1. Introduction
The presence of physical, biological, and chemical factors that produce dangerous conditions in water bodies is called water pollution for some useful uses. Contamination level is extremely dependent upon the water body's location and its uses. Water which is considered unfit for human beings may be fit for other uses like recreation, habitat, and for irrigation (Li and Wu, 2019). Some natural processes are responsible for water pollution. Here our attention will be on human activities that cause pollution known as anthropogenic pollution (Schweitzer & Noblet, 2018).
The compounds in which nitrogen is present act as nutrients for both plants and algae. However, the extreme existence of nitrate ions in water causes eutrophication that is related to the excessive presence of the growth of algae and aquatic plants (Paerl et al., 2001). It is also related to the depletion of O2. The number of nitrates in drinking water is 10 mg/L and in wastewater is 30ml/L (Ran et al., 2018). Nitrates pollute the groundwater and cause different diseases like malformation, methemoglobinemia, and carcinoma. The organic and inorganic nitrogen-containing fertilizers cause the removal of nitrate which pollutes the water (Sevda et al., 2018). Different pesticides are present in agricultural wastes and different salts present. Wastewater contains nitrates which may be treated or untreated is reach the groundwater (Re and Sacchi, 2017). The main source of nitrates is the use of nitrogen-containing fertilizers which cause water pollution. High levels of nitrates in drinking water cause health problems especially related to infants and pregnant women. Infants aged six months or younger are extremely affected by nitrates levels because certain bacteria are present in water that live in the digestive system (Parvizishad et al., 2017). These bacteria cause the change of nitrate into nitrite and this nitrite reacts with hemoglobin and forms methemoglobin this molecule does not carry oxygen and causes the depletion of oxygen in the blood and causes the disease of blue baby syndrome (Gutiérrez et al., 2018). Water productivity is limited by the excess of phosphorus (Farag et al., 2018). Industrial products like pesticides, fertilizers, water softeners, and detergents in which a large amount of phosphorous is present cause the production of wastewater (Kanu & Achi, 2011). In the production of paints, the amount of phosphate in wastewater, from the degreasing contains thousands of mg/L of cations and anions which cause different health problems so, the removal of phosphate is very important from the water (Singh et al., 2017).
The other inorganic Pollutants under investigation is phosphate. High amounts of phosphate ions are present in waste water which is secreted from industry. Many techniques have been available that help in the removal of phosphate ions (Xu et al., 2017). Many diseases like chronic kidney disease (CKD), cardiovascular disease, and death rates increase by the removal of phosphate ions from many years and are also responsible for genetic disorders (Eddington et al., 2010). Excess amounts of phosphorus cause some complications in human beings like skeletal muscle myopathy, and childhood rickets, and also cause osteomalacia. Only 1 mg-1 /L of phosphorus causes arrhythmias due to ATP depletion and acute hemolytic (Kinoshita & Fukumoto, 2018). In the current scenario, nanotechnology has great importance in the removal of environmental pollution due to some special properties of the nanomaterials. Nanotechnology contains a nanoscale dimension which is used for designing new technologies that improve the working of already existing processes (Kelsall et al., 2005). In water treatment, contaminant sensing, and in energy production nanomaterials have many applications (Hashim et al., 2018). The recent method that is used for the treatment of wastewater is the heterogeneous photocatalysis process (Ahmed & Haider, 2018). During this process oxide semi-conductor which is mostly titanium oxide (TiO2) used in the form of rutile or anatase, emits photo-excited electrons and generates holes which is positively charged. UV light changes the energy states of electrons from the valance band to the conduction band in a solid. The photo-catalysis process is used due to the property of deactivation of photo-catalysts when photo-catalysis is used for water treatment (Ani et al., 2018). Photocatalysis is a green technology that follows the advanced oxidation Process and can produce various reactive species like reactive nitrogen species, hydroxyl radicals, oxygen species, and oxygen radicals that attracted more attention in the degradation of organic and biological wastes due to their potential application (Saxena et al., 2016). In the present study, Al2O3 nanoparticles will be synthesized at different pH conditions. 50 of 0.1M Aluminum nitrate nanohydrate will be added dropwise in 50ml of leaf extract mean (1:1 ratio) by using a peristaltic pump at room temperature. After 30 minutes yellow color precipitates will be formed which indicates the formation of Al2O3 nanoparticles. The reaction mixture will be stored at room temperature for 24 hours and precipitates will be settled down. The solution will be centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 15 minutes. Precipitates will be isolated and washed with ethanol three times to remove organic impurities. At last, the product will be calcinated at 800OC for one hour in a muffle furnace to obtain Al2O3 nanoparticles (Manikandan et al., 2019)
Lemongrass has lignocellulose biomass which consists of almost 40% cellulose that is anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-fungal. Lemongrass is a common plant in which lignocellulose material is present which contains 28.5 % lignin, 39.5% cellulose, and 22.6% hemicellulose. Green tea also lowers blood pressure and cures the sore ion (Cai et al., 2019).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
The chemicals Aluminum Nitrate nano hydrate having molecular formula 375.13 g/mol, NaOH, HCl, Distilled Water, Ethanol, Formic Acid, and Nitrate Solution were received from the chemical store of Agriculture University of Pakistan. The plant materials were collected from the new botanical garden and recognized by referring to the senior professor of the Botany department of the University of Agriculture, Faisalabad. Cymbopogan citratus plant leaves were collected, washed with distilled water, dried, and cut into small pieces. Cymbupogen citrate leaves were collected from the Botanical Garden of the University of Agriculture, Faisalabad. The collected leaves were washed to remove dust particles using distilled water dried at room temperature for a week and ground into fine powder. After that 1.0 g of dried powder was transferred to 250 ml conical flask and added 100ml deionized water. The mouth of the conical flask was covered with aluminum foil and kept on an orbital shaker for 24 hours for continuous agitation at 250 rpm for the thorough mixing during which a dark yellow color leaf extract was formed. The resulting leaf extract was stored at a cold temperature (4°C), filtered with Whatman No.1 filter paper, and used for the green synthesis of Al2O3 nanoparticles (Zaheer et al., 2020).
2.2. Green Synthesis of Aluminum Oxide NPs by leaf extract of Cymbupogen Citrate at pH 2 to 12.
The salt used in this research work was Aluminum Nitrate nano hydrate having molecular formula 375.13 g/mol. A 0.1M molar solution was prepared by adding a specific amount of salt in distilled water. The salt used in this research work was Aluminum Nitrate nano hydrate having molecular formula 375.13 g/mol. A 0.1M molar solution was prepared by adding a specific amount of salt in distilled water. Biosynthesis of Al2O3 NPs was carried out according to the method. For the preparation of 0.1 M of Aluminum nitrate nano hydrate, 1.87g salt was dissolved in 50 ml distilled water and kept in a stirrer for 30 minutes, then the 50 ml of plant extract was added into the salt solution at continuous shaking. The mixture solution was kept on a magnetic heater stirrer at room temperature for 30 minutes, at 700 rpm. After 30 minutes, 2 M NaOH solution was added dropwise into the above solution to make pH 7. Different pH solutions like 2, 4, 7, 8, 10, and 12 were prepared respectively (Awad et al., 2020). After an overnight stay for the separation of nanoparticles, the centrifugation process is used and samples are transferred into tubes and placed in a centrifuge at 12,000rpm for 15 minutes. After centrifugation the pellets are present at the bottom and the supernatant is present at the upper surface. The upper portion is separated and pellets are washed with ethanol to remove organic impurities (Yusuf et al., 2017).
Viscous liquid was washed with ethanol so that the sample was transferred to the crucible and placed in a muffle furnace at 800 °C temperature for 1 hour. After 1 hour the liquid was converted into the white powder form and the crucible was removed from the furnace. The furnace is used for converting a liquid solution of salt and plant extract into solid nanoparticles. The solution is transferred into a crucible and the crucible is placed in the furnace. After heating in the furnace at 800 °C for 1 hour the crucible is removed from the furnace and the solution is converted into white solid powder. These are the nanoparticles of Al2O3.
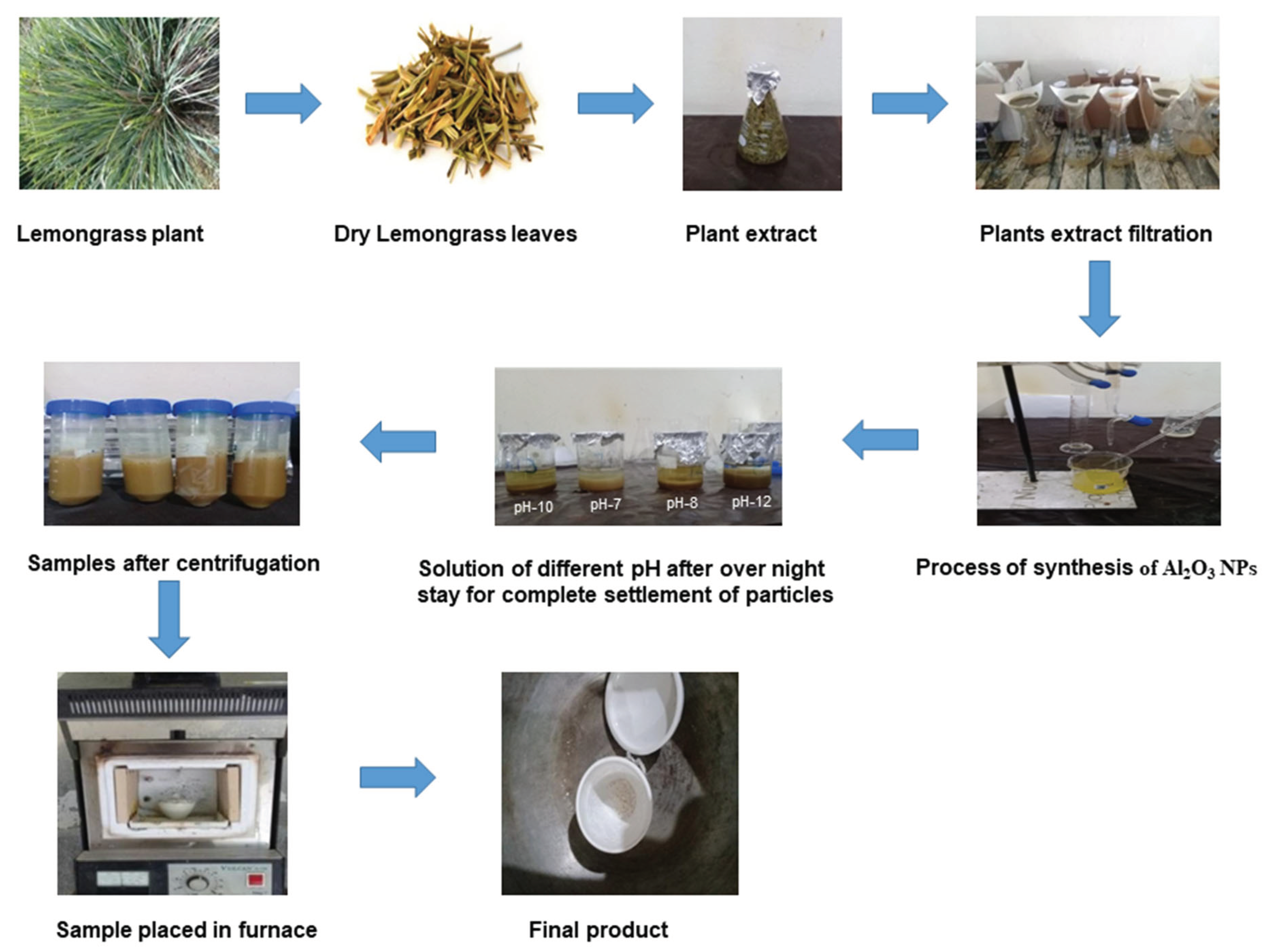
Figure 1.1.
