Submitted:
16 January 2024
Posted:
16 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
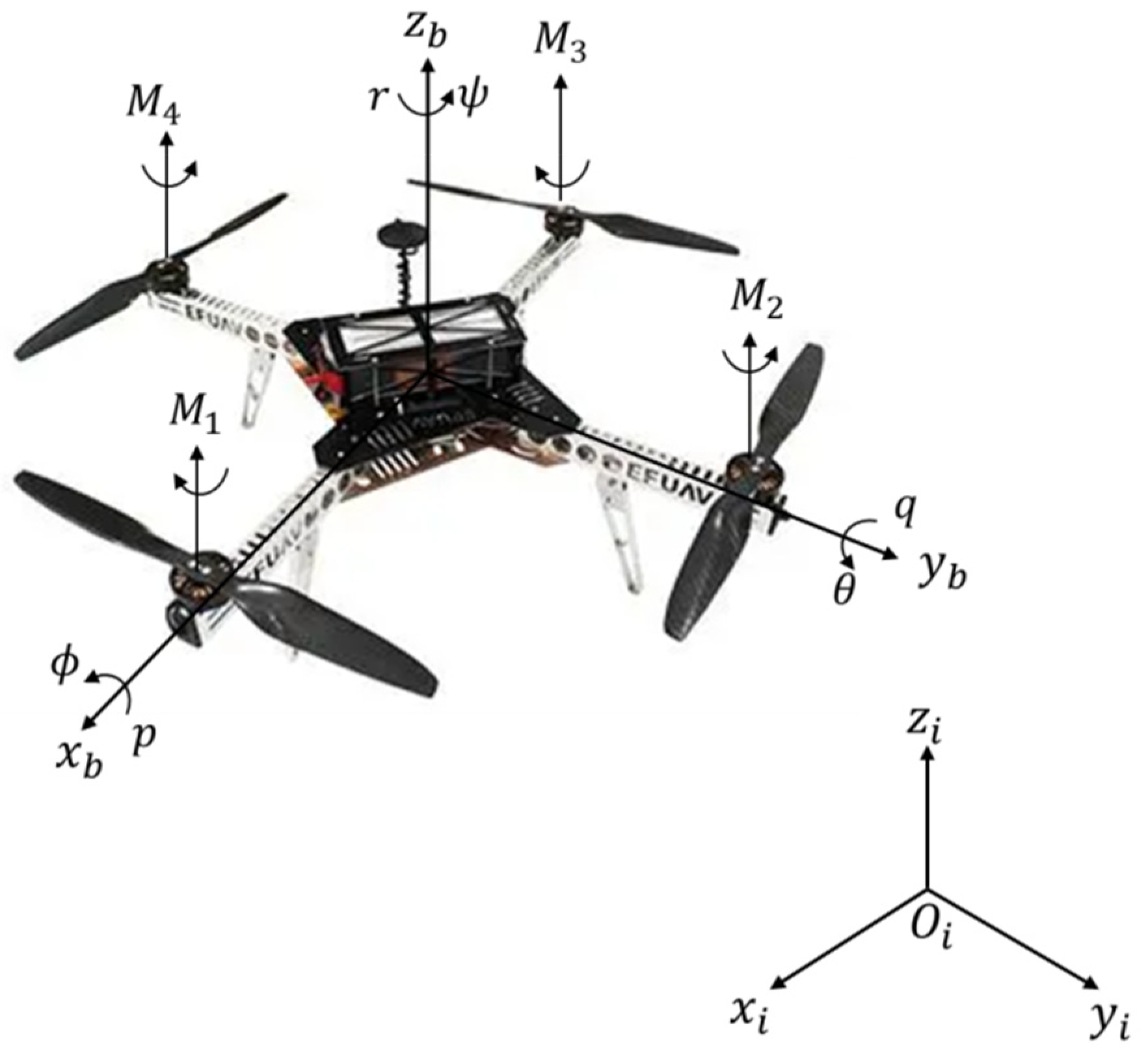
2. Attitude Dynamics Modeling for Quadrotor UAV
3. Control Design for Attitude Control
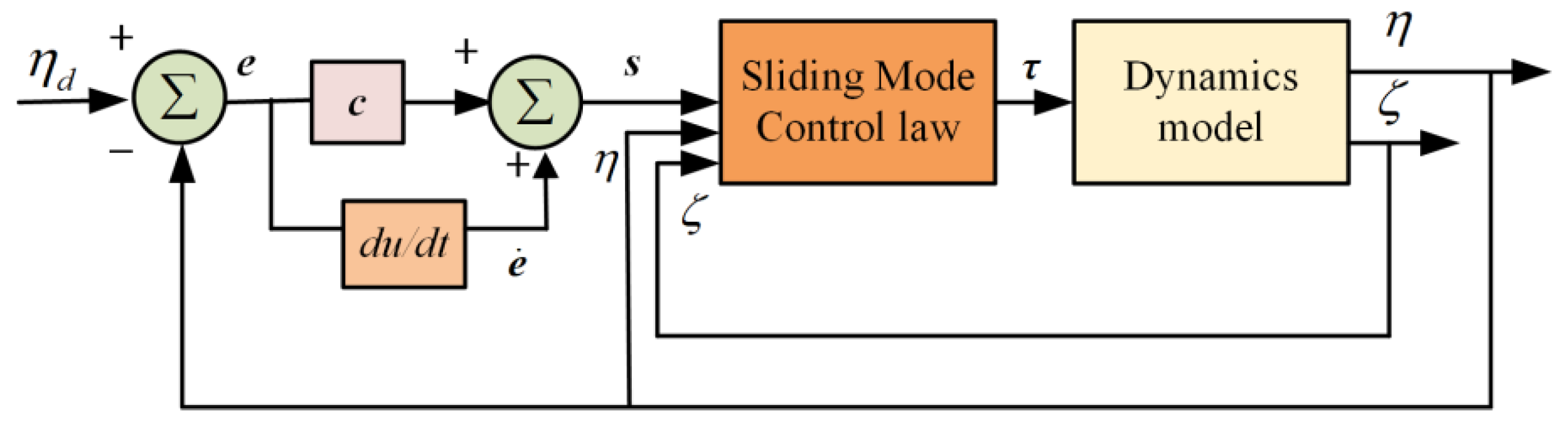
3.1. SMC Design
| SMC Algorithm |
|
Input: (1) Desired attitude angles (2) Actual attitude angles (3) Model parameters of the quadrotor Output: The control signals for attitude dynamics model Step 1: Design of the control signal (a) Define the sliding mode surface s (b) Select the reaching law (c) Compute the control signal Step 2: Proof of the stability of closed-loop system (a) Select a Lyapunov candidate function (b) Calculate the first-order derivative of (c) Analyze the sign of the above derivative of (d) Conclude the convergence of the attitude motion Step 3: Termination If the attitude control errors meet the requirements, conduct the algorithm termination and output the control signal . Otherwise, go to step 1 until the convergence of control errors. |
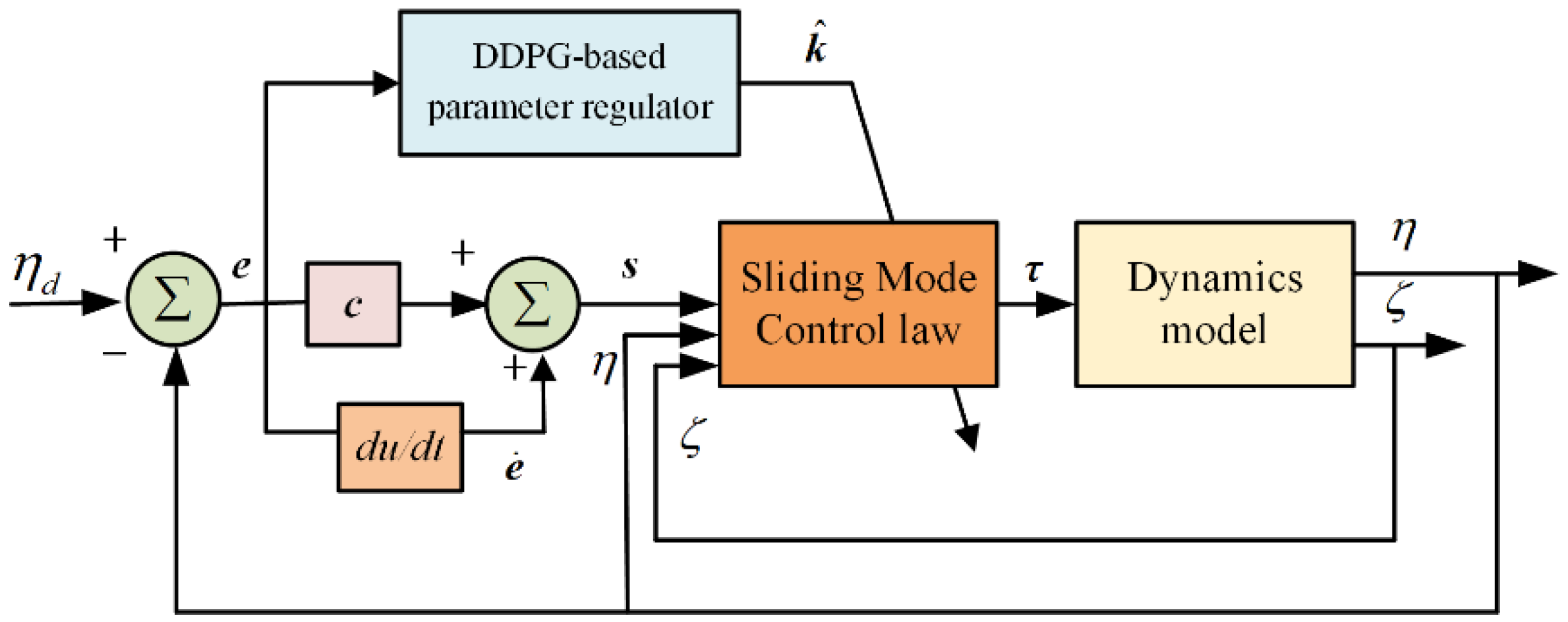
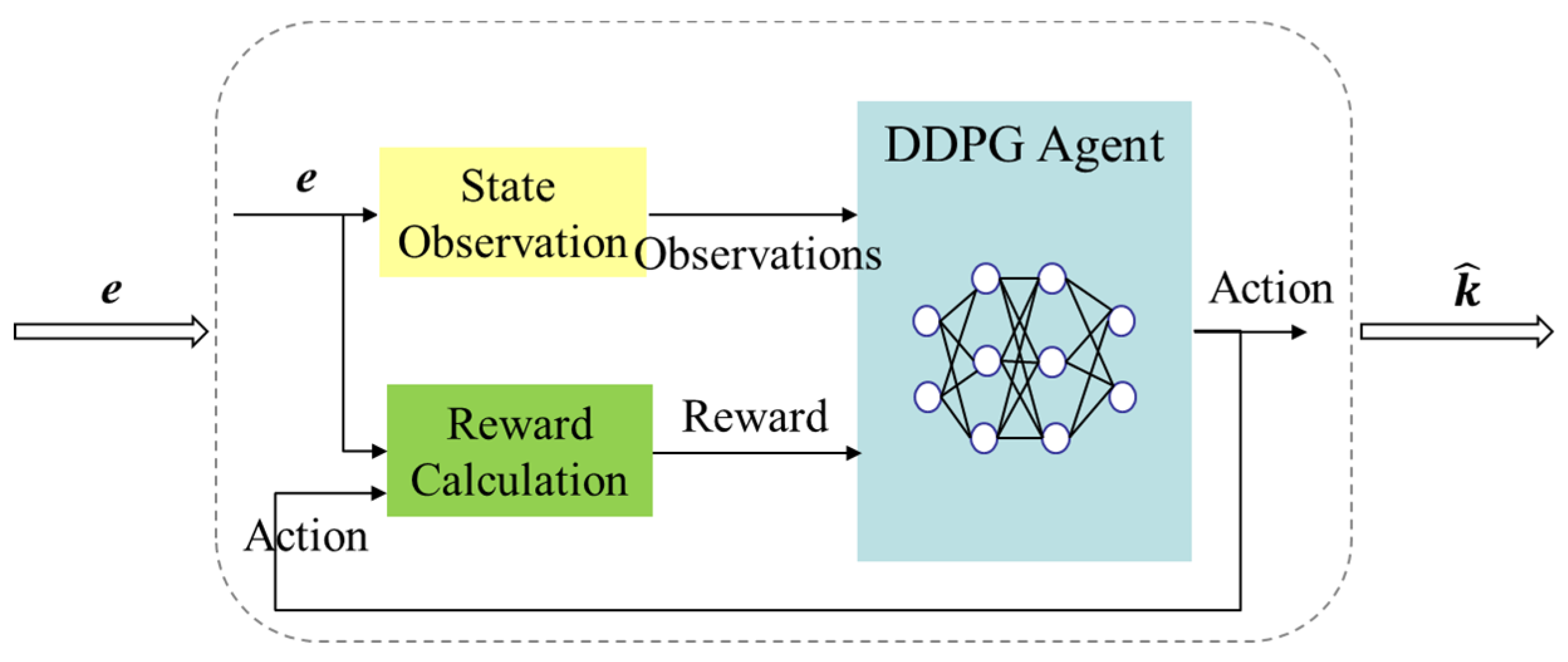
3.2. DDPG-SMC Design
| DDPG Algorithm |
|
