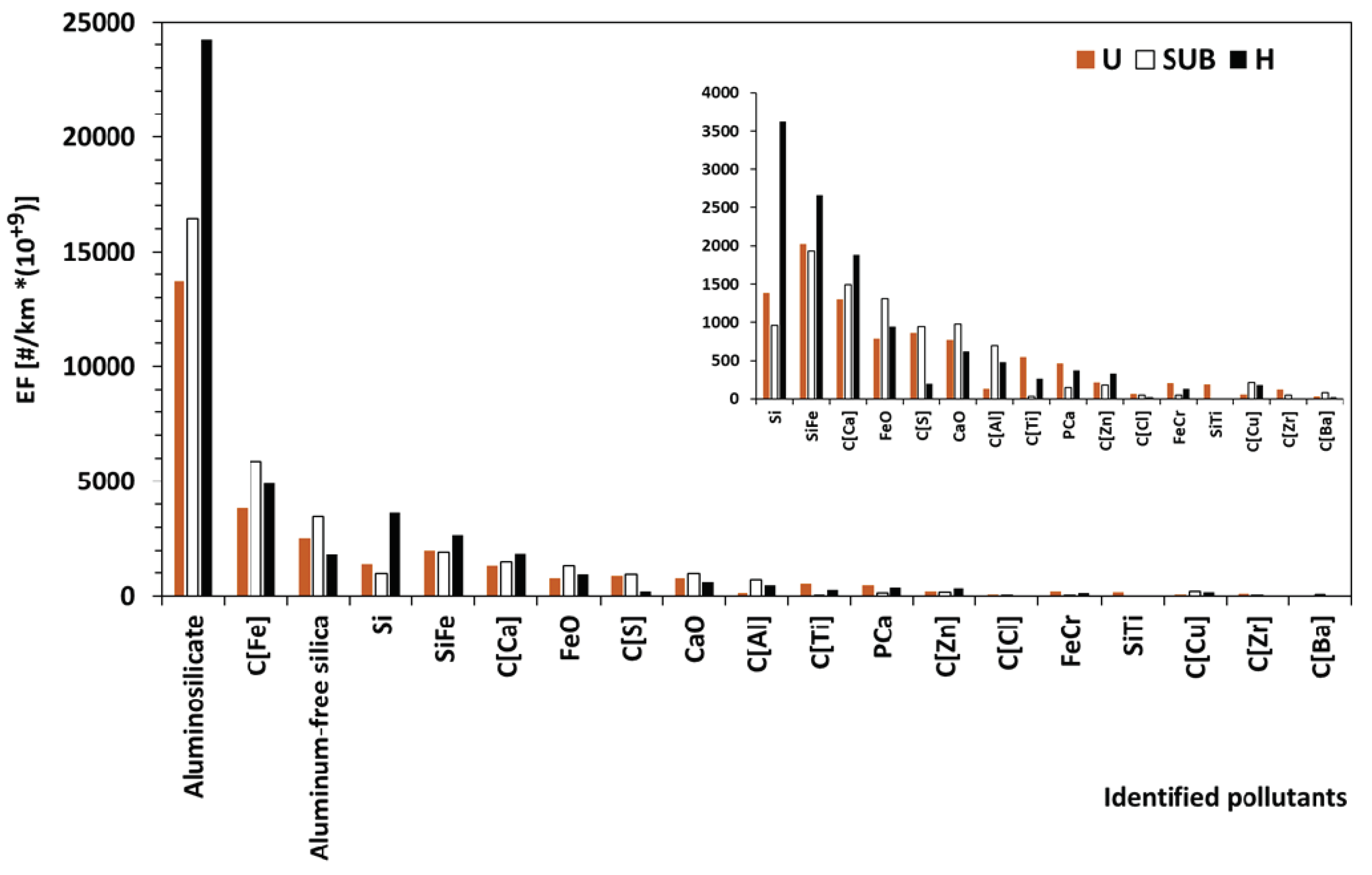
Figure 8 which shows the
average emission factors EF for the 19 identified pollutants.
Figure 8.
Emission Factors for the identified individual pollutants in real driving.
Figure 8.
Emission Factors for the identified individual pollutants in real driving.
We note the predominance of
aluminosilicate, Fe components, aluminum free of silica, Si, SIFe, Ca
components, and FeO. For the rest of the pollutants, the A_EFs are low. This
does not mean that they should not be taken-into-account in any environmental or
health impact analysis, as this will naturally depend on the volume of the
vehicle fleet.