Step-by-step process of preparation of Al2O3 NPs.
Figure 1.1.
Step-by-step process of preparation of Al2O3 NPs.
2.3. Characterization of Al2O3 Nps with Different pH Range
Aluminum oxide nanoparticles were synthesized by green method using Al
2NO
3.6H
2O (Aluminum nitrate nanohydrate) salt and extract of
Cymbopogan citratus. The leaf extract is used as a reducing and stabilizing agent which makes the nanoparticles eco-friendly and safe for use. Nanoparticles have more surface area and can be used for the removal of pollutants from water. The preparation of Al
2O
3 nanoparticles was confirmed by the white color of particles and UV-visible spectroscopy. The Aluminum oxide nanoparticles were synthesized by using the plant extract. The plant extract is used as a reducing agent and also acts as a stabilizing agent at different pH ranges. The formation of Aluminum oxide nanoparticles was confirmed by observing the color difference at various pH. But at pH- 7 a high amount of the particles is produced because at pH- 7 the solution is converted into yellow means that the formation of the yellow precipitate was made in 10 minutes which indicates the maximum amount of the Aluminum oxide nanoparticles. These particles were used for the removal of the nitrate and phosphate ions from waste water The Al
2O
3 nanoparticles show the maximum absorbance at 212nm which was confirmed by the UV/visible spectroscopy. The result confirmed the synthesis of Al
2O
3 nanoparticles. The maximum absorbance peak was observed at 212nm and according to the already reported literature where peak was observed at 217nm. The Al
2O
3 nanoparticles were synthesized at different pH by using plant extract. At 354 cm
-1, 2998 cm
-1, and 189 cm
-1 represent the strong peaks which show the symmetrical stretching vibration of the methyl and hydroxyl groups. Alkyl and amide groups in the nanoparticles show peaks at 838 cm
-1. In this method, the nanoparticles were prepared by plant 56 extract which is lemongrass, and confirm the polyhydroxy group’s presence which is bound with the Al
2O
3 NPs
Figure 1.3 (b). The acidic NPs exhibit functional groups such as the stretching bands of the hydroxyl (-OH) group at 2774 cm
-1, the -CH stretching bands at 1961 cm
-1, and the C = O stretch bands at 1508 cm
-1. The peaks of 1250 cm
-1 correspond to the -N-O stretch bands, the peaks in the region 1600–1400 cm
-1 are ascribed to the aromatic groups, and the -CO stretching bands of the ester and ether groups at 1026 cm
-1 and shown in
Figure 1.3(a). Manikandan et al., 2019 observed that the strong peaks at 3618 cm
-1, 3521 cm
-1 and 3443 cm
-1 correspond to the symmetrical stretching vibrations of the hydroxyl (-OH) group and vibrations of methyl and methoxy groups, respectively. The peaks at 1391 cm
-1 and 1011 cm
-1 correspond to bending vibrations of -OH groups and carboxylate groups. A small peak at 777 cm
-1 - 476 cm
-1 revealed the alkyl and amide groups in the Al
2O
3 NPs. The X-ray diffraction pattern of the powder is presented in
Figure 1.4. The absence of peaks corresponding to distinct crystalline polymorphs of Al
2O
3 confirms the amorphous nature of the obtained material. Because systematic calorimetric measurements of nanoscale materials require a series of samples with varying surface area and Al
2O
3 nanoparticles were heat-treated at different temperatures to diminish the surface area. The XRD profile of the sample indicates that the material was not crystallized. Manikandan et al., 2019 observed the strong peak at 2θ indicating the crystalline nature of the Al
2O
3 NPs. The X-ray diffraction peaks at 38.7°, 45.0°, and 65.4° were assigned as (111), (200), and (220) lattice planes which are in good agreement with those of the standard pure Al
2O
3 nanoparticles.
2.4. Photocatalytic Removal of Inorganic Ions
Removal of nitrate from wastewater under sunlight irradiation was used to find out the photocatalytic activity of the Al
2O
3 nanoparticles. The solutions were prepared at different pH and the reaction was carried out in test tubes and added the particles of different pH ranges in test tubes.10ppm solution of nitrate and phosphate was prepared and placed in sunlight and after some time the 0.05M formic acid was added to test tubes to increase the photocatalytic activity after 105 minutes the solutions were centrifuged at 12000rpm and then filtered by using a filter paper. The maximum absorbance was 410nm and at this wavelength, the removal of nitrate and phosphate ions was observed.
This formula was used for calculating the removal percentage of the nitrate and phosphate ions from wastewater. In this equation the Ci represents the initial concentration of the nitrate and phosphate ion and Ce represents the final concentration of the nitrates and phosphates after a time interval.
3. Result and Discussion
Different methods like ion exchange, precipitation, solvent extraction, and adsorption are used for the removal of the inorganic ions from the wastewater, these methods are time-consuming and costly. Other than these conventional methods the photo-catalytic degradation method is used for the removal of contaminants from waste water. This method is cheap and environmentally friendly. Work aimed to synthesize the Aluminum oxide nanoparticles through photo-catalytic degradation by using (Cymbopogan citratus) lemongrass plant extract which was used for the removal of inorganic ions from wastewater. The parameters that affect the removal of inorganic ions are pH, concentration of inorganic ions, and wavelength. The spectrophotometric analysis method is among the most useful analytical tools, due to its sensitivity, cost-effectiveness, accuracy, rapidity, simplicity, and low waste-producing techniques. Spectrophotometric analysis of the inorganic ions was performed and their maximum wavelength was calculated at the range of 360-800nm. The maximum absorbance is measured at about 350nm. Results were statistically analyzed by Simple linear regression.
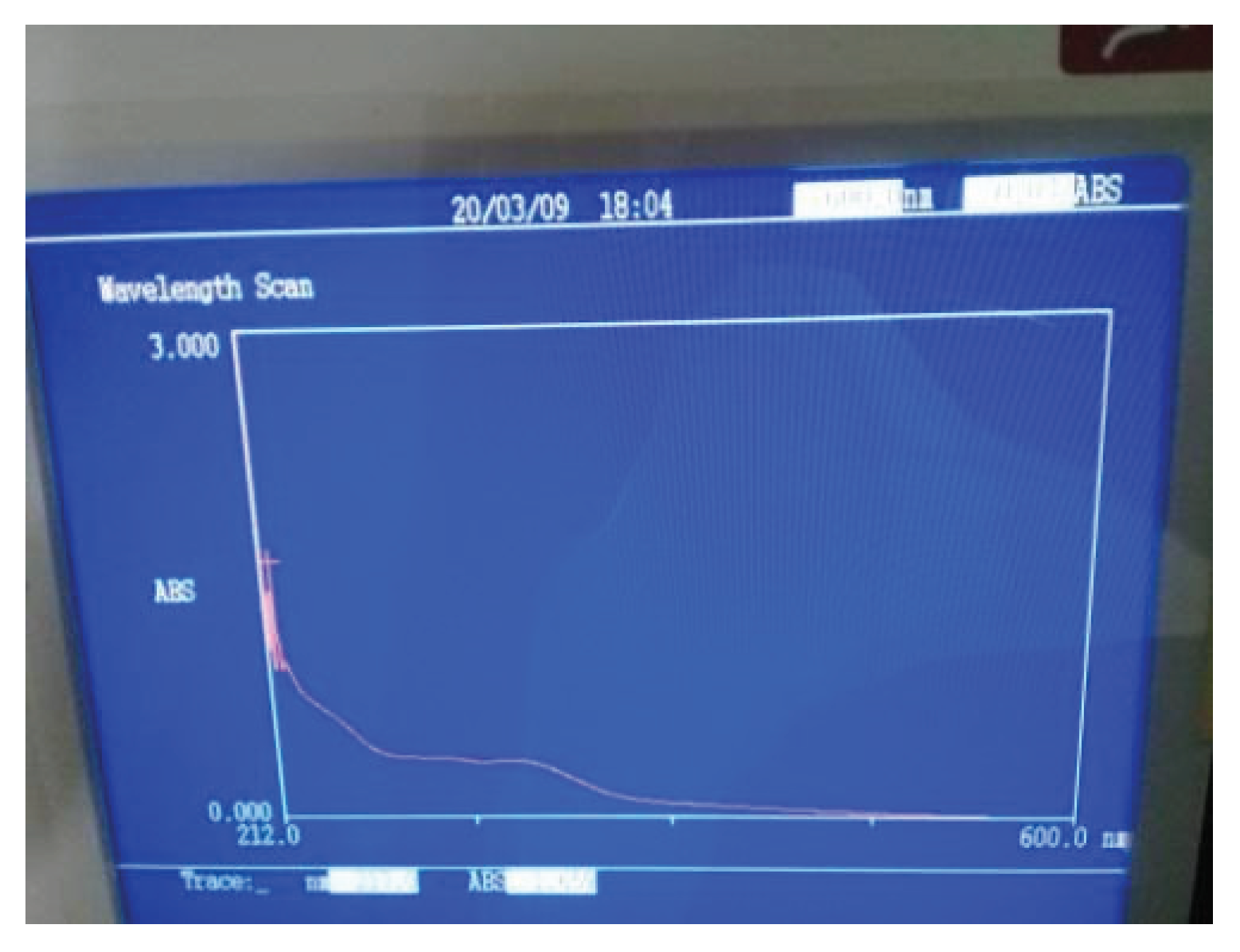
Aluminum oxide nanoparticles were synthesized by green method using Al2NO3.6H2O (Aluminum nitrate nanohydrate) salt and extract of Cymbopogan citratus. The leaf extract is used as a reducing and stabilizing agent which makes the nanoparticles eco-friendly and safe for use. Nanoparticles have more surface area and can be used for the removal of pollutants from water. The preparation of Al2O3 nanoparticles was confirmed by the white color of particles and UV-visible spectroscopy. The Aluminum oxide nanoparticles were synthesized by using the plant extract. The plant extract is used as a reducing agent and also acts as a stabilizing agent at different pH ranges. The formation of Aluminum oxide nanoparticles was confirmed by observing the color difference at various pH. But at pH- 7 a high amount of the particles is produced because at pH- 7 the solution is converted into yellow means that the formation of the yellow precipitate was made in 10 minutes which indicates the maximum amount of the Aluminum oxide nanoparticles. These particles were used for the removal of the nitrate and phosphate ions from waste water The Al2O3 nanoparticles show the maximum absorbance at 212nm which was confirmed by the UV-visible spectroscopy. The result confirmed the synthesis of Al2O3 nanoparticles. The maximum absorbance peak was observed at 212nm and according to the already reported literature where peak was observed at 217nm.