Input: Experience replay buffer , Initial critic networks’ Q-function parameters , actor networks’ policy parameters , target networks and . Initialize the target network parameters: . for episode =1 to M do Initialize stochastic process to add exploration to the action. Observe initial state . for time step =1 to T do Select action . Perform action and transfer to next state , then acquire the reward value and the termination signal . Store the state transition data in experience replay buffer . Calculate the target function: Update the critic network by the minimized loss function: Update the actor network by policy gradient method: Update target networks: end for end for |
4. Simulation Results
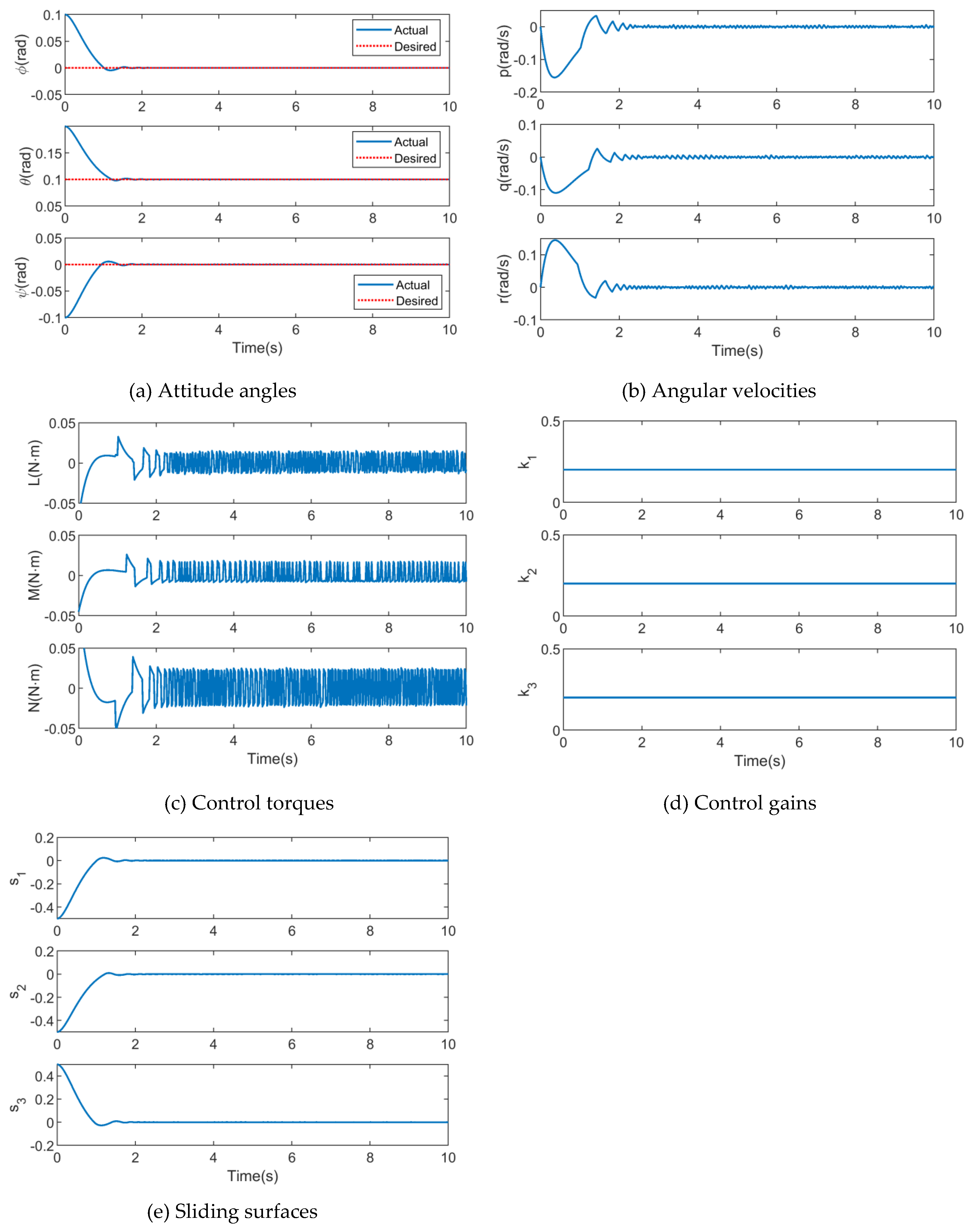
4.1. Simulation Results of SMC
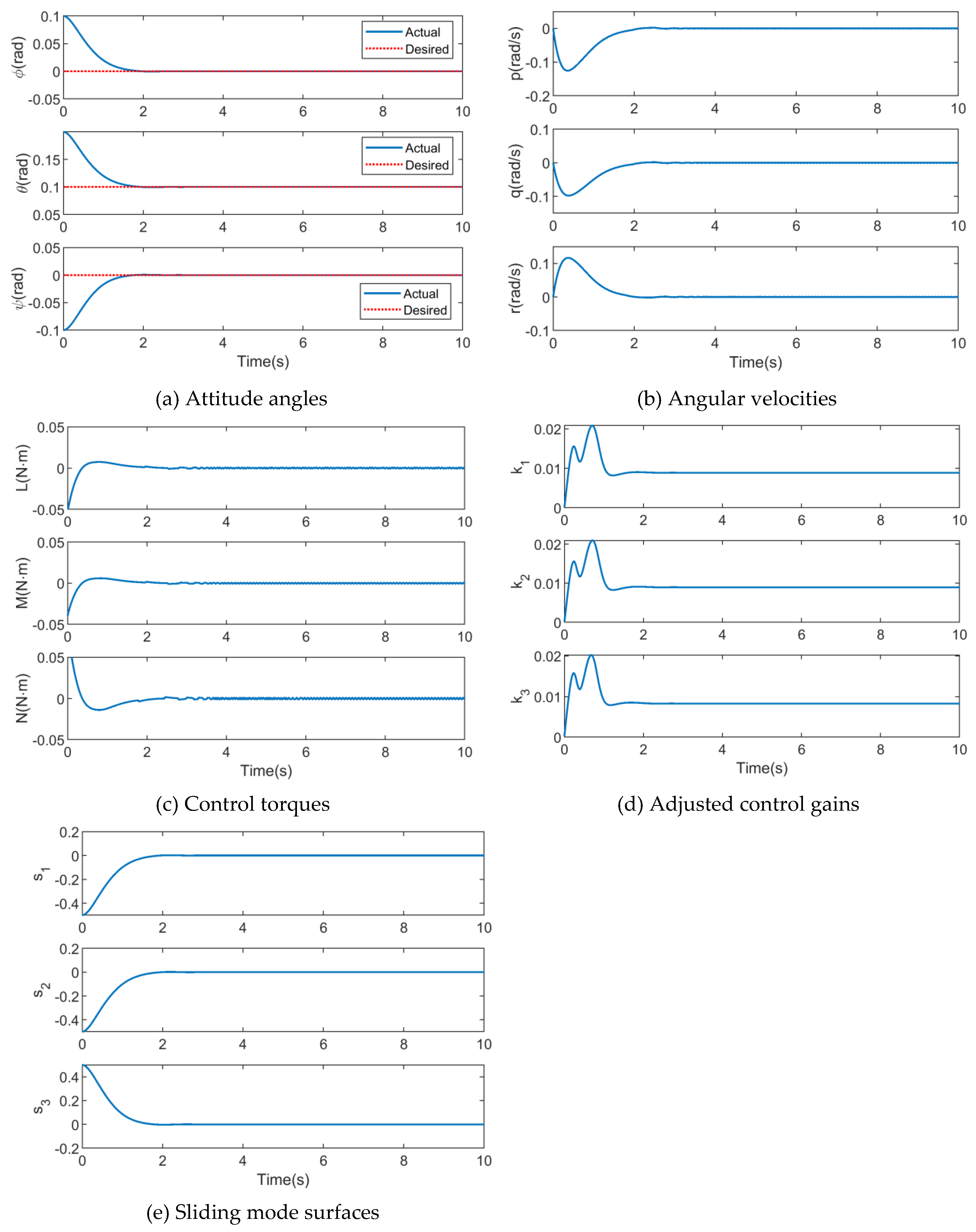
4.2. Simulation Results of AFGS-SMC
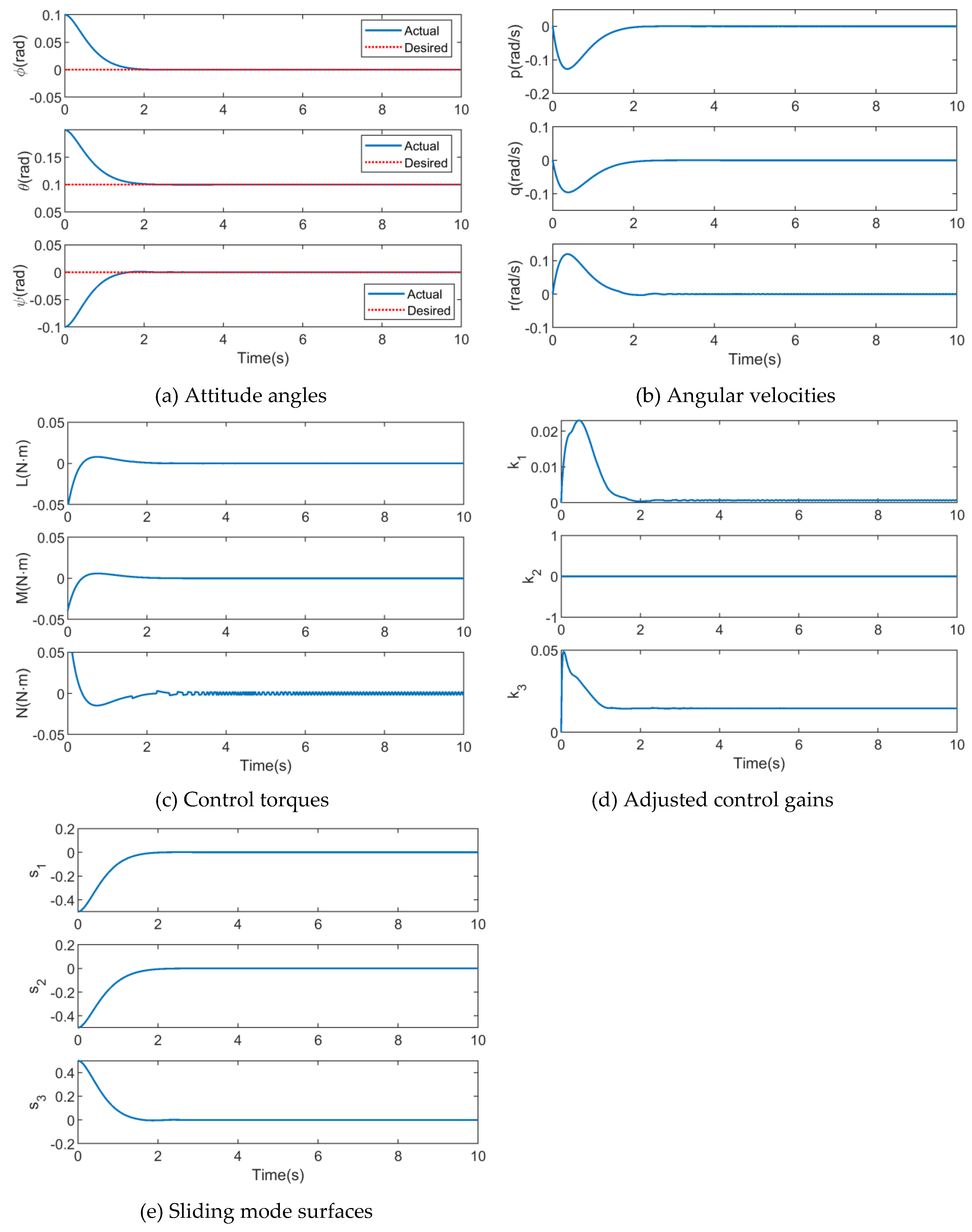
4.3. Simulation Results of DDPG-SMC
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grima, S.; Lin, M.; Meng, Z.; Luo, C.; Chen, Y. The application of unmanned aerial vehicle oblique photography technology in online tourism design. Plos One. 2023, 18 (9). [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, R. Understanding the drone epidemic. Computer Law & Security Review. 2014, 30 (3), 230–246. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Wang, W.; Falzon, G.; Kwan, P.; Guo, L.; Chen, G.; Tait, A.; Schneider, D. Automated cattle counting using Mask R-CNN in quadcopter vision system. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture. 2020, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrissi, M.; Salami, M.; Annaz, F. A review of quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicles: applications, architectural design and control algorithms. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems. 2022, 104 (2). [Google Scholar]
- Adiguzel, F.; Mumcu, T. V. Robust discrete-time nonlinear attitude stabilization of a quadrotor UAV subject to time-varying disturbances. Elektronika ir Elektrotechnika. 2021, 27 (4), 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, B. M.; Bu, R.; Jin, B. Review on wind resistance for quadrotor UAVs: modeling and controller design. Unmanned Systems. 2022, 11(01), 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gün, A. Attitude control of a quadrotor using PID controller based on differential evolution algorithm. Expert Systems with Applications. 2023, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Pljonkin, A.; Singh, P. K. Modeling and PID control of quadrotor UAV based on machine learning. Journal of Intelligent Systems. 2022, 31 (1), 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, S.; Nasiruddin, I.; Shahid, M. Design and simulation of a hybrid PD-ANFIS controller for attitude tracking control of a quadrotor UAV. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering 2017, 42 (12), 5211–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, B.; Deits, R.; Florence, P. R.; Tedrake, R. Aggressive quadrotor flight through cluttered environments using mixed integer programming. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bouabdallah, S.; Noth, A.; Siegwart, R. PID vs LQ control techniques applied to an indoor micro quadrotor. In Proceedings of the 2004 1EEE/RSJ Internationel Conference On Intelligent Robots and Systems, Sendal, Japan; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda-Colorado, R.; Aguilar, L. T. Robust PID control of quadrotors with power reduction analysis. ISA Transactions. 2020, 98, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N. Onboard actuator model-based incremental nonlinear dynamic inversion for quadrotor attitude control: Method and application. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics. 2021, 34 (11), 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeur, E. J. J.; Chu, Q.; de Croon, G. C. H. E. Adaptive incremental nonlinear dynamic inversion for attitude control of micro air vehicles. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics. 2016, 39 (3), 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, R. R.; Chu, Q. P.; Mulder, J. A. Reentry flight controller design using nonlinear dynamic inversion. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets. 2003, 40(1), 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y. INDI-based aggressive quadrotor flight control with position and attitude constraints. Robotics and Autonomous Systems. 2023, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. A composite adaptive fault-tolerant attitude control for a quadrotor UAV with multiple uncertainties. Journal of Systems Science and Complexity. 2022, 35 (1), 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Li, T.; Chen, C. L. P.; Li, Y. Attitude stabilization for a quadrotor using adaptive control algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, K.; Zhang, W. Adaptive attitude control for foldable quadrotors. IEEE Control Systems Letters. 2023, 7, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Long, Y.; Li, T.; Huang, T. Attitude tracking control for quadrotor based on time-varying gain extended state observer. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part I: Journal of Systems and Control Engineering. 2022, 237 (4), 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Su, X.; Jiang, T.; Huang, J. Robust dynamic geofencing attitude control for quadrotor systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. 2023, 70 (2), 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, Y. Attitude regulation for unmanned quadrotors using adaptive fuzzy gain-scheduling sliding mode control. Aerospace Science and Technology. 2016, 54, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Tang, H.; Xie, Y. A novel variable exponential discrete time sliding mode reaching law. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs. 2021, 68 (7), 2518–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, S.; Meng, W.; Lin, Z.; Shao, K.; Zheng, J.; Li, H.; Lu, R. Adaptive attitude control of a quadrotor using fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. 2022, 69(2), 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Yang, K. Attitude control of the quadrotor UAV with mismatched disturbances based on the fractional-order sliding mode and backstepping control subject to actuator faults. Fractal and Fractional. 