Submitted:
21 March 2024
Posted:
22 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
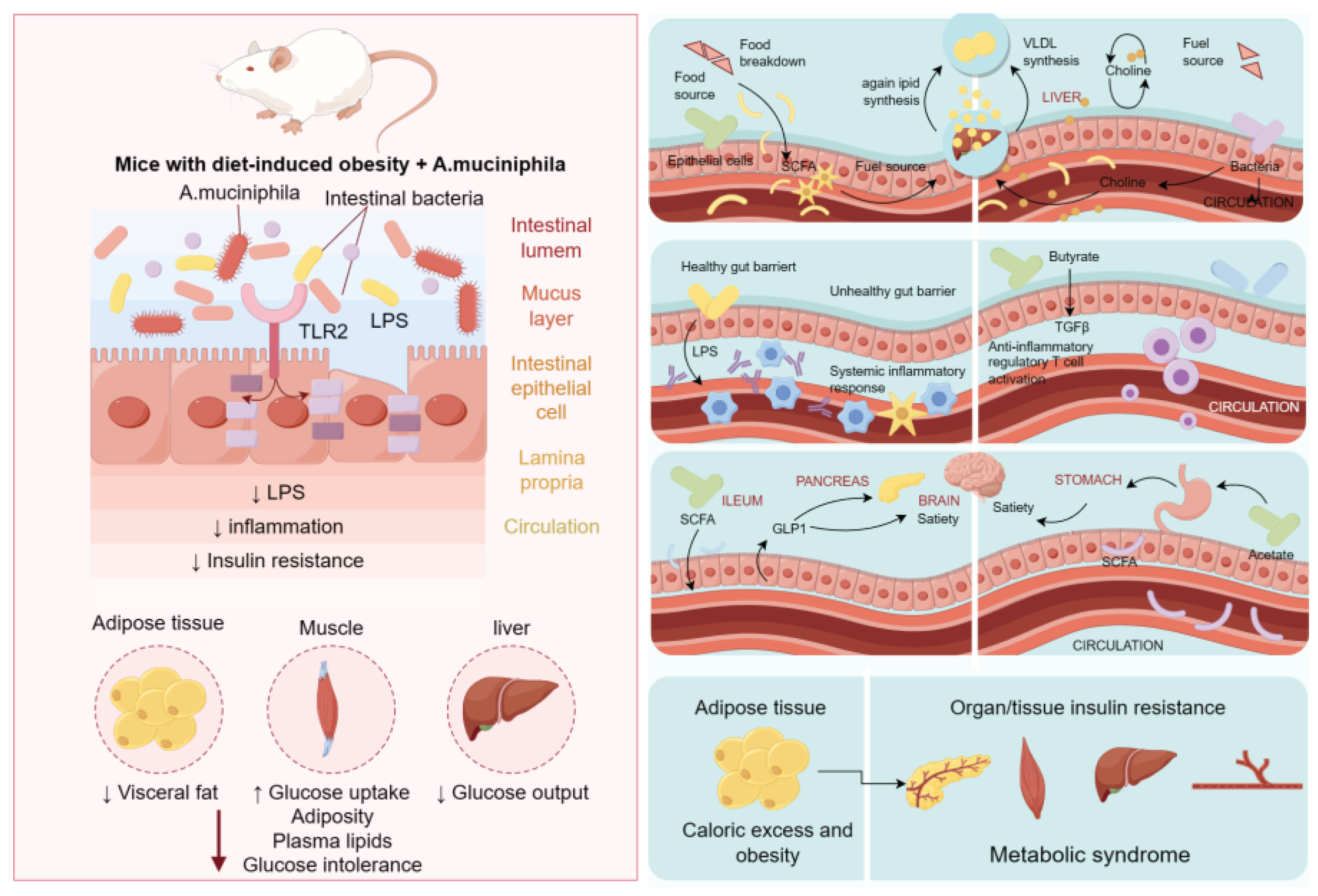
2. Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Syndrome
3. Gut Microbiota and Obesity
4. Gut Microbiota and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
5. Gut Microbiota and Hypertension
6. Gut Microbiota and Hyperlipidemia
7. Probiotics, Prebiotics, Metabiotics, and Synbiotics
8. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
9. Others
10. Conclusion
| Biotherapy | Resource | Disease | Outcomes | Mechanism of action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
PNS (notoginsenoside R1 and ginsenosides Rb1, Rd, Re, Rf, and Rg1) |
Male C57BL/6J mice (About 4-Week-old) | Obesity | PNS reduced adiposity in DIO mice but not in mice with induced obesity and impaired leptin signaling | The leptin-AMPK/STAT3 pathway induced by the PNSmediated modulations in the gut microbiota was involved in beige adipocyte reconstruction |
(Gupta, Osadchiy et al. 2020) |
| the “W-LHIT” capsules | Thirty-seven patients aged 18 to 60 from Wei-En hospital |
Obesity | W-LHIT significantly improved body weight and comorbid conditions without obvious adverse reaction or rebound weight gain. | Increase abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila and Enterococcus faecium, and decrease abundance of Proteobacteria in gut microbiota |
(Cao, et al. 2023) |
|
Probiotics+ BBR |
T2D patients | Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2 |
Anti diabetes effect | BBR can reduce intestinal microbiota bile acid (BA) conversion, thereby reducing intestinal farnesol X receptor (FXR) activity |
(Zhang, Gu et al. 2020) |
|
Intermittent Fasting |
Adults with MS, age 30 to 50 years |
Cardiome tabolic Risk Factors |
IF induces a significant alteration of the gut microbial community and functional pathways in a manner closely associated with the mitigation of cardiometabolic risk factors. |
IF induced significant changes in gut microbiota communities, increased the production of short-chain fatty acids, and decreased the circulating levels of lipopolysaccharides | (Guo, Luo et al. 2023) |
| GP-derived seasonings | high-risk cardiovascular subjects and in healthy subjects | Hyperten sion |
GP-seasoning may help in the modulation of cardiometabolic risk factors, mainly in the early stages | modulation of gut microbiota and functional bacterial communities by grape pomace | (Taladrid, Celis et al. 2022) |
| sodium reduction with slow sodium or placebo tablets | 145 participans (42%blacs, 19% Asian, and 34% females) |
Hyperten sion |
Reducing dietary intake can lower blood pressure and improve arterial compliance | Reducing dietary sodium can increase short chain fatty acids in the circulation, supporting the potential impact of dietary sodium on human gut microbiota | (Chen, He et al. 2020) |
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cristofori, F.; Dargenio, V. N.; Dargenio, C.; Miniello, V. L.; Barone, M.; Francavilla, R. , AntiInflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics in Gut Inflammation: A Door to the Body. Frontiers in immunology 2021, 12, 578386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puschhof, J.; Pleguezuelos-Manzano, C.; Clevers, H. , Organoids and organs-on-chips: Insights into human gut-microbe interactions. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira Rossi, J. L.; Barbalho, S. M.; Reverete de Araujo, R.; Bechara, M. D.; Sloan, K. P.; Sloan, L. A. Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases: Going beyond traditional risk factors. Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews 2022, 38(e3502). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemieux, I.; Despres, J. P. Metabolic Syndrome: Past, Present and Future. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Allam, S.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H. I. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J. E.; Kim, J. S.; Jo, M. J.; Cho, E.; Ahn, S. Y.; Kwon, Y. J.; Ko, G. J. The Roles and Associated Mechanisms of Adipokines in Development of Metabolic Syndrome. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsimardou, A.; Imprialos, K.; Stavropoulos, K.; Sachinidis, A.; Doumas, M.; Athyros, V. , Hypertension in Metabolic Syndrome: Novel Insights. Current hypertension reviews 2020, 16, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reitmeier, S.; Kiessling, S.; Clavel, T.; List, M.; Almeida, E. L.; Ghosh, T. S.; Neuhaus, K.; Grallert, H.; Linseisen, J.; Skurk, T.; Brandl, B.; Breuninger, T. A.; Troll, M.; Rathmann, W.; Linkohr, B.; Hauner, H.; Laudes, M.; Franke, A.; Le Roy, C. I.; Bell, J. T.; Spector, T.; Baumbach, J.; O'Toole, P. W.; Peters, A.; Haller, D. Arrhythmic Gut Microbiome Signatures Predict Risk of Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 258–272.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wen, X.; Yang, J. , Simiao Wan modulates the gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism during improving type 2 diabetes mellitus in mice. Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology 2022, 104, 154264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ouyang, M.; Gao, X.; Wang, S.; Fu, C.; Zeng, J.; He, X. , Phocea, Pseudoflavonifractor and Lactobacillus intestinalis: Three Potential Biomarkers of Gut Microbiota That Affect Progression and Complications of Obesity-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity : targets and therapy 2020, 13, 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Arora, K.; Prakash, S. Microbial Medicine: Prebiotic and Probiotic Functional Foods to Target Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, P. F.; Frissen, M. N.; de Clercq, N. C.; Nieuwdorp, M. , Fecal microbiota transplantation in metabolic syndrome: History, present and future. Gut microbes 2017, 8, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahayu, E. S.; Mariyatun, M.; Putri Manurung, N. E.; Hasan, P. N.; Therdtatha, P.; Mishima, R.; Komalasari, H.; Mahfuzah, N. A.; Pamungkaningtyas, F. H.; Yoga, W. K.; Nurfiana, D. A.; Liwan, S. Y.; Juffrie, M.; Nugroho, A. E.; Utami, T. , Effect of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum Dad-13 powder consumption on the gut microbiota and intestinal health of overweight adults. World journal of gastroenterology 2021, 27, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piche, M. E.; Tchernof, A.; Despres, J. P. , Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circulation research 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meslier, V.; Laiola, M.; Roager, H. M.; De Filippis, F.; Roume, H.; Quinquis, B.; Giacco, R.; Mennella, I.; Ferracane, R.; Pons, N.; Pasolli, E.; Rivellese, A.; Dragsted, L. O.; Vitaglione, P.; Ehrlich, S. D.; Ercolini, D. Mediterranean diet intervention in overweight and obese subjects lowers plasma cholesterol and causes changes in the gut microbiome and metabolome independently of energy intake. Gut 2020, 69, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Ni, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tu, W.; Ni, L.; Zhuge, F.; Zheng, A.; Hu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, L.; Fu, Z. , Spermidine improves gut barrier integrity and gut microbiota function in diet-induced obese mice. Gut microbes 2020, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, N.; Tan, H. Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y. , Panax notoginseng saponins modulate the gut microbiota to promote thermogenesis and beige adipocyte reconstruction via leptinmediated AMPKα/STAT3 signaling in diet-induced obesity. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1302–11323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X. J.; Liu, K.; Zhuang, P.; Tian, R.; Liu, S.; Clairmont, C.; Lin, X.; Sherman, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Fong, M.; Li, A.; Wang, B. K.