Figure 1.2.
UV-visible spectrum of Al2O3 NPs.
Figure 1.2.
UV-visible spectrum of Al2O3 NPs.
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
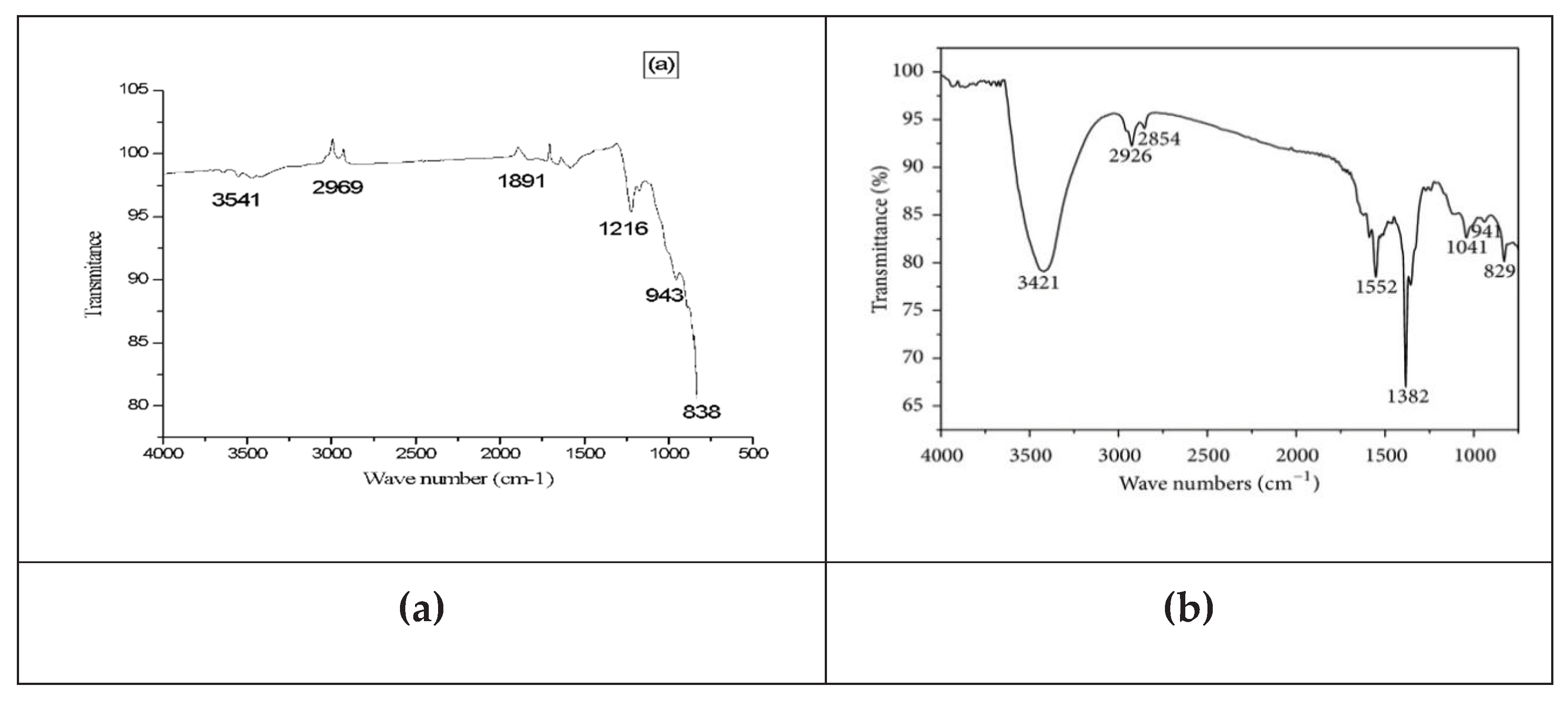
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is a very important analytical technique used to determine the functional groups of powered nanoparticles. Leaves extract of Cymbopogan citratus were used as a reducing agent, stabilizing, and capping agent for the synthesis of Al2O3 nanoparticles. FTIR is one of the most important analytical techniques that show the high spectral resolution peaks in the infrared region. Variations occur in vibrational energy levels when IR radiation is absorbed by nanoparticles of different pH. After the interaction of IR radiation, minor frequency changes occur in the vibrational energy level of functional groups detected by the FTIR spectrophotometer. FT-IR spectra give information about the non-spherical structure which produced large-sized particles (He et al., 2018). The Al2O3 nanoparticles were synthesized at different pH by using plant extract. At 3541 cm-1, 2998 cm-1, and 1891 cm-1 represent the strong peaks which show the symmetrical stretching vibration of the methyl and hydroxyl groups. Alkyl and amide groups in the nanoparticles show peaks at 838 cm -1. In this method, the nanoparticles were prepared by the plant extract which is lemongrass, and confirm the polyhydroxy group’s presence which is bound with the Al2O3 NPs. The acidic NPs exhibit functional groups such as the stretching bands of the hydroxyl (-OH) group at 2774 cm−1, the -CH stretching bands at 1961 cm−1, and the C = O stretch bands at 1508 cm−1. The peaks of 1250 cm−1 correspond to the -N-O stretch bands, the peaks in the region 1600–1400 cm−1 are ascribed to the aromatic groups, and the -CO stretching bands of the ester and ether groups at 1026 cm−1. Manikandan et al., 2019 observed that the strong peaks at 3618cm−1, 3521cm-1 3443cm−1 correspond to the symmetrical stretching vibrations of the hydroxyl (-OH) group and vibrations of methyl and methoxy groups, respectively. The peaks at 1391 cm-1 and 1011 cm−1 correspond to bending vibrations of −OH groups and carboxylate groups. A small peak at 777 cm−1- 476 cm−1 revealed the alkyl and amide groups in the Al2O3 NPs.
Figure 1.3.
(a) FT-IR spectra of acidic Al2O3 NPs. (b) FT-IR spectra of basic Al2O3 NPs.
Figure 1.3.
(a) FT-IR spectra of acidic Al2O3 NPs. (b) FT-IR spectra of basic Al2O3 NPs.
3.2. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
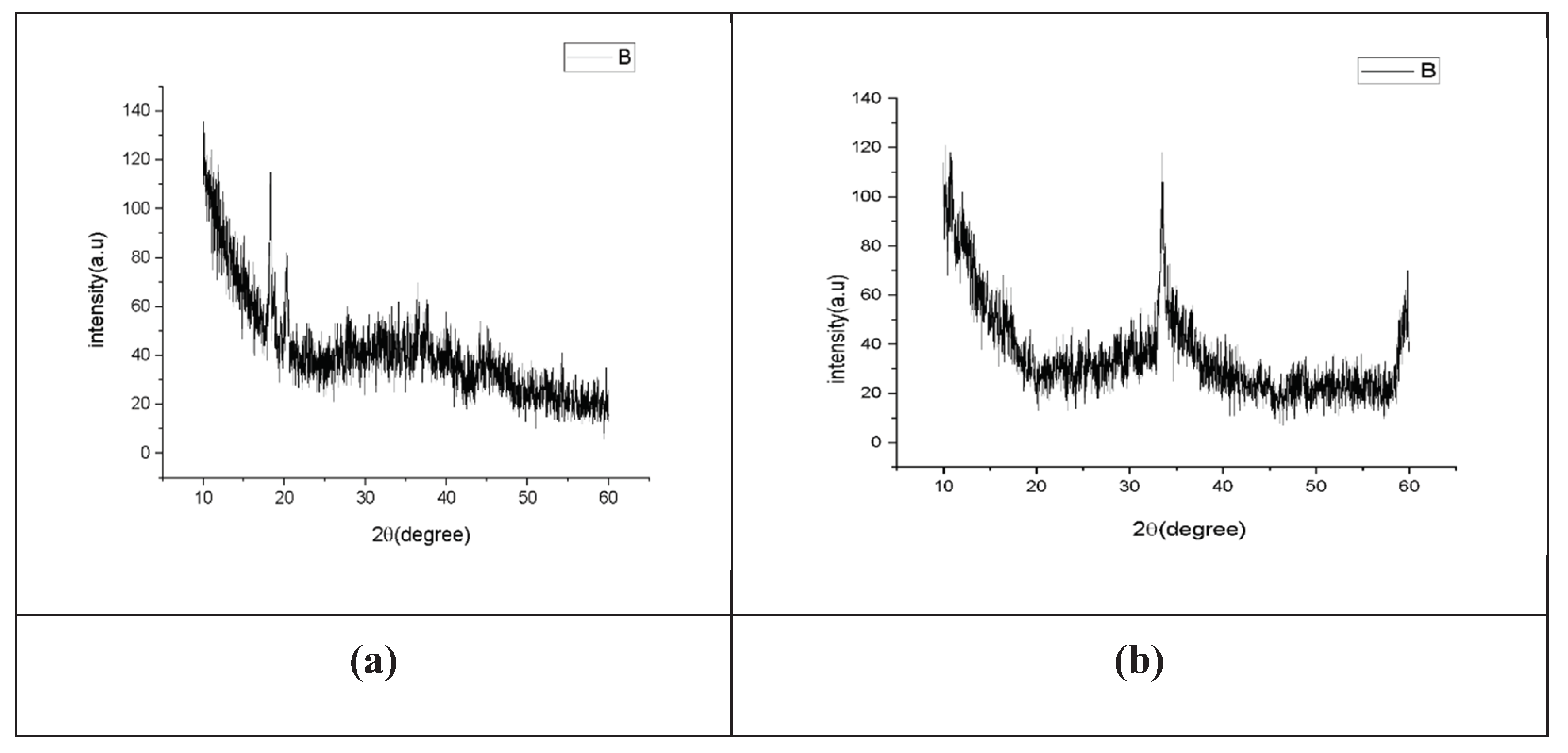
X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) is a rapid analytical technique primarily used for phase identification of a crystalline material and can provide information on unit cell dimensions. The analyzed material is finely ground, and homogenized, and average bulk composition is determined. X-ray diffraction is now a common technique for the study of crystal structures and atomic spacing. X-ray diffraction is based on constructive interference of monochromatic X-rays and a crystalline sample. These X-rays are generated by a cathode ray tube, filtered to produce monochromatic radiation, collimated to concentrate, and directed toward the sample. The interaction of the incident rays with the sample produces constructive interference (and a diffracted ray) when conditions satisfy Bragg's Law (nλ=2d sin θ). This law relates the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation to the diffraction angle and the lattice spacing in a crystalline sample. These diffracted X-rays are then detected, processed, and counted. By scanning the sample through a range of 2θangles, all possible diffraction directions of the lattice should be attained due to the random orientation of the powdered material. The X-ray diffraction pattern of the powder is presented in
Figure 1.4. Absence of peaks corresponding to distinct crystalline polymorphs of Al
2O
3 confirms the amorphous nature of the obtained material. Because systematic calorimetric measurements of nanoscale materials require a series of samples with varying surface area and Al
2O
3 nanoparticles were heat-treated at different temperatures to diminish the surface area. The XRD profile of the sample indicates that the material was not crystallized. Manikandan et al., 2019 observed the strong peak at 2θ indicating the crystalline nature of the Al
2O
3 NPs. The X-ray diffraction peaks at 38.7°, 45.0°, and 65.4° were assigned as (111), (200), and (220) lattice planes which are in good agreement with those of the standard pure Al
2O
3 nanoparticles.