2023, 7 (3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shen, Y.; Sha, Q. Adaptive DDPG design-based sliding-mode control for autonomous underwater vehicles at different speeds. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Underwater Technology (UT), Kaohsiung, Taiwan; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nicola, M.; Nicola, C.-I.; Selișteanu, D. Improvement of the control of a grid connected photovoltaic system based on synergetic and sliding mode controllers using a reinforcement learning deep deterministic policy gradient agent. Energies 2022, 15 (7). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillicrap, T. P.; Hunt, J. J.; Pritzel, A.; Heess, N.; Erez, T.; Tassa, Y.; Silver, D.; Wierstra, D. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mechali, O.; Xu, L.; Huang, Y.; Shi, M.; Xie, X. Observer-based fixed-time continuous nonsingular terminal sliding mode control of quadrotor aircraft under uncertainties and disturbances for robust trajectory tracking: Theory and experiment. Control Engineering Practice. 2021, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Lin, D.; Zheng, D.; Fan, S.; Ye, J. Observer based finite-time fault tolerant quadrotor attitude control with actuator faults. Aerospace Science and Technology. 2020, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiguzel, F.; Mumcu, T. V. Robust discrete-time nonlinear attitude stabilization of a quadrotor UAV subject to time-varying disturbances. Elektronika ir Elektrotechnika. 2021, 27 (4), 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, I.; Pérez-Alcocer, R.; Moreno-Valenzuela, J. Trajectory tracking double two-loop adaptive neural network control for a Quadrotor. Journal of the Franklin Institute. 2023, 360 (5), 3770–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, A.; Kiong Nguang, S.; Swain, A. Adaptive sliding mode control for a class of MIMO nonlinear systems with uncertainties. Journal of the Franklin Institute. 2014, 351 (4), 2048–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, D.; Lever, G.; Heess, N. Deterministic policy gradient algorithms. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning, Beijing, China; 2014. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Mass m /kg | 3.350 |
| Inertia moment about obxb Jx / (kg·m2) | 0.0588 |
| Inertia moment about obyb Jy / (kg·m2) | 0.0588 |
| Inertia moment about obzb Jz /(kg·m2) | 0.1076 |
| Lift factor b | 8.159×10-5 |
| Drag factor d | 2.143×10-6 |
| Distance between the center of mass and the rotation axis of any propeller l /m | 0.195 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





