Submitted:
21 March 2024
Posted:
22 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
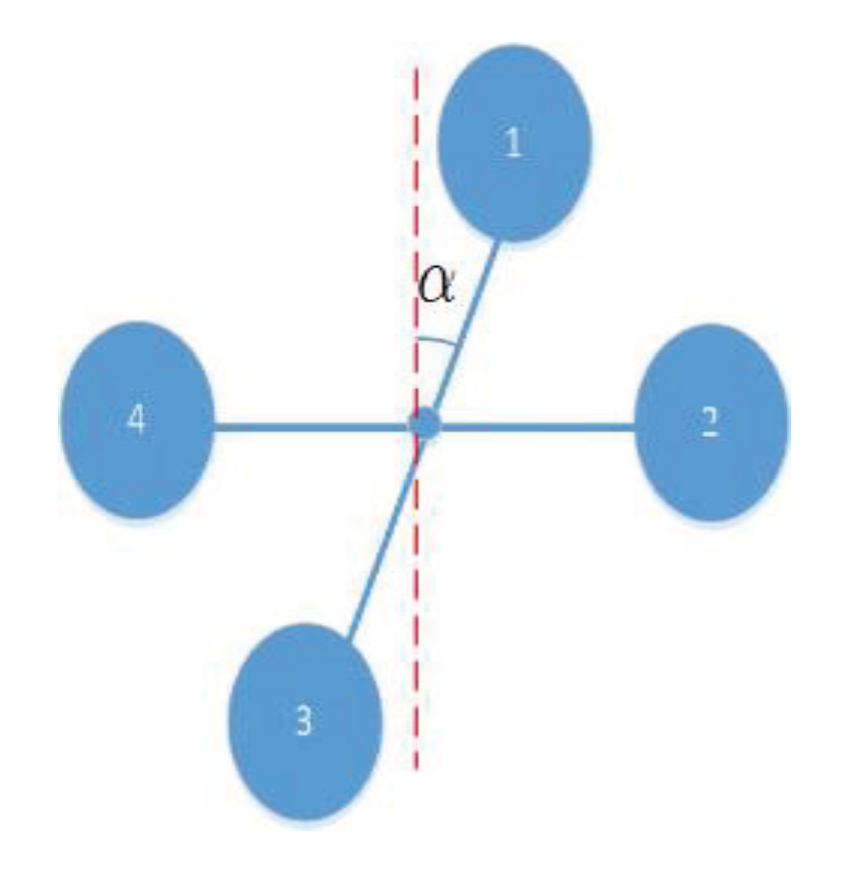
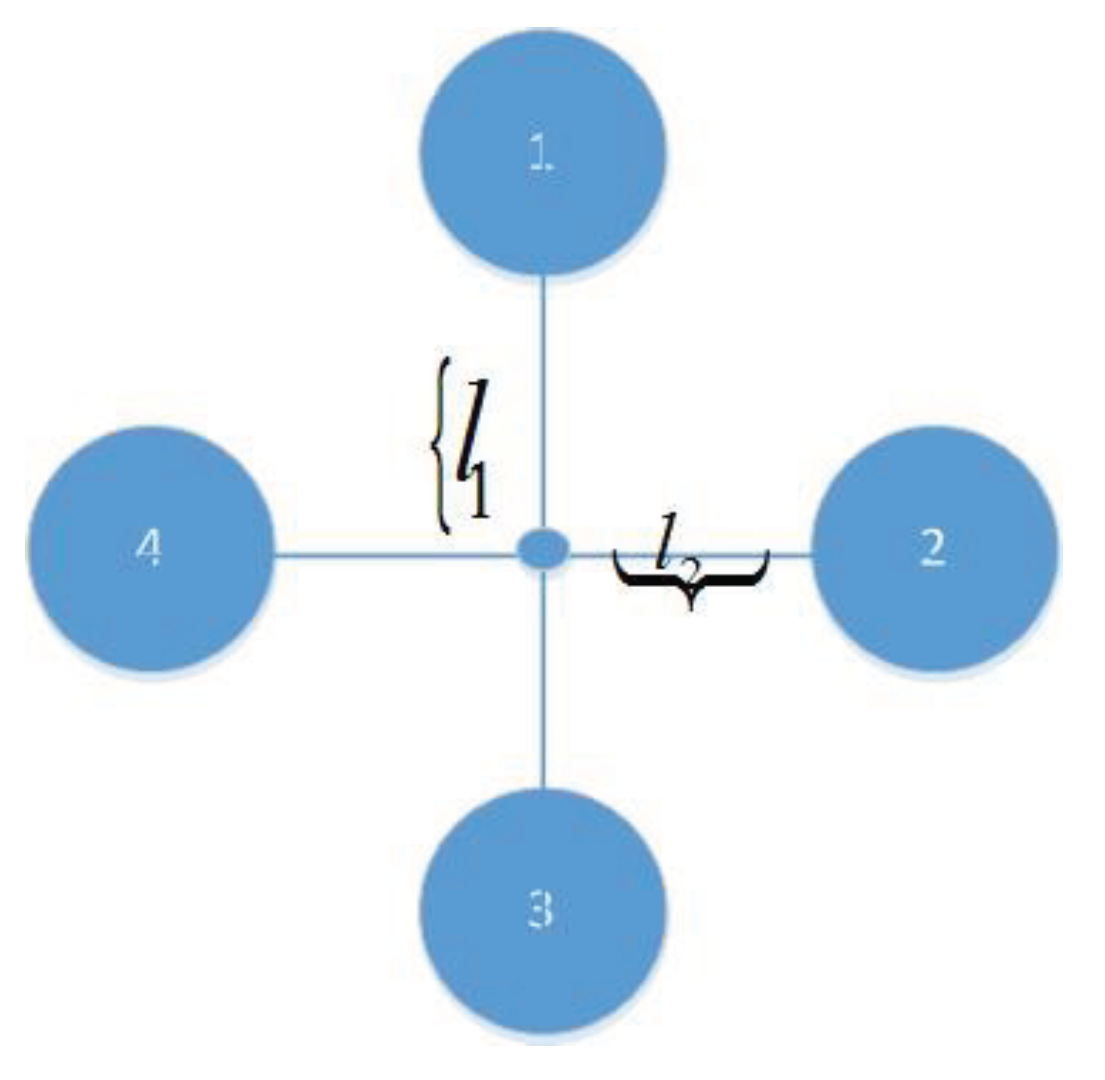
3. Modeling and Control Law Design
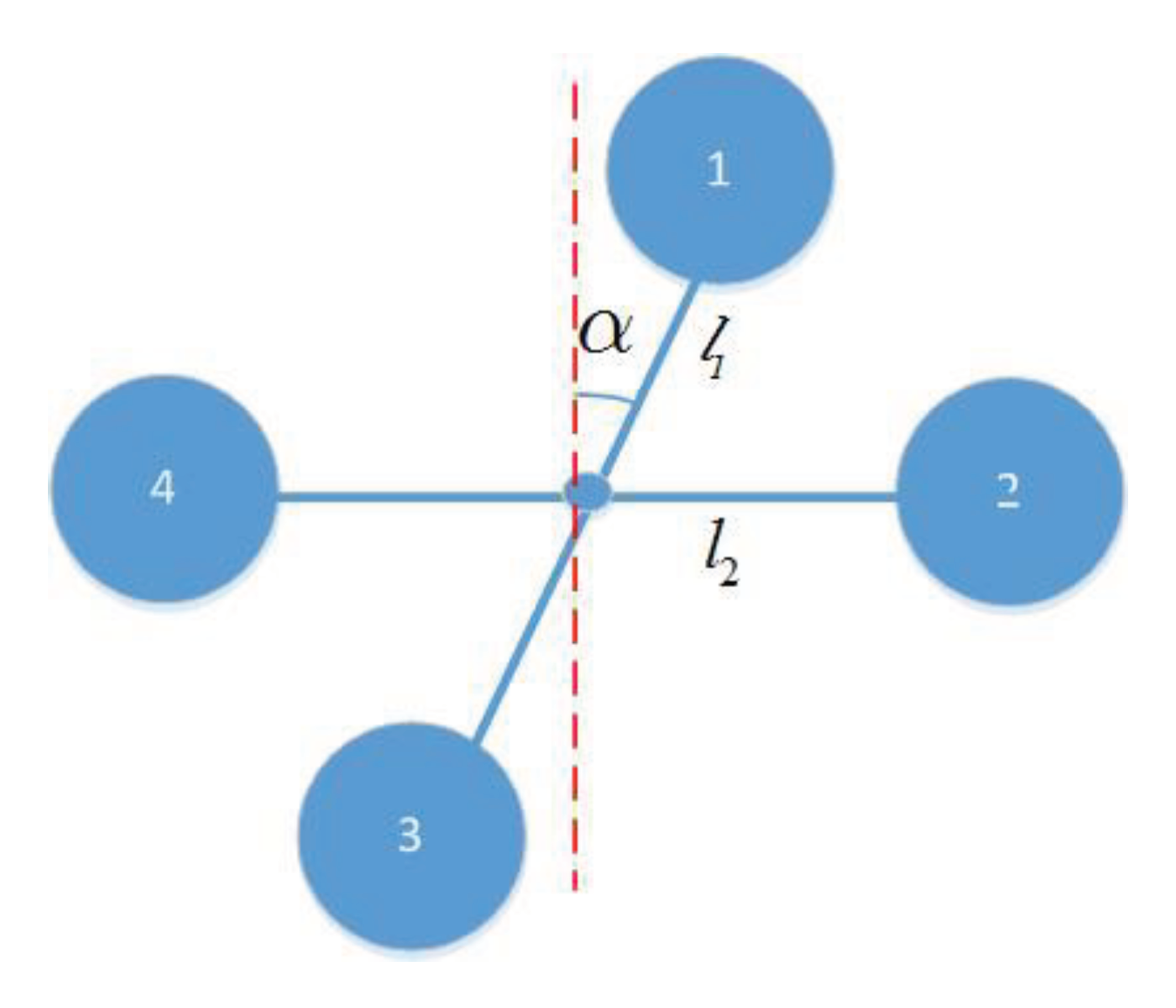
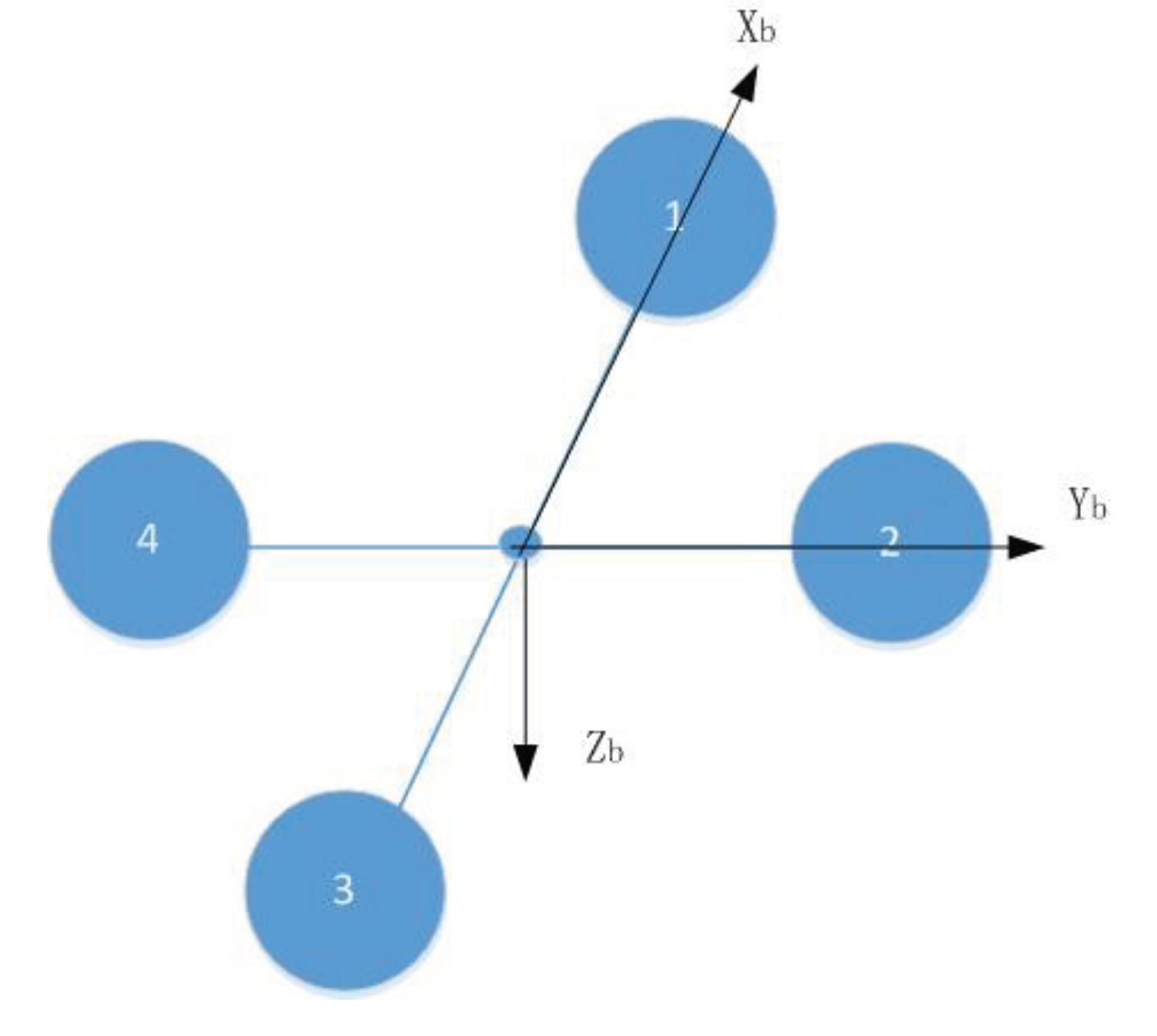
3.1. Kinematic Model and Dynamic Model
3.2. Model of Pure Translational Reconfiguration
3.4. Model of Translational Plus Rotational Reconfiguration
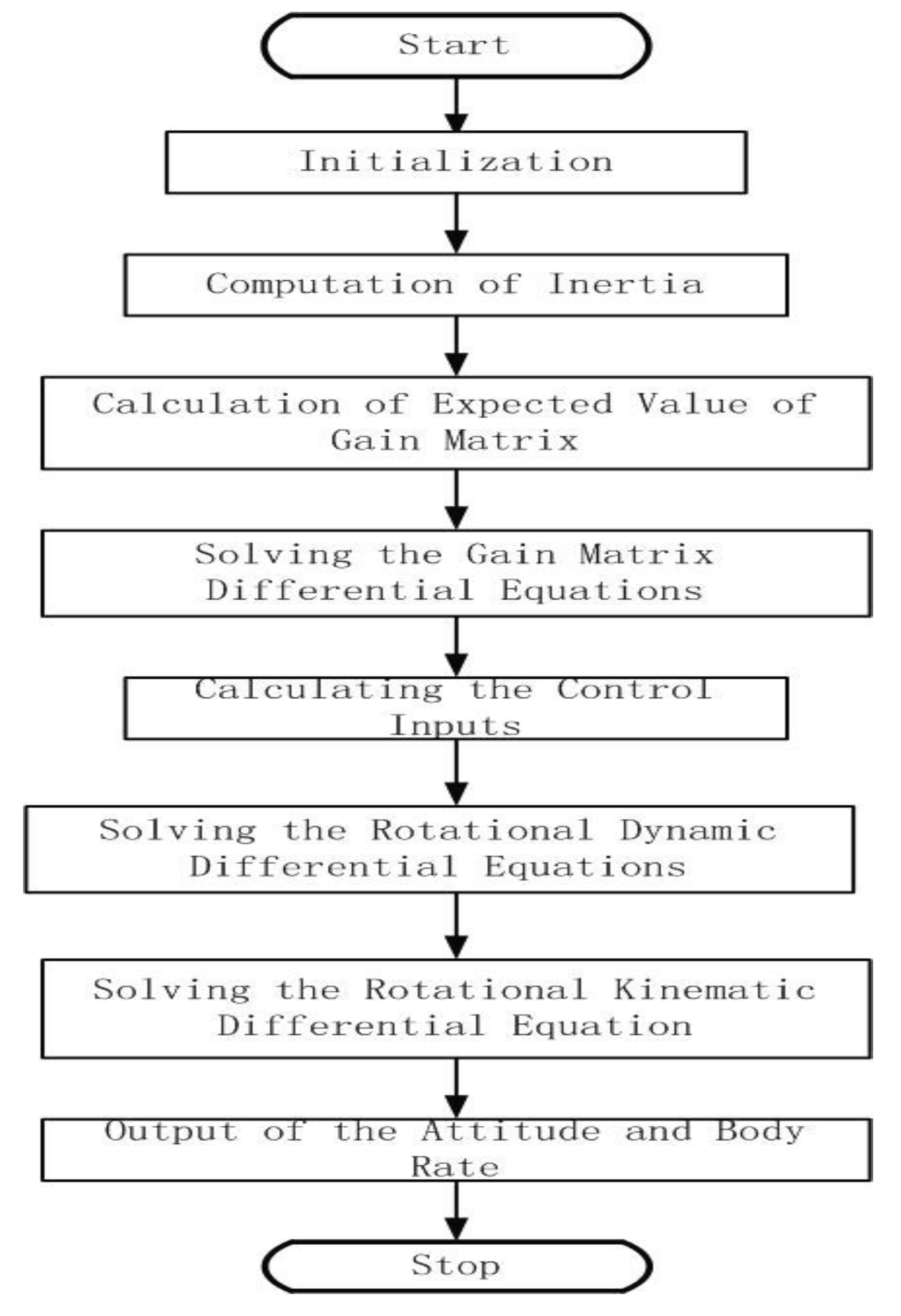
3.5. Model Reference Adaptive Control Law Design
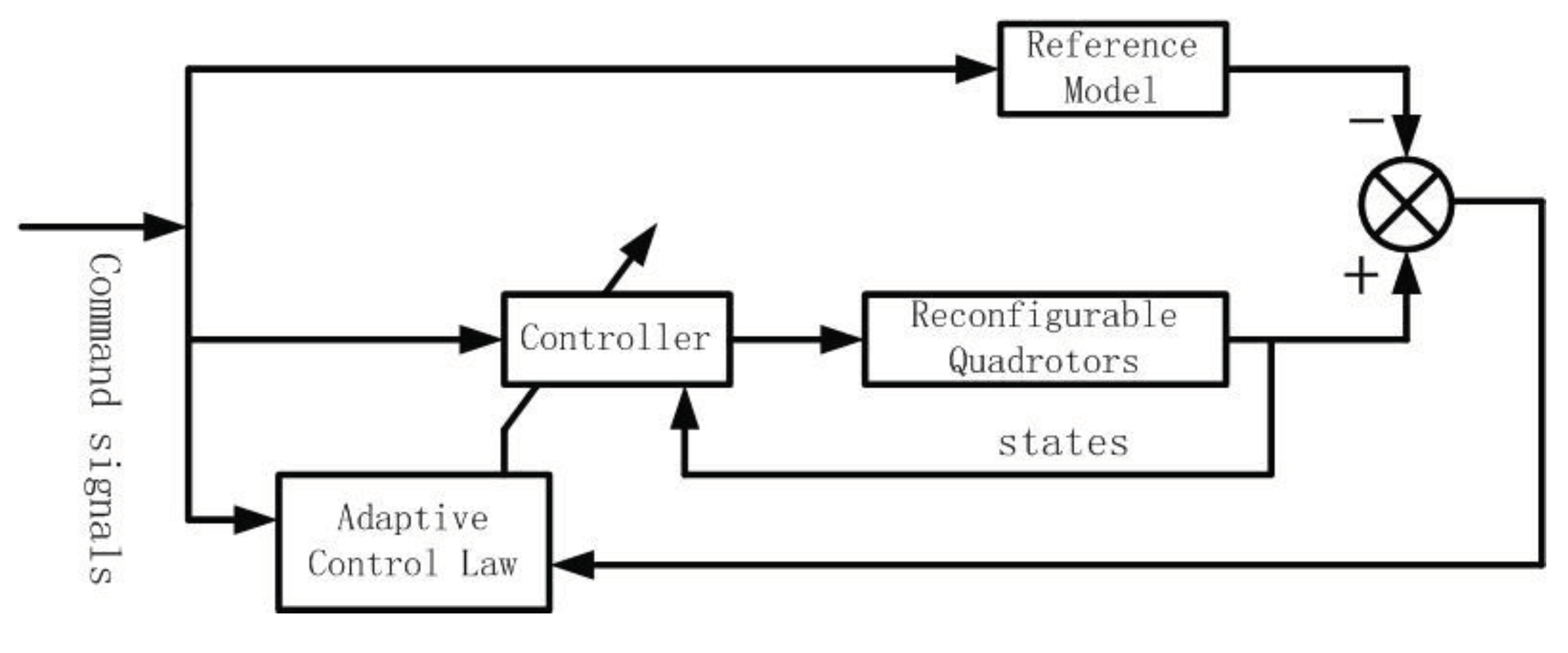
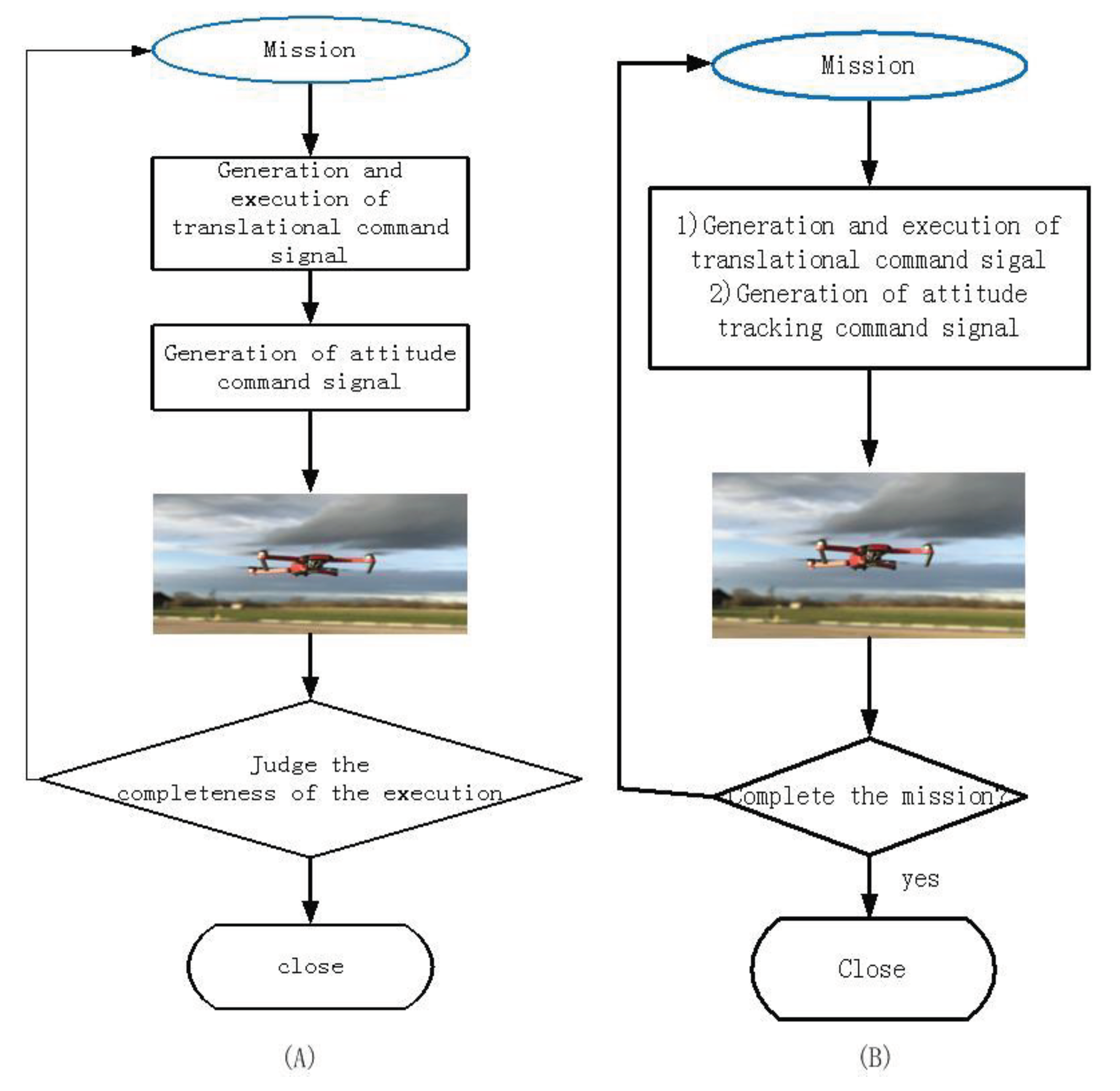
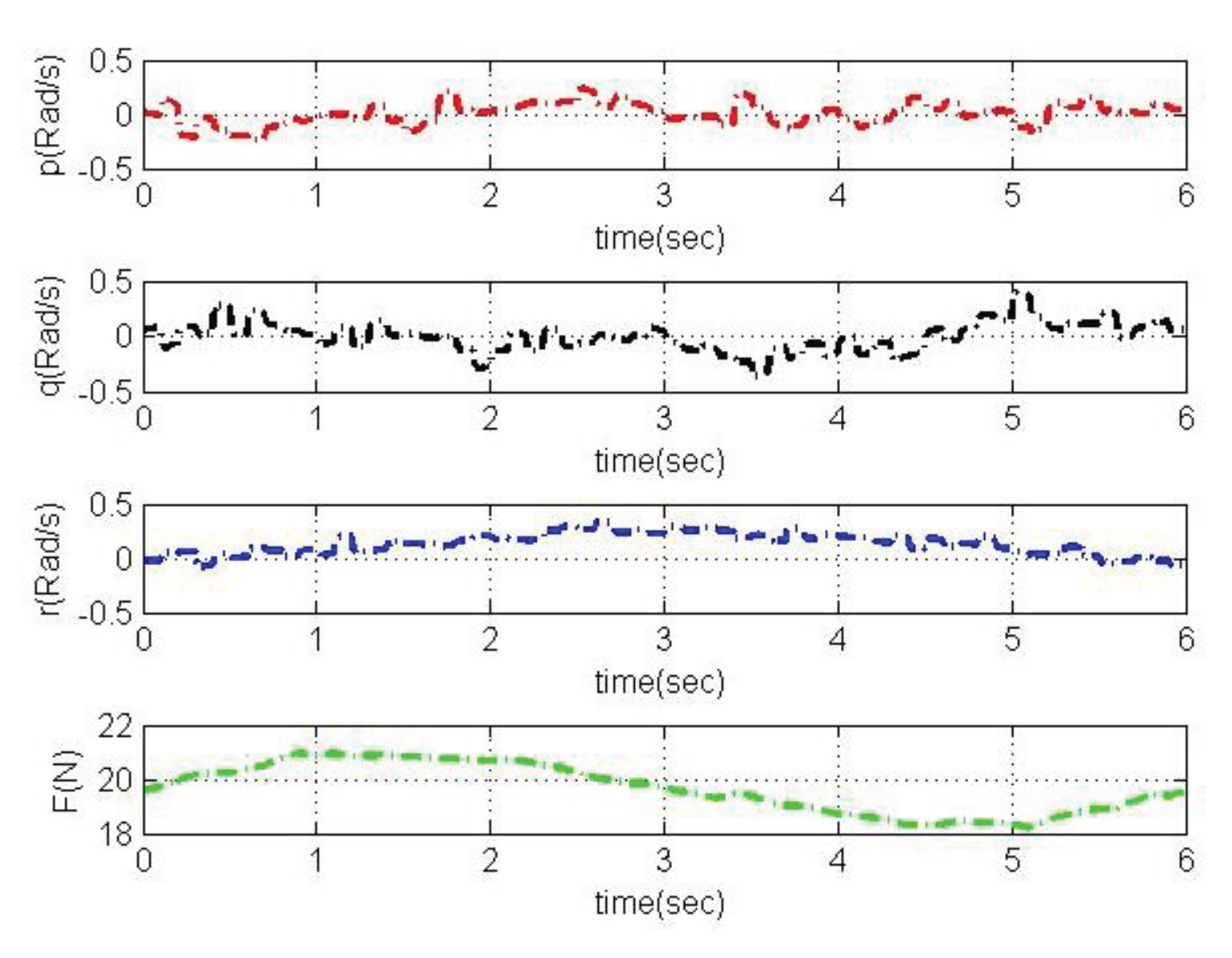
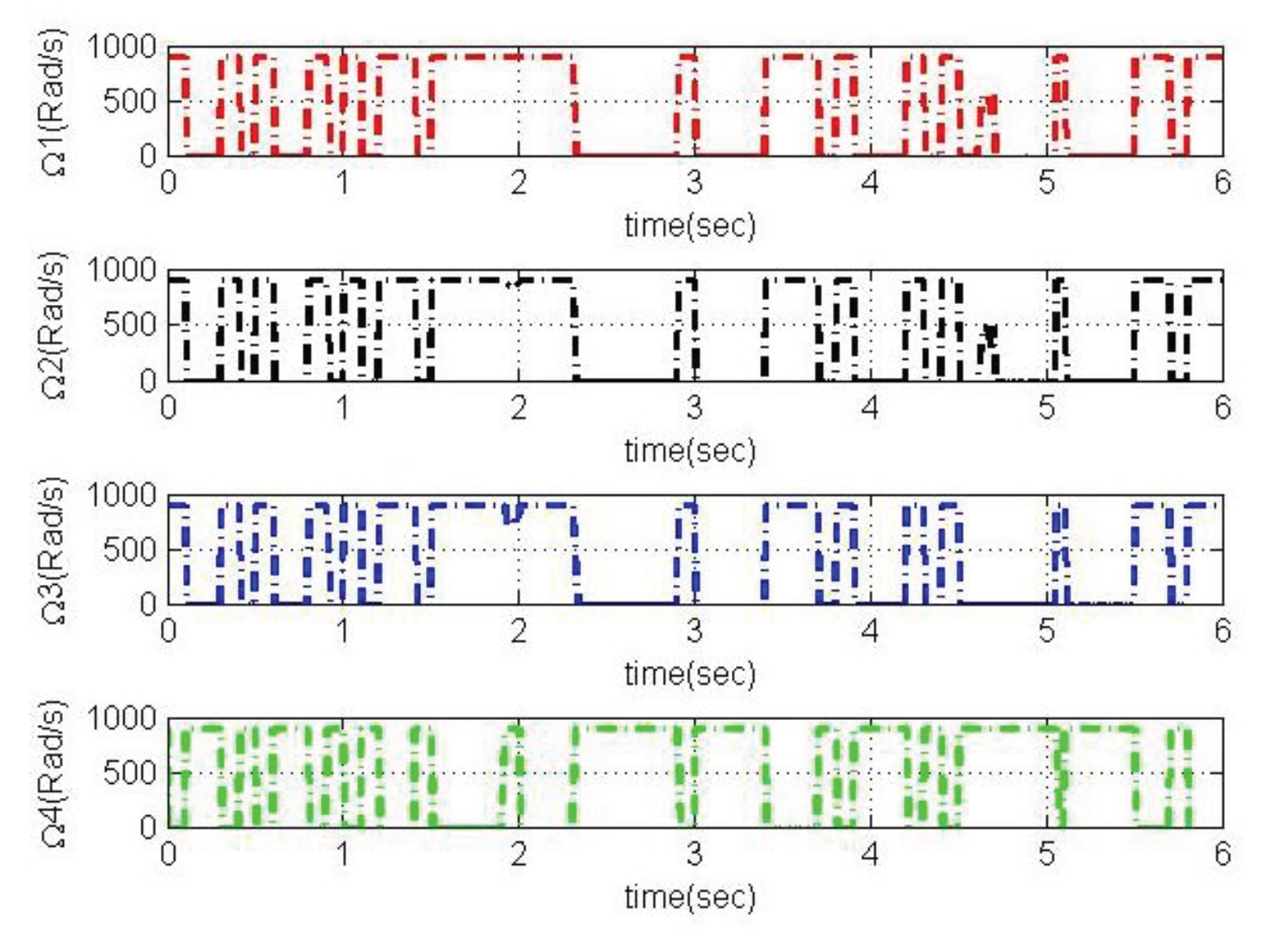
4. Simulation and Analysis
4.1. Initialization of simulation
4.2. Simulation based on MRAC
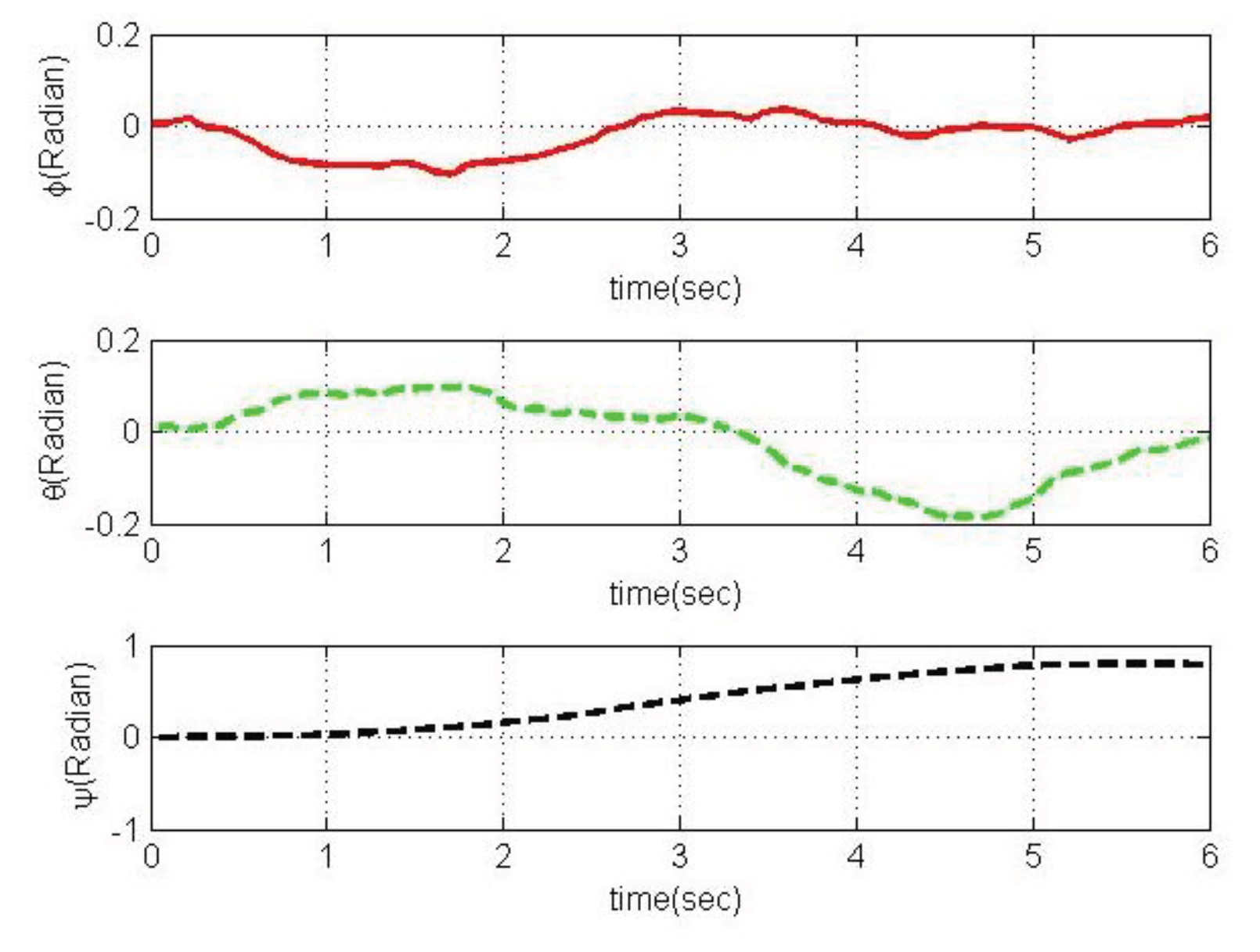
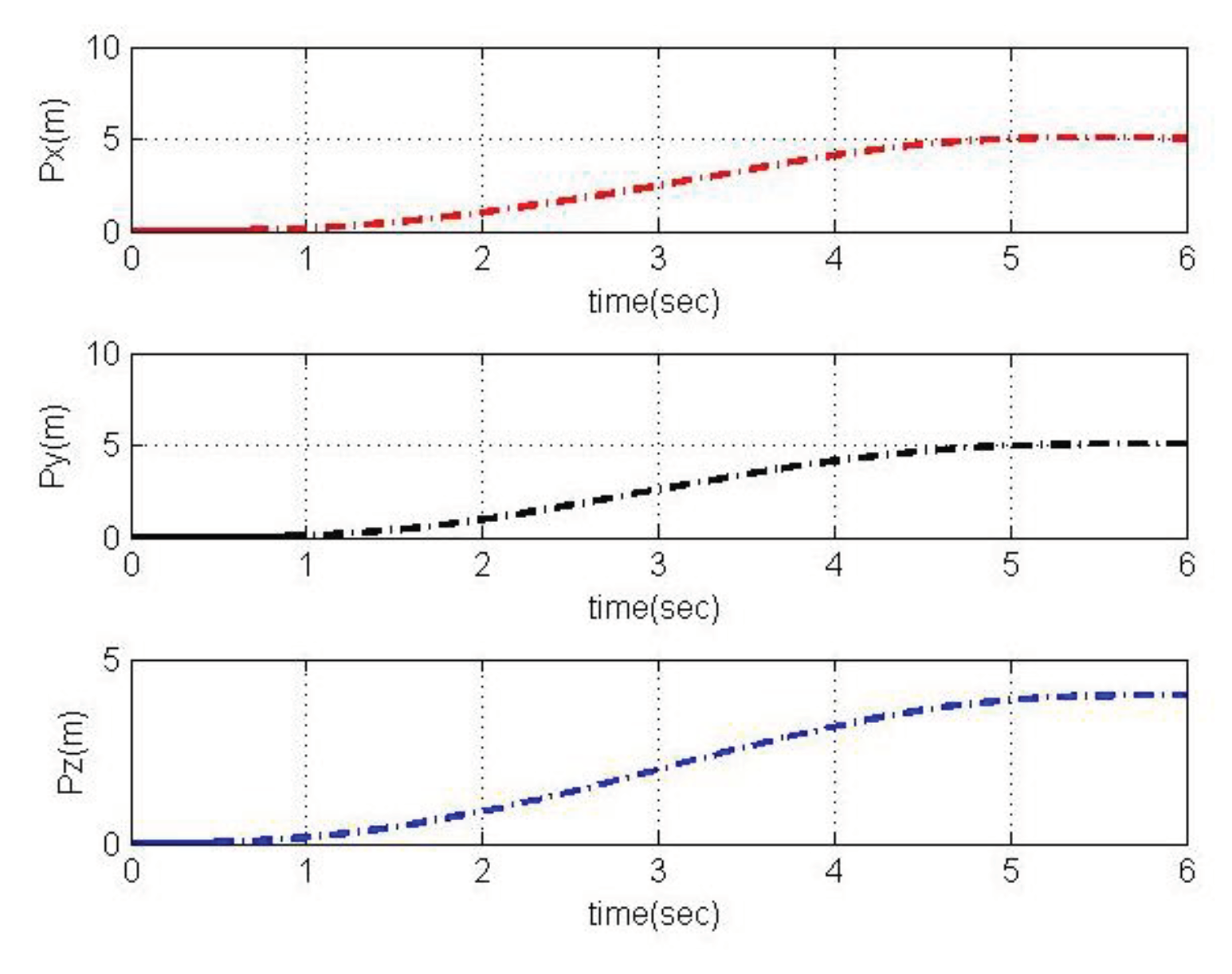
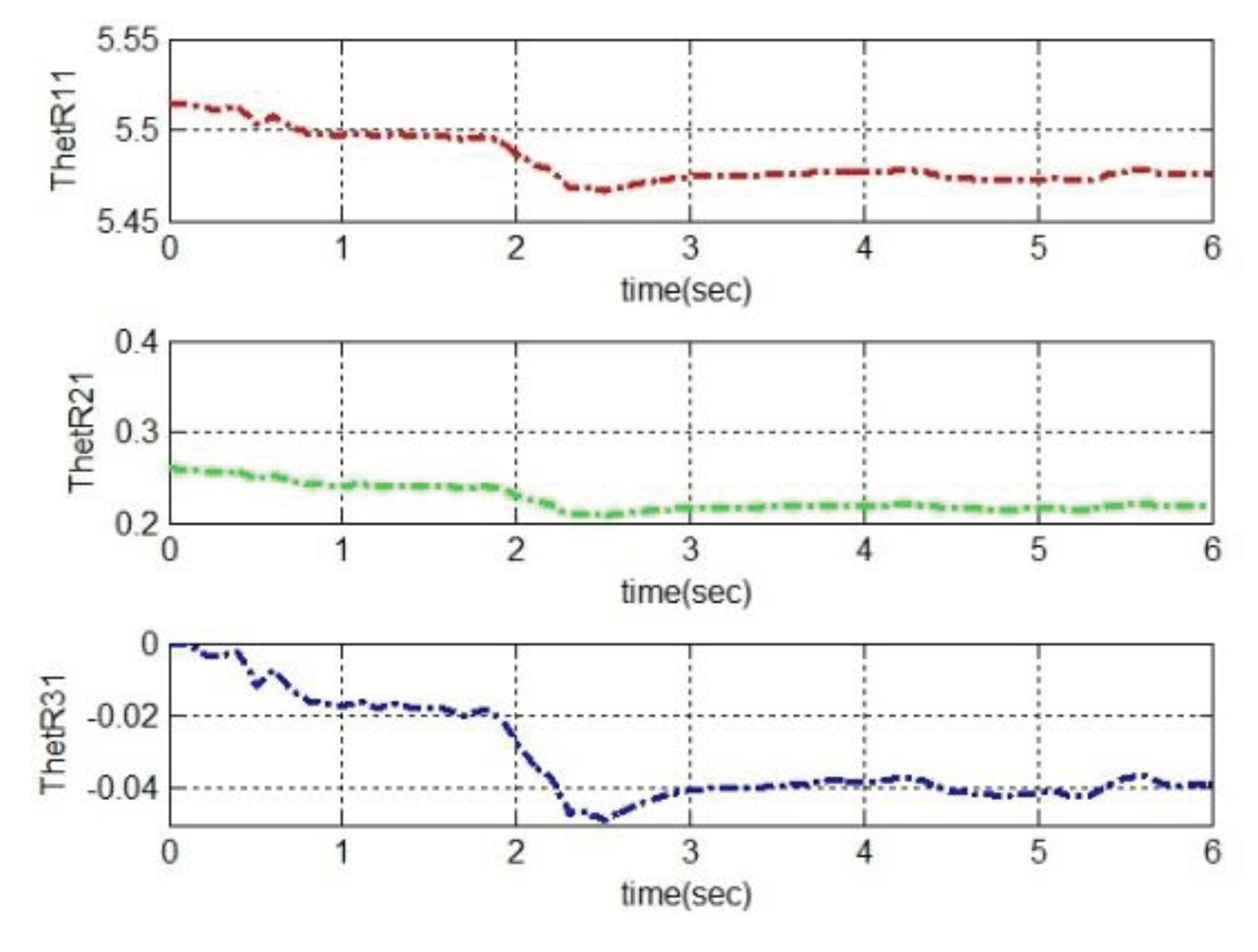
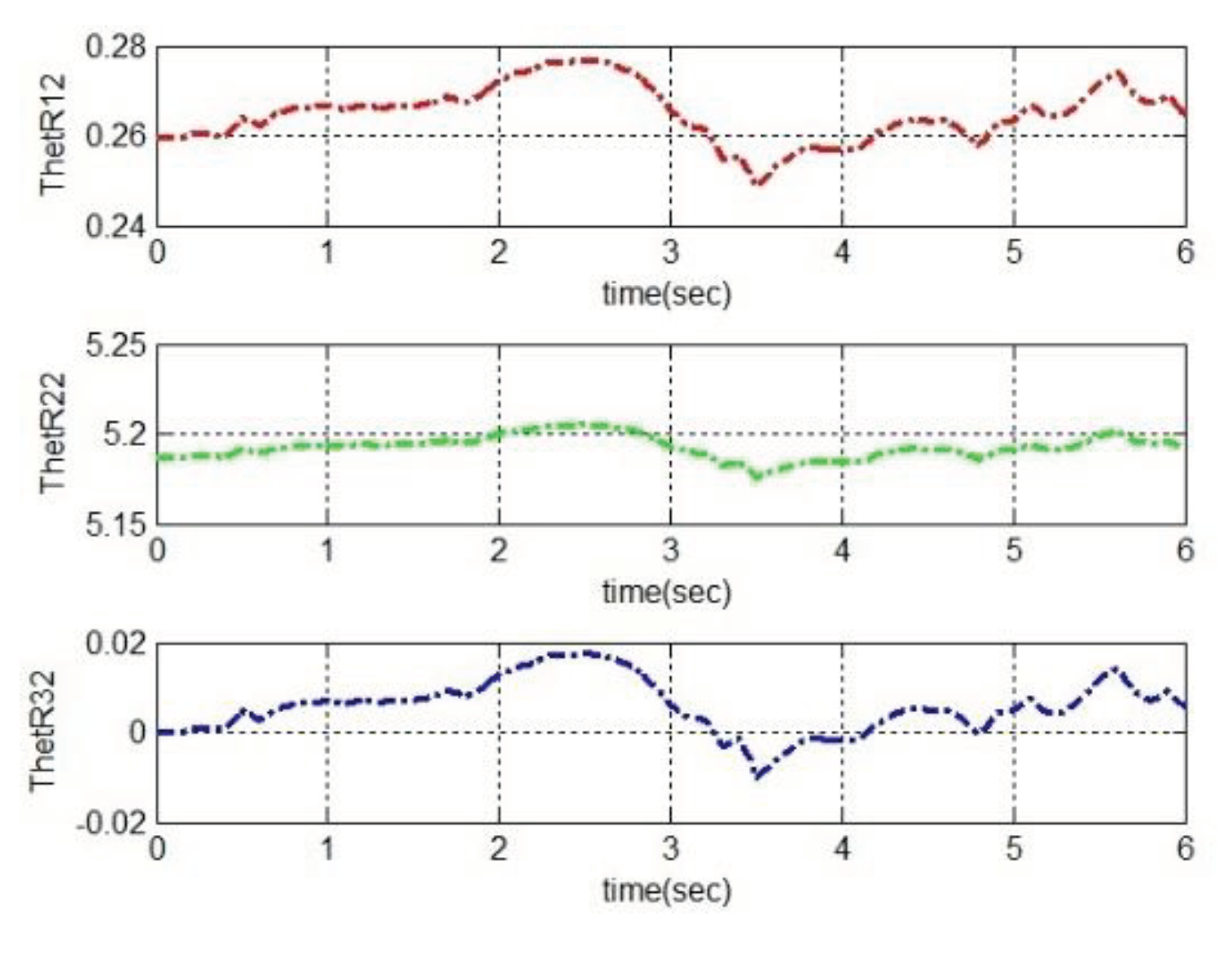
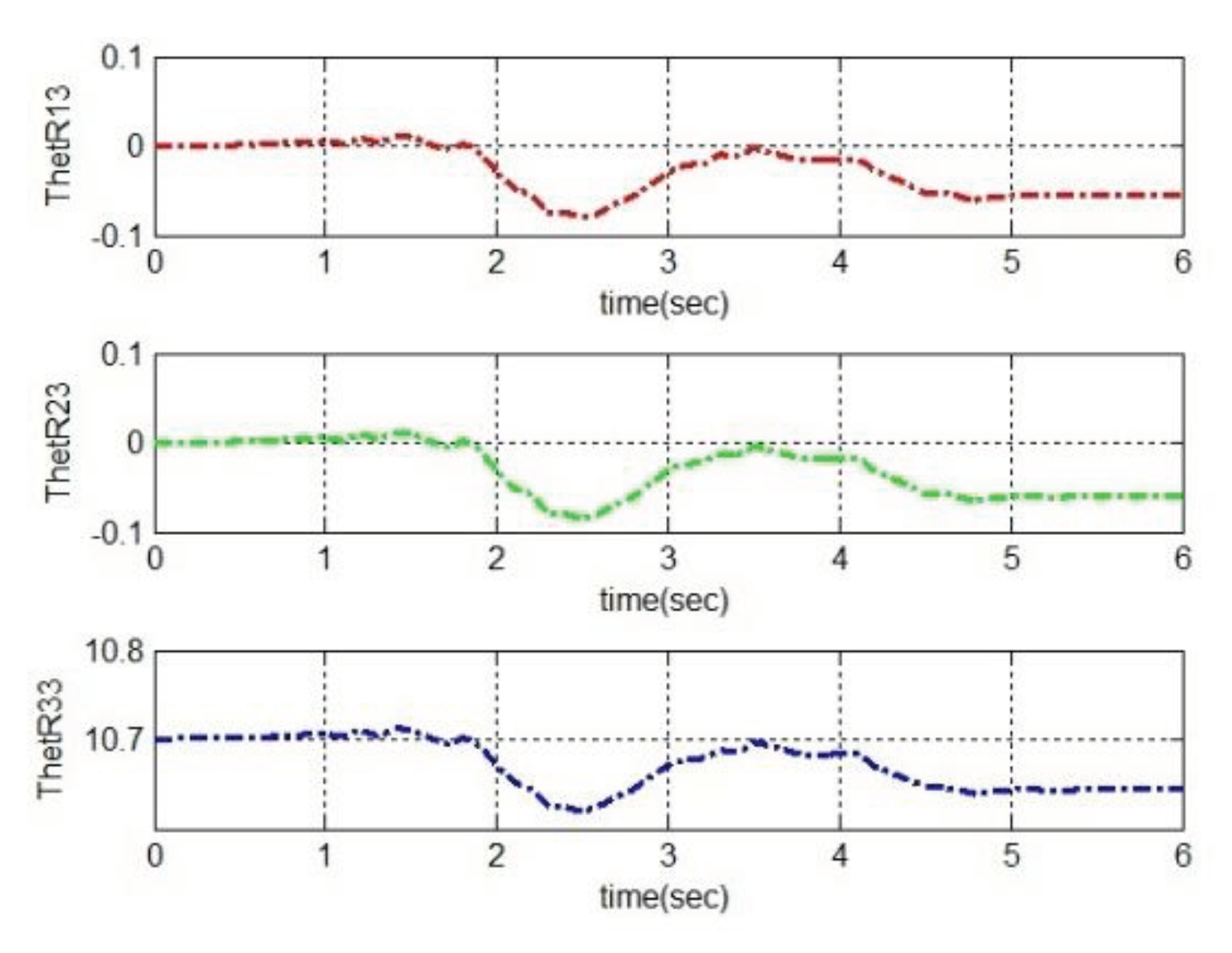