Figure 1.4.
(a) X-ray diffraction analysis of neutral Al2O3 NPs. (b) X-ray diffraction analysis of acidic Al2O3 NPs.
Figure 1.4.
(a) X-ray diffraction analysis of neutral Al2O3 NPs. (b) X-ray diffraction analysis of acidic Al2O3 NPs.
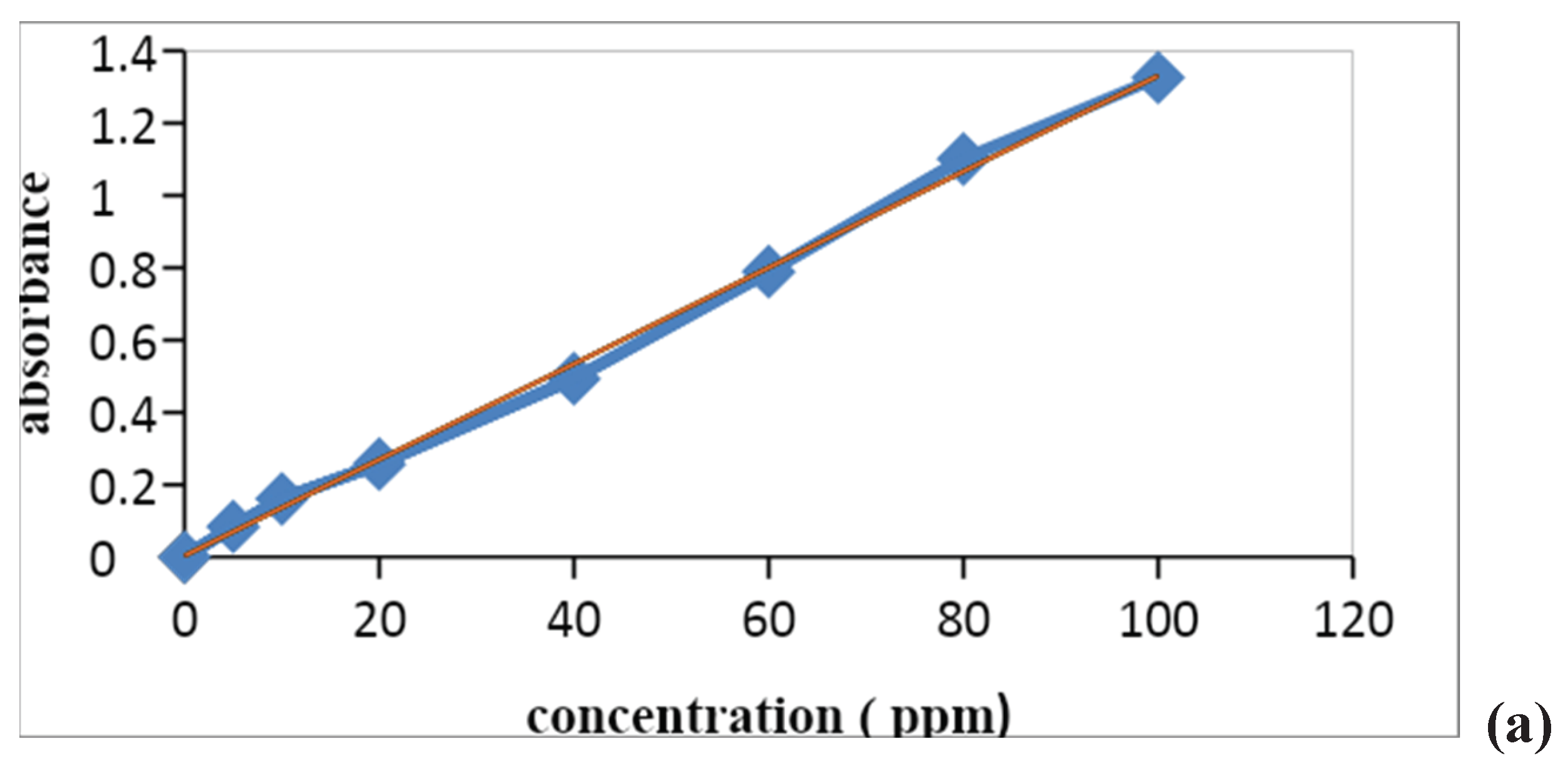
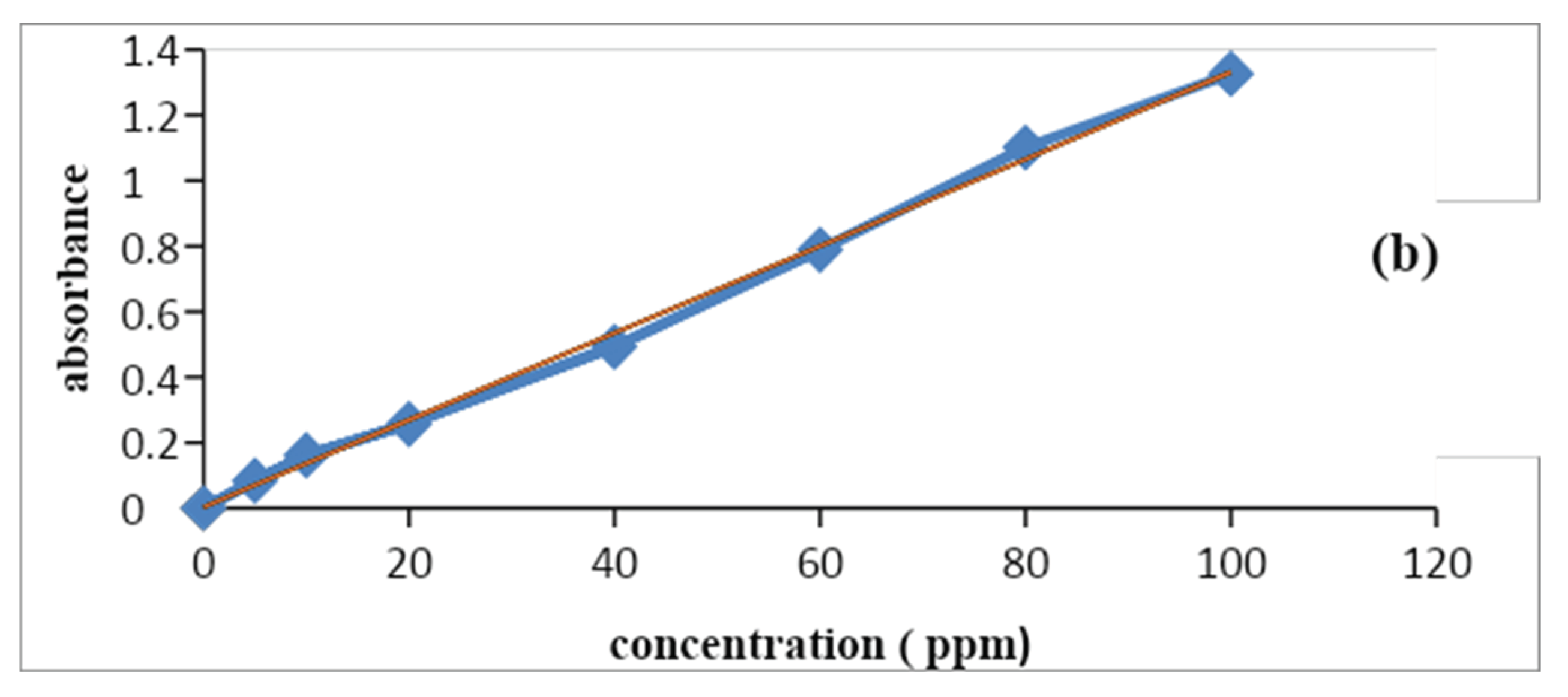
3.3. Calibration Curve
The calibration curve is also called the standard curve and this curve is commonly used for determining the concentration of target material in the unknown sample by comparing it with the standard solution whose concentration is known. The calibration curve of inorganic ions was observed by using a stock solution of nitrates and phosphate consequently at different concentrations from 10-100ppm. The pH of the solutions was adjusted in 7 and using HCl (0.01 M) and NaOH (0.01 M), the absorbance was measured at maximum absorbance wavelength. After the predetermined time of reaction, the absorbance of these solutions was measured on a UV–Vis spectrophotometer. Inorganic ions showed a maximum absorbance in the visible region at 410nm (Wang et al., 2019). These wavelengths are used to construct a calibration curve of absorbance vs. concentration. Thus, according to Beer Lambert’s law, it is verified that concentration is directly proportional to concentration.
A= absorbance
€= the mo1ar absorptivity
l= the path length of the sample
C= the concentration of the inorganic ion
The R2 values of the nitrate were about 0.9976 and phosphate was 0.997.
Figure 1.5.
Calibration curve of (a) nitrate and (b) phosphate ions.
Figure 1.5.
Calibration curve of (a) nitrate and (b) phosphate ions.
3.4. Optimization of the Experimental Variables
Different variables like pH, contact time, and initial and final concentration affect the photocatalytic activity in the removal of inorganic ions like nitrate and phosphate. These different parameters were optimized in various ways.