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Shen, C.; Cui, X.; Cao, H.; Du, T.; Wan, G.; Cao, X. The Effects of Limosilactobacillus reuteri LR-99 Supplementation on Body Mass Index, Social Communication, Fine Motor Function, and Gut Microbiome Composition in Individuals with Prader-Willi Syndrome: a Randomized Double-Blinded Placebo-Controlled Trial. Probiotics and antimicrobial proteins 2021, 13, 1508–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegretti, J. R.; Kassam, Z.; Mullish, B. H.; Chiang, A.; Carrellas, M.; Hurtado, J.; Marchesi, J. R.; McDonald, J. A. K.; Pechlivanis, A.; Barker, G. F.; Miguens Blanco, J.; Garcia-Perez, I.; Wong, W. F.; Gerardin, Y.; Silverstein, M.; Kennedy, K.; Thompson, C. Effects of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation With Oral Capsules in Obese Patients. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology : the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association 2020, 18, 855–863.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solito, A.; Bozzi Cionci, N.; Calgaro, M.; Caputo, M.; Vannini, L.; Hasballa, I.; Archero, F.; Giglione, E.; Ricotti, R.; Walker, G. E.; Petri, A.; Agosti, E.; Bellomo, G.; Aimaretti, G.; Bona, G.; Bellone, S.; Amoruso, A.; Pane, M.; Di Gioia, D.; Vitulo, N.; Prodam, F. Supplementation with Bifidobacterium breve BR03 and B632 strains improved insulin sensitivity in children and adolescents with obesity in a cross-over, randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Clinical nutrition 2021, 40, 4585–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motiani, K. K.; Collado, M. C.; Eskelinen, J. J.; Virtanen, K. A.; Loyttyniemi, E.; Salminen, S.; Nuutila, P.; Kalliokoski, K. K.; Hannukainen, J. C. , Exercise Training Modulates Gut Microbiota Profile and Improves Endotoxemia. Medicine and science in sports and exercise 2020, 52(1), 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiroga, R.; Nistal, E.; Estebanez, B.; Porras, D.; Juarez-Fernandez, M.; Martinez-Florez, S.; Garcia-Mediavilla, M. V.; de Paz, J. A.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J.; Sanchez-Campos, S.; Cuevas, M. J. Exercise training modulates the gut microbiota profile and impairs inflammatory signaling pathways in obese children. Experimental & molecular medicine 2020, 52, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Sbierski-Kind, J.; Grenkowitz, S.; Schlickeiser, S.; Sandforth, A.; Friedrich, M.; Kunkel, D.; Glauben, R.; Brachs, S.; Mai, K.; Thurmer, A.; Radonić, A.; Drechsel, O.; Turnbaugh, P. J.; Bisanz, J. E.; Volk, H. D.; Spranger, J.; von Schwartzenberg, R. J. Effects of caloric restriction on the gut microbiome are linked with immune senescence. Microbiome 2022, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Li, Q.; Yi, H.; Kuang, T.; Tang, Y.; Fan, G. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as key actors in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2022, 149, 112839. [Google Scholar]
- A.; Witjes, J.; Wortelboer, K.; Majait, S.; Prodan, A.; Levin, E.; Herrema, H.; Winkelmeijer, M.; Aalvink, S.; Bergman, J.; Havik, S.; Hartmann, B.; Levels, H.; Bergh, P. O.; van Son, J.; Balvers, M.; Bastos, D. M.; Stroes, E.; Groen, A. K.; Henricsson, M.; Kemper, E. M.; Holst, J.; Strauch, C. M.; Hazen, S. L.; Backhed, F.; De Vos, W. M.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Rampanelli, E. Duodenal Anaerobutyricum soehngenii infusion stimulates GLP-1 production, ameliorates glycaemic control and beneficially shapes the duodenal transcriptome in metabolic syndrome subjects: a randomised doubleblind placebo-controlled cross-over study. Gut 2022, 71, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Ren, H.; Wang, S.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, X.; Ma, J.; Gu, X.; Xue, Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, G.; Qu, S.; Liang, J.; Qin, L.; Huang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Kong, P.; Hou, G.; Gao, M.; Shi, Z.; Li, X.; Qiu, Y.; Zou, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, G.; Lai, S.; Li, J.; Ning, G.; Wang, W. Gut microbiome-related effects of berberine and probiotics on type 2 diabetes (the PREMOTE study). Nature communications 2020, 11, 5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ren, H.