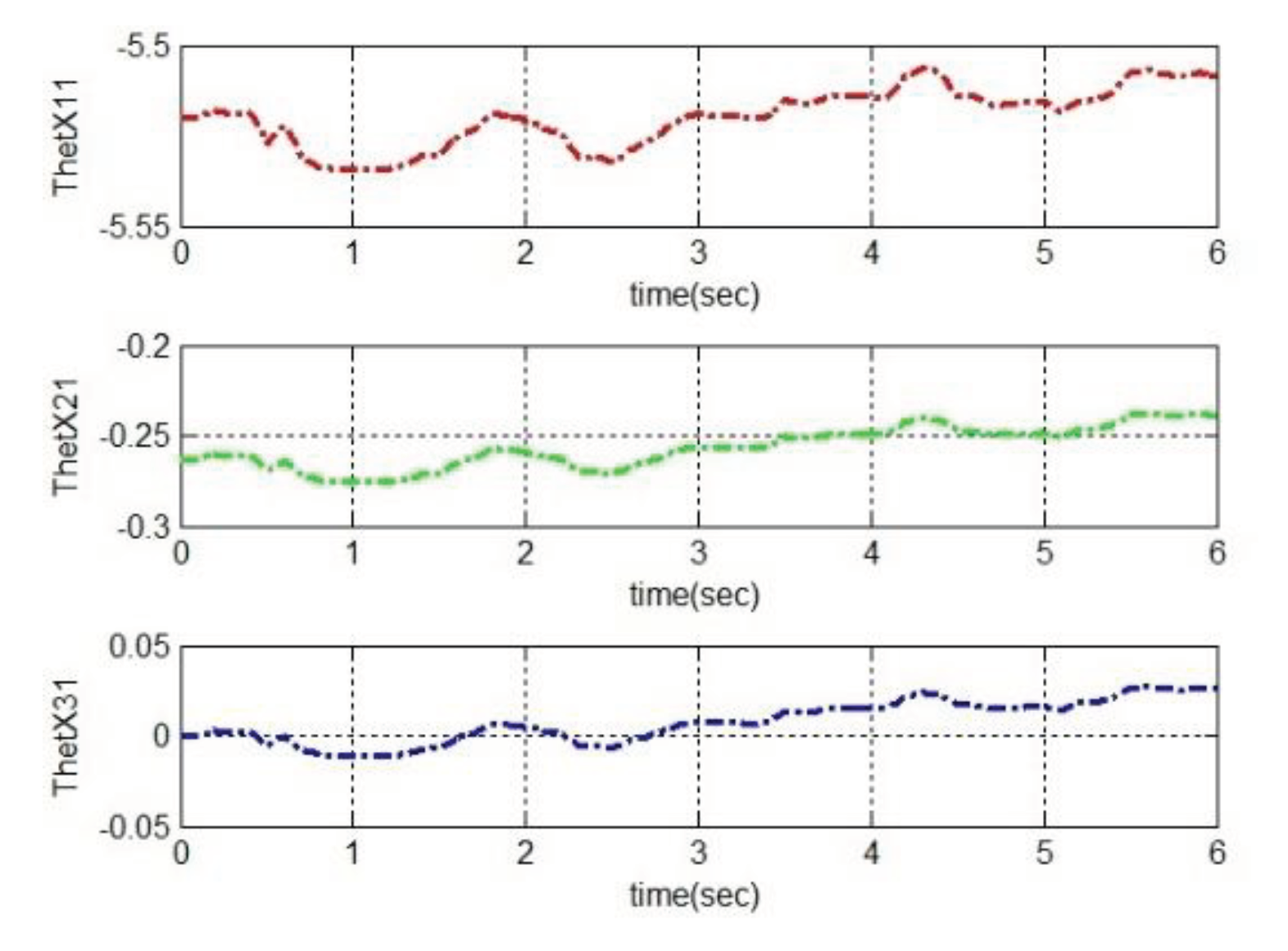
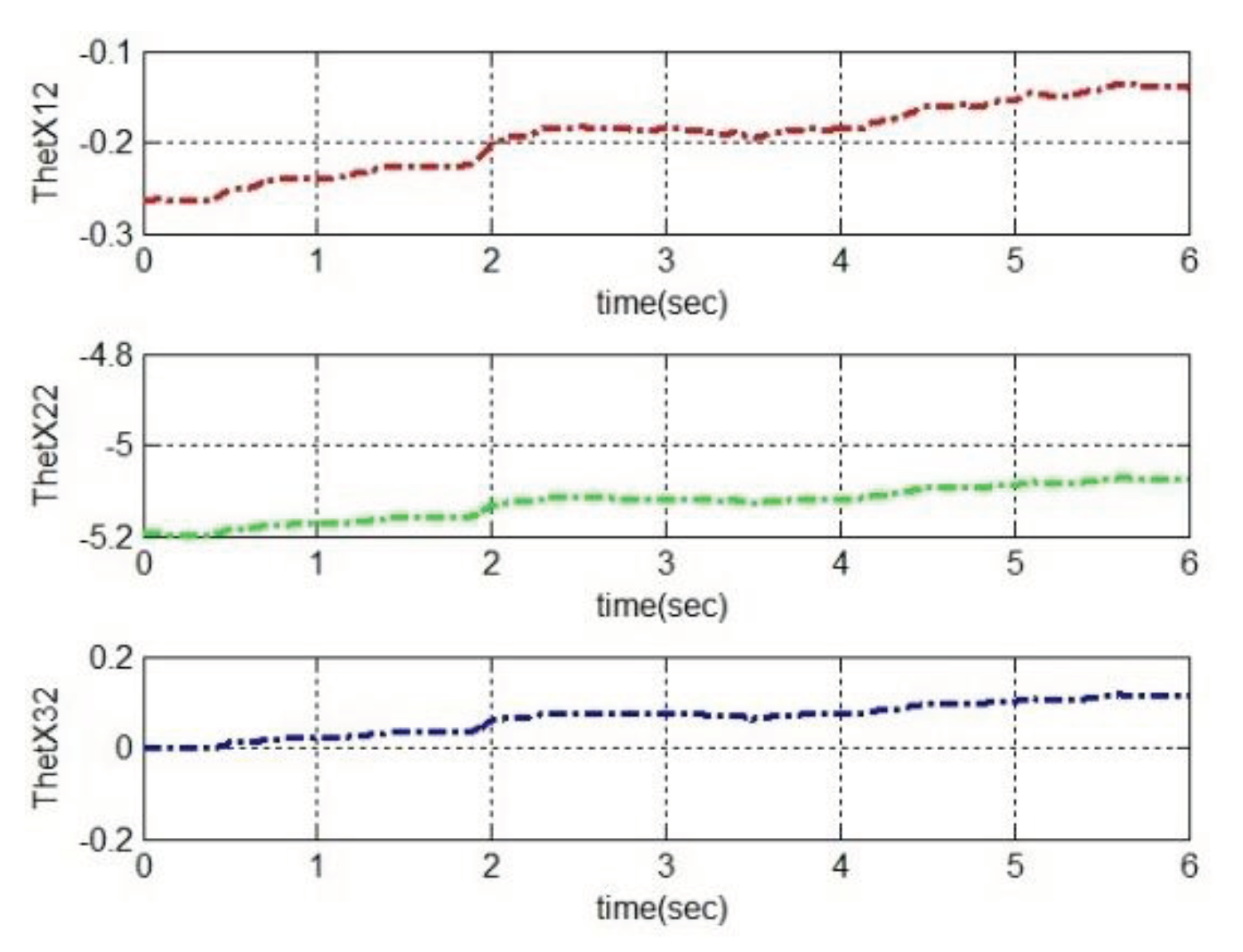
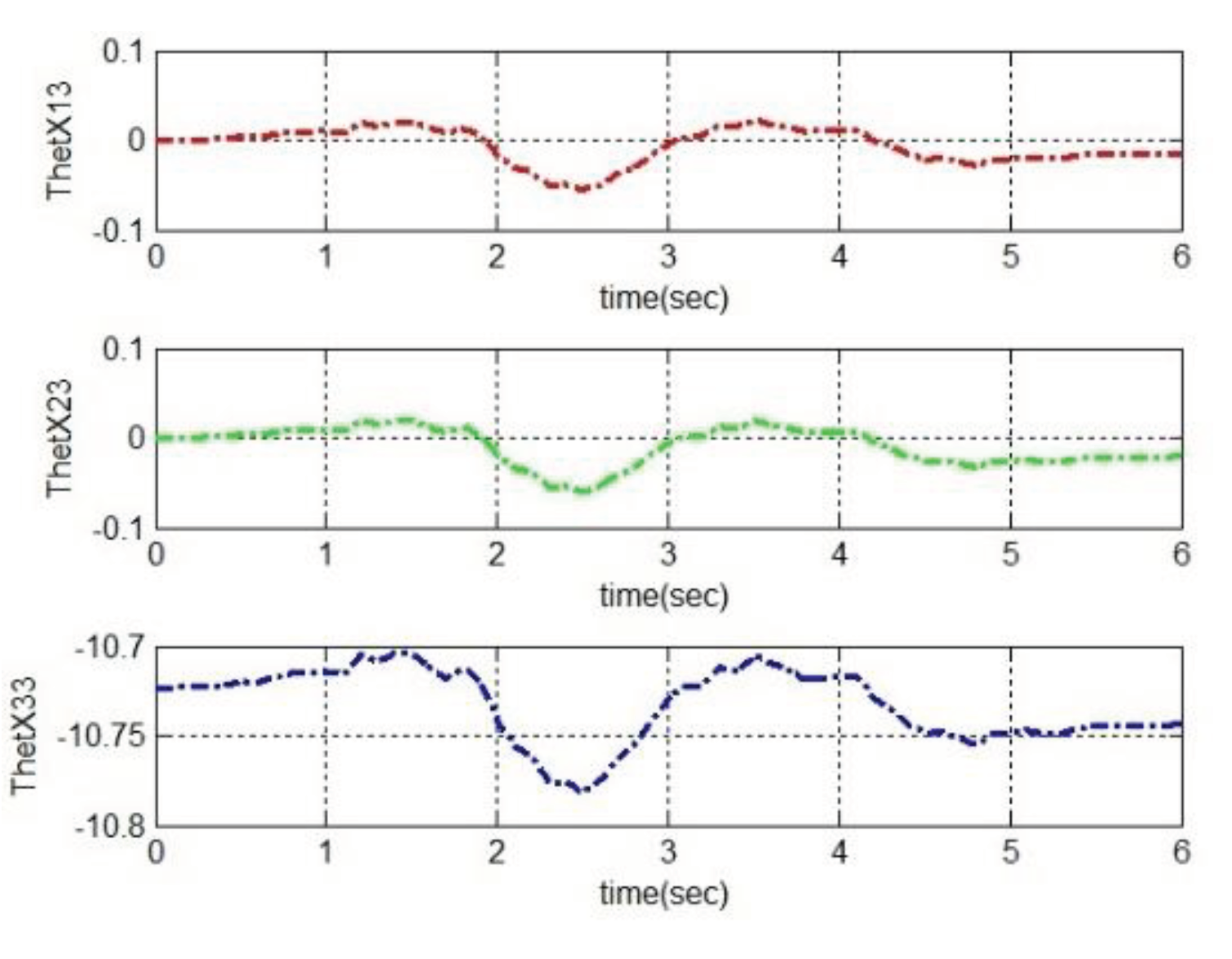
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bangura, M.; Hou, X.; Allibert, G.; Mahony, R.; Michael, N. Supervisory Control of Multirotor Vehicles in Challenging Conditions Using Inertial Measurements. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 34, 1490–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L. Bauersfeld, L. Spannagl, G. Ducard, and C. Onder, MPC Flight Control for a Tilt-Rotor VTOL Aircraft, IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57, 2395–2409.
- Borkar, A.V.; Hangal, S.; Arya, H.; Sinha, A.; Vachhani, L. Reconfigurable formations of quadrotors on Lissajous curves for surveillance applications. Eur. J. Control. 2020, 56, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N. Bucki and M. W. Mueller, Design and Control of a Passively Morphing Quadcopter, 2019 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Montreal, Canada, -24, 2019. 20 May.