Table 3 gives the emission factors for 19 pollutants identified using the
SEM EDX technique. These are emission factors obtained experimentally in the
region closest to their emission sources (tyres - road surface). Analysis of
pollutants taken individually, EF ranges from 0.003 to 18.142 10+12
#/km.
Table 3.
Emission factor for 19 individual pollutants.
Table 3.
Emission factor for 19 individual pollutants.
Identified pollutants
by SEM-EDX |
Emission Factor
[#/km *10+9] |
Percentages (compared to the total number) |
| 1 |
Aluminosilicate |
18142±597 |
50,9% |
| 2 |
C[Fe] |
4881±175 |
13,7% |
| 3 |
Aluminum
-free silica |
2612±57 |
7,3% |
| 4 |
SiFe |
2206±60 |
6,2% |
| 5 |
Si |
1989±36 |
5,6% |
| 6 |
C[Ca] |
1558±32 |
4,4% |
| 7 |
FeO |
1013±33 |
2,8% |
| 8 |
CaO |
789±26 |
2,2% |
| 9 |
C[S] |
667±25 |
1,9% |
| 10 |
C[Al] |
436±27 |
1,2% |
| 11 |
PCa |
329±17 |
0,9% |
| 12 |
C[Ti] |
281±11 |
0,8% |
| 13 |
C[Zn] |
240±8 |
0,7% |
| 14 |
C[Cu] |
152±5 |
0,4% |
| 15 |
FeCr |
129±9 |
0,4% |
| 16 |
SiTi |
64±7 |
0,2% |
| 17 |
C[Zr] |
58±9 |
0,2% |
| 18 |
C[Ba] |
46±11 |
0,1% |
| 19 |
C[Cl] |
39±11 |
0,1% |
By way of comparison, the euro 6 standard is set at 6 10+11 #/km for both diesel and gasoline. For diesel vehicles not fitted with a filter, the given value is 6 10+13.
Experiments do not take into-account a heterogeneous mixture of components from (P, Cl, Fe, Ba, Cr, Zr) which represents a percentage of less than 0.1% of the total number of particles identified.
Pearson and Spearman correlations [92] applied to the data according to the different variables (urban, suburban and highway routes, the same vehicle equipped with the same tyres, the weight of the vehicle, nature of the road, …), showed that correlations were significant (with p< 0.02).
In addition, analysis of the inertia of chemical species ‘i’ has been carried out to confirm the homogeneity of their identification. Assessment of v_test was also done especially for the comparison between identified pollutants and their numbers. Characterization of each pollutant and the significance test was calculated:
v_test is equal to 1.92 for urban sets of data of pollutants, 1.97 for suburban, and -1.87 for highway (p ≌ 5%). The inertia of chemical species, in the three trips, is definitively homogeneous, and analysis is therefore considered significant (v_test ≌ ±2).
It should be remembered that this finding completes and provides additional information to the work by Dahl et al. [37], Panko et al. [85], Piscitello et al. [86], Iijima et al. [90], Zhang et al. [92] and Kaul and Sharma [93]. Piscitello et al. [86] had confirmed that the emission rate of the non-exhaust pollutants reached 90% by mass of total traffic-related PM emitted. They gave emission factors as follows: 0.3 mg/km to 7.4 mg/km for tire wear; resuspended dust: 5.4 mg/km to 330 mg/km.
Finally, an attempt was made to approximate the EF of the PM10 and PM2.5 from the calculations by Zhang et al. [91]. Indeed, by assessing the density of those two major air pollution determinants, with a conversion of the number into mass and assuming that all the particles are identical and spherical, the obtained FE is of 1.45 mg/km for PM10 and 0.35 mg/km for PM2.5. These FE values are close to those obtained by Zhang et al. [91] (0.21 mg/km for PM2.5 and 1.27 mg/km for PM10), who carried out experiments on a tyre dynamometer. The small difference can be attributed to the fact that this new additional work assesses all the emissions from the tyre-road surface wear and not the emissions from the tyre alone.
This shows that the new methodological approach used in this paper is particularly effective in assessing pollutant emission factors. It is a new alternative to existing methods that are sometimes very difficult and costly to implement. In addition, Alves et al. [89] had generated wear particles on a road simulator to study the interactions between tyres and a composite road surface. They found that the emission factor due to wear between their particular road surface and the tyres was of the order of 2 mg/km. On the one hand, work carried out on any simulator under controlled conditions often deviates from reality or from actual vehicle use. On the other hand, this estimate is not very far removed from the new results being produced and obtained with experiments carried out in real driving situations.