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, C.; Ma, J.; Gu, X.; Xue, Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, G.; Qu, S.; Liang, J.; Qin, L.; Huang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Zou, Y.; Shi, Z.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Yang, H.; Lai, S.; Xu, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wang, W. Combined berberine and probiotic treatment as an effective regimen for improving postprandial hyperlipidemia in type 2 diabetes patients: a double blinded placebo controlled randomized study. Gut microbes 2022, 14, 2003176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perraudeau, F.; McMurdie, P.; Bullard, J.; Cheng, A.; Cutcliffe, C.; Deo, A.; Eid, J.; Gines, J.; Iyer, M.; Justice, N.; Loo, W. T.; Nemchek, M.; Schicklberger, M.; Souza, M.; Stoneburner, B.; Tyagi, S.; Kolterman, O. Improvements to postprandial glucose control in subjects with type 2 diabetes: a multicenter, double blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial of a novel probiotic formulation. BMJ open diabetes research & care 2020, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Adeshirlarijaney, A.; Gewirtz, A. T. Considering gut microbiota in treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Gut microbes 2020, 11, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Sha, L.; Li, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, P.; Dong, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. Dietary flaxseed oil rich in omega-3 suppresses severity of type 2 diabetes mellitus via anti-inflammation and modulating gut microbiota in rats. Lipids in Health and Disease 2020, 19, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, B.; Ren, L.; Du, H.; Fei, C.; Qian, C.; Li, B.; Zhang, R.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Ma, Z. Highfiber diet ameliorates gut microbiota, serum metabolism and emotional mood in type 2 diabetes patients. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2023, 13, 1069954. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Ding, Q.; Wei, Y.; Gou, X.; Tian, J.; Li, M.; Tong, X. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine on gut microbiota in adults with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology 2021, 88, 153455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siew, C. N.; Zhilu, X.; Joyce Wing Yan, M.; Keli, Y.; Qin, L.; Tao, Z.; Whitney, T.; Louis, L.; Rashid, N. L.; Sunny, H. W.; Yee Kit, T.; Amy, Y. L. L.; Kitty, C.; Jessica, Y. L. C.; Vincent, W. S. W.; Alice, P. S. K.; Ronald, C. W. M.; Elaine, Y. K. C.; Simon, K. H. W.; Ivan Chak Hang, H.; Paul, K. S. C.; Francis, K. L. C. Microbiota engraftment after faecal microbiota transplantation in obese subjects with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Gut 2022, 71(4), 716. [Google Scholar]
- Birkeland, E.; Gharagozlian, S.; Birkeland, K. I.; Valeur, J.; Mage, I.; Rud, I.; Aas, A.-M. Prebiotic effect of inulin-type fructans on faecal microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial. European Journal of Nutrition 2020, 59(7), 3325–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, C.; Sciatti, E.; Favero, G.; Bonomini, F.; Vizzardi, E.; Rezzani, R. Essential Hypertension and Oxidative Stress: Novel Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Cui, L.; Qi, J.; Ojo, O.; Du, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. The effect of dietary fiber (oat bran) supplement on blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases 2021, 31, 2458–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Donnell, J. A.; Zheng, T.; Meric, G.; Marques, F. Z. The gut microbiome and hypertension. Nature reviews. Nephrology 2023, 19(3), 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahler, A.; Wilck, N.; Rauch, G.; Dechend, R.; Muller, D.N. Effect of a probiotic on blood pressure in grade 1 hypertension (HYPRO): protocol of a randomized controlled study. Trials 2020, 21(1), 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Ren, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Bu, P.; Yang, J.; Ma, W.; Zhu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, J. Effect of fecal microbiota transplantation on primary hypertension and the underlying mechanism of gut microbiome restoration: protocol of a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled study. Trials 2022, 23(1), 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, E. M.; Li, J.; Stevens, B. R.; Pepine, C. J.; Raizada, M. K. Gut Microbiome and Neuroinflammation in Hypertension. Circulation research 2022, 130(3), 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W. J.; Xu, M. L.; Yu, X. J.; Du, M. M.; Li, X. H.; Yang, T.