- R. R. D'Sa, Design of a Transformable Unmanned Aerial Vehicle, PhD thesis of University of Minnesota, 2020.
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lyu, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. Research on Manipulation Strategy and Flight Test of the Quad Tilt Rotor in Conversion Process. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 40286–40307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, W.; Yeo, D.; Paley, D.A. Geometric Attitude and Position Control of a Quadrotor in Wind. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2020, 43, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkordi, M.D.; Danesh, M. Positionable Rotor Quadrotor: Dynamic Modeling and Adaptive Finite-Time Sliding-Mode Controller Design. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2022, 45, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Lu, L. A Tilting-Rotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicle for Enhanced Aerial Locomotion and Manipulation Capabilities: Design, Control, and Applications. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2020, 26, 2237–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falanga, D.; Kleber, K.; Mintchev, S.; Floreano, D.; Scaramuzza, D. The Foldable Drone: A Morphing Quadrotor That Can Squeeze and Fly. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 4, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, N.; Saldana, D.; Kumar, V.; Phan, L.T.X. Self-Reconfiguration in Response to Faults in Modular Aerial Systems. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 2522–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, R.A.; Wells, S.R. Sliding Mode Control Applied to Reconfigurable Flight Control Design. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2003, 26, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. J. Cutler, Design and Control of an Autonomous Variable-Pitch Quadrotor Helicopter, Master's thesis of Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2012.