4. Conclusions
This paper presents an original experimental approach combining collection of particles emissions induced by the tyres-road surface wear in real driving conditions, in urban, suburban and highway routes. Comparatively, the data was collected on a site located in the city, on a boulevard where traffic is very important. To determine the chemical compositions and then emission factors of particles emitted by tyre-road surface wear without contamination from brake dust, measurements were performed in real driving conditions. The SEM-EDX has been used to identify the measured chemical elements and their nature. Predominant particles emitted by tyres-road surface have been analysed and emission factors for 19 identified pollutants assessed for the first time using this new approach. The major findings of this study can be summarized as follows:
1. The mainly most measured tyres-road surface particles were smaller than 1 µm for the three road routes; followed by interval size particles [1 µm, 2 µm]. Then, in the third position we have the size range [2 µm, 3 µm] for suburban and highway; and in the fourth position the range [3 µm, 4 µm] for highway alone. It should be noted that particles of sizes between 2 and 4 µm are emitted in urban, between 3 to 4 µm in suburban experiments but at low proportions due to emissions dynamics (vehicle-tire-pavement) related to the movement of the vehicle and the tribology of the materials that constitute the tyres and the road surface.
2. Data processing showed a wide variety of chemical elements emitted in real driving situations. The systematic presence of carbon and oxygen was noticed.
3. Emission factors EF were calculated on the basis of granulometric and global chemical analysis of the measured date: average values for all measured pollutants are 30 10+12 #/km and 35 10+12 #/km respectively for urban and sub-urban. However, on highway, EF is equal to 5 10+12 #/km, about 6 to 7 times lower than the previous two. Analysis for pollutants taken individually, the EF ranges from 0.003 to 18.142 10+12#/km. Significance test analysis was carried-out for the identified pollutant and their EF. v_test is found to be varied between 1.87 and 1.97 (p ≌ 5%). The inertia of chemical pollutants is definitively homogeneous, and analysis is therefore considered significant because the v_test is ≌ ±2.
4. The obtained EF are above the value of the euro 6 standard of 6 10+11 #/km for both diesel and petrol vehicles. EFs are below the values corresponding to diesel vehicles not equipped with particulate filter (6 10+13#/km). As a reminder, the New European Driving Cycle gave a limit value of 6 10+11#/km (Euro 6b) for PN (number of particles per km) for spark-ignition engines (gasoline, LPG, etc.), including hybrids, and a limit value of 6 10+12 #/km for diesel engines only, including hybrids.
5. Assessment of EF of the PM10 and PM2.5 emitted by the tyre-road surface wear are 1.45 mg/km and 0.35 mg/km, respectively.
6. The number of particles number per volume element in static situation in the city is ≈ 42.8 10+12 #/cm3. This number of particles is stable almost every day except for summer holiday periods and Sundays when urban traffic is low in the city. In real driving situation, we obtained 30 10+12 #/cm3 in urban and 35 10+12 #/cm3 in suburban. The larger measured number on the fixed site is due both to the dispersion of pollutants and also to the effect of accumulation in a localized unpoint.
These results show that the methodological approach, used in this paper, is particularly effective in assessing pollutant emission factors. This kind of approach is a new alternative to existing methods. The significant obtained results in this paper thus provide reliable information to help improve emission models, making them more accurate and applicable. Further research, integrating the phenomena of resuspension of particles in the air, is necessary. These researchers will bring other scientific knowledge to the work presented in this paper. They will have to consider the nature of the materials of the road surfaces and tyres. Their physico-chemical characteristics must therefore be specified. Thus, a metrological and methodological development must be carried-out to separate the sources of particles emitted by the tyres, the road surface and the resuspension. These particles will have to be analysed individually, and if possible online to avoid chemical transformations that induce secondary pollution because airborne particles can differ significantly from friction materials. Then, experimental conditions will have to be controlled, and if necessary supported by new tool developments. The problem could become insoluble if we were not to take into-account the “complex” mixing effect between exhaust and non-exhaust emissions.
The results presented in this paper will contribute to future regulations for road vehicles (thermal, hybrid, electric, autonomous). Further scientific work, i.e., analysing exposure-impact relationships to particles emitted by abrasion of tyres and road surface, is needed to complete the development of technical and legislative recommendations, as well as health guidelines. Appropriate regulations will provide the framework for public and environmental policies. They will also provide the necessary support for emerging technologies which objectives are the well-being of population and improvement of the environment.