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Kang, K. B.; Su, Q.; Xu, J. X.; Shi, X. L.; Wang, X. M.; Li, H. B.; Kang, Y. M. , Antihypertensive effects of exercise involve reshaping of gut microbiota and improvement of gut-brain axis in spontaneously hypertensive rat. Gut microbes 2021, 13(1), 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taladrid, D.; de Celis, M.; Belda, I.; Bartolome, B.; Moreno-Arribas, M. V. Hypertension- and glycaemia-lowering effects of a grape-pomace-derived seasoning in high-cardiovascular risk and healthy subjects. Interplay with the gut microbiome. Food & function 2022, 13, 2068–2068. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, R. D.; Tang, Z. Z.; Chen, G.; Huang, S.; Ferguson, J. F. Soy food intake associates with changes in the metabolome and reduced blood pressure in a gut microbiota dependent manner. Nutrition, metabolism, and cardiovascular diseases : NMCD 2020, 30, 1500–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yang, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Guo, L.; Zhao, H. , Alterations of gut microbiota are associated with blood pressure: a cross-sectional clinical trial in Northwestern China. Journal of translational medicine 2023, 21(1), 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; He, F. J.; Dong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, C.; Harshfield, G. A.; Zhu, H. Modest Sodium Reduction Increases Circulating Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Untreated Hypertensives: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex. : 1979) 2020, 76, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Adachi, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Katsuyama, H. Postprandial Hyperlipidemia: Its Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Atherogenesis, and Treatments. International journal of molecular sciences 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S. J.; Lee, Y. J.; Lee, S. J.; Hong, B. K.; Kang, W. C.; Lee, J. Y.; Lee, J. B.; Yang, T. H.; Yoon, J.; Ahn, C. M.; Kim, J. S.; Kim, B. K.; Ko, Y. G.; Choi, D.; Jang, Y.; Hong, M. K. Treat-to-Target or HighIntensity Statin in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama 2023, 329, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Wu, S. , Impact of Gut Microbiota and MicrobiotaRelated Metabolites on Hyperlipidemia. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2021, 11, 634780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Feng, M.; Chu, Y.; Wang, S.; Shete, V.; Tuohy, K. M.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Kamil, A.; Pan, D.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, C.; Zhu, B.; Lv, N.; Xiong, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Sun, G.; Yang, Y. The Prebiotic Effects of Oats on Blood Lipids, Gut Microbiota, and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Mildly Hypercholesterolemic Subjects Compared With Rice: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Frontiers in immunology 2021, 12, 787797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; A, L.; Yang, C.; Zhao, F.; Han, H.; Shang, D.