- Hu, D.; Pei, Z.; Shi, J.; Tang, Z. Design, Modeling and Control of a Novel Morphing Quadrotor. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 8013–8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, M.; Nguyen, H.; Alexis, K. The Reconfigurable Aerial Robotic Chain: Shape and Motion Planning. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 9295–9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B. Li, L. Ma, D. Wang, and Y. Sun, Driving and Tilt-Hovering – An Agile and Maneuverable Aerial Vehicle with Tiltable rotors, IET Cyber-Systems and Robotics, 2021, 3(2): 103–115.
- Mofid, O.; Mobayen, S. Adaptive sliding mode control for finite-time stability of quad-rotor UAVs with parametric uncertainties. ISA Trans. 2018, 72, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F. M. M. Marques, P. A. Q. de Assis, and R. M. F. Neto, Position Tracking of a Tilt-Rotor Quad-copter with Small Attitude Variation Using Model Predictive Control, AIAA Aviation Forum, June 15-19, 2020. 15 June.
- Niemiec, R.; Gandhi, F.; Singh, R. Control and Performance of a Reconfigurable Multicopter. J. Aircr. 2018, 55, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outeiro, P.; Cardeira, C.; Oliveira, P. Multiple-model adaptive control architecture for a quadrotor with constant unknown mass and inertia. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 117, 106899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pose, C.D.; Giribet, J.I.; Mas, I. Fault Tolerance Analysis for a Class of Reconfigurable Aerial Hexarotor Vehicles. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2020, 25, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Seo, J. Paik, and M. Yim, Modular Reconfigurable Robotics, Annual Review of Control, Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2019, 2: 63–88.