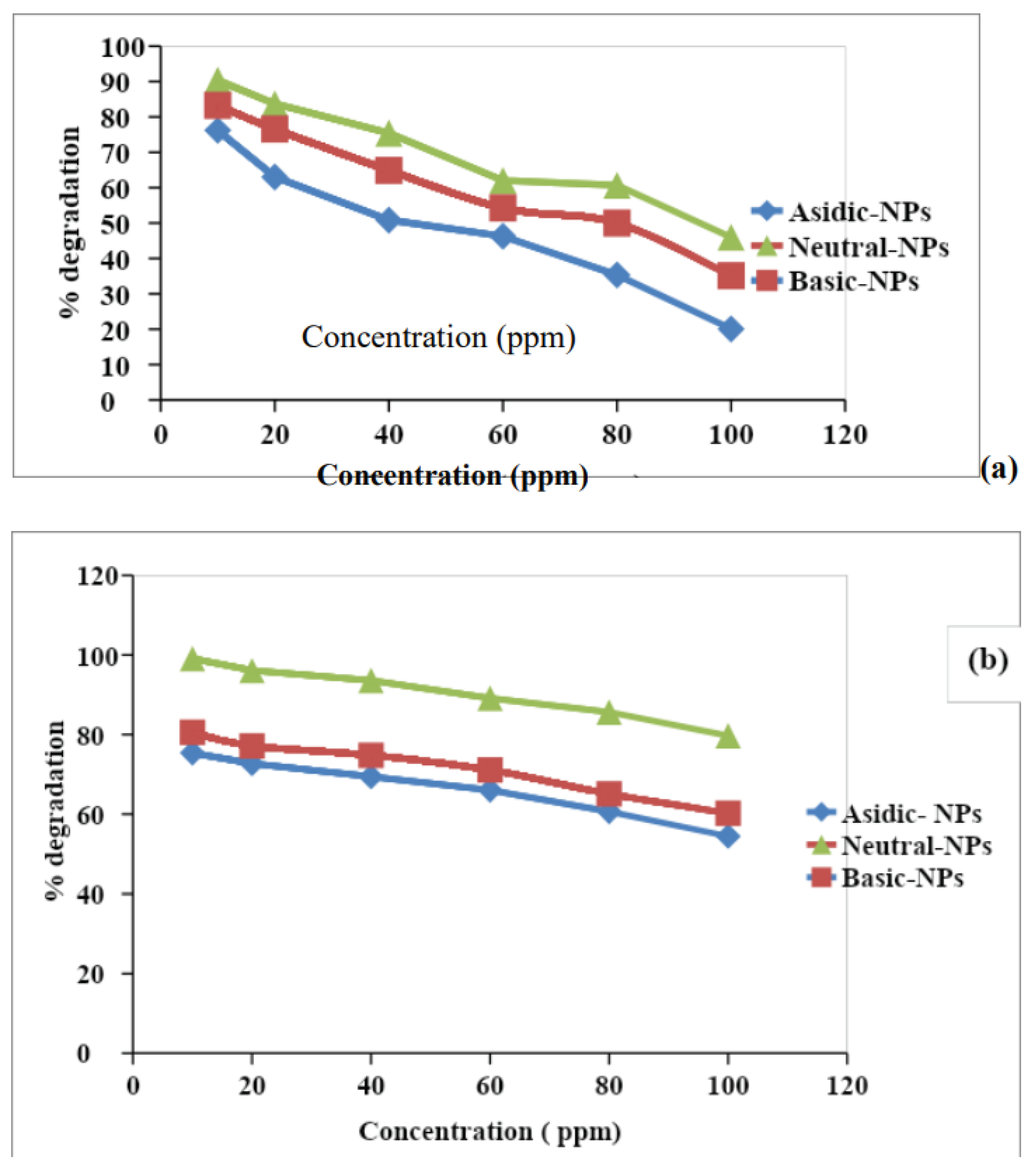
3.4.1. Effect of Initial Concentration on Degradation
As the concentration increased from 10 to 100 ppm the % degradation decreased from 76% to 20%. The highest % degradation occurred at 10ppm. The degradation capacity of the different pH-based NPs at different concentrations of the inorganic ions was evaluated. The maximum % degradation of inorganic ions, obtained at 10ppm concentration in the following order Acidic NPs (76%) < Basic NPs (83%) < Neutral NPs (90%). Shah & Shah, 2020 observed that maximum % degradation occurred at a neutral pH level because it is amphoteric and has a good surface area causing the 90% degradation of the phosphate ion. For the nitrate ion % degradation is about 95%.
Figure 1.6.
Effect of different concentrations on the % degradation of the (a) nitrate (b) phosphate ion.
Figure 1.6.
Effect of different concentrations on the % degradation of the (a) nitrate (b) phosphate ion.
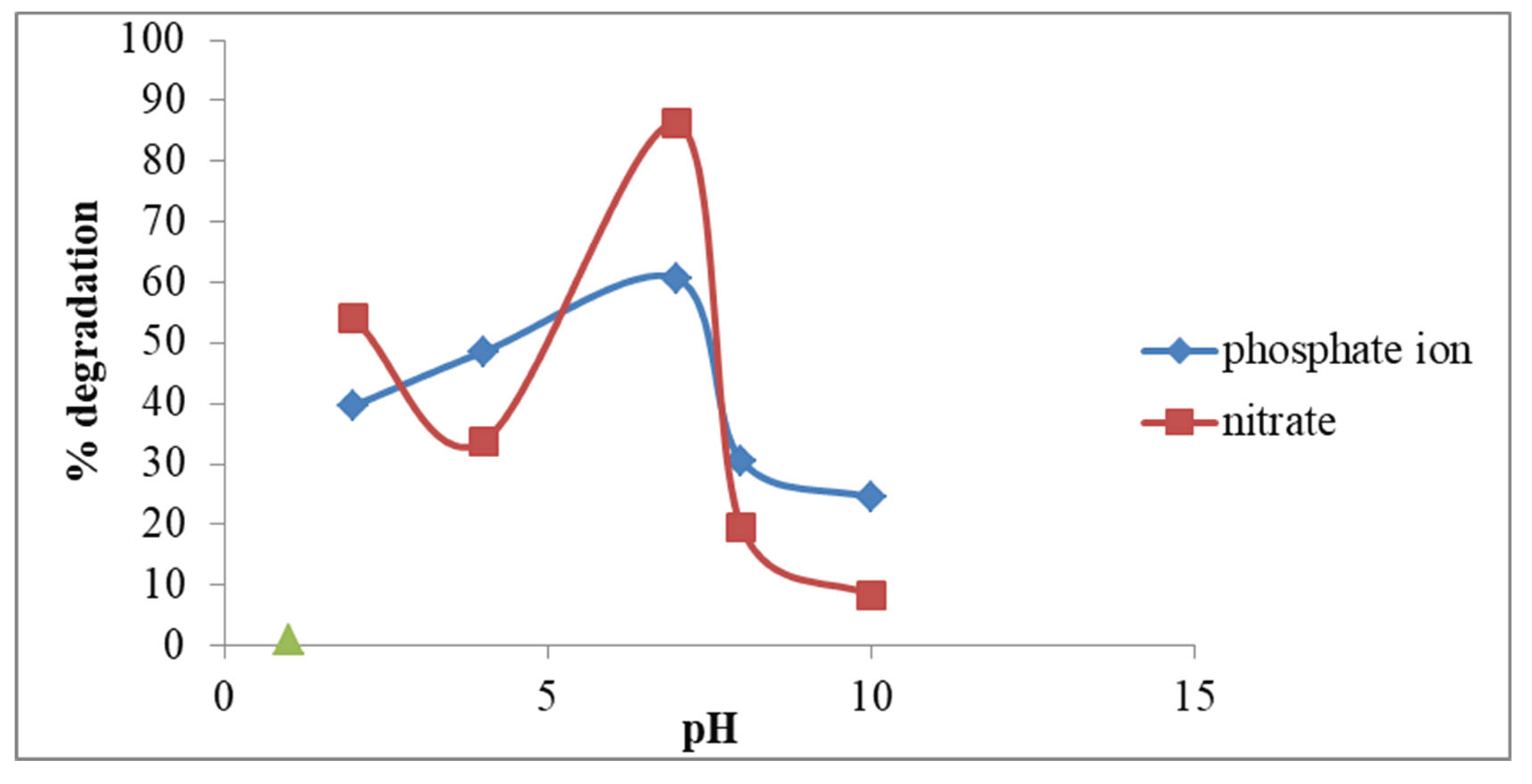
3.4.2. Effect of pH on Removal of Inorganic Ions
In this research, the pH effect was investigated for the removal of inorganic ions at different pH ranges (2-10). Decreasing the pH of the solution decreases the % of removal that occurs for inorganic ions. Maximum degradation capacity for the inorganic ions was attained at higher pH-7. For the removal of inorganic ions, the neutral medium is suitable. In a neutral medium, the neutralization of the positive charges causes the diffusion easy by decreasing the protonation at their surface. Due to changes in equilibrium the change in pH. At pH-7 the maximum removal of the inorganic ions was observed in which 86% was due to the activated carbon. The trend for the % degradation is that Neutral NPs> Basic NPs> Acidic NPs.
Manikandan et al., 2019 observed that % degradation was about 94% and 86% of nitrate and phosphate respectively and my results were about 60% and 86% of nitrate and phosphate ions.
The inorganic ions are removed from the waste water by reducing carbon dioxide radical (CO2.) which is produced during the reaction when electrons are generated from in conduction band and hydrogen is produced at the conduction band from the aqueous solution. The electrons of the Al2O3 nanoparticles from the valance band have transferred to the Plasmon states by leaving positive charges in the valance band in this way. OH radicals are increased in the aqueous solution. For minimizing the electron-hole recombination and for providing more electrons for the oxygen molecule reduction into the superoxide radicals which is the anion. In the oxidation and reduction process, the photo-generated holes and electrons are involved. So, for minimization of these electron-hole productions, the catalyst formic acid is added to the reaction which acts as a sacrificial reagent and reduces the recombination of the electron-holes process. During the photocatalysis process, carboxyl anion radical production has a strong reducing ability and reduces the inorganic ions into different gases like nitrate and phosphate reducing them into nitrogen and phosphorus respectively.
Figure 1.7.
Effect of pH on degradation of the nitrate and phosphate ion.
Figure 1.7.
Effect of pH on degradation of the nitrate and phosphate ion.