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Guo, R. Probio-X Relieves Symptoms of Hyperlipidemia by Regulating Patients' Gut Microbiome, Blood Lipid Metabolism, and Lifestyle Habits. Microbiology spectrum 2023, 11(3), e0444022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, R. R. X.; Park, M. A.; Wong, L. H.; Haldar, S.; Lim, K. J.; Nagarajan, N.; Henry, C. J.; Jiang, Y. R.; Moskvin, O. V. Gut microbiome responses to dietary intervention with hypocholesterolemic vegetable oils. NPJ biofilms and microbiomes 2022, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H. F.; Fang, C. Y.; Shen, Y. C.; Venkatakrishnan, K.; Wang, C. K. Efficacy of Probiotic Milk Formula on Blood Lipid and Intestinal Function in Mild Hypercholesterolemic Volunteers: A Placebo control, Randomized Clinical Trial. Probiotics and antimicrobial proteins 2021, 13, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storm-Larsen, C.; Hande, L. N.; Kummen, M.; Thunhaug, H.; Vestad, B.; Hansen, S. H.; Hovland, A.; Trøseid, M.; Lappegard, K. T.; Hov, J. R. , Reduced gut microbial diversity in familial hypercholesterolemia with no effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids intervention - a pilot trial. Scandinavian journal of clinical and laboratory investigation 2022, 82(5), 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szajewska, H.; Berni Canani, R.; Domellof, M.; Guarino, A.; Hojsak, I.; Indrio, F.; Lo Vecchio, A.; Mihatsch, W. A.; Mosca, A.; Orel, R.; Salvatore, S.; Shamir, R.; van den Akker, C. H. P.; van Goudoever, J. B.; Vandenplas, Y.; Weizman, Z. Probiotics for the Management of Pediatric Gastrointestinal Disorders: Position Paper of the ESPGHAN Special Interest Group on Gut Microbiota and Modifications. Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition 2023, 76, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Y.; Zhou, D. D.; Gan, R. Y.; Huang, S. Y.; Zhao, C. N.; Shang, A.; Xu, X. Y.; Li, H. B. Effects and Mechanisms of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics on Metabolic Diseases Targeting Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, P.; Joyce, S. A.; O'Toole, P. W.; O'Connor, E. M. Dietary Fibre Modulates the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S. L.; Li, S. Z.; Xiao, P. T.; Cai, Y. Y.; Chu, C.; Chen, B. Z.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Liu, E. H. Citrus polymethoxyflavones attenuate metabolic syndrome by regulating gut microbiome and amino acid metabolism. Science advances 2020, 6, eaax6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Luo, S.; Ye, Y.; Yin, S.; Fan, J.; Xia, M. Intermittent Fasting Improves Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and Alters Gut Microbiota in Metabolic Syndrome Patients. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 2021, 106, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpal, A.; Ismail-Beigi, F., Intermittent fasting and 'metabolic switch': Effects on metabolic syndrome, prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism 2020, 22 (9), 1496-1510. 60. Mocanu, V.; Zhang, Z.; Deehan, E. C.; Kao, D. H.; Hotte, N.; Karmali, S.; Birch, D. W.; Samarasinghe, K. K.; Walter, J.; Madsen, K. L., Fecal microbial transplantation and fiber supplementation in patients with severe obesity and metabolic syndrome: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Nature medicine 2021, 27 (7), 1272-1279.
- Belvoncikova, P.; Maronek, M.; Gardlik, R. Gut Dysbiosis and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Autoimmune Diseases. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, K. S. W.; Jayasinghe, T. N.; Wilson, B. C.; Derraik, J. G. B.; Albert, B. B.; Chiavaroli, V.; Svirskis, D. M.; Beck, K. L.; Conlon, C. A.; Jiang, Y.; Schierding, W.; Vatanen, T.; Holland, D. J.; O'Sullivan, J. M.; Cutfield, W. S. , Effects of Fecal Microbiome Transfer in Adolescents With Obesity: The Gut Bugs Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA network open 2020, 3, e2030415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S. C.; Xu, Z.; Mak, J. W. Y.; Yang, K.; Liu, Q.; Zuo, T.; Tang, W.; Lau, L.; Lui, R. N.; Wong, S. H.; Tse, Y. K.; Li, A. Y. L.; Cheung, K.; Ching, J. Y. L.; Wong, V. W. S.; Kong, A. P. S.; Ma, R. C. W.; Chow, E. Y. K.; Wong, S. K. H.; Ho, I. C. H.; Chan, P. K. S.; Chan, F. K. L. , Microbiota engraftment after faecal microbiota transplantation in obese subjects with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Gut 2022, 71, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