- Wang, N.; Deng, Q.; Xie, G.; Pan, X. Hybrid finite-time trajectory tracking control of a quadrotor. ISA Trans. 2019, 90, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Li, Z.; Zhou, P.; Lu, J. Control System Design for Tiltable Quad-rotor with Propeller Failure. 2020 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, ChinaDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 7473–7478.
- S. Zhang, Development of Unconventional Unmanned Aerial Vehicle With Tilt-Rotor Platform, PhD thesis of National University of Singapore, 2018.
- N. Zhao, Y. Luo, H. Deng, and Y. Shen, The deformable quad-rotor: Design, Kinematics and Dynamics Characterization, and Flight Performance Validation, 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, September 24-28, 2017.
- Zheng, P.; Tan, X.; Kocer, B.B.; Yang, E.; Kovac, M. TiltDrone: A Fully-Actuated Tilting Quadrotor Platform. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 6845–6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Jang, I.; Kim, H.J. Fully Actuated Autonomous Flight of Thruster-Tilting Multirotor. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2020, 26, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A.M. Anaswamy, Adaptive Control and Intersections with Reinforcement Learning, Annual Review of Control, Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2023, 6:65-93.
- Z.T. Dydek, Adaptive Control of Unmanned Aerial Systems, PhD thesis of Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2010.
| Physical parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Mass of motor on the rotor | 60g |
| Mass of driving motor | 80g |
| Length of arm | 40cm |
| Displacement of arm(max) | 20cm |
| Mass of arm | 30g |
| Mass of battery | 400g |
| Mass of ECS | 25g |
| Mass of payload | 250g |
| Parameter Value |
| 0 |
| Parameter |
| 0.2m 2~6 -0.5~1.0 -0.5~0.5 |
| 0.2m 2~6 -0.5~1.0 -0.5~0.5 |
| 0.2m 2~6 -0.5~1.0 -0.5~0.5 |
| 0.1rad 2~6 -0.5~1.0 -0.5~0.5 |
| 0.15rad 2~6 -0.5~1.0 -0.5~0.5 |
| 0.2rad 2~6 -0.5~1.0 -0.5~0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