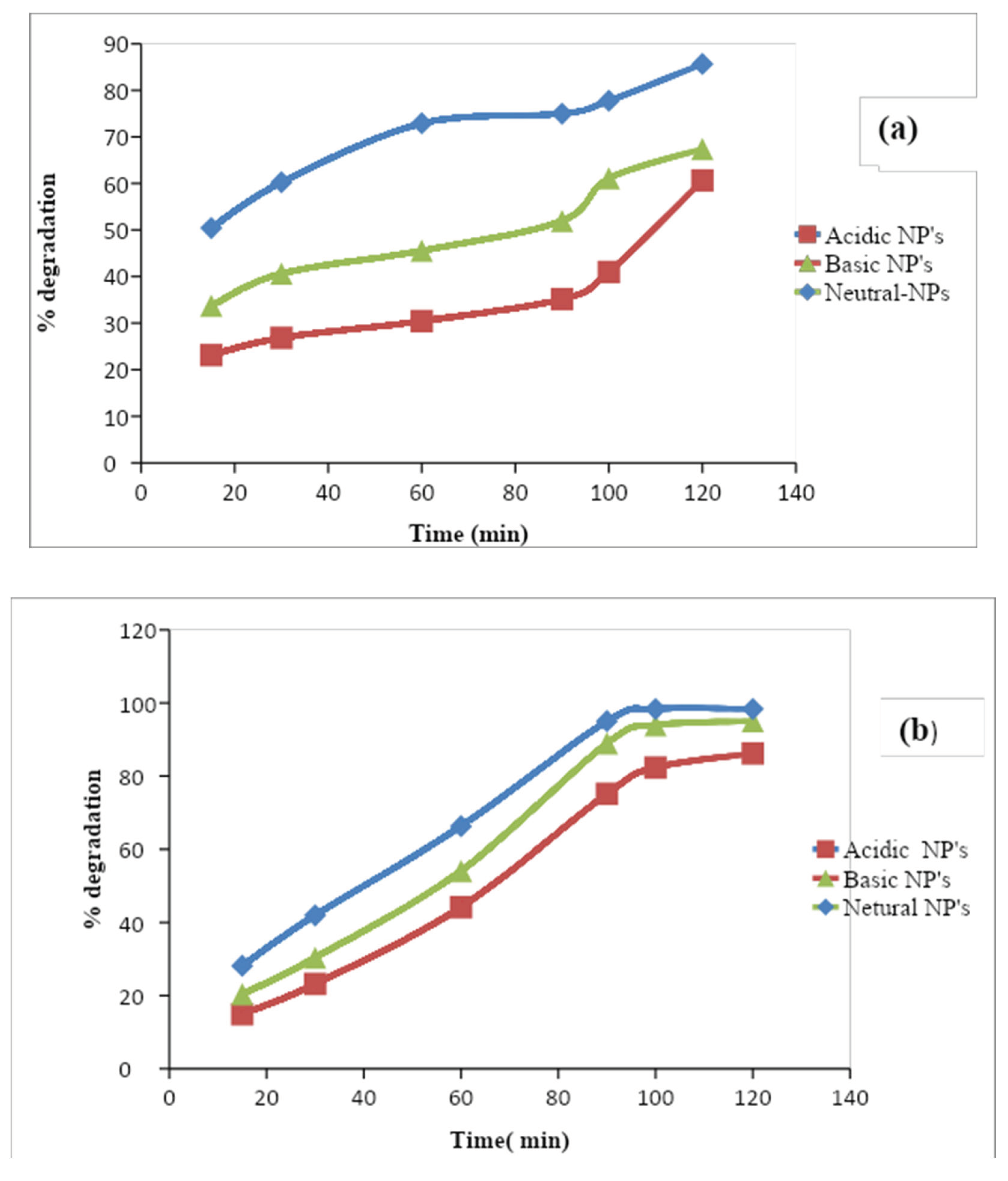
3.4.3. Effect of Contact Time
For a longer-scale application system, the contact time among the catalysis is very important for the cost-effective wastewater treatment method.
According to present research, the % degradation was increased with time. The maximum % degradation obtained by the neutral nanoparticles is about 85% and 98% for the phosphate and nitrate ions respectively. In acidic medium % degradation was less which was about 60% and 86% of phosphate and nitrate respectively. Because for the degradation the hydroxyl radicals are important but in this medium quantity of the radical is enough for the % degradation but the basic medium shows more % degradation as compared to the acidic medium. The photochemical degradation of inorganic ions was studied by using UV irradiation, Al2O3 NPs, and Formic acid as a catalyst for 15 to 120 minutes. The effect of the initial concentration of the target ion and formic acid effect was observed. The presence of the formic acid as a catalyst in the solution resulted in significantly increased % degradation which is 2.5 times higher than without it after 120 minutes and then the reaction goes into the equilibrium form. The trend is Neutral NPs> Basic NPs> Acidic NPs. Malakootian et al., 2020 observed that reaction-neutral Al2O3 NPs show the maximum degradation from the synthetic solution was obtained at the optimum pH of 7, contact time 120min, and initial concentration of the inorganic ion was 10mg/L. The % degradation for the nitrate and Phosphate ions was observed at about 95% and 98% respectively.
Figure 1.8.
Effect of contact time on the % degradation of the (a) phosphate (b) nitrate ion.
Figure 1.8.
Effect of contact time on the % degradation of the (a) phosphate (b) nitrate ion.
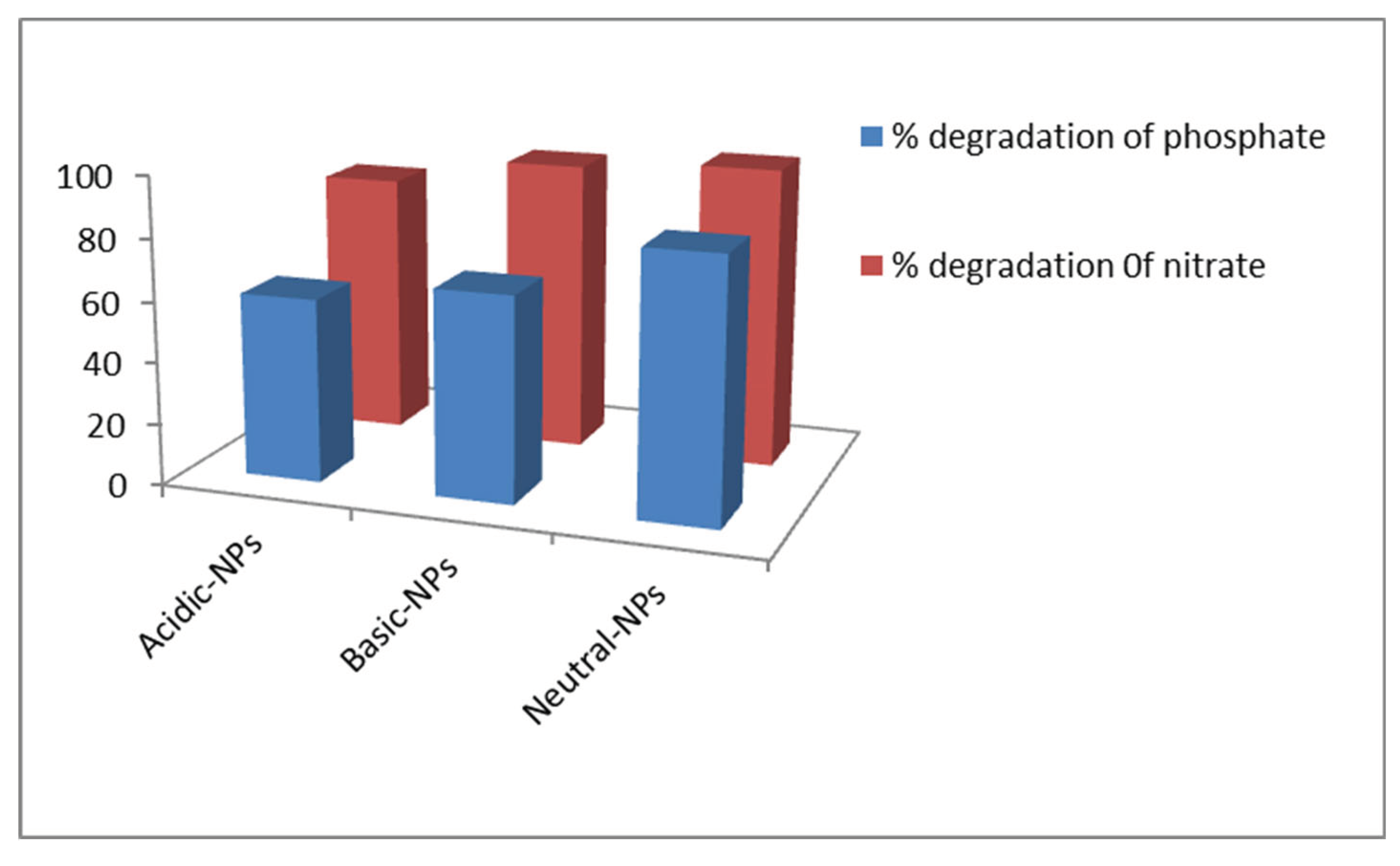
3.4.4. Comparison between Different Catalysts
Comparison studies of different catalysts at optimum conditions were performed. To evaluate the effect of different catalysts, a 10ppm solution of the inorganic ions was placed in sunlight radiation for 60 min with 0.1g of acidic, basic, and neutral particles of Al
2O
3 nanoparticles. The optimum pH was 2, 7, and 10. The degradation ability of different nanoparticles is depicted in
Figure 1.7. The order of degradation was about acidic<basic< neutral.
Wang et al., 2020) observed that the % degradation of nitrate and phosphate ions by Al2O3 NPs catalysts is very high at pH = 7, whereas it is much less at pH-4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, and also in dark conditions. Further, we could also observe that there was a decrease in the % degradation of nitrate after degradation of the NPs on altering the pH. Concurrently, the color of the solution changed gradually, suggesting that the nitrate ions were diverted by an oxidation process.
Figure 1.9.
Comparison between different catalyst.
Figure 1.9.
Comparison between different catalyst.
3.5. Kinetic Modeling
From the experimental kinetic data, for throwing light on steps of potential controlling rate like mass transfer, chemical process, and adsorption mechanism different models have been applied. In this experiment, the pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, and intra-particle diffusion models were used to test the degradation mechanisms of inorganic ions on Al2O3 nanoparticles (de Luna et al., 2013)
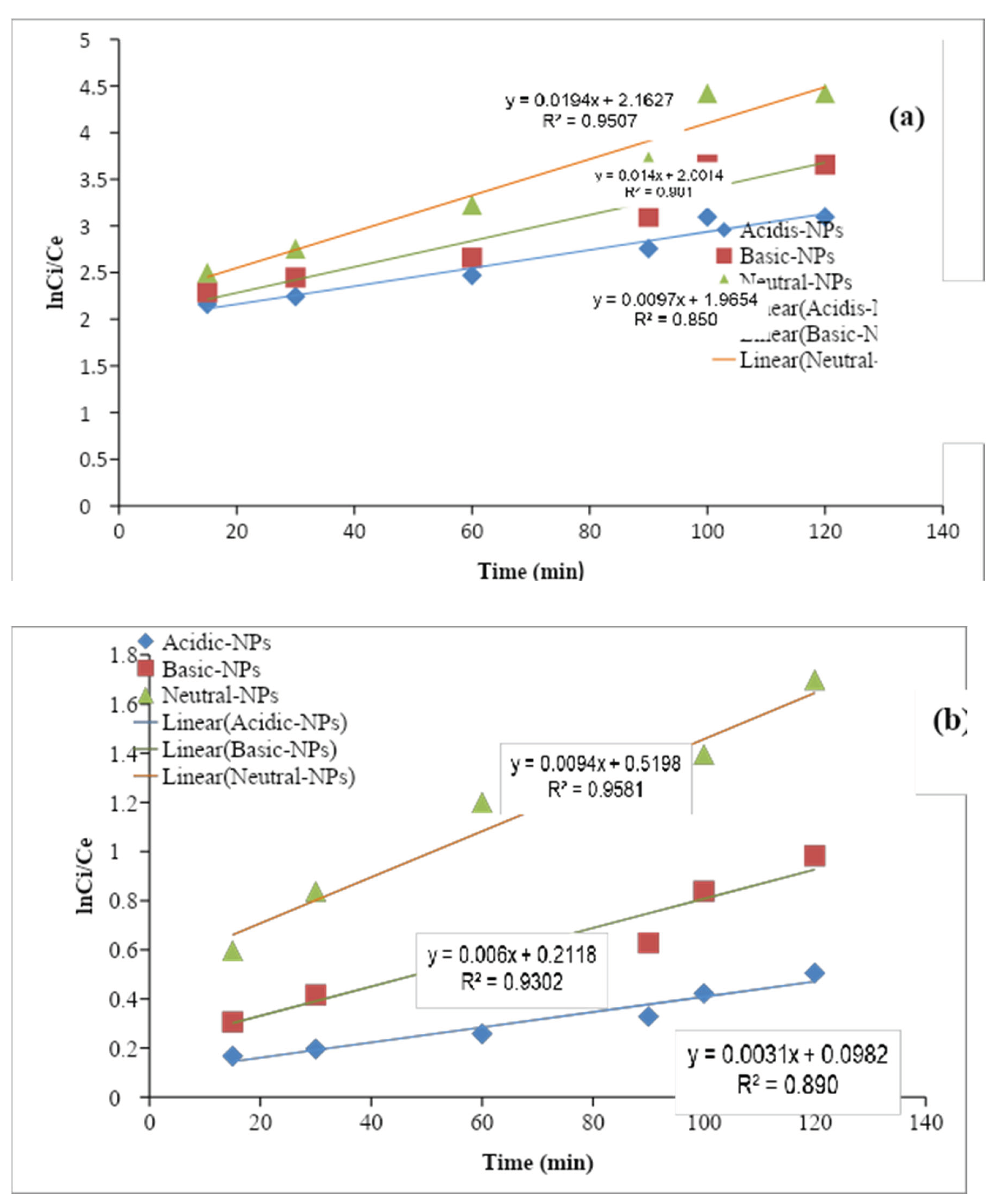
3.5.1. Pseudo-First-Order
The pseudo-first-order kinetic model is suitable for the explanation of liquid/solid biosorption systems. According to the pseudo-first-order kinetic model, the change in concentration of inorganic ions as a function of time is directly proportional to the power1 (Alemayehu and Lennartz, 2009). The linear integrated equation of pseudo-first-order is given as follows:
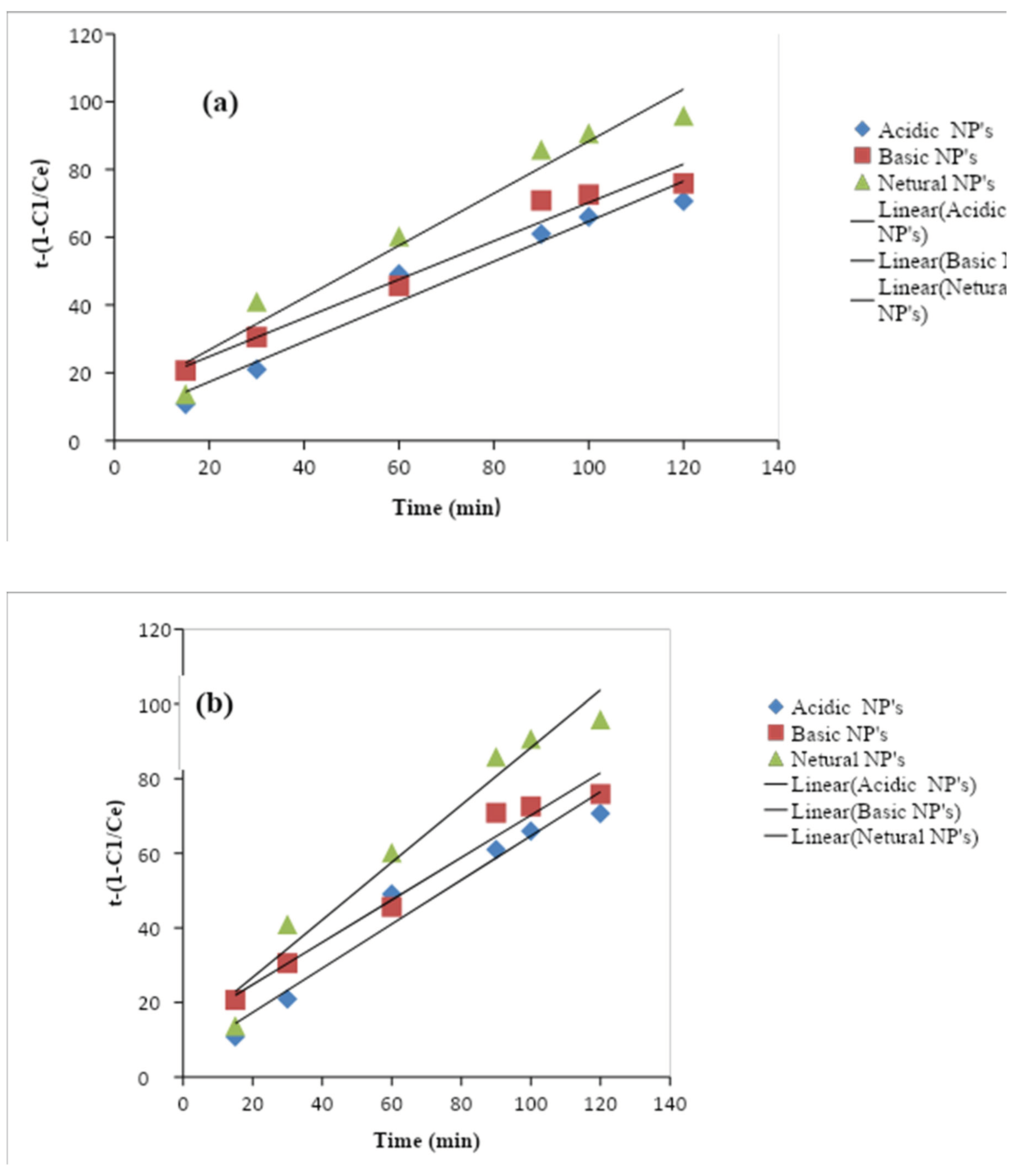
Here, C0 is the initial concentration Ct is the final concentration of nitrates in the aqueous solution, K is the pseudo-first-order rate constant (min−1), and t is the time (min). The K values were calculated from the slope of the ln (Ct/C0) at various times for each photocatalyst. And the rate constant (k) value for the adsorbents obtained through the kinetic measurements. The values of the reaction rate constants (k) Al2O3 NPs catalysts were estimated to be (R² = 0.9507), (R² = 0.905), and (R² = 0.850). All the plots indicate a linear relationship with a good correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.9866). Khanizadeh et al., 2020 observed that the removal of nitrate by the synthesized photocatalysts under natural sunlight irradiation follows the pseudo-first-order kinetic model. This increased rate constant (k) value for the Al2O3 NPs suggests that it has excellent photocatalytic activity under sunlight irradiation. The photocatalytic activity of as prepared Al2O3 NPs was compared to the earlier reported photocatalytic activity of various catalysts, it has cleared that the Al2O3 NPs catalyst exhibited better photocatalytic activity compared to the previously reported results of other nanoparticles. The photocatalytic efficiency of as prepared samples and the kinetic analysis of nitrate ions removal were carried out.
Figure 1.10.
Graph of pseudo first order of (a) nitrate and (b) phosphate ion.
Figure 1.10.
Graph of pseudo first order of (a) nitrate and (b) phosphate ion.
3.5.2. Pseudo 2nd Order
Figure 1.11.
Graph of pseudo-second order of(a) nitrate and(b) phosphate ions.
Figure 1.11.
Graph of pseudo-second order of(a) nitrate and(b) phosphate ions.
3.5.3. BMG
Figure 1.12.
Graph of BMG model of (a) nitrate and (b) phosphate ion.
Figure 1.12.
Graph of BMG model of (a) nitrate and (b) phosphate ion.
3.5.4. Comparison between the Pseudo 1st, 2st and BMG Models
The R2 values of pseudo1st, 2nd, and BMG models were 0.956, 0.837, 0.7007, and 0.95, 0.896, and 0.756 for the nitrate and phosphate ions which were investigated in the neutral medium and their values were different in different medium like in acidic and also in basic medium. Photocatalysis degradation follows the pseudo 1st order because in photocatalysis light is involved and excitation of elections takes place quickly. Manikandan et al., 2019 observed that Al2O3 NPs catalysts were estimated to be (R² = 0.9402), (R² = 0.9850), (R² = 0.9875), (R² = 0.9783), (R² = 0.9766), (R² = 0.9866), (R² = 0.9945), (R² = 0.9964), and (R² = 0.9922). All the plots indicate a linear relationship with a good correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.9866), demonstrating that the % degradation of nitrate and phosphate by the synthesized photocatalysts under natural sunlight irradiation follows the pseudo-first-order kinetic model. This increased rate constant (k) value for the Al2O3 NPs suggests that it has excellent photocatalytic activity under sunlight irradiation.
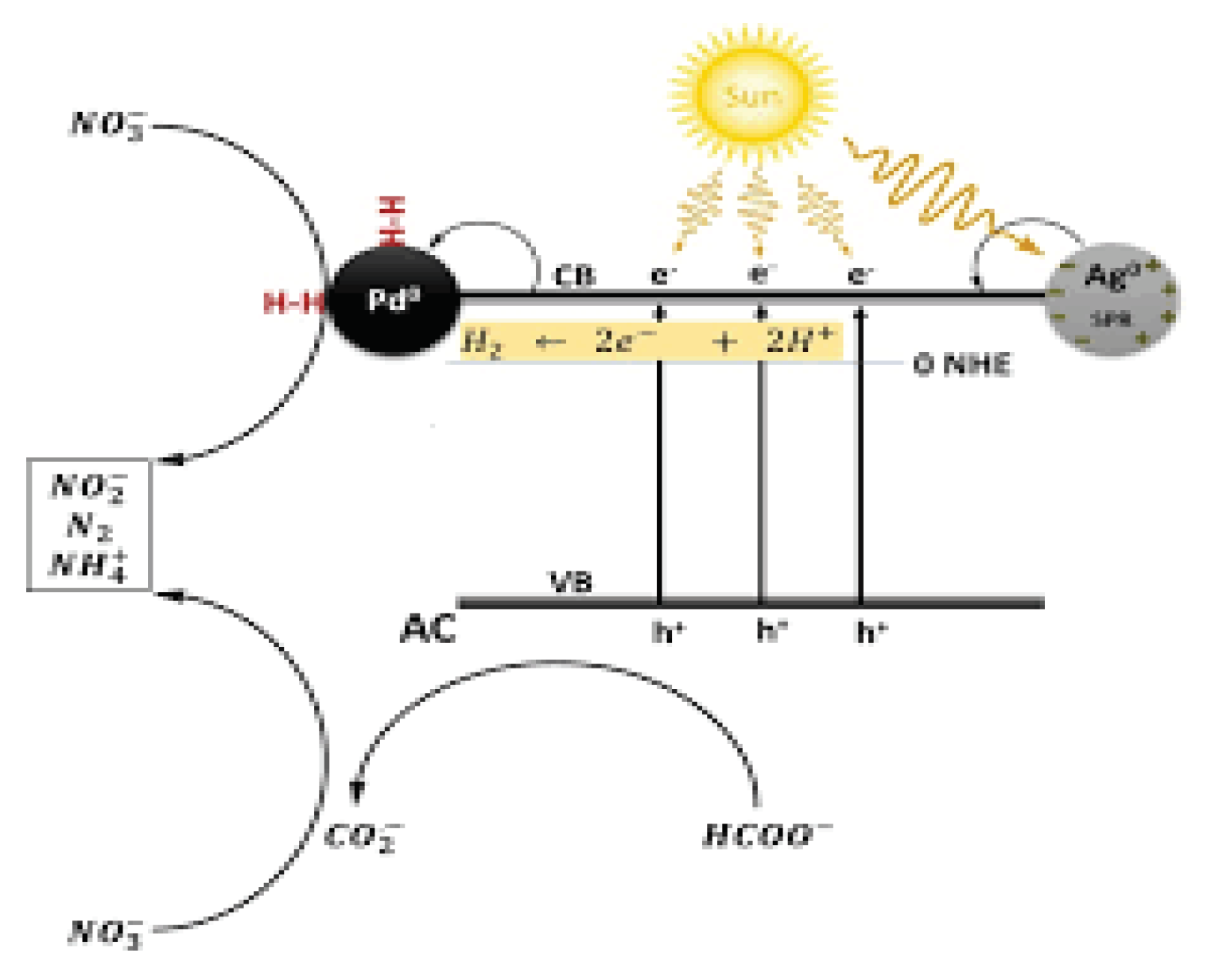
3.6. Mechanism of Photocatalytic Reactions
The most common photocatalytic method is heterogeneous photocatalysis which uses UV/TiO
2 which depends upon the adsorption of photons with energy higher than 3.2eV and wavelength lower than 390nm. Production of excited high-energy states of electron and hole pairs occurs when wide band gap semiconductors have irradiated higher than their bandgap energy. It results in the upgrade of an electron in the conductive band (e
CB−) and the production of a positive hole in the valence band (h
VB+). The h
VB+ and e
CB− have powerful oxidizing and reducing agents, respectively. The h
VB+ reacts with organic compounds and oxidation occurs which produces CO
2 and H
2O. The h
VB+ also oxidizes inorganic compounds by reacting with water to generate
•OH. Hydroxyl radical (
•OH) which is produced in this process has the two highest oxidation potential 2.80V whose energy is slightly lower than the strongest oxidant – fluorine. The hydroxyl radical is non-selective due to its electrophilic nature and oxide of all organic molecules which is electron-rich and converting them into the H
2O Carbon dioxide (Umar and Aziz, 2013).
Figure 1.13.
Mechanism of removal of inorganic ions.
Figure 1.13.
Mechanism of removal of inorganic ions.
3.7. Conclusions
In field of the industry and chemistry Aluminum oxide Al2O3 nanoparticles are used for different purposes. Like that these particles are used in metallurgy, optoelectronics electrons, petroleum refining, automotive emission, wear protection, and ceramic composites. Aluminum oxide nanoparticles were synthesized from different processes like laser ablation, sol-gel, hydrothermal reaction, and ball milling. These methods included toxic chemicals, high pressure, temperature, and removal of energy. All byproducts formed during processes are very dangerous and released into the environment and pollute it. Recently Aluminum oxide nanoparticles have been prepared by using plant extract and capturing attention because this process is free from toxicity. The main property is that this process is less costly and environmentally friendly. Additionally, the plants supply the capping agents. Photo-degradation is a modern method used for the removal of inorganic ions due to its environmentally friendly nature and cost-effectiveness.
In recent study Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) nanoparticles were synthesized via a green approach at different pH by using Cymbopogan citratus (lemongrass) plant extract and these nanoparticles are used for the degradation of inorganic ions from wastewater. The nanoparticles of different pH have shown different % degradation of the inorganic ions in acidic medium removal of inorganic waste is less, in basic media % 80 degradation is more as compared to acidic media but maximum % degradation has observed in neutral media like that average % degradation 91% and 81% have observed for nitrate and phosphate ions. The maximum absorbance occurred at 212nm and Al2O3 nanoparticles showed absorbance from 210nm-217nm. The R2 values of pseudo1st, 2st, and BMG models are 0.956, 0.837, 0.7007 0.95, 0.896, and 0.756 for the nitrate and phosphate ions. Characterizations of synthesized particles are investigated by using UV-visible spectroscopy and other analytical methods like X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The statistical analyses are done using Simple Linear regression (SLR).
References
- Ahmed, S. N., & Haider, W. Heterogeneous photocatalysis and its potential applications in water and wastewater treatment: a review. Nanotechnology 29, 342001. [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, E., & Lennartz, B. Virgin volcanic rocks: kinetics and equilibrium studies for the adsorption of cadmium from water. Journal of Hazardous Materials 169, 395–401. [CrossRef]
- Ani, I.; Akpan, U.; Olutoye, M.; Hameed, B. Photocatalytic degradation of pollutants in petroleum refinery wastewater by TiO2-and ZnO-based photocatalysts: recent development. Journal of cleaner production. 2018, 205, 930–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, Y.M., S.-E. Lee, M.B.M. Ahmed, N.T. Vu, M. Farooq, I.S. Kim, H.S. Kim, M. Vithanage.
- A.R.A. Usman and M. Al-Wabel. Biochar, a potential hydroponic growth substrate, enhances the nutritional status and growth of leafy vegetables. Journal of Cleaner Production 156, 581–588. [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Remadevi, R.; Faruque, M.A. Al; Setty, M.; Fan, L.; Haque, A.N.M.A.; Naebe, M. Fabrication of a cost-effective lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus) membrane with antibacterial activity for dye removal. RSC advances. 2019, 9, 34076–34085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luna, M. D. G., Flores, E. D., Genuino, D. A. D., Futalan, C. M., & Wan, M.-W. Adsorption of Eriochrome Black T (EBT) dye using activated carbon prepared from waste rice hulls—Optimization, isotherm and kinetic studies. Journal of the Taiwan institute of chemical engineers 44, 646–653. [CrossRef]
- Eddington, H., Hoefield, R., Sinha, S., Chrysochou, C., Lane, B., Foley, R. N.,... Middleton, R. J. Serum phosphate and mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clinical journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN 5, 2251. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, A.M.; Sokker, H.H.; Zayed, E.M.; Eldien, F.a.N.; Alrahman, N.M.A. Removal of hazardous pollutants using bifunctional hydrogel obtained from modified starch by grafting copolymerization. International journal of biological macromolecules. 2018, 120, 2188–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Biagioni, R.N.; Alarcón-Herrera, M.T.; Rivas-Lucero, B.A. An overview of nitrate sources and operating processes in arid and semiarid aquifer systems. Science of the total environment. 2018, 624, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.C., S.M.M. Rafie, N.S. Ismail and D. Nordin. Effect of the interaction of graphene oxide nanoparticles on a biological model cell membrane. Eurasian J. Anal. Chem 13.
- He, C.; Liu, J.; Cui, J.; Li, J.; Wu, X. A gel polymer electrolyte based on Polyacrylonitrile/organic montmorillonite membrane exhibiting dense structure for lithium ion battery. Solid State Ionics. 2018, 315, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanu, I., & Achi, O. Industrial effluents and their impact on water quality of receiving rivers in Nigeria. Journal of applied technology in environmental sanitation 1, 75–86.
- Kelsall, R. W., Hamley, I. W., & Geoghegan, M. (2005). Nanoscale Science and Technology.
- Khanizadeh, B., Khosravi, M., Behnajady, M. A., Shamel, A., & Vahid, B. Mg and La Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method: synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity. Periodica Polytechnica Chemical Engineering 64, 61–74. [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Fukumoto, S. X-linked hypophosphatemia and FGF23-related hypophosphatemic diseases: prospect for new treatment. Endocrine reviews. 2018, 39, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P., & Wu, J. Drinking water quality and public health. Exposure and health 11, 73–79. [CrossRef]
- Malakootian, M., Nasiri, A., & Amiri Gharaghani, M. Photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin antibiotic by TiO2 nanoparticles immobilized on a glass plate. Chemical Engineering Communications 207, 56–72. [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, V.; Jayanthi, P.; Priyadharsan, A.; Vijayaprathap, E.; Anbarasan, P.; Velmurugan, P. Green synthesis of pH-responsive Al2O3 nanoparticles: Application to rapid removal of nitrate ions with enhanced antibacterial activity. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry. 2019, 371, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H. W., Fulton, R. S., Moisander, P. H., & Dyble, J. Harmful freshwater algal blooms, with an emphasis on cyanobacteria. The Scientific World Journal 1, 76–113. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizishad, M., Dalvand, A., Mahvi, A. H., & Goodarzi, F. A review of adverse effects and benefits of nitrate and nitrite in drinking water and food on human health. Health Scope 6.
- Ran, M., Li, J., Cui, W., Li, Y., Li, P., & Dong, F. Efficient and stable photocatalytic NO removal on C self-doped gC 3 N 4: Electronic structure and reaction mechanism. Catalysis Science & Technology 8, 3387–3394.
- Re, V.; Sacchi, E. Tackling the salinity-pollution nexus in coastal aquifers from arid regions using nitrate and boron isotopes. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2017, 24, 13247–13261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, G., R. Chandra and R.N. Bharagava. 2016. Environmental pollution, toxicity profile and treatment approaches for tannery wastewater and its chemical pollutants. (eds.) Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology Volume 240. Springer.
- Schweitzer, L., & Noblet, J. (2018). Water contamination and pollution. In Green chemistry (pp. 261-290): Elsevier.
- Sevda, S.; Sreekishnan, T.; Pous, N.; Puig, S.; Pant, D. Bioelectroremediation of perchlorate and nitrate contaminated water: A review. Bioresource technology. 2018, 255, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A., & Shah, M. Characterisation and bioremediation of wastewater: a review exploring bioremediation as a sustainable technique for pharmaceutical wastewater. Groundwater for Sustainable Development 11, 100383. [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K.; Kumar, V.; Mohan, S.; Hasan, S.H. Polylysine functionalized graphene aerogel for the enhanced removal of Cr (VI) through adsorption: kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic modeling of the process. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data. 2017, 62, 1732–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Umar, M., & Aziz, H. A. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in water. Organic pollutants-monitoring, risk and treatment 8, 196–197.
- Wang, G.; Li, J.; Sun, W.; Xue, B.; Yinglan, A.; Liu, T. Non-point source pollution risks in a drinking water protection zone based on remote sensing data embedded within a nutrient budget model. Water research. 2019a, 157, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y., Wang, C., Hou, J., Wang, P., Miao, L., & You, G. Strategies and relative mechanisms to attenuate the bioaccumulation and biotoxicity of ceria nanoparticles in wastewater biofilms. Bioresource technology 265, 102–109. [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.; Khan, M.A.; Otero, M.; Abdullah, E.; Hosomi, M.; Terada, A.; Riya, S. Synthesis of CTAB intercalated graphene and its application for the adsorption of AR265 and AO7 dyes from water. Journal of colloid and interface science. 2017, 493, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaheer, I. E., Ali, S., Saleem, M. H., Imran, M., Alnusairi, G. S., Alharbi, B. M.,... Soliman, M. H. Role of iron–lysine on morpho-physiological traits and combating chromium toxicity in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) plants irrigated with different levels of tannery wastewater. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 155, 70–84. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).